Dynamic System Identification and Prediction Using a Self-Evolving Takagi–Sugeno–Kang-Type Fuzzy CMAC Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
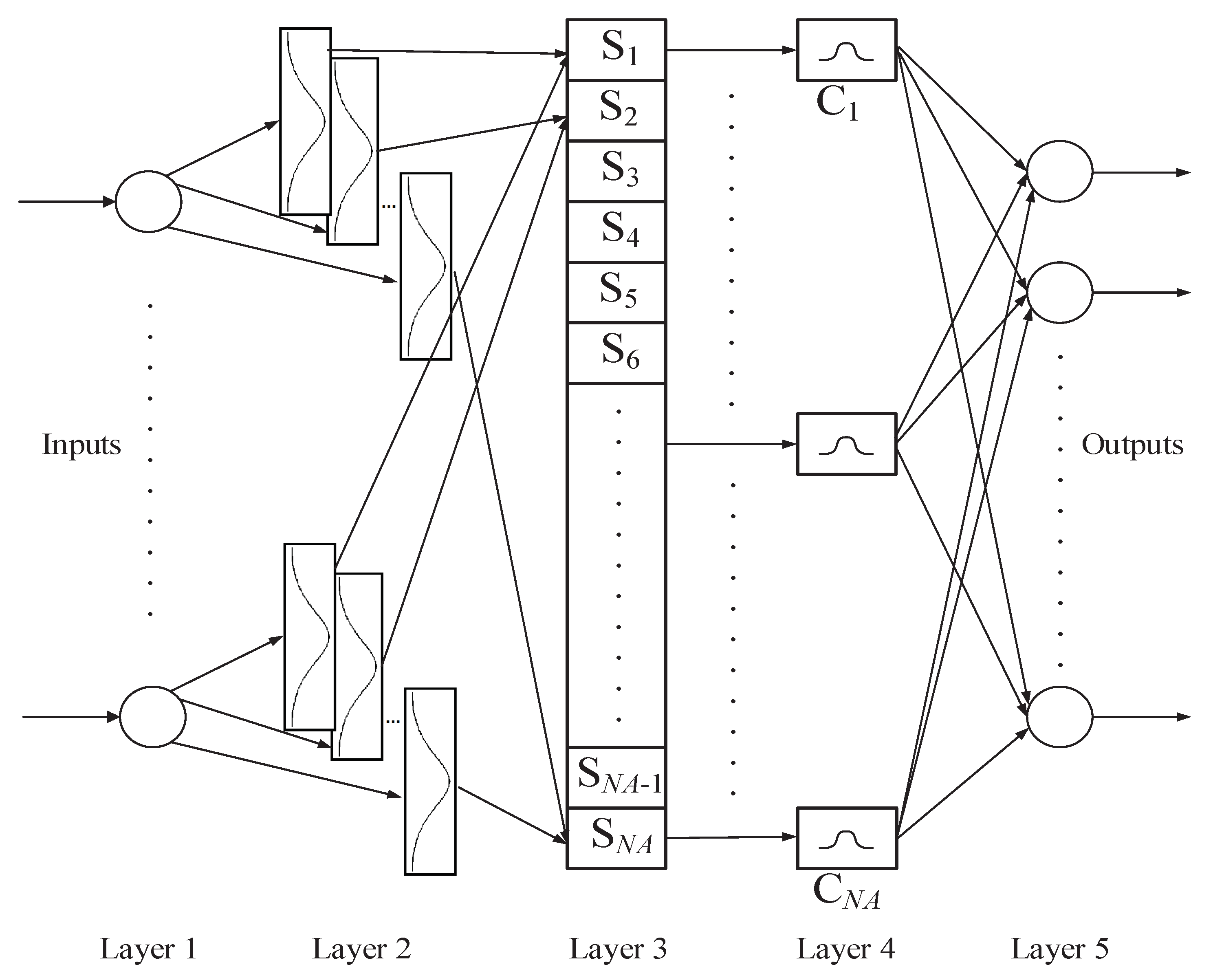
2. Review Fuzzy CMAC (FCMAC) Models
Fuzzy CMAC Model
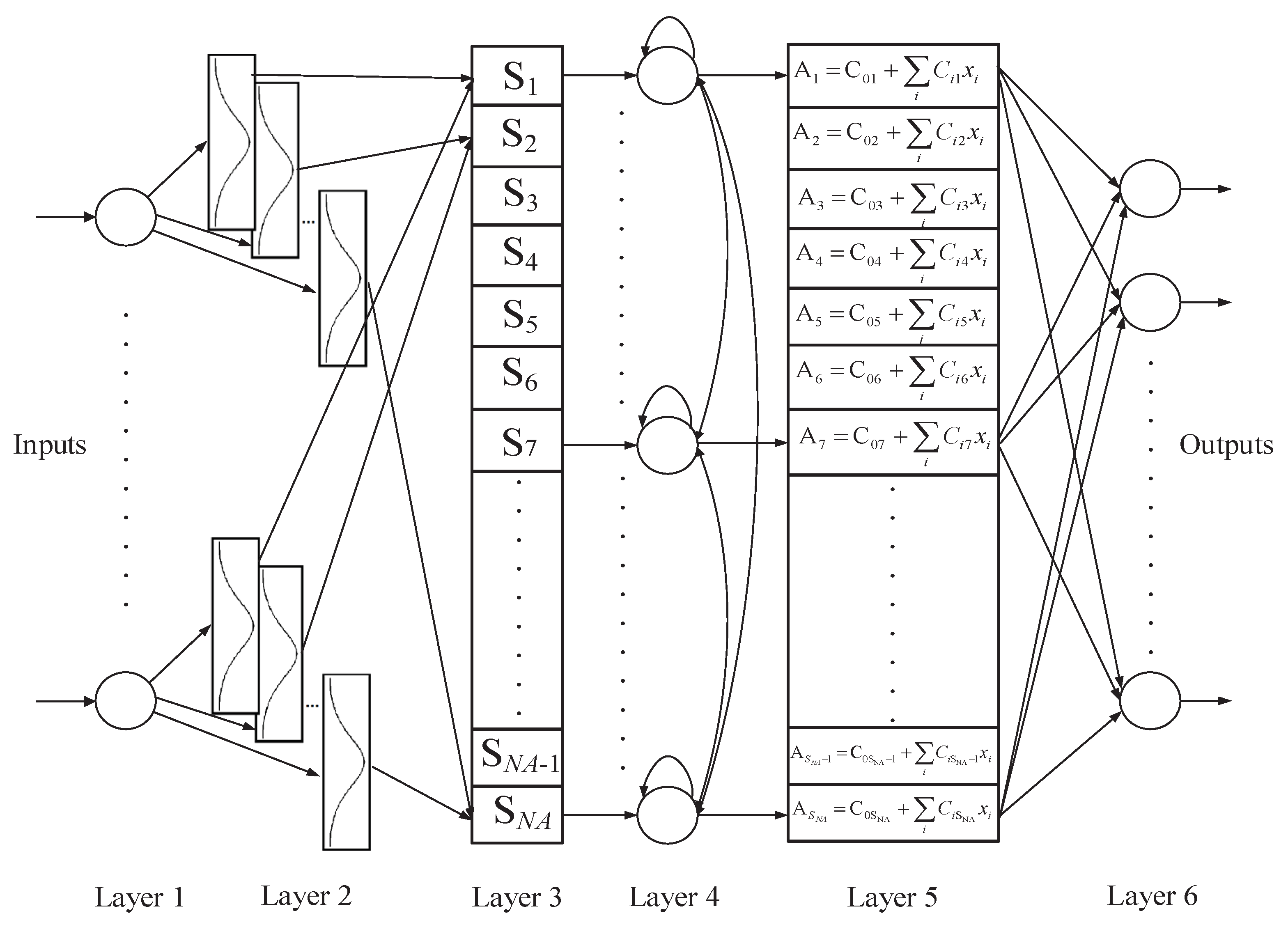
3. Proposed STFCMAC Model
