Virtualization Based Efficient Service Matching and Discovery in Internet of Things
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
- Service functionality is not clearly expressed by its input-output parameters.
- The service execution is not guaranteed on the basis of input-output parameters match.
- Strict syntactic matching;
- Matching based on capability;
- Deficiency of customization support;
- Absence of accurate ranking of matched services.
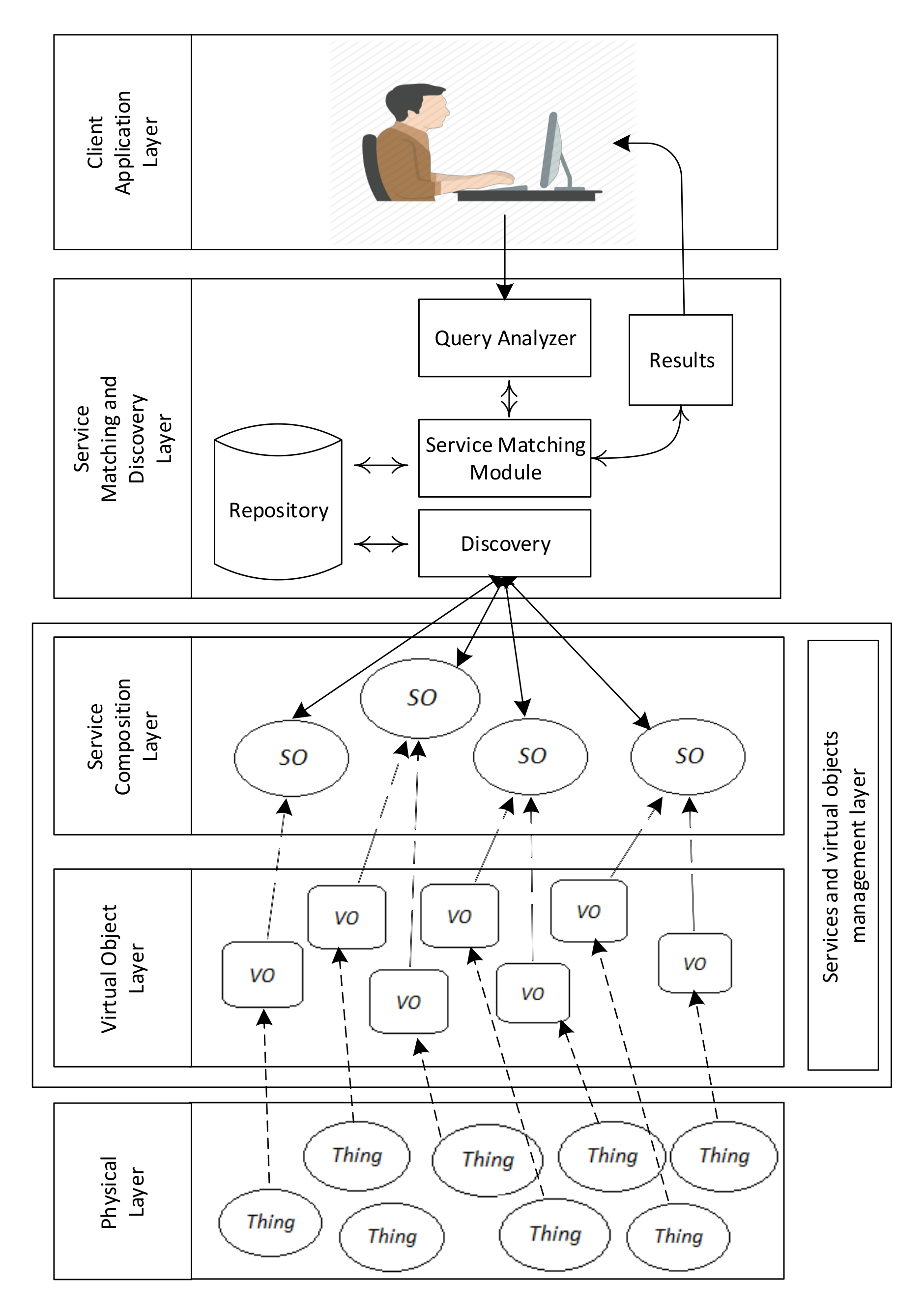
3. Proposed Model
- 1.
