Helicobacter pylori: Routes of Infection, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Alternative Therapies as a Means to Develop Infection Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodological Methods
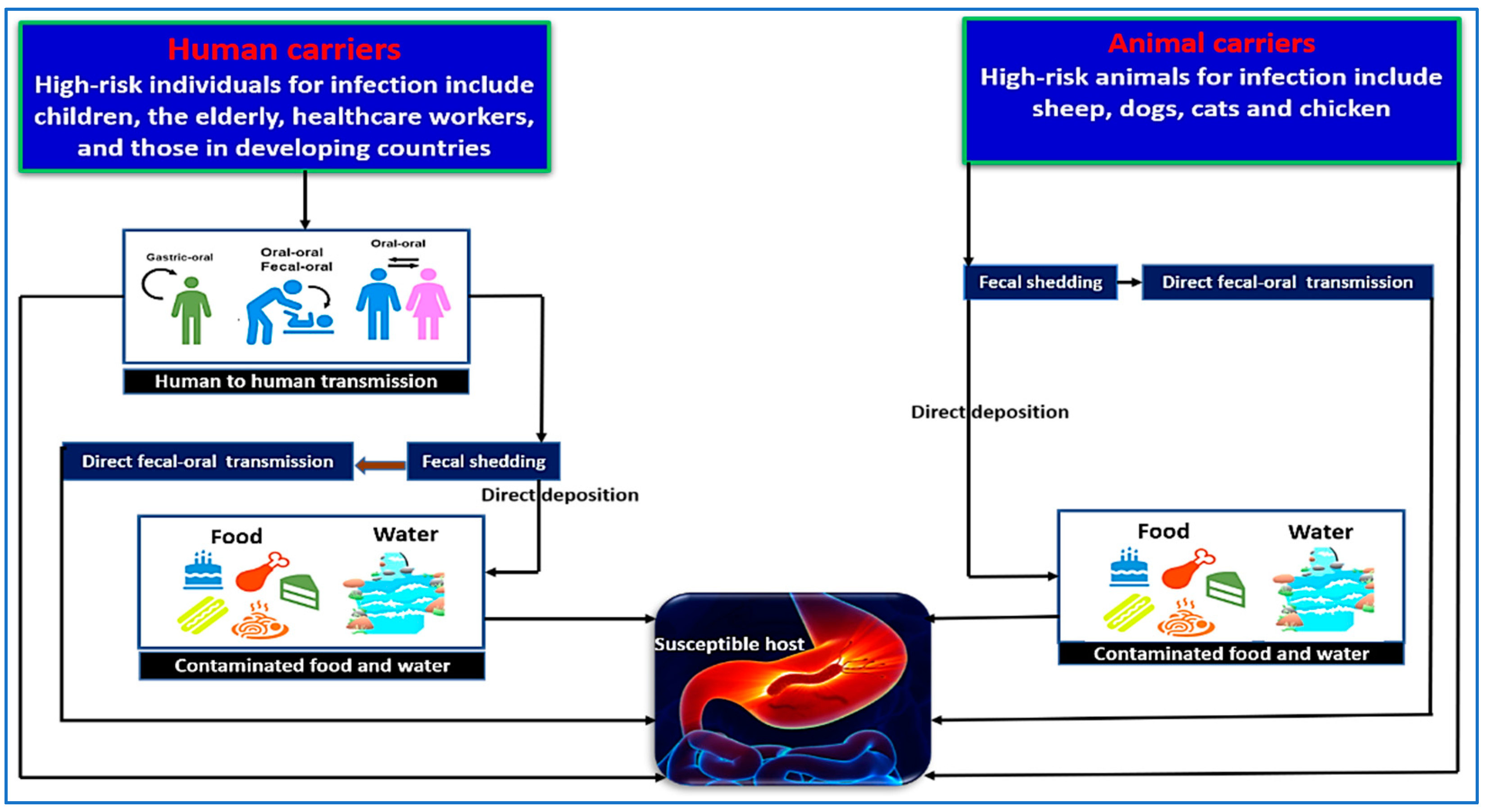
3. The Transmission Patterns of Helicobacter pylori
3.1. Human-to-Human Transmission
3.2. Animals to Human’s Transmission
3.3. Transmission Through Water and Food
4. H. pylori Infection: Standard Therapy, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Failure of Treatment
5. Alternative Therapies
5.1. Enhancing Eradication Therapy
5.2. Adjuvant Therapies (Probiotics and Anti-Biofilm Agents)
6. Other Developing Therapies
6.1. Lactoferrin Therapy
6.2. Herbal Therapy (Phytotherapy)
6.3. Photodynamic Therapy
6.4. Phage Therapy
6.5. Vaccination Against H. pylori: Potential Uses
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Aldubaib, M.; Abalkhail, A.; Anagreyyah, S.; Anajirih, N.; Abu-Okail, A. Helicobacter pylori infection: Current status and future prospects on diagnostic, therapeutic and control challenges. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burz, C.; Pop, V.; Silaghi, C.; Lupan, I.; Samasca, G. Helicobacter pylori Infection in Patients with Gastric Cancer: A 2024 Update. Cancers 2024, 16, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Boneca, I.G. The shapeshifting Helicobacter pylori: From a corkscrew to a ball. Mol. Microbiol. 2024, 121, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, P.; Wright, D.H. Malignant lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. A distinctive type of B-cell lymphoma. Cancer 1983, 52, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharndama, H.C.; Mba, I.E. Helicobacter pylori: An up-to-date overview on the virulence and pathogenesis mechanisms. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogiatzi, P.; Cassone, M.; Luzzi, I.; Lucchetti, C.; Otvos, L., Jr.; Giordano, A. Helicobacter pylori as a class I carcinogen: Physiopathology and management strategies. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 102, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori virulence factor cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA)-mediated gastric pathogenicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukri, A.; Hanafiah, A.; Mohamad Zin, N.; Kosai, N.R. Epidemiology and role of Helicobacter pylori virulence factors in gastric cancer carcinogenesis. Apmis 2020, 128, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolinjivadi, A.M.; Sankar, H.; Choudhary, R.; Tay, L.S.; Tan, T.Z.; Murata-Kamiya, N.; Ito, Y. The H. pylori CagA oncoprotein induces DNA double strand breaks through Fanconi Anemia pathway downregulation and replication fork collapse. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadvar, N.; Akrami, S.; Mousavi Sagharchi, S.-M.-A.; Askandar, R.H.; Merati, A.; Aghayari, M.; Kashfi, M. A review for non-antibiotic treatment of Helicobacter pylori: New insight. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1379209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil-Costa, I.; Souza, C.d.O.; Monteiro, L.C.R.; Santos, M.E.S.; Oliveira, E.H.C.D.; Burbano, R.M.R. H. pylori infection and virulence factors cagA and vacA (s and m regions) in gastric adenocarcinoma from Pará State, Brazil. Pathogens 2022, 11, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, S.; Karkhah, A.; Darvish, H.; Validi, M.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Nouri, H.R. Influence of Helicobacter pylori virulence factors CagA and VacA on pathogenesis of gastrointestinal disorders. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; AlHussaini, K.I. Helicobacter pylori: A contemporary perspective on pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment strategies. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Hu, B. The role of adhesion in Helicobacter pylori persistent colonization. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afra, L.G.; Afkhami, H.; Khaledi, M.; Fathi, J.; Taghadosi, R.; Hoseini, M.H.M.; Heidari, M. Detection of H. pylori in tissues with benign prostatic hyperplasia isolates from hospitalized patient in Qom, Iran. Gene Rep. 2021, 23, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Survival of Helicobacter pylori in gastric acidic territory. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheok, Y.Y.; Lee, C.Y.Q.; Cheong, H.C.; Vadivelu, J.; Looi, C.Y.; Abdullah, S.; Wong, W.F. An overview of Helicobacter pylori survival tactics in the hostile human stomach environment. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, V.E. Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastric cancer. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsberger, V.; Gerhard, M.; Mejías-Luque, R. Effects of Helicobacter pylori infection on intestinal microbiota, immunity and colorectal cancer risk. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1339750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoldi, A.; Carrara, E.; Graham, D.Y.; Conti, M.; Tacconelli, E. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: A systematic review and meta-analysis in World Health Organization regions. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1372–1382.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Fan, C.; Xie, H. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on the risk of acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e18348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo-Amer, Y.E.-E.; Sabal, A.; Ahmed, R.; Hasan, N.F.E.; Refaie, R.; Mostafa, S.M.; Abd-Elsalam, S. Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a developing country: A cross-sectional study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoder, G.; Muhammad, J.S.; Mahmoud, I.; Soliman, S.S.; Burucoa, C. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori and its associated factors among healthy asymptomatic residents in the United Arab Emirates. Pathogens 2019, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefano, K.; Marco, M.; Federica, G.; Laura, B.; Barbara, B.; Gioacchino, L.; Gian, L.d.A. Helicobacter pylori, transmission routes and recurrence of infection: State of the art. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parm. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 8), 72. [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet, J.; Shmuely, H.; Haggerty, T. Fecal and oral shedding of Helicobacter pylori from healthy infected adults. JAMA 1999, 282, 2240–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyermann, M.; Rothenbacher, D.; Brenner, H. Acquisition of Helicobacter pylori infection in early childhood: Independent contributions of infected mothers, fathers, and siblings. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2009, 104, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luman, W.; Zhao, Y.; Ng, H.; Ling, K. Helicobacter pylori infection is unlikely to be transmitted between partners: Evidence from genotypic study in partners of infected patients. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 14, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivi, M.; Tindberg, Y.; Sörberg, M.; Casswall, T.H.; Befrits, R.; Hellström, P.M.; Granstrom, M. Concordance of Helicobacter pylori strains within families. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5604–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, R.J.; Vial, P.A.; Ferreccio, C.; Ovalle, J.; Prado, P.; Sotomayor, V.; Morris, J.G., Jr. Seroprevalence of Helicobacter pylori in Chile: Vegetables may serve as one route of transmission. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizri, A.R.N.; Nuwayhid, I.A.; Hamadeh, G.N.; Steitieh, S.W.; Choukair, A.M.; Musharrafieh, U.M. Association between hepatitis A virus and Helicobacter pylori in a developing country: The saga continues. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 21, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Xia, H.X.; Zhuang, Z.H.; Zhong, J. ‘true’re-infection of Helicobacter pylori after successful eradication–worldwide annual rates, risk factors and clinical implications. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Moussa, I.; Mushayt, Y.; Algarni, A.A.; Alrashed, O.A.; Alghamdi, K.S.; Almutairi, N.A.; Anagreyyah, S.A.; Alzahrani, A.; et al. The prevalence of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and its vaccination status among healthcare providers. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Moussa, I.M.; Dawoud, T.M.; Mubarak, A.S.; Al-Sarar, D.; Alsubki, R.A.; Alhaji, J.H.; Hamada, M.; Zahran, R.N. Acinetobacter baumannii as a community foodborne pathogen: Peptide mass fingerprinting analysis, genotypic of biofilm formation and phenotypic pattern of antimicrobial resistance. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Aldubaib, M.; Moussa, I.; Abalkhail, A.; Ibrahem, M.; Hamada, M.; Sindi, S.; Alzaben, F.; Mohammad, A.; et al. Pseudomonas species prevalence, protein analysis, and antibiotic resistance: An evolving public health challenge. Amb Express 2022, 12, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehiry, A.; Al-Dubaib, M.; Marzouk, E.; Moussa, I. Antibacterial effects and resistance induction of silver and gold nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis and the potential toxicity in rats. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Abdeen, E.; Al-Dubaib, M.; Alsayeqh, A.; Ibrahem, M.; Hemeg, H.A. Proteomic characterization and discrimination of Aeromonas species recovered from meat and water samples with a spotlight on the antimicrobial resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Abalkhail, A.; El-Garawany, Y.; Anagreyyah, S.; Alnafea, Y.; Draz, A. The development of technology to prevent, diagnose, and manage antimicrobial resistance in healthcare-associated infections. Vaccines 2022, 10, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalkhail, A.; AlYami, A.S.; Alrashedi, S.F.; Almushayqih, K.M.; Alslamah, T.; Alsalamah, Y.A.; Elbehiry, A. (Eds.) The prevalence of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli producing ESBL among male and female patients with urinary tract infections in Riyadh Region, Saudi Arabia. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalkhail, A.; Elbehiry, A. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in diabetic foot infections: Protein profiling, virulence determinants, and antimicrobial resistance. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, K.M.; Badr, J.; Orabi, A.; Elbehiry, A.; Saad, A.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Hanafy, M.H. Poultry as a vector for emerging multidrug resistant Enterococcus spp.: First report of vancomycin (van) and the chloramphenicol–florfenicol (cat-fex-cfr) resistance genes from pigeon and duck faeces. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edrees, H.M.; Elbehiry, A.; Elmosaad, Y.M. Hypoglycemic and anti-inflammatory effect of gold nanoparticles in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes in experimental rats. Nanotechnology 2017, 3, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Van Khien, V.; Thang, D.M.; Hai, T.M.; Duat, N.Q.; Khanh, P.H.; Ha, D.T.; Yamaoka, Y. Management of antibiotic-resistant Helicobacter pylori infection: Perspectives from Vietnam. Gut Liver 2019, 13, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, E.; Rhead, J.; Suffian, S.; Whiley, D.; Mahmood, F.; Bakshi, N.; Robinson, K. High incidence of antibiotic resistance amongst isolates of Helicobacter pylori collected in Nottingham, UK, between 2001 and 2018. J. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 72, 001776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gao, H.; Miao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Li, F.; Zhuo, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Sun, J.; et al. Helicobacter pylori infection in humans and phytotherapy, probiotics, and emerging therapeutic interventions: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1330029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez de Santiago, E.; Martín de Argila de Prados, C.; Marcos Prieto, H.M.; Jorge Turrión, M.Ã.; Barreiro Alonso, E.; Flores de Miguel, A.; Albillos Martinez, A. Limited effectiveness with a 10-day bismuth-containing quadruple therapy (Pylera®) in third-line recue treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection. A real-life multicenter study. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xia, X.-J.; Zhang, L.-F.; Chi, J.-S.; Liu, P.; Wu, H.; Xu, C.X. Comparative study of allicin-containing quadruple therapy vs. bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: A prospective randomized study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 33, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonyam, P.; Chotivitayatarakorn, P.; Vilaichone, R.-K. High effective of 14-day high-dose PPI-bismuth-containing quadruple therapy with probiotics supplement for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A double blinded-randomized placebo-controlled study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2019, 20, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Hu, Y.; Ge, Z.-M.; Zou, Q.-M.; Lyu, N.-H. Diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infections in children and elderly populations. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2019, 5, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Yang, H. Using probiotics as supplementation for Helicobacter pylori antibiotic therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Expósito, L.; Illescas-Montes, R.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Ruiz, C.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; de Luna-Bertos, E. Multifunctional capacity and therapeutic potential of lactoferrin. Life Sci. 2018, 195, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoto, I.; Yasuma, T.; D’Alessandro-Gabazza, C.N.; Oka, S.; Misaki, M.; Horiki, N.; Gabazza, E.C. Antimicrobial effects of lactoferrin against Helicobacter pylori infection. Pathogens 2023, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaad, G.F.; Mostafa, R.E. Lactoferrin mitigates ethanol-induced gastric ulcer via modulation of ROS/ICAM-1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in Wistar rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 1522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, Q.; Cheng, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Luo, J.; Zhang, A.; Bian, L.; Chen, J.; Lv, J.; et al. Recombinant human lactoferrin enhances the efficacy of triple therapy in mice infected with Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedon, S.T. Use of phage therapy to treat long-standing, persistent, or chronic bacterial infections. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 145, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, A.B.; Stepanian, J.; Trespalacios, A.A.; Vale, F.F. Bacteriophages of Helicobacter pylori. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 549084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuse, T.; Blanchard, T.G.; Czinn, S.J. Inflammation, immunity, and vaccine development for the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. In Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation: Induction, Resolution and Escape by Helicobacter pylori; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Shan, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L. Perspectives from recent advances of Helicobacter pylori vaccines research. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukri, A.; Hanafiah, A.; Patil, S.; Lopes, B.S. The potential of alternative therapies and vaccine candidates against Helicobacter pylori. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Banerjee, S.; Halder, P.; Dutta, S.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Koley, H. A review for the prevention and management of Helicobacter pylori induced gastritis through development of novel vaccine candidates. Microbe 2024, 4, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, V.; Gerhard, M. Vaccination against Helicobacter pylori–An approach for cancer prevention? Mol. Asp. Med. 2023, 92, 101183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Morelli, G.; Kusecek, B.; Manica, A.; Balloux, F.; Owen, R.J.; Graham, D.Y.; van der Merwe, S.; Achtman, M.; Suerbaum, S. Horizontal versus familial transmission of Helicobacter pylori. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskito, L.A.; Yamaoka, Y. The story of Helicobacter pylori: Depicting human migrations from the phylogeography. In Helicobacter Pylori in Human Diseases: Advances in Microbiology, Infectious Diseases and Public Health Volume 11; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mladenova, I. Clinical relevance of Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, D. Helicobacter pylori Infection: An Up to Date on the Pathogenic Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Clinical Management; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kotilea, K.; Bontems, P.; Touati, E. Epidemiology, diagnosis and risk factors of Helicobacter pylori infection. In Helicobacter Pylori in Human Diseases: Advances in Microbiology, Infectious Diseases and Public Health Volume 11; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Borka Balas, R.; Meliț, L.E.; Mărginean, C.O. Worldwide prevalence and risk factors of Helicobacter pylori infection in children. Children 2022, 9, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, M.J.B.; Velecela, Á.J.F.; Díaz, V.A.V.; Jerez, A.M.G.; Sailema, J.S.T.; Verdezoto, M.A.D. Helicobacter pylori infection and its association with digestive diseases: A comprehensive review. Medicina 2024, 9, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, J.; Kotilea, K.; Bontems, P.; Miendje Deyi, V.Y. Helicobacter pylori infections in Children. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.-Z.; Du, Y.-Q.; Lu, H.; Wang, W.-H.; Cheng, H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Chen, M.-H.; Chen, W.-C.; Chen, Y.; Fang, J.-Y.; et al. Chinese consensus report on family-based Helicobacter pylori infection control and management (2021 edition). Gut 2022, 71, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Suzuki, H.; Hirose, M.; Shida, T.; Ikezawa, K.; Matsui, H.; Yanaka, A. Influence of living environment during childhood on Helicobacter pylori infection in Japanese young adults. Digestion 2020, 101, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N. Prevalence and transmission routes of H. pylori. In Helicobacter pylori; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Konno, M.; Yokota, S.-I.; Suga, T.; Takahashi, M.; Sato, K.; Fujii, N. Predominance of mother-to-child transmission of Helicobacter pylori infection detected by random amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprinting analysis in Japanese families. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urita, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Kawagoe, N.; Takemoto, I.; Tanaka, H.; Kijima, S.; Urita, C. Role of infected grandmothers in transmission of Helicobacter pylori to children in a Japanese rural town. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2013, 49, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, K.J.; Correa, P. Transmission of Helicobacter pylori among siblings. Lancet 2000, 355, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialho, A.M.; Braga, A.B.; Neto, M.B.B.; Carneiro, J.G.; Rocha, A.M.; Rodrigues, M.N.; Queiroz, D.M.; Braga, L.L. Younger siblings play a major role in Helicobacter pylori transmission among children from a low-income community in the Northeast of Brazil. Helicobacter 2010, 15, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Mendall, M.; Khulusi, S.; Northfield, T.; Strachan, D. Helicobacter pylori infection in childhood: Risk factors and effect on growth. BMJ 1994, 309, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, H.; Weyermann, M.; Rothenbacher, D. Clustering of Helicobacter pylori infection in couples: Differences between high-and low-prevalence population groups. Ann. Epidemiol. 2006, 16, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheyre, H.; Morais, S.; Ferro, A.; Costa, A.R.; Norton, P.; Lunet, N.; Peleteiro, B. The occupational risk of Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2018, 91, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, T.K.F.; Lambert, J.R.; Wahlqvist, M.L. Hsu-Hage BHH. Helicobacter pylori in Melbourne Chinese immigrants: Evidence for oral-oral transmission via chopsticks. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1995, 10, 562–569. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, W.; Sung, J.J.; Ling, T.K.; Siu, K.L.; Cheng, A.F. Does the use of chopsticks for eating transmit Helicobacter pylori? Lancet 1997, 350, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F.; Flahou, B.; Chiers, K.; Baele, M.; Meyns, T.; Ducatelle, R. Gastric helicobacters in domestic animals and nonhuman primates and their significance for human health. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 202–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietti, P.C.; Bietta, A.; Brachelente, C.; Lepri, E.; Davidson, I.; Franciosini, M.P. Detection of Helicobacter spp. in gastric, fecal and saliva samples from swine affected by gastric ulceration. J. Vet. Sci. 2010, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, F.S.; Jamshidi, S.; Moosakhani, F.; Sasani, F. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Detection of Helicobacter spp. DNA in the colonic biopsies of stray dogs: Molecular and histopathological investigations. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Chung, Y.; Kang, W.-G.; Choi, Y.-S.; Kim, O. Comparison of three diagnostic assays for the identification of Helicobacter spp. in laboratory dogs. Lab. Anim. Res. 2015, 31, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bulck, K.; Decostere, A.; Baele, M.; Driessen, A.; Debongnie, J.-C.; Burette, A.; Haesebrouck, F. Identification of non-Helicobacter pylori spiral organisms in gastric samples from humans, dogs, and cats. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2256–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIsaac, W.J.; Leung, G.M. Peptic ulcer disease and exposure to domestic pets. Am. J. Public Health 1999, 89, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenova, I.; Durazzo, M.; Pellicano, R. Transmission of Helicobacter pylori: Are there evidences for a fecal-oral route? Minerva Medica 2006, 97, 15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Y.; Han, Z.; Wan, M.; Lin, M.; Lin, B.; Kong, Q.; et al. Transmission routes and patterns of helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter 2023, 28, e12945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papież, D.; Konturek, P.; Bielanski, W.; Plonka, M.; Dobrzanska, M.; Kaminska, A.; Szczyrk, U.; Bochenek, A.; Wierzchos, E. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in Polish shepherds and their families. Dig. Liver Dis. 2003, 35, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soloski, M.J.; Poulain, M.; Pes, G.M. Does the trained immune system play an important role in the extreme longevity that is seen in the Sardinian blue zone? Front. Aging 2022, 3, 1069415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmatinezhad, B.; Momtaz, H.; Rahimi, E. VacA, cagA, iceA and oipA genotypes status and antimicrobial resistance properties of Helicobacter pylori isolated from various types of ready to eat foods. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, S.I.; Talat, D.; Khatab, S.A.; Nossair, M.A.; Ayoub, M.A.; Ewida, R.M.; Diab, M.S. An investigative study on the zoonotic potential of Helicobacter pylori. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Moussa, I.M.; Hessain, A.M.; Alhaji, J.H.; Heme, H.A.; Zahran, R.; Abdeen, E. Helicobacter pylori in a poultry slaughterhouse: Prevalence, genotyping and antibiotic resistance pattern. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.K.; Khalifa, M.M.; Sharaf, R.R. Contaminated water as a source of Helicobacter pylori infection: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, N.C.; Dambrosio, A. Helicobacter pylori: A foodborne pathogen? World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Zhou, F.; Lu, D.; Xu, S.; Luo, J.; Gan, H.; Gao, D.; Yao, Z.; He, W.; Kurup, P.U.; et al. Quantification and cultivation of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) from various urban water environments: A comprehensive analysis of precondition methods and sample characteristics. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellini, L. Helicobacter pylori: A chameleon-like approach to life. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, P.D.; Opekun, A.; Smith, E.; Graham, D.; Gaillour, A. Group GPW. Water source as risk factor for Helicobacter pylori infection in Peruvian children. Lancet 1991, 337, 1503–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirhooshang, A.; Ramin, A.; Ehsan, A.; Mansour, R.; Shahram, B. High frequency of Helicobacter pylori DNA in drinking water in Kermanshah, Iran, during June–November 2012. J. Water Health 2014, 12, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, R.; Khamesipour, F.; Jonaidi-Jafari, N.; Rahimi, E. Helicobacter pylori in bottled mineral water: Genotyping and antimicrobial resistance properties. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesga, F.-J.; Venegas, C.; Martinez, V.F.; Sánchez-Alfonso, A.C.; Trespalacios, A.A. Origin of fecal contamination in lettuce and strawberries: From microbial indicators, molecular markers, and H. pylori. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashak, Z.; Jafariaskari, S.; Alavi, I.; Sakhaei Shahreza, M.; Safarpoor Dehkordi, F. Phenotypic and genotypic assessment of antibiotic resistance and genotyping of vacA, cagA, iceA, oipA, cagE, and babA2 alleles of Helicobacter pylori bacteria isolated from raw meat. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.-Y.; Leung, W.K.; Cheung, K.-S. Antibiotic resistance, susceptibility testing and stewardship in Helicobacter pylori infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, V.; Zullo, A.; Manta, R.; Satriano, A.; Fiorini, G.; Pavoni, M.; Vaira, D. Culture-based antibiotic susceptibility testing for Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2022, 35, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiotani, A.; Roy, P.; Lu, H.; Graham, D.Y. Helicobacter pylori diagnosis and therapy in the era of antimicrobial stewardship. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2021, 14, 17562848211064080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Dore, M.P.; Graham, D.Y. Diagnosis and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, Z.; Tang, J.-W.; Marshall, B.J.; Tay, A.C.Y.; Wang, L. Rapid diagnosis and precision treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in clinical settings. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B.; Winte, M.; DeSipio, J.; Phadtare, S. Clinical factors implicated in antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori patients. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thung, I.; Aramin, H.; Vavinskaya, V.; Gupta, S.; Park, J.; Crowe, S.; Valasek, M. The global emergence of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 514–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zama, D.; Bossù, G.; Leardini, D.; Muratore, E.; Biagi, E.; Prete, A.; Pession, A.; Masetti, R. Insights into the role of intestinal microbiota in hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2020, 11, 2040620719896961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.T.; Vítor, J.M.; Santos, A.; Oleastro, M.; Vale, F.F. Trends in Helicobacter pylori resistance to clarithromycin: From phenotypic to genomic approaches. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, e000344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón-Millán, J.; Fernández-Tilapa, G.; Cortés-Malagón, E.M.; Castañón-Sánchez, C.A.; De Sampedro-Reyes, J.; Carmen, I.C.-D.; Betancourt-Linares, R.; Román-Román, A. Clarithromycin resistance and prevalence of Helicobacter pylori virulent genotypes in patients from Southern México with chronic gastritis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 44, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyanova, L.; Gergova, G.; Kandilarov, N.; Boyanova, L.; Yordanov, D.; Gergova, R.; Markovska, R. Geographic distribution of antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori: A study in Bulgaria. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2023, 70, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Shao, Y.; Yan, J.; Ye, G. Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: From potential biomolecular mechanisms to clinical practice. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2023, 37, e24885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierardi, E.; Giorgio, F.; Losurdo, G.; Di Leo, A.; Principi, M. How antibiotic resistances could change Helicobacter pylori treatment: A matter of geography? World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2013, 19, 8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Treviño, S.; Mendoza-Olazarán, S.; Bocanegra-Ibarias, P.; Maldonado-Garza, H.J.; Garza-González, E. Helicobacter pylori drug resistance: Therapy changes and challenges. