Association of COVID-19 Infection with Sociodemographic, Anthropometric and Lifestyle Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Older Adults’ Population Aged over 65 Years Old
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Association of COVID-19 Infection with Sociodemographic and Anthropometric Parameters of the Enrolled Older Adults
3.2. Association of COVID-19 Infection with Lifestyle Factors of the Enrolled Older Adults
3.3. Multivariate Binary Logistic Regression Analysis Examining Whether COVID-19 Infection May Exert an Independent Effect in Sociodemographic, Anthropometric, and Lifestyle Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19---11-march-2020 (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2022. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 22 March 2023).
- Yan, Z. Unprecedented pandemic, unprecedented shift, and unprecedented opportunity. Hum. Behav. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 2, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.K.; Webster, R.K.; Smith, L.E.; Woodland, L.; Wessely, S.; Greenberg, N.; Rubin, G.J. The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: Rapid review of the evidence. Lancet 2020, 395, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sideli, L.; Lo Coco, G.; Bonfanti, R.C.; Borsarini, B.; Fortunato, L.; Sechi, C.; Micali, N. Effects of COVID-19 lockdown on eating disorders and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2021, 29, 826–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Di, Y.; Ye, J.; Wei, W. Study on the public psychological states and its related factors during the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in some regions of China. Psychol. Health Med. 2021, 26, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minihan, S.; Orben, A.; Songco, A.; Fox, E.; Ladouceur, C.D.; Mewton, L.; Moulds, M.; Pfeifer, J.H.; Van Harmelen, A.L.; Schweizer, S. Social determinants of mental health during a year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Dev. Psychopathol. 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.; Patel, P. Stopping the spread of COVID-19. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaskheli, M.B.; Wang, S.; Hussain, R.Y.; Butt, M.; Yan, X.S.; Majid, S. Global law, policy, and governance for effective prevention and control of COVID-19: A comparative analysis of the law and policy of Pakistan, China, and Russia. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1035536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser Abed, S.; Kassab Shandaway Al-Zamali, S.; Mahdi Muslim, T. The epidemiological profile associated with lifestyle risk factors and nutritional status for COVID-19 patients in the Iraqi population. J. Public Health Afr. 2023, 14, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaim, A.; Saban, M. Dynamic Trends in Sociodemographic Disparities and COVID-19 Morbidity and Mortality—A Nationwide Study during Two Years of a Pandemic. Healthcare 2023, 11, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamelund, S.E. A socially neutral disease? Individual social class, household wealth and mortality from Spanish influenza in two socially contrasting parishes in Kristiania 1918–19. Soc. Sci. Med. 2006, 62, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, P.D.; Mytton, O.T.; Mak, M.; Donaldson, L.J. Socio-economic disparities in mortality due to pandemic influenza in England. Int. J. Public Health 2012, 57, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holaday, L.W.; Oladele, C.R.; Miller, S.M.; Dueñas, M.I.; Roy, B.; Ross, J.S. Loneliness, sadness, and feelings of social disconnection in older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2022, 70, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, R.; Nellums, L.B. COVID-19 and the consequences of isolating the elderly. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valtorta, N.K.; Kanaan, M.; Gilbody, S.; Ronzi, S.; Hanratty, B. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for coronary heart disease and stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal observational studies. Heart 2016, 102, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacioppo, J.T.; Hawkley, L.C.; Thisted, R.A. Perceived social isolation makes me sad: 5-year cross-lagged analyses of loneliness and depressive symptomatology in the Chicago Health, Aging, and Social Relations Study. Psychol. Aging 2010, 25, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.S.; Krueger, K.R.; Arnold, S.E.; Schneider, J.A.; Kelly, J.F.; Barnes, L.L.; Tang, Y.; Bennett, D.A. Loneliness and risk of Alzheimer disease. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotwal, A.A.; Cenzer, I.S.; Waite, L.J.; Covinsky, K.E.; Perissinotto, C.M.; Boscardin, W.J.; Hawkley, L.C.; Dale, W.; Smith, A.K. The epidemiology of social isolation and loneliness among older adults during the last years of life. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 69, 3081–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72,314 Cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.W.; Wu, X.X.; Jiang, X.G.; Xu, K.J.; Ying, L.J.; Ma, C.L.; Li, S.B.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.N.; et al. Clinical findings in a group of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) outside of Wuhan, China: Retrospective case series. BMJ 2020, 368, m606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, Y. WHO International Health Regulations Emergency Committee for the COVID-19 outbreak. Epidemiol. Health 2020, 42, e2020013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wang, B.; Yuan, T.; Chen, X.; Ao, Y.; Fitzpatrick, T.; Li, P.