In Silico Evaluation of the Potential Association of the Pathogenic Mutations of Alpha Synuclein Protein with Induction of Synucleinopathies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
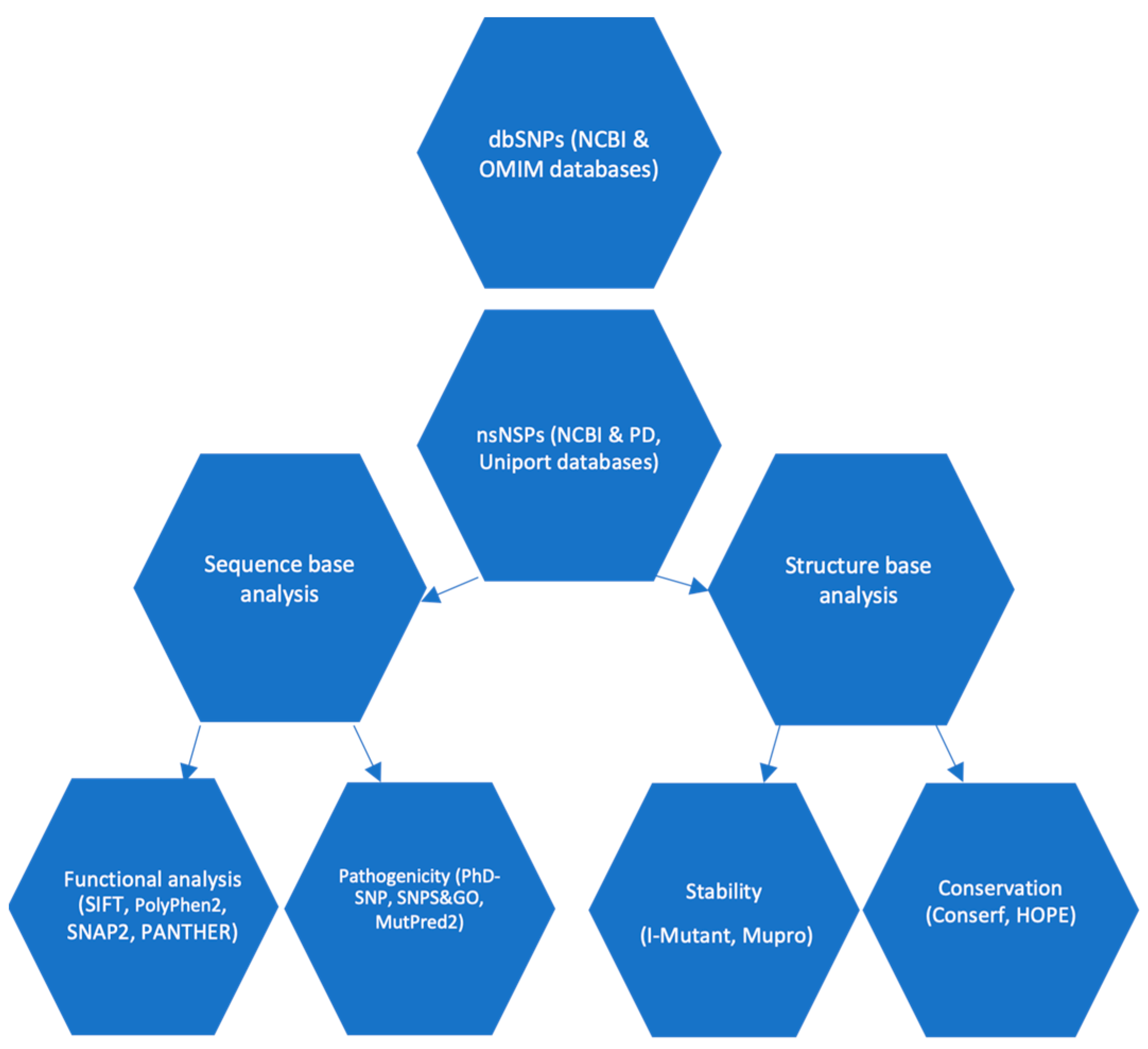
2. Methodology
2.1. Plane of Work
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Exploring the Influence of SNPs on Protein Function
2.4. Prediction of SNP-Disease Associations
2.5. Predicting the Impact of SNPs on Protein Stability
2.6. Prediction of SNPs on α-Syn Protein Functionality in Relation to Structure Using Mut-Pred Server
2.7. Analyzing Protein Sequence Conservation Using ConSurf
2.8. Analysis of Properties of Proteins
2.9. Determine the Active Binding Site Using PyMol Software
2.10. Performing of Molecular Dynamics Simulations (MDS)
3. Results
3.1. Predicting nsSNP Deleterious on α-Syn Protein
3.2. Analysis of Disease-Associated nsSNPs
3.3. The Impact of Predicted Deleterious Mutations on α-Syn Protein Stability
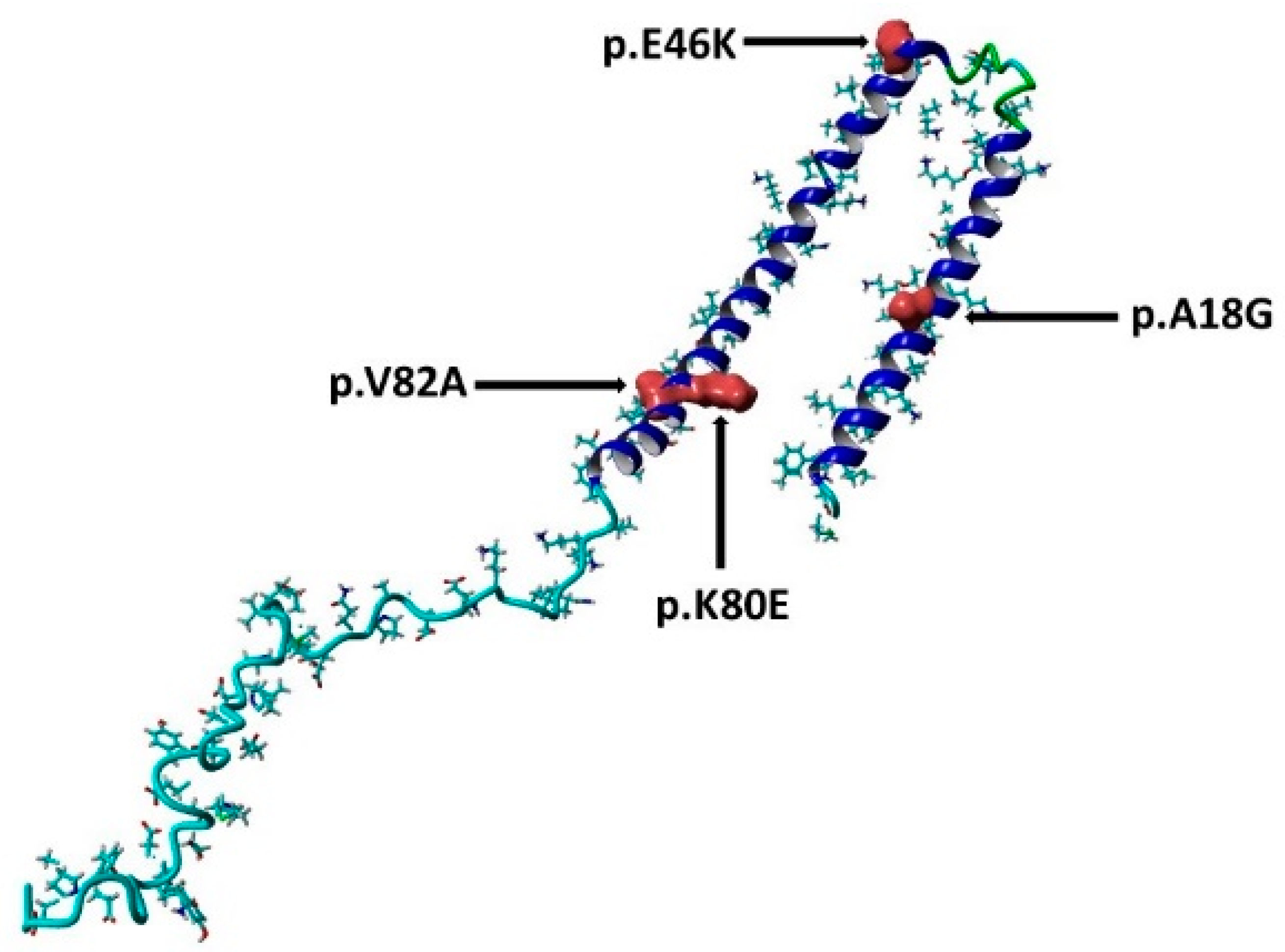
3.4. Investigation the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Pathogenicity
3.5. Analysis of the Phylogenetic Conservation of nsSNP
3.6. HOPE Predications of the α-Syn Protein Properties
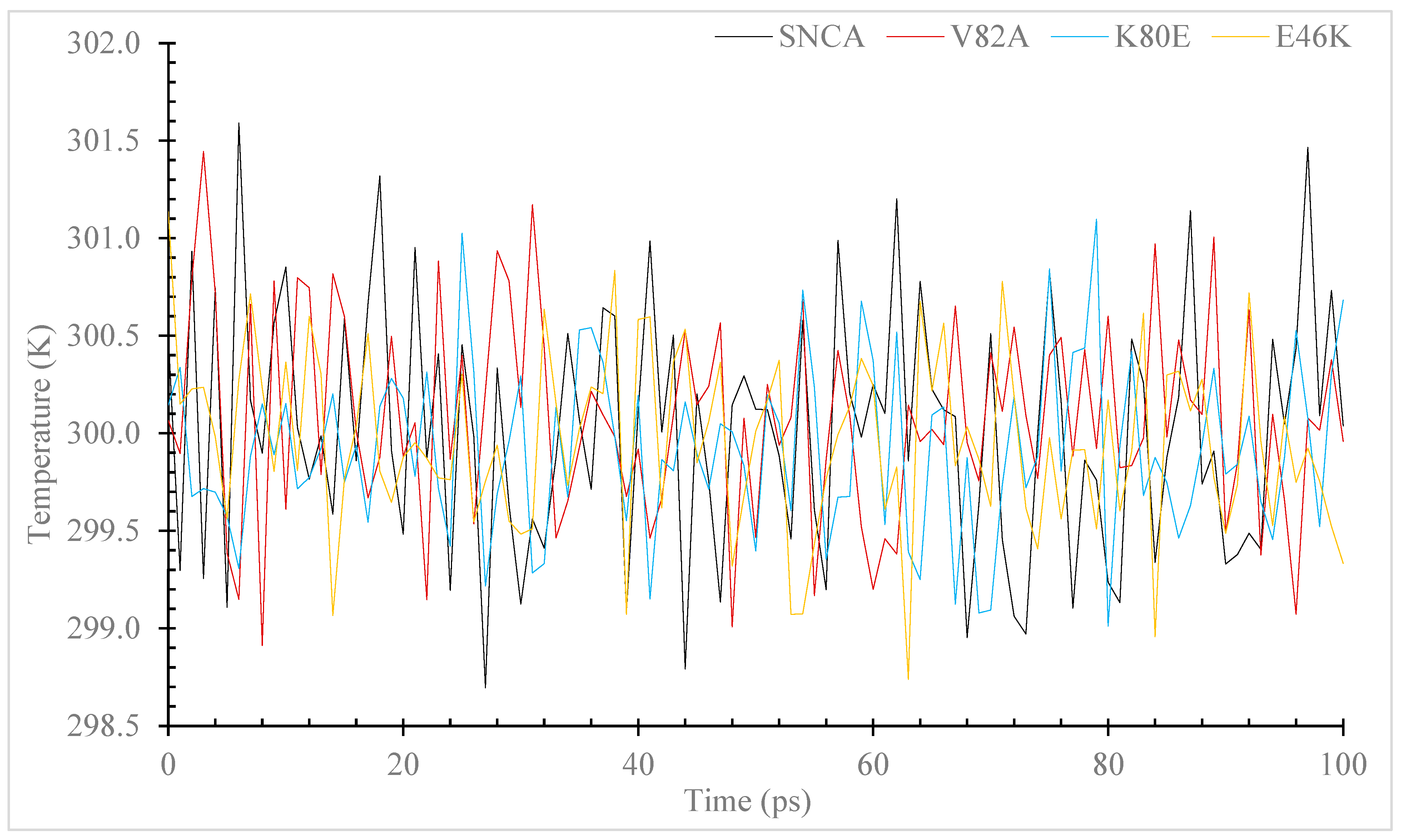
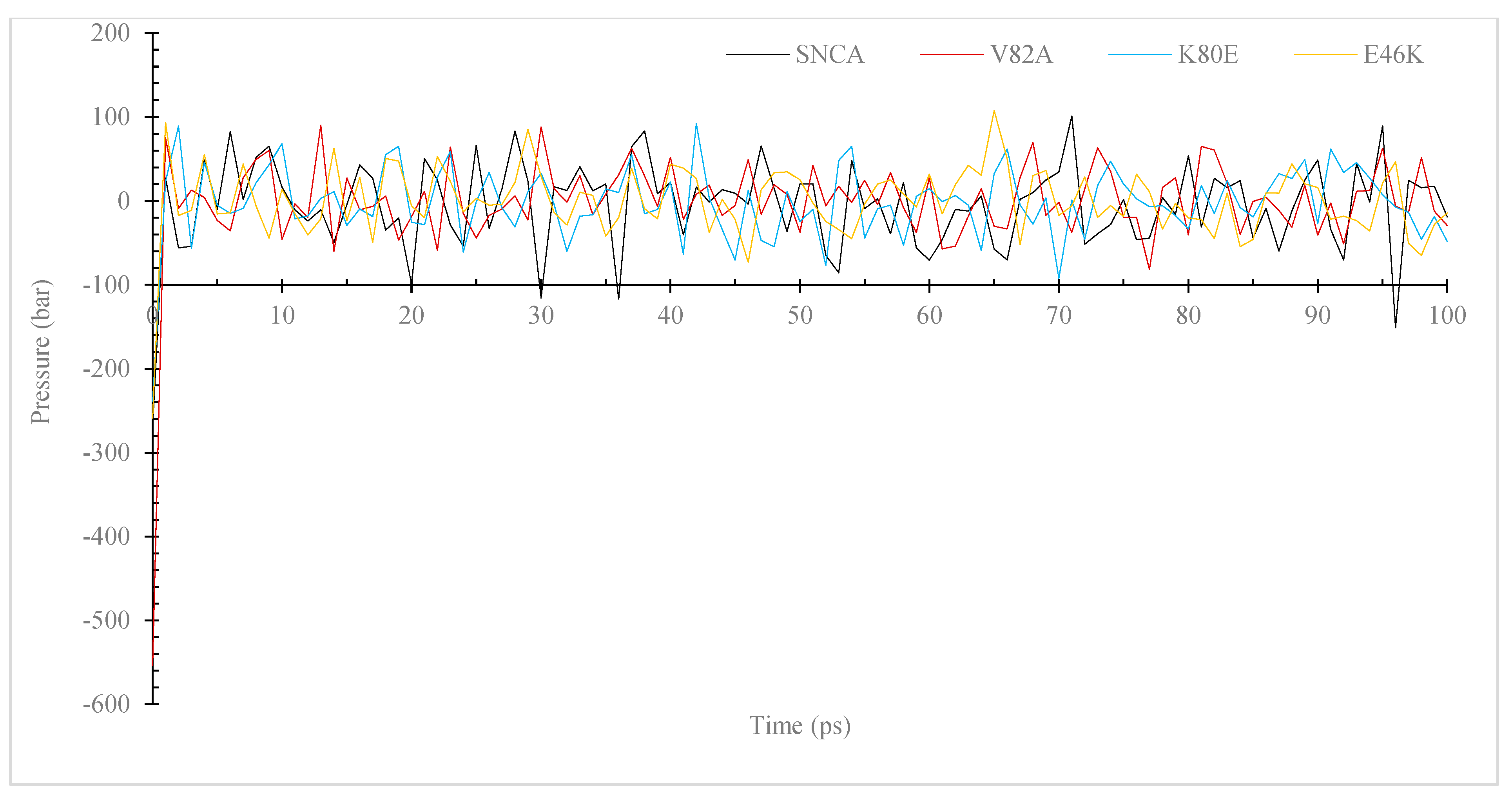
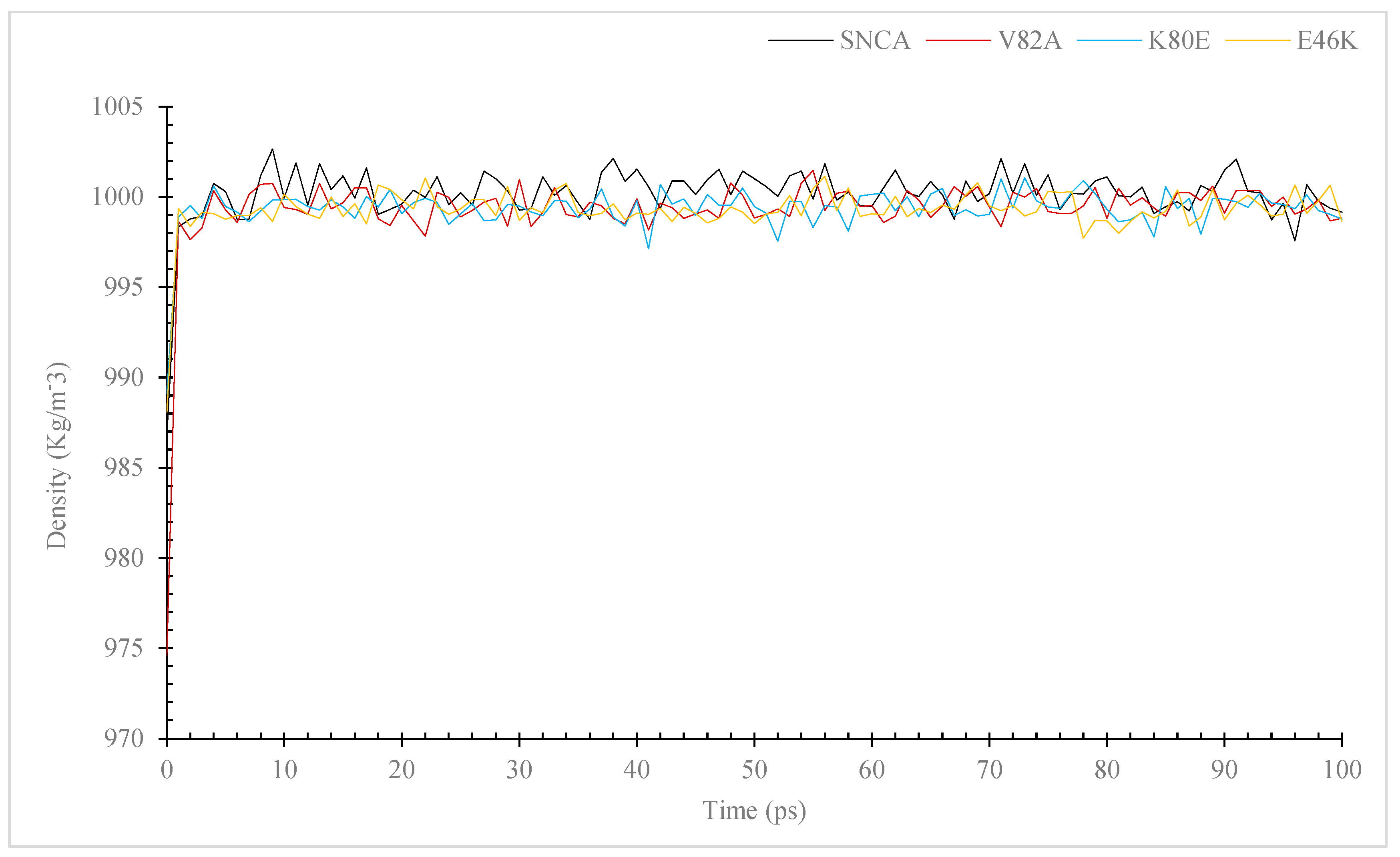
3.7. Molecular Dynamic (MD) Simulation of α-Syn Protein and Its Mutants
3.7.1. Temperature, Pressure, and Density
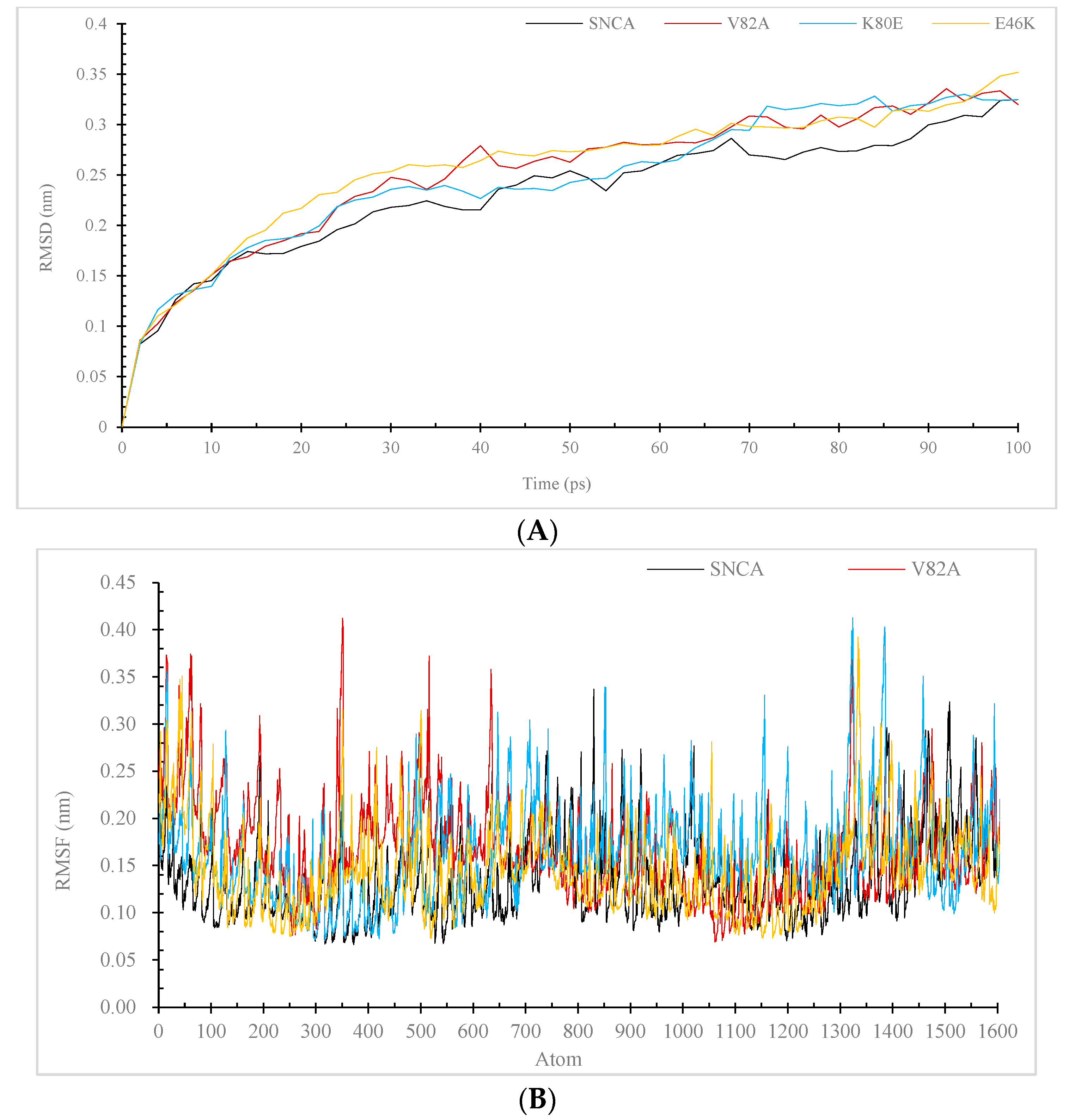
3.7.2. RMSD and RMSF
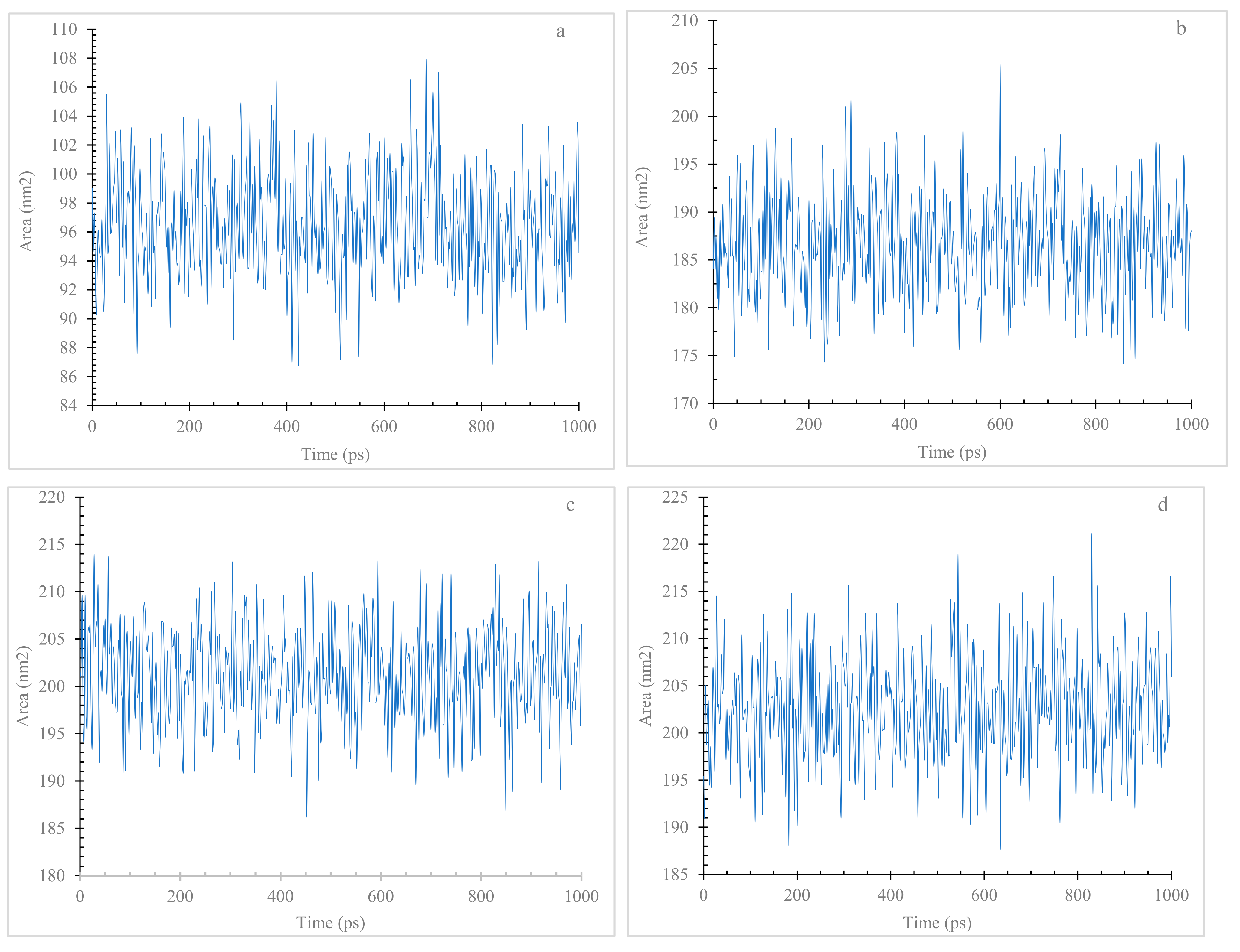
3.7.3. Radius of Gyration (Rg) and Solvent Accessible Surface Area (SASA)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maiti, P.; Manna, J.; Dunbar, G.L. Current understanding of the molecular mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease: Targets for potential treatments. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarsland, D.; Batzu, L.; Halliday, G.M.; Geurtsen, G.J.; Ballard, C.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Weintraub, D. Parkinson disease-associated cognitive impairment. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teil, M.; Arotcarena, M.L.; Faggiani, E.; Laferriere, F.; Bezard, E.; Dehay, B. Targeting alpha-synuclein for PD Therapeutics: A Pursuit on All Fronts. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadi, C. Clinical Features of Parkinson’s Disease: The Evolution of Critical Symptoms. Biology 2020, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabresi, P.; Mechelli, A.; Natale, G.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.; Di Lazzaro, G.; Ghiglieri, V. Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies: From overt neurodegeneration back to early synaptic dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wei, G.; Ding, F.; Sun, Y. Molecular Insights into the Misfolding and Dimerization Dynamics of the Full-Length alpha-Synuclein from Atomistic Discrete Molecular Dynamics Simulations. