Logic Locking Using Hybrid CMOS and Emerging SiNW FETs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
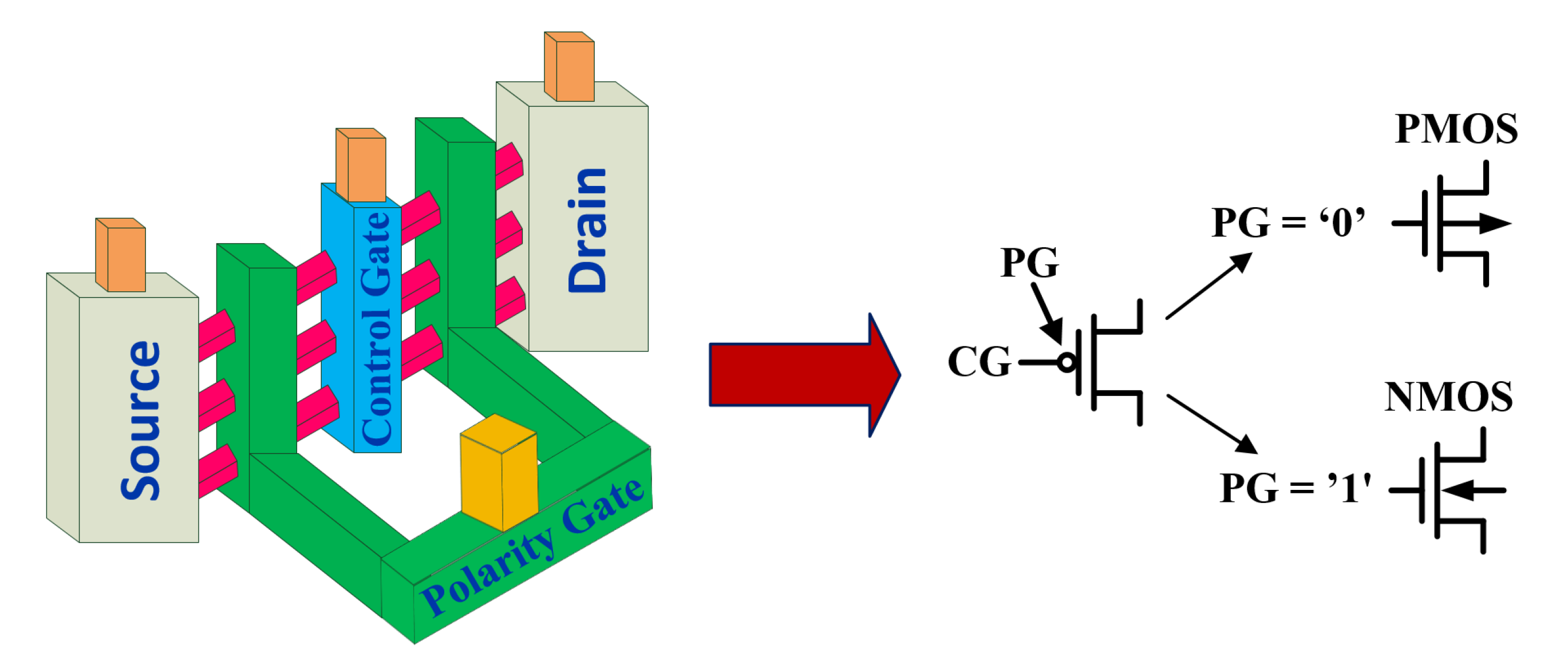
- We first present the polymorphic logic gate based on emerging SiNW polarity-contrallable FET and its advantages over conventional CMOS technology.
- We then incorporate polymorphic logic gates for encrypting combinational circuits. A polymorphic gate based logic encryption algorithm is further proposed with theoretical analysis.
- We evaluate the proposed SiNW FETs and CMOS hybrid logic encryption, achieving a hamming distance of 50% for most of the ISCAS’85 benchmark circuits.
- The performance penalty of the proposed technique has also been evaluated, where a much smaller overhead is incurred compared to the previous literature. A genuine energy-efficient logic locking is achieved.