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Duan, Q.; et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filatov, A.; Sharma, P.; Hindi, F.; Espinosa, P.S. Neurological Complications of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Encephalopathy. Cureus 2020, 12, e7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi-Pooya, A.A.; Simani, L. Central nervous system manifestations of COVID-19: A systematic review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 413, 116832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Y.; Lin, R.; Han, K. Clinical features of COVID-19 in elderly patients: A comparison with young and middle-aged patients. J. Infect. 2020, 80, e14–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindegaard, N.; Benros, M.E. COVID-19 pandemic and mental health consequences: Systematic review of the current evidence. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, C.; Ricci, E.; Biondi, S.; Colasanti, M.; Ferracuti, S.; Napoli, C.; Roma, P. A Nationwide Survey of Psychological Distress among Italian People during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Immediate Psychological Responses and Associated Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rashid, M.R.; Syed Mohamad, S.N.; Tajjudin, A.I.A.; Roslan, N.; Jaffar, A.; Mohideen, F.B.S.; Addnan, F.H.; Baharom, N.; Ithnin, M. COVID-19 Pandemic Fatigue and Its Sociodemographic, Mental Health Status, and Perceived Causes: A Cross-Sectional Study Nearing the Transition to an Endemic Phase in Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.S.S.; Chin, S.A.F.X.; Sathapan, M.S.P.; Dewi, A.D.; Amini, F.; Bustami, N.A.; Tan, P.Y.; Ho, Y.B.; Tan, C.K. Mental Health and the COVID-19 Pandemic: Observational Evidence from Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, M.L.; Tee, C.A.; Anlacan, J.P.; Aligam, K.J.G.; Reyes, P.W.C.; Kuruchittham, V.; Ho, R.C. Psychological impact of COVID-19 pandemic in the Philippines. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.; Sultana, M.S.; Hossain, S.; Hasan, M.T.; Ahmed, H.U.; Sikder, M.T. The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health & wellbeing among home-quarantined Bangladeshi students: A cross-sectional pilot study. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 277, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klok, F.A.; Boon, G.J.A.M.; Barco, S.; Endres, M.; Geelhoed, J.J.M.; Knauss, S.; Rezek, S.A.; Spruit, M.A.; Vehreschild, J.; Siegerink, B. The Post-COVID-19 Functional Status scale: A tool to measure functional status over time after COVID-19. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2001494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed Elias, S.M.; Rohinmi, N.R. Knowledge, attitudes, and sociodemographic factors related to COVID-19 among older people living in the community in Malaysia. J. Educ. Health Promot. 2022, 11, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maracy, M.; Rahimi, M.; Shahraki, R.A. A survey of knowledge, attitude and practice of the older people about COVID-19 pandemic in Isfahan, Iran. J. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 68, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pue, S.; Gillebert, C.; Dierckx, E.; Vanderhasselt, M.A.; De Raedt, R.; Van den Bussche, E. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on wellbeing and cognitive functioning of older adults. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Charness, N.; Fingerman, K.; Kaye, J.; Kim, M.T.; Khurshid, A. When Going Digital Becomes a Necessity: Ensuring Older Adults’ Needs for Information, Services, and Social Inclusion During COVID-19. J. Aging Soc. Policy 2020, 32, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow-Howell, N.; Galucia, N.; Swinford, E. Recovering from the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Focus on Older Adults. J. Aging Soc. Policy 2020, 32, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Luan, W. Social isolation, depression, nutritional status and quality of life during COVID-19 among Chinese community-dwelling older adults: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e072305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuutila, M.T.; Rautiainen, L.; Lehti, T.E.; Karppinen, H.; Kautiainen, H.; Strandberg, T.E.; Öhman, H.; Savikko, N.M.; Jansson, A.H.; Pitkälä, K.H. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Older People’s Loneliness: Findings from a Longitudinal Study between 2019 and 2021 among Older Home-Dwellers in Finland. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2023, 27, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosato, M.; Ciciarello, F.; Zazzara, M.B.; Janiri, D.; Pais, C.; Cacciatore, S.; Montenero, R.; Leone, M.S.; Chisci, E.; Picca, A.; et al. Lifestyle Changes and Psychological Well-Being in Older Adults During COVID-19 Pandemic. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2022, 38, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perracini, M.R.; de Amorim, J.S.C.; Lima, C.A.; da Silva, A.; Trombini-Souza, F.; Pereira, D.S.; Pelicioni, P.H.S.; Duim, E.; Batista, P.P.; Dos Santos, R.B.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Life-Space Mobility of Older Adults Living in Brazil: REMOBILIZE Study. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 643640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delinasios, G.J.; Fragkou, P.C.; Gkirmpa, A.M.; Tsangaris, G.; Hoffman, R.M.; Anagnostopoulos, A.K. The Experience of Greece as a Model to Contain COVID-19 Infection Spread. In Vivo 2021, 35, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Organism of Public Health. Available online: https://eody.gov.gr/ (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 2004, 363, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Waist Circumference and Waist-Hip Ratio. Report of a WHO Expert Consultation. World Health Organization, Geneva. 2008. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/44583/9789241501491_eng.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2023).