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 3126–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahul-Mellier, A.L.; Burtscher, J.; Maharjan, N.; Weerens, L.; Croisier, M.; Kuttler, F.; Leleu, M.; Knott, G.W.; Lashuel, H.A. The process of Lewy body formation, rather than simply alpha-synuclein fibrillization, is one of the major drivers of neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4971–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.D. The Roles of Post-translational Modifications on alpha-Synuclein in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Benito, M.; Granado, N.; Garcia-Sanz, P.; Michel, A.; Dumoulin, M.; Moratalla, R. Modeling Parkinson’s Disease with the Alpha-Synuclein Protein. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.L.; Brown, D.R. Seeking a mechanism for the toxicity of oligomeric alpha-synuclein. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 282–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G. The Synucleinopathies: Twenty Years On. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2017, 7, S51–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meade, R.M.; Fairlie, D.P.; Mason, J.M. Alpha-synuclein structure and Parkinson’s disease—Lessons and emerging principles. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lashuel, H.A.; Overk, C.R.; Oueslati, A.; Masliah, E. The many faces of alpha-synuclein: From structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuber, S.; Rajsombath, M.; Minakaki, G.; Winkler, J.; Muller, C.P.; Ericsson, M.; Caldarone, B.; Dettmer, U.; Selkoe, D.J. Abrogating Native alpha-Synuclein Tetramers in Mice Causes a L-DOPA-Responsive Motor Syndrome Closely Resembling Parkinson’s Disease. Neuron 2018, 100, 75–90 e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shu, L.; Sun, Q.; Pan, H.; Guo, J.; Tang, B. A Comprehensive Analysis of the Association Between SNCA Polymorphisms and the Risk of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.H.; Alghrably, M.; Dhahri, M.; Sharfalddin, A.; Alsiary, R.; Jaremko, M.; Faa, G.; Campagna, M.; Congiu, T.; Piras, M.; et al. Living with the enemy: From protein-misfolding pathologies we know, to those we want to know. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, S.; Houot, M.; Mangone, G.; Tesson, C.; Bertrand, H.; Forlani, S.; Anheim, M.; Brefel-Courbon, C.; Broussolle, E.; Thobois, S.; et al. Genetic and Phenotypic Basis of Autosomal Dominant Parkinson’s Disease in a Large Multi-Center Cohort. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flagmeier, P.; Meisl, G.; Vendruscolo, M.; Knowles, T.P.; Dobson, C.M.; Buell, A.K.; Galvagnion, C. Mutations associated with familial Parkinson’s disease alter the initiation and amplification steps of alpha-synuclein aggregation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10328–10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kala, D.; Dhiman, G.; Yadav, V.; Krokhotin, A.; Dokholyan, N.V. Predicting the functional consequences of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in IL8 gene. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George Priya Doss, C.; Rajith, B. A new insight into structural and functional impact of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in PTEN gene. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 66, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Parves, M.R.; Mahmud, S.; Tithi, F.A.; Reza, M.A. Assessment of structurally and functionally high-risk nsSNPs impacts on human bone morphogenetic protein receptor type IA (BMPR1A) by computational approach. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 80, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, P.C.; Henikoff, S. SIFT: Predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3812–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013, 76, 7.20.1–7.20.41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, M.; Bromberg, Y.; Rost, B. Better prediction of functional effects for sequence variants. BMC Genom. 2015, 16 (Suppl. S8), S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.D.; Ebert, D.; Muruganujan, A.; Mushayahama, T.; Albou, L.P.; Mi, H. PANTHER: Making genome-scale phylogenetics accessible to all. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capriotti, E.; Calabrese, R.; Casadio, R. Predicting the insurgence of human genetic diseases associated to single point protein mutations with support vector machines and evolutionary information. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2729–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, R.; Capriotti, E.; Fariselli, P.; Martelli, P.L.; Casadio, R. Functional annotations improve the predictive score of human disease-related mutations in proteins. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pejaver, V.; Urresti, J.; Lugo-Martinez, J.; Pagel, K.A.; Lin, G.N.; Nam, H.J.; Mort, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Sebat, J.; Iakoucheva, L.M.; et al. Inferring the molecular and phenotypic impact of amino acid variants with MutPred2. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazy, H.; Erez, E.; Martz, E.; Pupko, T.; Ben-Tal, N. ConSurf 2010: Calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W529–W533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venselaar, H.; Te Beek, T.A.; Kuipers, R.K.; Hekkelman, M.L.; Vriend, G. Protein structure analysis of mutations causing inheritable diseases. An e-Science approach with life scientist friendly interfaces. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrino, R.; Schapira, A.H.V. Parkinson disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burre, J. The Synaptic Function of alpha-Synuclein. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2015, 5, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, S.; Sekiya, H.; Kondru, N.; Ross, O.A.; Dickson, D.W. Neuropathology and molecular diagnosis of Synucleinopathies. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerman, A.L.; Watts, J.C.; Aoyagi, A.; Giles, K.; Middleton, L.T.; Prusiner, S.B. alpha-Synuclein: Multiple System Atrophy Prions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a024588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspita, L.; Chung, S.Y.; Shim, J.W. Oxidative stress and cellular pathologies in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Vicente, M.; Talloczy, Z.; Kaushik, S.; Massey, A.C.; Mazzulli, J.; Mosharov, E.V.; Hodara, R.; Fredenburg, R.; Wu, D.C.; Follenzi, A.; et al. Dopamine-modified alpha-synuclein blocks chaperone-mediated autophagy. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulson, B.G.; Szczepski, K.