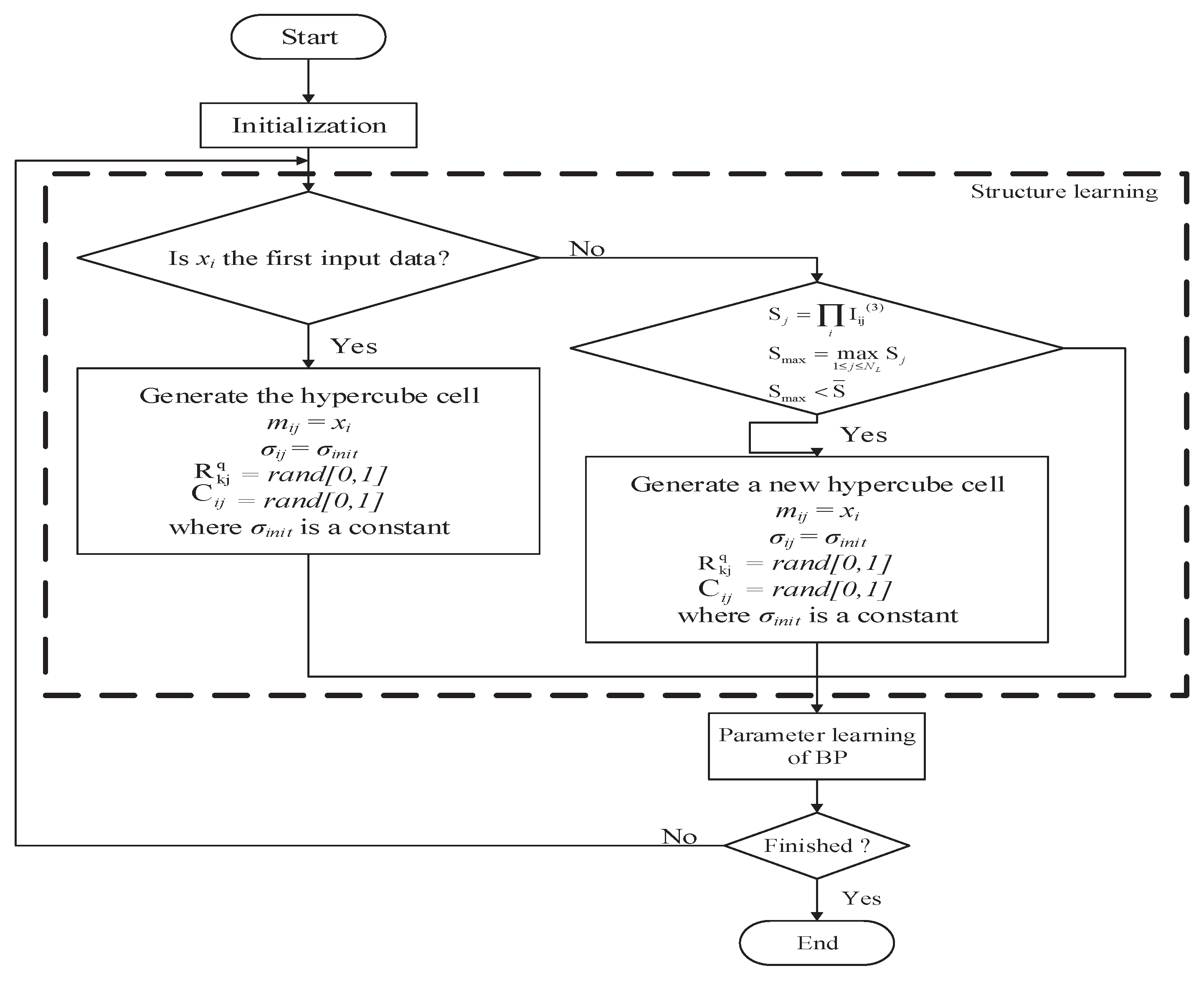
4. Learning Algorithm for Proposed STFCMAC Model
4.1. Structure Learning Scheme
4.2. Parameter Learning Scheme
5. Experimental Results
