Efficiency of IL-6 in Early Prognosis and Follow-Up in Critically Ill Patients with Septic Shock
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biochemical Assessment
2.2. Assessment of Interleukin-6
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
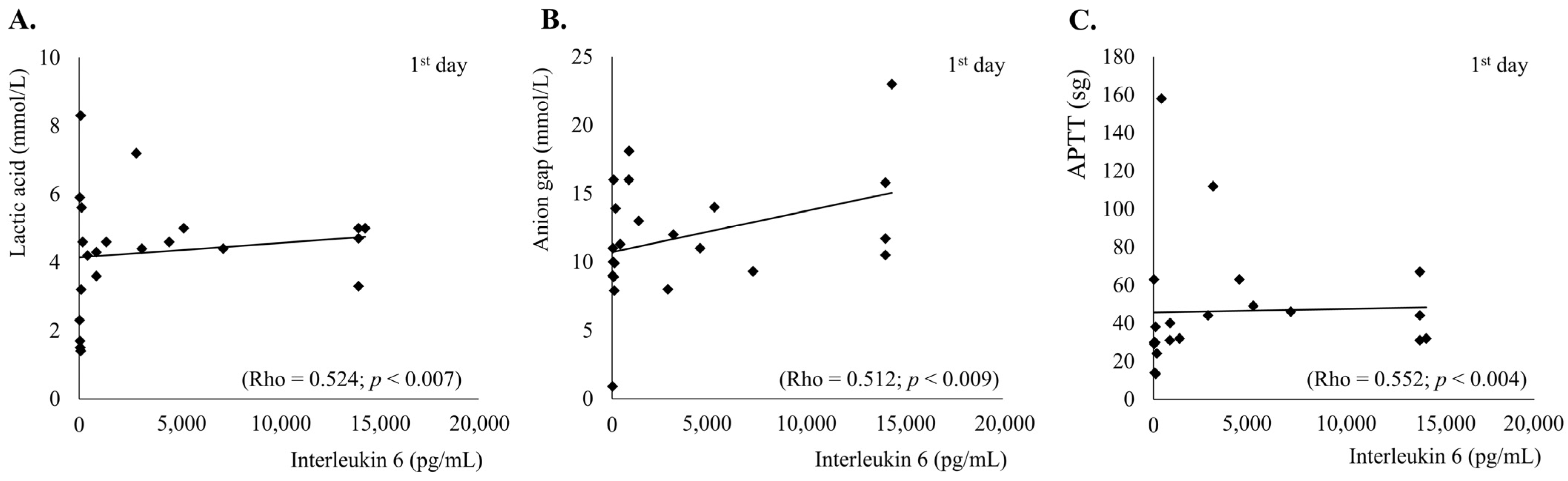
3.2. Biochemical Parameters
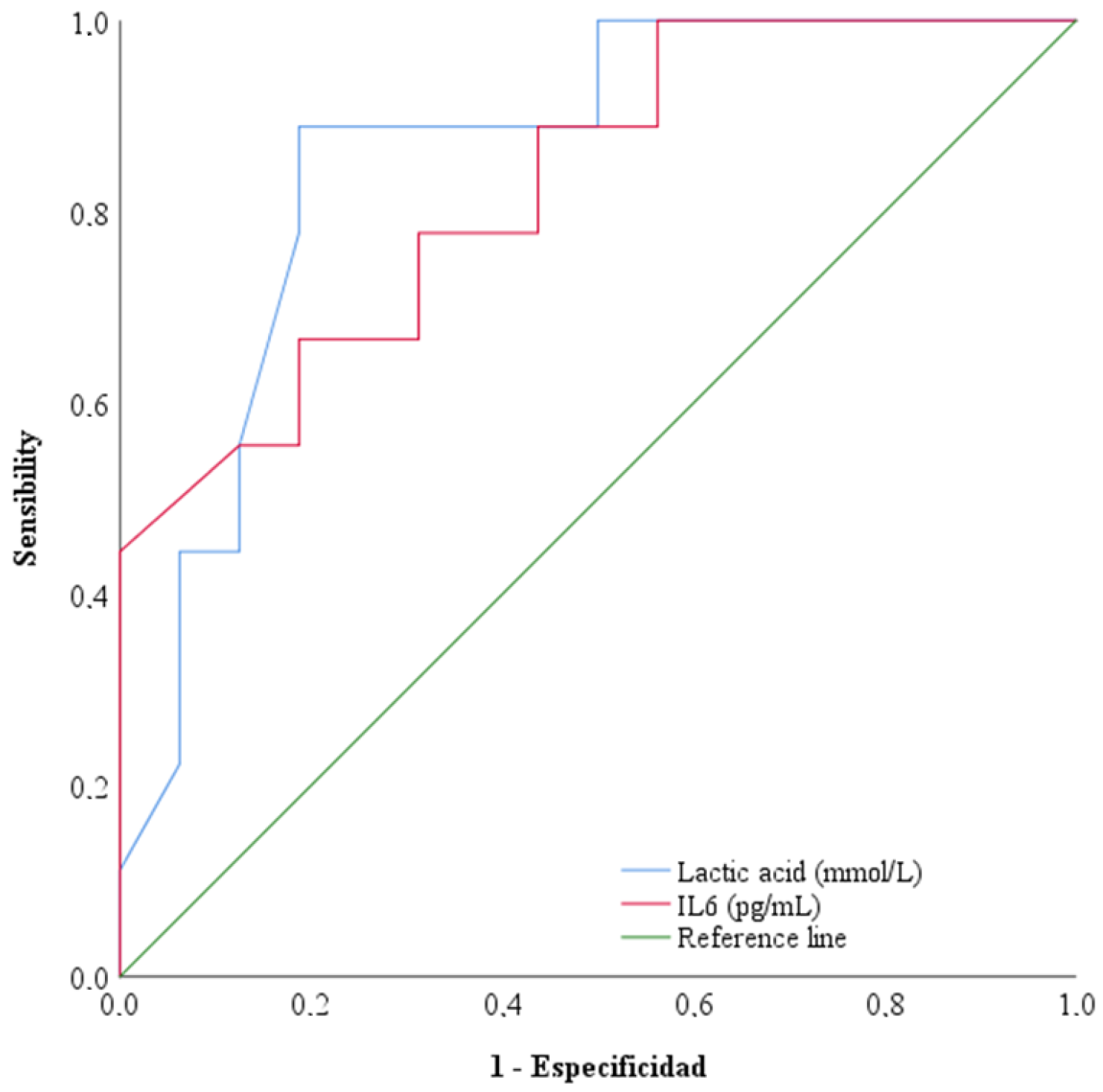
3.3. Interleukin-6 and Morbimortality Parameters
3.4. Interleukin-6, Acute Phase Reactants and Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, D.C.; van der Poll, T. Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, R.; Humphrey, J.H.; Mutasa, K.; Ntozini, R.; Stoltzfus, R.J. Short Communication: Predicting Adverse HIV-Related Outcomes in a Resource-Limited Setting: Use of the Inflammation Marker α(1)-Acid Glycoprotein. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2010, 26, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, W.; Xie, J. Circulating Interleukin-6 Levels and Cardiovascular and All-Cause Mortality in the Elderly Population: A Meta-Analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2017, 73, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, H.T.; Herbertz, A.; Bertram, M.; Diehl, V. Increase in Interleukin-6 Serum Level Preceding Fever in Granulocytopenia and Correlation with Death from Sepsis. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 171, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hack, C.E.; De Groot, E.R.; Felt-Bersma, R.J.; Nuijens, J.H.; Strack Van Schijndel, R.J.; Eerenberg-Belmer, A.J.; Thijs, L.G.; Aarden, L.A. Increased Plasma Levels of Interleukin-6 in Sepsis. Blood 1989, 74, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, M.; Czerlinski, S.; Friedel, N.; Liebenthal, C.; Hasper, D.; von Baehr, R.; Hetzer, R.; Volk, H.D. Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-8 Concentrations as Predictors of Outcome in Ventricular Assist Device Patients before Heart Transplantation. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 22, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.; Bundschu, J.; Gallati, H.; Bartmann, P.; Pohlandt, F. Interleukin-6: A Sensitive Parameter for the Early Diagnosis of Neonatal Bacterial Infection. Pediatrics 1994, 93, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Hermanns, H.M.; Schaper, F.; Müller-Newen, G.; Grötzinger, J.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. Plasticity and Cross-Talk of Interleukin 6-Type Cytokines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012, 23, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, S.; Hirasawa, H.; Shiga, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Matsuda, K.; Nakamua, M. Sequential Measurement of IL-6 Blood Levels in Patients with Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)/Sepsis. Cytokine 2005, 29, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloos, F.; Reinhart, K. Rapid Diagnosis of Sepsis. Virulence 2014, 5, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, K.; Meisner, M.; Brunkhorst, F.M. Markers for Sepsis Diagnosis: What Is Useful? Crit. Care Clin. 2006, 22, 503–519, ix–x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahaba, A.A.; Metzler, H. Procalcitonin’s Role in the Sepsis Cascade. Is Procalcitonin a Sepsis Marker or Mediator? Minerva Anestesiol. 2009, 75, 447–452. [Google Scholar]