2. Background
2.1. Introduction to Silicon NanoWire FET
2.2. Logic Encryption Technique
2.3. Prior Works
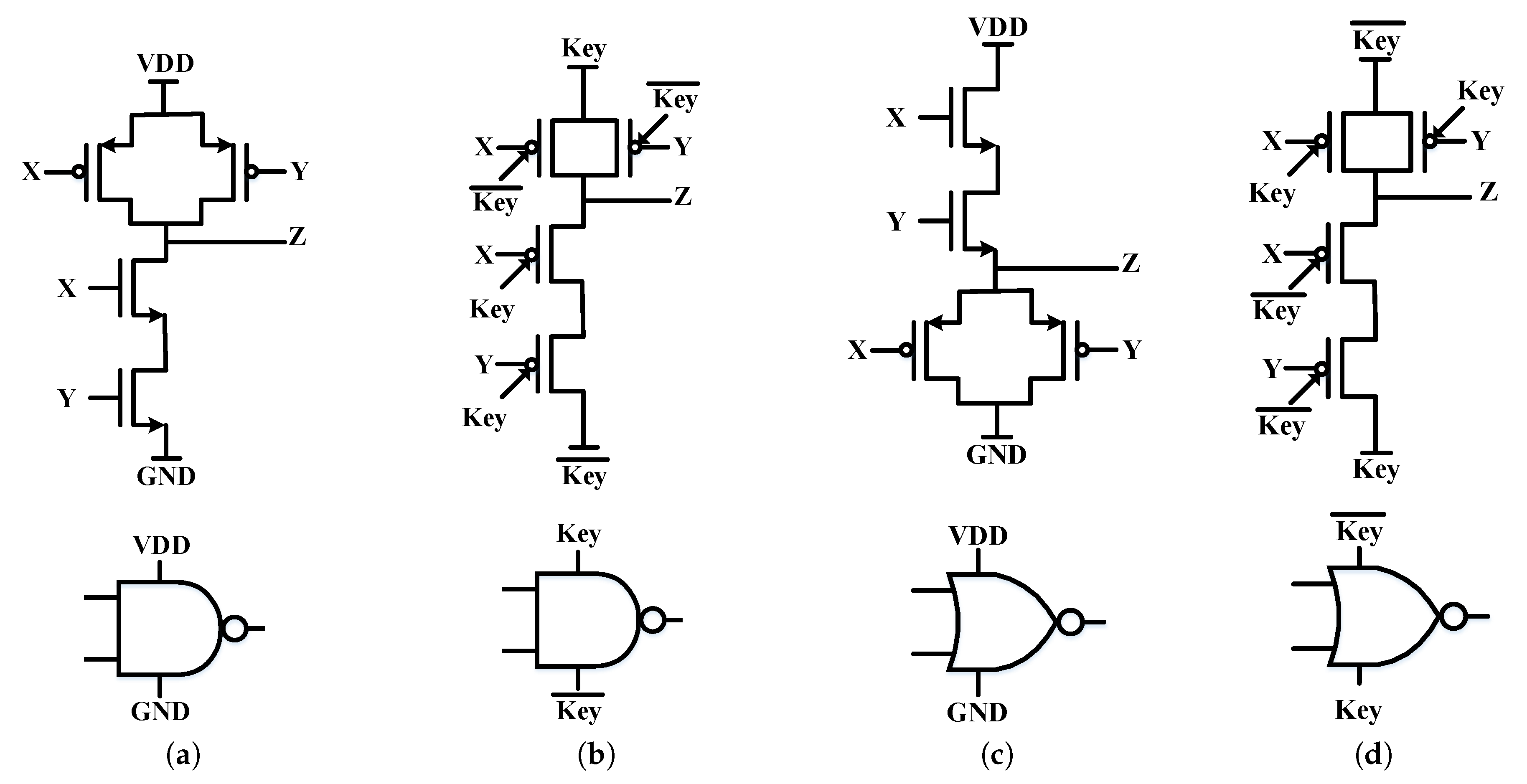
3. Designing Polymorphic Gates Using SiNW FETs
4. SiNW in Logic Encryption
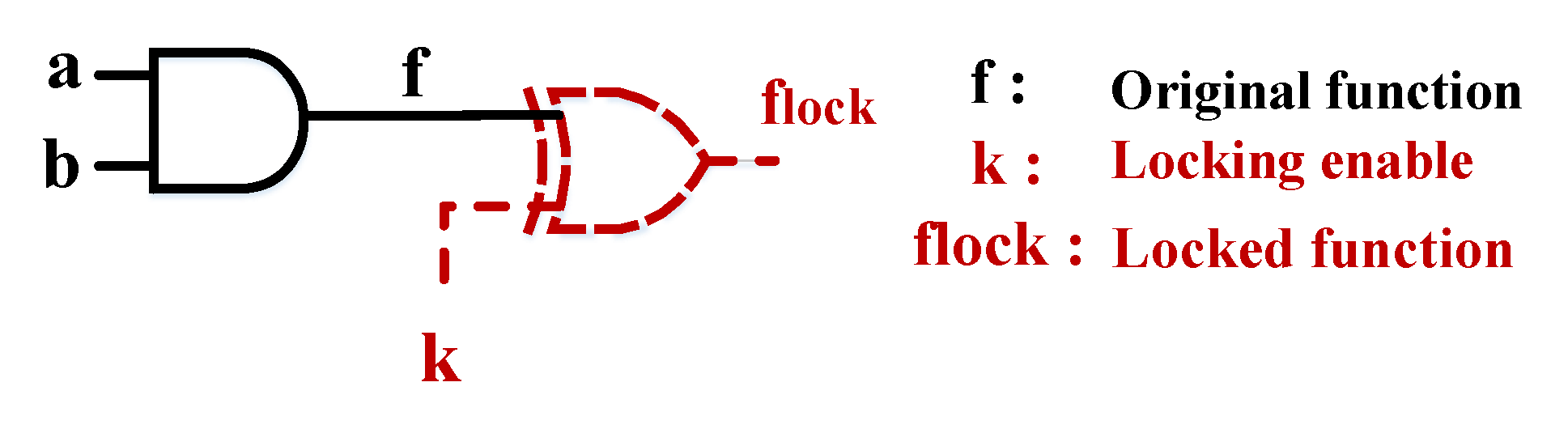
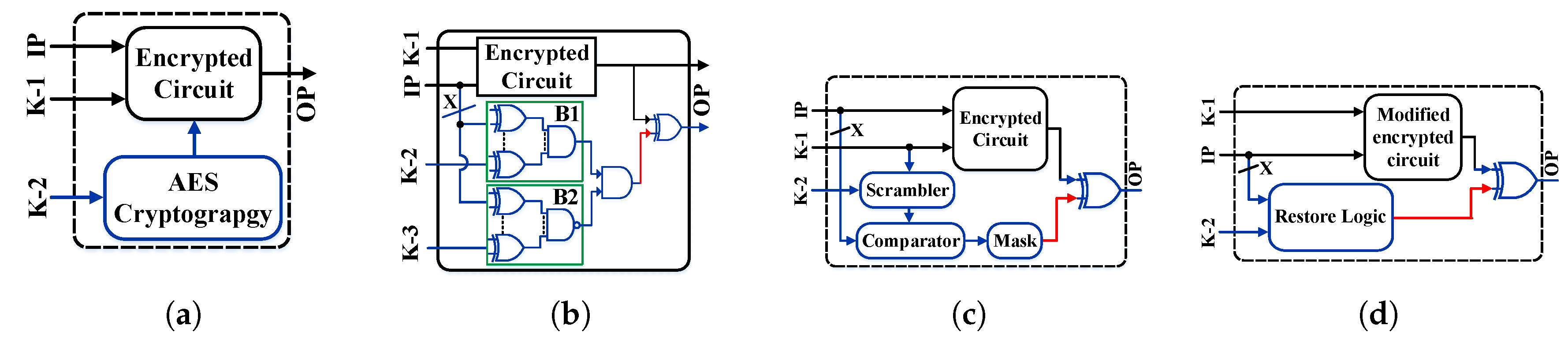
