Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy: A Complementary Approach Differentiating PID Mechanisms in Photovoltaics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Causes for PID Mechanisms
3. Methodology
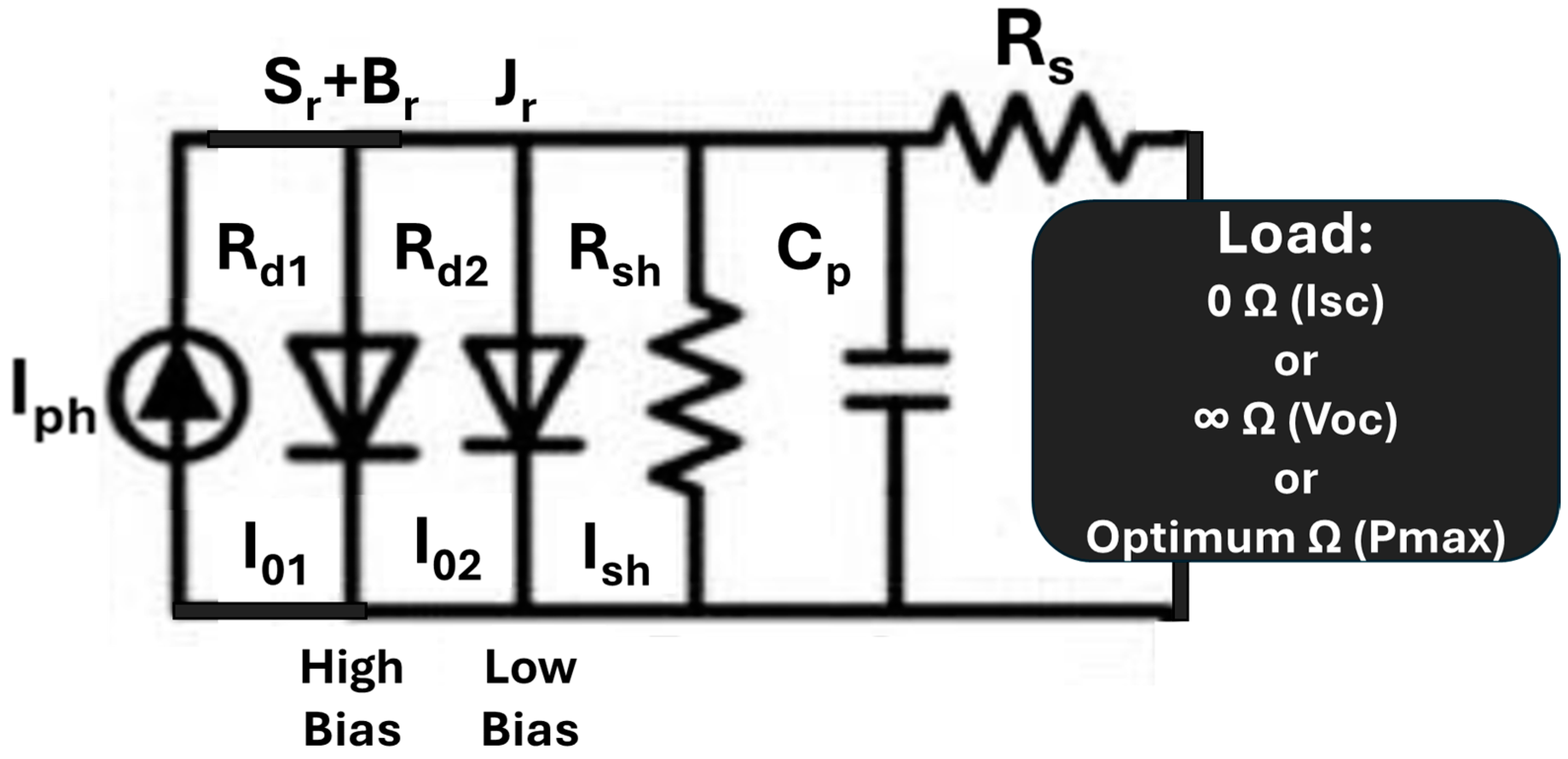
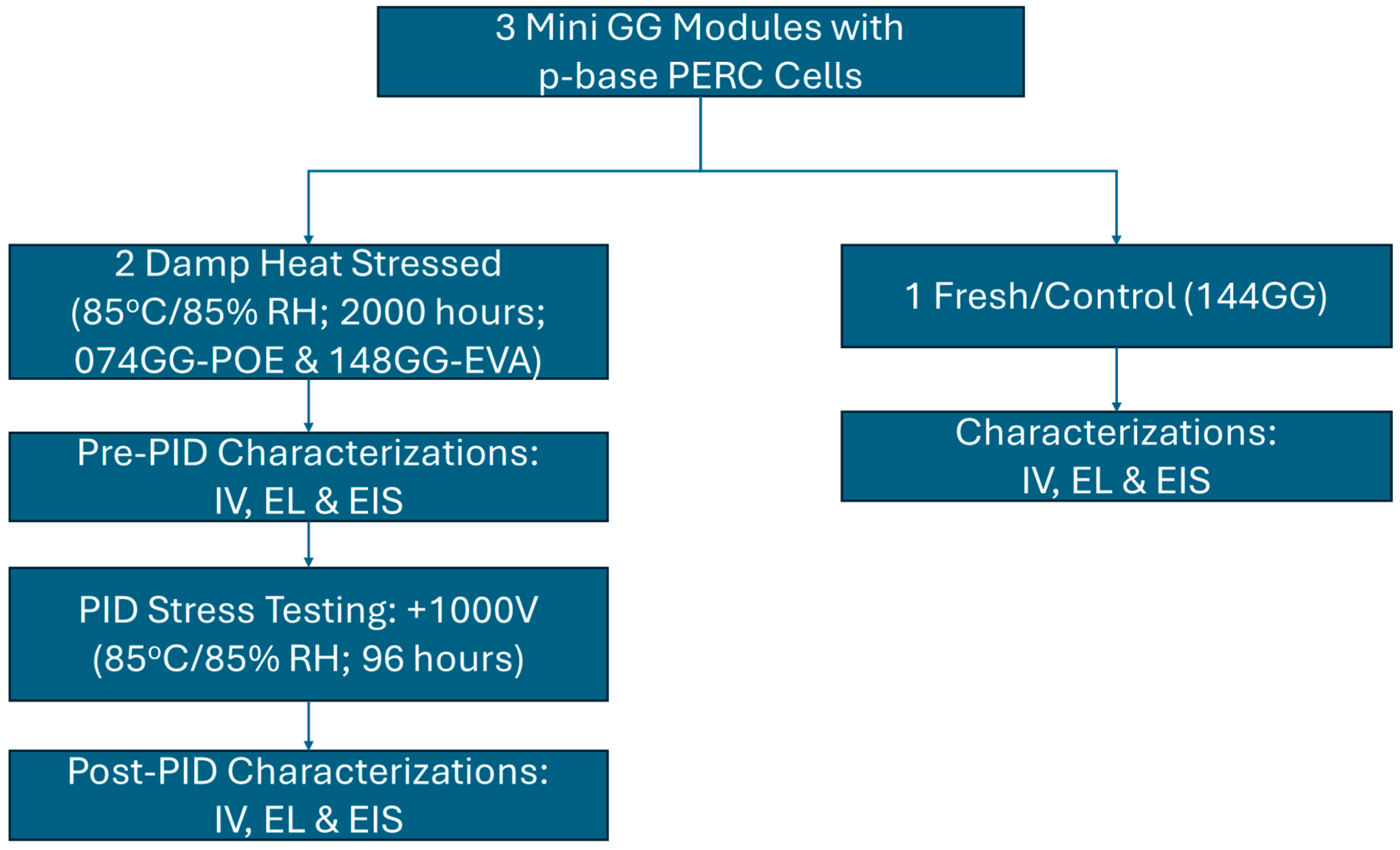
3.1. Construction, DH, and PID Stressing of PV Modules
3.2. Current–Voltage (I–V) Measurements
3.3. Electroluminescence (EL) Imaging
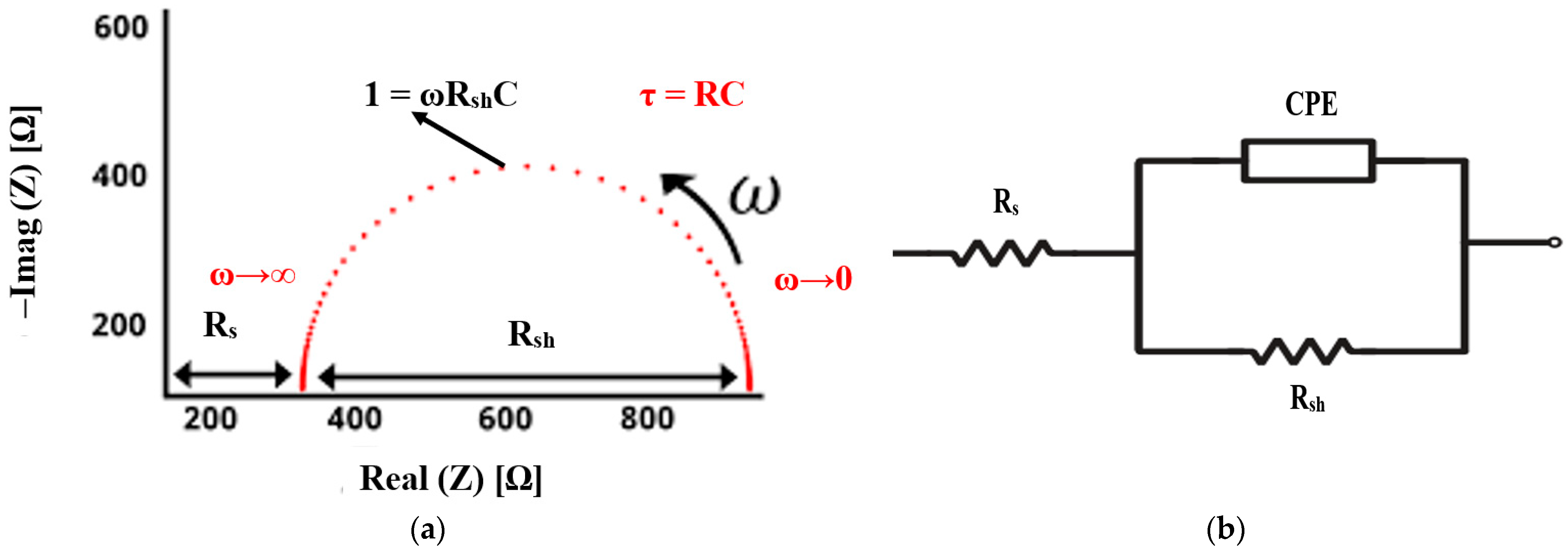
3.4. Electrochemical/Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) Measurements
4. Results and Discussion
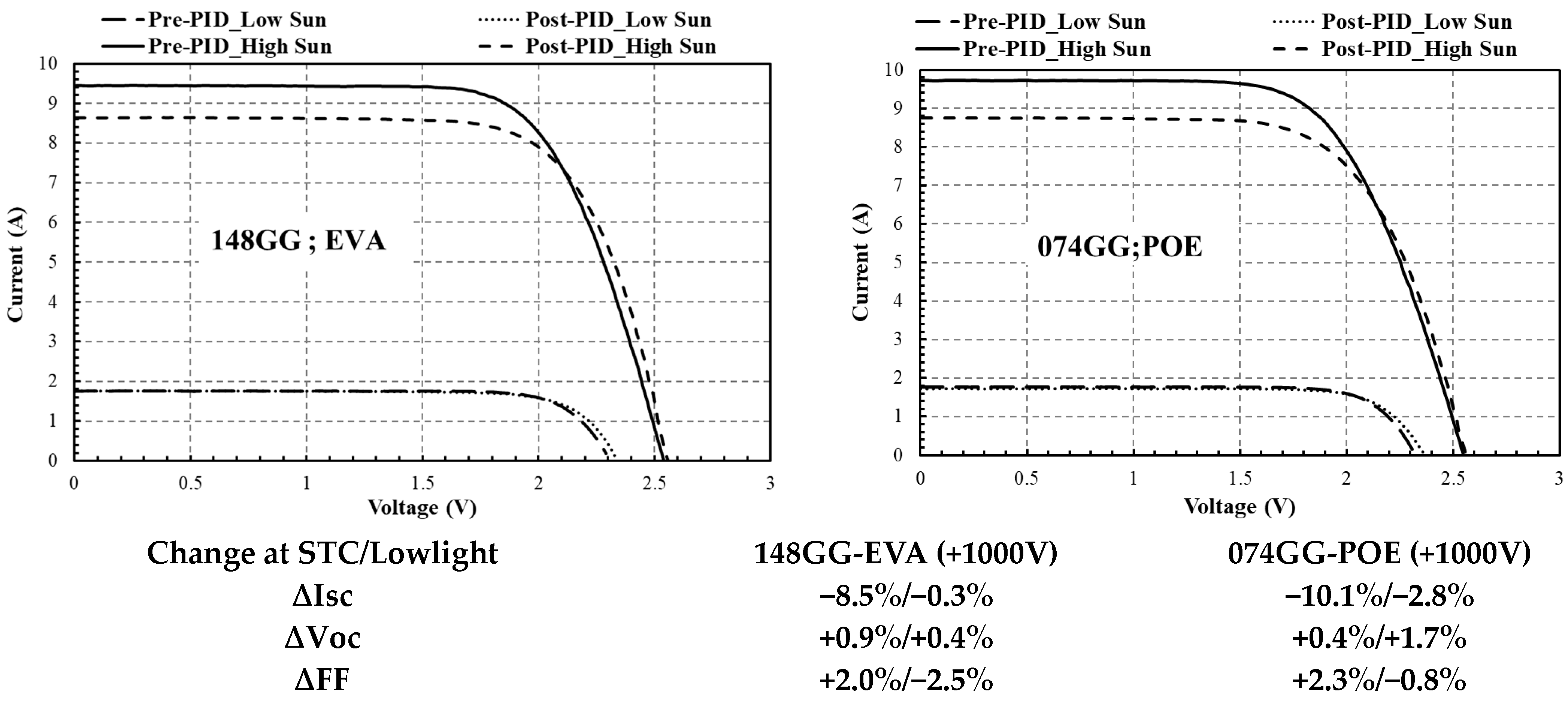
4.1. I–V Results
4.2. EL Results
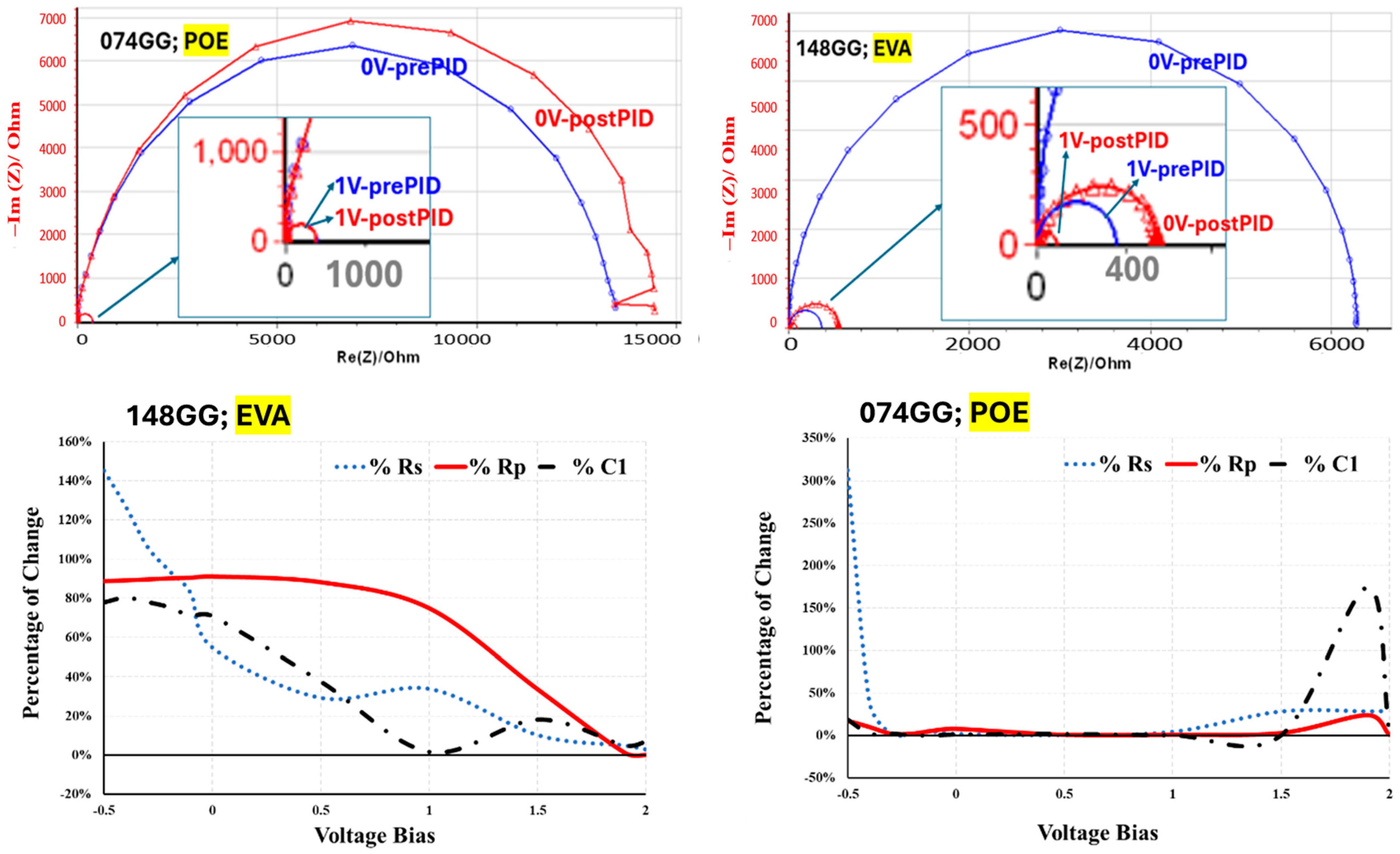
4.3. EIS Results
4.4. EIS Complementing I–V for PID Differentiation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahdi, H.A.; Leahy, P.G.; Alghoul, M.; Morrison, A.P. A Review of Photovoltaic Module Failure and Degradation Mechanisms: Causes and Detection Techniques. Solar 2024, 4, 43–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Khoo, Y.S.; Hacke, P.; Naumann, V.; Lausch, D.; Harvey, S.P.; Singh, J.P.; Chai, J.; Wang, Y.; Aberle, A.G.; et al. Potential-induced degradation in photovoltaic modules: A critical review. Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingel, S.; Frank, O.; Winkler, M.; Daryan, S.; Geipel, T.; Hoehne, H.; Berghold, J. Potential Induced Degradation of solar cells and panels. In Proceedings of the 35th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 20–25 June 2010; pp. 2817–2822. [Google Scholar]
- Naumann, V.; Lausch, D.; Bauer, J.; Breitenstein, O.; Graff, A.; Hagendorf, C. Explanation of potential-induced degradation in crystalline silicon solar cells by Na-based doping at the SiO2/Si interface. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2013, 120, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, W.; Watanabe, A. Degradation behaviors of encapsulant materials in field-aged photovoltaic modules. Renew. Energy 2017, 102, 208–217. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, D.C.; Silverman, T.J.; Wohlgemuth, J.H.; Kurtz, S.R.; Van Sant, K.T. Photovoltaic failure and degradation modes. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 2017, 25, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacke, P.; Terwilliger, K.; Glick, S.H.; Smith, R.; Pankow, J.; Kempe, M. System voltage potential-induced degradation mechanisms in PV modules and methods for test. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2015, 5, 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Molto, C.; Oh, J.; Mahmood, F.I.; Li, M.; Hacke, P.; Li, F.; Smith, R.; Colvin, D.; Matam, M.; Di Rubio, C.; et al. Review of Potential-Induced Degradation in Bifacial Photovoltaic Modules. Energy Technol. 2023, 11, 2200943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeow, T.; Sun, J.; Yao, Z.; Jaubert, J.-N.; Musselman, K.P. Evaluation of impedance spectroscopy as a tool to characterize degradation mechanisms in silicon photovoltaics. Sol. Energy 2019, 184, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Jonai, S.; Nakamura, K.; Marumoto, K.; Ohshita, Y.; Masuda, A. Polarization-Type Potential-Induced Degradation in Front-Emitter p-Type and n-Type Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 36277–36285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.A. Commercial progress and challenges for photovoltaics. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullal, H.S.; von Roedern, B. Thin-film CIGS and CdTe photovoltaics: Technology and market status. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar]
