A Computationally Efficient Algorithm for Feedforward Active Noise Control Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Step 1:Calculate the DFTs of the vectors and
- Step 2:Calculate according to (10).
- Step 3:Adjust the vector by adding the first L elements of the inverse DFT of .
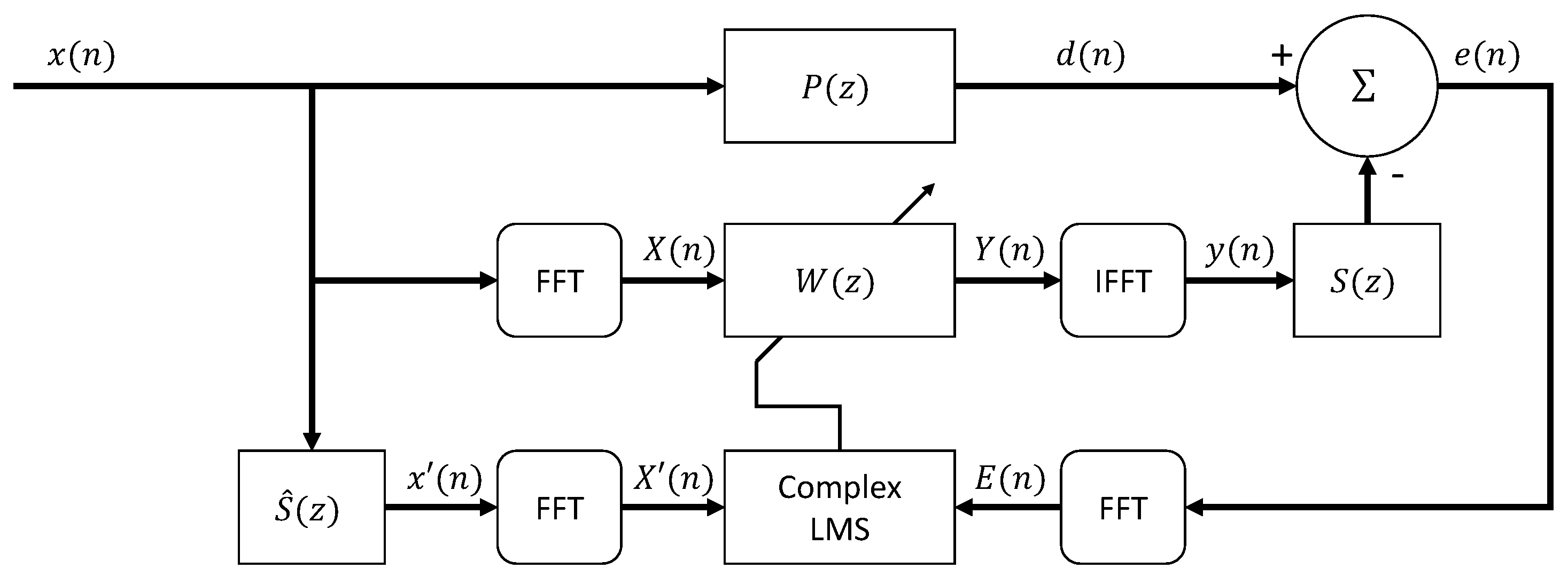
