A New Impedance Measurement Method for Wind Farms Considering the Influence of Background Harmonics
Abstract
1. Introduction
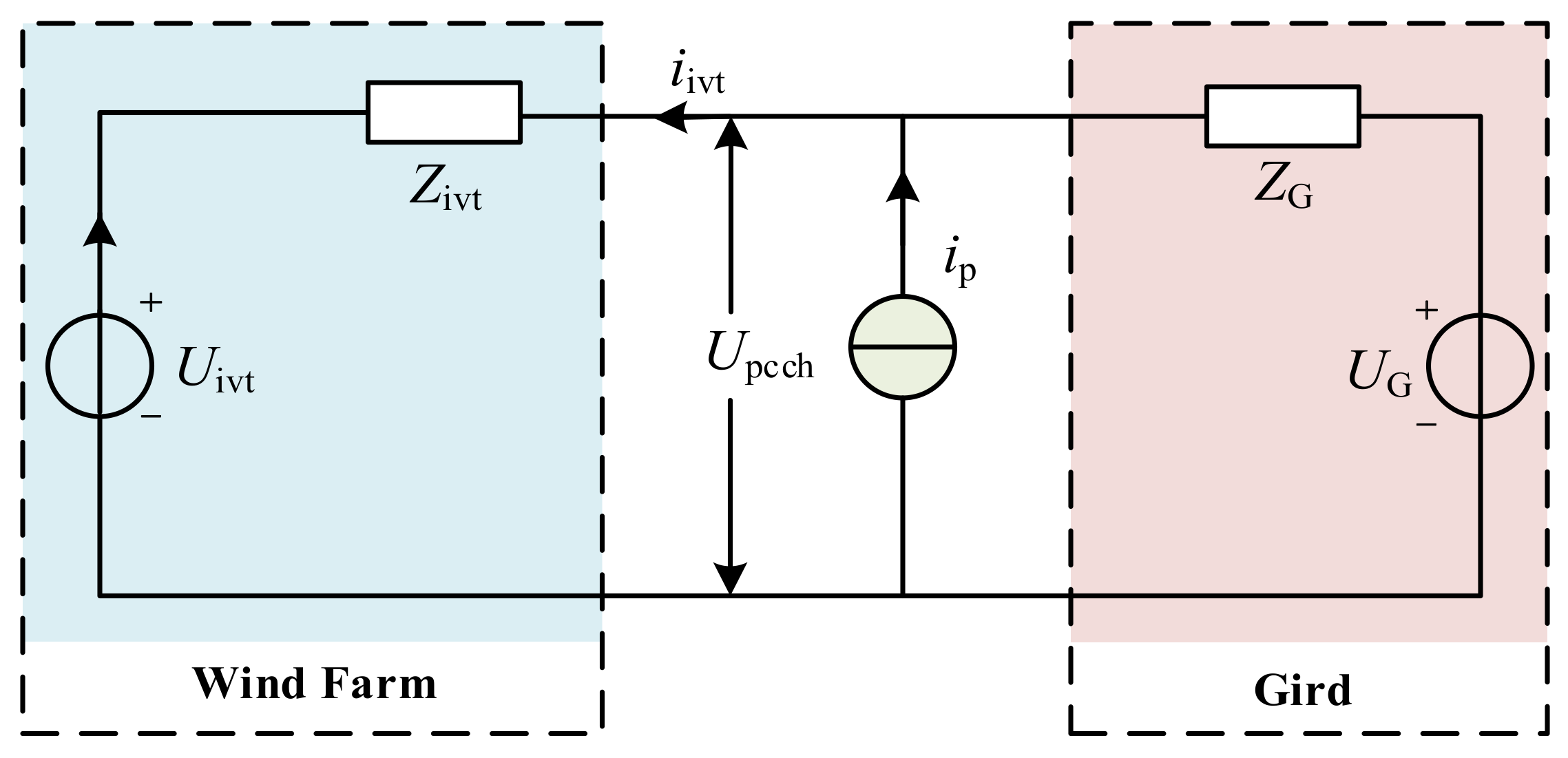
2. Impedance Measurement Device for Current Disturbance
2.1. Measurement Object and Disturbance Injection Unit
2.2. Control Strategy of the Disturbance Injection Unit
2.3. Process of Perturbation Injection
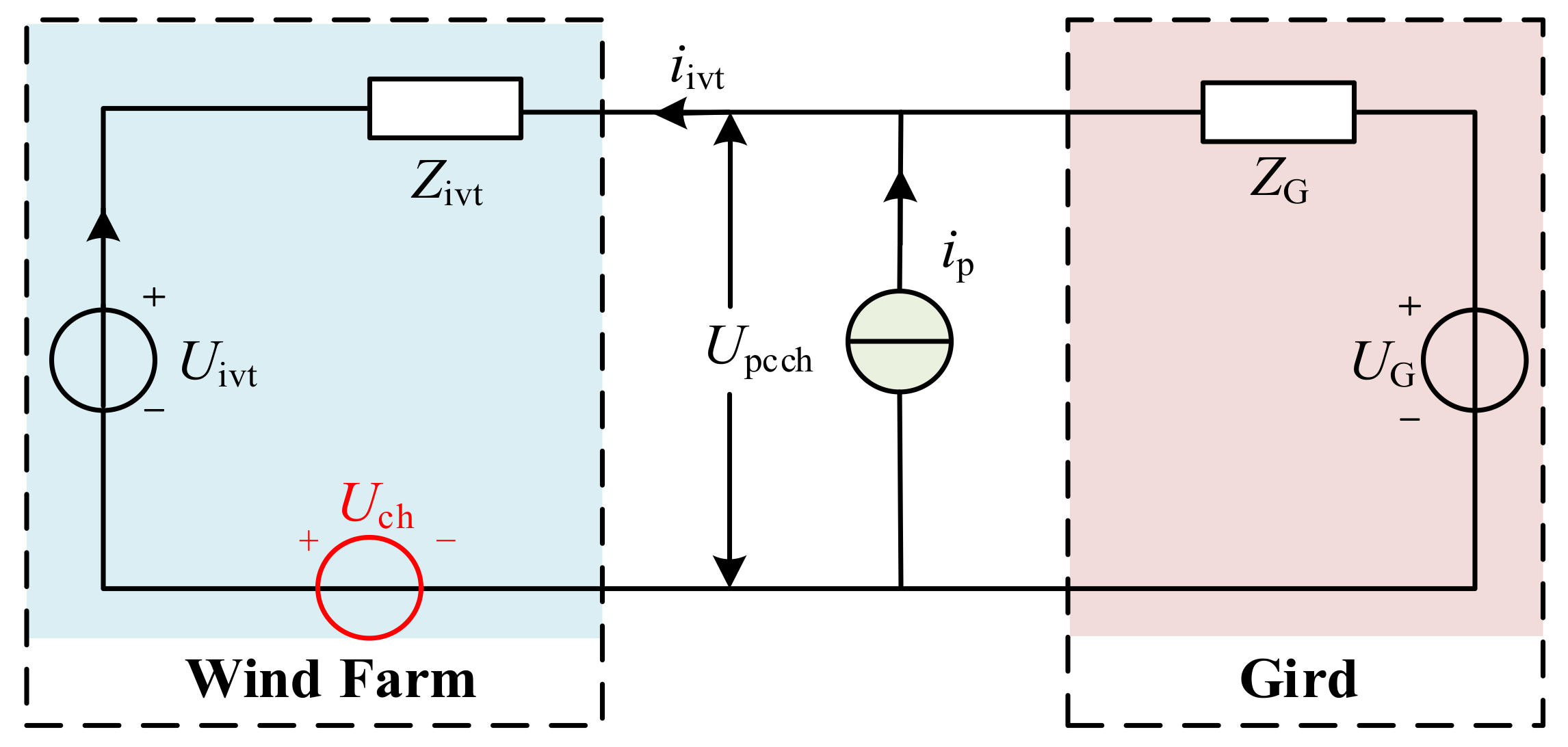
3. The Effect of Background Harmonic on Measurement and Its Simulation Analysis
3.1. Analysis of the Effect of Background Harmonic on Measurement
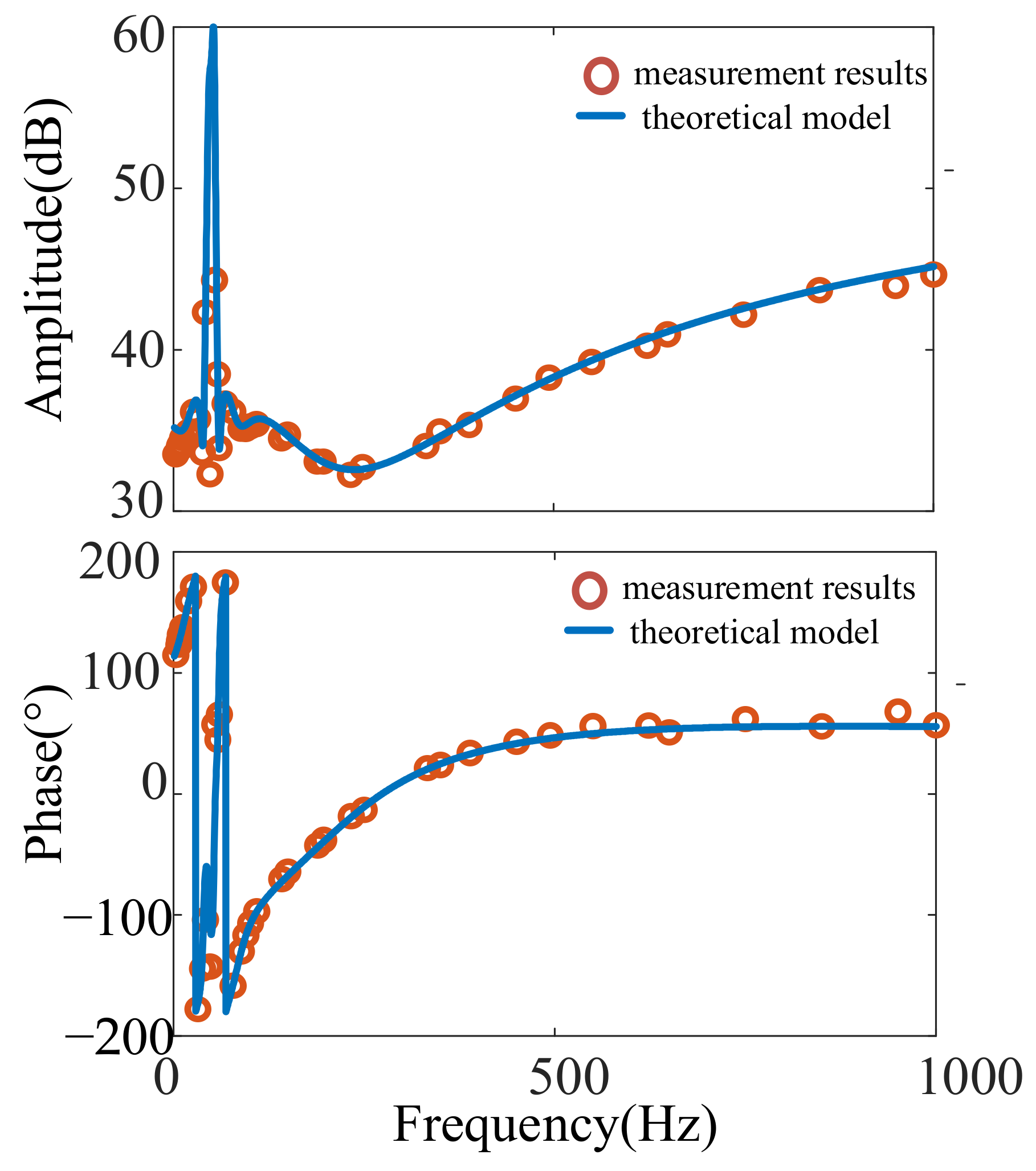
3.2. Simulation Verification of the Effect of Background Harmonic on Measurement
4. Adaptive Measurement Method
5. Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J. Impedance-based stability criterion for grid-connected inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 11, 3075–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, X.; Zhao, Y. A Novel Control Strategy for Enhancing System Stability in Weak Grids by Mitigating Additional Disturbance Components from PLL. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2024, 35, 02793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shen, H.; Du, X.; Chen, R. Condition Monitoring the Inhomogeneous Thermal Fatigue of Multichip IGBT Module Based on the Thermal Attenuation Coefficient. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 11, 2114–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, X.; Shi, Y.; Tai, H.-M. A new impedance measurement method and its application to stability analysis of the inverter-grid system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2021, 15, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Du, X.; Wang, G.; Tai, H.-M. Single stationary domain equivalent inverter admittance for three-phase grid-inverter system considering the interaction between grid and inverter. