Actigraphy Analysis of Sleep Associates with Salivary IL-6 Concentration in Institutionalized Older Individuals
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To evaluate sleep with actigraphy in institutionalized older individuals, comparing the results between individuals with or without dementia.
- (2)
- To analyze the associations between salivary IL-6 concentration and sleep parameters.
- (3)
- To determine the influence of psychotropic medications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Objective Sleep Assessment with Actigraphy
2.4. Cognitive Assessment
2.5. Polypharmacy
2.6. Measurement of Salivary IL-6
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic Data and Polypharmacy
3.2. Relationship between Sleep Parameters and Age and Gender
3.3. Relationship between Sleep and Polypharmacy
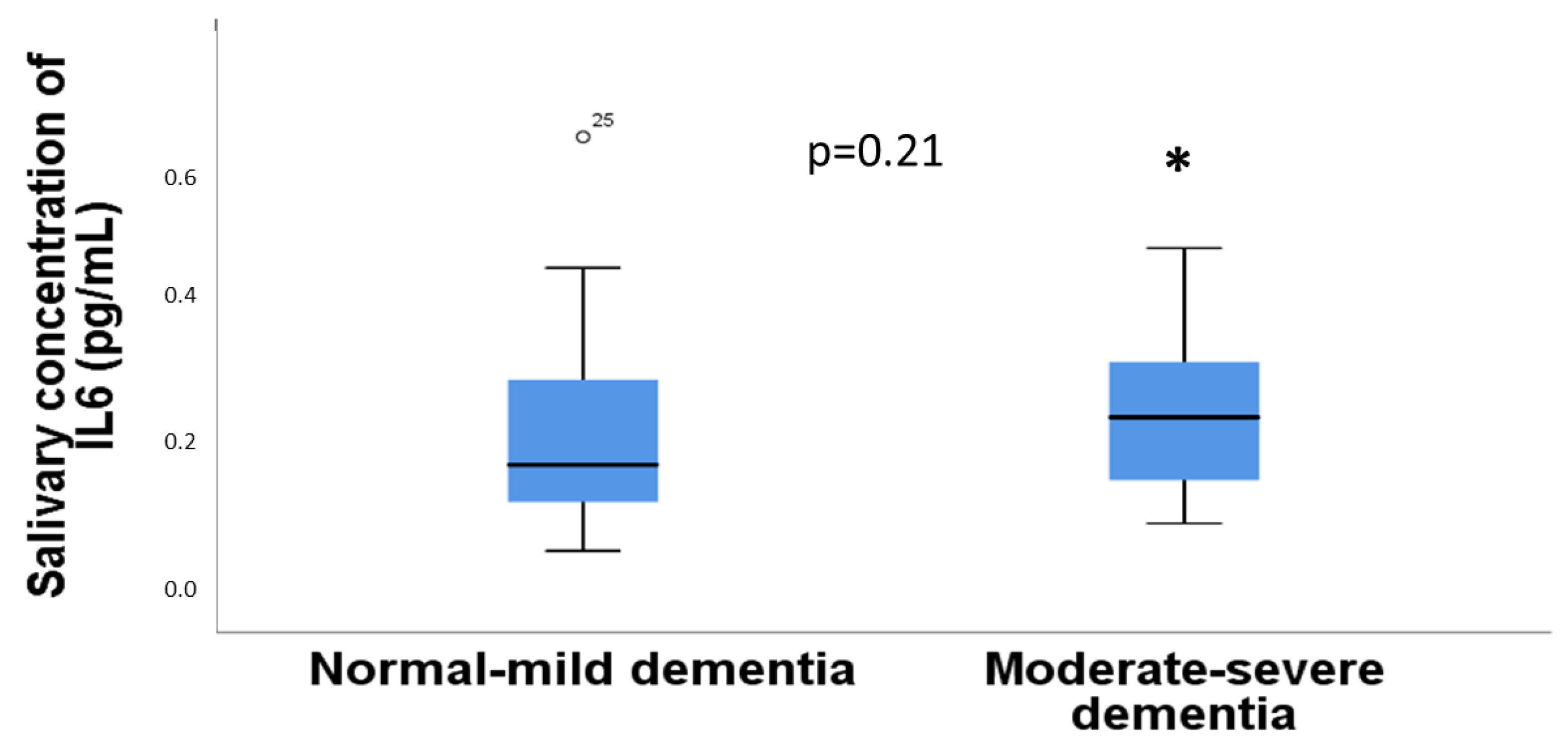
3.4. Relationship between IL-6 in Saliva with Sleep Assessment
3.5. Relationship between the Concentration of IL6 in Saliva with Age, Gender, and Comorbidities
3.6. Relationship between the Concentration of IL6 in Saliva and Cognitive Function
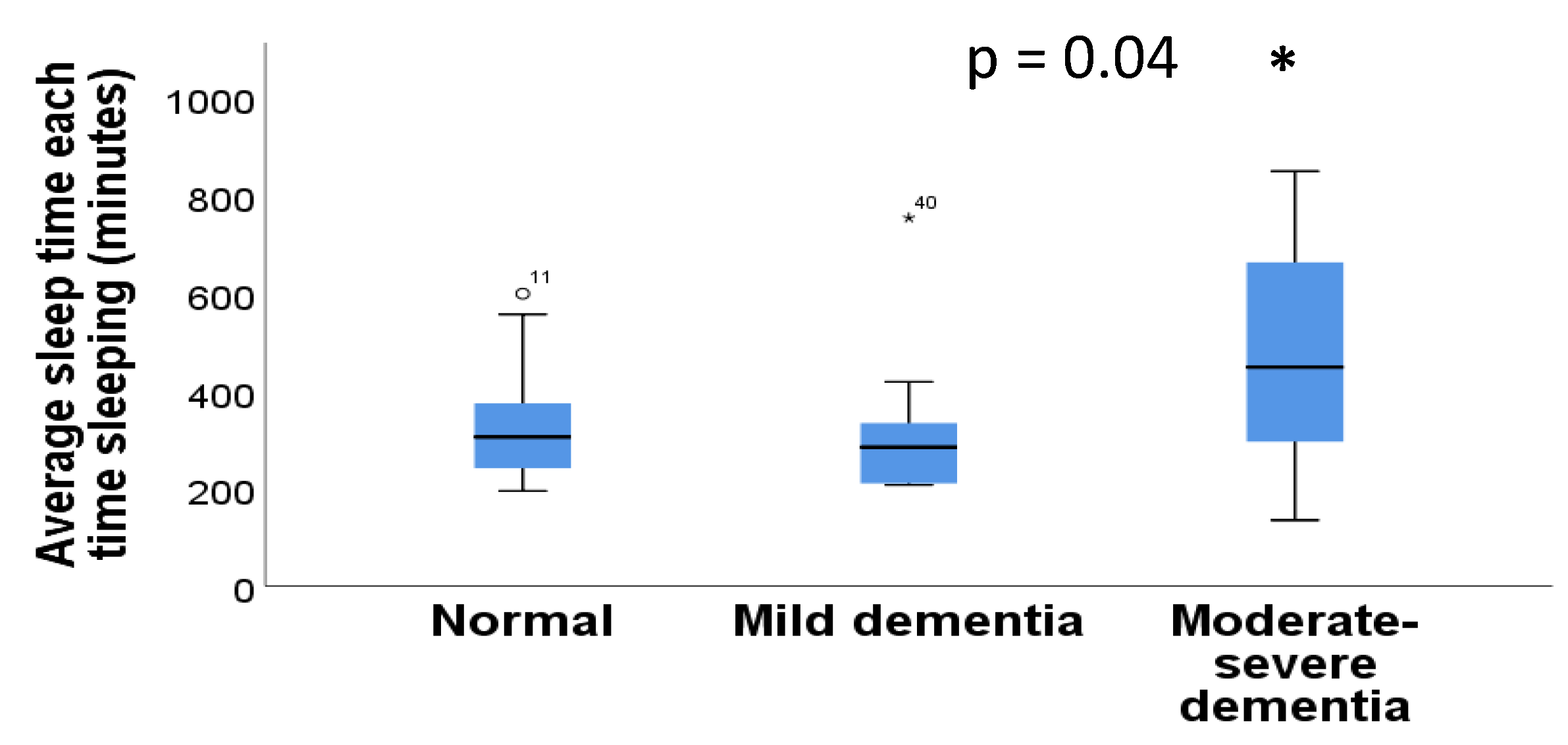
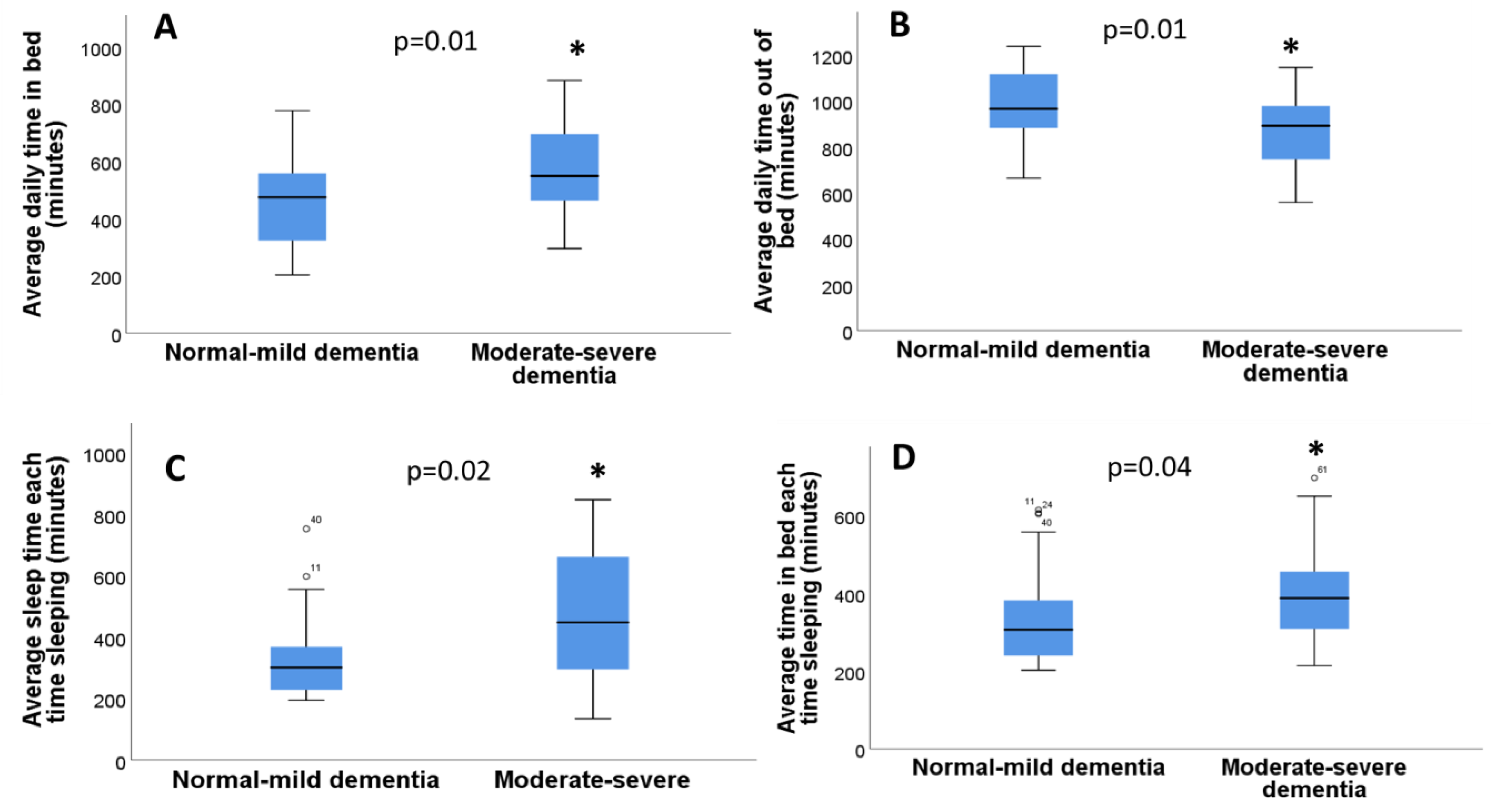
3.7. Actigraphy Sleep Parameters in Individuals with or without Dementia
3.8. Dementia and Polypharmacy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diem, S.J.; Blackwell, T.L.; Stone, K.L.; Yaffe, K.; Tranah, G.; Cauley, J.A.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Redline, S.; Spira, A.P.; Hillier, T.A.; et al. Measures of Sleep-Wake Patterns and Risk of Mild Cognitive Impairment or Dementia in Older Women. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2016, 24, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirelli, C.; Tononi, G. The Sleeping Brain. Cerebrum 2017, 2017, cer-07-17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bellesi, M.; de Vivo, L.; Chini, M.; Gilli, F.; Tononi, G.; Cirelli, C. Sleep Loss Promotes Astrocytic Phagocytosis and Microglial Activation in Mouse Cerebral Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 5263–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubu, O.M.; Brannick, M.; Mortimer, J.; Umasabor-Bubu, O.; Sebastião, Y.V.; Wen, Y.; Schwartz, S.; Borenstein, A.R.; Wu, Y.; Morgan, D.; et al. Sleep, Cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep 2017, 40, zsw032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenker, J.I.; Singh, G. Sleep and Dementia. Missouri. Med. 2017, 114, 311–315. [Google Scholar]