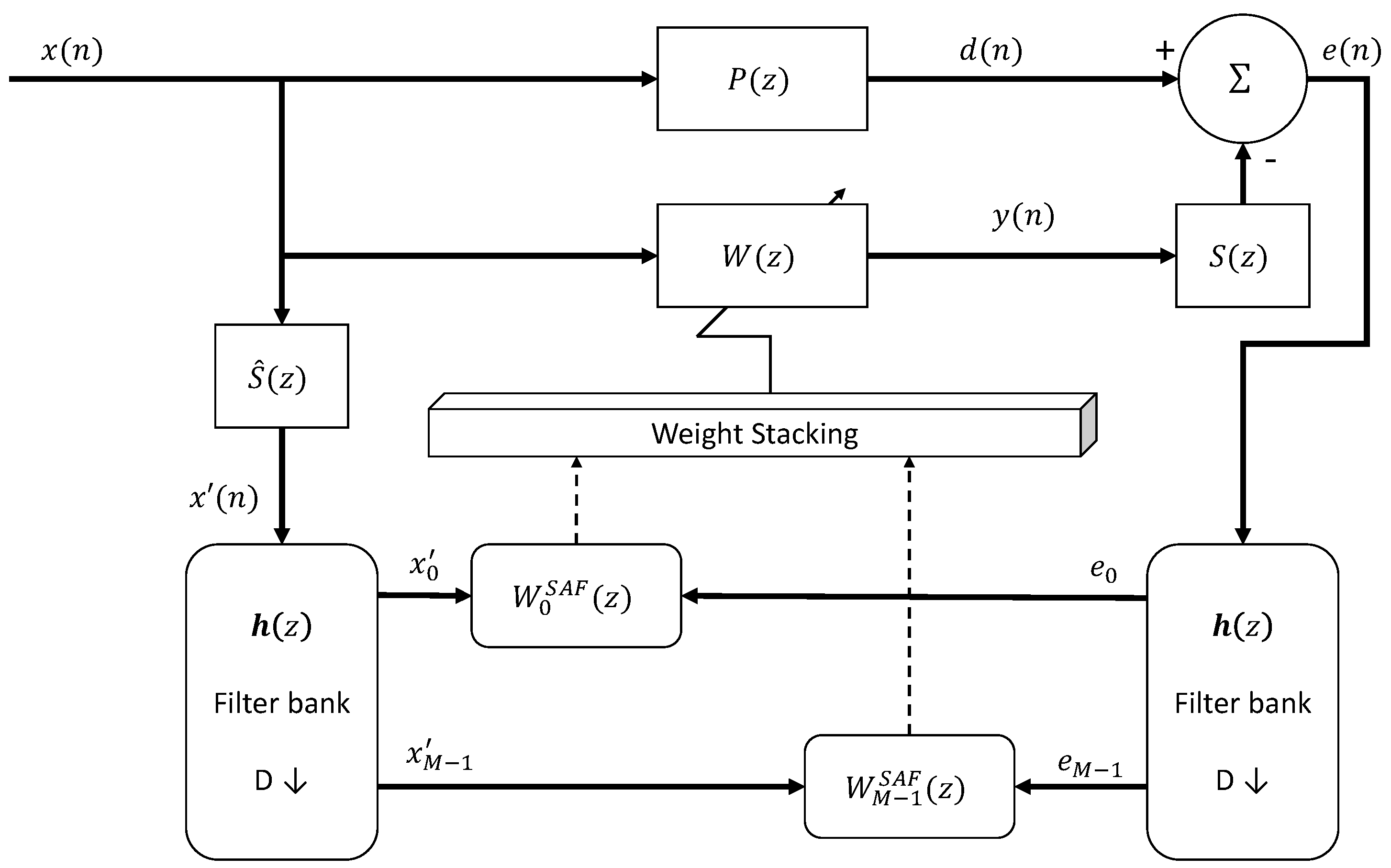
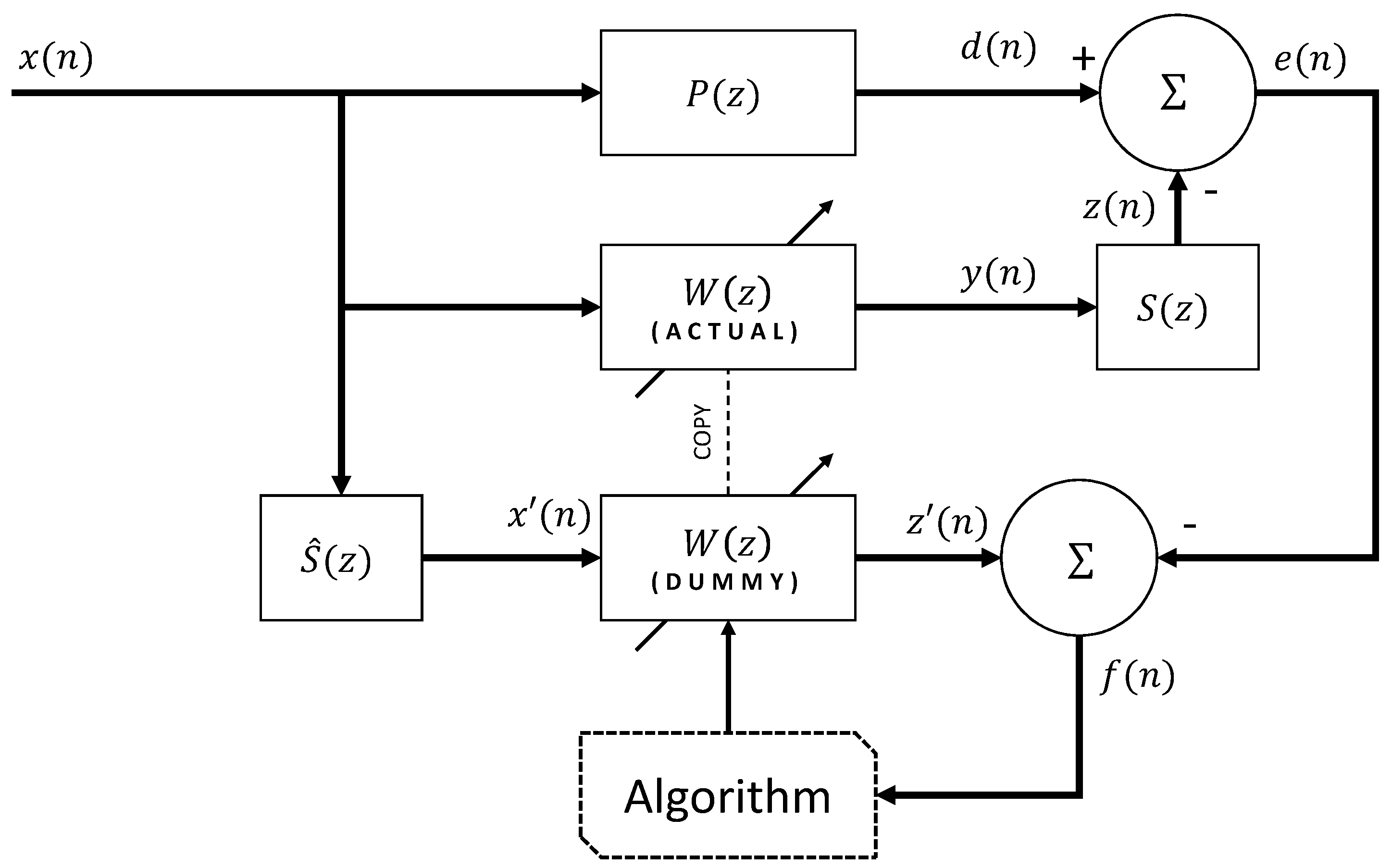
Theory and Calculations
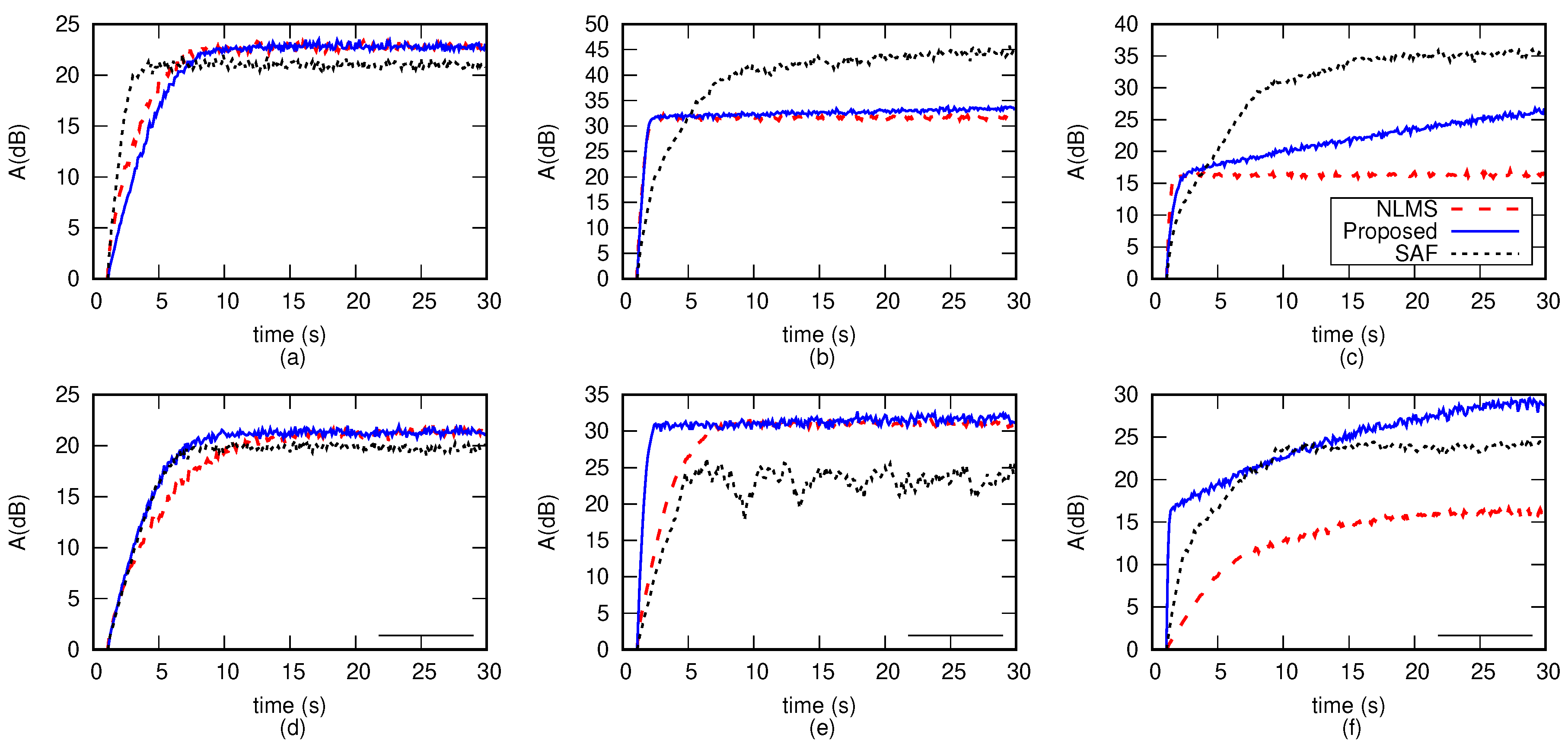
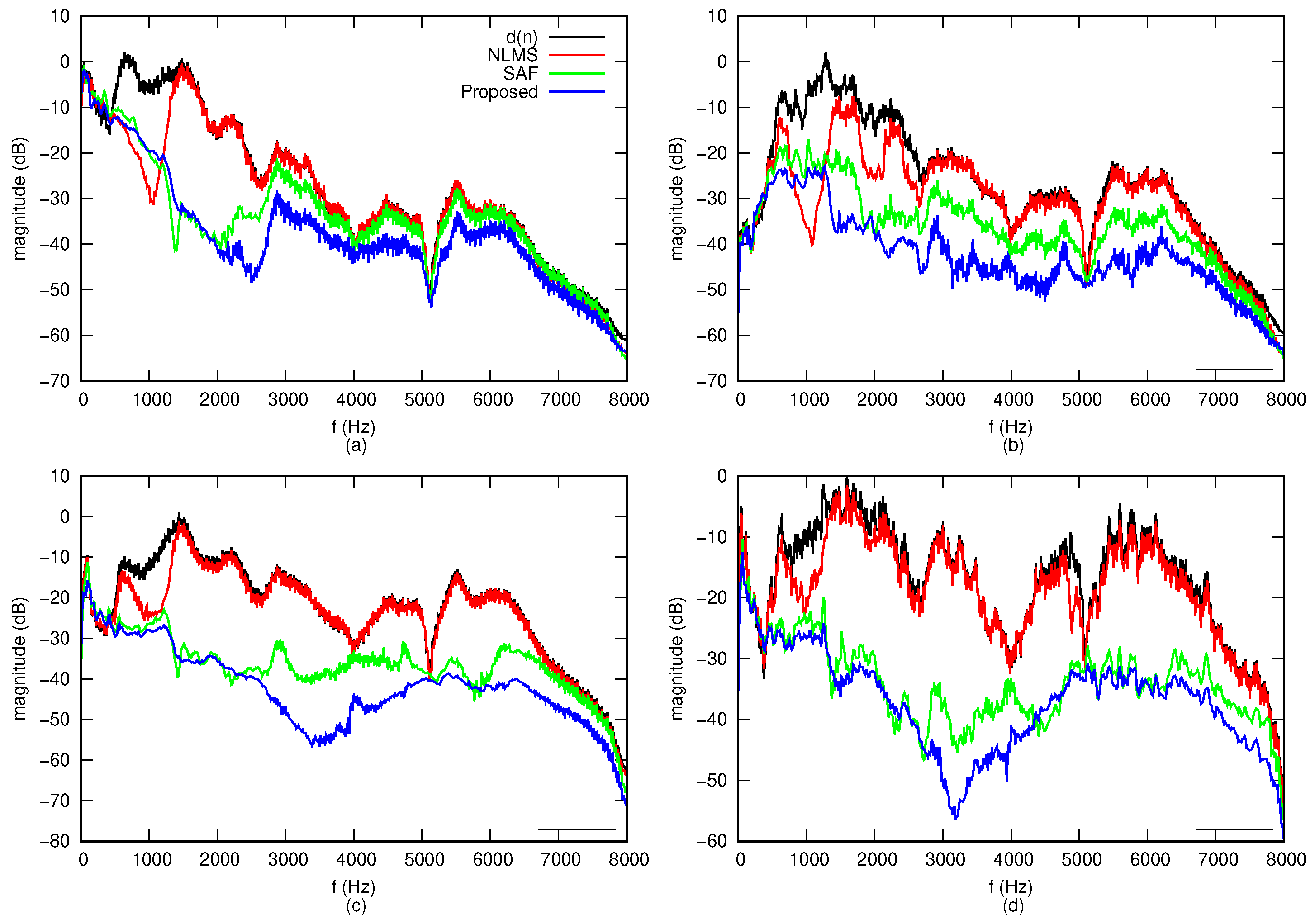
3. Results
- Test case 1 involves a short control filter with length and synthetic reference signals . Effectiveness in reducing the noise and computational efficiency are assessed.
- Test case 2 involves a long control filter with length and synthetic reference signals . Effectiveness in reducing the noise and computational efficiency are assessed.
- Test case 3 involves a long control filter with length and three real world noises as reference signals . Effectiveness in reducing noise from signals with rich and variable spectra are assessed.
- Test case 4 involves both short and long control filters with length and and synthetic reference signals . Robustness is assessed by introducing a step-like variation in the secondary path and plant noise.
- Test case 5 involves a long control filter with length and synthetic reference signals . Robustness is assessed by introducing a step-like variation in the harmonic content of the reference signals
- Test case 6 involves a long control filter with length and impulsive synthetic noises . The test purpose is to push the algorithm comparison to the limit being impulsive noise very short but with elevated intensity.