- Pepys, M.B.; Hirschfield, G.M. C-Reactive Protein: A Critical Update. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsokos, M.; Reichelt, U.; Jung, R.; Nierhaus, A.; Püschel, K. Interleukin-6 and C-Reactive Protein Serum Levels in Sepsis-Related Fatalities during the Early Postmortem Period. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2001, 119, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.-L.; Guo, W.-Z.; Ma, Y.-Q.; Wang, Y.-B.; Shu, C.; Dong, L.-Q. Role of Interleukin-6 to Differentiate Sepsis from Non-Infectious Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. Cytokine 2016, 88, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A.; Evans, L.E.; Alhazzani, W.; Levy, M.M.; Antonelli, M.; Ferrer, R.; Kumar, A.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 304–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Pan, J.; Chen, D.; Li, Y. Serum Procalcitonin and Interleukin-6 Levels May Help to Differentiate Systemic Inflammatory Response of Infectious and Non-Infectious Origin. Chin. Med. J. 2003, 116, 538–542. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Pan, J. Serum procalcitonin and interleukin-6 help differentiate between severe sepsis and systemic inflammatory response syndrome of non-infectious origin. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2002, 82, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierson-Perry, J.F. EP17 A2|Evaluation of Detection Capability for Clinical Laboratory Measurement Procedures, 2nd ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012; Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/method-evaluation/documents/ep17/ (accessed on 4 August 2024).
