Impact of Laser Attacks on the Switching Behavior of RRAM Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
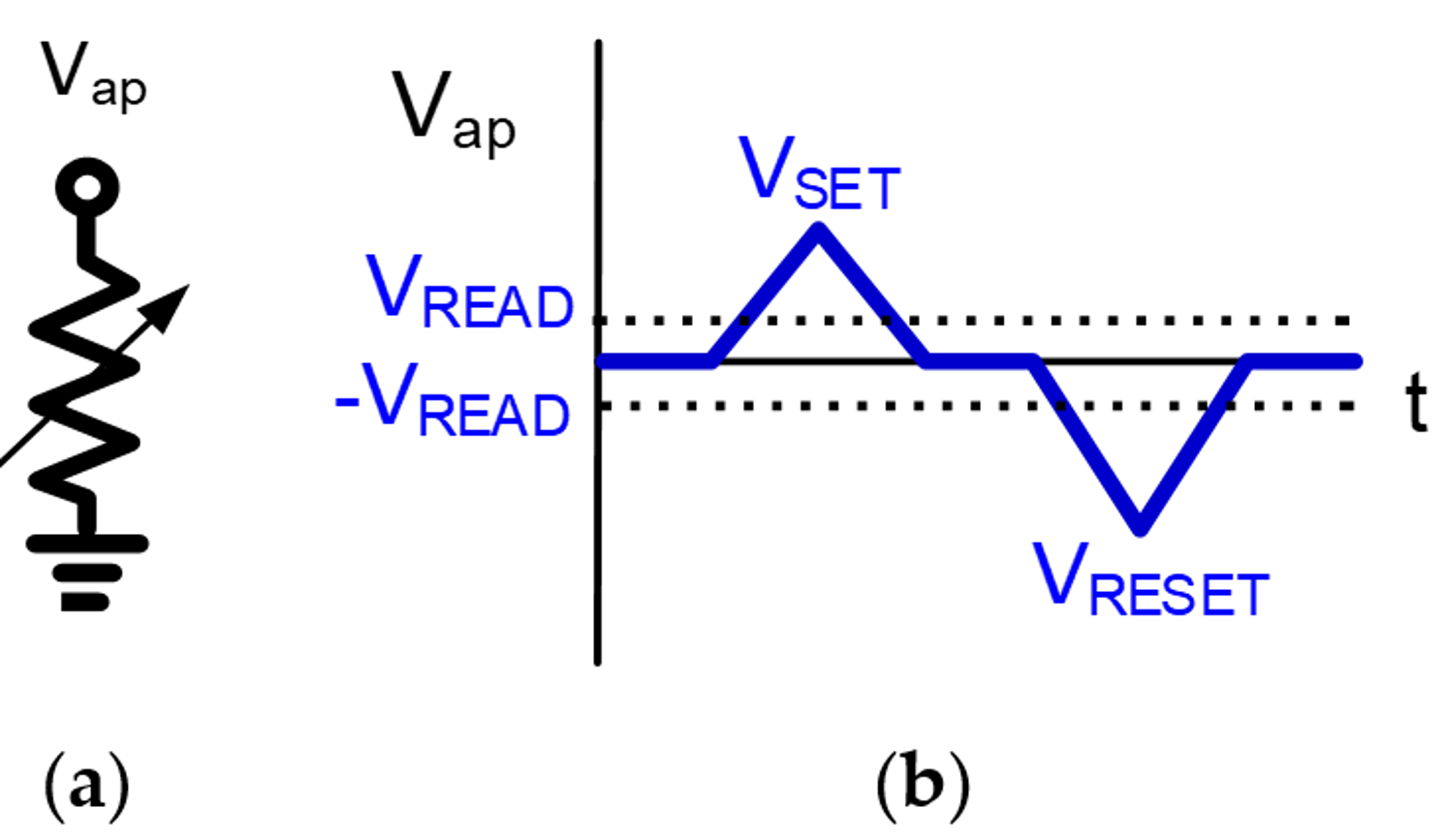
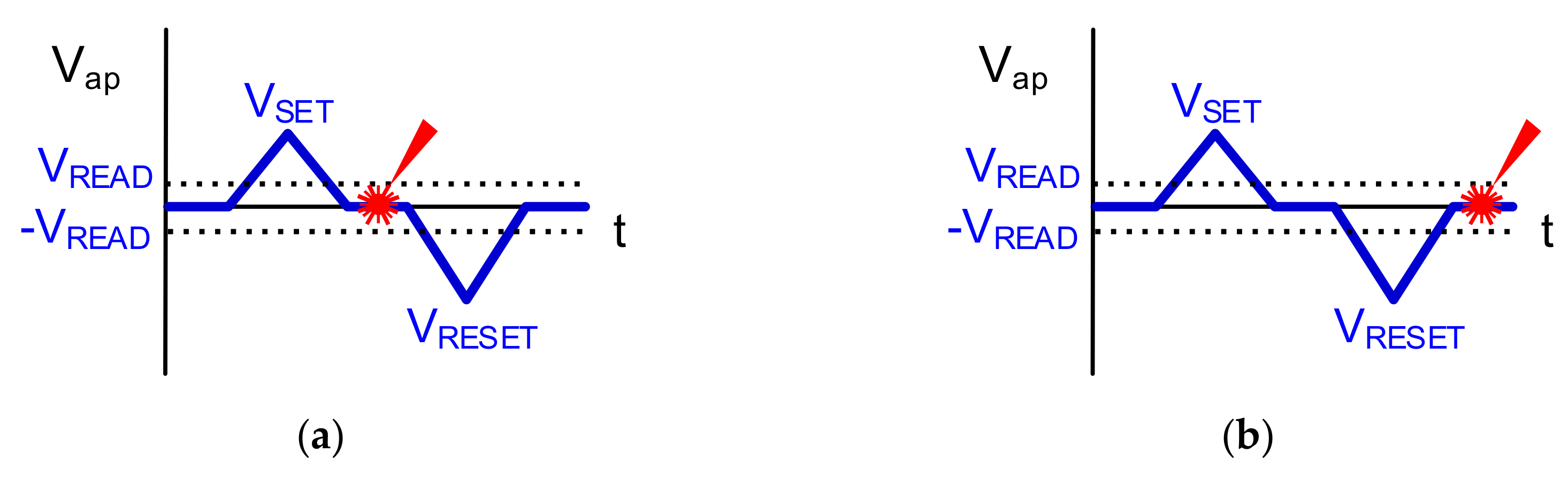
2. Materials and Methods
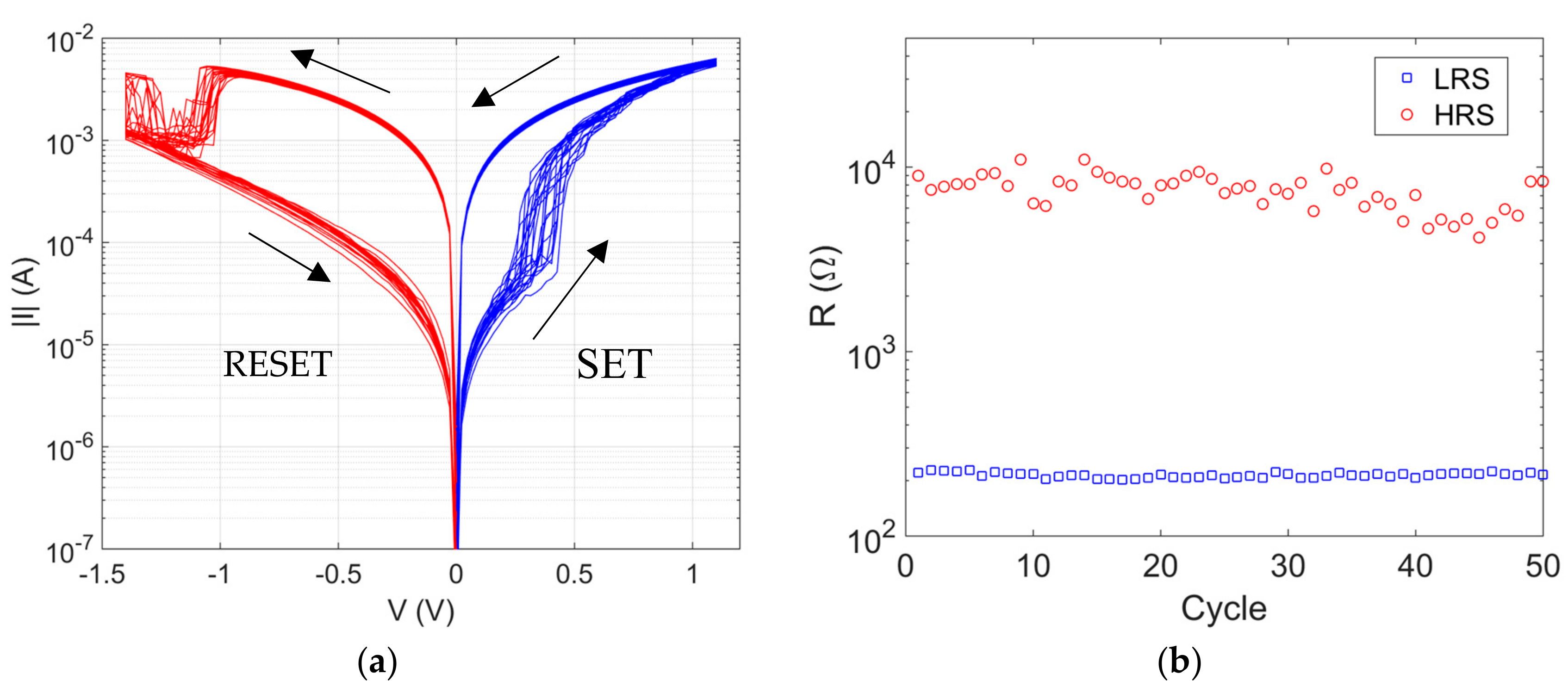
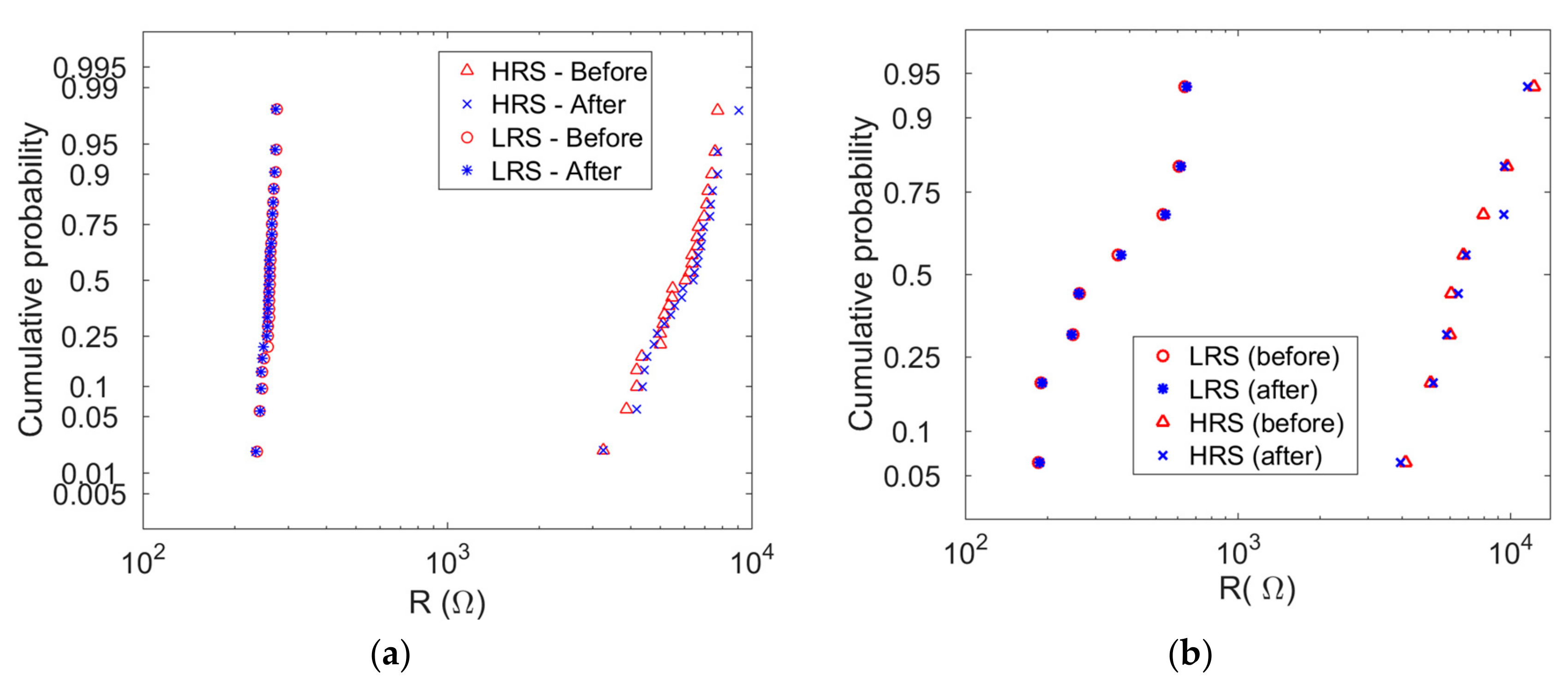
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torrezan, A.C.; Strachan, J.P.; Medeiros-Ribeiro, G.; Williams, R.S. Sub-nanosecond switching of a tantalum oxide memristor. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.Y.; Yu, S.; Gao, B.; Huang, P.; Kang, J.; Wong, H.-S.P. HfOx based vertical resistive random access memory for cost-effective 3D cross-point architecture without cell selector. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Device Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–13 December 2012; pp. 20.7.1–20.7.4. [Google Scholar]
- Lanza, M. A Review on Resistive Switching in High-k Dielectrics: A Nanoscale Point of View Using Conductive Atomic Force Microscope. Materials 2014, 7, 2155–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.-S.P.; Lee, H.-Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.-S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, P.-S.; Lee, B.; Chen, F.T.; Tsai, M.-J. Metal–Oxide RRAM. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 1951–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.W.; Ismail, R. Conduction Mechanism of Valence Change Resistive Switching Memory: A Survey. Electronics 2015, 4, 586–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Gao, B.; Fang, Z.; Yu, H.Y.; Kang, J.F.; Wong, H.