- Krishnamoorthy, Y.; Rajaa, S.; Rehman, T. Diagnostic accuracy of various forms of geriatric depression scale for screening of depression among older adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 87, 104002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barile, J.P.; Horner-Johnson, W.; Krahn, G.; Zack, M.; Miranda, D.; DeMichele, K.; Ford, D.; Thompson, W.W. Measurement characteristics for two health-related quality of life measures in older adults: The SF-36 and the CDC Healthy Days items. Disabil. Health J. 2016, 9, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulakis, K.N.; Tsolaki, M.; Chantzi, H.; Kazis, A. Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE): A validation study in Greece. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2000, 15, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Smailagic, N.; Roqué-Figuls, M.; Ciapponi, A.; Sanchez-Perez, E.; Giannakou, A.; Pedraza, O.L.; Bonfill Cosp, X.; Cullum, S. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the early detection of dementia in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 7, CD010783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tluczek, A.; Henriques, J.B.; Brown, R.L. Support for the reliability and validity of a six-item state anxiety scale derived from the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. J. Nurs. Meas. 2009, 17, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Cai, G.; Lu, Y.; Xu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wong, L.P.; Hu, Z.; Yamamoto, T.; Morita, K.; Aoyagi, K.; et al. Exploring Factors and Associate Responses for Anxiety in the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: A Web-Based Survey in Japan. Front. Psychol. 2022, 12, 795219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, E.; Alexopoulos, E.C.; Lionis, C.; Varvogli, L.; Gnardellis, C.; Chrousos, G.P.; Darviri, C. Perceived Stress Scale: Reliability and validity study in Greece. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 3287–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. A global measure of perceived stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1983, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, M.; Maru, T.T.; Kumalo, A.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Bahammam, A.S.; Manzar, M.D. Validation of the Pittsburgh sleep quality index in community dwelling Ethiopian adults. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2017, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Stefanadis, C. Dietary patterns: A Mediterranean diet score and its relation to clinical and bio-logical markers of cardiovascular disease risk. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvaniti, F.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Healthy indexes in public health practice and research: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadkhanizadeh, A.; Nikbakht, F. Investigating the potential mechanisms of depression induced-by COVID-19 infection in patients. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 91, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.P.; Chesney, E.; Oliver, D.; Pollak, T.A.; McGuire, P.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Zandi, M.S.; Lewis, G.; David, A.S. Psychiatric and neuropsychiatric presentations associated with severe coronavirus infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis with comparison to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Rathore, F.A. Neurological manifestations and complications of COVID-19: A literature review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 77, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.; Shalev, D.; Hsu, I.; Shenoy, A.; Cheung, S.; Nash, S.; Wiener, I.; Fedoronko, D.; Allen, N.; Shapiro, P.A. Depression, Anxiety, and Acute Stress Disorder among Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Acad. Consult. Liaison Psychiatry 2021, 62, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouças, A.P.; Rheinheimer, J.; Lagopoulos, J. Why severe COVID-19 patients are at greater risk of developing depression: A molecular perspective. Neuroscientist 2022, 28, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Simani, L.; Karimialavijeh, E.; Rezaei, O.; Hajiesmaeili, M.; Pakdaman, H. The Role of Anxiety and Cortisol in Outcomes of Patients with COVID-19. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhou, F.; Hou, W.; Silver, Z.; Wong, C.Y.; Chang, O.; Huang, E.; Zuo, Q.K. The prevalence of depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances in COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2021, 1486, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzunova, G.; Pallanti, S.; Hollander, E. Presentation and management of anxiety in individuals with acute symptomatic or asymptomatic COVID-19 infection, and in the post-COVID-19 recovery phase. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2021, 25, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa Moreira, J.L.; Barbosa, S.M.B.; Vieira, J.G.; Chaves, N.C.B.; Felix, E.B.G.; Feitosa, P.W.G.; da Cruz, I.S.; da Silva, C.G.L.; Neto, M.L.R. The psychiatric and neuropsychiatric repercussions associated with severe infections of COVID-19 and other coronaviruses. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry. 2021, 106, 110159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velayudhan, L.; Aarsland, D.; Ballard, C. Psychiatric and neuropsychiatric syndromes and COVID-19. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köverová, M.; Ráczová, B.; Kováčová Holevová, B. Predictors of Anxiety, Stress, and Concern of COVID-19 Infection in Older Adults During the First and the Second Waves of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Slovakia. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 7, 23337214211047642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, Y.S.; Cohen-Fridel, S.; Shrira, A.; Bodner, E.; Palgi, Y. COVID-19 health worries and anxiety symptoms among older adults: The moderating role of ageism. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2020, 32, 1371–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriedo, A.; Cecchini, J.A.; Fernandez-Rio, J.; Méndez-Giménez, A. COVID-19, Psychological Well-being and Physical Activity Levels in Older Adults During the Nationwide Lockdown in Spain. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2020, 28, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, C.E.; de Jager, C.A.; Ahmadi-Abhari, S.; Giannakopoulou, P.; Udeh-Momoh, C.; McKeand, J.; Price, G.; Car, J.; Majeed, A.; Ward, H.; et al. Associations of Social Isolation with Anxiety and Depression During the Early COVID-19 Pandemic: A Survey of Older Adults in London, UK. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 591120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidzan-Bluma, I.; Bidzan, M.; Jurek, P.; Bidzan, L.; Knietzsch, J.; Stueck, M.; Bidzan, M. A Polish and German Population Study of Quality of Life, Well-Being, and Life Satisfaction in Older Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 585813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, E.S.; Hoffman, Y.S.G.; Palgi, Y.; Shrira, A. COVID-19 related loneliness and sleep problems in older adults: Worries and resilience as potential moderators. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2021, 168, 110371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olgun Yıldızeli, S.; Kocakaya, D.; Saylan, Y.H.; Tastekin, G.; Yıldız, S.; Akbal, Ş.; Özkan, S.; Arıkan, H.; Karakurt, S. Anxiety, Depression, and Sleep Disorders after COVID-19 Infection. Cureus 2023, 15, e42637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badenoch, J.B.; Rengasamy, E.R.; Watson, C.; Jansen, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Sundaram, R.D.; Hafeez, D.; Burchill, E.; Saini, A.; Thomas, L.; et al. Persistent neuropsychiatric symptoms after COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Commun. 2021, 4, fcab297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, S.; Ferreira, A.R.; Fernandes, J.; Vieira, T.; Fontes, L.; Coimbra, I.; Paiva, J.A.; Fernandes, L. Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms in Severe COVID-19 Survivors: A Prospective Cohort Study. Psychiatr. Q. 2022, 93, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.M.; Sultana, A.; Purohit, N. Mental health outcomes of quarantine and isolation for infection prevention: A systematic umbrella review of the global evidence. Epidemiol. Health 2020, 42, e2020038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Oh, K.R.; Jun, M.G. COVID-19 Obesity: Differences in Infection Risk Perception, Obesity Stress, Depression, and Intention to Participate in Leisure Sports Based on Weight Change. Healthcare 2023, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Health Promotion Institute. Changes in Life after COVID-19. Available online: https://www.khealth.or.kr/board/view?linkId=1001442&menuId=MENU00907 (accessed on 26 March 2023).