3.1. Test Case 1—Short Control Filter
3.2. Test Case 2—Long Control Filter
3.3. Test Case 3—Real World Noise Sources
3.4. Test Case 4—Robustness against Secondary Path Variations
3.5. Test Case 5—Robustness against Reference Signal Variations
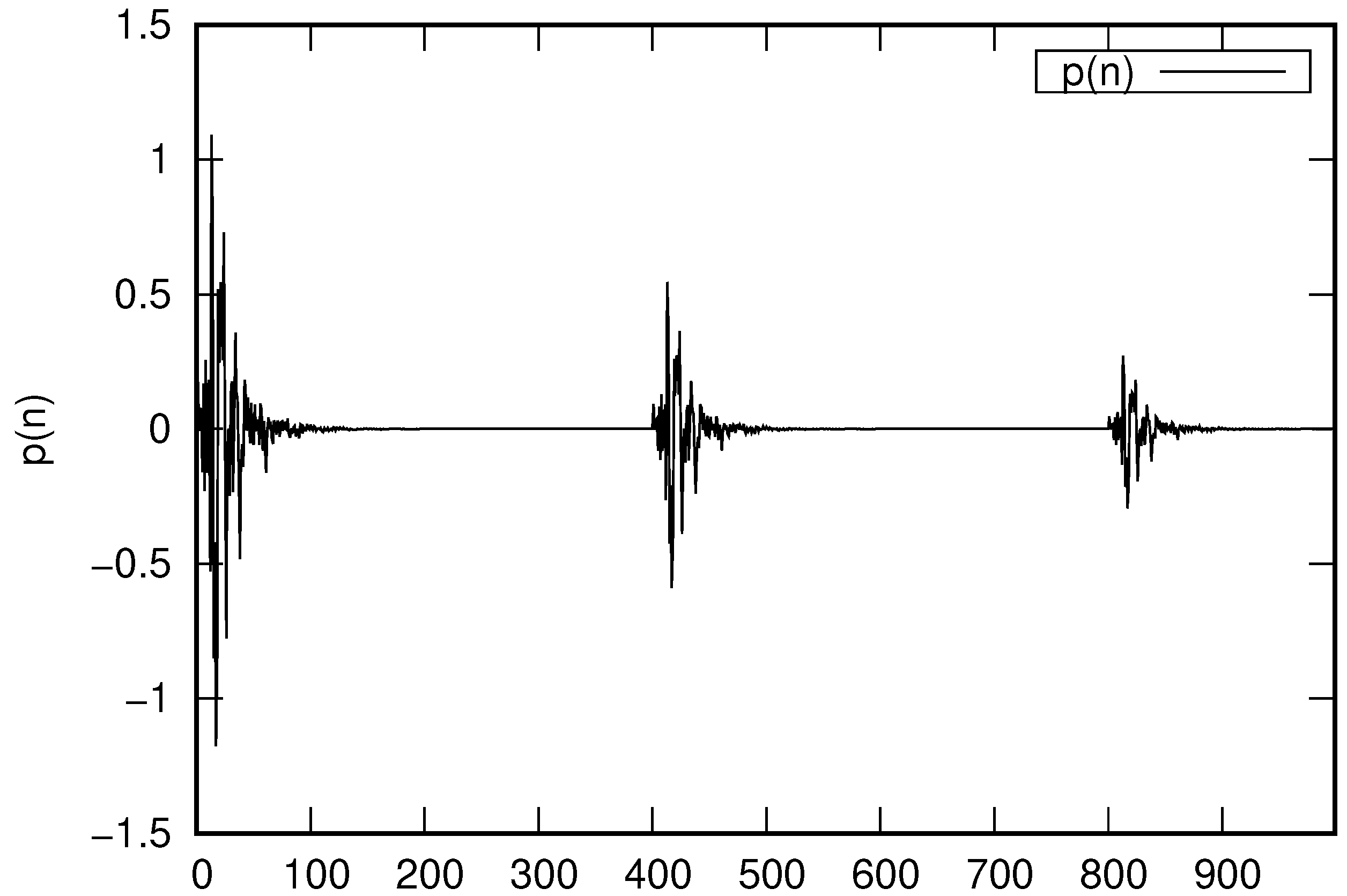
3.6. Test Case 6—Impulsive Noise
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Astola, J.; Kuosmanen, P. Fundamentals of Nonlinear Digital Filtering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Pitas, I.; Venetsanopoulos, A.N. Nonlinear Digital Filters: Principles and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 84. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.A.; Gan, W.S.; Kuo, S.M. Subband Adaptive Filtering: Theory and Implementation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce, H.; Ponce, P.; Molina, A. Adaptive noise filtering based on artificial hydrocarbon networks: An application to audio signals. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 6512–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmunk, D.V. Neural Network Filtering Techniques for Compensating Linear and Non-Linear Distortion of an Audio Transducer. U.S. Patent 7,593,535, 22 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane, D.; Chen, D.Y.; Boroyevic, D. Passive cancellation of common-mode noise in power electronic circuits. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2003, 18, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglia, G.; Ala, G.; Di Piazza, M.C.; Giaconia, G.C.; Luna, M.; Vitale, G.; Zanchetta, P. Automatic EMI filter design for power electronic converters oriented to high power density. Electronics 2018, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widrow, B.; Glover, J.R.; McCool, J.M.; Kaunitz, J.; Williams, C.S.; Hearn, R.H.; Zeidler, J.R.; Dong, J.E.; Goodlin, R.C. Adaptive noise cancelling: Principles and applications. Proc. IEEE 1975, 63, 1692–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, Y.; Gan, W.S.; Kuo, S.M. Recent advances on active noise control: Open issues and innovative applications. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, S.M.; Morgan, D.R. Active noise control: A tutorial review. Proc. IEEE 1999, 87, 943–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Ferrer, M.; De Diego, M.; Pinero, G.; Garcia-Bonito, J. Sound quality of low-frequency and car engine noises after active noise control. J. Sound Vib. 2003, 265, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarasinghe, P.N.; Zhang, W.; Abhayapala, T.D. Recent advances in active noise control inside automobile cabins: Toward quieter cars. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2016, 33, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McJury, M.; Stewart, R.; Crawford, D.; Toma, E. The use of active noise control (ANC) to reduce acoustic noise generated during MRI scanning: Some initial results. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1997, 15, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, C.; Wu, C.Y. Acoustic noise cancellation techniques for switched reluctance drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1997, 33, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, T.; Pettersen, O.K.Ø.; Soersdal, S. Active cancellation of transformer noise: Field measurements. Appl. Acoust. 1988, 23, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, J.D. Active Noise Cancellation Aircraft Headset System. U.S. Patent 6,278,786, 21 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, L.Y.L.; Koh, Y.K.; Lee, H.P. The performance of active noise-canceling headphones in different noise environments. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 122, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebich, S.; Fabry, J.; Jax, P.; Vary, P. Signal processing challenges for active noise cancellation headphones. In Speech Communication; 13th ITG-Symposium; VDE: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.Y.; Siswanto, A.; Ho, C.Y.; Yeh, T.K.; Chen, Y.R.; Kuo, S.M. Listening in a noisy environment: Integration of active noise control in audio products. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2016, 5, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.; Snyder, S.; Qiu, X.; Brooks, L.; Moreau, D. Active Control of Noise and Vibration; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, J.C. Active adaptive sound control in a duct: A computer simulation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 70, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Qiu, X.; Chen, G. An overlap-save frequency-domain implementation of the delayless subband ANC algorithm. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2008, 16, 1706–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.K.; Satapathy, J.K. Frequency-domain block filtered-x NLMS algorithm for multichannel ANC. In Proceedings of the 2008 First International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Technology (ICETET’08), Nagpur, India, 16–18 July 2008; pp. 1293–1297. [Google Scholar]
- Shynk, J.J. Frequency-domain and multirate adaptive filtering. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1992, 9, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, E.; Cowan, C.; Grant, P. Frequency-domain adaptive filtering. Adapt. Filters 1985, 6, 145–179. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Cao, Y.; Wu, M.; Albu, F.; Yang, J. Frequency-domain filtered-x LMS algorithms for active noise control: A review and new insights. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerwen, P.J.V.; van de Laar, F.A.; Kotmans, H.J. Digital Echo Canceller. U.S. Patent 4,903,247, 20 February 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cioffi, J.M.; Bingham, J.A. A data-driven multitone echo canceller. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1994, 42, 2853–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merched, R.; Sayed, A.H. An embedding approach to frequency-domain and subband adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2000, 48, 2607–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pradham, S.S.; Reddy, V. A new approach to subband adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1999, 47, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheer, J.; Daley, S. An investigation of delayless subband adaptive filtering for multi-input multi-output active noise control applications. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2016, 25, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan, D.R.; Thi, J.C. A delayless subband adaptive filter architecture. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1995, 43, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milani, A.A.; Kannan, G.; Panahi, I.M.; Briggs, R. Analysis and optimal design of delayless subband active noise control systems for broadband noise. Signal Process. 2010, 90, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, A.A.; Panahi, I.M.; Loizou, P.C. A new delayless subband adaptive filtering algorithm for active noise control systems. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2009, 17, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D. An analysis of multiple correlation cancellation loops with a filter in the auxiliary path. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1980, 28, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proakis, J.G.; Salehi, M.; Zhou, N.; Li, X. Communication Systems Engineering; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1994; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Estlab. 2018. Available online: http://www.dea.uniroma3.it/elettrotecnica/ANC_Algorithm.zip (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Cooley, J.W.; Tukey, J.W. An algorithm for the machine calculation of complex Fourier series. Math. Comput. 