Robust Offset-Free Speed Tracking Controller of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Wind Power Generation Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dynamics of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator with Wind Turbine in Rotational d-q Axis
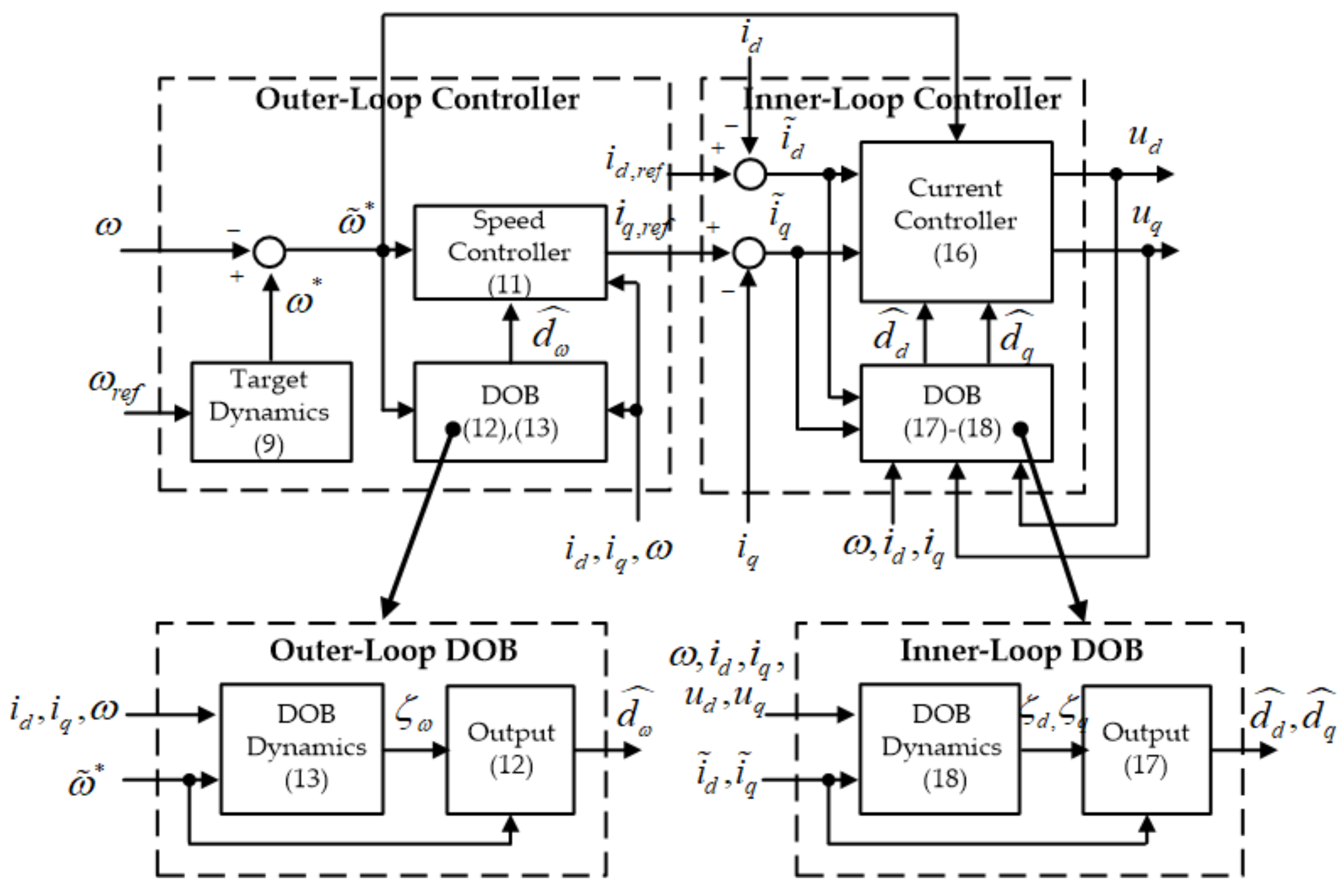
3. Speed Tracking Algorithm Design
3.1. Outer-Loop Controller Design
3.2. Inner-Loop Controller Design and Closed-Loop Property Analysis
4. Simulations
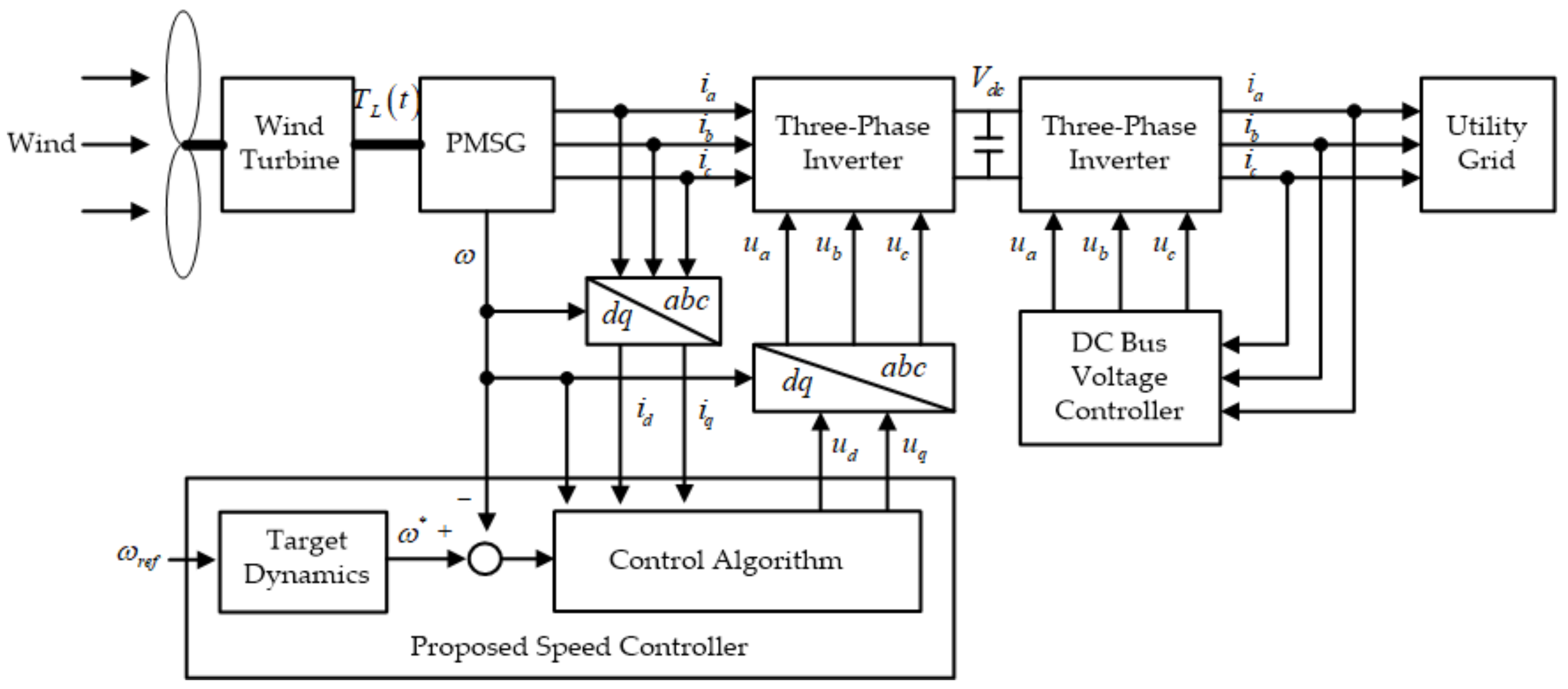
4.1. Wind Power System Configuration
4.2. Controller Configuration
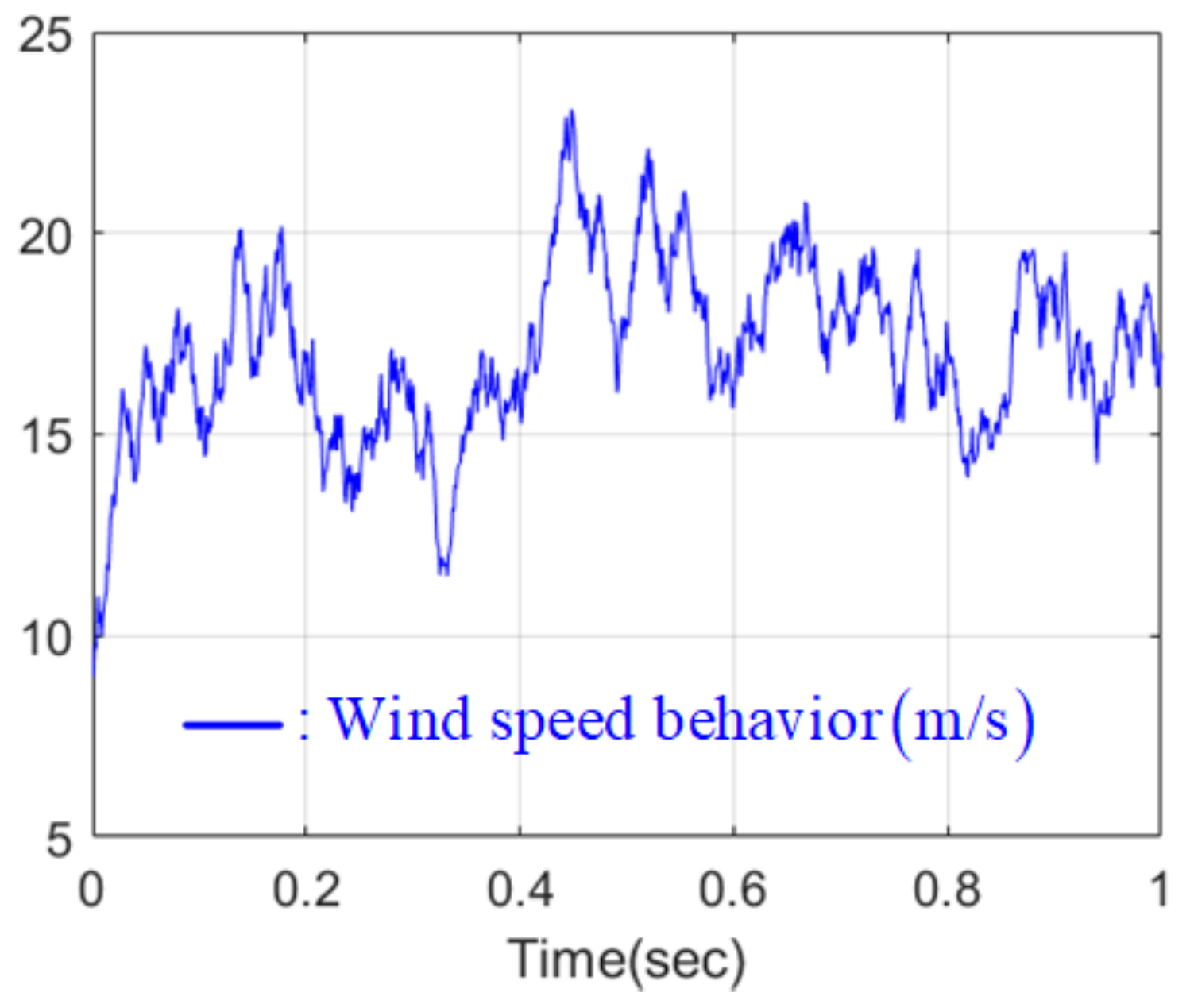
4.3. Simulation Scenario and Evaluation Metric
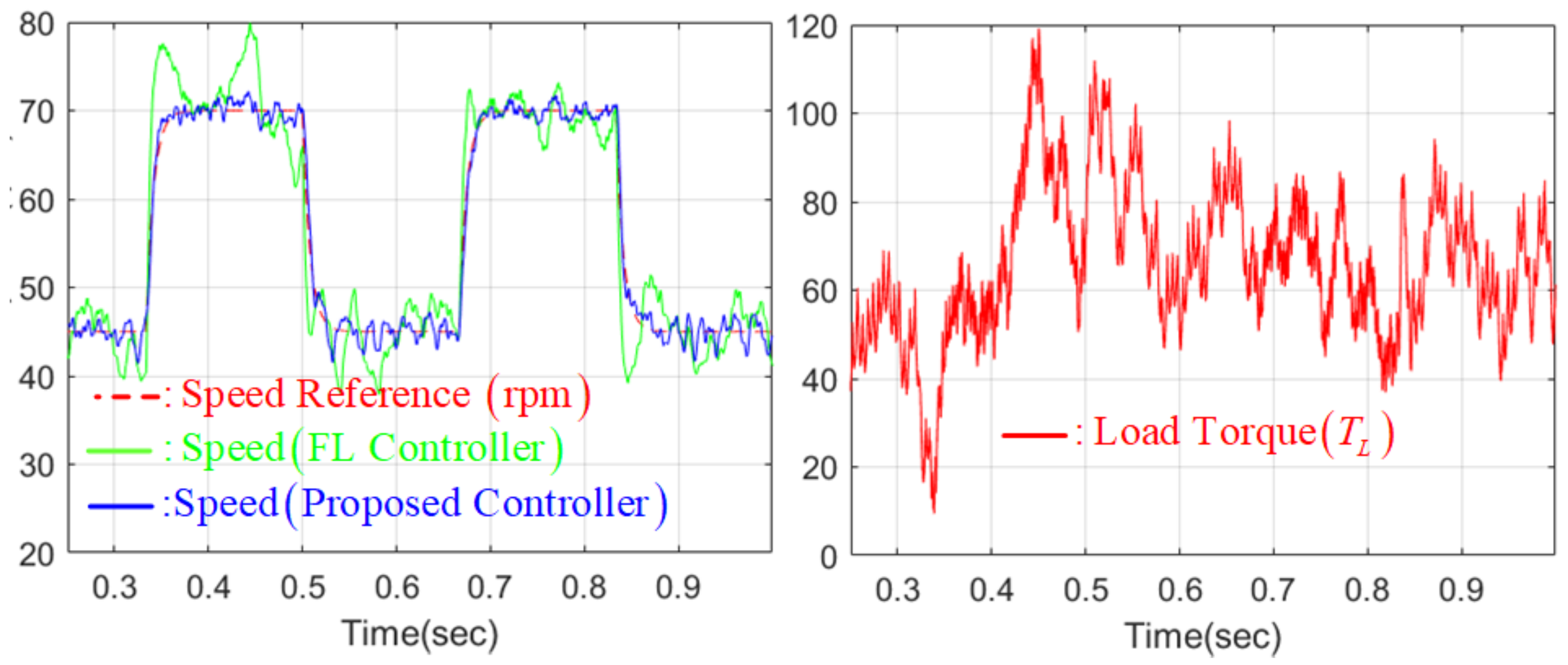
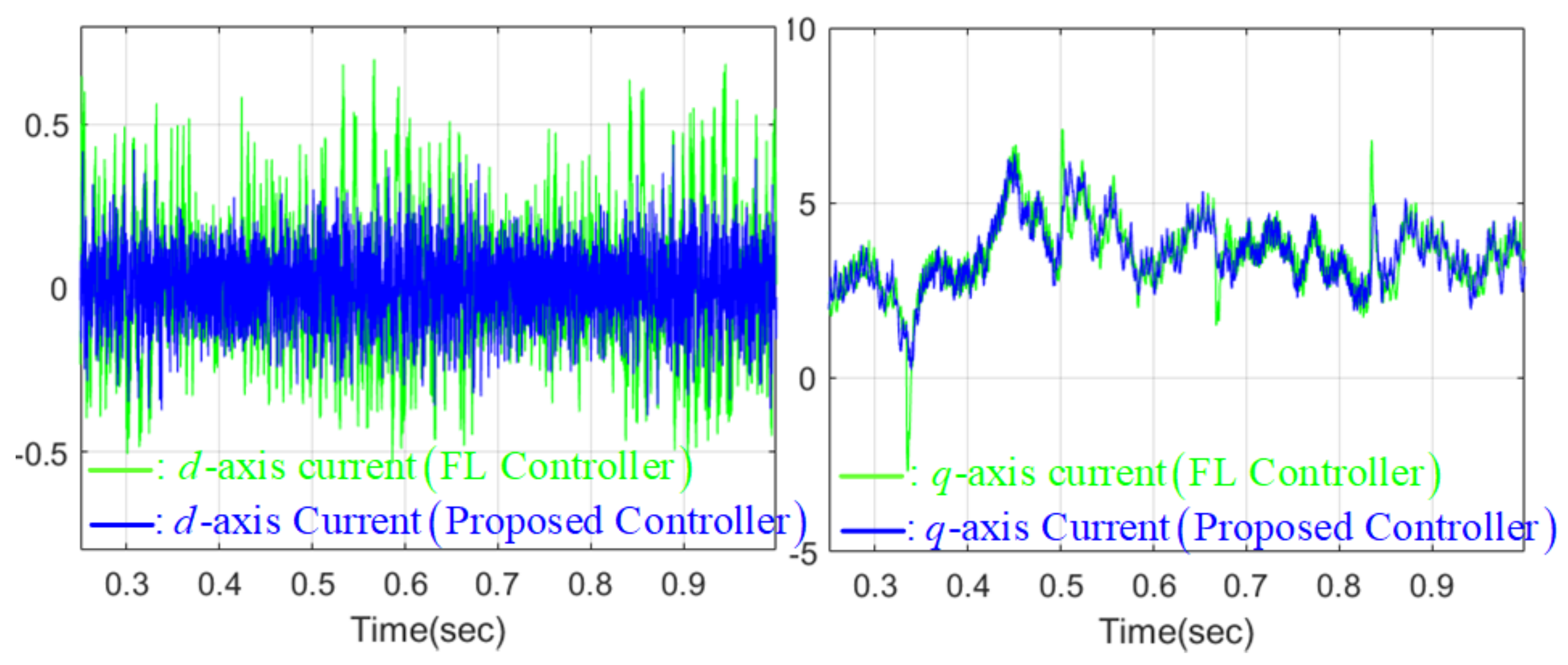
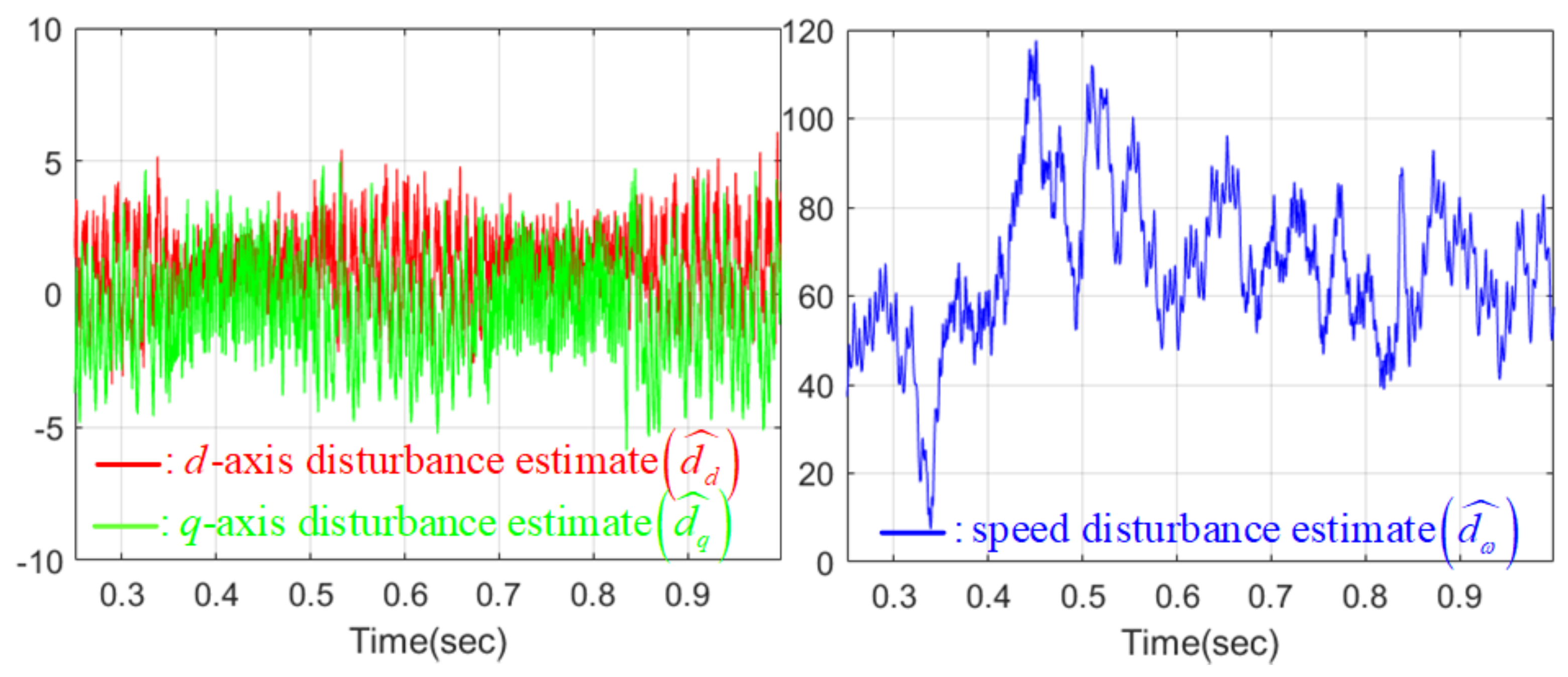