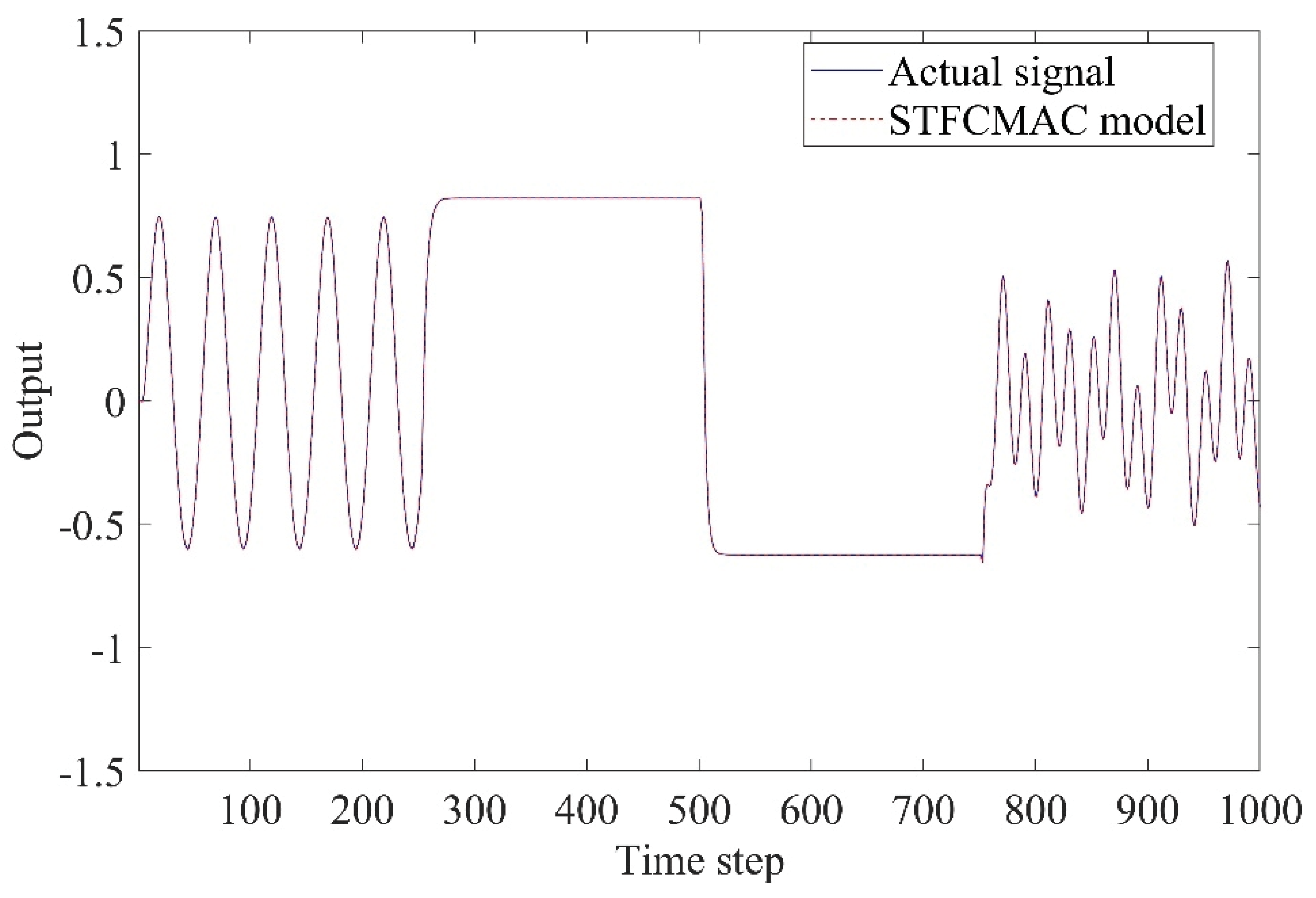
5.1. Example 1: Identification of Nonlinear System
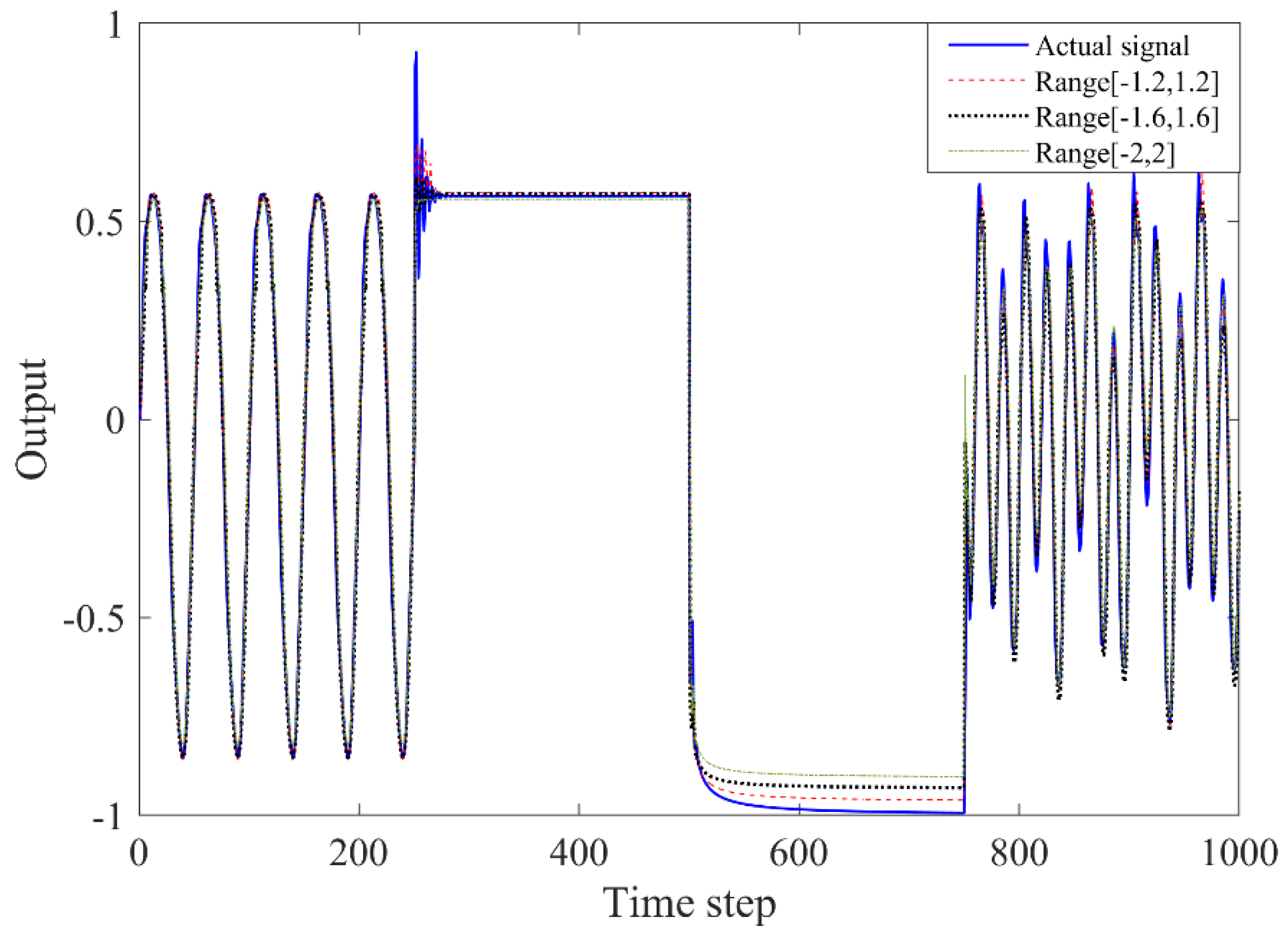
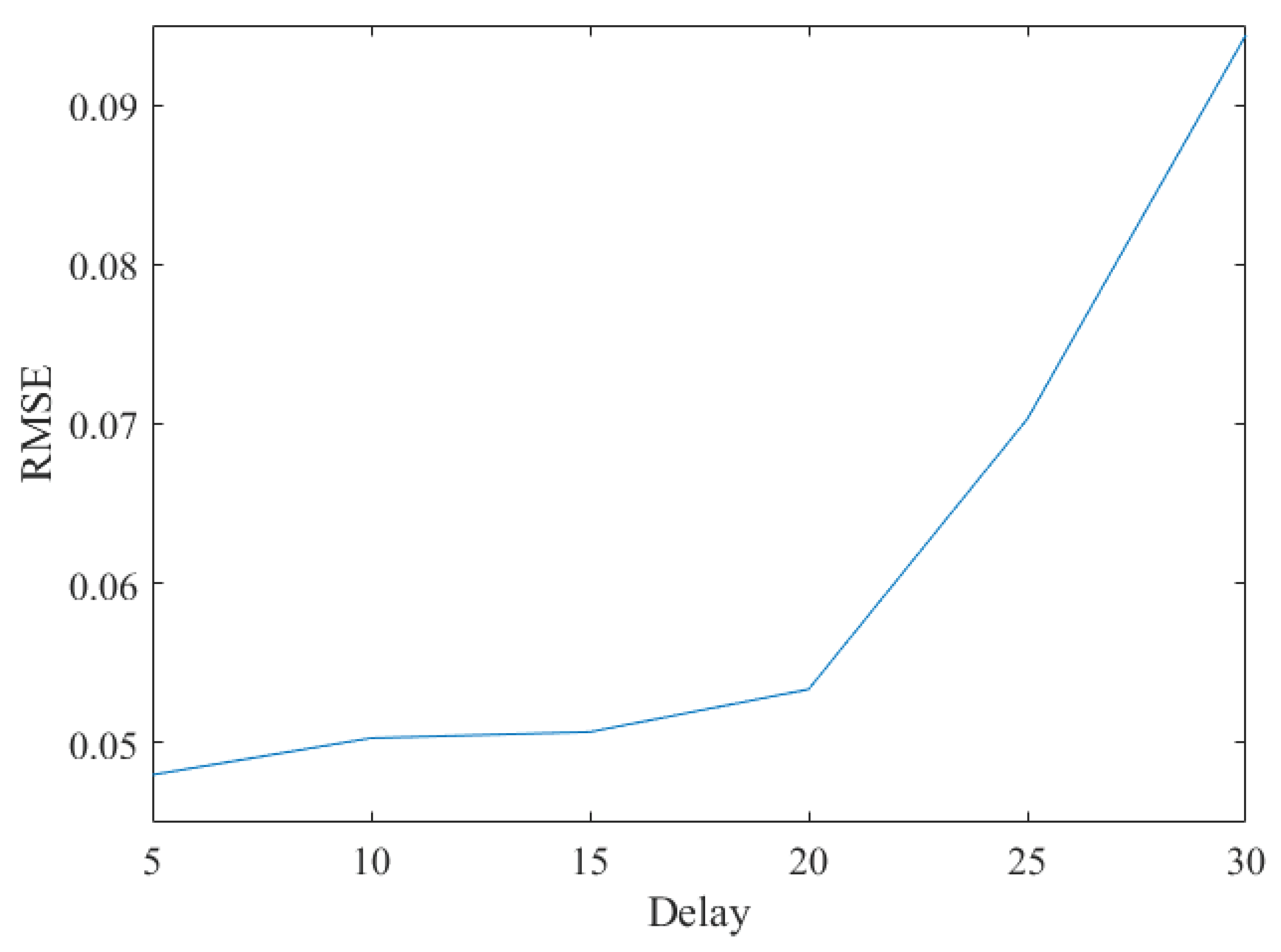
