Abstract
Aerial-assisted vehicular edge computing (AVEC) has emerged as a transformative approach to addressing the limitations of traditional vehicular edge computing (VEC) in dynamic vehicular environments. By integrating platforms such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), high-altitude platforms (HAPs), and satellites, AVEC systems offer enhanced scalability, flexibility, and responsiveness, enabling efficient resource allocation and adaptive decision-making. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of resource allocation techniques in AVEC, addressing both traditional and reinforcement learning-based approaches. These techniques aim to optimize the allocation of bandwidth, computation, and energy resources across heterogeneous platforms, ensuring reliable and efficient operations in diverse scenarios. Additionally, the study examines key challenges inherent in AVEC, including achieving seamless interoperability among diverse platforms, addressing scalability in large-scale systems, and adapting to real-time environmental dynamics. To address these challenges, the paper proposes future research directions, such as leveraging advanced technologies like quantum computing for solving complex optimization problems, employing tiny machine learning (TinyML) to enable resource-efficient intelligence on low-power devices, and predictive task offloading to enhance proactive resource management. By presenting a detailed analysis of existing techniques and identifying critical research opportunities, this paper seeks to guide researchers and practitioners in developing more efficient, secure, and adaptive AVEC systems. The insights from this study contribute to advancing the design and deployment of resilient intelligent transportation networks, paving the way for the next generation of vehicular connectivity.
1. Introduction
In recent years, vehicular edge computing (VEC) has gained prominence as transportation systems increasingly leverage real-time data for safer, smarter, and more efficient travel. This shift is primarily due to the rapid increase in the number of connected vehicles equipped with sensors, cameras, and communication tools that produce large amounts of data. Applications such as accident prevention, traffic management, and in-car entertainment require fast processing and responses. Traditional cloud computing cannot meet these demands because it often involves delays and high data loads [1]. VEC addresses these challenges by bringing the processing power closer to that of vehicles, allowing for faster decisions, reducing the need to rely on distant cloud servers, and preventing network congestion [2]. VEC processes, stores, and analyzes data directly within vehicular networks, which reduces dependency on distant cloud servers and helps prevent network congestion [3]. By managing data closer to vehicles, VEC ensures reliable service even in fast-changing environments. This approach is adaptable and supports the increasing data demands of connected vehicles while providing quick responses and consistent connectivity, which are key factors for the advancement of smart transportation systems.
Although VEC has significantly improved the data processing and response times in vehicular networks, it is still limited by the stationary nature of edge servers, which cannot be readily adapted to rapidly changing traffic patterns or varying levels of network demand. Fixed-edge servers are effective in urban areas with established infrastructure but struggle in areas with limited connectivity, such as rural, mountainous, or disaster-stricken regions. Additionally, high-density environments such as city centers or highways during peak hours place heavy demands on fixed VEC infrastructures, often resulting in reduced service quality, increased latency, and lower throughput.
The concept of aerial-assisted vehicular edge computing (AVEC) has emerged to address these challenges. AVEC integrates aerial computing platforms (ACPs) such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and high-altitude platforms (HAPs) with a VEC infrastructure to provide flexible mobile edge resources. ACPs offer unique advantages because of their ability to move quickly to areas of high demand, provide temporary coverage in underserved regions, and adjust their positions based on real-time network conditions [4]. For instance, UAVs can be deployed to support accident-prone zones, highly congested intersections, or highway segments with poor cellular coverage, delivering data processing and connectivity when necessary. This mobility allows AVEC to enhance the quality of service (QoS) by reducing latency and minimizing service interruptions, even in highly dynamic vehicular environments.
Moreover, ACPs can act as “on-demand” edge nodes, which can be deployed as additional processing resources when local edge servers are overloaded [4]. This flexibility not only extends the reach of VEC but also introduces a scalable approach to managing vehicular tasks, as UAVs can be dispatched to areas based on need and then returned to charging stations or maintenance hubs. By reducing the load on the stationary edge infrastructure and filling coverage gaps, UAVs can enable AVEC systems for handling peak loads, achieving lower latency, and maintaining reliable connectivity across diverse operational scenarios. With the rise of AVEC systems, efficient resource management is essential for maximizing their potential. AVEC systems must address various challenges, including real-time task offloading, energy management for aerial platforms, bandwidth allocation, and QoS maintenance across dynamic environments. Efficient resource management is vital because UAVs and other ACPs have limited energy supplies and restricted computational power, and rely on wireless connectivity that can fluctuate based on weather, obstacles, or high-demand zones. The effective management of resources in AVEC is crucial for ensuring low latency, reducing operational costs, and improving overall system reliability. Additionally, the integration of advanced resource management techniques, such as machine learning (ML) and optimization algorithms, has shown promise for enhancing AVEC performance.
