A Lithium-Ion Battery Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method Based on Mode Decomposition and Informer-LSTM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Algorithm Theory
2.1. Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise
- (1) Add a white noise sequence, drawn from a Gaussian distribution, to the original capacity sequence:
- (2) Perform EMD on the noise-enhanced sequence Xi(t). Then, compute the average of the resulting decompositions to obtain IMF1 and the first residual sequence:
- (4) This procedure is repeated to extract successive IMFs and terminates when the residual sequence becomes a monotonic function:
2.2. Pearson Correlation Coefficient
2.3. Long Short-Term Memory Network
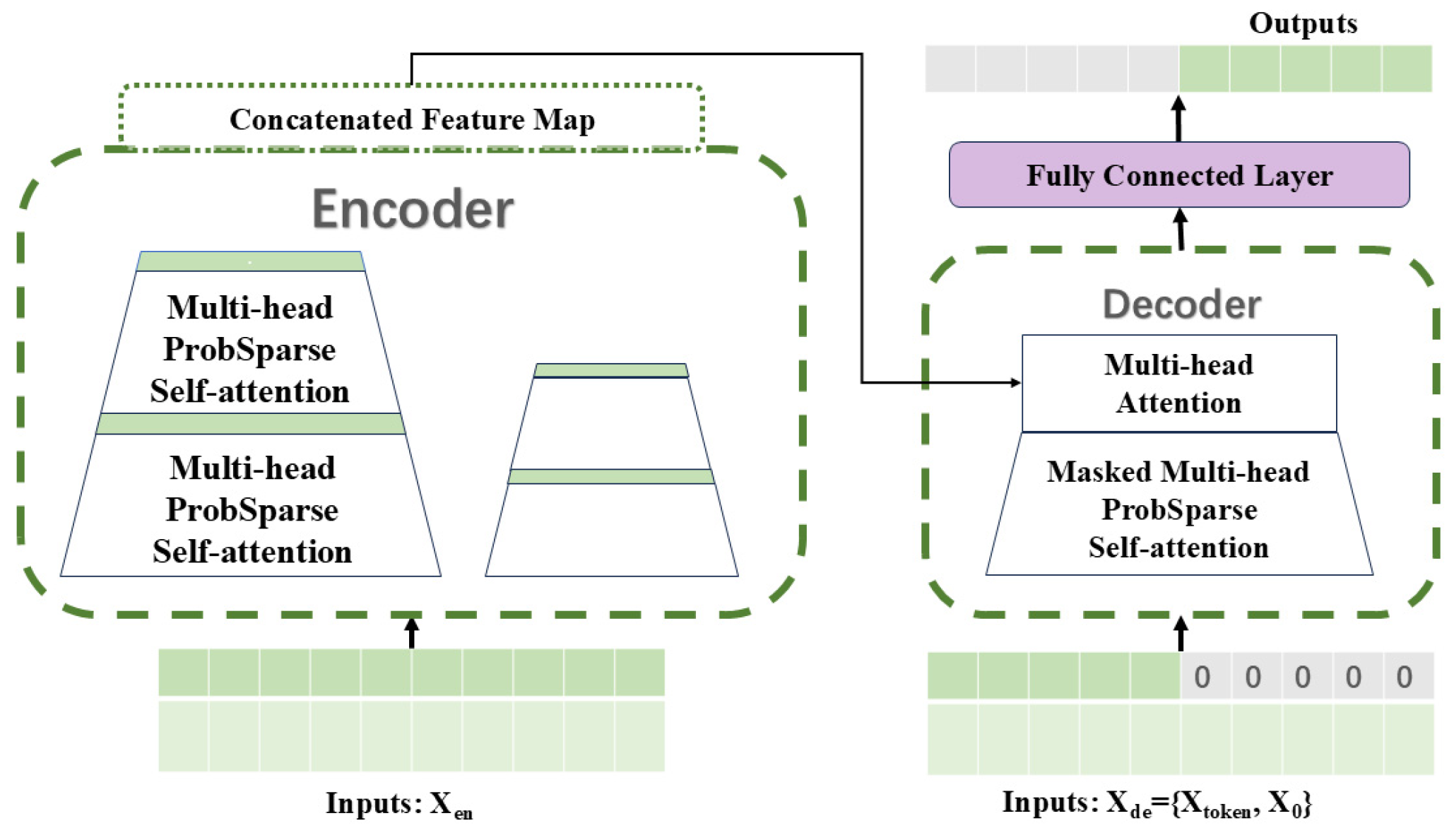
2.4. Informer
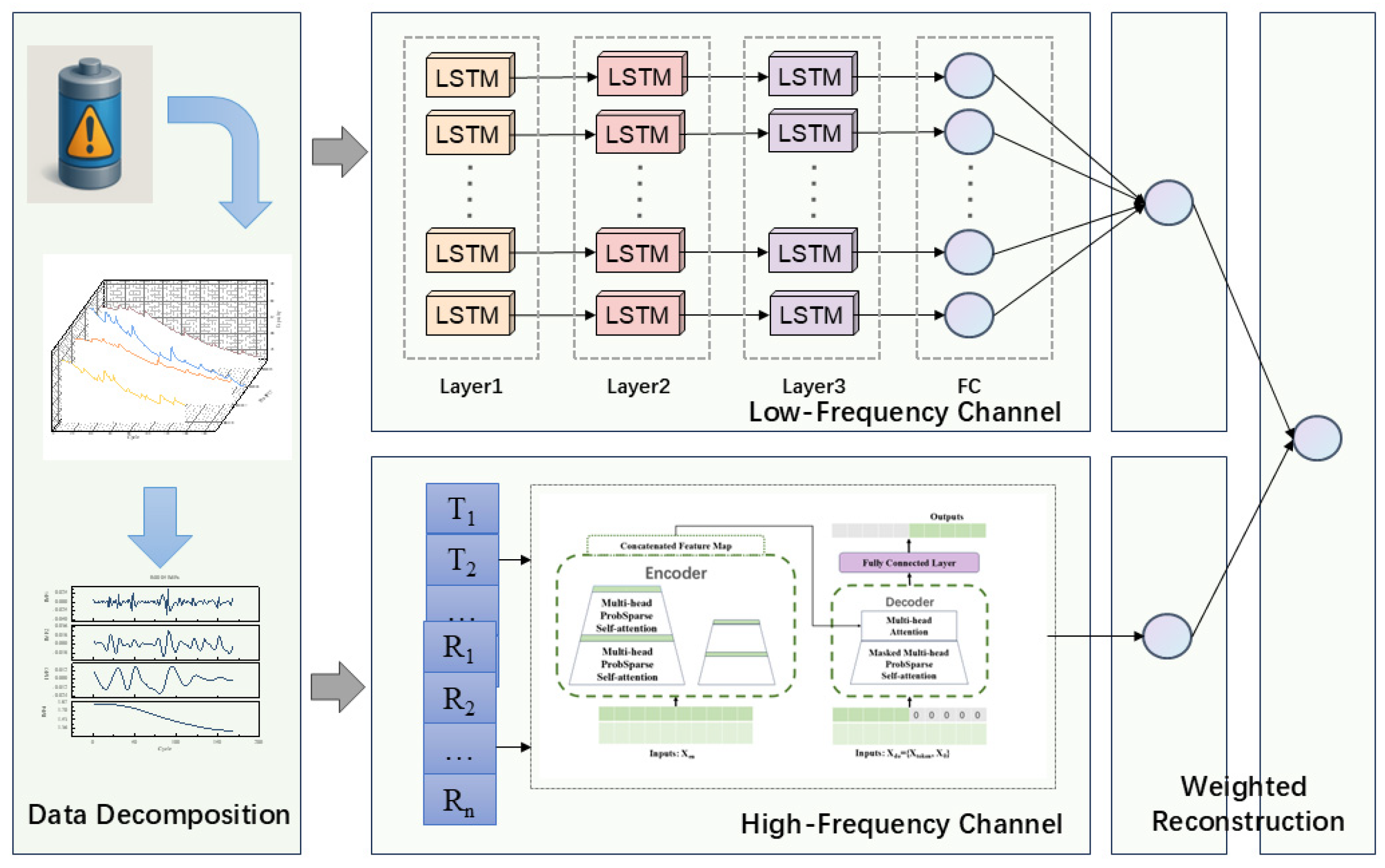
2.5. The Proposed Method
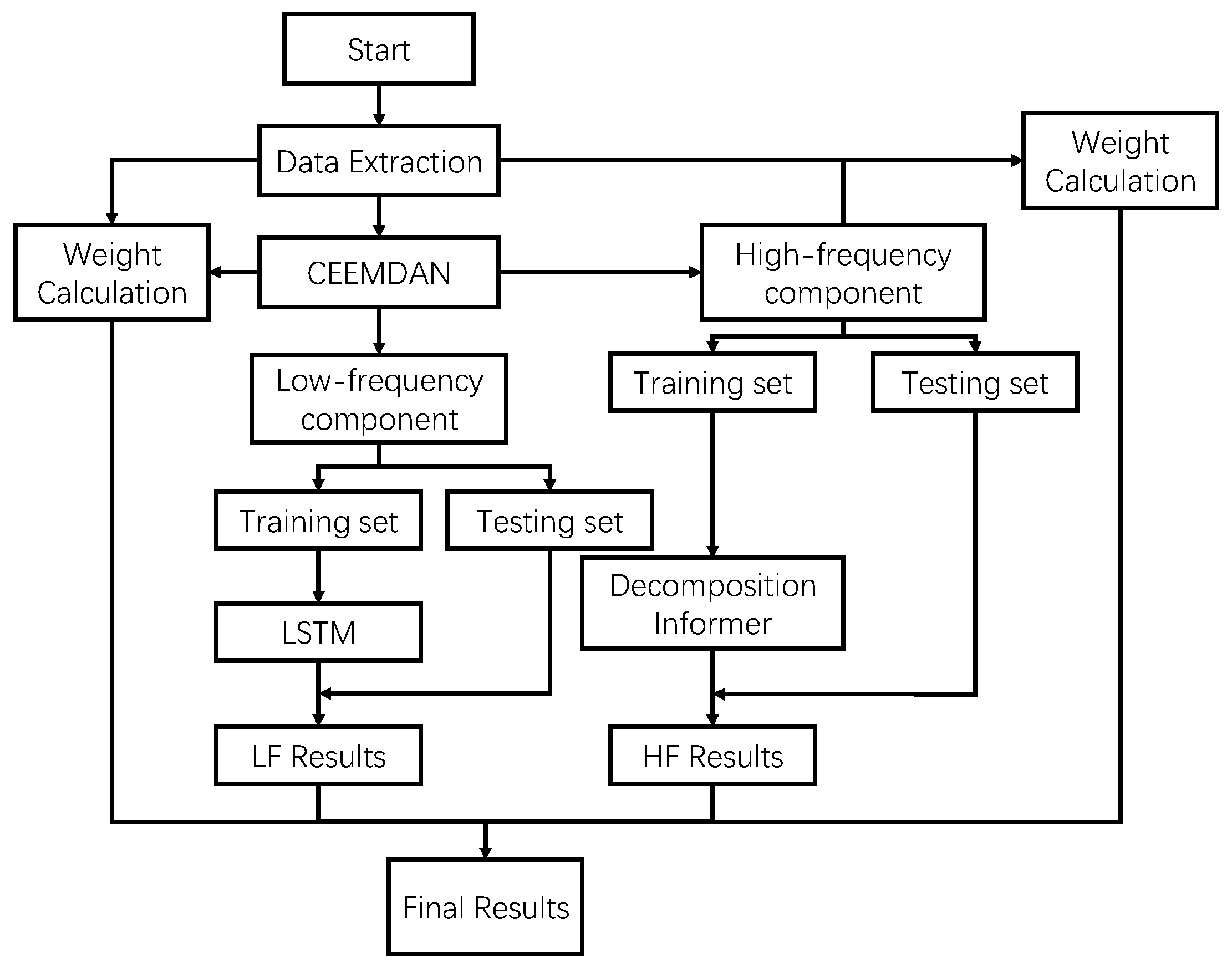
3. Prediction Procedure and Evaluation Metrics
3.1. Prediction Procedure
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
4. Experiments and Results Analysis
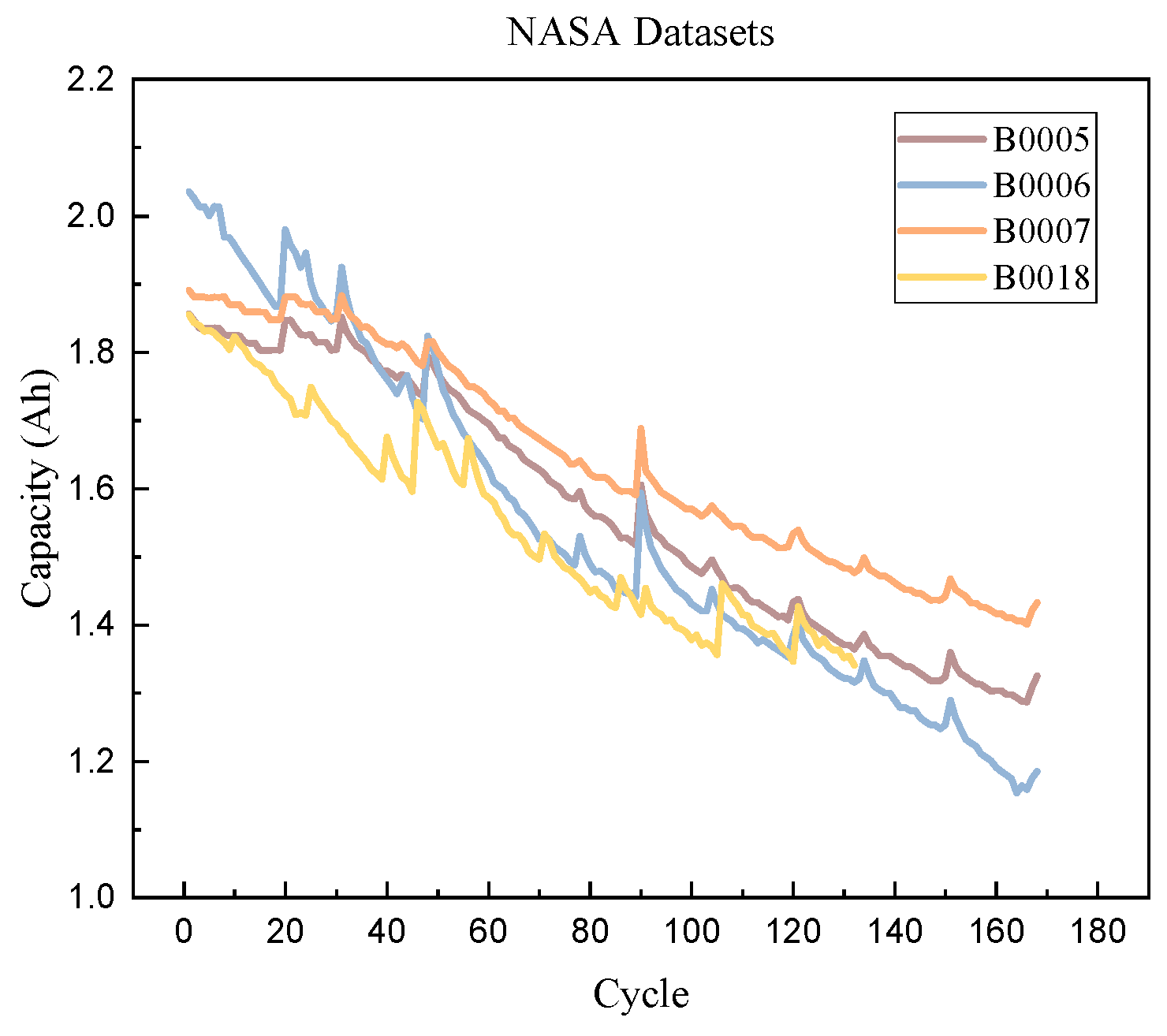
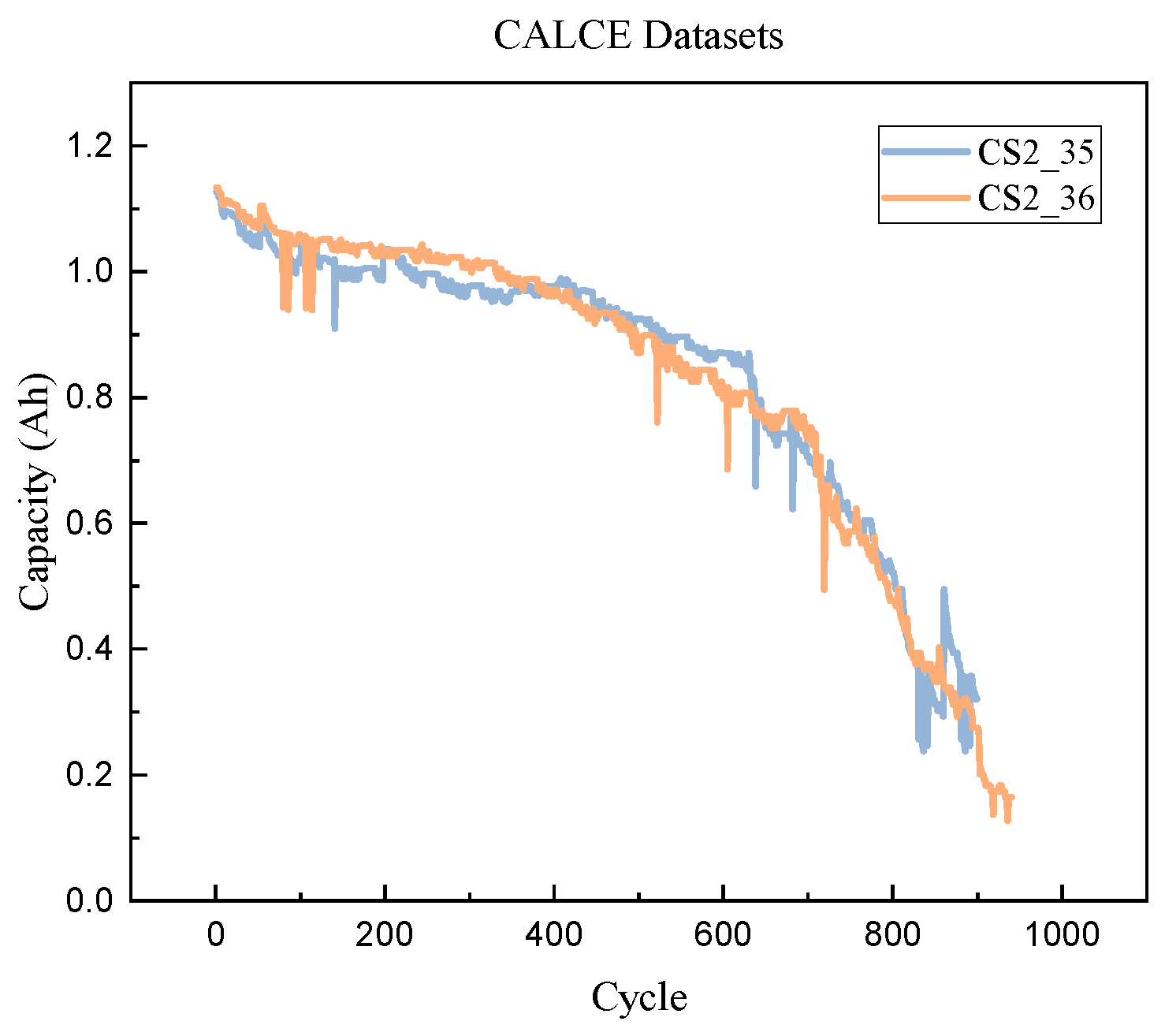
4.1. Datasets
4.2. CEEMDAN
4.3. Pearson Correlation Coefficient
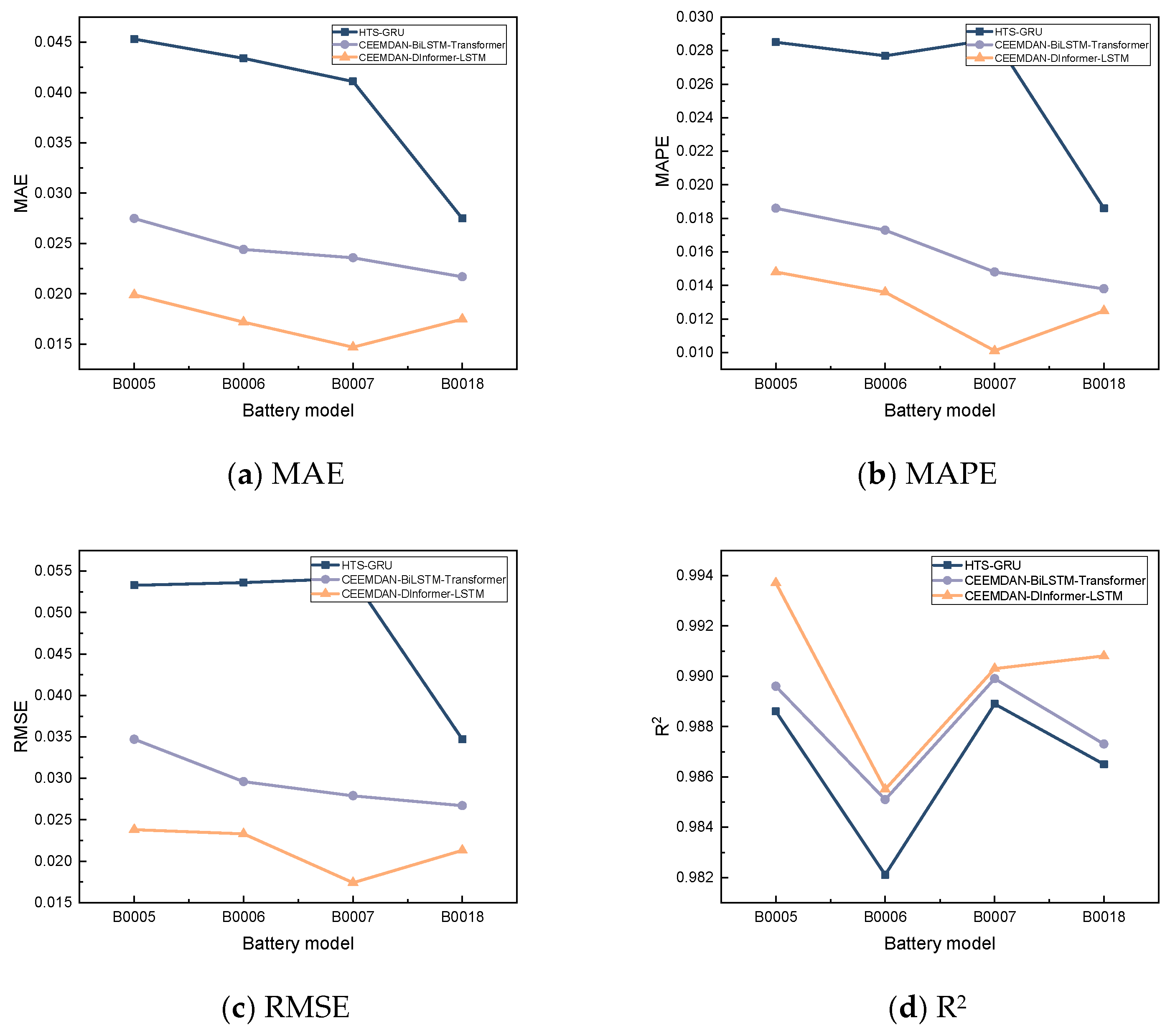
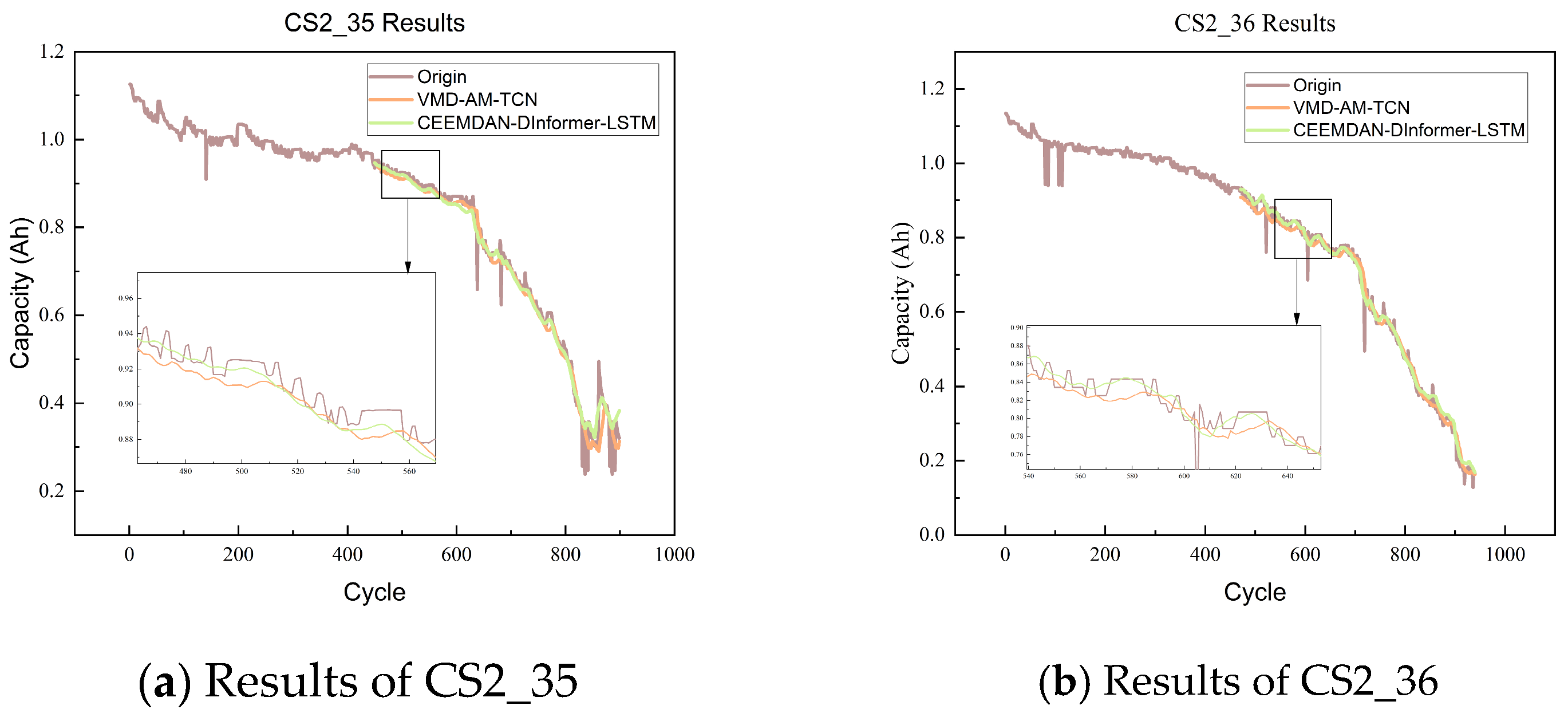
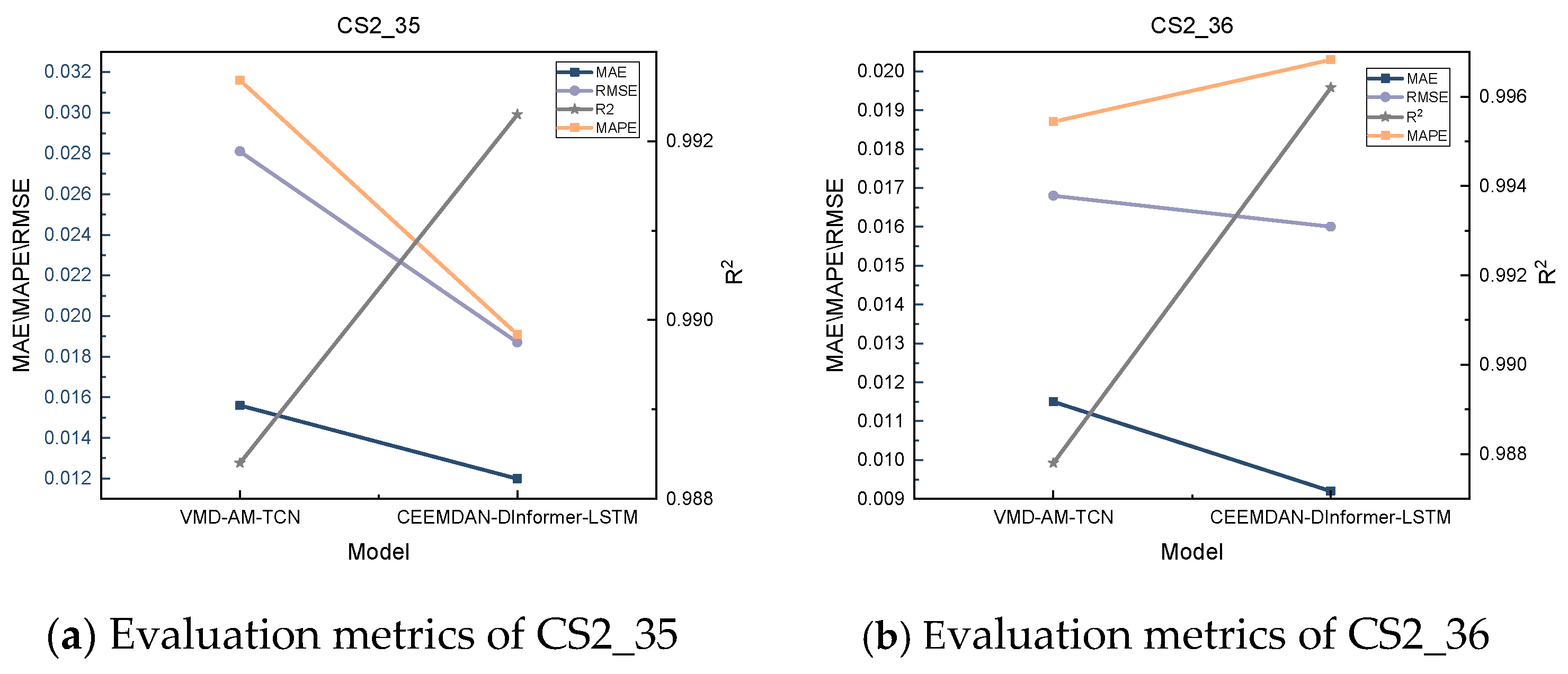