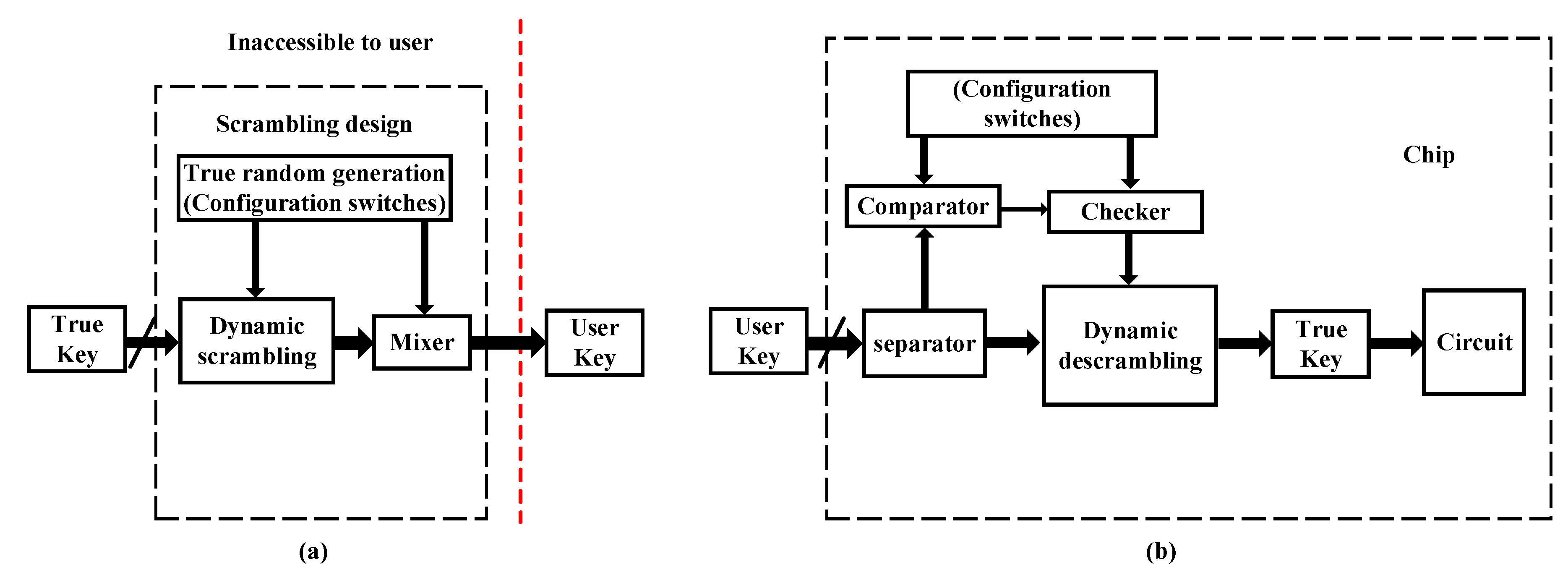
4.1. Fundamental of Logic Locking
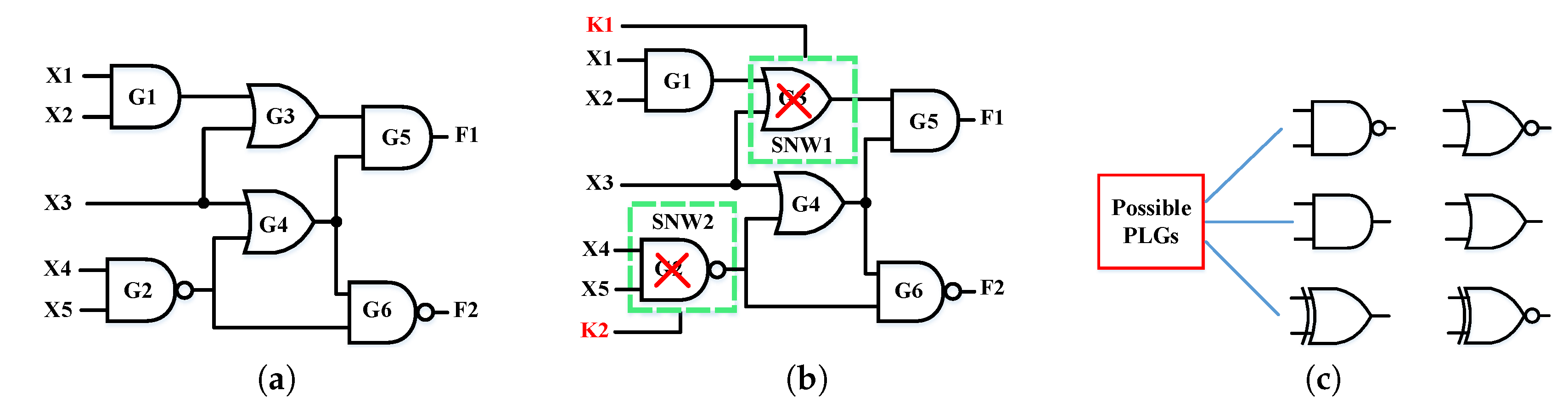
4.2. Encrypted Logic Circuit Leveraging Polymorphic Logic Gates
4.3. Security Metrics
- On employing the valid secret key k, the function produces correct outputs for all input test patterns.
