A Low-Complexity Hybrid Phase Shifter Network with Shared-Control Voltage for High-Scan-Gain Phased Arrays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design and Implementation of a Hybrid PSN with Shared-Control Voltage
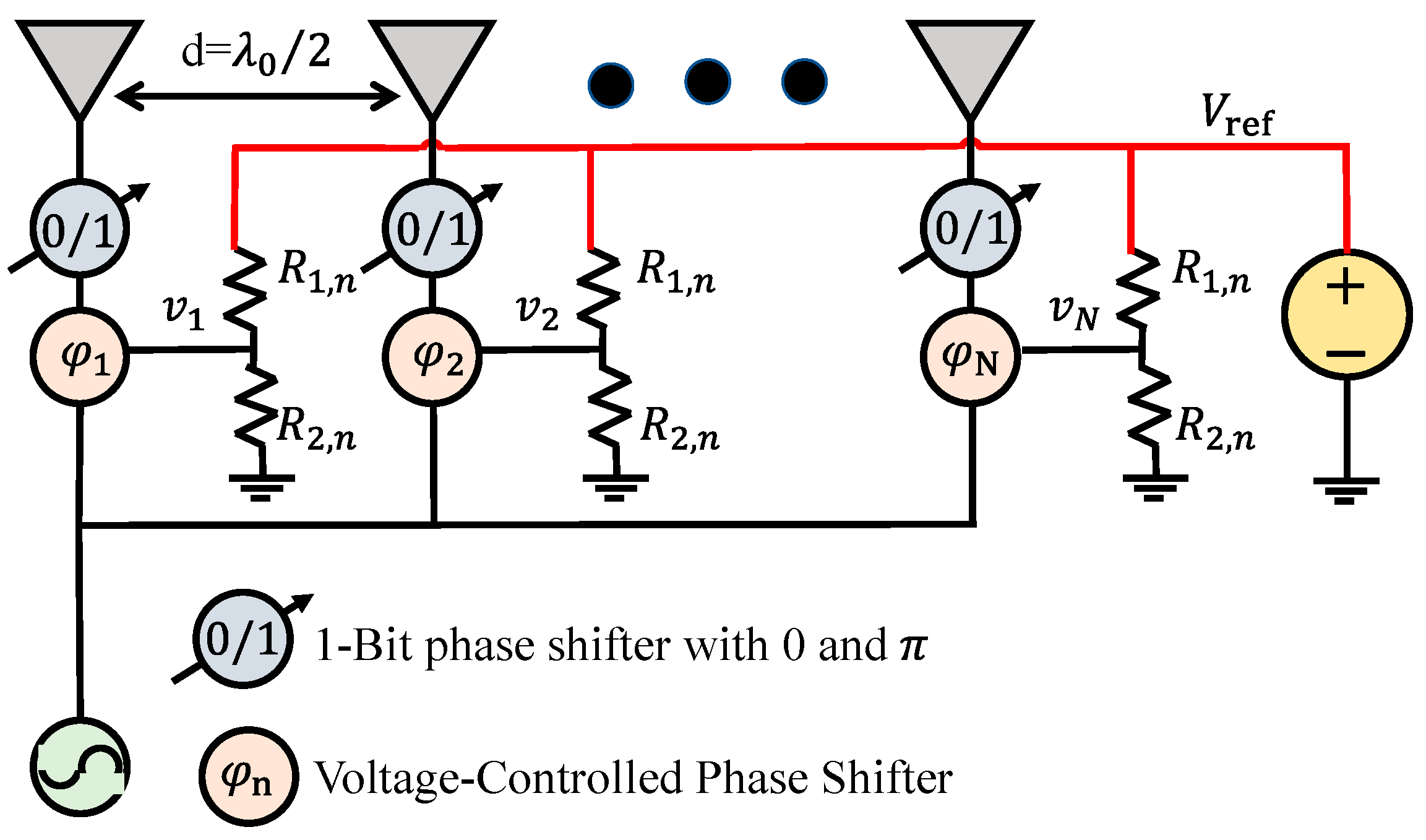
2.1. System Overview
2.2. System Performance Analysis
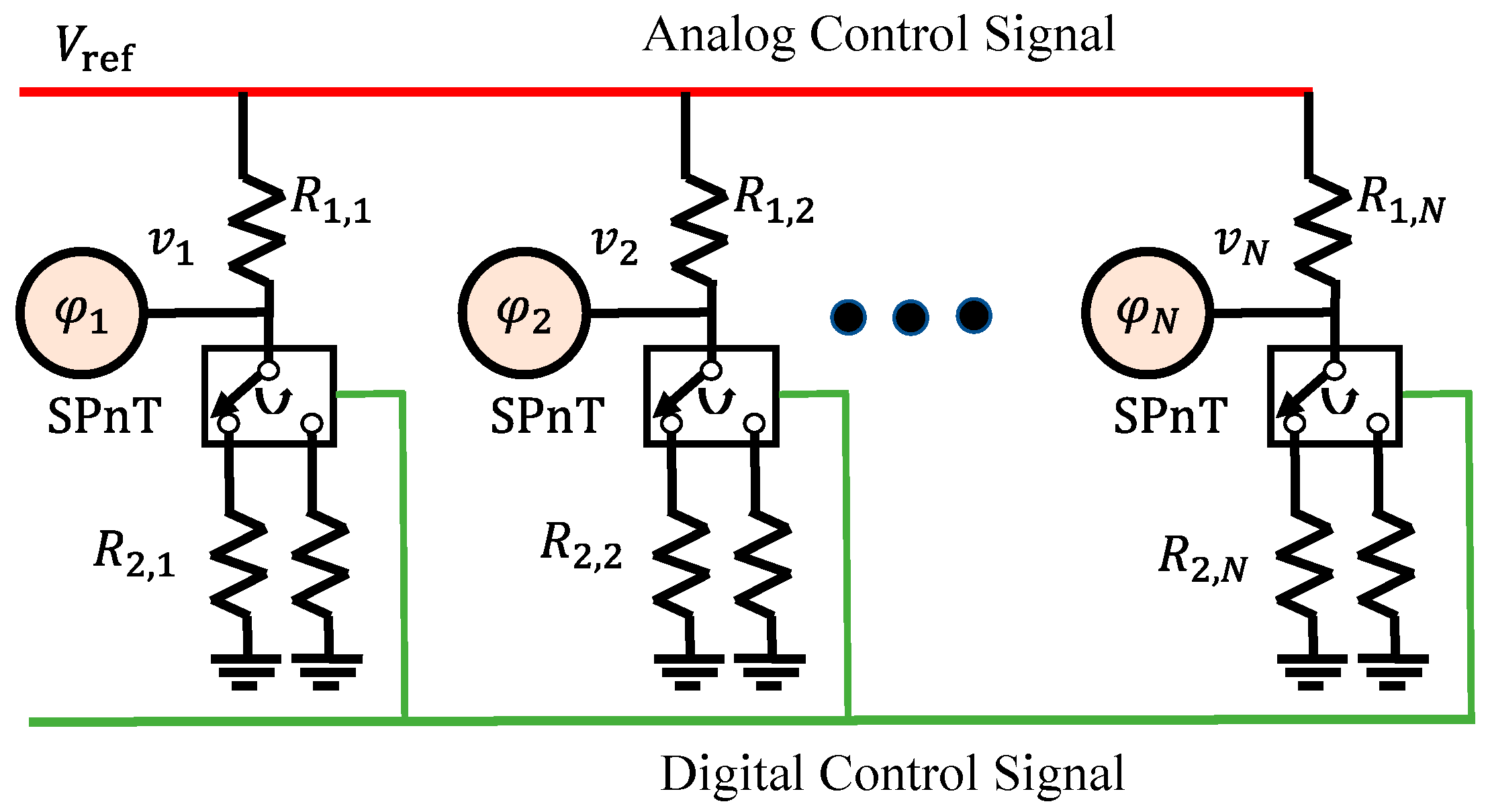
2.3. Design of the Hybrid PSN with a Shared-Control Voltage Scheme
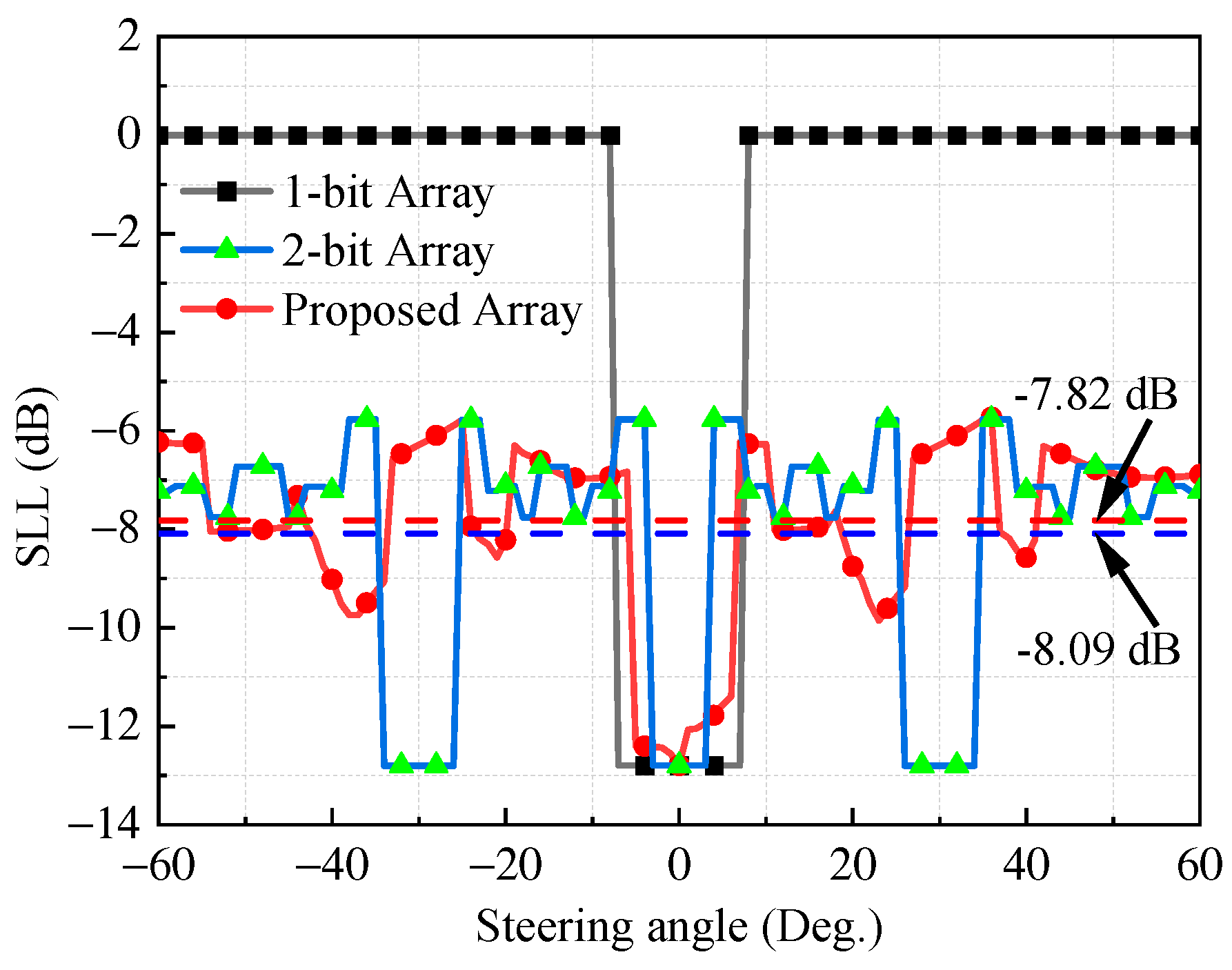
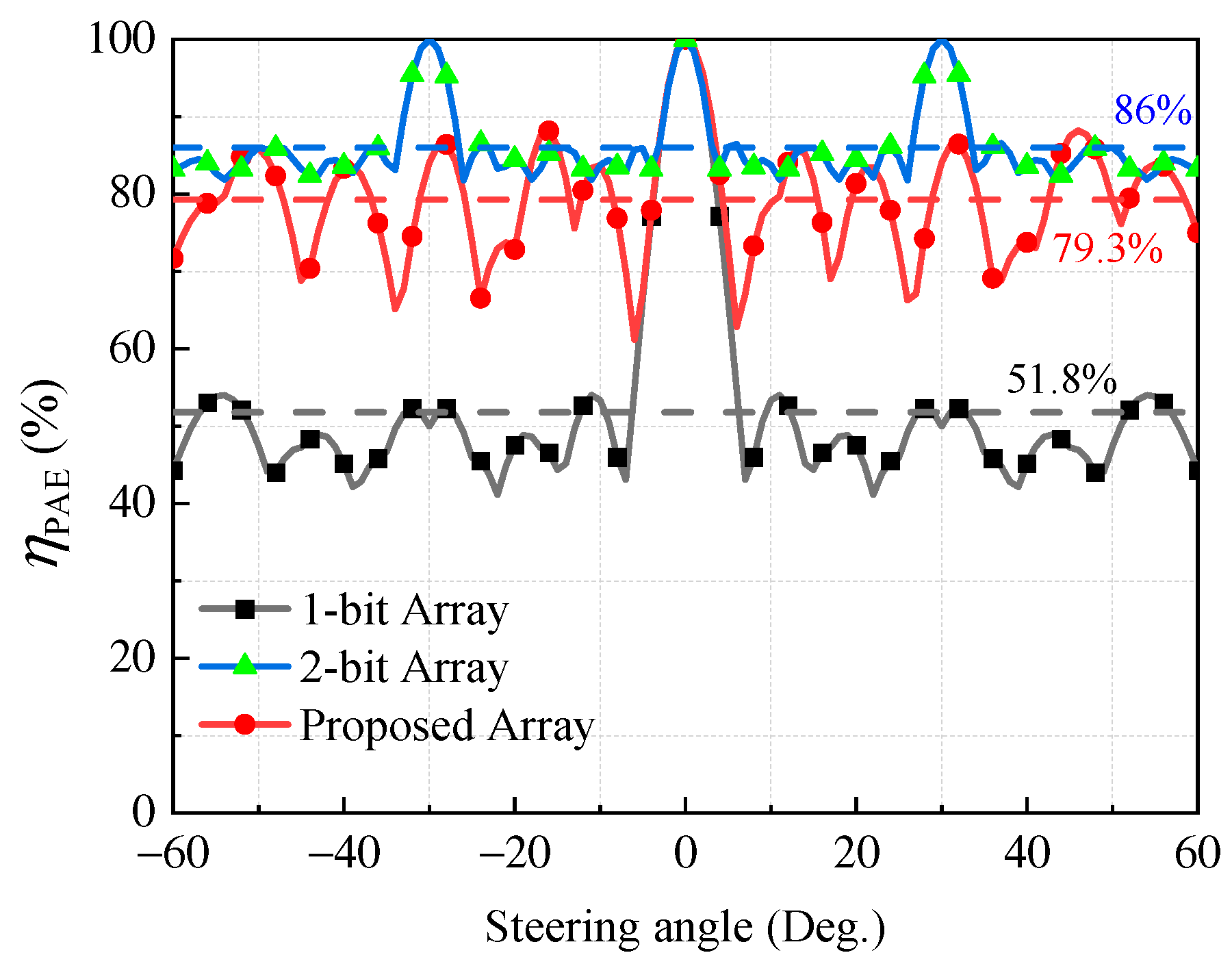
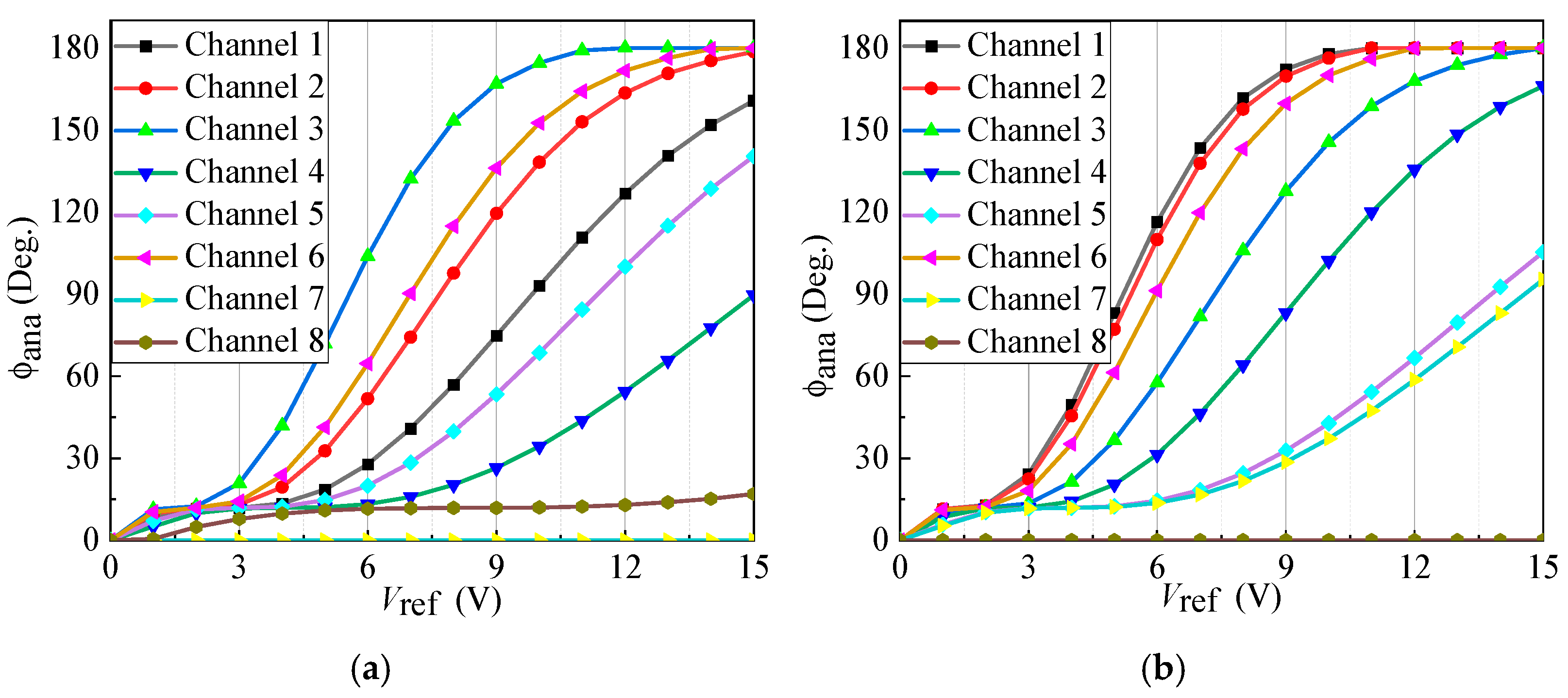
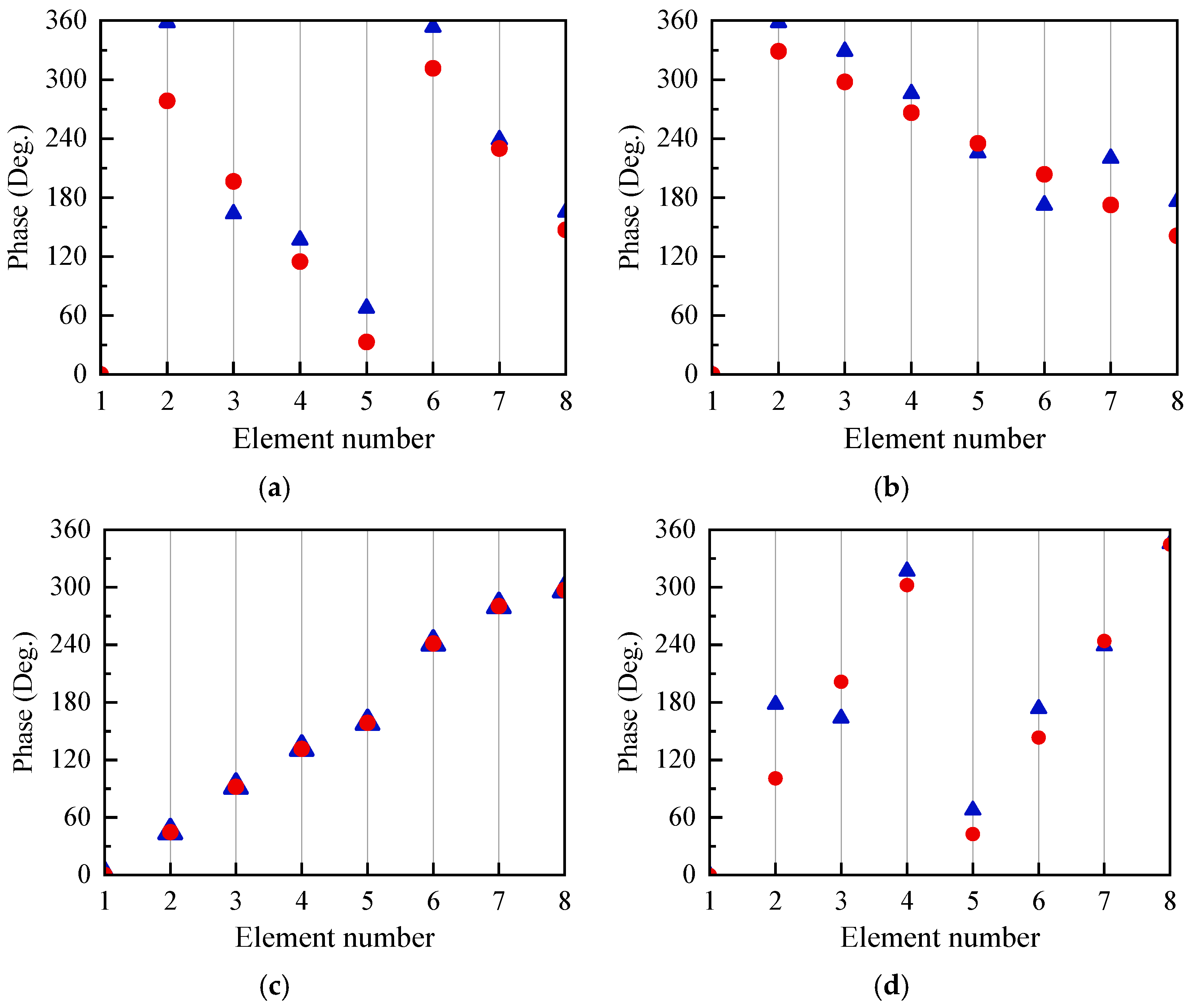
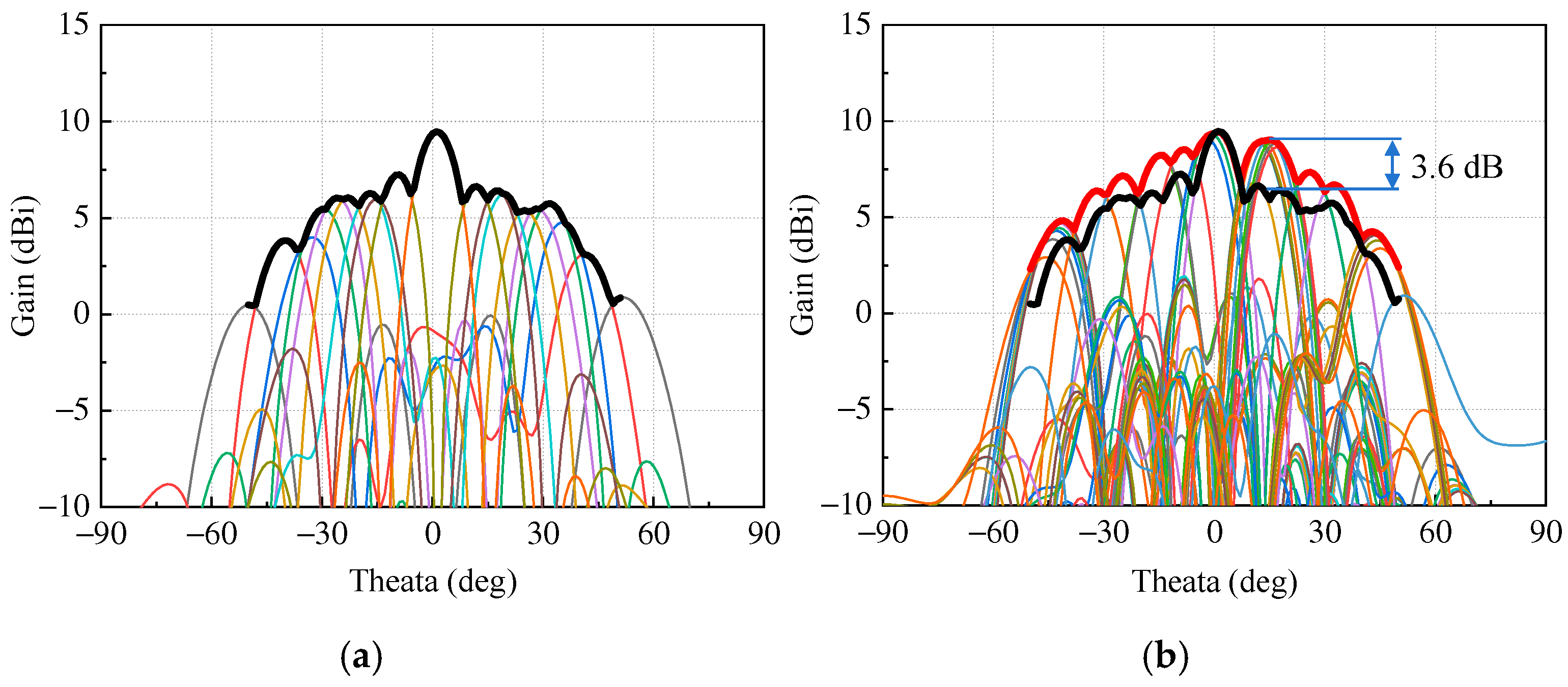
3. Numerical Results and Performance Evaluation
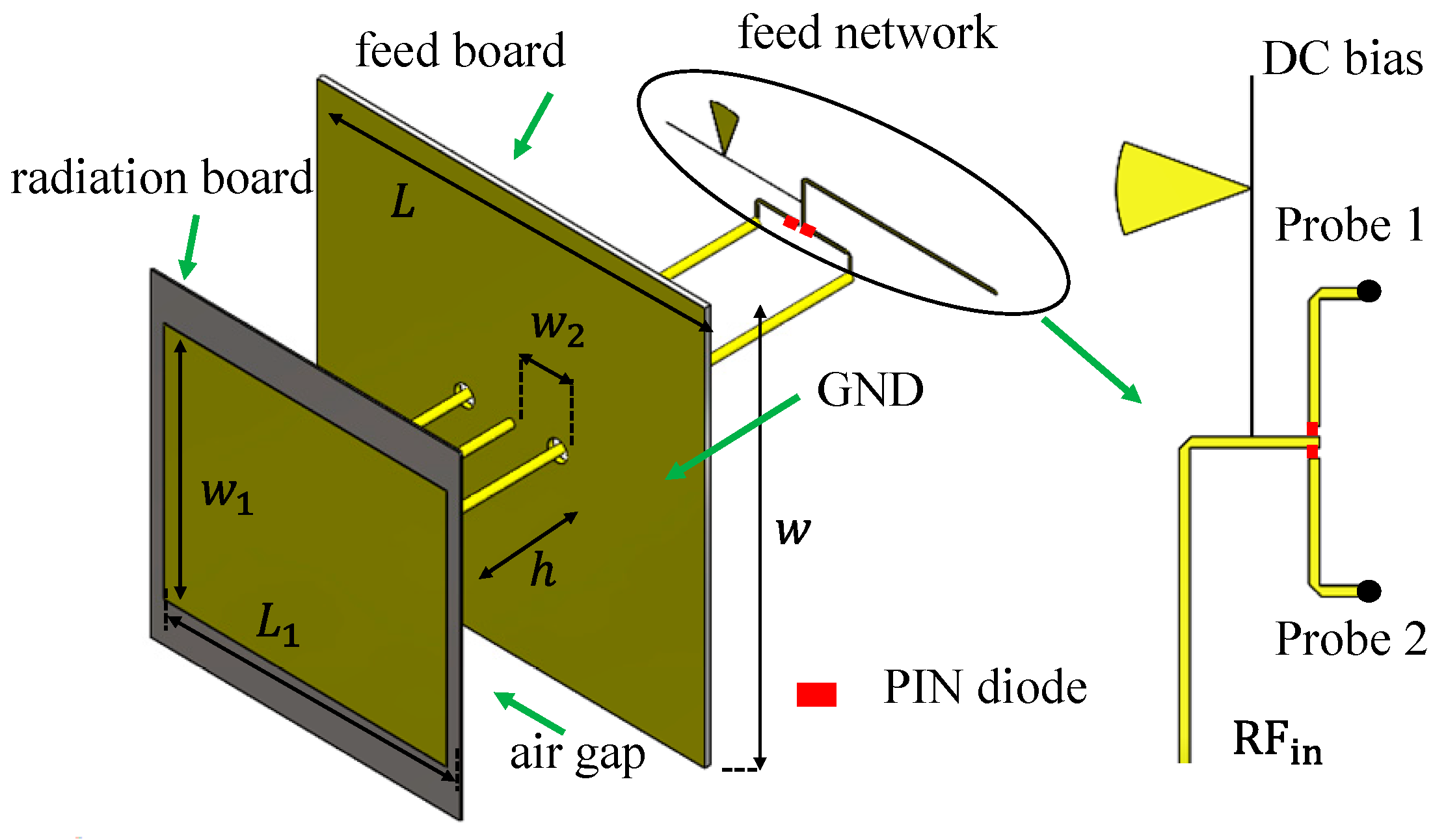
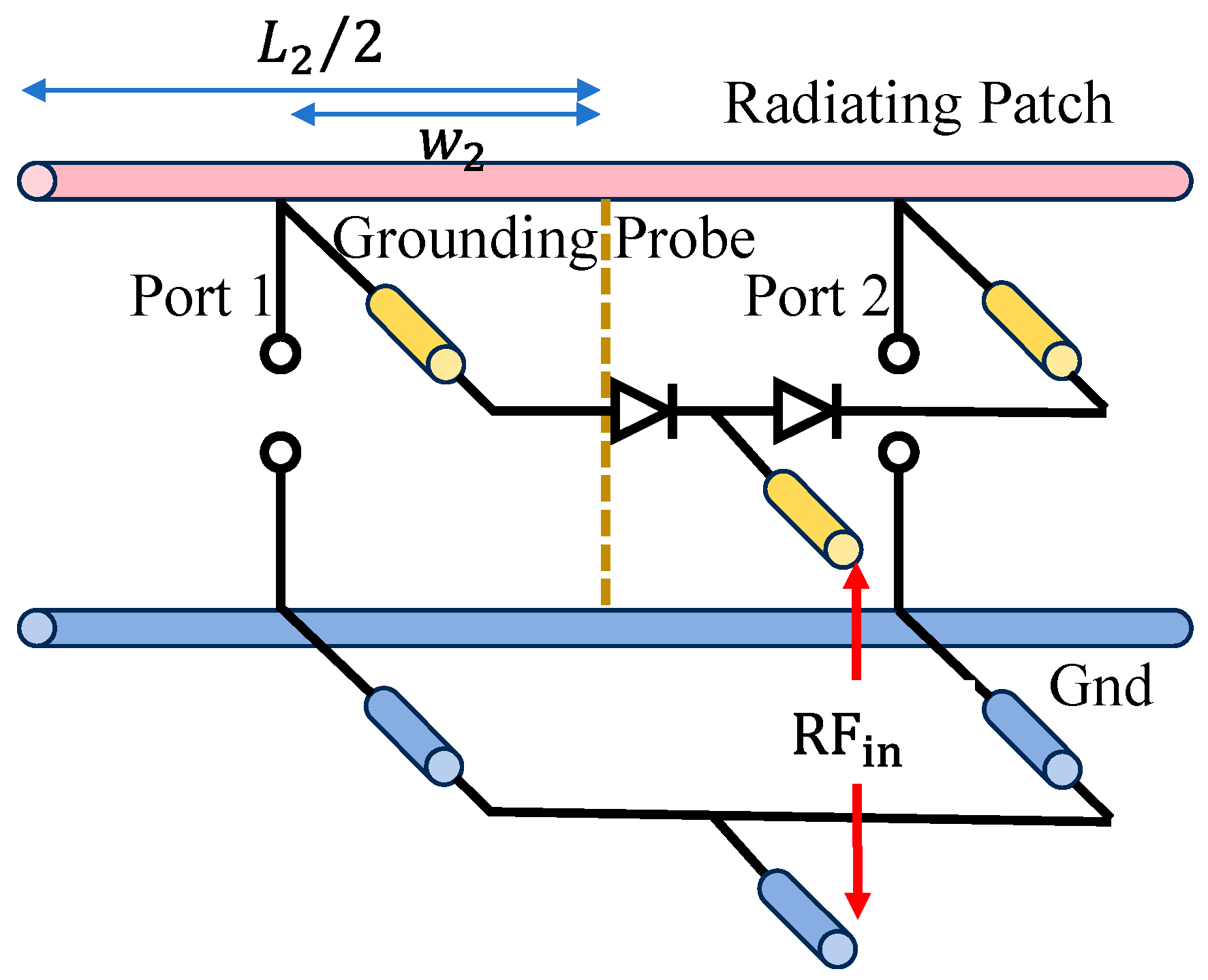
4. Element Design and Simulated Results
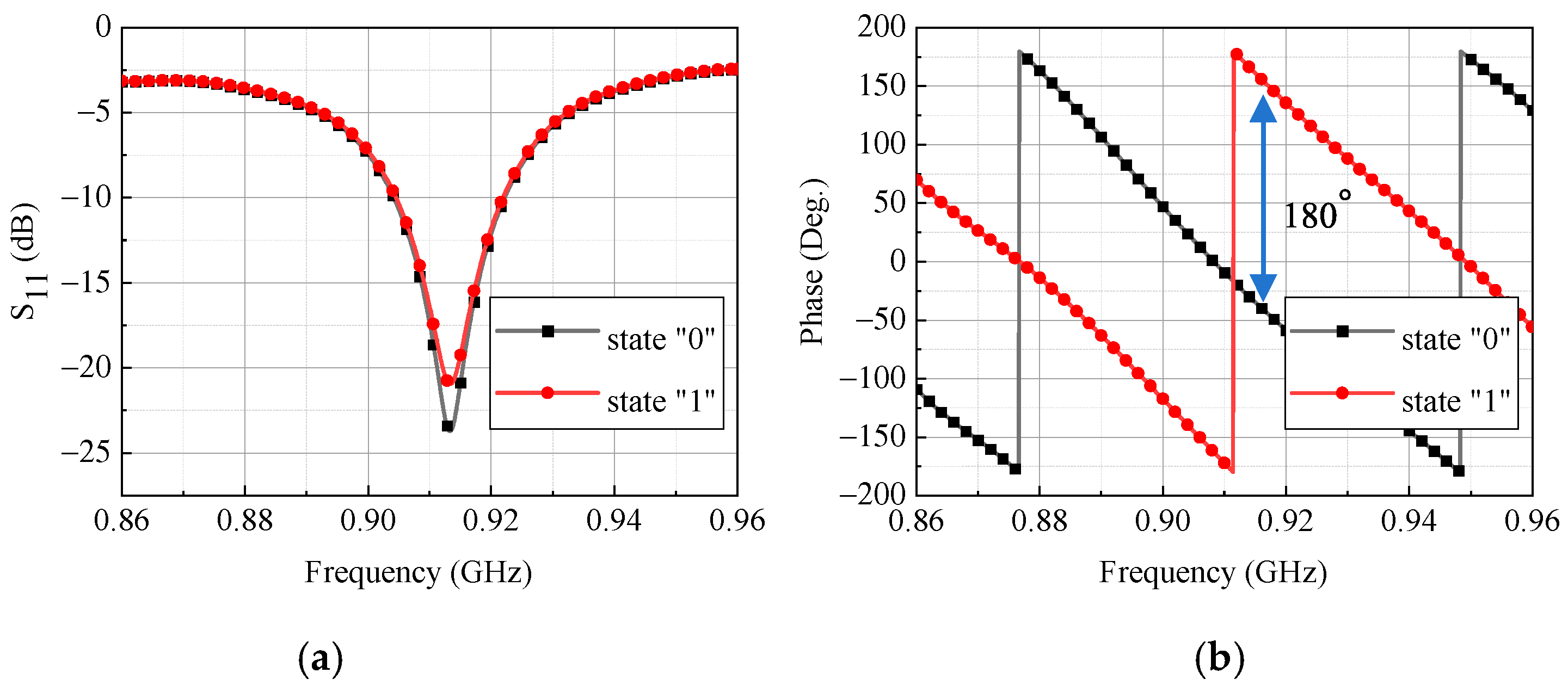
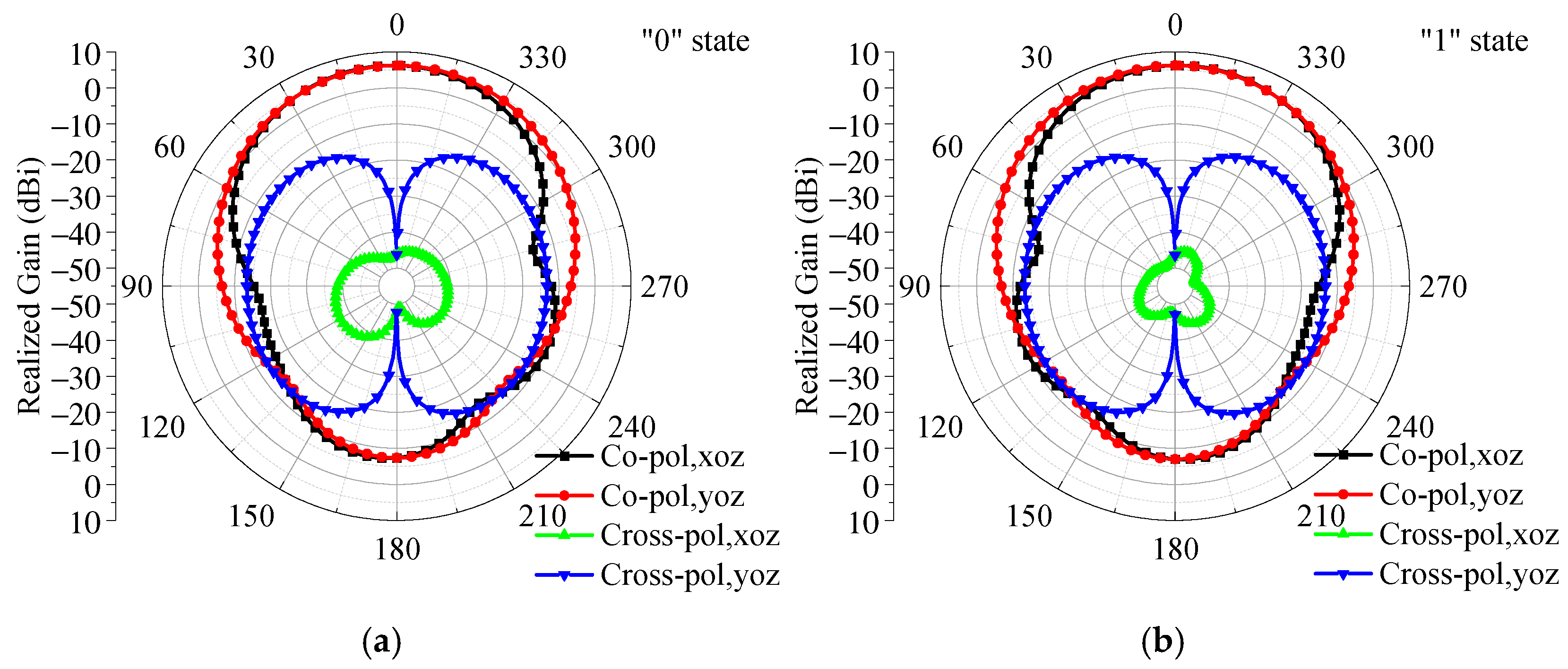
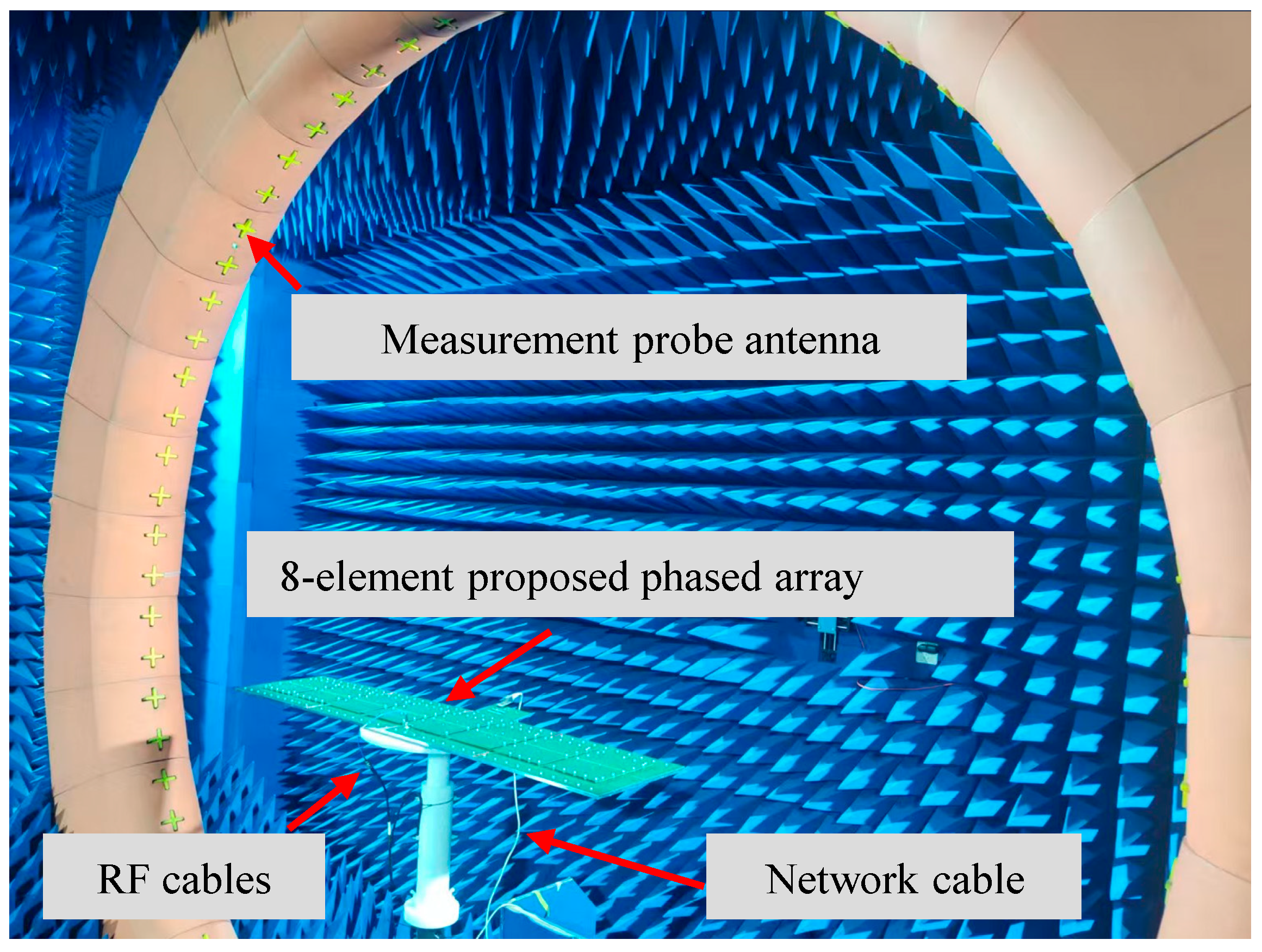
5. Experimental Validation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naqvi, A.H.; Lim, S. Review of Recent Phased Arrays for Millimeter-Wave Wireless Communication. Sensors 2018, 18, 3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, M. Advancements in Terahertz Communication: Harnessing the 300 GHz Band for High-Efficiency, High-Capacity Wireless Networks. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2024, E107C, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Wada, Y.; Yoshida, S. Recent Advances in Phased Array Weather Radar. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2024, E107C, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, T. Japanese Institutionalization and Global Standardization of Wireless Power Transmission, and Recently R&D Trend in Japan. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2024, E107C, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Guo, Y.C.; Liu, T.H.; Shen, W.F.; Cao, W. Comparison of random phasing methods for reducing beam pointing errors in phased array. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2003, 51, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebe, M.; Yagoub, M.C.E.; Amaya, R.E. A Survey of Phase Shifters for Microwave Phased Array Systems. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2025, 53, 3719–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wu, R.; Wang, Y.; Dome, M.; Kato, H.; Huang, H.; Narayanan, A.T.; Liu, H.; Liu, B.; Nakamura, T.; et al. A 28-GHz CMOS Phased-Array Transceiver Based on LO Phase-Shifting Architecture with Gain Invariant Phase Tuning for 5G New Radio. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avitabile, G.; Man, K.L.; Talarico, C. DDS-PLL Architecture for Adaptive Beam Steering. In Proceedings of the 2024 21st International SoC Design Conference (ISOCC), Sapporo, Japan, 19–22 August 2024; pp. 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, A.; Coviello, G.; Talarico, C.; Avitabile, G. Adaptive DDS-PLL Beamsteering Architecture based on Real-Time Angle-of-Arrival Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 67th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Springfield, MA, USA, 11–14 August 2024; pp. 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, A.; Coviello, G.; Talarico, C.; Avitabile, G. Adaptive Beamsteering Architecture Based on AoA Estimation with Phase Shift on LO-Path for 5G NR. In Proceedings of the 2024 9th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech), Bol and Split, Croatia, 25–28 June 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Rebeiz, G.M. An Eight-Element 136–147 GHz Wafer-Scale Phased-Array Transmitter with 32 dBm Peak EIRP and >16 Gbps 16QAM and 64QAM Operation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2022, 7, 1635–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Rupakula, B.; Rebeiz, G.M. An Eight-Element 140-GHz Wafer-Scale IF Beamforming Phased-Array Receiver with 64-QAM Operation in CMOS RFSOI. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 57, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verho, S.; Chung, J.-Y. Design of a Compact and Minimalistic Intermediate Phase Shifting Feed Network for Ka-Band Electrical Beam Steering. Sensors 2024, 24, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, G.; Avitabile, G.; Coviello, G.; Talarico, C. DDS-PLL Phase Shifter Architectures for Phased Arrays: Theory and Techniques. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 19461–19470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibaroglu, K.; Sayginer, M.; Rebeiz, G.M. A Low-Cost Scalable 32-Element 28-GHz Phased Array Transceiver for 5G Communication Links Based on a 2 × 2 Beamformer Flip-Chip Unit Cell. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 1260–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, B.; Tousi, Y.; Hallin, J.; Sahl, S.; Reynolds, S.K.; Renström, Ö.; Sjögren, K.; Haapalahti, O.; Mazor, N.; Bokinge, B.; et al. A 28-GHz 32-Element TRX Phased-Array IC with Concurrent Dual-Polarized Operation and Orthogonal Phase and Gain Control for 5G Communications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 3373–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Yan, Y.; Liang, X. A novel 6.5–13.5GHz 6-bit digital phase shifter with ultra low RMS phase error in 0.25-µm GaAs p-HEMT technology. IEICE Electron. Express 2024, 21, 20240143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.T.; Entesari, K.; Hoyos, S. Multi-Channel Analog Beamforming Transceiver for mmWave Communications. IEEE. Trans. Mob. Comput. 2025, 24, 6106–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Lee, W. A Low-Loss Passive D-Band Phase Shifter for Calibration-Free, Precise Phase Control. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2024, 59, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jeong, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, S. A 19.5 GHz 5-bit digitally programmable phase shifter for active antenna arrays. Electronics 2023, 12, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Shin, H. A 28 GHz GaN 6-Bit Phase Shifter MMIC with Continuous Tuning Calibration Technique. Sensors 2024, 24, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.S.; Chang, S.F.; Chang, C.C.; Shu, Y.H. Design of a Reflection-Type Phase Shifter with Wide Relative Phase Shift and Constant Insertion Loss. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2007, 55, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.C.; Chang, C.C.; Chang, S.F.; Chin, T.Y. A 24-GHz full-360° CMOS reflection-type phase shifter MMIC with low loss-variation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 15–17 June 2008; pp. 327–330. [Google Scholar]