5.2. Example 2: System Identification of Longer Input Delays
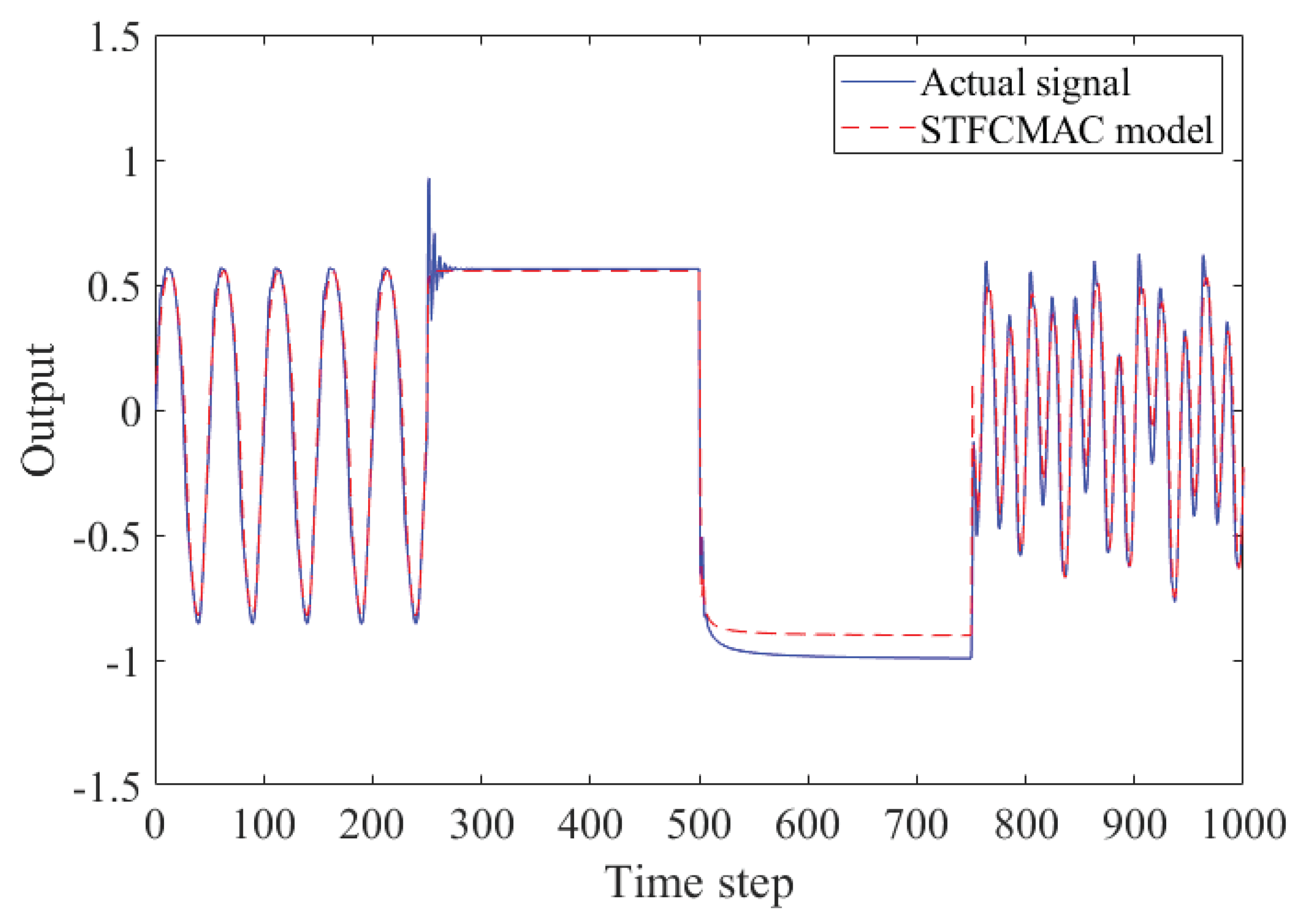
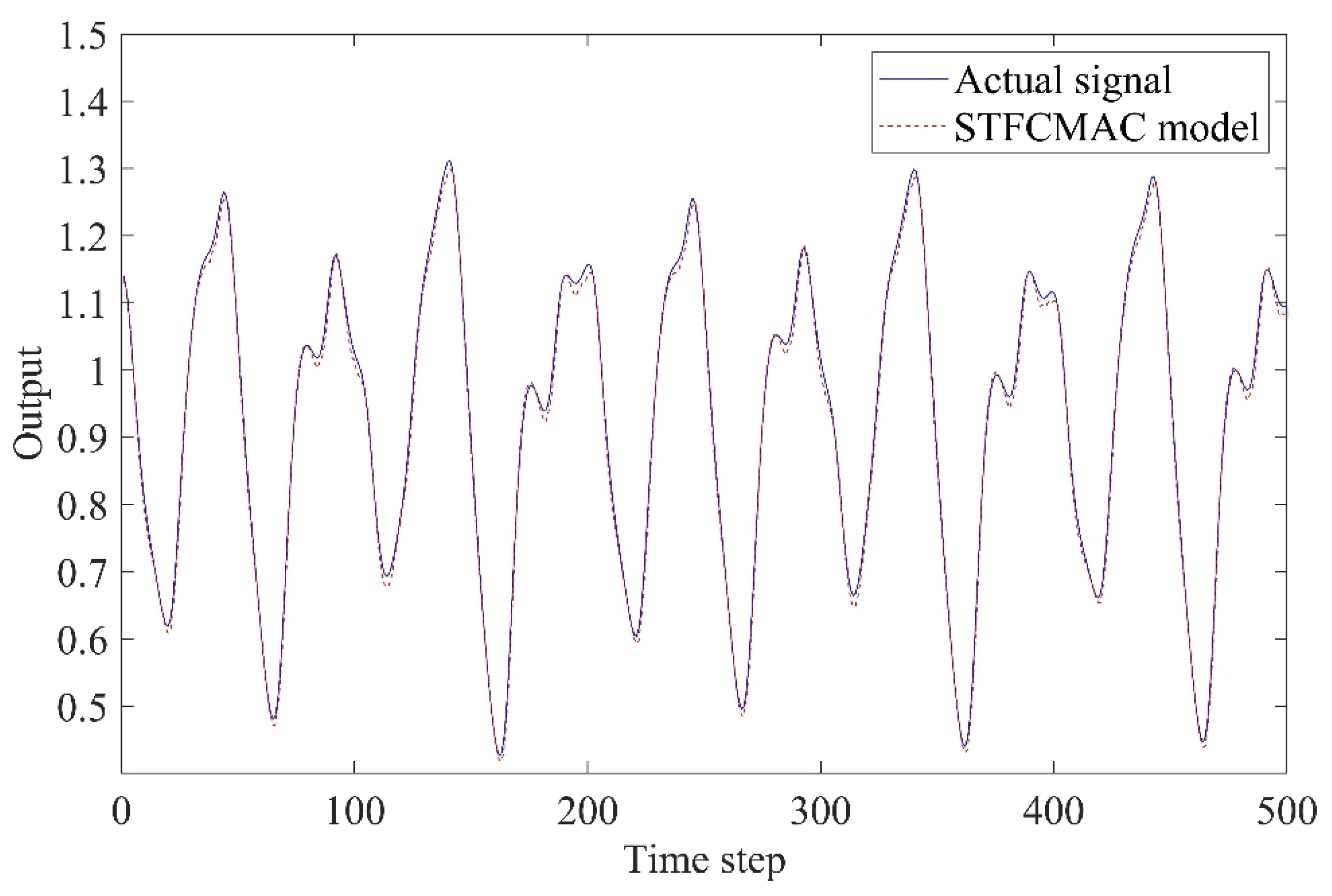
5.3. Example 3: Prediction of Chaotic Time Series
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- The proposed model requires less memory and fewer hypercubes/fuzzy rules.