- IEC 61215; Terrestrial Photovoltaic (PV) Modules—Design Qualification and Type Approval. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- IEC 63209-1; Photovoltaic Modules—Extended-Stress Testing—Part 1: Modules. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Sacco, G.; Rizzo, A.; Acciarri, M. Impedance spectroscopy characterization of photovoltaic modules. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 157, 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Shelembe, B.; Alamoud, A.R.M.; Reddy, K.T.R. Analysis of electrical characteristics of thin-film solar cells using impedance spectroscopy. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2019, 9, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar]
- Bisquert, J.; Garcia-Belmonte, G.; Bueno, P.; Longo, E.; Bulhões, L.O.S. Impedance of constant phase element (CPE)-blocked diffusion in film electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1998, 452, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Bias Voltage | 144GG (Fresh/Control) | 074GG, Pre-PID (PID-Stressed) | 074GG, Post-PID (PID-Stressed) | 148GG, Pre-PID (PID-Stressed) | 148GG, Post-PID (PID-Stressed) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 (Ω) | R2 (KΩ) | C1 (µF) | R1 (Ω) | R2 (KΩ) | C1 (µF) | R1 (Ω) | R2 (KΩ) | C1 (µF) | R1 (Ω) | R2 (KΩ) | C1 (µF) | R1 (Ω) | R2 (KΩ) | C1 (µF) | |
| Bias_−0.5 | 0.050 | 12.671 | 2.526 | 0.020 | 51.540 | 2.628 | 0.081 | 42.530 | 3.127 | 0.055 | 7.477 | 2.884 | 0.136 | 0.832 | 5.128 |
| Bias_−0.4 | 0.051 | 12.474 | 2.609 | 0.057 | 46.588 | 3.083 | 0.080 | 41.881 | 3.163 | 0.060 | 7.586 | 2.958 | 0.136 | 0.814 | 5.331 |
| Bias_−0.3 | 0.051 | 12.009 | 2.668 | 0.079 | 37.283 | 3.066 | 0.080 | 36.476 | 3.139 | 0.066 | 7.591 | 3.028 | 0.135 | 0.777 | 5.389 |
| Bias_−0.2 | 0.051 | 11.200 | 2.701 | 0.080 | 27.917 | 3.050 | 0.082 | 28.518 | 3.067 | 0.069 | 7.431 | 3.085 | 0.135 | 0.721 | 5.411 |
| Bias_−0.1 | 0.028 | 9.898 | 2.684 | 0.082 | 19.400 | 3.000 | 0.086 | 20.543 | 3.012 | 0.075 | 6.998 | 3.132 | 0.137 | 0.657 | 5.353 |
| Bias_0 | 0.046 | 8.528 | 2.649 | 0.086 | 13.433 | 2.957 | 0.084 | 14.488 | 2.917 | 0.092 | 6.305 | 3.096 | 0.142 | 0.552 | 5.286 |
| Bias_0.5 | 0.046 | 2.258 | 2.700 | 0.113 | 2.070 | 2.670 | 0.112 | 2.053 | 2.618 | 0.101 | 2.014 | 2.886 | 0.130 | 0.235 | 3.971 |