-S.P. Stochastic learning in oxide binary synaptic device for neuromorphic computing. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogio, S.; Balatti, S.; Cubeta, A.; Calderoni, A.; Ramaswamy, N.; Ielmini, D. Statistical Fluctuations in HfOx Resistive-Switching Memory: Part I—Set/Reset Variability. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2014, 61, 2912–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, A.; Walczyk, D.; Zambelli, C.; Miranda, E.; Olivo, P.; Stikanov, V.; Feriani, A.; Schoof, G.; Kraemer, R.; Tillack, B.; et al. Impact of Intercell and Intracell Variability on Forming and Switching Parameters in RRAM Arrays. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 2502–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogio, S.; Balatti, S.; Cubeta, A.; Calderoni, A.; Ramaswamy, N.; Ielmini, D. Statistical Fluctuations in HfOx Resistive-Switching Memory: Part II—Random Telegraph Noise. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2014, 61, 2920–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cordero, G.; González, M.B.; Campabadal, F.; Jiménez-Molinos, F.; Roldán, J.B. A new technique to analyze RTN signals in resistive memories. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, J.; Rose, G.S.; Karri, R.; Potkonjak, M. Nano-PPUF: A memristor-based security primitive. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI 2012, Amherst, MA, USA, 19–21 August 2012; pp. 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A. Utilizing the variability of resistive Random Access Memory to implement reconfigurable physical unclonable functions. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2015, 36, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, H.; Pang, Y.; Qian, H.; Yu, S. Experimental characterization of physical unclonable function based on 1 kb Resistive Random Access Memory arrays. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2015, 36, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazady, A.; Rahman, M.T.; Forte, D.; Anwar, M. Memristor PUF—A Security Primitive: Theory and Experiment. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2015, 5, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Wu, H.; Gao, B.; Deng, N.; Liu, R.; Yu, S.; Chen, A.; Qian, H. Optimization of RRAM-based physical unclonable function with a novel differential read-out method. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, R.; Ghosh, S.; Katkoori, S. Design, Analysis and Application of Embedded Resistive RAM based Strong Arbiter PUF. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumí, D.; Gonzalez, M.B.; Campabadal, F. RRAM serial configuration for the generation of random bits. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 178, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumí, D.; Gómez-Pau, Á.; Manich, S.; Rodríguez-Montañés, R.; González, M.B.; Campabadal, F. Unpredictable Bits Generation Based on RRAM Parallel Configuration. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2019, 40, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.S.; Kim, G.H.; Kwak, K.; Jeong, D.S.; Ju, H. Enhanced Reconfigurable Physical Unclonable Function Based on Stochastic Nature of Multilevel Cell RRAM. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2019, 66, 1717–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Shen, W.C.; Tseng, Y.H.; King, Y.C.; Lin, C.J. A Contact-Resistive Random-Access-Memory-Based True Random Number Generator. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2012, 33, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balatti, S.; Ambrogio, S.; Carboni, R.; Milo, V.; Wang, Z.; Calderoni, A.; Ramaswamy, N.; Ielmini, D. Physical unbiased generation of random numbers with coupled resistive switching devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2016, 63, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, S.; Kumar, A.; Parmar, V.; Suri, M. OxRAM RNG Circuits Exploiting Multiple Undesirable Nanoscale Phenomena. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2017, 16, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, R.; Ghosh, S.; Katkoori, S. CSRO-Based Reconfigurable True Random Number Generator Using RRAM. IEEE Trans. Very Larg. Scale Integr. Syst. 2018, 26, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.G.; Hooten, N.C.; Schrimpf, R.D.; Reed, R.A.; Mendenhall, M.H.; Alles, M.L.; Bi, J.; Zhang, E.X.; Linten, D.; Fantini, A.; et al. Single- and Multiple-Event Induced Upsets in HfO2/Hf 1T1R RRAM. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2014, 61, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakovinsky, A.; Bocquet, M.; Wacquez, R.; Coignus, J.; Deleruyelle, D.; Djaou, C.; Reimbold, G.; Portal, J.M. Impact of a laser pulse on HfO2-based RRAM cells reliability and integrity. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Microelectronic Test Structures (ICMTS), Yokohama, Japan, 28–31 March 2016; pp. 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakovinsky, A.; Bocquet, M.; Wacquez, R.; Coignus, J.; Portal, J.M. Thermal laser attack and high temperature heating on HfO2-based OxRAM cells. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on On-Line Testing and Robust System Design (IOLTS), Thessaloniki, Greece, 3–5 July 2017; pp. 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehonic, A.; Gerard, T.; Kenyon, A. Light-activated resistance switching in SiOx RRAM devices. J. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 111, 233502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, X.; Feng, Z.; Jin, L.; Lanlong, J.; Cong, F.; Jing, L.; Ming, L.; Jinshun, B. Pulsed-laser testing for single event effects in a stand-alone resistive random access memory. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 24th International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits (IPFA), Chengdu, China, 4–7 July 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Han, Z. Mitigation of soft errors in resistive switching random-access-memories. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits, Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2014; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


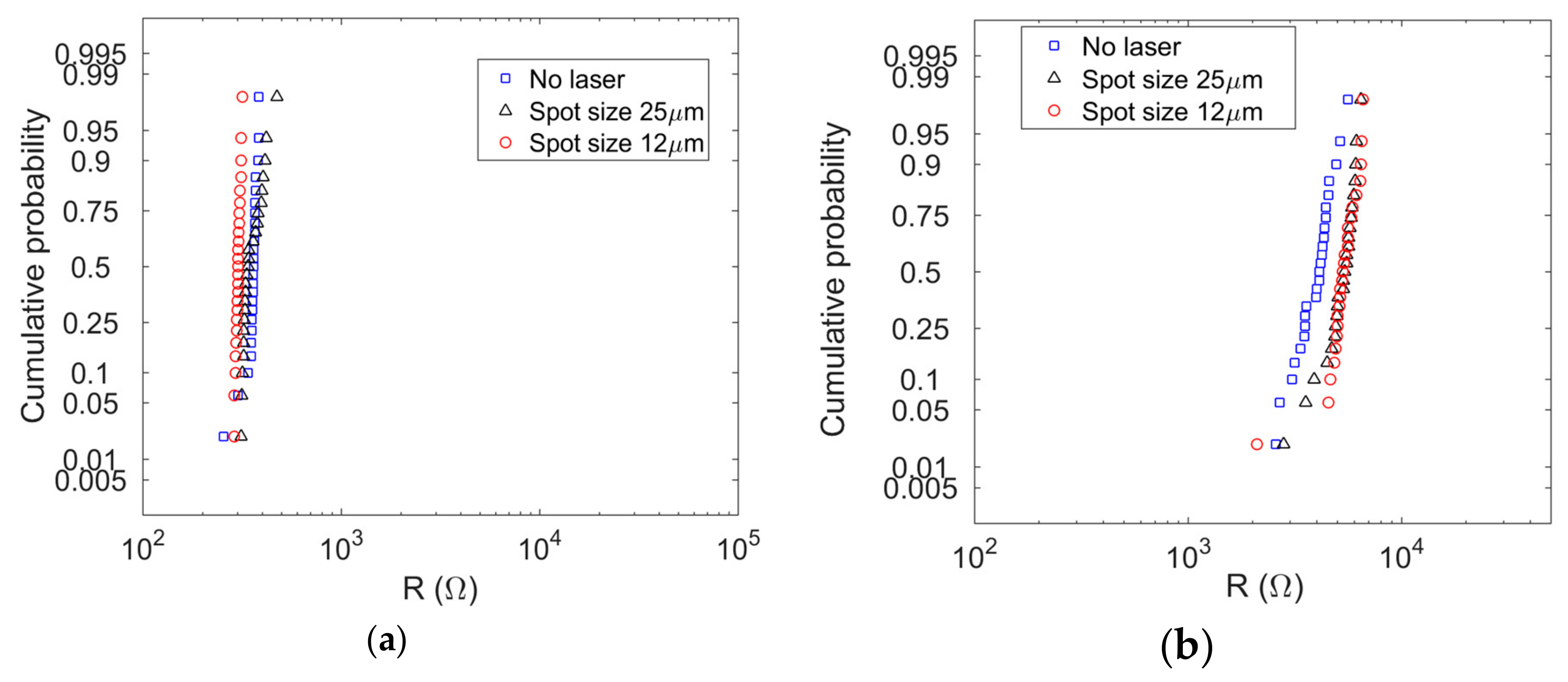

| Work | Structure | Dimensions (nm) | Size (µm × µm) | Cell | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | TiN/Hf/HfO2/TiN | ?2/10/5/?2 | 105 × 120 | 1T1R | HRS to LRS transitions when the transistor is irradiated |
| [25] | TiN/Ti/HfO2/TiN | 50/10/5/10 | 3 × 3 | 1R | HRS to LRS transitions |
| [26] | Ti/HfO2/TiN | 10/10/101 | 3 × 31 | 1T1R | HRS to LRS transitions |
| [28] | ?2/HfOx/?2 | ?2/?2/?2 | ?2 | 1T1R | Transitions when peripheral circuits are irradiated |
| This work | TiN/Ti/HfO2/W | 200/10/10/200 | 2 × 2 5 × 5 15 × 15 | 1R | No transitions |
| Laser Source | Type | Maximum Power (W) | Wavelenght (nm) | Spot Size (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | single photon absorption | 2 | 1064 | 3, 12 and 25 |
| 2 | 5.2 | 1024 | ||
| 3 | 2 | 976 |
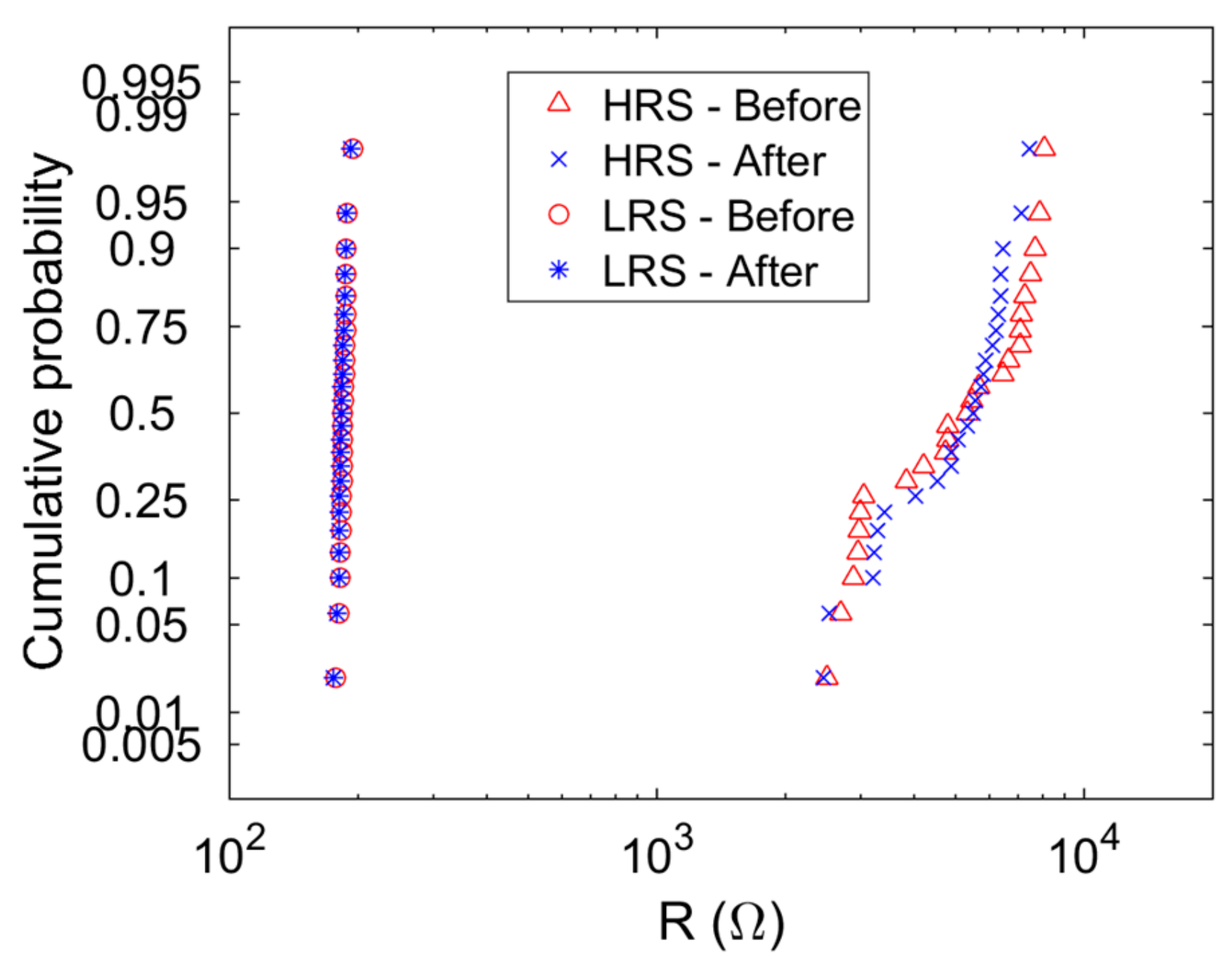
| DUT | Size (µm × µm) | RLRS-Before (Ω) | RLRS-After (Ω) | RHRS-Before (Ω) | RHRS-After (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 × 2 | 185 | 187 | 7945 | 9436 |
| 2 | 5 × 5 | 637 | 648 | 12,199 | 11,532 |