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Jaremko, L.; Emwas, A.H.; Jaremko, M. Aggregation of biologically important peptides and proteins: Inhibition or acceleration depending on protein and metal ion concentrations. RSC Adv. 2019, 10, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelise, N.; Schmitz, M.; Thune, K.; Cramm, M.; Rabano, A.; Zafar, S.; Stoops, E.; Vanderstichele, H.; Villar-Pique, A.; Llorens, F.; et al. Effect of the micro-environment on alpha-synuclein conversion and implication in seeded conversion assays. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhahri, M.; Alghrably, M.; Mohammed, H.A.; Badshah, S.L.; Noreen, N.; Mouffouk, F.; Rayyan, S.; Qureshi, K.A.; Mahmood, D.; Lachowicz, J.I.; et al. Natural Polysaccharides as Preventive and Therapeutic Horizon for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, O.R.; Alatwi, H.E.; Alharbi, A.A.; Alessa, A.H.; Al-Amer, O.M.; Alanazi, A.F.R.; Shams, A.M.; Alomari, E.; Naser, A.Y.; Alzahrani, F.A.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Novel Mutations in Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD) in Saudi Subjects by Whole-Exome Sequencing. Medicina 2022, 58, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, O.R.; Mir, R.; Alatwi, H.E.; Hawsawi, Y.M.; Alharbi, A.A.; Alessa, A.H.; Albalawi, E.S.; Elfaki, I.; Alalawi, Y.; Moharam, L.; et al. Potential Impact of PI3K-AKT Signaling Pathway Genes, KLF-14, MDM4, miRNAs 27a, miRNA-196a Genetic Alterations in the Predisposition and Progression of Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfaki, I.; Mir, R.; Abu-Duhier, F.M.; Khan, R.; Sakran, M. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase Glu545Lys and His1047Tyr Mutations are not Associated with T2D. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfaki, I.; Mir, R.; Almutairi, F.M.; Duhier, F.M.A. Cytochrome P450: Polymorphisms and Roles in Cancer, Diabetes and Atherosclerosis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 2057–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaki, I.; Mir, R.; Duhier, F.M.A.; Alotaibi, M.A.; Alalawy, A.I.; Barnawi, J.; Babakr, A.T.; Mir, M.M.; Altayeb, F.; Mirghani, H.; et al. Clinical Implications of MiR128, Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene Abnormalities and Their Association with T2D. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 1859–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, C.K.; Mir, R.; Elfaki, I.; Javid, J.; Babakr, A.T.; Banu, S.; Chahal, S.M.S. Evaluation of the Association of Omentin 1 rs2274907 A>T and rs2274908 G>A Gene Polymorphisms with Coronary Artery Disease in Indian Population: A Case Control Study. J. Pers. Med. 2019, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghipour, I.; Bina, A.R.; Mogharrabi, M.R.; Fanoodi, A.; Ebrahimian, A.R.; Khojasteh Kaffash, S.; Babazadeh Baghan, A.; Khorashadizadeh, M.E.; Taghehchian, N.; Moghbeli, M. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms as important risk factors of diabetes among Middle East population. Hum. Genom. 2022, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.A.; Scott, L.J.; Magi, R.; Marullo, L.; Gaulton, K.J.; Kaakinen, M.; Pervjakova, N.; Pers, T.H.; Johnson, A.D.; Eicher, J.D.; et al. An Expanded Genome-Wide Association Study of Type 2 Diabetes in Europeans. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2888–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfaki, I.; Mir, R.; Abu-Duhier, F.M.; Jha, C.K.; Ahmad Al-Alawy, A.I.; Babakr, A.T.; Habib, S.A.E. Analysis of the Potential Association of Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes CYP2C9*3 and CYP2C19*3 Gene Variations with Type 2 Diabetes: A Case-Control Study. Curr. Drug Metab. 2020, 21, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q. Mutation analysis of pathogenic non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) in WFS1 gene through computational approaches. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhou, Q.; He, J.; Jiang, Z.; Peng, C.; Tong, R.; Shi, J. Recent advances in the development of protein-protein interactions modulators: Mechanisms and clinical trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chang, I.; Yu, W. Atomic insights into the effects of pathological mutants through the disruption of hydrophobic core in the prion protein. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Koros, C.; Strohaker, T.; Schulte, C.; Bozi, M.; Varvaresos, S.; Ibanez de Opakua, A.; Simitsi, A.M.; Bougea, A.; Voumvourakis, K.; et al. A Novel SNCA A30G Mutation Causes Familial Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1624–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiely, A.P.; Ling, H.; Asi, Y.T.; Kara, E.; Proukakis, C.; Schapira, A.H.; Morris, H.R.; Roberts, H.C.; Lubbe, S.; Limousin, P.; et al. Distinct clinical and neuropathological features of G51D SNCA mutation cases compared with SNCA duplication and H50Q mutation. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, A.; Mohammad, T.; Anjum, F.; Shafie, A.; Singh, I.K.; Abdullaev, B.; Pasupuleti, V.R.; Adnan, M.; Yadav, D.K.; Hassan, M.I. Comparative analysis of web-based programs for single amino acid substitutions in proteins. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.P.; Balana, A.T.; Galesic, A.; Rakshit, A.; Pratt, M.R. Ubiquitination Can Change the Structure of the alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Fiber in a Site Selective Fashion. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malecki, J.M.; Davydova, E.; Falnes, P.O. Protein methylation in mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z.; Lv, H.; Li, X. In silico analysis of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) in the human GJA3 gene associated with congenital cataract. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Long, H.; Zhao, C.; Luo, F.; Sun, Y.; Tao, Y.; Su, X.D.; Li, D.; et al. Parkinson’s disease associated mutation E46K of alpha-synuclein triggers the formation of a distinct fibril structure. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftabuddin, M.; Kundu, S. Hydrophobic, hydrophilic, and charged amino acid networks within protein. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Diaz, S.; Pujols, J.; Pinheiro, F.; Santos, J.; Pallares, I.; Navarro, S.; Conde-Gimenez, M.; Garcia, J.; Salvatella, X.; Dalfo, E.; et al. Inhibition of alpha-Synuclein Aggregation and Mature Fibril Disassembling with a Minimalistic Compound, ZPDm. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 588947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.H.; Sudhakar, D.R.; Kalaiarasan, P.; Subbarao, N.; Wadhawa, G.; Lohani, M.; Khan, M.K.; Khan, A.U. Insight into the effect of inhibitor resistant S130G mutant on physico-chemical properties of SHV type beta-lactamase: A molecular dynamics study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfaki, I.; Bayer, P.; Mueller, J.W. A potential transcriptional regulator is out-of-frame translated from the metallothionein 2A messenger RNA. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 409, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfaki, I.; Knitsch, A.; Matena, A.; Bayer, P. Identification and characterization of peptides that bind the PPIase domain of Parvulin17. J. Pept. Sci. 2013, 19, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimavicius, L.; Livesey, B.J.; Marsh, J.A. Loss-of-function, gain-of-function and dominant-negative mutations have profoundly different effects on protein structure. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor-Vivas, C.; Hernandez-Lemus, E.; Dorantes-Gilardi, R. Linking protein structural and functional change to mutation using amino acid networks. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| SIFT | Polyphen2 | SNAP2 | PANTHER | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant ID | Alleles | MAF | Transcript ID | Mutation | Sift Score | Prediction | Polyphen Score | Prediction | Prediction | Accuracy % | pdel | Prediction |
| rs1319839593 | A|G | G = 0.000008/2 | ENST00000673718.1 | V82A | 0 | deleterious | 0.999 | probably damaging | effect | 0.8 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1261243630 | T|C | C = 0.000004/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | K80E | 0 | deleterious | 0.96 | probably damaging | effect | 0.75 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1239518140 | A|G | G = 0.000004/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | V52A | 0 | deleterious | 1 | probably damaging | effect | 0.8 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs104893875 | C|T | T = 0./0 | ENST00000673718.1 | E46K | 0 | deleterious | 0.959 | probably damaging | effect | 0.66 | 455 | probably damaging |
| rs750512067 | C|T | T = 0.000008/2 | ENST00000673718.1 | G41D | 0 | deleterious | 0.998 | probably damaging | effect | 0.95 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs750745088 | C|A | T = 0.000008/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | V37F | 0 | deleterious | 0.949 | possibly damaging | effect | 0.8 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1342686707 | C|G | G = 0.000004/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | G36R | 0 | deleterious | 1 | probably damaging | effect | 0.8 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1342686707 | C|T | G = 0.000004/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | G36S | 0 | deleterious | 0.999 | probably damaging | effect | 0.71 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1330229174 | T|C | C = 0.000004/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | K34E | 0 | deleterious | 0.96 | probably damaging | effect | 0.66 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs104893878 | C|G | N/A | ENST00000673718.1 | A30P | 0 | deleterious | 0.996 | probably damaging | effect | 0.8 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs753674628 | C|T | T = 0.000008/2 | ENST00000673718.1 | V26M | 0 | deleterious | 0.996 | probably damaging | effect | 0.53 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1433622151 | C|T | T = 0.000004/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | G25S | 0 | deleterious | 0.999 | probably damaging | effect | 0.75 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1273319141 | G|A | A = 0.000004/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | T22I | 0 | deleterious | 0.999 | probably damaging | effect | 0.8 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs778867145 | T|C | C = 0.000016/2 | ENST00000673718.1 | E20G | 0 | deleterious | 1 | probably damaging | effect | 0.85 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs752472160 | G|C | C = 0.003975/467 | ENST00000673718.1 | A18G | 0 | deleterious | 0.998 | probably damaging | effect | 0.75 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1289802008 | A|G | G = 0.000004/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | V16A | 0 | deleterious | 1 | probably damaging | effect | 0.63 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1739238968 | A|G | G = 0.000007/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | V15A | 0 | deleterious | 1 | probably damaging | effect | 0.85 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1219278381 | C|A | A = 0.000004/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | A11S | 0 | deleterious | 0.887 | possibly damaging | effect | 0.75 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1188720061 | T|G | G = 0.000004/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | K6N | 0 | deleterious | 1 | possibly damaging | effect | 0.75 | 456 | probably damaging |
| rs1168809349 | A|T | T = 0.000007/1 | ENST00000673718.1 | V3E | 0 | deleterious | 0.972 | possibly damaging | effect | 0.71 | 456 | probably damaging |
| PhD-SNP | SNP&GO | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant ID | Alleles | Mutation | Score | Prediction | Score | Prediction |
| rs1319839593 | A|G | V82A | 1 | Disease | 5 | Disease |
| rs1261243630 | T|C | K80E | 3 | Disease | 8 | Disease |
| rs1239518140 | A|G | V52A | 3 | Neutral | 6 | Disease |
| rs104893875 | C|T | E46K | 0 | Disease | 9 | Disease |
| rs750512067 | C|T | G41D | 5 | Neutral | 9 | Disease |
| rs750745088 | C|A | V37F | 2 | Neutral | 9 | Disease |
| rs1342686707 | C|G | G36R | 3 | Neutral | 9 | Disease |
| rs1342686707 | C|T | G36S | 7 | Neutral | 9 | Disease |
| rs1330229174 | T|C | K34E | 1 | Neutral | 9 | Disease |
| rs104893878 | C|G | A30P | 1 | Neutral | 10 | Disease |
| rs753674628 | C|T | V26M | 3 | Neutral | 8 | Disease |
| rs1433622151 | C|T | G25S | 1 | Neutral | 9 | Disease |
| rs1273319141 | G|A | T22I | 3 | Neutral | 9 | Disease |
| rs778867145 | T|C | E20G | 1 | Neutral | 8 | Disease |
| rs752472160 | G|C | A18G | 0 | Disease | 8 | Disease |
| rs1289802008 | A|G | V16A | 5 | Neutral | 5 | Disease |
| rs1739238968 | A|G | V15A | 1 | Neutral | 5 | Disease |
| rs1219278381 | C|A | A11S | 5 | Neutral | 9 | Disease |
| rs1188720061 | T|G | K6N | 4 | Neutral | 8 | Disease |
| rs1168809349 | A|T | V3E | 4 | Neutral | 8 | Disease |
| Variant ID | Allele | Mutation | I-Mutant | MuPro |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1319839593 | A|G | V82A | Decrease | Decrease |
| rs1261243630 | T|C | K80E | Decrease | Decrease |
| rs104893875 | C|T | E46K | Decrease | Decrease |