- Weidhase, L.; Wellhöfer, D.; Schulze, G.; Kaiser, T.; Drogies, T.; Wurst, U.; Petros, S. Is Interleukin-6 a Better Predictor of Successful Antibiotic Therapy than Procalcitonin and C-Reactive Protein? A Single Center Study in Critically Ill Adults. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; St-Pierre, C.; Bhaumik, P.; Nieminen, J. Galectins in Innate Immunity: Dual Functions of Host Soluble Beta-Galactoside-Binding Lectins as Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs) and as Receptors for Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs). Immunol. Rev. 2009, 230, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michie, H.R.; Manogue, K.R.; Spriggs, D.R.; Revhaug, A.; O’dwyer, S.; Dinarello, C.A.; Cerami, A.; Wolff, S.M.; Wilmore, D.W. Detection of Circulating Tumor Necrosis Factor after Endotoxin Administration. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulie, P.G.; Cayphas, S.; Vink, A.; Uyttenhove, C.; Van Snick, J. Interleukin-HP1-Related Hybridoma and Plasmacytoma Growth Factors Induced by Lipopolysaccharide in Vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 1987, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, W.; Nakada, T.-A.; Yazaki, M.; Oda, S. Interleukin-6 Levels Act as a Diagnostic Marker for Infection and a Prognostic Marker in Patients with Organ Dysfunction in Intensive Care Units. Shock 2016, 46, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Khalid, S.; Jiang, L. Diagnostic and Predictive Performance of Biomarkers in Patients with Sepsis in an Intensive Care Unit. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházka, V.; Lacina, L.; Smetana, K.; Svoboda, M.; Skřivanová, K.; Beňovská, M.; Jarkovský, J.; Křen, L.; Kala, Z. Serum Concentrations of Proinflammatory Biomarker Interleukin-6 (IL-6) as a Predictor of Postoperative Complications after Elective Colorectal Surgery. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tocu, G.; Mihailov, R.; Serban, C.; Stefanescu, B.I.; Tutunaru, D.; Firescu, D. The Contribution of Procalcitonin, C-Reactive Protein and Interleukin-6 in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Surgical Sepsis: An Observational and Statistical Study. J. Multidiscip. Health 2023, 16, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zeng, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Q.; Bai, T.; Xu, Y. PCT, IL-6, and IL-10 Facilitate Early Diagnosis and Pathogen Classifications in Bloodstream Infection. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatraju, P.K.; Morrell, E.D.; O’Connor, N.G.; Choi, A.; Fitzpatrick, M.; Smith, C.H.; Wurfel, M.M.; Liles, W.C. Differential Absolute Plasma IL-6 Concentrations between Two Immunoassay Platforms in Intensive Care Unit Patients with COVID-19. Biomark Med. 2023, 17, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnes, M.; Bertsch, T.; Lepiorz, D.; Lang, S.; Trinkmann, F.; Brueckmann, M.; Borggrefe, M.; Hoffmann, U. Diagnostic and Prognostic Utility of Soluble CD 14 Subtype (Presepsin) for Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock during the First Week of Intensive Care Treatment. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricarte-Bratti, J.P.; Brizuela, N.Y.; Jaime-Albarran, N.; Montrull, H.L. IL-6, MMP 3 and Prognosis in Previously Healthy Sepsis Patients. Rev. Fac. Cien. Med. Univ. Nac. Cordoba 2017, 74, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Chen, Y.-X.; Yin, Q.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Li, C.-S. Diagnostic Value and Prognostic Evaluation of Presepsin for Sepsis in an Emergency Department. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Li, G. Serum Soluble Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-1 and Procalcitonin Can Reflect Sepsis Severity and Predict Prognosis: A Prospective Cohort Study. Mediat. Inflamm 2014, 2014, 641039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Clec’h, C.; Ferriere, F.; Karoubi, P.; Fosse, J.P.; Cupa, M.; Hoang, P.; Cohen, Y. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Procalcitonin in Patients with Septic Shock. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.P.; Yilmaz, Y.; Kleespies, A.; Jauch, K.-W.; Hartl, W.H. Accuracy of Procalcitonin for Outcome Prediction in Unselected Postoperative Critically Ill Patients. Shock 2009, 31, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloos, F.; Marshall, J.C.; Dellinger, R.P.; Vincent, J.-L.; Gutierrez, G.; Rivers, E.; Balk, R.A.; Laterre, P.-F.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K.; et al. Multinational, Observational Study of Procalcitonin in ICU Patients with Pneumonia Requiring Mechanical Ventilation: A Multicenter Observational Study. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, N.I.; Howell, M.D.; Talmor, D.; Nathanson, L.A.; Lisbon, A.; Wolfe, R.E.; Weiss, J.W. Serum Lactate as a Predictor of Mortality in Emergency Department Patients with Infection. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2005, 45, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.W.; Mackenhauer, J.; Roberts, J.C.; Berg, K.M.; Cocchi, M.N.; Donnino, M.W. Etiology and Therapeutic Approach to Elevated Lactate Levels. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Lorente, H.; Molina-López, J.; Herrera-Quintana, L.; Gamarra-Morales, Y.; López-González, B.; Planells, E. Association between Body Fatness and Vitamin D3 Status in a Postmenopausal Population. Nutrients 2020, 12, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyland, D.K.; Dhaliwal, R.; Jiang, X.; Day, A.G. Identifying Critically Ill Patients Who Benefit the Most from Nutrition Therapy: The Development and Initial Validation of a Novel Risk Assessment Tool. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, L.J.; Bistrian, B.R. Appropriate Protein Provision in Critical Illness: A Systematic and Narrative Review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyland, D.K.; Weijs, P.J.M.; Coss-Bu, J.A.; Taylor, B.; Kristof, A.S.; O’Keefe, G.E.; Martindale, R.G. Protein Delivery in the Intensive Care Unit: Optimal or Suboptimal? Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 58S–71S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberda, C.; Gramlich, L.; Jones, N.; Jeejeebhoy, K.; Day, A.G.; Dhaliwal, R.; Heyland, D.K. The Relationship between Nutritional Intake and Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: Results of an International Multicenter Observational Study. Intensive Care Med. 2009, 35, 1728–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Day, A.G.; Ouellette-Kuntz, H.; Heyland, D.K. The Association Between Nutritional Adequacy and Long-Term Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients Requiring Prolonged Mechanical Ventilation: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyland, D.K.; Cahill, N.; Day, A.G. Optimal Amount of Calories for Critically Ill Patients: Depends on How You Slice the Cake! Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 2619–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyland, D.K.; Stephens, K.E.; Day, A.G.; McClave, S.A. The Success of Enteral Nutrition and ICU-Acquired Infections: A Multicenter Observational Study. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamarra-Morales, Y.; Molina-López, J.; Machado-Casas, J.F.; Herrera-Quintana, L.; Vázquez-Lorente, H.; Castaño-Pérez, J.; Perez-Villares, J.M.; Planells, E. Influence of Nutritional Parameters on the Evolution, Severity and Prognosis of Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1ª Day Median (IQR) | 3ª Day Median (IQR) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, (years) | 52.0 (22.0) | - | - |
| Male, number (%) | 22 (78.6) | - | - |
| SOFA score | 12.0 (4.0) | 9.0 (7.0) | 0.013 |
