Position Estimation of a PMSM in an Electric Propulsion Ship System Based on High-Frequency Injection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
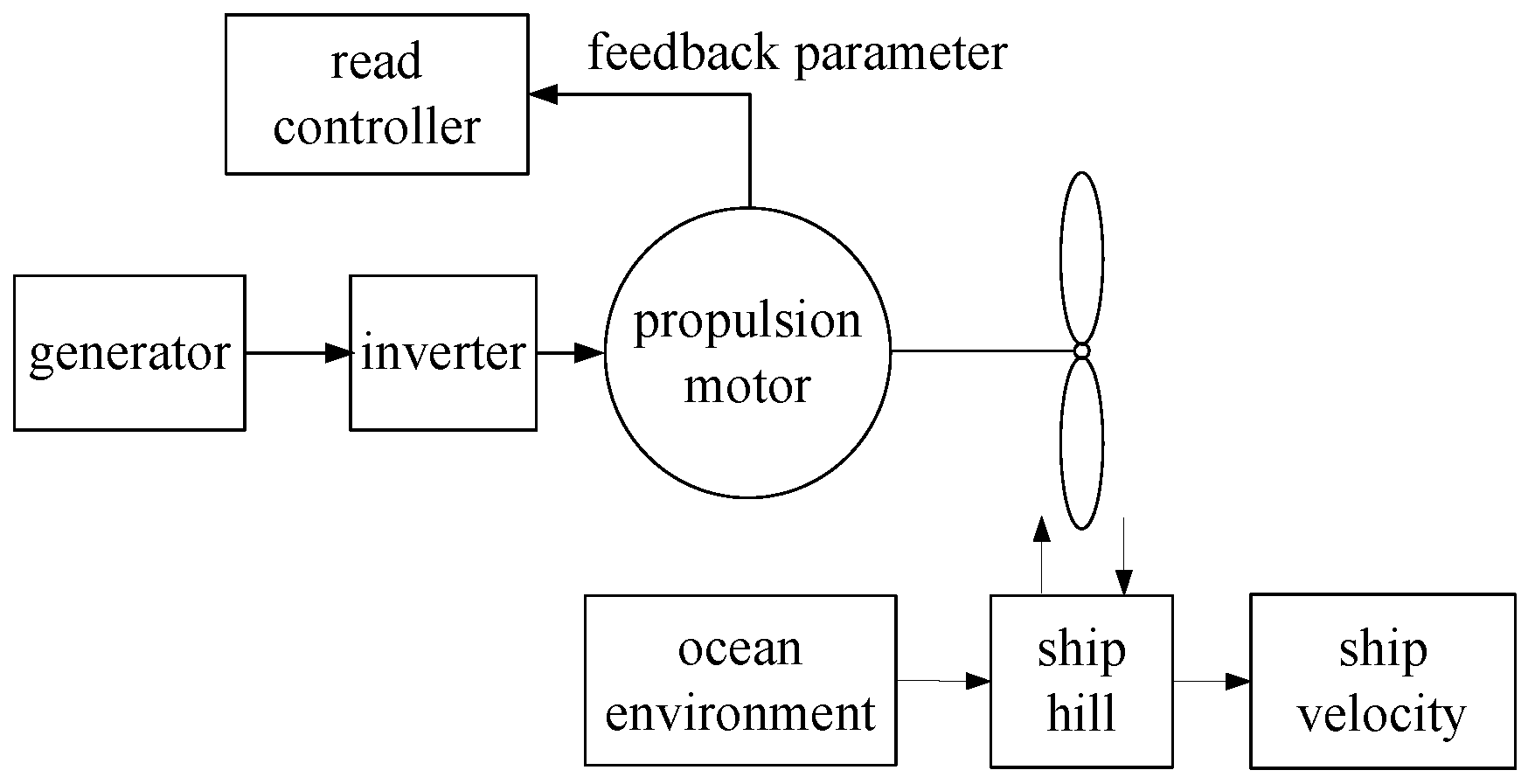
2. Model of the Electric Propulsion Ship System
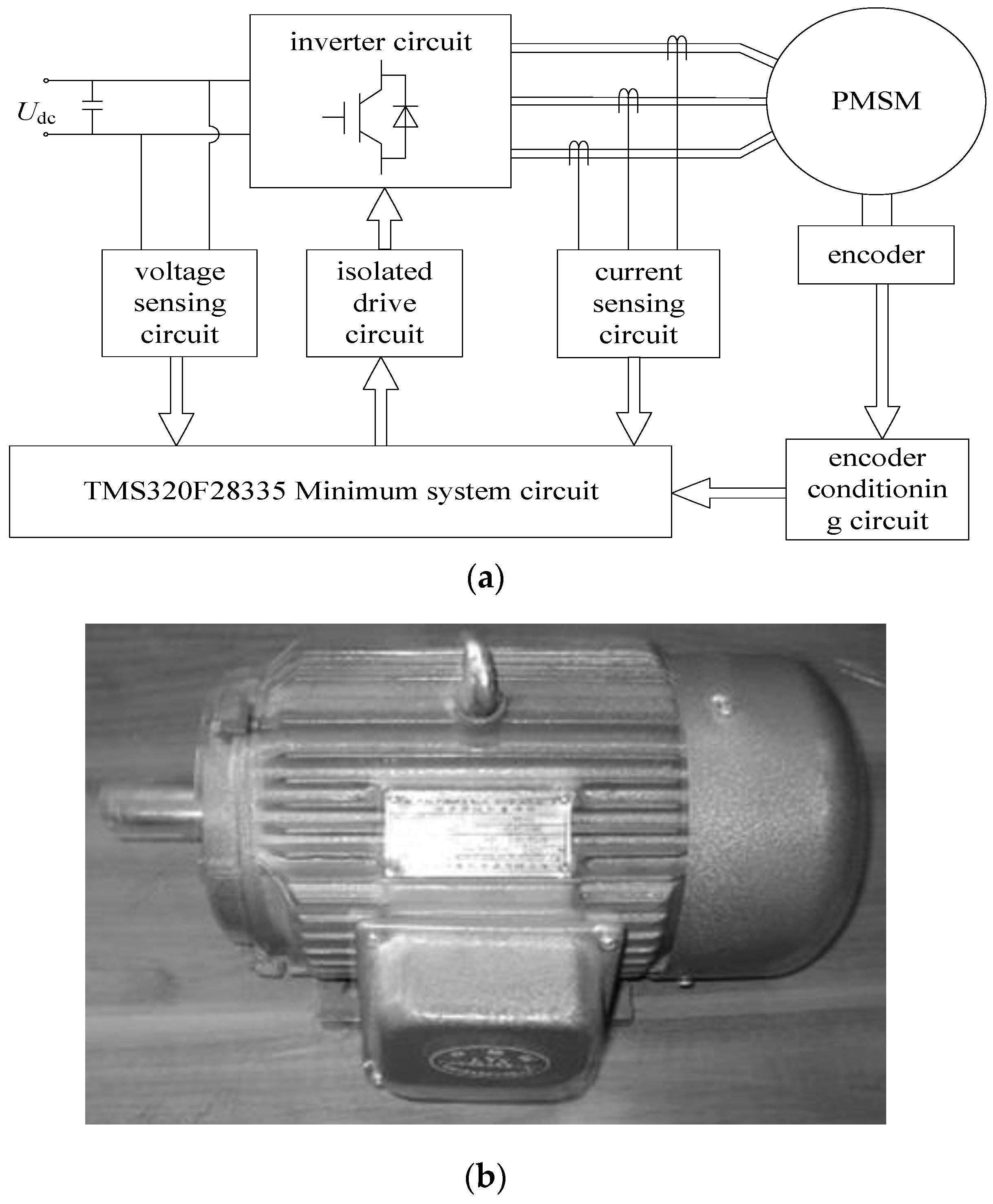
2.1. System Description
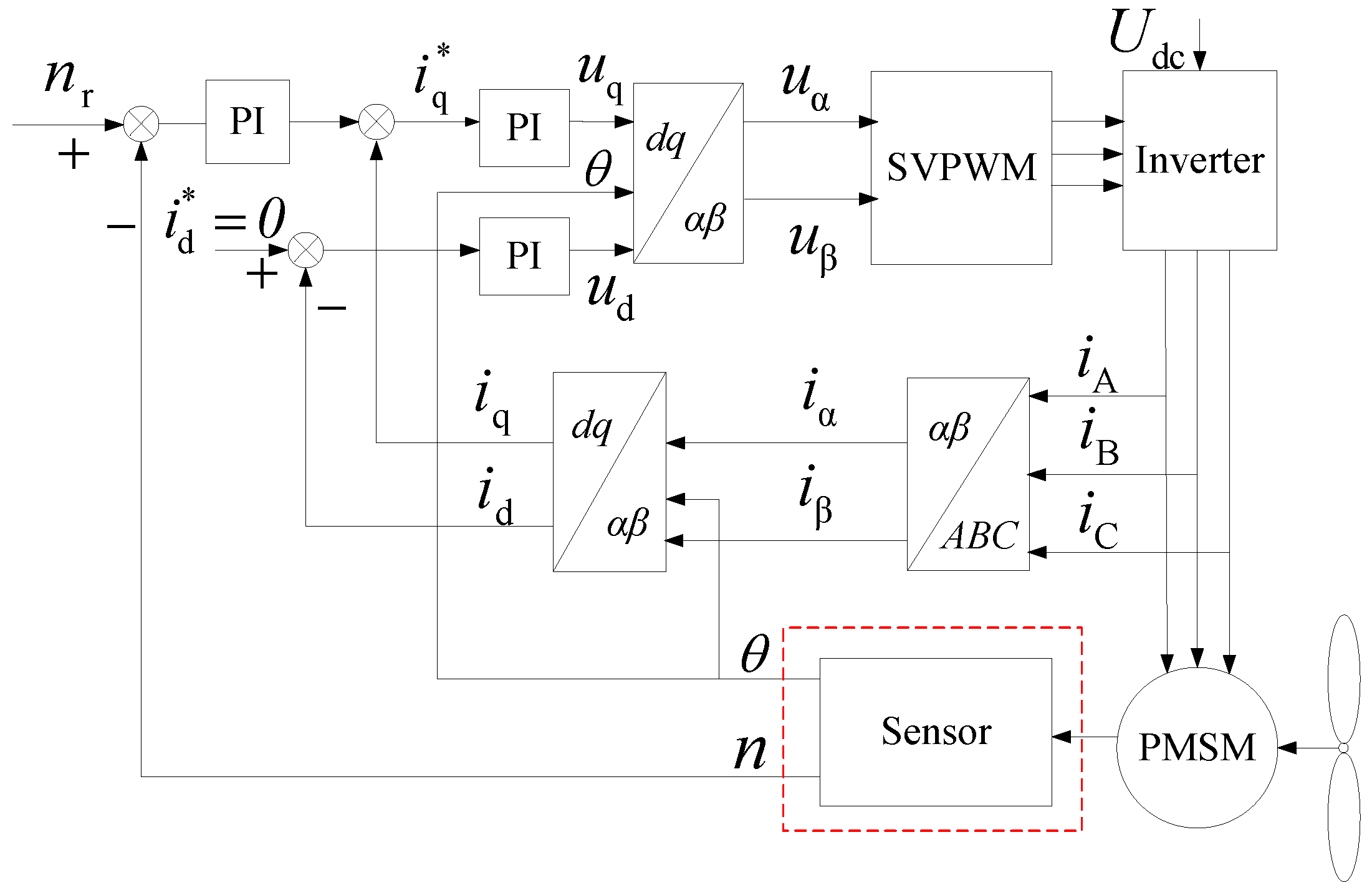
2.2. System Mathematical Model
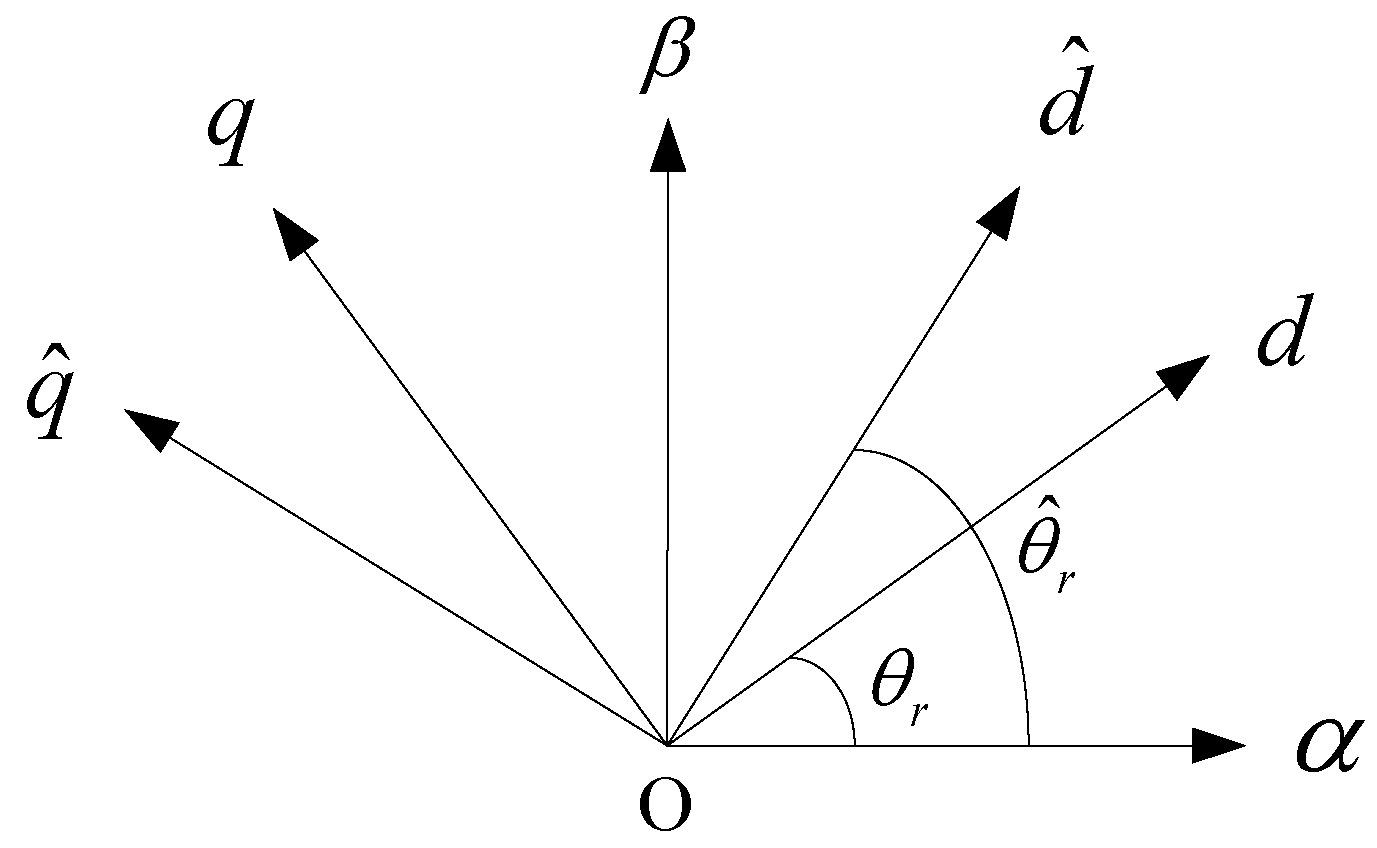
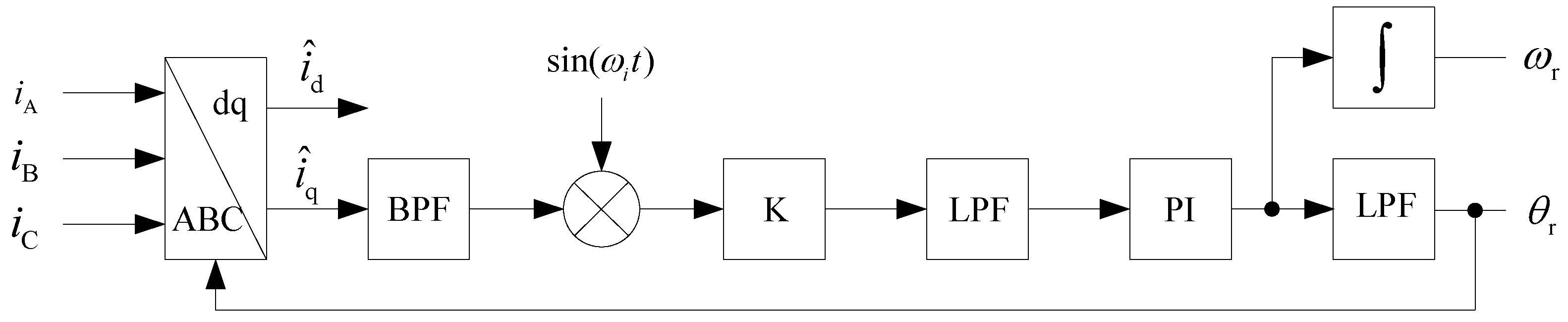
3. Principle of the High-Frequency Voltage Injection Algorithm Based on the SOGI
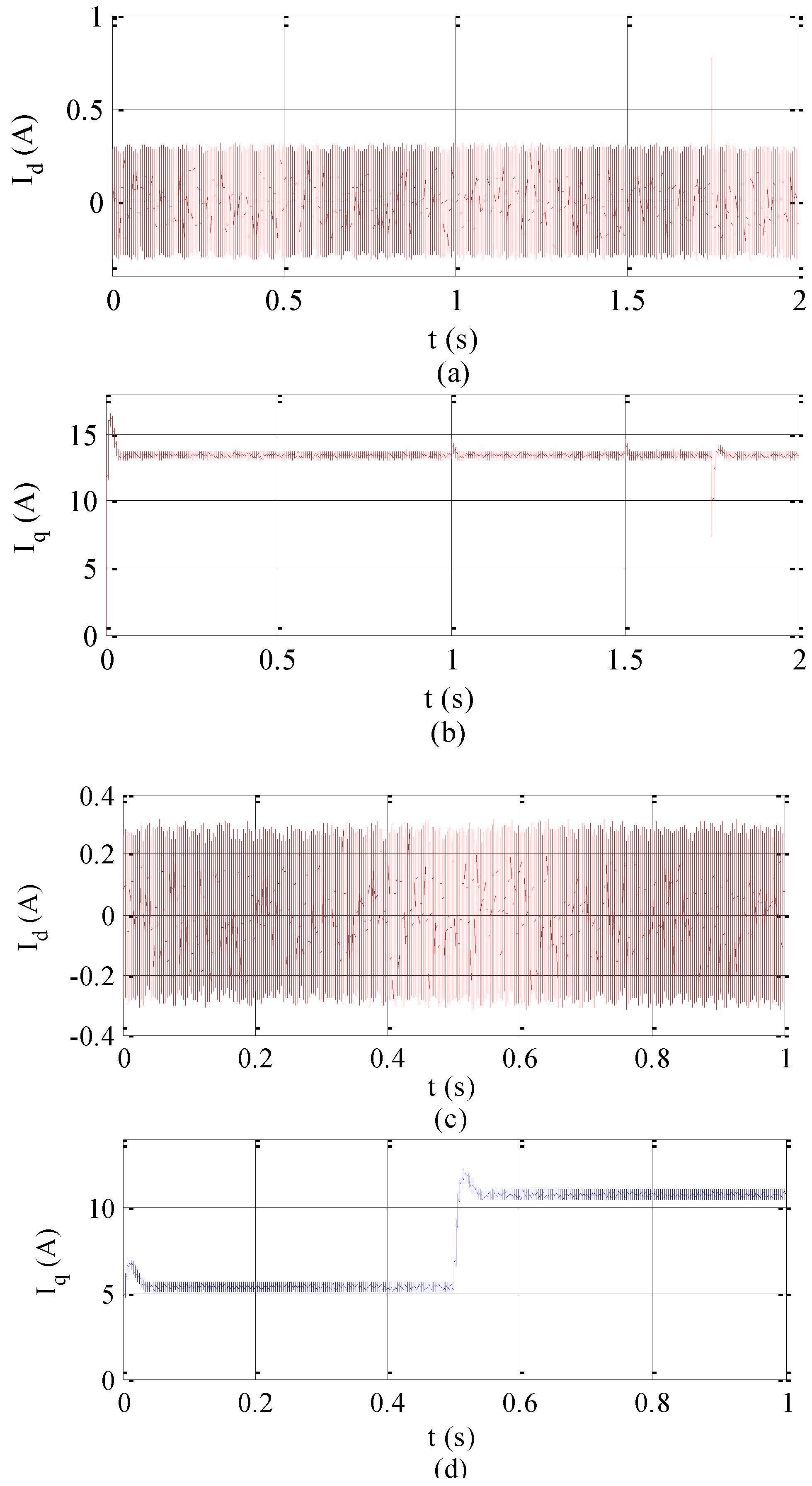
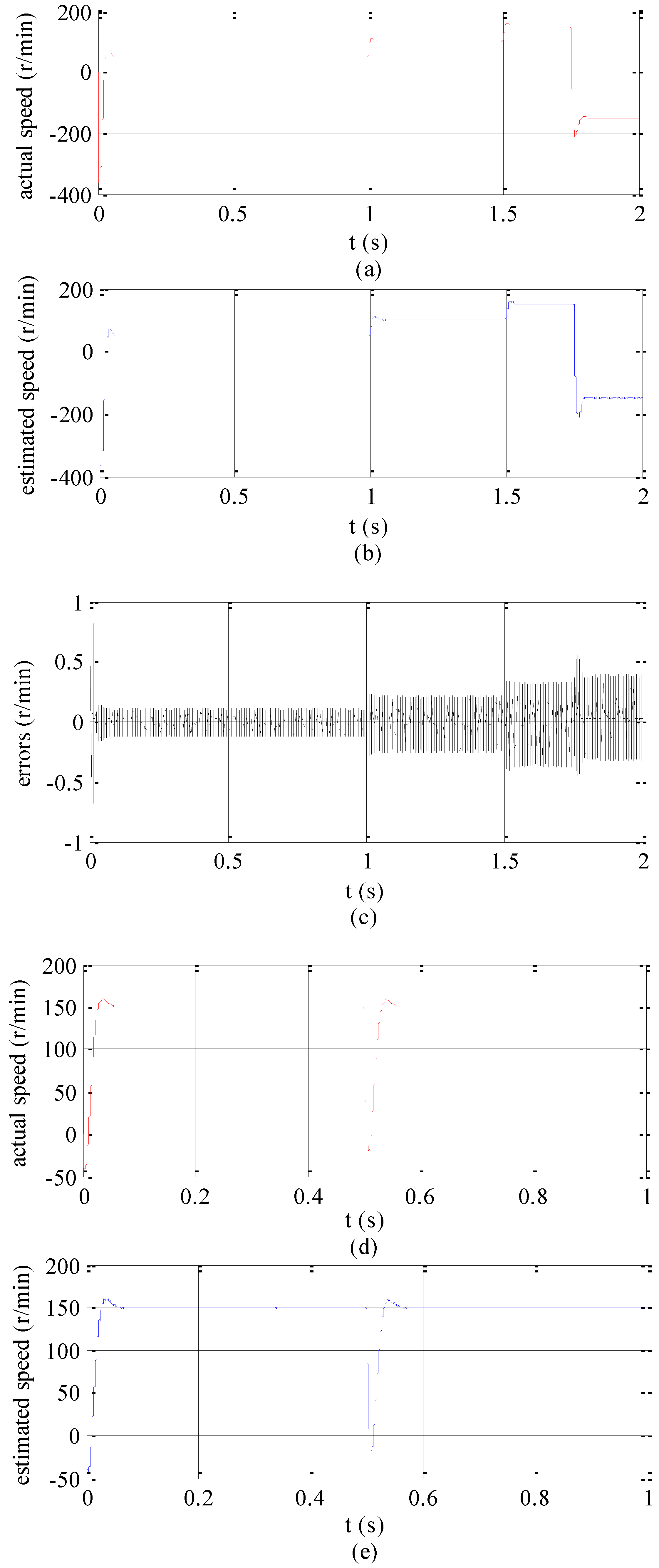
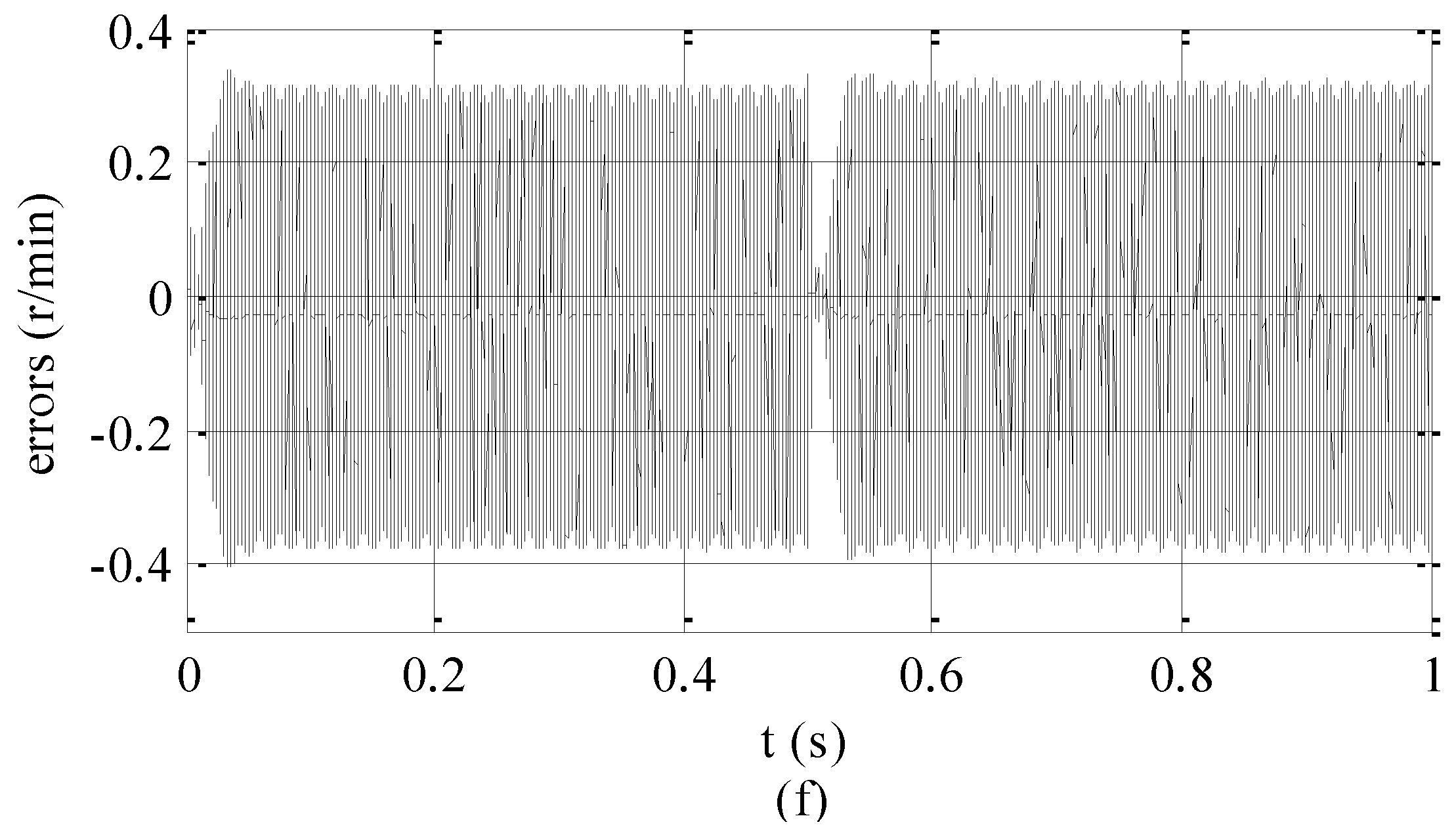
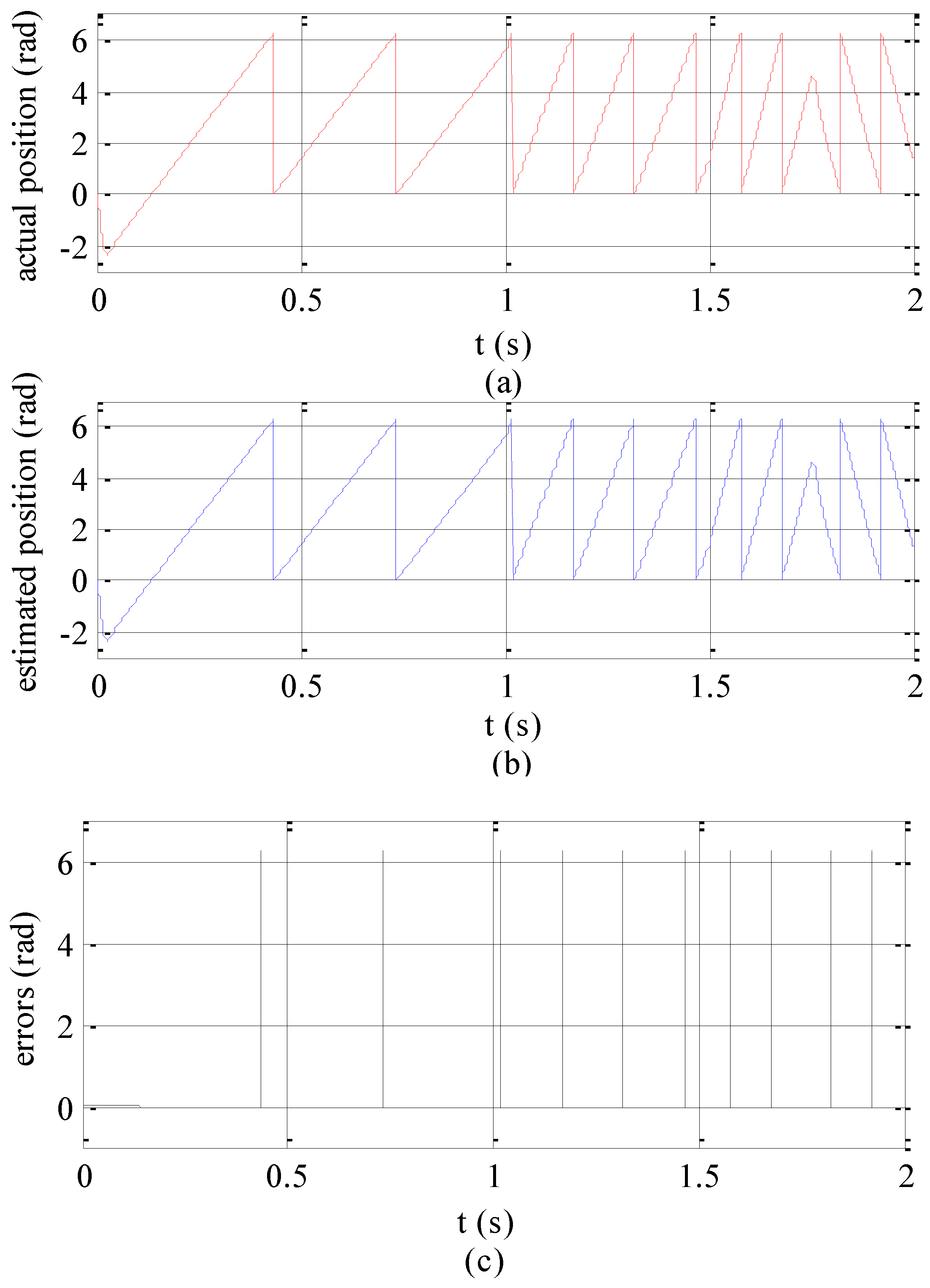
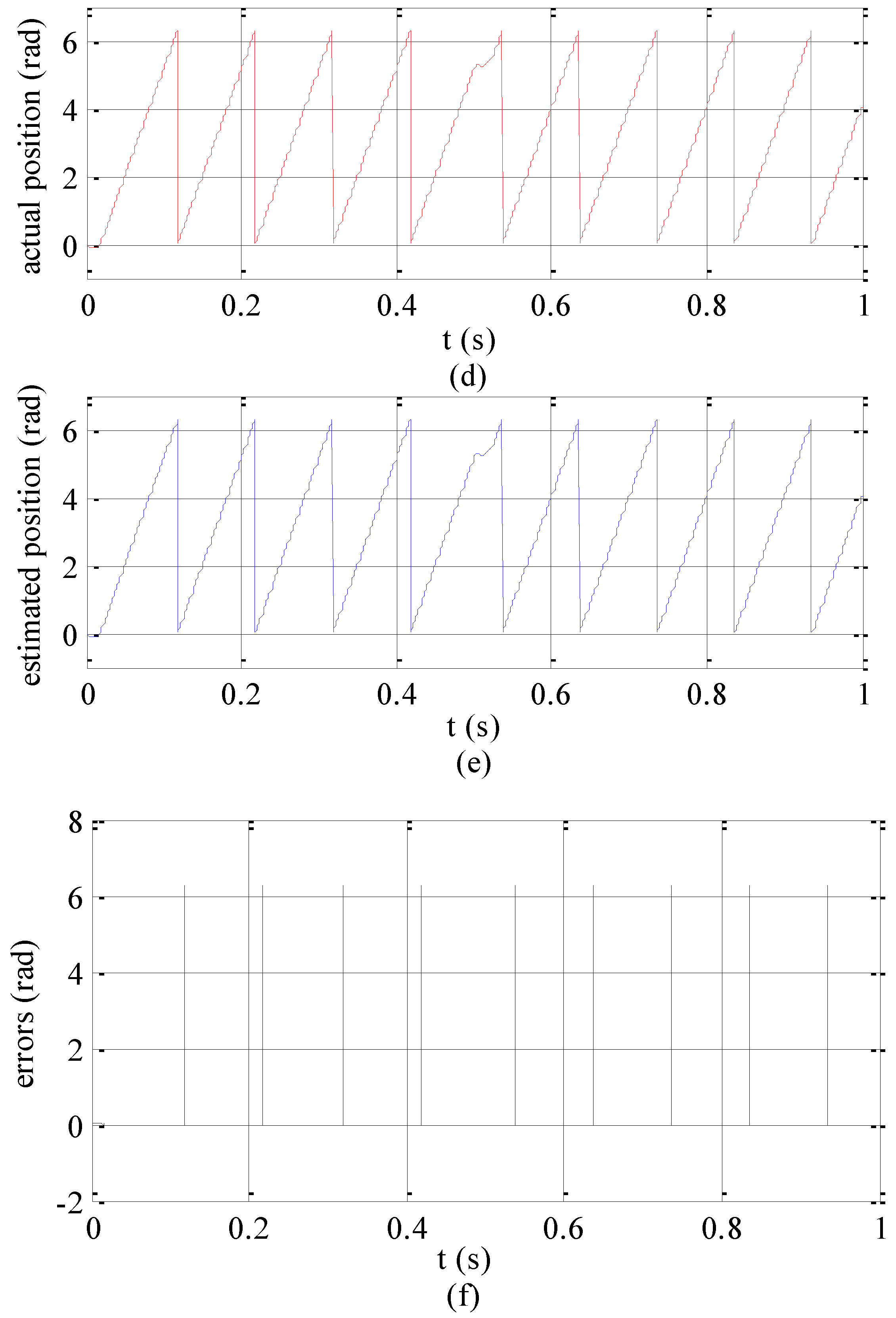
4. Simulation Analysis
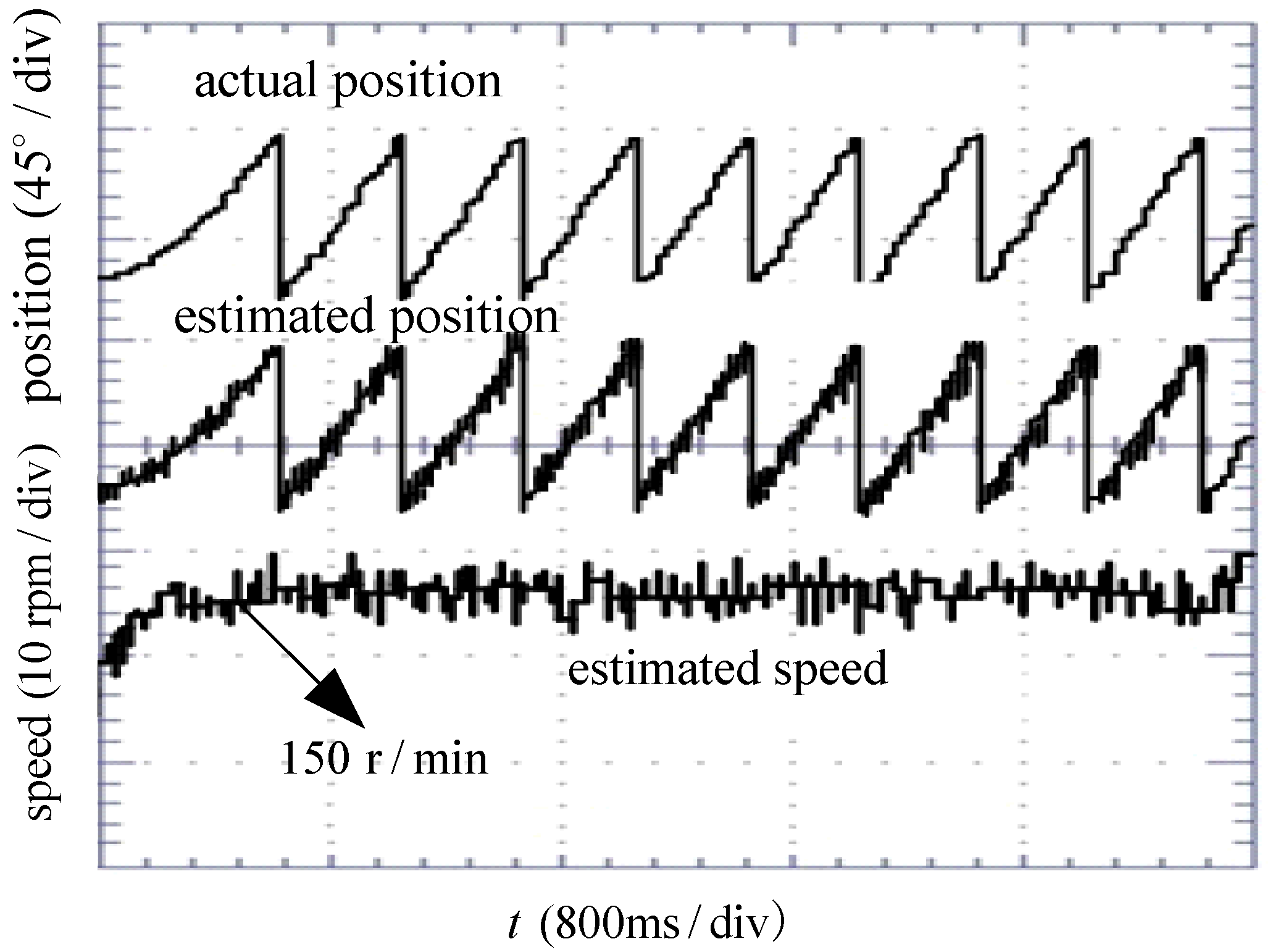
5. Experimental Analysis
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, S. Sensorless control of ship propulsion interior permanent magnet synchronous motor based on a new sliding mode observer. ISA Trans. 