| rs752472160 | G|C | A18G | Decrease | Decrease |
| MutPred | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant ID | Allele | Mutation | Score | Effect | Function Affected |
| rs1319839593 | A|G | V82A | 0.637 | − | Loss of Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid at Q79 |
| rs1261243630 | T|C | K80E | 0.701 | − | Loss of Methylation at K80; Loss of Ubiquitylation at K80 |
| rs104893875 | C|T | E46K | 0.646 | + | Gain of Methylation at E46; Altered Disordered interface; Altered Transmembrane protein |
| rs752472160 | G|C | A18G | 0.433 | no results | No effects produced |
| Mutation | V82A | K80E | E46K |
|---|---|---|---|
| AA Properties | |||
| Size | Mutant is smaller than wild type | Mutant is smaller than wild type | Mutant is bigger than wild type |
| Charge | No charge change | Wildtype charge: POSITIVE | Wildtype charge: NEGATIVE |
| Mutant charge: NEGATIVE | Mutant charge: POSITIVE | ||
| Structure | Preferred secondary structure for wild type, destabilized by mutant | ||
| secondary structure preference for mutant | |||
| Conservation | |||
| Conservation | Mutant located near a highly conserved position | Only this residue type at position, mutation possibly damaging | Mutant located near a highly conserved position |
| Mutation may be damaging | Mutation may be damaging | ||
| Conclusion | |||
| AA Properties | Mutant residue’s smaller size may lead to loss of interactions | Charge difference between wild type and mutant could cause repulsion | Charge difference between wild type and mutant could cause repulsion |
| Mutant residue’s smaller size may lead to loss of interactions | Mutant residue’s bigger size may lead to bumps |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elnageeb, M.E.; Elfaki, I.; Adam, K.M.; Ahmed, E.M.; Elkhalifa, E.M.; Abuagla, H.A.; Ahmed, A.A.E.M.; Ali, E.W.; Eltieb, E.I.; Edris, A.M. In Silico Evaluation of the Potential Association of the Pathogenic Mutations of Alpha Synuclein Protein with Induction of Synucleinopathies. Diseases 2023, 11, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11030115
Elnageeb ME, Elfaki I, Adam KM, Ahmed EM, Elkhalifa EM, Abuagla HA, Ahmed AAEM, Ali EW, Eltieb EI, Edris AM. In Silico Evaluation of the Potential Association of the Pathogenic Mutations of Alpha Synuclein Protein with Induction of Synucleinopathies. Diseases. 2023; 11(3):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11030115
Chicago/Turabian StyleElnageeb, Mohamed E., Imadeldin Elfaki, Khalid M. Adam, Elsadig Mohamed Ahmed, Elkhalifa M. Elkhalifa, Hytham A. Abuagla, Abubakr Ali Elamin Mohamed Ahmed, Elshazali Widaa Ali, Elmoiz Idris Eltieb, and Ali M. Edris. 2023. "In Silico Evaluation of the Potential Association of the Pathogenic Mutations of Alpha Synuclein Protein with Induction of Synucleinopathies" Diseases 11, no. 3: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11030115
APA StyleElnageeb, M. E., Elfaki, I., Adam, K. M., Ahmed, E. M., Elkhalifa, E. M., Abuagla, H. A., Ahmed, A. A. E. M., Ali, E. W., Eltieb, E. I., & Edris, A. M. (2023). In Silico Evaluation of the Potential Association of the Pathogenic Mutations of Alpha Synuclein Protein with Induction of Synucleinopathies. Diseases, 11(3), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases11030115