While AVEC systems are predominantly utilized for civilian applications such as traffic management and autonomous driving, there is growing interest in applying these technologies in non-civilian sectors. Military organizations are increasingly exploring the use of UAVs and edge computing for applications like border surveillance, reconnaissance, and strike missions [5]. For example, UAVs in AVEC can enhance real-time data processing for advanced reconnaissance in special missions [6]. Platforms like FogSurv, integrating edge computing and UAVs, can also support armed forces by improving communication and data processing capabilities in remote and conflict areas.
Recently, numerous studies have been conducted on AVEC, with resource allocation as a central focus. However, we identified a gap in the existing surveys that comprehensively addressed resource allocation in AVEC. Therefore, in this survey, we discuss the techniques for resource allocation in AVEC by covering recent studies, highlighting key research issues, comparing the resource allocation techniques, and presenting future research directions. Our goal is to consolidate and review the various strategies developed thus far, provide insights into their strengths and limitations, and offer guidance on which techniques may be most suitable for different AVEC scenarios. By addressing this gap, this survey will support researchers and practitioners in designing more adaptive, resilient, and efficient AVEC systems. Figure 1 illustrates a high-level overview of the AVEC.
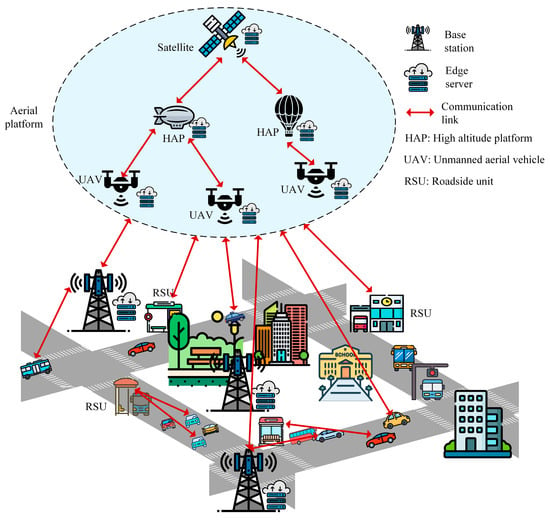
Figure 1.
High-level overview and interaction of aerial-assisted vehicular edge computing.
1.1. Related Surveys
Several surveys have explored resource management and optimization techniques for VEC and UAV systems. These studies have primarily focused on areas such as task offloading, energy efficiency, and network optimization. However, most studies address these topics in isolation, overlooking the combined potential of AVEC. This section reviews the existing surveys, highlighting their contributions, and identifying the gaps that this study aimed to address. Table 1 presents a comparison of related surveys in this field.

Table 1.
Comparison of related surveys.
Liu et al. [3] conducted a comprehensive survey on VEC, highlighting its integration with mobile edge computing (MEC) to address the challenges of low latency, bandwidth consumption, and computational demands in vehicular networks. This paper reviews the VEC architecture, key enablers, and application scenarios, emphasizing task offloading, content caching, and data management techniques. It also discusses challenges, such as high mobility and resource limitations, while identifying future research directions. Their survey classified existing models in detail but did not cover aerial-assisted solutions such as UAVs, leaving the scope for further study. In [7], a detailed survey of collaborative vehicular edge computing networks (CVECN) was presented, focusing on architectural design and associated research challenges. This study introduced a novel CVECN framework that integrates MEC with vehicular networks to enhance computational efficiency and resource utilization. The key contributions include the design principles of the CVECN, functional modules, and a collaborative computation offloading scheme based on a constrained Markov decision process. The study also discussed mobility management and other challenges such as scalability, reliability, and energy efficiency.
In [8], the authors surveyed multi-access edge computing and its integration with vehicular networks, emphasizing the role of MEC in enabling low-latency, resource-efficient vehicular applications. This paper reviews the MEC architecture, applications, and enabling technologies, such as software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization, while highlighting challenges such as mobility, resource management, and security. Naren et al. [9] studied computational resource allocation in an IoT-enabled VEC. The study classified resource allocation schemes based on optimization goals, mathematical models, and enabling technologies, such as AI, SDN, and blockchain. It emphasizes challenges such as power consumption, network latency, and task offloading efficiency while identifying future research directions. The authors of [10] reviewed resource-allocation techniques in vehicular networks, focusing on DSRC, cellular V2X, and heterogeneous network types. This paper discusses the challenges of high mobility, spectrum congestion, and QoS demands while highlighting recent advancements such as ML-based solutions and network slicing. Article [11] provides a comprehensive review of resource scheduling in edge computing, covering key topics such as computation offloading, resource allocation, and resource provisioning. The survey classified resource scheduling strategies into centralized and distributed methods and discussed their performance across application scenarios, such as UAVs and smart cities. Although the study highlighted edge-cloud collaboration, it did not explore aerial-assisted VEC in depth.