- Crowley, K. Sleep and sleep disorders in older adults. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2011, 21, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.C.; Dzierzewski, J.M.; Alessi, C.A. Sleep problems in the elderly. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 99, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins da Silva, R.; Afonso, P.; Fonseca, M.; Teodoro, T. Comparing sleep quality in institutionalized and non-institutionalized elderly individuals. Aging Ment. Health 2020, 24, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkadhi, K.; Zagaar, M.; Alhaider, I.; Salim, S.; Aleisa, A. Neurobiological consequences of sleep deprivation. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, B.G. Insomnia and cognitive function in the elderly patient. Am. Fam. Physician 2002, 65, 1184–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Ancoli-Israel, S. Insomnia in the elderly: A review for the primary care practitioner. Sleep 2000, 23 (Suppl. S1), S23–S38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.; Caranasos, G.J. Neuropsychiatric effects of drugs in the elderly. J. Fla. Med. Assoc. 1992, 79, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schroeck, J.L.; Ford, J.; Conway, E.L.; Kurtzhalts, K.E.; Gee, M.E.; Vollmer, K.A.; Mergenhagen, K.A. Review of Safety and Efficacy of Sleep Medicines in Older Adults. Clin. Ther. 2016, 38, 2340–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, V.; Silva, J.; Cauli, O. A survey on sleep assessment methods. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyos, C.M.; Gordon, C.; Terpening, Z.; Norrie, L.; Lewis, S.J.G.; Hickie, I.B.; Naismith, S.L. Circadian rhythm and sleep alterations in older people with lifetime depression: A case-control study. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhmer, M.N.; Oppewal, A.; Bindels, P.J.E.; Tiemeier, H.; van Someren, E.J.W.; Festen, D.A.M. Comparison of sleep-wake rhythms in elderly persons with intellectual disabilities and the general population. Sleep Med. 2020, 76, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekert, M.; der Lek, R.F.; Swaab, D.F.; Kaufer, D.; Van Someren, E.J. Comparison between informant-observed and actigraphic assessments of sleep-wake rhythm disturbances in demented residents of homes for the elderly. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2006, 14, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.R.; Olmstead, R.; Carroll, J.E. Sleep Disturbance, Sleep Duration, and Inflammation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies and Experimental Sleep Deprivation. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Hohagen, F.; Ebert, T.; Timmer, J.; Ganter, U.; Krieger, S.; Lis, S.; Postler, E.; Voderholzer, U.; Berger, M. Interleukin-6 serum levels in healthy persons correspond to the sleep-wake cycle. Clin. Investig. 1994, 72, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez-Del Valle, V.; Navarro-Martínez, R.; Ballestar-Tarin, M.L.; Cauli, O. Salivary Inflammatory Molecules as Biomarkers of Sleep Alterations: A Scoping Review. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, J.; Frishman, W.H. Inflammation and atherosclerosis: A review of the role of interleukin-6 in the development of atherosclerosis and the potential for targeted drug therapy. Cardiol. Rev. 2014, 22, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanikowska, D.; Roszak, M.; Rutkowski, R.; Sato, M.; Sikorska, D.; Orzechowska, Z.; Bręborowicz, A.; Witowski, J. Seasonal differences in rhythmicity of salivary cortisol in healthy adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 126, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, R.J.; Kripke, D.F.; Gruen, W.; Mullaney, D.J.; Gillin, J.C. Automatic sleep/wake identification from wrist activity. Sleep 1992, 15, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudor-Locke, C.; Barreira, T.V.; Schuna, J.M., Jr.; Mire, E.F.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Fully automated waist-worn accelerometer algorithm for detecting children’s sleep-period time separate from 24-h physical activity or sedentary behaviors. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 39, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobo, A.; Saza, P.; Marcos, G.; Díaz, J.L.; De la Cámara, C.; Ventura, T. Revalidación y normalización del Mini-Examen Cognoscitivo (primera versión en castellano del Mini-Mental Status Examination) en la población general geriátrica. Med. Clin. 1999, 112, 767–774. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Real, J.M.; Vayreda, M.; Richart, C.; Gutierrez, C.; Broch, M.; Vendrell, J.; Ricart, W. Circulating interleukin 6 levels, blood pressure, and insulin sensitivity in apparently healthy men and women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Negro, R.W.; Carone, M.; Cuttitta, G.; Gallelli, L.; Pistolesi, M.; Privitera, S.; Ceriana, P.; Pirina, P.; Balbi, B.; Vancheri, C.; et al. Prevalence and clinical features of most frequent phenotypes in the Italian COPD population: The CLIMA Study. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2021, 16, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelnik, C.M.; Lambert, M.; Drumez, E.; Martin, C.; Grolaux, G.; Launay, D.; Hachulla, E.; Rogeau, S.; Dubucquoi, S.; Boulanger, E.; et al. Relevance of inflammatory and complement activation biomarkers profiling in antiphospholipid syndrome patients outside acute thrombosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Han, T.T.; Chang, Y.H.; Cui, X.C. Levetiracetam attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive impairment and microglia polarization by suppressing neuroinflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1145819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.S.; Kuo, C.L.; Huang, C.S.; Cheng, Y.S.; Lin, S.S.; Liu, C.S. The relationship between pulse pressure with plasma PCSK9 and interleukin-6 among patients with acute ischemic stroke and dyslipidemia. Brain Res. 2022, 1795, 148080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallelli, L.; Galasso, O.; Falcone, D.; Southworth, S.; Greco, M.; Ventura, V.; Romualdi, P.; Corigliano, A.; Terracciano, R.; Savino, R.; et al. The effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on clinical outcomes, synovial fluid cytokine concentration and signal transduction pathways in knee osteoarthritis. A randomized open label trial. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.P.; Lee, Y.S.; Choe, Y.; Kim, K.T.; Song, G.J.; Hwang, S.C. Knee osteoarthritis accelerates amyloid beta deposition and neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Brain 2023, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.K.; Kang, H.