- Name plus location (optional) matching;
- 2.
- Functionality matching;
- 3.
- QoS matching.
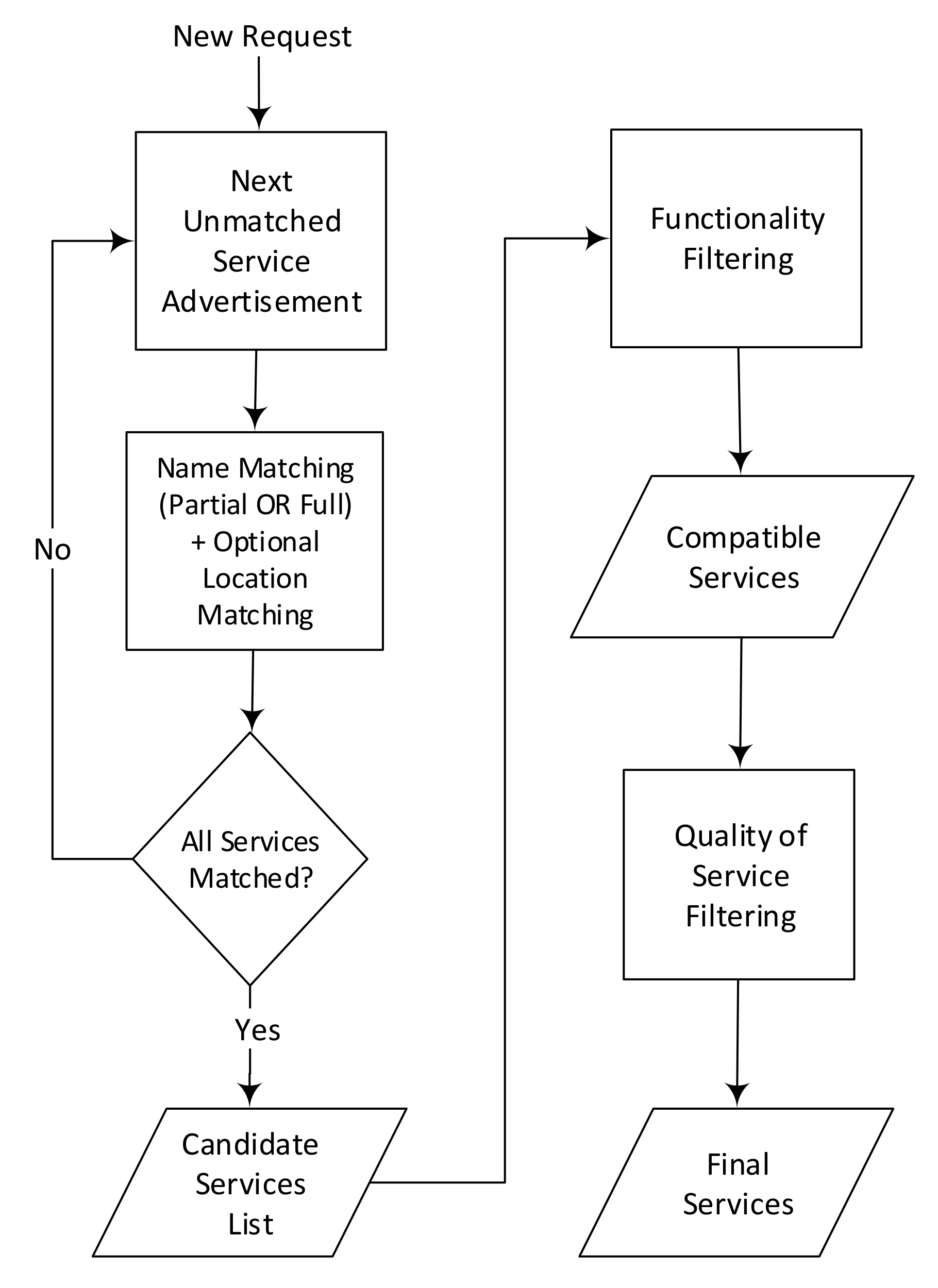