2015, 54, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Zhu, J.; Qin, J. Performance study of three-phase fault-tolerant permanent magnet motor drive for marine propulsion system based on structure design. J. Ship Res. 2017, 61, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Jia, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F. Performance analysis of sliding mode position observer for marine SPMSM sensorless control. In Proceedings of the PEAC, Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z. Sensorless control for PMSM drives using the cubature Kalman filter based speed and flux observer. In Proceedings of the ESARS-ITEC, Nottingham, UK, 7–9 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.A.; Rahman, M. Speed and position sensorless permanent magnet synchronous motor drives. In Proceedings of the CCECE. 1994, pp. 689–692. Available online: https://research.library.mun.ca/5398/ (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- Lu, K.; Lei, X.; Blaabjerg, F. Artificial inductance concept to compensate nonlinear inductance effects in the back EMF-based sensorless control method for PMSM. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Fang, J.; Han, B.; Zheng, S. Adaptive compensation method for high-speed surface PMSM sensorless drives of EMF-based position estimation error. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, D.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wang, X.; Li, K. Improved sensorless control method combining SMO and MRAS for surface PMSM drives. In Proceedings of the IAS, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1–5 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D.; Li, J.; Qu, R. Sensorless control of permanent magnet synchronous machine based on second-order sliding-mode observer with online resistance estimation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 3672–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y. A review of sensorless control methods for AC motor drives. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2018, 2, 104–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Kuang, J.