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Stewart, R.; Kim, J.M. Interaction effect of the serum interleukin-6 level and anxiety on the 12-week pharmacotherapeutic responses of patients with depressive disorders. J. Affect Disord. 2022, 1, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wu, M.; Sun, R.; Chen, Z.; Yu, P.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; et al. IL-6 and IL-8 are likely associated with psychological status in treatment naïve general population. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 298 Pt A, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Papanicolaou, D.A.; Bixler, E.O.; Kales, A.; Tyson, K.; Chrousos, G.P. Elevation of plasma cytokines in disorders of excessive daytime sleepiness: Role of sleep disturbance and obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaVoy, E.C.; Palmer, C.A.; So, C.; Alfano, C.A. Bidirectional relationships between sleep and biomarkers of stress and immunity in youth. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2020, 158, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Shen, Y.; Qiao, S.; Hui, Z.; Chen, J. Shimian granules improve sleep, mood and performance of shift nurses in association changes in melatonin and cytokine biomarkers: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Chronobiol. Int. 2020, 37, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, G.M.; Kim, S.; Mikhail, A.; Malhas, R.; McMillan, L.; Hollearn, M.; Granger, D.A.; Mapstone, M.; Yassa, M.A.; Thomas, E.A. Associations between saliva and plasma cytokines in cognitively normal, older adults. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2023, 35, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, C.C.; Ushakova, A.; Skogseth, R.E.; Alves, G.; Tysnes, O.B.; Aarsland, D.; Lange, J.; Maple-Grødem, J. Inflammatory Biomarkers in Newly Diagnosed Patients With Parkinson Disease and Related Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 10, e200132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tan, C.C.; Zou, J.J.; Cao, X.P.; Tan, L. Sleep problems and risk of all-cause cognitive decline or dementia: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakuijala, A.; Sarkanen, T.; Jokela, T.; Partinen, M. Accuracy of Actigraphy Compared to Concomitant Ambulatory Polysomnography in Narcolepsy and Other Sleep Disorders. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 629709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinnirello, A.; Mazzoleni, S.; Santi, C. Chronic Pain in the Elderly: Mechanisms and Distinctive Features. Biomolecules 2021, 23, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abell, J.E.; Hootman, J.M.; Helmick, C.G. Prevalence and impact of arthritis among nursing home residents. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postler, A.; Ramos, A.L.; Goronzy, J.; Günther, K.P.; Lange, T.; Schmitt, J.; Zink, A.; Hoffmann, F. Prevalence and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis in people aged 60 years or older in Germany: An analysis based on health insurance claims data. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 2339–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caroleo, M.; Carbone, E.A.; Greco, M.; Corigliano, D.M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Fazia, G.; Rania, M.; Aloi, M.; Gallelli, L.; Segura-Garcia, C.; et al. Brain-Behavior-Immune Interaction: Serum Cytokines and Growth Factors in Patients with Eating Disorders at Extremes of the Body Mass Index (BMI) Spectrum. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fábrega-Cuadros, R.; Cruz-Díaz, D.; Martínez-Amat, A.; Aibar-Almazán, A.; Redecillas-Peiró, M.T.; Hita-Contreras, F. Associations of sleep and depression with obesity and sarcopenia in middle-aged and older adults. Maturitas 2020, 142, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Vecino, B.; Arija-Blázquez, A.; Pedrero-Chamizo, R.; Gómez-Cabello, A.; Alegre, L.M.; Pérez-López, F.R.; González-Gross, M.; Casajús, J.A.; Ara, I.; EXERNET Group. Sleep disturbance, obesity, physical fitness and quality of life in older women: EXERNET study group. Climacteric 2017, 20, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysen, T.S.; Luik, A.I.; Ikram, M.K.; Tiemeier, H.; Ikram, M.A. Actigraphy-estimated sleep and 24-hour activity rhythms and the risk of dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2020, 16, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Lee, W.T.; Yang, H.L.; Weng, W.C.; Lee, C.C.; Jeng, S.F.; Tsai, S.Y. Screen Time Exposure and Altered Sleep in Young Children With Epilepsy. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 2020, 52, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ren, Y.; Hou, T.; Liang, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cong, L.