- Fakharzadeh, M.; Mousavi, P.; Safavi-Naeini, S.; Jamali, S.H. The effects of imbalanced phase shifters loss on phased array gain. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2008, 7, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.; Natarajan, A. A 28-GHz Low-Power Phased-Array Receiver Front-End with 360° RTPS Phase Shift Range. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 4703–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-W.; Wang, H. A Millimeter-Wave Fully Integrated Passive Reflection-Type Phase Shifter with Transformer-Based Multi-Resonance Loads for 360° Phase Shifting. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 65, 1406–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.F.; Wang, Y.T.; Feng, J.H.; Wu, L.S.; Qiu, L.F.; Mao, J.F. A Compact Ka-Band Hybrid Analog/Digital Phase Shifter with GaAs Technology. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2024, 71, 1834–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Z.; Jiang, C.; Xu, H. A 22.5~28.5-GHz Low-Amplitude-Variation Low-Phase-Error Hybrid Phase Shifter Using Flatness Enhancement Techniques for 5G NR in 40nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2025, 72, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.J.; Farouk, M.; Boumaiza, S. Digitally-Assisted 27–33 GHz Reflection-Type Phase Shifter with Enhanced Accuracy and Low IL-Variation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), Boston, MA, USA, 2–4 June 2019; pp. 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Khalidi, A.H.; Ahmed, M.M.; Abdullah, S.A. Uniform Linear Antenna array Beamsteering Based on Progressive Phase. Electronics 2023, 12, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sevilleja, S.; García-Rodríguez, M.; Masa-Campos, J.L.; Cuerda-Muñoz, J.M. Antenna Model with Pattern Optimization Based on Genetic Algorithm for Satellite-Based SAR Mission. Sensors 2025, 25, 4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Chip Model | Type | Number of Control Lines | Maximum Insertion Loss | Insertion Loss Fluctuation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMC936 | Dig. | 6 | −5 dB | ±1 dB |
| SPHSA-152 | Ana. | 1 | −3.8 dB | ±1 dB |
| hybrid configuration | hybrid | 2 | −1.2 dB | ±0.2 dB |
| Input: Steering angle set Target sidelobe level ; GA parameters: population size P, crossover probability , mutation probability , and maximum generation Performance threshold convergence threshold . Output: Optimized set of division ratio vectors |
|
| 0.047 | 0.146 | 0.877 | 0.428 | 0.420 | 0.950 | 0.178 | 0.867 | |