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 12, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghotaslou, R.; Leylabadlo, H.E.; Asl, Y.M. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: A recent literature review. World J. Methodol. 2015, 5, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba, C.; Blanco, A.; Alarcón, T. Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 30, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyanova, L.; Hadzhiyski, P.; Gergova, R.; Markovska, R. Evolution of Helicobacter pylori resistance to antibiotics: A topic of increasing concern. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisuphanunt, M.; Wilairatana, P.; Kooltheat, N.; Duangchan, T.; Katzenmeier, G.; Rose, J.B. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance and novel treatment strategies for Helicobacter pylori infections. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, K.; Kishi, K.; Sakamoto, U.; Ishimura, N.; Ishihara, S. Degree of Gastric Mucosal Atrophy Correlated Well with Gastric Cancer Occurrence in Patients with Helicobacter pylori-eradicated Status. Intern. Med. 2023, 62, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokkas, T.; Graham, D.Y. How widespread and convenient H. pylori susceptibility testing will result in pharmacological opportunities. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, S. Antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori among children and adolescents in East Asia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, R.B.; Meliț, L.E.; Mărginean, C.O. Current worldwide trends in pediatric Helicobacter pylori antimicrobial resistance. Children 2023, 10, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujanda, L.; Nyssen, O.P.; Ramos, J.; Bordin, D.S.; Tepes, B.; Perez-Aisa, A.; Gisbert, J.P. Effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori treatments according to antibiotic resistance. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2024, 119, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.J.; Navarro, M.; Sawyer, K.; Elfanagely, Y.; Moss, S.F. Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance in the United States between 2011 and 2021: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2022, 117, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Chen, M.; Peng, C.; Yan, J.; Shen, X.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Gan, G.; Luo, X.; Zhu, W.; et al. In vitro anti-bactrical activity and its preliminary mechanism of action of the non-medicinal parts of Sanguisorba officinalis L. against Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 318, 116981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Lu, B.; Dai, J. Helicobacter pylori and antibiotic resistance, a continuing and intractable problem. Helicobacter 2016, 21, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.; Song, Z.; Suo, B.; Tian, X.; Xue, Y.; Meng, L.; Zhou, L. Correlation analysis among genotype resistance, phenotype resistance and eradication effect of Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandan, V.; Logan, S.M.; Harrison, B.A.; Vinogradov, E.; Aubry, A.; Stupak, J.; Li, J.; Altman, E. Characterization of a waaF mutant of Helicobacter pylori strain 26695 provides evidence that an extended lipopolysaccharide structure has a limited role in the invasion of gastric cancer cells. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Wen, Y.; Chen, H.; She, F. A newly discovered drug resistance gene rfaF in Helicobacter pylori. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 3507–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.J.; Sheikh, A.F.; Goodarzi, H.; Yadyad, M.J.; Seyedian, S.S.; Aslani, S.; Assarzadegan, M.-A. Genetic basis for metronidazole and clarithromycin resistance in Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from patients with gastroduodenal disorders. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Yin, F.; Wang, S.; Zhao, A.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Helicobacter pylori biofilm-related drug resistance and new developments in its anti-biofilm agents. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Little, B.J.; Neu, T.R.; Nielsen, P.H.; Seviour, T.; Stoodley, P.; Wingender, J.; Wuertz, S. Microbial extracellular polymeric substances in the environment, technology and medicine. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, D.; Xie, S. Current progress and prospects of organic nanoparticles against bacterial biofilm. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 294, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżek, P.; Grande, R. Transformation of Helicobacter pylori into coccoid forms as a challenge for research determining activity of antimicrobial substances. Pathogens 2020, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamasu, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Saito, M.; Harada, M.; Fukuda, K. Helicobacter pylori results in lysis and death after exposure to water. Helicobacter 2022, 27, e12921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaput, C.; Ecobichon, C.; Cayet, N.; E Girardin, S.; Werts, C.; Guadagnini, S.; Prévost, M.-C.; Mengin-Lecreulx, D.; Labigne, A.; Boneca, I.G. Role of AmiA in the morphological transition of Helicobacter pylori and in immune escape. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-X.; Wang, X.-F. Cloning and sequencing of cagA gene fragment of Helicobacter pylori with coccoid form. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2004, 10, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, L.J.; Grande, R.; Iorio, D.D.; Giulio, M.D.; Campli, E.D.; Cellini, L. Helicobacter pylori free-living and biofilm modes of growth: Behavior in response to different culture media. Apmis 2013, 121, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yuan, Y. Resistance mechanisms of Helicobacter pylori and its dual target precise therapy. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, F.; Chi, W.; Ding, L.; Liu, T.; Zhu, F.; Ji, D.; Zhou, J.; Fang, Y.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance patterns and genetic elements associated with the antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori strains from Shanghai. Gut Pathog. 2022, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, D.S.; Kesavan, D.K.; Muthusamy, N.; Umamaheswari, S. Efflux pumps potential drug targets to circumvent drug Resistance–Multi drug efflux pumps of Helicobacter pylori. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 2976–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, H.; Osaki, T.; Hojo, F.; Kamiya, S. Effect of Helicobacter pylori biofilm formation on susceptibility to amoxicillin, metronidazole and clarithromycin. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżek, P.; Migdał, P.; Grande, R.; Gościniak, G. Biofilm formation of Helicobacter pylori in both static and microfluidic conditions is associated with resistance to clarithromycin. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 868905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regeimbal, J.M.; Jacobs, A.C.; Corey, B.W.; Henry, M.S.; Thompson, M.G.; Pavlicek, R.L.; Quinones, J.; Hannah, R.M.; Ghebremedhin, M.; Crane, N.J.; et al. Bifunctional enzyme SpoT is involved in biofilm formation of Helicobacter pylori with multidrug resistance by upregulating efflux pump Hp1174 (gluP). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, 5806–5816. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanuzzaman; Bang, C.S.; Gong, E.J. Antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter pylori: Mechanisms and clinical implications. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2024, 39, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujanda, L.; Nyssen, O.P.; Vaira, D.; Saracino, I.M.; Fiorini, G.; Lerang, F.; Georgopoulos, S.; Tepes, B.; Heluwaert, F.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Antibiotic resistance prevalence and trends in patients infected with Helicobacter pylori in the period 2013–2020: Results of the European Registry on H. pylori Management (Hp-EuReg). Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tshibangu-Kabamba, E.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori infection and antibiotic resistance—From biology to clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Choi, K.D.; Jung, H.; Kim, J.M.; Baik, G.H.; Kim, B.; Park, J.C.; Jung, H.; Cho, S.J.; et al. Nationwide antibiotic resistance mapping of Helicobacter pylori in Korea: A prospective multicenter study. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagari, R.M.; Rabitti, S.; Eusebi, L.H.; Bazzoli, F. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: A clinical practice update. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumpan, N.; Mahachai, V.; Vilaichone, R.K. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection. JGH Open 2023, 7, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Megraud, F.; Rokkas, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Liou, J.-M.; Schulz, C.; El-Omar, E.M. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: The Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report. Gut 2022, 71, 1724–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, M.P.; Lu, H.; Graham, D.Y. Role of bismuth in improving Helicobacter pylori eradication with triple therapy. Gut 2016, 65, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botija, G.; Galicia, G.; Martínez, B.; Cuadrado, C.; Soria, M.; Fernández, S.; Seghnp, H. Efficacy of Bismuth Therapy in Eradicating Helicobacter pylori in Children—Data From the RENIHp Registry. Helicobacter 2024, 29, e13142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Chung, W.C.; Lee, S.J. Bismuth supplements as the first-line regimen for Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: Systemic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter 2019, 24, e12565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijevitch, A.A.; Sataev, V.U.; Akhmadeyeva, E.N.; Arsamastsev, A.G. Nifuratel-containing initial anti-Helicobacter pylori triple therapy in children. Helicobacter 2007, 12, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascălu, R.I.; Bolocan, A.; Păduaru, D.N.; Constantinescu, A.; Mitache, M.M.; Stoica, A.D.; Andronic, O. Multidrug resistance in Helicobacter pylori infection. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1128497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestrovic, A.; Perkovic, N.; Tonkic, A.; Sundov, Z.; Kumric, M.; Bozic, J. Personalized approach in eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyssen, O.P.; Espada, M.; Gisbert, J.P. Empirical vs. susceptibility-guided treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 913436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gingold-Belfer, R.; Niv, Y.; Schmilovitz-Weiss, H.; Levi, Z.; Boltin, D. Susceptibility-guided versus empirical treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 2649–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Moss, S.F.; Daniele, P.; Pelletier, C.; Jacob, R.; Tremblay, G.; Hubscher, E.; Leifke, E.; Chey, W.D. Potassium-competitive acid blocker and proton pump inhibitor–based regimens for first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication: A network meta-analysis. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanu, J.E.; Soldera, J. Treatment of Helicobacter pylori with potassium competitive acid blockers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljaberi, H.; Ansari, N.K.; Xiong, M.; Peng, H.; He, B.; Wang, S. Current Understanding of the Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of H. pylori Infection: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Med. Pharm. Drug Res. 2023, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, T.; Graham, D.Y. Pharmacologic aspects of eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterol. Clin. 2010, 39, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echizen, H. The first-in-class potassium-competitive acid blocker, vonoprazan fumarate: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 55, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elazazi, N.A.D.A.; Eltabbakh, M.; Hussein, H.M.; Mahmood, Y.M.; Elwakil, R. Efficacy of Potassium-competitive Acid Blockers versus Proton Pump Inhibitors in First-and Second-line Eradication Regimens for Helicobacter pylori in Egyptian Patients. J. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2024, 2, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.Y. Why the vonoprazan Helicobacter pylori therapies in the US-European trial produced unacceptable cure rates. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sue, S.; Maeda, S. Is a potassium-competitive acid blocker truly superior to proton pump inhibitors in terms of Helicobacter pylori eradication? Gut Liver 2021, 15, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mestre, A.; Narayanan, R.S.; Rivas, D.; John, J.; Abdulqader, M.A.; Khanna, T.; Gupta, S. Role of Probiotics in the Management of Helicobacter pylori. Cureus 2022, 14, e26463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionetti, E.; Indrio, F.; Pavone, L.; Borrelli, G.; Cavallo, L.; Francavilla, R. Role of probiotics in pediatric patients with Helicobacter pylori infection: A comprehensive review of the literature. Helicobacter 2010, 15, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesbros-Pantoflickova, D.; Corthèsy-Theulaz, I.; Blum, A.L. Helicobacter pylori and Probiotics1. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 812S–818S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batdorj, B.; Trinetta, V.; Dalgalarrondo, M.; Prévost, H.; Dousset, X.; Ivanova, I.; Haertlé, T.; Chobert, J.-M. Isolation, taxonomic identification and hydrogen peroxide production by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis T31, isolated from Mongolian yoghurt: Inhibitory activity on food-borne pathogens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtasham, M.; Joukar, F.; Maroufizadeh, S.; Mojtahedi, K.; Asgharnezhad, M.; Mansour-Ghanaei, F. Lactobacillus ruteri compared with placebo as an adjuvant in quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Arab. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 24, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, X.-Y.; Zhu, H.-L.; Miao, L. Comparative effectiveness of different probiotics supplements for triple Helicobacter pylori eradication: A network meta-analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1120789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goderska, K.; Agudo Pena, S.; Alarcon, T. Helicobacter pylori treatment: Antibiotics or probiotics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, M.; Yu, S.; Deng, J.; Yan, Q.; Yang, C.; Xia, G.; Zhou, X. Efficacy of probiotic supplementation therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, D.; Nigam, P.S. Antibiotic-therapy-induced gut dysbiosis affecting gut microbiota—Brain axis and cognition: Restoration by intake of probiotics and synbiotics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Éliás, A.J.; Barna, V.; Patoni, C.; Demeter, D.; Veres, D.S.; Bunduc, S.; Erőss, B.; Hegyi, P.; Földvári-Nagy, L.; Lenti, K. Probiotic supplementation during antibiotic treatment is unjustified in maintaining the gut microbiome diversity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Xiao, S.; Li, S.; Suo, B.; Wang, Y.; Meng, L.; Zhou, L. The impact of Helicobacter pylori infection, eradication therapy, and probiotics intervention on gastric microbiota in young adults. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotta, C.; Tognon, M.; Martini, F.; Torreggiani, E.; Rotondo, J.C. Probiotics mechanism of action on immune cells and beneficial effects on human health. Cells 2023, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevia, A.; Delgado, S.; Sánchez, B.; Margolles, A. Molecular players involved in the interaction between beneficial bacteria and the immune system. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boger, M.C.L.; van Bueren, A.L.; Dijkhuizen, L. Cross-feeding among probiotic bacterial strains on prebiotic inulin involves the extracellular exo-inulinase of Lactobacillus paracasei strain W20. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01539-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turroni, F.; Serafini, F.; Foroni, E.; Duranti, S.; Motherway, M.O.; Taverniti, V.; Mangifesta, M.; Milani, C.; Viappiani, A.; Roversi, T.; et al. Role of sortase-dependent pili of Bifidobacterium bifidum PRL2010 in modulating bacterium–host interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11151–11156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, W.; Lee, A.; He, J.; Huang, B.; Zheng, W.; Su, T.; Lai, S.; Long, Y.; Chu, H.; et al. The impact of Helicobacter pylori infection, eradication therapy and probiotic supplementation on gut microenvironment homeostasis: An open-label, randomized clinical trial. EBioMedicine 2018, 35, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clardy, J.; Fischbach, M.A.; Currie, C.R. The natural history of antibiotics. Current Biol. 2009, 19, R437–R441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melander, R.J.; Basak, A.K.; Melander, C. Natural products as inspiration for the development of bacterial antibiofilm agents. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 1454–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradori, S.; Di Giacomo, N.; Lobefalo, M.; Luisi, G.; Campestre, C.; Sisto, F. Biofilm and quorum sensing inhibitors: The road so far. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2020, 30, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccelli, A.; Carradori, S.; Puca, V.; Sisto, F.; Lanuti, P.; Crestoni, M.E.; Lasalvia, A.; Muraro, R.; Bysell, H.; Di Sotto, A.; et al. Correlation between the antimicrobial activity and metabolic profiles of cell free supernatants and membrane vesicles produced by Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Hang, X.; Bi, H. Armeniaspirol A: A novel anti-Helicobacter pylori agent. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lodovico, S.; Napoli, E.; Di Campli, E.; Di Fermo, P.; Gentile, D.; Ruberto, G.; Nostro, A.; Marini, E.; Cellini, L.; Di Giulio, M. Pistacia vera L. Pistacia vera L. oleoresin and levofloxacin is a synergistic combination against resistant Helicobacter pylori strains. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, V.; Di Bartolomeo, S.; Di Campli, E.; Nostro, A.; Cellini, L.; Di Giulio, M. In vitro activity of Aloe vera inner gel against microorganisms grown in planktonic and sessile phases. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2015, 28, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenório, M.C.D.S.; Graciliano, N.G.; Moura, F.A.; Oliveira, A.C.M.D.; Goulart, M.O.F. N-acetylcysteine (NAC): Impacts on human health. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, E.P.; Conceição, E.L.; Costa, D.L.; Rocha, M.S.; Marinho, J.M.; Cordeiro-Santos, M.; Andrade, B.B. N-acetyl-cysteine exhibits potent anti-mycobacterial activity in addition to its known anti-oxidative functions. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Bak, E.-J.; Cha, J.-H. N-acetylcysteine prevents the development of gastritis induced by Helicobacter pylori infection. J. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, L.E.S.; Martimbianco, A.L.C.; Zanin, C.; Riera, R. N-acetylcysteine as an adjuvant therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feridouni, F.; Gerist, F.; Malekzadeh, J. The Effect of N-Acetylcysteine on the Treatment of Persistent Helicobacter pylori Infection. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2021, 3, 2497–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Branca, G.; Ardito, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Ianiro, G.; Cianci, R.; Torelli, R.; Masala, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Fadda, G.; et al. Biofilm demolition and antibiotic treatment to eradicate resistant Helicobacter pylori: A clinical trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 817–820.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, P.; Shen, Y.; Zou, Y.; Yuan, G.; Hu, H. Rhamnolipid-involved antibiotics combinations improve the eradication of Helicobacter pylori biofilm in vitro: A comparison with conventional triple therapy. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 131, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.J.; Chan, S.S.; Khoo, K.S.; Munawaroh, H.S.H.; Lim, H.R.; Chew, K.W.; Ling, T.C.; Saravanan, A.; Ma, Z.; Show, P.L. Recent advances and discoveries of microbial-based glycolipids: Prospective alternative for remediation activities. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 68, 108198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, B.; Saeed, F.; Ahmed, A.; Imran, M.; Maan, A.A.; Khan, M.K.I.; Tufail, T.; Anjum, F.M.; Hussain, S.; Suleria, H.A.R. Lactoferrin (LF): A natural antimicrobial protein. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1626–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Chávez, S.A.; Arévalo-Gallegos, S.; Rascón-Cruz, Q. Lactoferrin: Structure, function and applications. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 33, 301.e1–301.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ren, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wang, K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.-S.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z. Lactoferrin: A glycoprotein that plays an active role in human health. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1018336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, N.; Yamauchi, K.; Kawase, K.; Hayasawa, H.; Nakao, K.; Imoto, I. Antibacterial effects of lactoferrin and a pepsin-generated lactoferrin peptide against Helicobacter pylori in vitro. J. Infect. Chemother. 1997, 3, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Aiba, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Takagi, A.; Miwa, T.; Koga, Y. The therapeutic effect of bovine lactoferrin in the host infected with Helicobacter pylori. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 34, 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Ciccaglione, A.F.; Di Giulio, M.; Di Lodovico, S.; Di Campli, E.; Cellini, L.; Marzio, L. Bovine lactoferrin enhances the efficacy of levofloxacin-based triple therapy as first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: An in vitro and in vivo study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dial, E.J.; Hall, L.R.; Serna, H.; Fox, J.G.; Lichtenberger, L.M. Antibiotic properties of bovine lactoferrin on Helicobacter pylori. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 2750–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, A.; Nagpal, J. Meta-analysis: Efficacy of bovine lactoferrin in Helicobacter pylori eradication. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 29, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Haley, K.P.; Francis, J.D.; Guevara, M.A.; Doster, R.S.; Craft, K.M.; Moore, R.E.; Chambers, S.A.; Delgado, A.G.; Piazuelo, M.B.; et al. The innate immune glycoprotein lactoferrin represses the Helicobacter pylori cag type IV secretion system. Chembiochem 2021, 22, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, T.; Moreira, C.; Cária, N.; Victoriano, G.; Silva, W., Jr.; Magalhães, J. Phytotherapy: An introduction to its history, use and application. Rev. Bras. Plantas Med. 2014, 16, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, F.F.; Oleastro, M. Overview of the phytomedicine approaches against Helicobacter pylori. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathianarayanan, S.; Ammanath, A.V.; Biswas, R.; Sukumaran, S.; Venkidasamy, B. A new approach against Helicobacter pylori using plants and its constituents: A review study. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 168, 105594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bent, S. Herbal medicine in the United States: Review of efficacy, safety, and regulation: Grand rounds at University of California, San Francisco Medical Center. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2008, 23, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítor, J.M.; Vale, F.F. Alternative therapies for Helicobacter pylori: Probiotics and phytomedicine. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 63, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.Z.; Ke, F.; Yadav, P.K. Herbal medicine in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Xu, J.-Y.; Wang, X.; Liao, L.-J.; Huang, L.; Huang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-F. BanXiaXieXin decoction treating gastritis mice with drug-resistant Helicobacter pylori and its mechanism. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Moaty, H.I.A.; Soliman, N.A.; Hamad, R.S.; Ismail, E.H.; Sabry, D.Y.; Khalil, M.M. Comparative therapeutic effects of Pituranthos tortuosus aqueous extract and phyto-synthesized gold nanoparticles on Helicobacter pylori, diabetic and cancer proliferation. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 139, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Valle, M.; Orellana-Palma, P.; Petzold, G. Plant-based polyphenols: Anti-Helicobacter pylori effect and improvement of gut microbiota. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, N.M.; Al-Sayed, E.; Michel, H.E.; El-Shazly, M.; Singab, A.N.B. Gastroprotective effects of Erythrina speciosa (Fabaceae) leaves cultivated in Egypt against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 248, 112297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardast, M.; Namakin, K.; Kaho, J.E.; Hashemi, S.S. Assessment of antibacterial effect of garlic in patients infected with Helicobacter pylori using urease breath test. Avicenna J. Phytomedicine 2016, 6, 495. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub, I.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Elhady, S.S.; Bagalagel, A.A.; Malatani, R.T.; Elkady, W.M. Valorization of Pimenta racemosa essential oils and extracts: GC-MS and LC-MS phytochemical profiling and evaluation of Helicobacter pylori inhibitory activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shmuely, H.; Domniz, N.; Yahav, J. Non-pharmacological treatment of Helicobacter pylori. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.; Chen, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, Y. The effects and mechanisms of natural products on Helicobacter pylori eradication. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1360852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Wu, Y.; Song, Z.; Li, S.; Du, M.; Deng, J.; Xu, Q.; Deng, L.; Bahlol, H.S.; Han, H. Tea polyphenol liposomes overcome gastric mucus to treat Helicobacter pylori infection and enhance the intestinal microenvironment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 13001–13012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, S.; Shen, C.; Xiang, J.; Chen, N.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Berberine for gastric cancer prevention and treatment: Multi-step actions on the Correa’s cascade underlie its therapeutic effects. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 184, 106440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Wu, G.; Du, J.; Ye, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ji, R. The comparative efficacy and safety of 9 traditional Chinese medicines combined with standard quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Tan, Z. An overview of traditional Chinese medicine therapy for Helicobacter pylori–related gastritis. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, B.N.; Shin, H.; Lim, B.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.S.; Park, J.M.; Na, K. Helicobacter pylori-targeting multiligand photosensitizer for effective antibacterial endoscopic photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 271, 120745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dąbrowski, J.M. Reactive oxygen species in photodynamic therapy: Mechanisms of their generation and potentiation. In Advances in Inorganic Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 70, pp. 343–394. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbani, J.; Rahban, D.; Aghamiri, S.; Teymouri, A.; Bahador, A. Photosensitizers in antibacterial photodynamic therapy: An overview. Laser Ther. 2018, 27, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Gomes, I.; Saavedra, M.; Simões, M. Photodynamic therapy and combinatory treatments for the control of biofilm-associated infections. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, C.; Ferreira, R.; Azevedo, N.F.; Oleastro, M.; Azeredo, J.; Figueiredo, C.; Melo, L.D.R. Helicobacter pylori infection: From standard to alternative treatment strategies. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 48, 376–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.-Y.; Kankala, R.K.; Wang, S.-B.; Chen, A.-Z. Sonodynamic therapy-based nanoplatforms for combating bacterial infections. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2023, 100, 106617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, D. Research progress in photodynamic therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 2024, 29, e13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.; Kim, K.S.; Ahn, J.Y.; Na, K. Overcoming antibiotic resistance caused by genetic mutations of Helicobacter pylori with mucin adhesive polymer-based therapeutics. Biomaterials 2024, 308, 122541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, C.; Dolan, B.; Clyne, M. Factors that mediate colonization of the human stomach by Helicobacter pylori. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.-L.; Cheng, D.-D.; Xu, W.-T.; Lu, N.-H. Adhesion and invasion of gastric mucosa epithelial cells by Helicobacter pylori. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, P.M.; Goode, P.L.; Mobasseri, A.; Zopf, D. Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori binding to gastrointestinal epithelial cells by sialic acid-containing oligosaccharides. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins Antunes de Melo, W.C.; Celiešiūtė-Germanienė, R.; Šimonis, P.; Stirkė, A. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) for biofilm treatments. Possible synergy between aPDT and pulsed electric fields. Virulence 2021, 12, 2247–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo, W.C.M.A.; Avci, P.; De Oliveira, M.N.; Gupta, A.; Vecchio, D.; Sadasivam, M.; Chandran, R.; Huang, Y.Y.; Yin, R.; Perussi, L.R.; et al. Photodynamic inactivation of biofilm: Taking a lightly colored approach to stubborn infection. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 669–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hamblin, M.R. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy to control clinically relevant biofilm infections. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosselli, R.; Millioni, R.; Puricelli, L.; Tessari, P.; Arrigoni, G.; Franchin, C.; Segalla, A.; Teardo, E.; Reddi, E. Molecular targets of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy identified by a proteomic approach. J. Proteom. 2012, 77, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.; Melo, T.; Santos, N.; Rosa, L.; Alves, E.; Gomes, M.C.; Cunha, Â.; Neves, M.G.; Faustino, M.A.; Domingues, M.R.M.; et al. Evaluation of the interplay among the charge of porphyrinic photosensitizers, lipid oxidation and photoinactivation efficiency in Escherichia coli. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2014, 141, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.; Jou, P.C.; Lattif, A.A.; Lee, Y.; Malbasa, C.L.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Oleinick, N.L.; Ghannoum, M.A.; Cooper, K.D.; Baron, E.D. Photodynamic therapy with Pc 4 induces apoptosis of Candida albicans. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011, 87, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beirão, S.; Fernandes, S.; Coelho, J.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Tomé, J.P.C.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Tomé, A.C.; Almeida, A.; Cunha, A. Photodynamic inactivation of bacterial and yeast biofilms with a cationic porphyrin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2014, 90, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka, K.; Goslinski, T. Photodynamic therapy in dentistry. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Fu, L.; Wei, C.; Fu, Q.; Pan, S. Antibacterial micro/nanomotors: Advancing biofilm research to support medical applications. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tong, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Men, C.; Yu, J.; Pan, J.; Wan, D.; et al. Phototherapy and Mechanism Exploration of Biofilm and Multidrug-Resistant Helicobacter pylori by Bacteria-Targeted NIR Photosensitizer. Small 2023, 19, 2205248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Peng, N.; Liang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Y. Phage therapy: Consider the past, embrace the future. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo Altamirano, F.L.; Barr, J.J. Phage therapy in the postantibiotic era. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathdee, S.A.; Hatfull, G.F.; Mutalik, V.K.; Schooley, R.T. Phage therapy: From biological mechanisms to future directions. Cell 2023, 186, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Datta, S.; Prasad, R.; Dubey, D.; Prasad, R.K.; Vairale, M.G. Bacteriophages and its applications: An overview. Folia Microbiol. 2017, 62, 17–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.; Gutiérrez, D.; García, P.; Rodríguez, A. The perfect bacteriophage for therapeutic applications—A quick guide. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Liu, N.; Pu, S.; Zhuang, Z.; Gong, H.; Zhang, D. A review on the research progress on non-pharmacological therapy of Helicobacter pylori. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1134254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.; Sousa, C.; Gonçalves, R.F.S.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Oleastro, M.; Wagemans, J.; Lavigne, R.; Figueiredo, C.; Azeredo, J.; Melo, L.D.R. Characterization and genomic analysis of a new phage infecting Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, P.; Papaianni, M.; Fulgione, A.; Guerra, F.; Capparelli, R.; Medaglia, C. An innovative approach to control H. pylori-induced persistent inflammation and colonization. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Thiagarajan, V.; Walmagh, M.; Sillankorva, S.; Lavigne, R.; Neves-Petersen, M.T.; Kluskens, L.D.; Azeredo, J. A thermostable Salmonella phage endolysin, Lys68, with broad bactericidal properties against gram-negative pathogens in presence of weak acids. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, H.; Melo, L.D.R.; Santos, S.B.; Nóbrega, F.L.; Ferreira, E.C.; Cerca, N.; Azeredo, J.; Kluskens, L.D. Molecular aspects and comparative genomics of bacteriophage endolysins. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 4558–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, H.; São-José, C.; Azeredo, J. Phage-derived peptidoglycan degrading enzymes: Challenges and future prospects for in vivo therapy. Viruses 2018, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lood, R.; Winer, B.Y.; Pelzek, A.J.; Diez-Martinez, R.; Thandar, M.; Euler, C.W.; Fischetti, V.A. Novel phage lysin capable of killing the multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii in a mouse bacteremia model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1983–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öcal, S. Managing Helicobacter pylori infection: Transitioning from conventional to alternative treatment approaches. Eur. Res. J. 2024, 10, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malfertheiner, P.; Selgrad, M.; Wex, T.; Romi, B.; Borgogni, E.; Spensieri, F.; Zedda, L.; Ruggiero, P.; Pancotto, L.; Censini, S.; et al. Efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of a parenteral vaccine against Helicobacter pylori in healthy volunteers challenged with a Cag-positive strain: A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunle, K.; Tong, W.; Jiyang, L.; Guojun, W. Advances in Helicobacter pylori vaccine research: From candidate antigens to adjuvants—A review. Helicobacter 2024, 29, e13034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, T.G.; Czinn, S.J. Identification of Helicobacter pylori and the evolution of an efficacious childhood vaccine to protect against gastritis and peptic ulcer disease. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 81, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banga Ndzouboukou, J.L.; Lei, Q.; Ullah, N.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, L.; Fan, X. Helicobacter pylori adhesins: HpaA a potential antigen in experimental vaccines for H. pylori. Helicobacter 2021, 26, e12758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Viana, I.; Cordeiro Santos, M.L.; Santos Marques, H.; Lima de Souza Goncalves, V.; Bittencourt de Brito, B.; Franca da Silva, F.A.; Freire de Melo, F. Vaccine development against Helicobacter pylori: From ideal antigens to the current landscape. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Ke, H.; Niu, X.; Li, S.; Lv, J.; Pan, L. Protection against Helicobacter pylori infection in BALB/c mouse model by oral administration of multivalent epitope-based vaccine of cholera toxin B subunit-HUUC. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Hong, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Tang, F.; Wu, T.; Chu, Y.; Liu, H.; He, M.; Yang, H.; et al. Therapeutic protection against H. pylori infection in Mongolian gerbils by oral immunization with a tetravalent epitope-based vaccine with polysaccharide adjuvant. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Ji, Q.; Liu, Q. Evaluation of an attenuated Listeria monocytogenes as a vaccine vector to control Helicobacter pylori infection. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 238, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Yin, R.; Xu, G.; Gong, X.; Chang, Z.; Hong, D.; Liu, K. Immunologic properties and therapeutic efficacy of a multivalent epitope-based vaccine against four Helicobacter pylori adhesins (urease, Lpp20, HpaA, and CagL) in Mongolian gerbils. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsande, P.M.; Nguyen, V.D.; Nguyen, T.L.P.; Mills, G.; Bailey, D.M.D.; Christie, G.; Hong, H.A.; Cutting, S.M. Prophylactic immunization to Helicobacter pylori infection using spore vectored vaccines. Helicobacter 2023, 28, e12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, M.; Mao, X.-H.; Li, J.-X.; Tong, W.-D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Guo, G.; Zhao, Z.-J.; Li, L.; Wu, D.-L.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of an oral recombinant Helicobacter pylori vaccine in children in China: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.; Boag, J.M. Status of vaccine research and development for Helicobacter pylori. Vaccine 2019, 37, 7295–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Therapy | Type of Study | Study Description | Outcomes and Endpoints | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triple therapy plus colloidal bismuth subcitrate (CBS) therapy | Clinical | The study included children aged 5 to 18 with H. pylori infection identified by endoscopy in the Spanish Registry. It analyzed patients who received CBS treatment between 2020 and 2023, with 38 patients (5.6%) treated out of 682 registered. |