4.4. Numerical Verification Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Tiwari, R.; Krishnamurthy, K.; Neelakandan, R.B.; Padmanaban, S. Neural Network Based Maximum Power Point Tracking Control with Quadratic Boost Converter for PMSG-Wind Energy Conversion System. Electronics 2018, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H. Use of Three-Level Power Converters in Wind-Driven Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Generators with Unbalanced Loads. Electronics 2015, 4, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, T.; Abdelkader, D.; Said, B.; Padmanaban, S.; Iqbal, A. Extended Kalman Filter Based Sliding Mode Control of Parallel-Connected Two Five-Phase PMSM Drive System. Electronics 2018, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, A.P.; Gomez, S.A.; Rodriguez-Amenedo, J.L.; Plaza, M.G.; Carrasco, J.E.G.; de las Morenas, J.M.A.M. A Voltage and Frequency Control Strategy for Stand-Alone Full Converter Wind Energy Conversion Systems. Energies 2018, 11, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, K.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, K.; Wang, M. A Steady-State Analysis Method for Modular Multilevel Converters Connected to Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator-Based Wind Energy Conversion Systems. Energies 2018, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Song, H.; Lee, J. Adaptive Disturbance Observer-Based Parameter-Independent Speed Control of an Uncertain Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine for Wind Power Generation Applications. Energies 2015, 8, 4496–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, M.G.; Farret, F.A.; Blaabjerg, F. Small Wind Energy Systems. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2015, 43, 1388–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andeescu, G.D.; Pitic, C.; Blaabjerg, F.; Boldea, I. Combined flux observer with signal injection enhancement for wide speed range sensorless