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Ren, J.; et al. Associations of sleep timing and time in bed with dementia and cognitive decline among Chinese older adults: A cohort study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2022, 70, 3138–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanHaitsma, K.; Lawton, M.P.; Kleban, M.H.; Klapper, J.; Corn, J. Methodological aspects of the study of streams of behavior in elders with dementing illness. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 1997, 11, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rose, K.M.; Lorenz, R. Sleep disturbances in dementia. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 2010, 36, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neikrug, A.B.; Ancoli-Israel, S. Sleep disturbances in nursing homes. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2010, 14, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baides Noriega, R.; Noriega Camporro, S.; Inclán Rodríguez, A.M. Nursing and no Drug for the Management of Insomnia Treatment. Enfermería. Global. 2019, 54, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.C.; Beck O’Sullivan, P.S.; Shue, V.M. Effect of individualized social activity on sleep in nursing home residents with dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
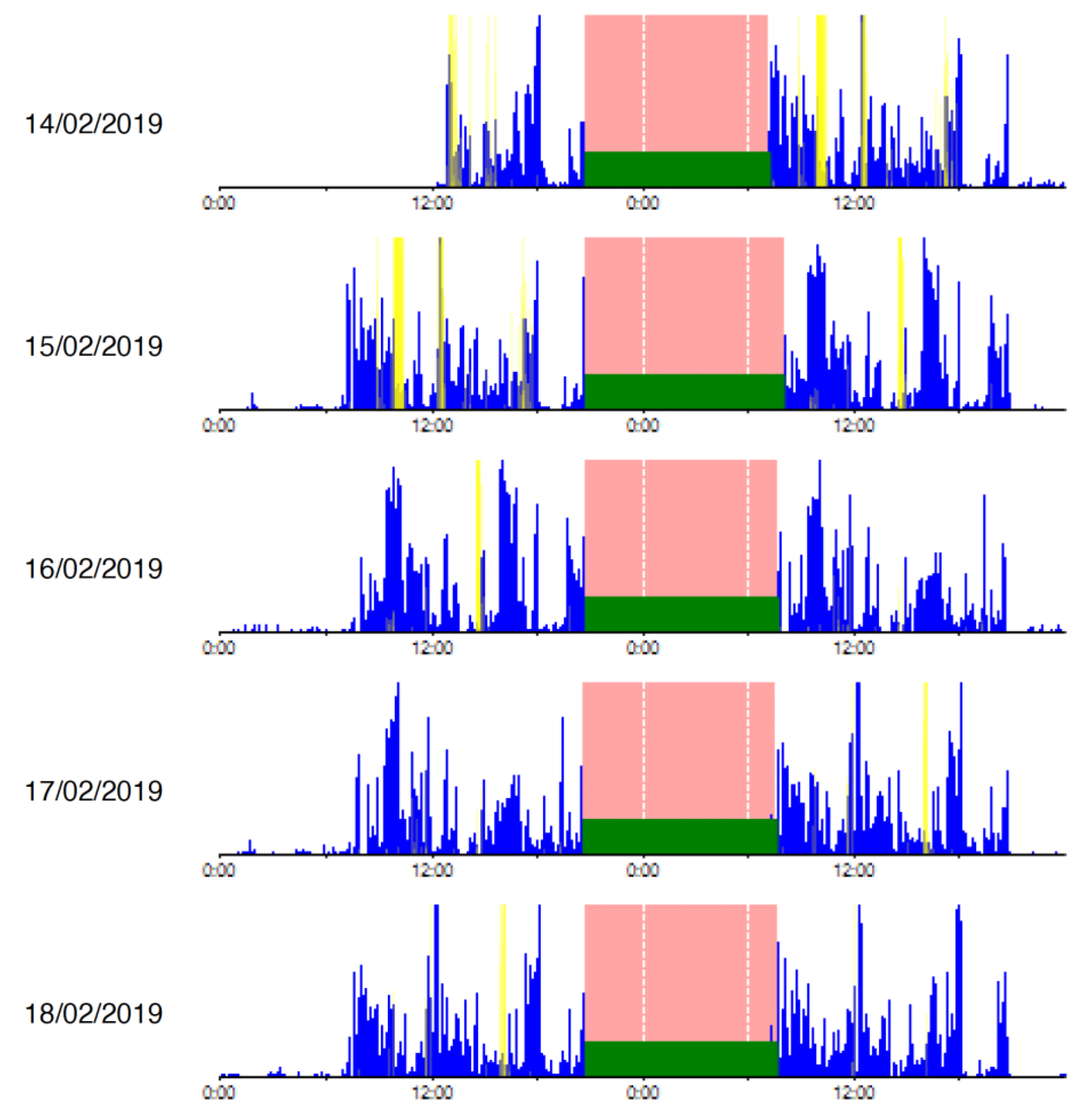
| Demographics | Actigraphy | Drugs |
|---|---|---|
| Gender Age Marital status | Time in bed Time out of bed Efficiency Total time in bed Total sleep time Waking after sleep onset Number of awakenings Avg. awakening time | Antipsychotics Antidepressants Hypnotics Anxiolytics Antiepileptics Opioids Analgesics |
| Comorbidities | Cognitive assessment | Saliva Test |
| Report | Lobo’s Mini-Mental State Examination (MEC) | IL-6 |
| Sleep Variable | Mean and Standard Error of the Mean (Min-Max Range) |
|---|---|
| Average Daily Time In Bed | 497 ± 22.3 (202–882 min) |
| Average Daily Time Out of Bed | 942 ± 22.3 (558–1238 min) |
| Efficiency | 95.4 ± 0.33 (88–100) |
| Average Sleep Time Each Time Sleeping (includes naps and split sleep) | 373.9 ± 23.3 (135.848 min) |
| Number of Awakenings | 5.6 ± 0.44 (1–15 times) |
| Total Awakening Time | 14.7 ± 1.19 (1–51 times) |
| Average Awakening Time | 2.49 ± 0.12 (0.29–5.57) |