| 3 | 5 × 5 | 529 | 541 | 5103 | 5205 |
| 4 | 15 × 15 | 189 | 190 | 9703 | 9510 |
| 5 | 5 × 5 | 604 | 617 | 4120 | 3939 |
| 6 | 2 × 2 | 363 | 371 | 5986 | 5840 |
| 7 | 15 × 15 | 261 | 259 | 6063 | 6424 |
| 8 | 15 × 15 | 248 | 245 | 6704 | 6850 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arumí, D.; Manich, S.; Gómez-Pau, Á.; Rodríguez-Montañés, R.; Montilla, V.; Hernández, D.; González, M.B.; Campabadal, F. Impact of Laser Attacks on the Switching Behavior of RRAM Devices. Electronics 2020, 9, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010200
Arumí D, Manich S, Gómez-Pau Á, Rodríguez-Montañés R, Montilla V, Hernández D, González MB, Campabadal F. Impact of Laser Attacks on the Switching Behavior of RRAM Devices. Electronics. 2020; 9(1):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010200
Chicago/Turabian StyleArumí, Daniel, Salvador Manich, Álvaro Gómez-Pau, Rosa Rodríguez-Montañés, Víctor Montilla, David Hernández, Mireia Bargalló González, and Francesca Campabadal. 2020. "Impact of Laser Attacks on the Switching Behavior of RRAM Devices" Electronics 9, no. 1: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010200
APA StyleArumí, D., Manich, S., Gómez-Pau, Á., Rodríguez-Montañés, R., Montilla, V., Hernández, D., González, M. B., & Campabadal, F. (2020). Impact of Laser Attacks on the Switching Behavior of RRAM Devices. Electronics, 9(1), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010200