| Bias_1 | 0.083 | 0.359 | 3.171 | 0.118 | 0.381 | 2.698 | 0.123 | 0.377 | 2.683 | 0.110 | 0.361 | 3.314 | 0.148 | 0.090 | 3.258 |
| Bias_1.5 | 0.134 | 0.037 | 3.967 | 0.201 | 0.036 | 3.467 | 0.144 | 0.035 | 3.454 | 0.156 | 0.038 | 4.086 | 0.172 | 0.025 | 4.830 |
| Bias_1.9 | 0.165 | 0.002 | 39.602 | 0.352 | 0.001 | 50.084 | 0.252 | 0.002 | 137.510 | 0.268 | 0.001 | 16.790 | 0.255 | 0.001 | 15.952 |
| Bias_2 | 0.161 | 0.001 | 24.032 | 0.397 | 0.0004 | 52.016 | 0.281 | 0.0004 | 50.041 | 0.282 | 0.0004 | 31.906 | 0.274 | 0.0004 | 29.673 |
| Dominant PID Loss Mechanism | Solar Cell Loss Mechanism | Affects Isc in IV * | Affects Voc in IV * | Affects FF in IV * | Affects Rs in EIS | Affects Rp in EIS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIDp (Polarization) | Surface recombination under +ve 1000V PID of 074GG with POE encapsulant (surface recombination increases) | −10.1%/−2.8% | +0.4%/+1.7% | +2.3%/−0.8% | 0% | 0% |
| PIDjr (Junction Recombination) | Junction recombination under +ve 1000V PID of 148GG with EVA encapsulant (diode dynamic resistance decrease) | −8.5%/+0.3% | +0.9%/+0.4% | +2.0%/−2.5% | 56% (0.09 → 0.14 Ω) | 91% (6.31 → 0.55 kΩ) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Tayeb, A.; Li, F.; Kumar, A.; Tamizhmani, G. Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy: A Complementary Approach Differentiating PID Mechanisms in Photovoltaics. Electronics 2025, 14, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14051021
El-Tayeb A, Li F, Kumar A, Tamizhmani G. Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy: A Complementary Approach Differentiating PID Mechanisms in Photovoltaics. Electronics. 2025; 14(5):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14051021
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Tayeb, A., Fang Li, Akash Kumar, and Govindasamy Tamizhmani. 2025. "Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy: A Complementary Approach Differentiating PID Mechanisms in Photovoltaics" Electronics 14, no. 5: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14051021
APA StyleEl-Tayeb, A., Li, F., Kumar, A., & Tamizhmani, G. (2025). Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy: A Complementary Approach Differentiating PID Mechanisms in Photovoltaics. Electronics, 14(5), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14051021