| Algorithm 1: Matchmaking Procedure |
 |
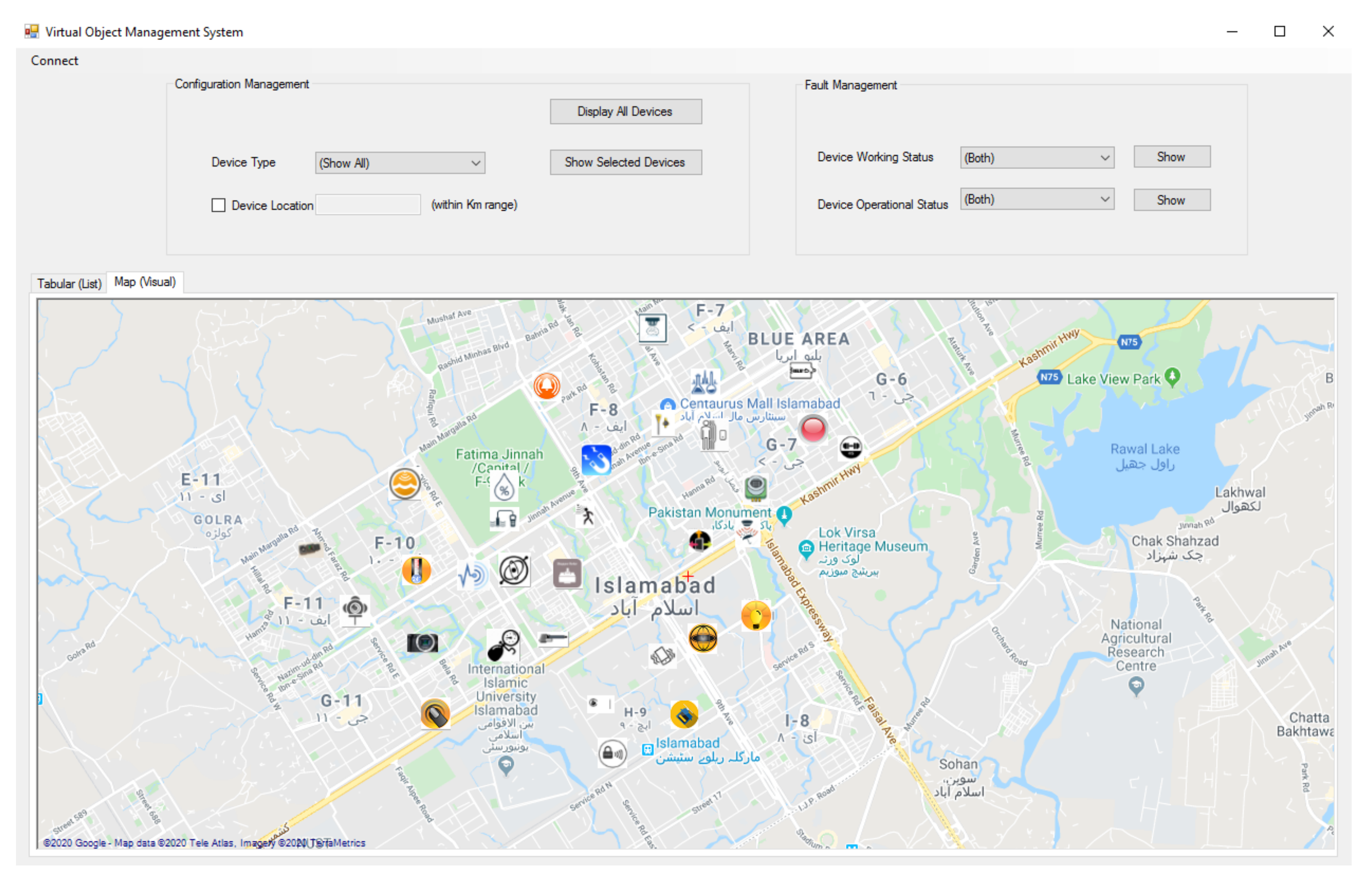
4. Implementation and Simulation
5. Results
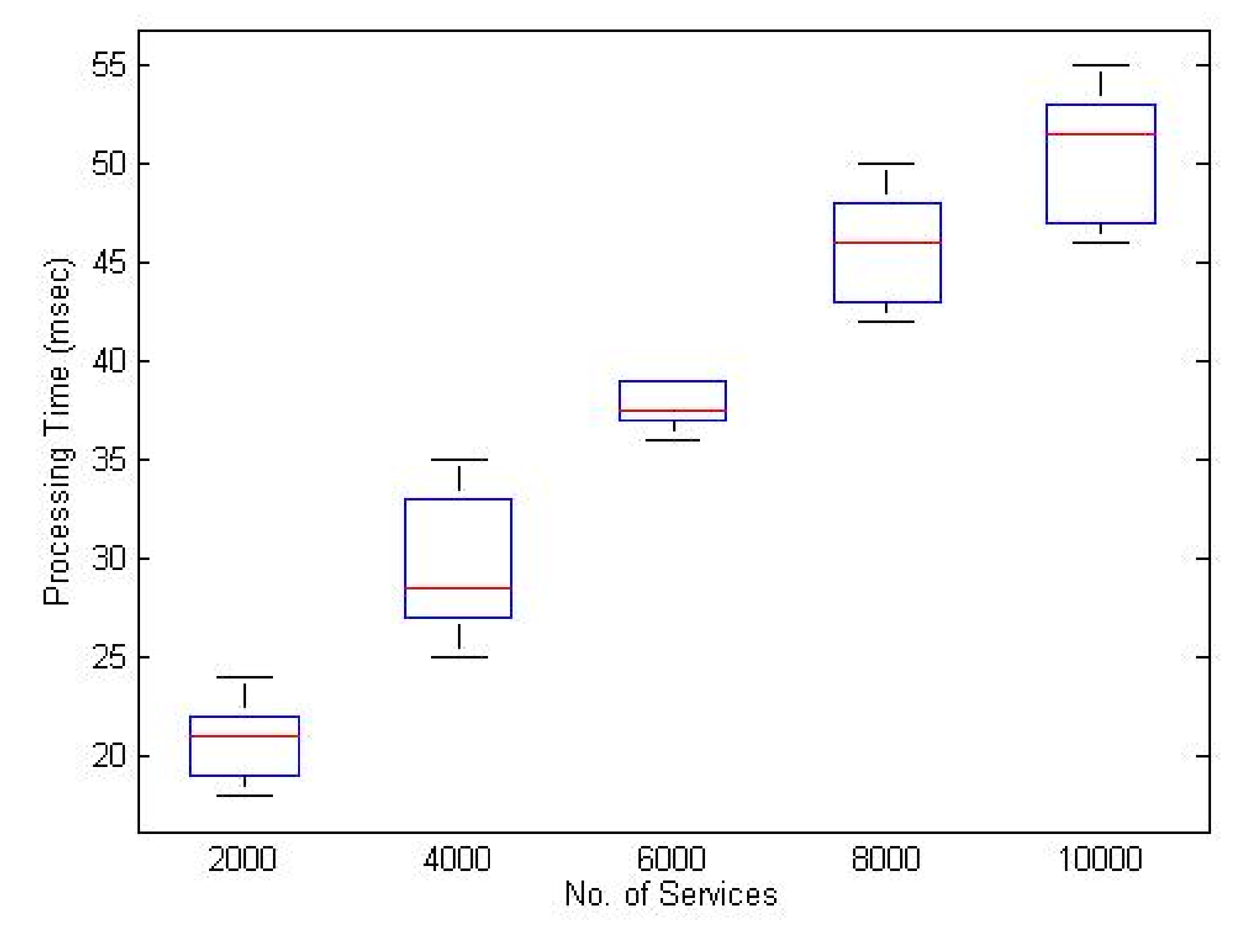
5.1. Total Services Matching versus Processing Time
5.2. Increase in Query Size versus Processing Time
5.3. No. of Matched Services after Each Filtering
- 1.