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, X.; Shi, Y.; Tai, H.-M. Impedance measurement of three-Phase inverter in the stationary frame using frequency response analyzer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 9390–9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Du, X. Model and stability analysis of grid-connected PV system considering the variation of solar irradiance and cell temperature. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 132, 107155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Du, X.; Tai, H.M. Two-variable admittance model for D-PMSG-based wind turbine and stability criterion based on magnitude and phase contour plot. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 1484–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Cai, H.; Song, Y.; Li, Z. Study on reactive power sharing of island microgrid based on synchronous compensatio. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2019, 34, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar]
- Gurumurthy, S.; Uhl, R.; Pitz, M.; Ponci, F.; Monti, A. Non-invasive wideband-frequency grid impedance measurement device. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 10th International Workshop on Applied Measurements for Power Systems, Aachen, Germany, 25–27 September 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Estevez, D.; Dovalgandoy, J. Grid impedance identification using the VSC switching ripple. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 September–3 October 2019; pp. 1506–1513. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Deng, H.; Goetzo, S. Grid impedance estimation through grid-forming power converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 2094–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, H.; Li, M.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y.; Hu, B. Measurement method for broadband frequency coupling characteristics of grid-con- nected inverter using multi-sine signal injection. Proc. CSEE 2020, 40, 7408–7420. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Zhuo, F.; Zhang, Z. Segmented binary tree method for power electronic system impedance measurement. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2015, 30, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Cvetkovic, I.; Shen, Z.; Boroyevich, D.; Burgos, R.; Liu, J. Imbalance mechanism and balancing control of DC voltages in a transformerless series injector based on paralleled H-bridge converters for AC impedance measurement. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 8175–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhuo, F.; Shi, H.; Zhang, D. New Techniques for Measuring Impedance Characteristics of an Islanded Microgrid Based on Stability Analysis. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2015, 30, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Ma, J.; Sun, R.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Liu, T. Adaptive current source intrusive sequence impedance measurement based on disturbance voltage orientation. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2022, 42, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Pu, T.; Chen, Y.; Luo, A.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.; Yang, L.; He, Z. Design and control method of megawatt broadband impedance measuring device. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2018, 38, 4096–4106. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Ganesh, K.; Kumar, A.; Jing, H. Recurrent Neural Networks Based Impedance Measurement Technique for Power Electronic Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 382–390. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Xiao, W.; Dong, Y.; Mads, C. Artificial Neural Network Based Identification of Multi-Operating-Point Impedance Model. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Nabil, M.; Wei, Z.; Behrooz, B.; David, H. Support Vector Machines for Predicting the Impedance Model of Inverter-Based Resources. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2024, 39, 7359–7375. [Google Scholar]











| Symbol | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Vg | Three-phase voltage sources | 66 V rms |
| m | Grid-connected current | 50 |
| Hsid | D-axis current controller of MSC | 0.89 + 147.98/s |
| Hsiq | Q-axis current controller of MSC | 1.93 + 2428.94/s |
| Hgi | Current controller of GSC | 0.22 + 217.82/s |
| Hv | Voltage controller of GSC | 0.89 + 147.98/s |
| Cdc | DC capacitor | 20 mF |
| Vdc | DC source voltage | 1500 V |
| kPLL_p | Proportion coefficient of PLL | 7.14 |
| kPLL_i | Integration coefficient of PLL | 3965.21 |
| Ts | Sampling period | 10−4 s |
| f0 | Grid frequency | 50 Hz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, T.; Wei, Z.; Du, X.; Liu, J. A New Impedance Measurement Method for Wind Farms Considering the Influence of Background Harmonics. Electronics 2025, 14, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030501
Xue T, Wei Z, Du X, Liu J. A New Impedance Measurement Method for Wind Farms Considering the Influence of Background Harmonics. Electronics. 2025; 14(3):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030501
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Teng, Ze Wei, Xiong Du, and Junliang Liu. 2025. "A New Impedance Measurement Method for Wind Farms Considering the Influence of Background Harmonics" Electronics 14, no. 3: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030501
APA StyleXue, T., Wei, Z., Du, X., & Liu, J. (2025). A New Impedance Measurement Method for Wind Farms Considering the Influence of Background Harmonics. Electronics, 14(3), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030501