4.4. Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nourianfar, H.; Abdi, H. Economic emission dispatch considering electric vehicles and wind power using enhanced multi-objective exchange market algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipu, M.H.; Abd Rahman, M.; Mansor, M.; Ansari, S.; Meraj, S.T.; Hannan, M. Hybrid and combined states estimation approaches for lithium-ion battery management system: Advancement, challenges and future directions. J. Energy Storage 2024, 92, 112107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction based on interpretable deep learning and network parameter optimization. Appl. Energy 2025, 379, 124713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, B.; Wei, X.; Dai, H. Nonlinear aging knee-point prediction for lithium-ion batteries faced with different application scenarios. Etransportation 2023, 18, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Naidu, P.A.; Sharma, S.; Panigrahi, B.K.; Garg, A. Review on technological advancement of lithium-ion battery states estimation methods for electric vehicle applications. J. Energy Storage 2023, 64, 107159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Han, X.; Lu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Bo, C. Evolving Elman neural networks based state-of-health estimation for satellite lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 59, 106571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Q. An interpretable remaining useful life prediction scheme of lithium-ion battery considering capacity regeneration. Microelectron. Reliab. 2022, 138, 114625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, G.; Zhang, H.; Miao, Q. Parallel state fusion LSTM-based early-cycle stage lithium-ion battery RUL prediction under Lebesgue sampling framework. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 236, 109315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Chen, K.; Geng, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, J. Accurate capacity and remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on improved particle swarm optimization and particle filter. Energy 2024, 293, 130555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, R.; He, H.; Pecht, M. Validation and verification of a hybrid method for remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Pham, H. Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life prediction using a two-phase degradation model with a dynamic change point. J. Energy Storage 2023, 59, 106457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzouhri, A.; Charouh, Z.; Ghogho, M.; Guennoun, Z. A data-driven-based framework for battery remaining useful life prediction. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 76142–76155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Wang, S.; Cao, W.; Zhou, H.; Fernandez, C. An improved variable forgetting factor recursive least square-double extend Kalman filtering based on global