| Average Time in Bed Each Time Sleeping (includes naps and split sleep) | 360 ± 17.3 (202–697 min) |
| Variables | Frequency % (Categorical Variables) or Mean and Standard Error of the Mean (Range Min-Max) (Discrete Variables) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HTA | Yes | 60.7% | |
| No | 39.3% | ||
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | Yes | 14.8% | |
| No | 85.2% | ||
| Diabetes | Yes | 49.2% | |
| No | 50.8% | ||
| Dyslipidemia | Yes | 41% | |
| No | 59% | ||
| Cognitive impairment: | Normal | 49.2% | |
| Mild | 18% | ||
| Moderate | 23% | ||
| Severe | 9.8% | ||
| Depression | Yes | 21.3% | |
| No | 78.7% | ||
| Anxiety | Yes | 8.2% | |
| No | 91.8% | ||
| Charlson comorbidity index | 6.87 ± 0.38 (2–16) | ||
| Polypharmacy | Opioids | Yes | 77% |
| No | 23% | ||
| Antidepressants | Yes | 45.9% | |
| No | 54.1% | ||
| Antipsychotics | Yes | 27.9% | |
| No | 72.1% | ||
| Anxiolytics | Yes | 41% | |
| No | 59% | ||
| Hypnotics | Yes | 54.1% | |
| No | 45.9% | ||
| Antiepileptic | Yes | 16.4% | |
| No | 83.6% | ||
| Number of daily psychotropic drugs | 3.07 ± 0.23 (0–8) | ||
| Total number of drugs prescribed daily | 11.1 ± 0.65 (3–24) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibáñez-del Valle, V.; Mafla-España, M.A.; Silva, J.; Cauli, O. Actigraphy Analysis of Sleep Associates with Salivary IL-6 Concentration in Institutionalized Older Individuals. Diseases 2023, 11, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11030093
Ibáñez-del Valle V, Mafla-España MA, Silva J, Cauli O. Actigraphy Analysis of Sleep Associates with Salivary IL-6 Concentration in Institutionalized Older Individuals. Diseases. 2023; 11(3):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11030093
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbáñez-del Valle, Vanessa, Mayra Alejandra Mafla-España, Josep Silva, and Omar Cauli. 2023. "Actigraphy Analysis of Sleep Associates with Salivary IL-6 Concentration in Institutionalized Older Individuals" Diseases 11, no. 3: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11030093
APA StyleIbáñez-del Valle, V., Mafla-España, M. A., Silva, J., & Cauli, O. (2023). Actigraphy Analysis of Sleep Associates with Salivary IL-6 Concentration in Institutionalized Older Individuals. Diseases, 11(3), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11030093