- On employing the incorrect secret key values, the function generates wrong outputs correspondingly:
4.4. Algorithm for Insertion of Polymorphic Logic Gates
| Algorithm 1 Logic Locking Algorithm |
 |
5. Results
5.1. Experimental Setup
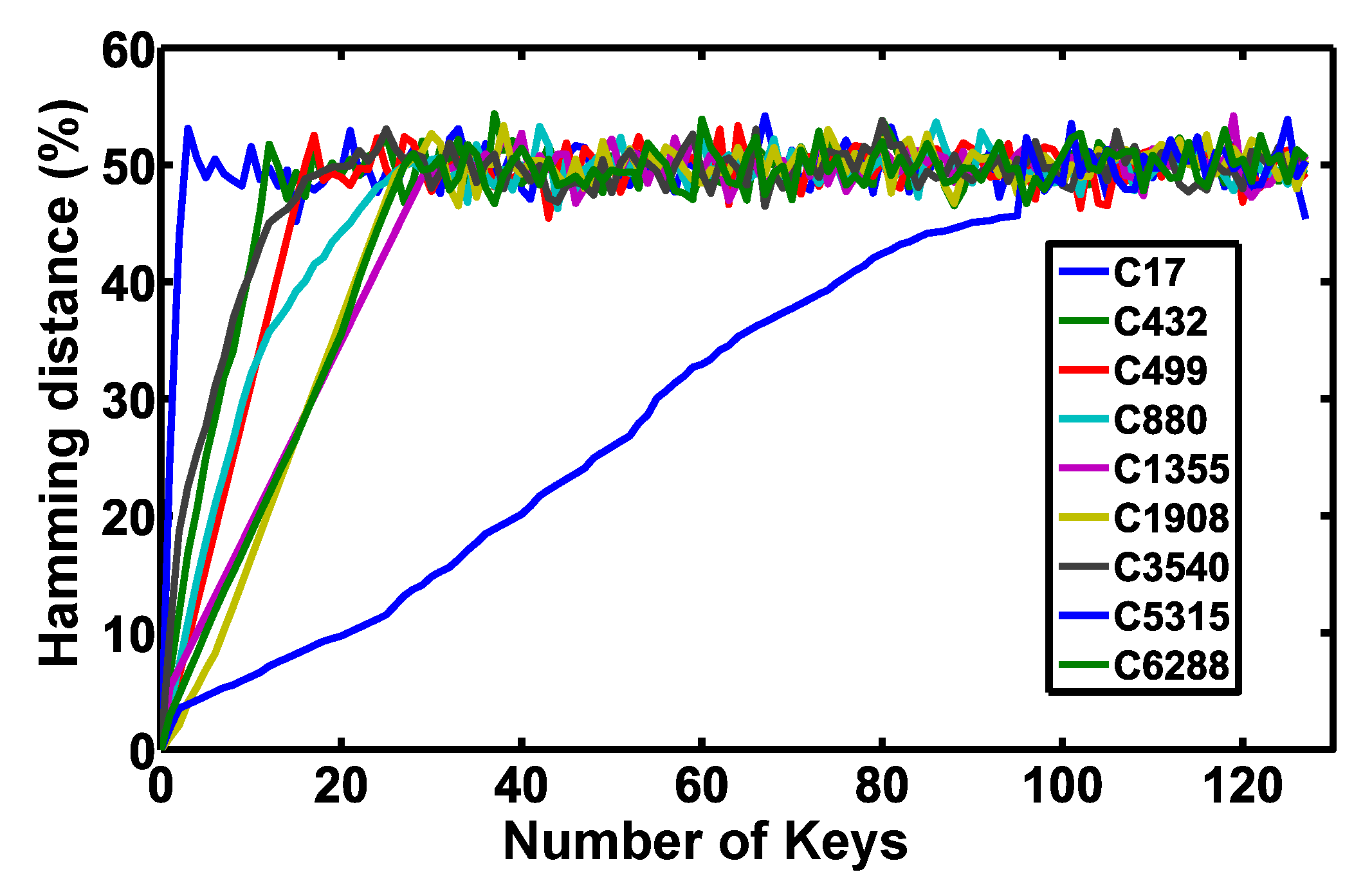
5.2. Security Evaluation
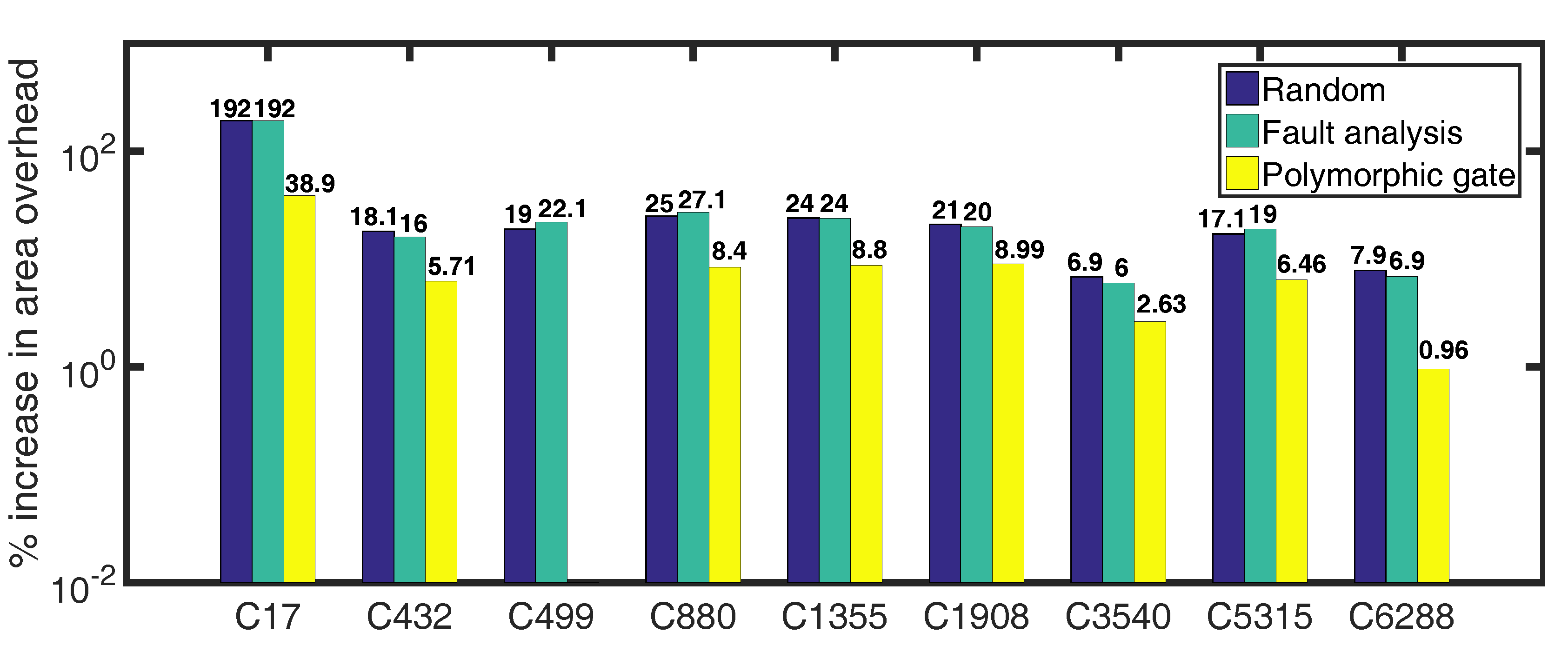