mean particle swarm optimization algorithm for collaborative state of energy and state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 450, 142270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Huang, Z.; Tian, J.; Li, X. State of charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on cubature Kalman filters with different matrix decomposition strategies. Energy 2022, 238, 121917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Meng, J.; Lin, M.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Stroe, D.-I. Lithium-ion battery state of health estimation using a hybrid model with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 252, 110450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Wei, Z.; Hu, X.; Tang, X.; Chen, Z. System identification and state estimation of a reduced-order electrochemical model for lithium-ion batteries. Etransportation 2023, 18, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jin, Y.; Kam, W.; Han, S. A practical semi-empirical model for predicting the SoH of lithium-ion battery: A novel perspective on short-term rest. J. Energy Storage 2024, 96, 112659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, J.; Fu, D. Lifetime prediction of power electrolytic capacitors based on IKH-UKF-PF. J. Power Supply 2024, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; He, W. Remaining useful life prediction method of lithium-ion batteries is based on variational modal decomposition and deep learning integrated approach. Energy 2023, 282, 128984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Mao, T.; Gao, H.; Peng, J.; Yang, J. Health state estimation of lithium ion battery based on TWP-SVR. Energy Storage Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 2585. [Google Scholar]
- JIN, H.; HU, Y.; GE, H.; HAO, Z.; ZENG, Z.; TANG, Z. Remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries based on an improved GWO–SVR algorithm. Chin. J. Eng. 2024, 46, 514–524. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Cai, F.; Li, H.; Huang, K.; Yin, H. A data-driven prediction model for the remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 180, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhao, K.; Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z. CNN-DBLSTM: A long-term remaining life prediction framework for lithium-ion battery with small number of samples. J. Energy Storage 2024, 97, 112947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Hong, W.; Zhou, X. Transformer network for remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 19621–19628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Azib, T.; Yue, M. Early-Stage end-of-Life prediction of lithium-Ion battery using empirical mode decomposition and particle filter. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2023, 237, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Flandrin, P. A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 4144–4147. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Ji, C.; Cao, L.; Wu, X.; Duan, Y. Prediction of Remaining Service Life of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise and BiLSTM-Transformer. Power Syst. Prot. Control 2024, 52, 167–177. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, W. Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; pp. 11106–11115. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, A.; Chen, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q. Are transformers effective for time series forecasting? In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; pp. 11121–11128. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, B.; Goebel, K. Battery data set. In NASA AMES Prognostics Data Repository; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.; Zhang, J. Lithium-ion battery life prediction based on improved HTS-GRU. J. Power Supply 2024, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Sun, L.; Wang, A.; Jiao, J.; Xie, J. Lithium battery remaining useful life prediction using VMD fusion with attention mechanism and TCN. J. Energy Storage 2024, 93, 112330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Model | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| dimension | 128 | |
| Informer | n_heads | 8 |
| n_encoder | 2 | |
| n_decoder | 1 | |
| learning_rate | 0.001 | |
| drop_out | 0.1 | |
| LSTM | hidden_size | 64 |
| num_layers | 2 | |
| learning_rate | 0.001 |
| Battery | IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0005 | 0.0623 | 0.1796 | 0.1325 | 1 |
| B0006 | 0.1325 | 0.1522 | 0.1424 | 1 |
| B0007 | 0.0747 | 0.1628 | 0.0153 | 1 |
| B0018 | 0.0731 | 0.1185 | 0.4271 | 1 |
| Battery | Model | MAE | MAPE | RMSE | R2 | RULerror (Cycle) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0005 | LSTM | 0.0422 | 0.0315 | 0.0482 | 0.9608 | 13 |
| Informer | 0.0384 | 0.0291 | 0.0442 | 0.9712 | 7 | |
| CEEMDAN-LSTM | 0.0256 | 0.0191 | 0.0304 | 0.9662 | 3 | |
| CEEMDAN-DInformer | 0.0215 | 0.0159 | 0.0261 | 0.9729 | 2 | |
| CEEMDAN-DInformer-LSTM | 0.0199 | 0.0148 | 0.0238 | 0.9937 | 0 | |
| B0006 | LSTM | 0.0576 | 0.0466 | 0.0684 | 0.9633 | 5 |
| Informer | 0.0492 | 0.0406 | 0.0629 | 0.9728 | 4 | |
| CEEMDAN-LSTM | 0.0529 | 0.0418 | 0.0595 | 0.9700 | 4 | |
| CEEMDAN-DInformer | 0.0214 | 0.0171 | 0.0275 | 0.9730 | 3 | |
| CEEMDAN-DInformer-LSTM | 0.0172 | 0.0136 | 0.0233 | 0.9855 | 1 | |
| B0007 | LSTM | 0.0408 | 0.0281 | 0.0468 | 0.9615 | 21 |
| Informer | 0.0272 | 0.0189 | 0.0341 | 0.9729 | 12 | |
| CEEMDAN-LSTM | 0.0337 | 0.0231 | 0.0379 | 0.9766 | 5 | |
| CEEMDAN-DInformer | 0.0218 | 0.0149 | 0.0246 | 0.9787 | 5 | |
| CEEMDAN-DInformer-LSTM | 0.0147 | 0.0101 | 0.0174 | 0.9903 | 2 | |
| B0018 | LSTM | 0.0324 | 0.0235 | 0.0352 | 0.9782 | 4 |