In [2], computational offloading, and content caching in vehicular edge networks were surveyed. They primarily focused on architecture, communication technologies, and edge-layer integration. This study categorizes the existing solutions for task offloading and content delivery while addressing the associated security concerns. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and the blockchain in VEC was reviewed in [12]. The survey introduced a multi-layered VEC-based architecture combining AI and hybrid blockchain models for a secure and efficient Internet of vehicles. It highlights challenges such as resource management and privacy concerns while proposing research directions. In [13], ML and DL methods were used for resource allocation in multi-access edge computing. The study categorized solutions into task offloading, scheduling, and joint resource allocation while discussing enabling technologies and key challenges. It highlights the advantages of Machine ML/DL over traditional methods, focusing on improving latency, energy efficiency, and task optimization. In [14] the authors reviewed resource allocation strategies in multi-access edge Computing for 5G-and-beyond networks, focusing on problem formulation frameworks. The survey classified resource allocation challenges according to target objectives, resource types, and assumptions, with an emphasis on ultra-reliable low-latency communication. This highlights the future directions for optimizing latency, dependability, and energy efficiency. However, they did not consider UAV-assisted MEC systems.
Zhang and Debroy [15] conducted a comprehensive survey of resource management in MEC, emphasizing task offloading, resource allocation, and system optimization. This paper reviews conventional and AI-based approaches such as deep reinforcement learning (RL) and optimization frameworks to address the challenges of low latency, energy efficiency, and mobility in edge systems. Article [16] surveyed resource scheduling techniques in edge computing and proposed a taxonomy that categorizes approaches by objectives, collaboration models, and algorithm paradigms. The study also highlighted challenges such as fairness, load balancing, and energy efficiency and identified future directions such as multi-objective optimization and fault-tolerant scheduling. Although this study provided a broad perspective on resource scheduling in edge computing, it did not specifically consider VEC.
Existing surveys offer valuable contributions to resource management and optimization of VEC and UAV systems. These cover important areas such as task offloading, energy efficiency, and advanced technologies such as AI and blockchain. However, most of these studies have focused on specific topics and have not explored the combined potential of AVEC. By bridging this gap, this survey aims to provide a clearer understanding of resource management in AVEC and guide future research in this area.
1.2. Contributions
This survey advances the field of AVEC through several significant contributions, which not only build upon the existing literature but also lay the groundwork for future research. The detailed contributions of this study are as follows:
- Integrated overview: Unlike prior surveys that focused on specific aspects of VEC or UAV-assisted edge computing, this survey provides a comprehensive overview of resource management strategies that integrate both domains. This highlights the enhancements that aerial platforms bring to vehicular networks by addressing key design issues.
- Incorporation of the latest technologies: This survey encapsulates the latest advancements in technology and methodologies, including ML algorithms, heuristic techniques, and RL approaches. It reviews these approaches and provides a comparative analysis of their applications in AVEC systems, offering insights into their effectiveness and limitations.
- Detailed analysis of performance metrics: We conducted an exhaustive analysis of essential performance metrics, such as latency, energy consumption, throughput, and computational overhead. This analysis is crucial for understanding the tradeoffs and optimization opportunities within different resource allocation technique.
- Comparative review of existing techniques: This survey offers a comparative review of recent research on resource management in AVEC. It presents a comprehensive review of the current findings and emerging trends, helping researchers understand the landscape of this field and exploit innovative topics for future investigation.
- Identification of research gaps and future directions: One of the key contributions of this survey is to identify current research gaps and suggest future research directions. This helps set a research agenda and promotes interdisciplinary approaches to address the immerging and complicated challenges of AVEC.
To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this is the first survey to uniquely synthesize AVEC-specific resource allocation issues by integrating the fields of VEC and UAV-assisted edge computing, which are often treated separately in existing reviews. With the growing volume of research in AVEC, it is crucial to review and consolidate these emerging advancements. By combining these two domains, we offer a comprehensive perspective that highlights how aerial platforms enhance vehicular networks, addressing key design challenges in a unified framework. This integrated approach sets this survey apart from others and lays the foundation for future research in AVEC systems.
1.3. Organization of the Survey
This study provides a thorough exploration of AVEC resource management. The organization of the survey is illustrated in Figure 2. Following the introduction, this paper is organized into several key sections.
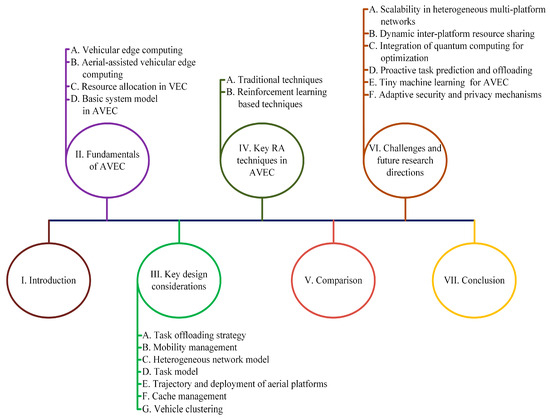
Figure 2.