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D. Rotor position estimation of PMSM in low-speed region and standstill using zero-voltage vector injection. IEEE Trans. Power Electr. 2018, 33, 7948–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Sul, S.K.; Ha, J.I.; Ide, K.; Sawamura, M. Sensorless drive of surface-mounted permanent-magnet motor by high-frequency signal injection based on magnetic saliency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yang, K.; Chen, K. An improved position-sensorless control method at low speed for PMSM based on high-frequency signal injection into a rotating reference frame. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 86510–86521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, M.; Tahami, F. Sensorless control of PMSMs with tolerance for delays and stator resistance uncertainties. IEEE Trans. Power Electr. 2013, 28, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reigosa, D.; Fernandez, D.; Yoshida, H.; Kato, T.; Briz, F. Permanent-magnet temperature estimation in PMSMs using pulsating high-frequency current injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3159–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busada, C.; Jorge, S.; Leon, A.; Solsona, J. Current controller based on reduced order generalized integrators for distributed generation systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electr. 2012, 59, 2898–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, B.; Ni, T.H. Enhanced position observer with a selective harmonic error eliminator and an error feed-forward compensator for sensor-less surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor drives. In Proceedings of the IFEEC-ECCE Asia, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 3–7 June 2017; pp. 1210–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; Xu, D.; Fu, Y.; Ni, R. Adaptive notch filter based rotor position estimation for interior permanent magnet synchronous motors. Proc. CSEE 2016, 36, 2521–2527. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zeng, D.; Li, H. Speed sensorless vector control of marine podded propulsion motor based on strong track filter. In Proceedings of the CCDC, Qingdao, China, 23–25 May 2015; pp. 1882–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Sulligoi, G.; Vicenzutti, A.; Menis, R. All-electric ship design: From electrical propulsion to integrated electrical and electronic power systems. IEEE Trans. Power. Electr. 2016, 2, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, R.; Behjati, H.; Ferdowsi, M. Dynamic modeling and stability analysis of an experimental test bench for electric-ship propulsion. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Electric Ship Technologies Symposium, Arlington, VA, USA, 22–24 April 2013; pp. 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ding, L.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhan, H.; Ni, R.; Xu, D. Enhanced position observer using second-order generalized integrator for sensorless interior permanent magnet synchronous motor drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2014, 29, 486–495. [Google Scholar]
- Szalai, T.; Berger, G.; Petzoldt, J. Stabilizing sensorless control down to zero speed by using the high-frequency current amplitude. IEEE Trans. Power Electr. 2014, 29, 3646–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, B.; Ni, T. Principle and Stability Analysis of an Improved Self-Sensing Control Strategy for Surface-Mounted PMSM Drives Using Second-Order Generalized Integrators. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, B.; Wei, J.; Wang, L.; Ni, T. A novel method for polarity detection of nonsalient PMSMs in initial position estimation. In Proceedings of the APEC, Long Beach, CA, USA, 20–24 March 2016; pp. 2754–2758. [Google Scholar]




| Symbol | Quantity | Values |
|---|---|---|
| np | number of pole pairs | 2 |
| R | stator resistance | 1.51 Ω |
| Ld | winding inductance | 0.0048 mH |
| Lq | winding inductance | 0.0134 mH |
| J | rotational inertia | 0.000244 kg.m2 |
| B | damping coefficient | 0.0002517 |
| Ψf | rotor flux | 0.1073 Wb |
| Udc | direct voltage | 380 V |
| P | rated power | 1 kW |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, H. Position Estimation of a PMSM in an Electric Propulsion Ship System Based on High-Frequency Injection. Electronics 2020, 9, 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9020276
Bai H. Position Estimation of a PMSM in an Electric Propulsion Ship System Based on High-Frequency Injection. Electronics. 2020; 9(2):276. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9020276
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Hongfen. 2020. "Position Estimation of a PMSM in an Electric Propulsion Ship System Based on High-Frequency Injection" Electronics 9, no. 2: 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9020276
APA StyleBai, H. (2020). Position Estimation of a PMSM in an Electric Propulsion Ship System Based on High-Frequency Injection. Electronics, 9(2), 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9020276