| Informer | 0.0358 | 0.0260 | 0.0398 | 0.9714 | 2 | |
| CEEMDAN-LSTM | 0.0261 | 0.0165 | 0.0310 | 0.9796 | 2 | |
| CEEMDAN-DInformer | 0.0241 | 0.0172 | 0.0283 | 0.9837 | 2 | |
| CEEMDAN-DInformer-LSTM | 0.0175 | 0.0125 | 0.0213 | 0.9908 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Li, L.; Wang, G.; Shi, N.; Li, Y.; Yang, X. A Lithium-Ion Battery Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method Based on Mode Decomposition and Informer-LSTM. Electronics 2025, 14, 3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193886
Zhu X, Li L, Wang G, Shi N, Li Y, Yang X. A Lithium-Ion Battery Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method Based on Mode Decomposition and Informer-LSTM. Electronics. 2025; 14(19):3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193886
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xiaolei, Longxing Li, Guoqiang Wang, Nianfeng Shi, Yingying Li, and Xianglan Yang. 2025. "A Lithium-Ion Battery Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method Based on Mode Decomposition and Informer-LSTM" Electronics 14, no. 19: 3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193886
APA StyleZhu, X., Li, L., Wang, G., Shi, N., Li, Y., & Yang, X. (2025). A Lithium-Ion Battery Remaining Useful Life Prediction Method Based on Mode Decomposition and Informer-LSTM. Electronics, 14(19), 3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14193886