- (2)
- The proposed model has a lower RMSE value.
- (3)
- The proposed model determines the number of hypercubes/fuzzy rules using the prespecified threshold value.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abiodun, O.I.; Jantan, A.; Omolar, A.E.; Dada, K.V.; Mohamed, N.A.; Arshad, H. State-of-the-art in artificial neural network applications: A survey. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malekabadi, M.; Haghparast, M.; Nasiri, F. Air Condition’s PID Controller Fine-Tuning Using Artificial Neural Networks and Genetic Algorithms. Computers 2018, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Sharma, L.; Sharma, V.; Kumar, A.; Darbari, H. Prediction of Diabetes Using Artificial Neural Network Approach: ICoEVCI 2018, India. In Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramazza, P.; Boccolini, A.; Buschek, D.; Hullin, M.; Higham, C.F.; Henderson, R.; Murray-Smith, R.; Faccio, D. Neural network identification of people hidden from view with a single-pixel, single-photon detector. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albus, J.S. A new approach to manipulator control: The cerebellar model articulation controller. Trans. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1975, 97, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albus, J.S. Data storage in the cerebellar model articulation controller. Trans. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1975, 97, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, V.P.; Dang, X.K. An Innovative Recurrent Cerebellar Model Articulation Controller for Piezo-driven Micro-motion Stage. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2018, 14, 1349–4198. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Yue, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Z. An improved cerebellar model articulation controller based on the compound algorithms of credit assignment and optimized smoothness for a three-axis inertially stabilized platform. Mechatronics 2018, 53, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.L.; Lin, C.J. Nonlinear system control using a fuzzy cerebellar model articulation controller involving reinforcement-strategy-based bacterial foraging optimization. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2018, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, P.E.M.; Simoes, M.G. Parametric CMAC networks: Fundamentals and applications of a fast convergence neural structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Peng, Y.F. Adaptive CMAC-based supervisory control for uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2004, 34, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Guo, C.; Li, H. General fuzzified CMAC based model reference adaptive control for ship steering. Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Intell. Control 2005, 2005, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, J.; Tung, W.L.; Quek, C. CMAC-Yager: A novel Yager-inference scheme-based fuzzy CMAC. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2006, 17, 1394–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.F.; Tsai, P.S.; Chang, F.R.; Wang, L.S. Adaptive fuzzy CMAC control for a class of nonlinear systems with smooth compensation. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. Control Theory Appl. 2006, 153, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Chen, H.J. A self-constructing fuzzy CMAC model and its applications. Inf. Sci. 2007, 177, 264–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnab, C.J.B. Using RBFs in a CMAC to prevent parameter drift in adaptive control. Neurocomputing 2016, 205, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.J.; Keane, J.A. Approximation capabilities of hierarchical fuzzy systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2005, 13, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Xu, Y.J. A parametric fuzzy CMAC model with hybrid evolutionary learning algorithms. J. Mult.-Valued Log. Soft Comput. 2007, 13, 89–114. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.H. Design of TSK-type fuzzy controllers using differential evolution with adaptive mutation strategy for nonlinear system control. Appl. Math. Comput. 2013, 219, 8277–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.C.; Lee, C.L.; Lin, C.J. Applications of TAIEX and enrollment forecasting using an efficient improved fuzzy time series model. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2016, 12, 459–466. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.C.; Chang, C.H. Practical stability issues in CMAC neural network control systems. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 1996, 4, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.G.; Gupta, M.M.; Nikiforuk, P.N.; Tan, M.; Cheng, L. A recurrent neural network for hierarchical control of interconnected dynamic systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2007, 18, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraziotis, I.A.; Dragomir, A.; Bezerianos, A. Gene networks reconstruction and time-series prediction from microarray data using recurrent neural fuzzy networks. IET Syst. Biol. 2007, 1, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.S. TSK-type self-organizing recurrent-neural-fuzzy control of linear microstepping motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 2253–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Lin, C.J.; Lin, H.Y.; Wang, J.G.; Yu, C.Y. Image Backlight Compensation Using Recurrent Functional Neural Fuzzy Networks Based on Modified Differential Evolution. Iran. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lin, C.J.; Huang, M.L.; Kuo, S.C.; Chen, Y.R. Mobile Robot Navigation Control Using Recurrent Fuzzy CMAC Based on Improved Dynamic Artificial Bee Colony. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Er, M.J. NARMAX time series model prediction: Feedforward and recurrent fuzzy neural network approaches. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2005, 150, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, J.B. A high-order recurrent neuro-fuzzy system with internal dynamics: Application to the adaptive noise cancellation. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2006, 157, 471–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.F. A TSK-type recurrent fuzzy network for dynamic systems processing by neural network and genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2002, 10, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.F.; Lin, Y.Y.; Huang, R.B. Dynamic system modeling using a recurrent interval-valued fuzzy neural network and its hardware implementation. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2011, 179, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Chang, J.Y.; Lin, C.T. Identification and prediction of dynamic systems using an interactively recurrent self-evolving fuzzy neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.F.; Lin, Y.Y.; Tu, C.C. A recurrent self-evolving fuzzy neural network with local feedbacks and its application to dynamic system processing. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2010, 161, 2552–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Chin, C.C. Prediction and identification using wavelet-based recurrent fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2004, 34, 2144–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastorocostas, P.A.; Theocharis, J.B. A recurrent fuzzy-neural model for dynamic system identification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2002, 32, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.J.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, C.T. Efficient self-evolving evolutionary learning for neuro-fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2008, 16, 1476–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, S.; Kumar, S. Subsethood-product fuzzy neural inference system. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 578–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, S.; Oysal, Y. Fuzzy wavelet neural network models for prediction and identification of dynamic system. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2010, 21, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Models | Lin and Chin [33] | Theocharis [28] | Juang [29] | Juang et al. [32] | Chen [24] | Proposed STFCMAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy Rules/ Hypercubes | 5 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| No. of Parameters | 55 | 45 | 33 | 32 | 24 | 27 |
| RMSE of Training Process | 0.064 | 0.054 | 0.032 | 0.02 | 0.022 | 0.019 |
| Training Time | 9.18 s | 13.93 s | 192.27 s | 13.78 s | 10.53 s | 12.37 s |
| RMSE of Testing Process | 0.098 | 0.082 | 0.047 | 0.04 | 0.036 | 0.033 |
| Models | Lin and Chin [33] | Theocharis [28] | Juang [29] | Juang et al. [32] | Chen [24] | Proposed STFCMAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy Rules/Hypercubes | 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| No. of Parameters | 55 | 33 | 30 | 32 | 24 | 27 |
| RMSE of Training Process | 0.057 | 0.007 | 0.016 | 0.0125 | 0.017 | 0.01 |
| Training Time | 10.35 s | 15.71 s | 203.49 s | 15.55 s | 11.88 s | 13.95 s |
| RMSE of Testing Process | 0.083 | 0.031 | 0.028 | 0.0288 | 0.034 | 0.025 |
| Models | FuzzyRules/ Hypercubes | No. of Parameters | RMSE of Training Process | Training Time | RMSE of Testing Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mastorocostas and Theocharis [34] | 10 | 100 | - | - | 0.0082 |
| Gao and Er [27] | 10 | 90 | - | - | 0.0056 |
| Lin et al. [35] | 9 | 198 | 0.0067 | 1375.38 s | 0.0068 |
| Paul and Kumar [36] | 10 | 94 | - | - | 0.0057 |
| Juang [29] | 5 | 95 | - | - | 0.0124 |
| Yilmaz and Oysal [37] | 16 | 128 | 0.0023 | 27.80 s | 0.0025 |
| Juang et al. [32] | 9 | 94 | 0.0032 | 17.44 s | 0.0034 |
| Lee et al. [18] | 5 | 65 | 0.0028 | 731.17 s | 0.0035 |
| Proposed STFCMAC | 3 | 42 | 0.0017 | 11.66 s | 0.0022 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-J.; Lin, C.-H.; Jhang, J.-Y. Dynamic System Identification and Prediction Using a Self-Evolving Takagi–Sugeno–Kang-Type Fuzzy CMAC Network. Electronics 2020, 9, 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040631
Lin C-J, Lin C-H, Jhang J-Y. Dynamic System Identification and Prediction Using a Self-Evolving Takagi–Sugeno–Kang-Type Fuzzy CMAC Network. Electronics. 2020; 9(4):631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040631
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Cheng-Jian, Cheng-Hsien Lin, and Jyun-Yu Jhang. 2020. "Dynamic System Identification and Prediction Using a Self-Evolving Takagi–Sugeno–Kang-Type Fuzzy CMAC Network" Electronics 9, no. 4: 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040631
APA StyleLin, C.-J., Lin, C.-H., & Jhang, J.-Y. (2020). Dynamic System Identification and Prediction Using a Self-Evolving Takagi–Sugeno–Kang-Type Fuzzy CMAC Network. Electronics, 9(4), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040631