- Name plus location (optional) matching;
- 2.
- Functionality matching;
- 3.
- QoS matching.
5.4. Varying Location Range versus Device Inclusion/Exclusion
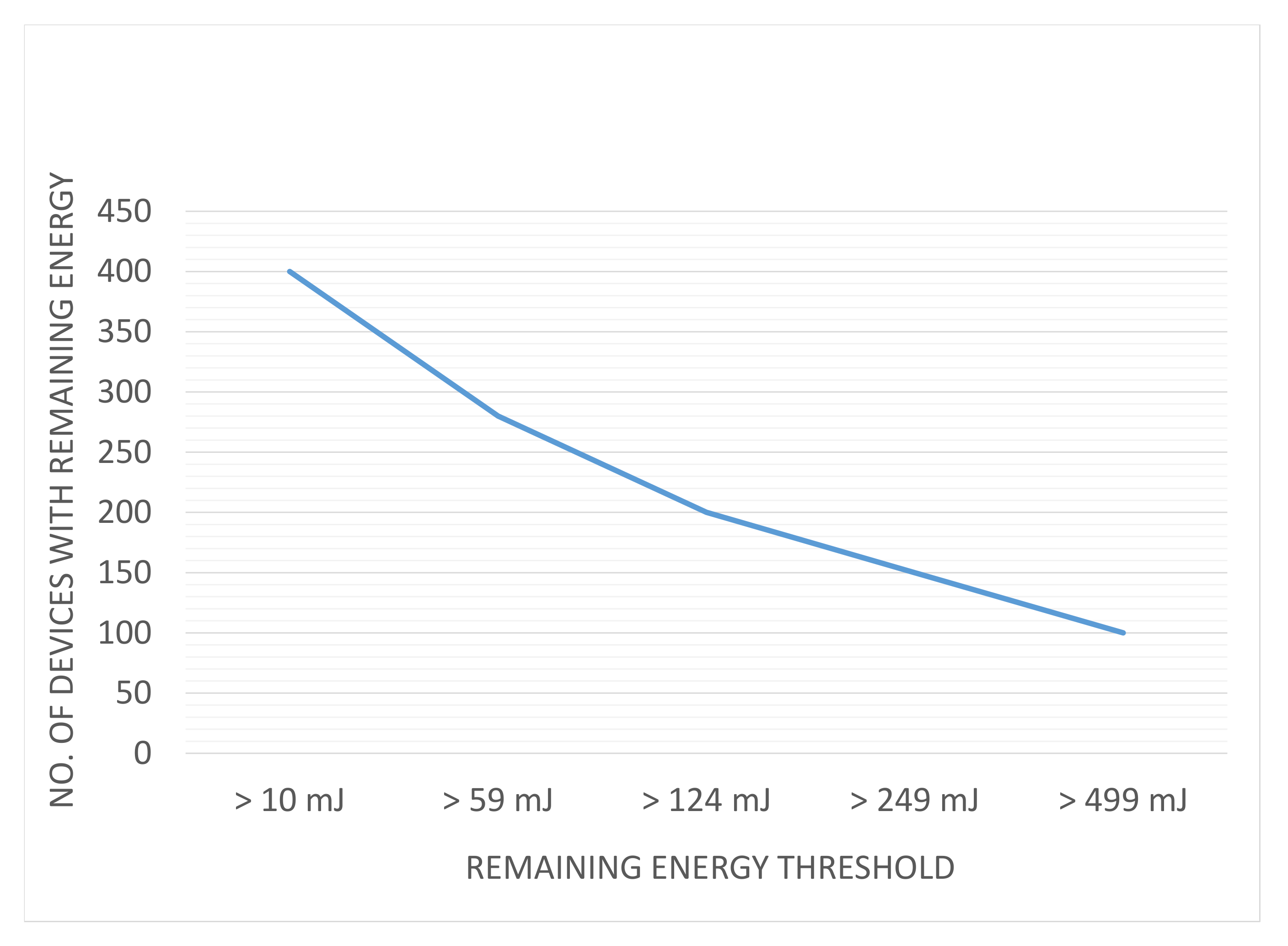
5.5. Varying Threshold versus Service Inclusion/Exclusion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dua, R.; Raj, G. Quality Analysis for Web Services Recommendation Using Functional and Non-Functional Requirement. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Internet of Things and Connected Technologies (ICIoTCT), Jaipur, India, 26–27 March 2018; pp. 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wilde, N.; Gonen, B.; El-Sheikh, E.; Zimmermann, A. Approaches to the evolution of SOA systems. In Emerging Trends in the Evolution of Service-Oriented and Enterprise Architectures; Springer: London, UK, 2016; pp. 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sheikh, E.; Zimmermann, A.; Jain, L.C. Emerging Trends in the Evolution of Service-Oriented and Enterprise Architectures; Springer: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Lu, C.; Wu, H.; Li, M. A semantic similarity measure integrating multiple conceptual relationships for web service discovery. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 67, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ahmad, S.; Mehmood, F.; Kim, D. Cloud Based IoT Network Virtualization for Supporting Dynamic Connectivity among Connected Devices. Electronics 2019, 8, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, G.; Olesen, H. A Survey on Service Discovery Mechanism. In Intelligent Computing and Information and Communication; Springer: London, UK, 2018; pp. 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, I.; Sohail Khan, M.; Kim, D. IoT Services and Virtual Objects Management in Hyperconnected Things Network. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, G.; Weninger, T. Ozy: A general orchestration container. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Web Services (ICWS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 27 June–2 July 2016; pp. 609–616. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera, C.; White, G.; Palade, A.; Clarke, S. The right service at the right place: A service model for smart cities. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications (PerCom), Athens, Greece, 19–23 March 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Zou, Y.; Tang, R.; Ng, J.; Nigul, L. An automatic approach for ontology-driven service composition. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing and Applications (SOCA), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–15 December 2009; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, B. A context-aware multimedia service scheduling framework in smart homes. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2012, 2012, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chirila, S.; Lemnaru, C.; Dinsoreanu, M. Semantic-based IoT device discovery and recommendation mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 12th International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing (ICCP), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 8–10 September 2016; pp. 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Pakari, S.; Kheirkhah, E.; Jalali, M. Web service discovery methods and techniques: A review. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2014, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TalebiFard, P.; Leung, V.C. A data fusion approach to context-aware service delivery in heterogeneous network environments. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2011, 5, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, T.; Zeng, R. A web service matching algorithm based on semantic similarity. COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2013, 32, 638–648. [Google Scholar]
- Gmati, F.E.; Ayadi, N.Y.; Bahri, A.; Chakhar, S.; Ishizaka, A. Customizable Web services matching and ranking tool: Implementation and evaluation. In International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies; Springer: London, UK, 2016; pp. 15–36. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, C.; Tila, F.; Kim, D.H.; Khan, M.S.; Kang, H.Y.; Park, D.H.; Lee, J.H. A Study of Integration Architecture Based on Service Provider in Heterogeneous Sensor Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 8th International Conference on Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity (DRBC), Jeju Island, Korea, 25–28 November 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Kim, D. Service-oriented process modelling for device control in future networks. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 2017, 14, 691–697. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, B.; Li, W.; Zhou, T. A centralized service discovery algorithm via multi-stage semantic service matching in Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (CSE) and IEEE International Conference on Embedded and Ubiquitous Computing (EUC), Guangzhou, China, 22–23 July 2017; Volume 1, pp. 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Calcina-Ccori, P.C.; De Biase, L.C.C.; Fedrecheski, G.; da Silva, F.S.C.; Zuffo, M.K. Enabling semantic discovery in the swarm. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2018, 65, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.H.; Omar, N.M.; Ibrahim, H.M. Secured Service Discovery Technique in IoT. JCM 2019, 14, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VisualStudio, October 2019. 2016. Available online: https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/vs/older-downloads/ (accessed on 21 October 2019).