| 0.495 | 0.973 | 0.679 | 0.339 | 0.481 | 0.948 | 0.667 | 0.323 |
| 200 | 200 | 120 | 48 | 146 | 5 |
| 1 | 0.966 | 0.709 | 0.556 | 0.377 | 0.873 | 0.357 | 0.001 | |
| 0.529 | 0.678 | 0.935 | 0.346 | 0.458 | 0.744 | 0.002 | 0.168 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Su, H.; Huang, R.; Zhao, D. A Low-Complexity Hybrid Phase Shifter Network with Shared-Control Voltage for High-Scan-Gain Phased Arrays. Electronics 2025, 14, 4605. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234605
Ma X, Su H, Huang R, Zhao D. A Low-Complexity Hybrid Phase Shifter Network with Shared-Control Voltage for High-Scan-Gain Phased Arrays. Electronics. 2025; 14(23):4605. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234605
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xin, Hansheng Su, Renke Huang, and Deshuang Zhao. 2025. "A Low-Complexity Hybrid Phase Shifter Network with Shared-Control Voltage for High-Scan-Gain Phased Arrays" Electronics 14, no. 23: 4605. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234605
APA StyleMa, X., Su, H., Huang, R., & Zhao, D. (2025). A Low-Complexity Hybrid Phase Shifter Network with Shared-Control Voltage for High-Scan-Gain Phased Arrays. Electronics, 14(23), 4605. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14234605