| APACHE II score | 22.0 (11.0) | - | - |
| Sepsis focus, number (%) | |||
| Respiratory (%) | 14 (50.0) | - | - |
| Urinary (%) | 6 (21.0) | - | - |
| Abdominal (%) | 8 (29.0) | - | - |
| MAP (mmHg) | 65.0 (18.0) | 80.0 (43.0) | 0.012 |
| FiO2 (%) | 0.60 (0.22) | 0.40 (0.26) | 0.001 |
| PaO2/FiO2 | 232.0 (101.0) | 242.0 (159.0) | 0.583 |
| PaCO2 (mmHg) | 40.5 (20.0) | 39.5 (14.5) | 0.345 |
| PEEP (cmH2O) | 10.0 (5.5) | 7.5 (4.5) | 0.276 |
| Cst (mL/cmH2O) | 37.5 (15.25) | 31.5 (12.25) | 0.593 |
| Reference Values | 1st Day Median (IQR) | 3rd Day Median (IQR) | p Value 1st–3rd Day | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactic acid (mmol/L) | 0.6–2.5 | 4.35 (1.78) | 1.55 (1.28) | 0.014 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 136–146 | 137.0 (7.5) | 138.5 (7.0) | 0.589 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 3.5–5.1 | 3.80 (1.1) | 3.80 (0.75) | 0.850 |
| Anion Gap (mmol/L) | 7–16 | 11.50 (6.02) | 9.50 (8.92) | 0.079 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.67–1.20 | 2.41 (3.09) | 1.79 (2.94) | 0.097 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.3–1.2 | 1.04 (1.70) | 1.40 (4.58) | 0.975 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 200–350 | 454.0 (210.0) | 475 (219) | 0.778 |
| LDH (U/L) | 110–295 | 645 (890) | 577 (1814) | 0.301 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 0.02–5 | 29.0 (15.4) | 15.4 (5.5) | 0.441 |
| Procalcitonin (ng/mL) | <0.5 | 27.2 (12.9) | 5 (18.63) | 0.018 |
| Leukocytes (*103/µL) | 3.5–10.5 | 11.69 (14.98) | 13.24 (81.28) | 0.679 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11–17 | 10.70 (3.57) | 8.75 (3.53) | 0.001 |
| Platelets (*103/µL) | 120–450 | 13.40 (13.03) | 68.50 (86.75) | 0.033 |
| INR (ratio) | 0.8–1.16 | 1.50 (0.33) | 1.25 (0.26) | 0.341 |
| APTT (sg) | 26–37 | 44.00 (41.50) | 36.00 (14.00) | 0.214 |
| Interleukin-6 (pg/mL) | <4.4 | 2860.9 (10,531.2) | 65.1 (335.2) | 0.005 |
| 1st Day (Mean ± SD) | 3rd Day (Mean ± SD) | p Value 1st Deceased vs. Non-Deceased | p Value 3rd Deceased vs. Non-Deceased | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Non-Deceased | Deceased | Non-Deceased | Deceased | ||
| Interleukin-6 (pg/mL) | 2879.9 ± 4786.5 | 43,828.2 ± 71,858.4 | 83.7 ± 142.3 | 2238.6 ± 2560.3 | 0.007 | 0.011 |
| Platelets (*103/µL) | 141.9 ± 88.5 | 96.2 ± 103.2 | 104.5 ± 55.6 | 29.3 ± 26.0 | 0.047 | 0.015 |
| Lactic acid (mmol/L) | 3.94 ± 1.77 | 5.76 ± 1.82 | 1.45 ± 0.36 | 5.22 ± 2.98 | 0.013 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gamarra-Morales, Y.; Molina-López, J.; Santiago-Ruiz, F.-C.; Herrera-Quintana, L.; Vázquez-Lorente, H.; Gascón-Luna, F.; Planells, E. Efficiency of IL-6 in Early Prognosis and Follow-Up in Critically Ill Patients with Septic Shock. Diseases 2024, 12, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12110298
Gamarra-Morales Y, Molina-López J, Santiago-Ruiz F-C, Herrera-Quintana L, Vázquez-Lorente H, Gascón-Luna F, Planells E. Efficiency of IL-6 in Early Prognosis and Follow-Up in Critically Ill Patients with Septic Shock. Diseases. 2024; 12(11):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12110298
Chicago/Turabian StyleGamarra-Morales, Yenifer, Jorge Molina-López, Felipe-Carlos Santiago-Ruiz, Lourdes Herrera-Quintana, Héctor Vázquez-Lorente, Félix Gascón-Luna, and Elena Planells. 2024. "Efficiency of IL-6 in Early Prognosis and Follow-Up in Critically Ill Patients with Septic Shock" Diseases 12, no. 11: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12110298
APA StyleGamarra-Morales, Y., Molina-López, J., Santiago-Ruiz, F.-C., Herrera-Quintana, L., Vázquez-Lorente, H., Gascón-Luna, F., & Planells, E. (2024). Efficiency of IL-6 in Early Prognosis and Follow-Up in Critically Ill Patients with Septic Shock. Diseases, 12(11), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12110298