- World Health Organization. Considerations for Sports Federations/Sports Event Organizers When Planning Mass Gatherings in the Context of COVID-19: Interim Guidance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/considerations-for-sports-federations-sports-event-organizers-when-planning-mass-gatherings-in-the-context-of-covid-19-interim-guidance (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Sidor, A.; Rzymski, P. Dietary choices and habits during COVID-19 lockdown: Experience from Poland. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Di Gessa, G.; Zaninotto, P. Changes in health behaviours during the COVID-19 pandemic and effect on weight and obesity among older people in England. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, B.J. Obesity Prevalence among U.S. Adults During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2022, 63, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutari, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. A 2022 update on the epidemiology of obesity and a call to action: As its twin COVID-19 pandemic appears to be receding, the obesity and dysmetabolism pandemic continues to rage on. Metabolism 2022, 133, 155217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilopoulou, E.; Bumbacea, R.S.; Pappa, A.K.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Bumbacea, D. Obesity and Infection: What Have We Learned from the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 931313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, M.; Ling, W.; Sui, Y.; Zhao, H.L. Obesity in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2020, 113, 154378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Fu, S.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y. Obesity or increased body mass index and the risk of severe outcomes in patients with COVID-19: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2022, 101, e28499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrityunjaya, M.; Pavithra, V.; Neelam, R.; Janhavi, P.; Halami, P.M.; Ravindra, P.V. Immune-Boosting, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Food Supplements Targeting Pathogenesis of COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 570122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordan, R.; Rando, H.M.; Greene, C.S. Dietary Supplements and Nutraceuticals under Investigation for COVID-19 Prevention and Treatment. mSystems 2021, 6, e00122-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Min, W. Mitochondria, Oxidative Stress and Innate Immunity. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanan, M.; Raynor, J.; Ogunsulire, I.; Malyshkina, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Hummel, S.A.; Ingram, J.T.; Saini, A.; Xie, M.M.; Alenghat, T.; et al. IL-10-producing Tfh cells accumulate with age and link inflammation with age-related immune suppression. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb0806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaz, E.; Bezemer, G.; Alipoor, S.D.; Varahram, M.; Mumby, S.; Folkerts, G.; Garssen, J.; Adcock, I.M. Nutritional Impact and Its Potential Consequences on Covid-19 Severity. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 698617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paces, J.; Strizova, Z.; Smrz, D.; Cerny, J. COVID-19 and the Immune System. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeming, E.R.; Johnson, A.J.; Spector, T.D.; Le Roy, C.I. Effect of Diet on the Gut Microbiota: Rethinking Intervention Duration. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishi, P.; Thakur, K.; Vij, S.; Rishi, L.; Singh, A.; Kaur, I.P.; Patel, S.K.S.; Lee, J.K.; Kalia, V.C. Diet, Gut Microbiota and COVID-19. Indian J. Microbiol. 2020, 60, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Costanzo, S.; Persichillo, M.; Panzera, T.; Ruggiero, E.; De Curtis, A.; Storto, M.; Cavallo, P.; Gianfagna, F.; et al. Habitual adherence to a traditional Mediterranean diet and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A longitudinal analysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 74, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khoury, C.N.; Julien, S.G. Inverse Association Between the Mediterranean Diet and COVID-19 Risk in Lebanon: A Case-Control Study. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 707359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Araluce, R.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Gea, A.; Carlos, S. Components of the Mediterranean Diet and Risk of COVID-19. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 805533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Araluce, R.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Fernández-Lázaro, C.I.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Gea, A.; Carlos, S. Mediterranean diet and the risk of COVID-19 in the ‘Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra’ cohort. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzo, V.; Pellegrini, M.; D’Eusebio, C.; Bioletto, F.; Goitre, I.; Buscemi, S.; Frea, S.; Ghigo, E.; Simona Bo, S. Mediterranean Diet and SARS-COV-2 Infection: Is There Any Association? A Proof-of-Concept Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidi, A.M.; Kokkinos, A.; Katechaki, E.; Ros, E.; Mantzoros, C.S. Mediterranean diet as a nutritional approach for COVID-19. Metabolism 2021, 114, 154407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorino, M.I.; Bellastella, G.; Longo, M.; Caruso, P.; Esposito, K. Mediterranean Diet and COVID-19: Hypothesizing Potential Benefits in People with Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 574315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, J.; Joshi, A.D.; Nguyen, L.H.; Leeming, E.R.; Mazidi, M.; Drew, D.A.; Gibson, R.; Graham, M.S.; Lo, C.-H.; Capdevila, J.; et al. Diet quality and risk and severity of COVID-19: A prospective cohort study. Gut 2021, 70, 2096–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Rebholz, C.M.; Hegde, S.; LaFiura, C.; Raghavan, M.; Lloyd, J.F.; Cheng, S.; Seidelmann, S.B. Plant-based diets, pescatarian diets and COVID-19 severity: A population-based case-control study in six countries. BMJ Nutr. Prev. Health 2021, 4, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreo-López, M.C.; Contreras-Bolívar, V.; Muñoz-Torres, M.; García-Fontana, B.; García-Fontana, C. Influence of the Mediterranean Diet on Healthy Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigalou, C.; Konstantinidis, T.; Paraschaki, A.; Stavropoulou, E.; Voidarou, C.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Mediterranean Diet as a Tool to Combat Inflammation and Chronic Diseases. An Overview. Biomedicine 2020, 8, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finicelli, M.; Di Salle, A.; Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G. The Mediterranean Diet: An Update of the Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantenbein, K.V.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C. Mediterranean Diet as an Antioxidant: The Impact on Metabolic Health and Overall Wellbeing. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgieva, E.; Ananiev, J.; Yovchev, Y.; Arabadzhiev, G.; Abrashev, H.; Abrasheva, D.; Atanasov, V.; Kostandieva, R.; Mitev, M.; Petkova-Parlapanska, K.; et al. COVID-19 Complications: Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Mitochondrial and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieder, A.S.; Wyse, A.T.S. Regulation of Inflammation by IRAK-M Pathway Can Be Associated with nAchRalpha7 Activation and COVID-19. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, Y.; Pantea Stoian, A.; Silva-Nunes, J.; Sonmez, A.; Rizvi, A.A.; Janez, A.; Rizzo, M. The role of GLP-1 receptor agonists during COVID-19 pandemia: A hypothetical molecular mechanism. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2021, 20, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
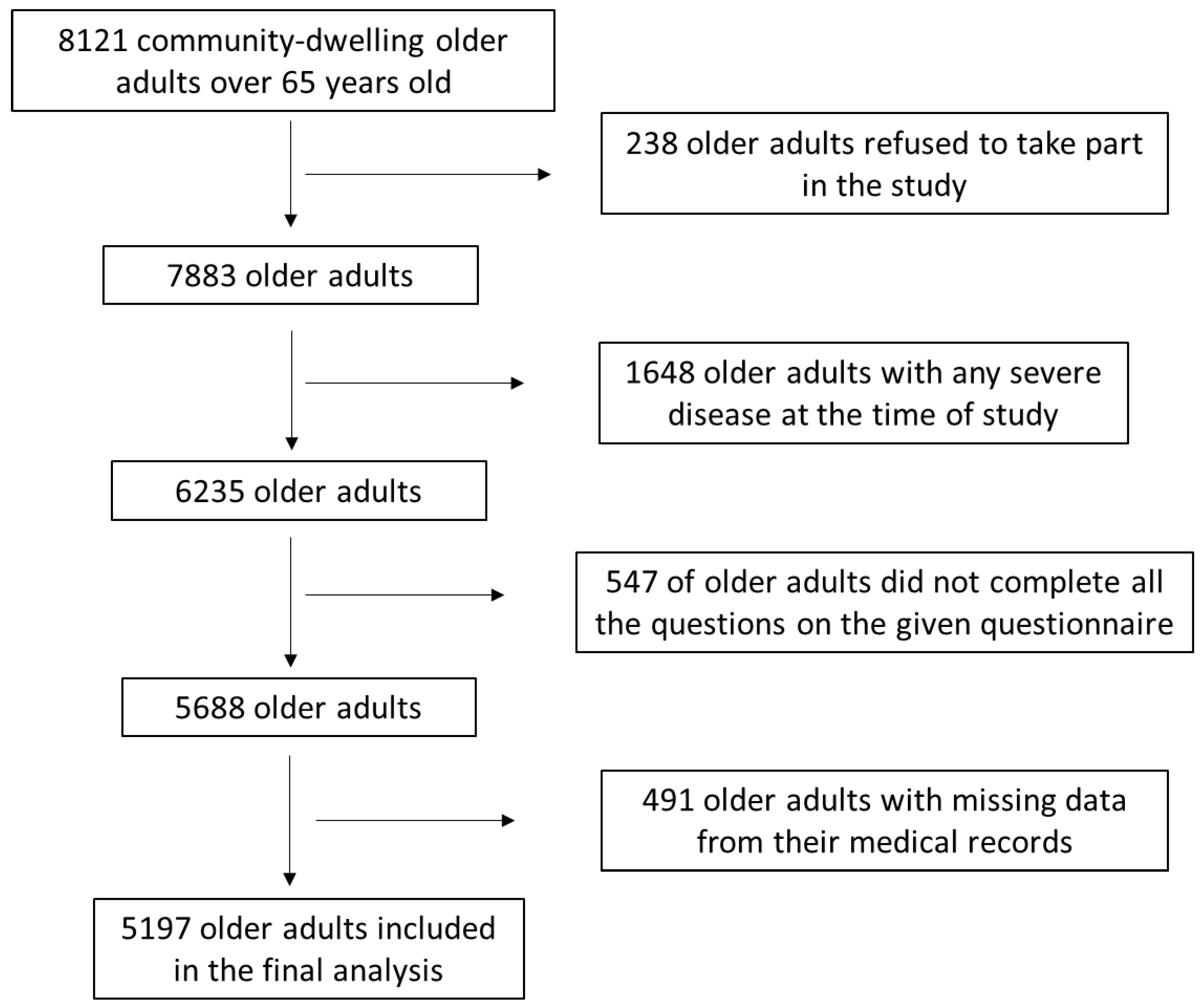
| Parameters (n = 5197) | COVID-19 Infection | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No 2987 (57.5%) | Yes 2210 (42.5%) | ||
| Age (mean ± SD years) | 71.8 ± 7.3 | 74.9 ± 7.8 | p = 0.0001 |
| Gender (n, %) | p = 0.0015 | ||
| Male | 1373 (46.0%) | 1124 (50.9%) | |
| Female | 1614 (54.0%) | 1086 (49.1%) | |
| Employment (n, %) | p = 0.0833 | ||
| Employed | 502 (16.8%) | 332 (15.0%) | |
| Unemployed | 2485 (83.2%) | 1878 (85%) | |
| Type of residence (n, %) | p = 0.0006 | ||
| Urban | 1735 (58.1%) | 1483 (67.1%) | |
| Rural | 1252 (41.9%) | 727 (32.9%) | |
| Living status (n, %) | p = 0.0023 | ||
| Living with others | 2419 (81.0%) | 1483 (67.1%) | |
| Living alone | 568 (19.0%) | 727 (32.9%) | |
| Educational level (n, %) | p = 0.0175 | ||
| Primary education | 993 (33.2%) | 846 (38.3%) | |
| Secondary education | 635 (21.3%) | 630 (28.5%) | |
| University studies | 1359 (45.5%) | 734 (33.2%) | |
| Family economic status (n, %) | p = 0.0294 | ||
| Low | 1730 (57.9%) | 1329 (60.1%) | |
| Medium | 760 (25.4%) | 623 (28.2%) | |
| High | 497 (16.6%) | 258 (11.7%) | |
| Smoking habits (n, %) | p = 0.0016 | ||
| Smokers | 1806 (60.5%) | 1507 (68.2%) | |
| Never smokers | 1181 (39.5%) | 703 (31.8%) | |
| BMI status (n, %) | p ˂ 0.0001 | ||
| Normal Weigh | 2354 (78.8%) | 1471 (66.6%) | |
| Overweight | 452 (15.1%) | 496 (22.4%) | |
| Obese | 181 (6.1%) | 243 (11.0%) | |
| WHR (n, %) | |||
| Low | 2144 (71.8%) | 1158 (52.4%) | p ˂ 0.0001 |
| Medium | 602 (20.1%) | 698 (31.6%) | |
| High | 241(8.1%) | 354 (16.0%) | |
| Depression (n, %) | p = 0.0021 | ||
| Yes | 873 (29.2%) | 783 (35.4%) | |
| No | 2114 (70.8%) | 1427 (64.6%) | |
| HRQOL score (mean ± SD) | 53.7 ± 11.3 | 49.9 ± 11.1 | p ˂ 0.0001 |
| PCS score (mean ± SD) | 52.1 ± 11.1 | 49.5 ± 11.2 | p = 0.0003 |
| MCS score (mean ± SD) | 49.5 ± 11.6 | 47.2 ± 11.8 | p = 0.0005 |
| Cognitive status (n, %) | p = 0.0032 | ||
| No cognitive impairment | 2108 (70.6%) | 1354 (61.3%) | |
| Mild cognitive impairment | 510 (17.1%) | 465 (21.0%) | |
| Moderate/severe cognitive impairment | 369 (12.3%) | 391 (17.7%) | |
| Sleep quality (n, %) | p ˂ 0.0001 | ||
| Adequate | 2035 (68.1%) | 1310 (59.3%) | |
| Inadequate | 952 (31.9%) | 900 (40.7%) | |
| Anxiety (n, %) | p = 0.0003 | ||
| No | 2072 (69.4%) | 1403 (63.5%) | |
| Yes | 915 (30.6%) | 807 (35.5%) | |
| Stress (n, %) | p ˂ 0.0001 | ||
| Low | 2016 (67.5%) | 1282 (58.0%) | |
| Moderate | 757 (25.3%) | 653 (29.5%) | |
| High | 214 (7.2%) | 275 (12.4%) | |
| IPAQ status (n, %) | p ˂ 0.0001 | ||
| Low | 1493 (50.0%) | 1346 (60.9%) | |
| Medium | 835 (27.9%) | 633 (28.1%) | |
| High | 659 (22.1%) | 243 (11.0%) | |
| MedDietScore (n, %) | p ˂ 0.0001 | ||