1965, 19, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.M.; Morgan, D. Active Noise Control Systems: Algorithms and DSP Implementations; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Carini, A.; Malatini, S. Optimal variable step-size NLMS algorithms with auxiliary noise power scheduling for feedforward active noise control. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2008, 16, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiotto, S. A tuning-less approach in secondary path modeling in active noise control systems. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2013, 21, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ETSI. 2020. Available online: https://docbox.etsi.org/stq/Open/EG%20202%20396-1%20Background%20noise%20database/Binaural_Signals (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Jayant, H.K.; Rana, K.; Kumar, V.; Nair, S.S.; Mishra, P. Efficient IIR notch filter design using Minimax optimization for 50 Hz noise suppression in ECG. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Signal Processing, Computing and Control (ISPCC), Waknaghat, India, 24–26 September 2015; pp. 290–295. [Google Scholar]
- Manikandan, S.; Natesan, K. A novel approach for the reduction of 50 Hz noise in electrocardiogram using variational mode decomposition. Curr. Signal Transduct. Ther. 2017, 12, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headrick, J.M.; Skolnik, M.I. Over-the-Horizon radar in the HF band. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Operation Type | Ops. per Input Sample |
|---|---|
| Algorithm | (S/N) (dB) | White Noise | Multi-Tonal | Real Noise |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAF | 60 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| SAF | 10 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| NLMS | 60 | 0.1 | 0.02 | 0.5 |
| NLMS | 10 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Algorithm | Multiplications per Input Sample |
|---|---|
| NLMS | 256 |
| SAF 1 | 160 |
| ZF-BAF 2 | 80 |
| Algorithm | Multiplications per Input Sample |
|---|---|
| NLMS | 1024 |
| SAF 1 | 184 |
| ZF-BAF 2 | 184 |
| Algorithm | (S/N) (dB) | White Noise | Multi-Tonal | Real Noise |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAF | 60 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| SAF | 10 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| NLMS | 60 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 1.0 |
| NLMS | 10 | 0.05 | 0.005 | 0.5 |
| Algorithm | L | White Noise | Multi-Tonal | Mono-Tonal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAF | 256 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| SAF | 1024 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.02 |
| NLMS | 256 | 0.1 | 0.02 | 0.2 |
| NLMS | 1024 | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaiotto, S.; Laudani, A.; Lozito, G.M.; Riganti Fulginei, F. A Computationally Efficient Algorithm for Feedforward Active Noise Control Systems. Electronics 2020, 9, 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091504
Gaiotto S, Laudani A, Lozito GM, Riganti Fulginei F. A Computationally Efficient Algorithm for Feedforward Active Noise Control Systems. Electronics. 2020; 9(9):1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091504
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaiotto, Stefano, Antonino Laudani, Gabriele Maria Lozito, and Francesco Riganti Fulginei. 2020. "A Computationally Efficient Algorithm for Feedforward Active Noise Control Systems" Electronics 9, no. 9: 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091504
APA StyleGaiotto, S., Laudani, A., Lozito, G. M., & Riganti Fulginei, F. (2020). A Computationally Efficient Algorithm for Feedforward Active Noise Control Systems. Electronics, 9(9), 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091504