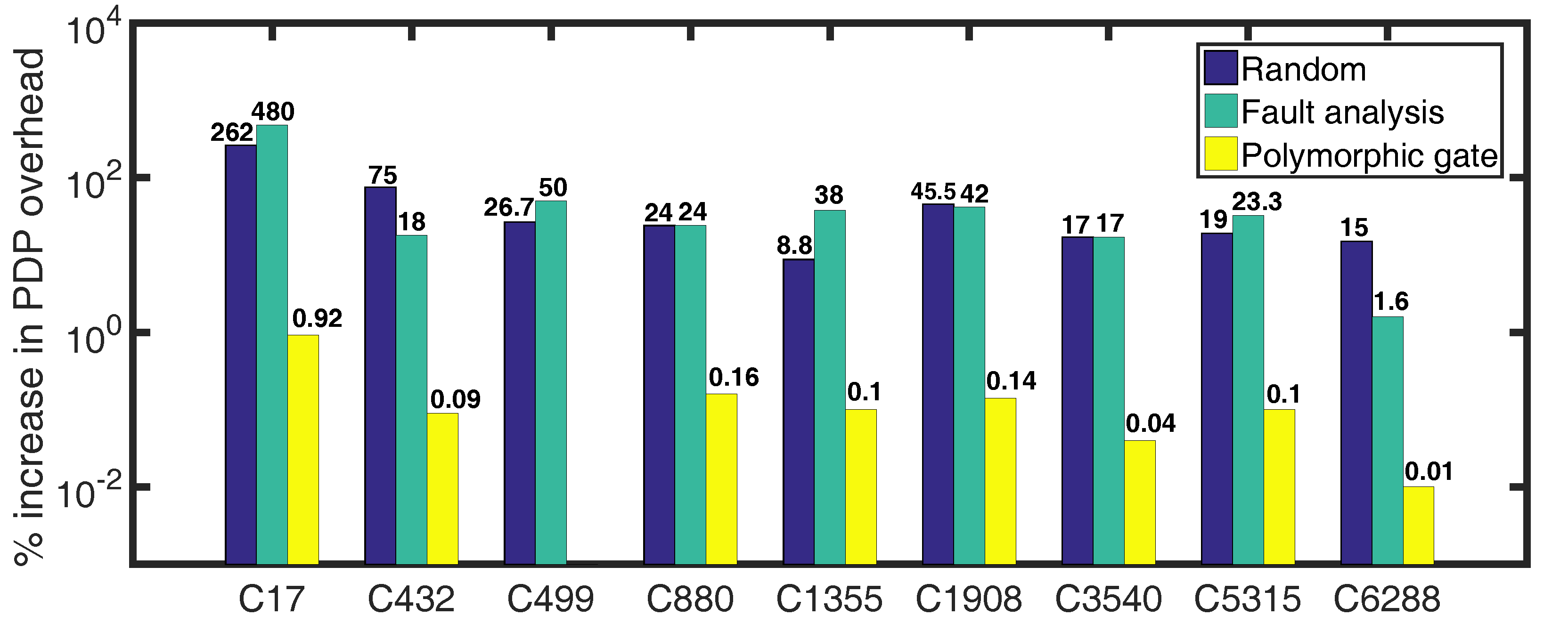
5.3. Performance Overhead
6. Discussion
6.1. Attacker’s Perspectives
6.1.1. SAT Based Attack
6.1.2. Sensitization of the Secret Key-Bits Based Attack
6.1.3. Applying Brute Force Attacks
6.2. Key Generations
6.3. Testing in an Untrusted Foundry
6.4. Beyond SiNW FETs
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Computing Research Association (CRA). Defense Science Board (DSB) Study on High Performance Microchip Supply. Available online: http://www.cra.org/govaffairs/images/2005-02-HPMS_Report_Final.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2016).