direct torque control of IPMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matausek, M.R.; Jeftenic, B.I.; Miljkovic, D.M.; Bebic, M.Z. Gain scheduling control of DC motor drive with field weakening. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 43, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.C.; Kim, S.; Sul, S.K. Six-Step Operation of PMSM with Instantaneous Current Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 2614–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, S.K. Control of Electric Machine Drive Systems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 88. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J. Direct Torque Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor With Reduced Torque Ripple and Commutation Frequency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.K.; Sul, S.K. New direct torque control of induction motor for minimum torque ripple and constant switching frequency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1999, 35, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errouissi, R.; Ouhrouche, M.; Chen, W.H.; Trzynadlowski, A.M. Robust Cascaded Nonlinear Predictive Control of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor With Antiwindup Compensator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sira-Ramirez, H.; Linares-Flores, J.; Garcia-Rodriguez, C.; Contreras-Ordaz, M.A. On the Control of the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor: An Active Disturbance Rejection Control Approach. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 2056–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, M.L.; Ippoliti, G.; Longhi, S.; Orlando, G. A Quasi-Sliding Mode Approach for Robust Control and Speed Estimation of PM Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, I.C.; Kim, K.H.; Youn, M.J. Robust nonlinear speed control of PM synchronous motor using boundary layer integral sliding mode control technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2000, 8, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, P.C.; Wasynczuk, O.; Sudhoff, S. Analysis of Electric Machinery; IEEE Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Shengquan, L.; Juan, L. Output Predictor-Based Active Disturbance Rejection Control for a Wind Energy Conversion System with PMSG. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 5205–5214. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, S. Wind Energy: Fundamentals, Resource Analysis and Economics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]

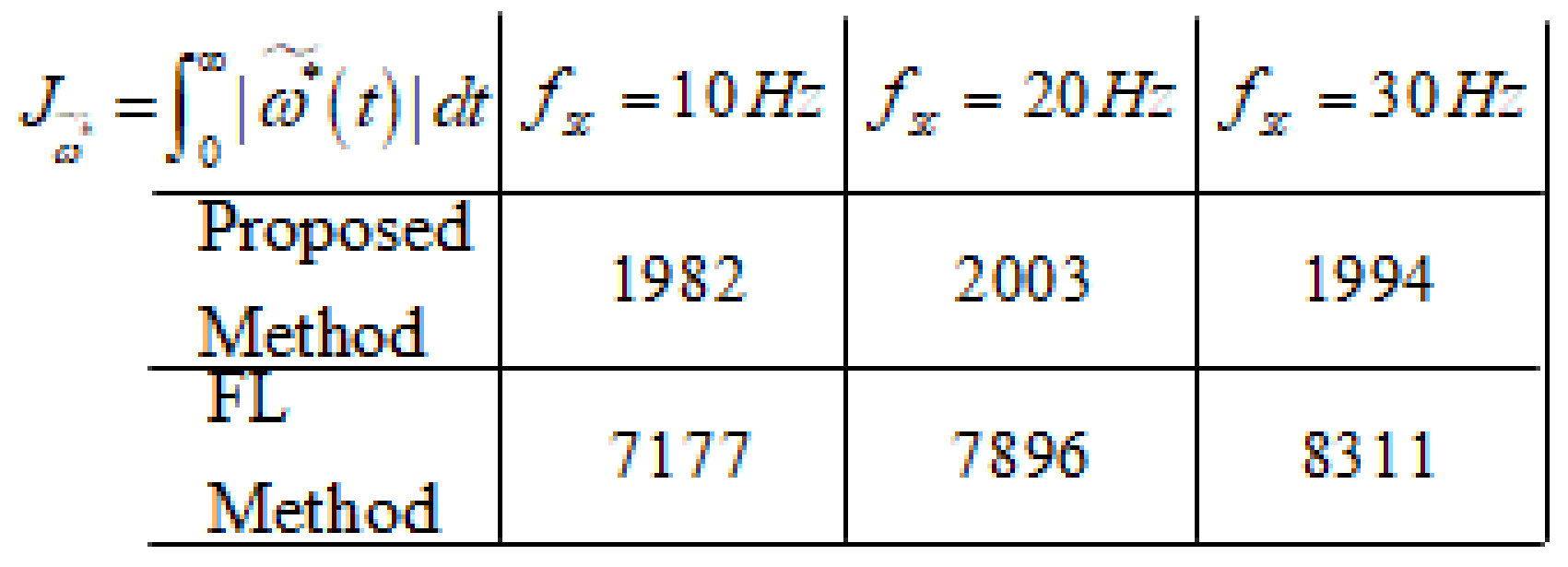
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-K.; Lee, K.-B. Robust Offset-Free Speed Tracking Controller of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Wind Power Generation Applications. Electronics 2018, 7, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7040048
Kim S-K, Lee K-B. Robust Offset-Free Speed Tracking Controller of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Wind Power Generation Applications. Electronics. 2018; 7(4):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7040048
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seok-Kyoon, and Kyo-Beum Lee. 2018. "Robust Offset-Free Speed Tracking Controller of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Wind Power Generation Applications" Electronics 7, no. 4: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7040048
APA StyleKim, S.-K., & Lee, K.-B. (2018). Robust Offset-Free Speed Tracking Controller of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Wind Power Generation Applications. Electronics, 7(4), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7040048