| Very low | 450 (15.1%) | 854 (38.6%) | |
| Low | 500 (16.7%) | 784 (35.5%) | |
| Moderate | 970 (32.5%) | 329 (14.9%) | |
| High | 1067 (35.7%) | 243 (11.0%) | |
| Participants’ Characteristics | COVID-19 Infection (No vs. Yes) | |
|---|---|---|
| OR * (95% CI **) | p-Value | |
| Age (Below/Over mean value) | 1.58 (1.02–2.11) | p = 0.1376 |
| Gender (Female/Male) | 1.13 (0.61–1.88) | p = 0.2463 |
| Employment (Employed/Unemployed) | 1.28 (0.71–1.87) | p = 0.2576 |
| Type of residence (Rural/Urban) | 1.38 (1.06–1.67) | p = 0.0107 |
| Living status (Living with others/Living alone) | 1.25 (0.59–1.91) | p = 0.0987 |
| Educational level (Primary and secondary education/Universities studies) | 1.06 (0.48–1.67) | p = 0.3173 |
| Family economic status (High/Moderate and low) | 1.12 (0.58–1.79) | p = 0.4094 |
| Smoking habits (No/Yes) | 1.72 (1.49–1.96) | p = 0.0218 |
| BMI status (Normal weight/Overweight + Obesity) | 2.08 (1.87–2.39) | p = 0.0036 |
| WHR (Low/Medium + High) | 2.17 (1.98–2.39) | p = 0.0008 |
| Depression (No/Yes) | 1.59 (1.35–1.86) | p = 0.0027 |
| HRQOL (Over/Below mean value) | 2.27 (2.02–2.68) | p = 0.0002 |
| Cognitive impairment (No/Yes) | 1.13 (0.58–1.79) | p = 0.1095 |
| Sleep quality (Adequate/Inadequate) | 1.68 (1.34–2.01) | p = 0.0108 |
| Anxiety (No/Yes) | 1.79 (1.52–2.03) | p = 0.0045 |
| Stress (Low/Moderate + high) | 1.98 (1.73–2.29) | p = 0.0038 |
| IPAQ (High and moderate/Low) | 1.73 (1.48–1.97) | p = 0.0012 |
| Mediterranean diet adherence (Moderate + High/Very low + Low) | 2.22 (1.98–2.45) | p = 0.0009 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavlidou, E.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Antasouras, G.; Vorvolakos, T.; Alexatou, O.; Tsourouflis, G.; Angelakou, E.-P.; Serdari, A.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Psara, E.; et al. Association of COVID-19 Infection with Sociodemographic, Anthropometric and Lifestyle Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Older Adults’ Population Aged over 65 Years Old. Diseases 2023, 11, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040165
Pavlidou E, Papadopoulou SK, Antasouras G, Vorvolakos T, Alexatou O, Tsourouflis G, Angelakou E-P, Serdari A, Grammatikopoulou MG, Psara E, et al. Association of COVID-19 Infection with Sociodemographic, Anthropometric and Lifestyle Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Older Adults’ Population Aged over 65 Years Old. Diseases. 2023; 11(4):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040165
Chicago/Turabian StylePavlidou, Eleni, Sousana K. Papadopoulou, Georgios Antasouras, Theofanis Vorvolakos, Olga Alexatou, Gerasimos Tsourouflis, Exakousti-Petroula Angelakou, Aspasia Serdari, Maria G. Grammatikopoulou, Evmorfia Psara, and et al. 2023. "Association of COVID-19 Infection with Sociodemographic, Anthropometric and Lifestyle Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Older Adults’ Population Aged over 65 Years Old" Diseases 11, no. 4: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040165
APA StylePavlidou, E., Papadopoulou, S. K., Antasouras, G., Vorvolakos, T., Alexatou, O., Tsourouflis, G., Angelakou, E.-P., Serdari, A., Grammatikopoulou, M. G., Psara, E., Vadikolias, K., Dakanalis, A., Lefantzis, N., & Giaginis, C. (2023). Association of COVID-19 Infection with Sociodemographic, Anthropometric and Lifestyle Factors: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Older Adults’ Population Aged over 65 Years Old. Diseases, 11(4), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11040165