- Adee, S. The Hunt for the Kill Switch. IEEE Spectr. 2008, 45, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, A. Trends in the Global IC Design Service Market; DIGITIMES Research: Taipei, Taiwan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). Estimating the Global Economic and Social Impacts of Counterfeiting and Piracy: A Report Commissioned by Business Action to Stop Counterfeiting and Piracy (BASCAP); Frontier Economics Ltd.: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, J.; Pino, Y.; Sinanoglu, O.; Karri, R. Security Analysis of Logic Obfuscation. In Proceedings of the DAC’12 49th Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 June 2012; pp. 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.; Shamsi, K.; Yuan, J.-S.; Gaillardon, P.-E.; De Micheli, G.; Yin, X.; Hu, X.S.; Michael, N.; Jin, Y. Emerging Technology based Design of Primitives for Hardware Security. J. Emerg. Technol. Comput. Syst. ACM 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Shamsi, K.; Yuan, J.S.; Standaert, F.X.; Jin, Y. Leverage Emerging Technologies for DPA-Resilient Block Cipher Design. In Proceedings of the 2016 Design, Automation Test in Europe Conference Exhibition (DATE), Dresden, Germany, 14–18 March 2016; pp. 1538–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y.; Shamsi, K.; Yuan, J.S.; Jin, Y.; Niemier, M.; Hu, X.S. Tunnel FET Current Mode Logic for DPA-Resilient Circuit Designs. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2016, 5, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colli, A.; Pisana, S.; Fasoli, A.; Robertson, J.; Ferrari, A.C. Electronic transport in ambipolar silicon nanowires. Phys. Status Solidi (b) 2007, 244, 4161–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, R.; Derycke, V.; Lavoie, C.; Appenzeller, J.; Chan, K.K.; Tersoff, J.; Avouris, P. Ambipolar Electrical Transport in Semiconducting Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 256805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appenzeller, J.; Knoch, J.; Tutuc, E.; Reuter, M.; Guha, S. Dual-gate silicon nanowire transistors with nickel silicide contacts. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEDM’06 International Electron Devices Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–13 December 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- De Marchi, M.; Sacchetto, D.; Frache, S.; Zhang, J.; Gaillardon, P.; Leblebici, Y.; De Micheli, G. Polarity control in double-gate, gate-all-around vertically stacked silicon nanowire FETs. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–13 December 2012; pp. 8.4.1–8.4.4. [Google Scholar]
- Gaillardon, P.-E.; Bobba, S.; De Marchi, M.; Sacchetto, D.; De Micheli, G. NanoWire Systems: Technology and Design. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 2014, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoica, A.; Zebulum, R.S.; Keymeulen, D.; Ferguson, M.I.; Duong, V. Taking evolutionary circuit design from experimentation to implementation: Some useful techniques and a silicon demonstration. IEE Proc. Comput. Digit. Tech. 2004, 151, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, A.; Zebulum, R.S.; Keymeulen, D. Polymorphic Electronics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka, R. New polymorphic NAND/XOR gate. In Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Applied Computer Science, Venice, Italy, 21–23 November 2007; Volume 2007, pp. 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Rose, G.S.; Pino, Y.; Sinanoglu, O.; Karri, R. Fault Analysis-Based Logic Encryption. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2015, 64, 410–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.A.; Koushanfar, F.; Markov, I.L. EPIC: Ending Piracy of Integrated Circuits. In Proceedings of the 2008 DATE ’08 Design, Automation and Test in Europe, Munich, Germany, 10–14 March 2008; pp. 1069–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, J.; Pino, Y.; Sinanoglu, O.; Karri, R. Logic encryption: A fault analysis perspective. In Proceedings of the Conference on Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Dresden, Germany, 12–16 March 2012; pp. 953–958. [Google Scholar]
- Baumgarten, A.; Tyagi, A.; Zambreno, J. Preventing IC Piracy Using Reconfigurable Logic Barriers. IEEE Des. Test Comput. 2010, 27, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasad, Q.; Bi, Y.; Yuan, J. E2LEMI:Energy-Efficient Logic Encryption Using Multiplexer Insertion. Electronics 2017, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanyan, P.; Ray, S.; Malik, S. Evaluating the security of logic encryption algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware Oriented Security and Trust (HOST), Washington, DC, USA, 5–7 May 2015; pp. 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Yasin, M.; Rajendran, J.; Sinanoglu, O.; Karri, R. On Improving the Security of Logic Locking. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2016, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasad, Q.; Yuan, J.; Fan, D. Leveraging All-Spin Logic to Improve Hardware Security. In Proceedings of the GLSVLSI’17 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI 2017, Banff, AB, Canada, 10–12 May 2017; pp. 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Srivastava, A. Mitigating SAT Attack on Logic Locking. Cryptology ePrint Archive, Report 2016/590, 2016. Available online: http://eprint.iacr.org/2016/590 (accessed on 17 January 2017).