| [155] |
| Clinical | Seventy-three pediatric outpatients (48 males, 25 females; ages 9–14) diagnosed with H. pylori-associated chronic gastritis and dyspeptic symptoms participated in the study. They underwent endoscopic evaluation and received a 10-day treatment of bismuth subcitrate (8 mg/kg/day), nifuratel (30 mg/kg/day), and amoxicillin (50 mg/kg/day), given four times daily. H. pylori infection status was evaluated before and 4 to 6 weeks after treatment using modified Giemsa staining. |
| [157] | |
| Tailored therapy | Clinical | A meta-analysis assessed empirical and susceptibility-guided treatment approaches for H. pylori, involving 54 studies with 6705 patients in the empirical cohort and 7895 in the susceptibility-guided cohort. |
| [160] |
| Clinical | This meta-analysis reviewed 16 randomized controlled trials comparing susceptibility-guided therapy and empirical therapy for H. pylori infection, involving 2451 patients on empirical treatment and 2374 on susceptibility-guided therapy. |
| [161] | |
| Potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs) | Clinical | The study included 232 treatment-naïve participants divided into two groups: Arm 1 (58 patients) received clarithromycin, amoxicillin, and vonoprazan, while Arm 2 (58 patients) received clarithromycin, amoxicillin, and esomeprazole. Treatment-experienced patients were in Group II, consisting of Arm 3 (intervention) and Arm 4 (comparator), each with 58 participants. Arm 3 received levofloxacin, vonoprazan, nitazoxanide, and doxycycline, while Arm 4 received levofloxacin, esomeprazole, nitazoxanide, and doxycycline. All participants followed their treatment for 14 days, with H. pylori eradication assessed four weeks later. |
| [167] |
| Probiotics | Clinical | This double-blind, randomized controlled trial enrolled 450 patients with H. pylori infection. Participants received a 14-day quadruple treatment of bismuth subcitrate, pantoprazole, amoxicillin, and clarithromycin, and were randomly assigned to either a probiotic (Lactobacillus ruteri, 100 mg) or a placebo. Eight weeks post-therapy, a urea breath test assessed H. pylori eradication rates, the primary outcome, while side effects were evaluated as a secondary outcome. |
| [174] |
| Clinical | The study involved 95 H. pylori-positive participants and 56 negative controls, aged 19 to 30, assigned to probiotics monotherapy, probiotics-supplemented quadruple therapy, or quadruple therapy alone. Gastric mucosal samples were collected before treatment and two months later for 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Two months after eradication, the gastric microbial composition significantly differed from that of H. pylori-negative participants, with decreased alpha diversity in gastric juice and increased diversity in gastric mucosa. |
| [180] | |
| Lactoferrin therapy | Preclinical in vitro | An investigation was conducted to evaluate the antibacterial properties of lactoferrin and Lactoferricin®, an antimicrobial peptide derived from lactoferrin, against H. pylori. |
| [204] |
| Preclinical in vivo | The impact of bovine lactoferrin (bLF) on germ-free BALB/c mice infected with H. pylori was examined. After oral inoculation with H. pylori, the mice were given bLF daily for either two or four weeks. The mice were then euthanized to evaluate serum antibody levels and bacterial counts in the stomach. To isolate H. pylori attached to the gastric epithelium, the stomachs were agitated in phosphate-buffered saline. |
| [205] | |
| Phytotherapy | Preclinical in vitro and in vivo | This study examines the effects of Banxia Xiexin Decoction (BXXXT), a traditional Chinese medicine prescription, on drug-resistant H. pylori-induced gastritis in mice using in vivo and in vitro methods. The aqueous extract of BXXXT was prepared by water decoction. In vitro tests indicated that BXXXT inhibits H. pylori. An acute gastritis model was established in vivo to assess H. pylori colonization, gastric mucosal repair, inflammation, and apoptosis in treated mice. |
| [216] |
| Preclinical In vitro and in silico | The essential oils and methanol extracts of Pimenta racemosa (P. racemosa) leaves and stems were studied for their potential inhibitory activities against H. pylori both in vitro and in silico. The antibacterial activity of the essential oils and methanol extracts against H. pylori was evaluated using the micro-well dilution technique. |
| [221] | |
| Phototherapy | Preclinical In vitro | A bacteria-targeted near-infrared (NIR) photosensitizer, designated T780T-Gu, has been developed through the combination of positively charged guanidinium (Gu) and the effective phototherapeutic agent T780T. |
| [248] |
| Preclinical In vivo | The authors have developed a poly-L-lysine-based photomedicine conjugated with multiple 3SL (p3SLP). They proposed a targeted PDT strategy utilizing an endoscopic laser system for the treatment of H. pylori. The antibacterial efficacy of p3SLP was evaluated in C57BL/6 mice infected with H. pylori. |
| [228] | |
| Phage therapy | Preclinical In vitro | Prophage isolation using H. pylori strains and UV radiation led to the identification of HPy1R, a new podovirus with a genome of 31,162 bp and a GC content of 37.1%. It encodes 36 predicted proteins, 17 of which are structural. The phage remains stable at 37 °C and pH levels from 3 to 11 for 24 h. |
| [255] |
| Preclinical In vitro | The effectiveness of H. pylori-specific lytic phage (H. pylori φ) alone and with lactoferrin adsorbed on hydroxyapatite (LF-HA) nanoparticles (H. pylori φ + LF-HA) in preventing H. pylori infection. The bacteria were obtained from human stomach biopsies and cultured in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth with 10% horse serum at 37 °C and 5% CO2 for phage isolation. |
| [256] | |
| Vaccine development | Preclinical in vivo | The multivalent epitope-based vaccine CFAdE was developed from antigenic fragments of four Helicobacter pylori adhesins: urease, Lpp20, HpaA, and cagL. Its specificity, immunogenicity, and ability to generate neutralizing antibodies were tested in BALB/c mice, followed by evaluations in H. pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils. |
| [270] |
| Preclinical In vivo | Bacillus subtilis spores were engineered to display potential H. pylori protective antigens, urease subunit A (ureA), and subunit B (ureB), on the spore surface. Immunity and colonization in mice challenged with H. pylori after orally administering these spores were tested. |
| [271] | |
| Clinical Phase 3 trial) | A phase 3 clinical study in China evaluated a three-dose oral recombinant H. pylori vaccine’s effectiveness, safety, and immunogenicity in healthy children aged six to fifteen. Participants without prior infection were randomly assigned to receive the vaccine or a placebo, with the primary outcome being the incidence of infection within one year. Registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02302170), the trial enrolled 4464 individuals from 2 December 2004, to 19 March 2005, with 4403 (99%) completing the regimen. |
| [272] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elbehiry, A.; Abalkhail, A.; Anajirih, N.; Alkhamisi, F.; Aldamegh, M.; Alramzi, A.; AlShaqi, R.; Alotaibi, N.; Aljuaid, A.; Alzahrani, H.; et al. Helicobacter pylori: Routes of Infection, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Alternative Therapies as a Means to Develop Infection Control. Diseases 2024, 12, 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12120311
Elbehiry A, Abalkhail A, Anajirih N, Alkhamisi F, Aldamegh M, Alramzi A, AlShaqi R, Alotaibi N, Aljuaid A, Alzahrani H, et al. Helicobacter pylori: Routes of Infection, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Alternative Therapies as a Means to Develop Infection Control. Diseases. 2024; 12(12):311. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12120311
Chicago/Turabian StyleElbehiry, Ayman, Adil Abalkhail, Nuha Anajirih, Fahad Alkhamisi, Mohammed Aldamegh, Abdullah Alramzi, Riyad AlShaqi, Naif Alotaibi, Abdullah Aljuaid, Hilal Alzahrani, and et al. 2024. "Helicobacter pylori: Routes of Infection, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Alternative Therapies as a Means to Develop Infection Control" Diseases 12, no. 12: 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12120311
APA StyleElbehiry, A., Abalkhail, A., Anajirih, N., Alkhamisi, F., Aldamegh, M., Alramzi, A., AlShaqi, R., Alotaibi, N., Aljuaid, A., Alzahrani, H., Alzaben, F., Rawway, M., Ibrahem, M., Abdelsalam, M. H., Rizk, N. I., Mostafa, M. E. A., Alfaqir, M. R., Edrees, H. M., & Alqahtani, M. (2024). Helicobacter pylori: Routes of Infection, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Alternative Therapies as a Means to Develop Infection Control. Diseases, 12(12), 311. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12120311