| Device No. | Name | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Camera | Get Frame, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 2 | Temperature Sensor | GetTempC, GetTempF, GetStatus |
| 3 | Proximity Sensor | ObjectPresent, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 4 | Pressure Sensor | GetPressure, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 5 | Level Sensor | GetSwitchStatus, GetLevelReading, Start, Stop |
| 6 | Image Sensor | GetFrame, Stop, Start, GetStatus |
| 7 | Motion Sensor | GetFrame, Stop, Start, GetStatus |
| 8 | Accelerometer | GetRateofChangeofVelocity, GetChangeinMagneticField, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 9 | Vibration Sensor | GetResonance, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 10 | Rain Sensor | GetTotalInternalReflection, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 11 | Weight Sensor | GetWeight, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 12 | Axis Sensor | GetXAngle, GetYAngle, GetZangle |
| 13 | Gyroscope | GetRotationSpeed, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 14 | Humidity Sensor | GetWaterVapours, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 15 | Optical Sensor | GetLightRays, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 16 | Touch Sensor | GetVoltageChange, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 17 | Gas Sensor | GetCarbonDioxide, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 18 | Smoke Sensor | GetIonConcentration, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 19 | Infrared Sensor | GetHeat, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 20 | Light Sensor | GetData, GetStatus |
| 21 | Water Quality Sensor | GetIonChlorineConcentration, GetPhConcentration, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 22 | Chemical Sensor | GetChemicalChange, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 23 | Garden Sensor | GetTempC, GetTempF, GetLight, GetMoisture, GetHumidity, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 24 | Magnetic Sensor | GetMagneticField, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 25 | Servo Motor | SetSpeed, GetSpeed, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 26 | Buzzer | TurnON, TurnOFF, GetStatus |
| 27 | Smart Lock | Open, Close, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 28 | Solenoid | GetFluxDensity, Active, NotActive, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 29 | Stepper Motor | SetSpeed, SetPhase, GetSpeed, GetPhase, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 30 | Linear Actuator | MoveForward, MoveBackward, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 31 | Relay | Active, NotActive, GetCurrent, Start, Stop, GetStatus |
| 32 | LED | TurnON, TurnOFF, GetStatus |
| Query Name | Structure | |
|---|---|---|
| Qry1 | = | ∀ |
| Qry2 | = | ∀ |
| = | ∀ | |
| Qry3 | = | ∀ |
| = | ∀ | |
| | | ||
| | | ∀ | |
| Qry4 | = | ∀ |
| = | ∀ | |
| | | ||
| | | ∀ | |
| = | ∀ | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, Z.A.; Ullah, I.; Ibrahim, M.; Fayaz, M.; Aljarbouh, A.; Qureshi, M.S. Virtualization Based Efficient Service Matching and Discovery in Internet of Things. Electronics 2020, 9, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9061007
Khan ZA, Ullah I, Ibrahim M, Fayaz M, Aljarbouh A, Qureshi MS. Virtualization Based Efficient Service Matching and Discovery in Internet of Things. Electronics. 2020; 9(6):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9061007
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Zulfiqar Ali, Israr Ullah, Muhammad Ibrahim, Muhammad Fayaz, Ayman Aljarbouh, and Muhammad Shuaib Qureshi. 2020. "Virtualization Based Efficient Service Matching and Discovery in Internet of Things" Electronics 9, no. 6: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9061007
APA StyleKhan, Z. A., Ullah, I., Ibrahim, M., Fayaz, M., Aljarbouh, A., & Qureshi, M. S. (2020). Virtualization Based Efficient Service Matching and Discovery in Internet of Things. Electronics, 9(6), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9061007