- Yasin, M.; Mazumdar, B.; Sinanoglu, O.; Rajendran, J. Security analysis of Anti-SAT. In Proceedings of the 2017 22nd Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), Chiba, Japan, 16–19 January 2017; pp. 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Yasin, M.; Mazumdar, B.; Rajendran, J.J.V.; Sinanoglu, O. SARLock: SAT attack resistant logic locking. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware Oriented Security and Trust (HOST), McLean, VA, USA, 3–5 May 2016; pp. 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Yasin, M.; Sengupta, A.; Schafer, B.; Makris, Y.; Sinanoglu, O.; Rajendran, J. What to Lock?: Functional and Parametric Locking. In Proceedings of the GLSVLSI’17 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI 2017, Banff, AB, Canada, 10–12 May 2017; pp. 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, R.S.; Bhunia, S. HARPOON: An Obfuscation-Based SoC Design Methodology for Hardware Protection. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2009, 28, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, J.; Kanuparthi, A.K.; Zahran, M.; Addepalli, S.K.; Ormazabal, G.; Karri, R. Securing Processors Against Insider Attacks: A Circuit-Microarchitecture Co-Design Approach. IEEE Des. Test 2013, 30, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.C.; Yalcin, H.; Hayes, J.P. Unveiling the ISCAS-85 Benchmarks: A Case Study in Reverse Engineering. IEEE Des. Test 1999, 16, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhou, H. Double DIP: Re-Evaluating Security of Logic Encryption Algorithms. In Proceedings of the GLSVLSI’17 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI 2017, Banff, AB, Canada, 10–12 May 2017; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsi, K.; Li, M.; Meade, T.; Zhao, Z.; Pan, D.Z.; Jin, Y. Cyclic Obfuscation for Creating SAT-Unresolvable Circuits. In Proceedings of the GLSVLSI’17 on Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI 2017, Banff, AB, Canada, 10–12 May 2017; pp. 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, R.; Kong, S. CycSAT: SAT-Based Attack on Cyclic Logic Encryptions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), Irvine, CA, USA, 13–16 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- El Massad, M.; Garg, S.; Tripunitara, M.V. Integrated circuit (IC) decamouflaging: Reverse engineering camouflaged ics within minutes. NDSS 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubeuf, J.; Hély, D.; Karri, R. Run-time detection of hardware Trojans: The processor protection unit. In Proceedings of the 2013 18th IEEE European Test Symposium (ETS), Avignon, France, 27–30 May 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yasin, M.; Sinanoglu, O. Transforming between logic locking and IC camouflaging. In Proceedings of the 2015 10th International Design Test Symposium (IDT), Amman, Jordan, 14–16 December 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, J.; Sinanoglu, O.; Karri, R. Regaining Trust in VLSI Design: Design-for-Trust Techniques. Proc. IEEE 2014, 102, 1266–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, G.K.; Rahman, M.T.; Tehranipoor, M. Secure Split-Test for preventing IC piracy by untrusted foundry and assembly. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Defect and Fault Tolerance in VLSI and Nanotechnology Systems (DFT), New York, NY, USA, 2–4 October 2013; pp. 196–203. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.T.; Forte, D.; Shi, Q.; Contreras, G.K.; Tehranipoor, M. CSST: Preventing distribution of unlicensed and rejected ICs by untrusted foundry and assembly. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Defect and Fault Tolerance in VLSI and Nanotechnology Systems (DFT), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1–3 October 2014; pp. 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta, S.; Rajashekhar, A.; Majumdar, K.; Agrawal, N.; Razavieh, A.; Trolier-Mckinstry, S.; Datta, S. Sub-kT/q Switching in Strong Inversion in PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 Gated Negative Capacitance FETs. IEEE J. Explor. Solid State Comput. Devices Circuits 2015, 1, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Polymorphic Gates | Techniques | # of Transistors | Publications |
|---|---|---|---|
| XOR/NAND | 3.3/0V External signal | 9 | [17] |
| NOR/NAND | 1.8/3.3V VDD | 6 | [15] |
| OR/AND | 3.3/1.2V VDD | 8 | [16] |
| XOR/AND/OR | 1.5/3.3/0.0V External signals | 10 | [16] |
| OR/AND | 0.0/3.3V External signals | 6 | [16] |
| AND/NAND/XOR/NOR | 1.8/0.0/1.1/0.9V External signals | 11 | [16] |
| OR/AND | 125/27 C Temperatures | 6 | [16] |
| NOR/NAND | exchanging key and | 4 | Our Work |
| Benchmark Circuits | # of XOR PLGs | # of NAND PLGs | # of AND PLGs | # of XOR/XNOR Gates [19,20] | Hamming Distance (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ran [19] | FA [20] | PLGs | |||||
| C17 | - | 3 | - | 6 | 42 | 51 | 53 |
| C432 | - | 10 | 1 | 17 | 29 | 50 | 50.06 |
| C499 | 16 | - | - | 40 | 26 | 50 | 50 |
| C880 | - | 18 | 13 | 28 | 19 | 50 | 48.3 |
| C1355 | - | 32 | 1 | 42 | 26 | 50 | 50 |
| C1908 | - | 23 | 4 | 28 | 26 | 50 | 49.9 |
| C3540 | - | 8 | 13 | 22 | 23 | 50 | 49.9 |
| C5315 | - | 4 | 91 | 97 | 15 | 44 | 45.6 |
| C6288 | - | 26 | 1 | 27 | 32 | 50 | 50 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alasad, Q.; Yuan, J.-S.; Bi, Y. Logic Locking Using Hybrid CMOS and Emerging SiNW FETs. Electronics 2017, 6, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics6030069
Alasad Q, Yuan J-S, Bi Y. Logic Locking Using Hybrid CMOS and Emerging SiNW FETs. Electronics. 2017; 6(3):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics6030069
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlasad, Qutaiba, Jiann-Shuin Yuan, and Yu Bi. 2017. "Logic Locking Using Hybrid CMOS and Emerging SiNW FETs" Electronics 6, no. 3: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics6030069
APA StyleAlasad, Q., Yuan, J.-S., & Bi, Y. (2017). Logic Locking Using Hybrid CMOS and Emerging SiNW FETs. Electronics, 6(3), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics6030069