Organization of the survey.
- Section 2 describes the foundational concepts necessary for understanding the VEC and its aerial-assisted enhancements.
- Section 3 discusses the key design considerations necessary to optimize the resources in AVEC systems.
- Section 4 reviews various resource management techniques for AVEC, such as heuristic methods, ML, and reinforcement learning. This section focuses on the manner in which these techniques improve resource management in AVEC.
- Section 5 provides a comparison of the various resource management techniques used in AVEC, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.
- Section 6 highlights the current challenges and suggests future directions for research, emphasizing the need for smarter resource management solutions.
- Section 7 concludes the paper by summarizing the main points and highlighting the importance of advanced resource management in enhancing VEC through aerial assistance.
2. Fundamentals of Aerial-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing
This section presents the basic knowledge required to understand resource allocation in AVEC. We begin by examining the core architecture of VEC and the integration of aerial platforms to enhance these systems. We discuss the types of resources that are critical for AVEC and the basic system model architecture. This foundation is crucial for exploring more detailed resource management strategies in the survey.
2.1. Vehicular Edge Computing
The necessity for VEC arises from the need to efficiently manage large volumes of tasks generated by vehicles while minimizing network congestion and bandwidth usage. VEC is a critical advancement designed to satisfy the unique requirements of modern intelligent transportation systems. Position computational and storage facilities are directly within the vehicular environment or at close network edges, such as vehicles and roadside units (RSUs). VEC significantly minimizes the latency and bandwidth constraints associated with traditional cloud computing [17]. This local processing capability is essential for applications where rapid response times are crucial, such as autonomous driving and real-time traffic management [18,19,20].
The VEC architectures typically comprise vehicles equipped with computing capabilities, RSUs with edge servers that facilitate task processing and communication, and terrestrial edge servers that provide additional computational power and storage [2]. The configuration allows for flexible processing strategies, where decisions on whether to process tasks directly within the vehicle, at an RSU, or at an edge server depend on task attributes such as task size, latency requirements, and task complexity.
Resource management within a VEC is crucial for maintaining the system’s performance and scalability. It involves the dynamic allocation of resources based on real-time network conditions and task demands. Proper management ensures that the system can handle increasing task volumes and a higher number of connected vehicles without degrading service quality or reliability. This strategic approach supports essential vehicular operations and ensures that transportation systems are safe, efficient, and reliable.
2.2. Aerial-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing
AVEC significantly enhances traditional VEC by incorporating various aerial platforms such as UAVs, HAPs, and satellites. This addition is crucial for extending the reach and effectiveness of edge-computing services, particularly in regions where ground infrastructure is sparse or entirely absent, thus broadening connectivity and service availability across expansive geographic areas [21]. In AVEC, these aerial platforms function as mobile computing nodes that can be deployed dynamically [22]. They directly provide essential computational support within a vehicular environment, thereby enabling real-time data processing, which is critical for latency-sensitive applications. For example, in emergency response scenarios or large-scale public events where rapid deployment and flexibility are necessary, these platforms can quickly establish a robust computing network to handle the immense data volumes generated by numerous vehicles [23].
Each type of aerial platform provides unique capabilities for the VEC. For example, UAVs can maneuver close to urban and rural areas, providing edge-computing services that reduce the load on terrestrial networks and lower communication latency by processing data closer to the point of collection [24]. HAPs offer a stable and persistent presence in the stratosphere, which is ideal for covering larger areas and ensuring consistent network services in regions without infrastructure [25]. Satellites can bridge the gaps in global coverage, ensuring that vehicular networks remain connected over vast and remote areas, thus supporting global navigation and communication tasks [26]. Integrating these platforms into VEC systems introduces challenges in coordination and resource management, with a focus on optimizing computational tasks and energy usage.
Effective management of resources involves dynamically allocating computational tasks based on the capabilities of each platform and the real-time demands of the network [27]. This includes deciding which tasks are processed by UAVs and which are better handled by HAPs or satellites, based on their complexity, required processing power, and urgency. The strategic deployment of these aerial platforms ensures that computational tasks are efficiently handled, thereby enhancing the overall performance of VEC [28,29,30]. Offloading intensive computing tasks from vehicles to aerial platforms significantly reduces on-ground network congestion and improves the speed and reliability of services such as autonomous driving support, real-time traffic management, and emergency response communications. As the role of aerial platforms in vehicular networks expands, continued advancements in technology will likely drive further research to optimize energy consumption, improve integration with terrestrial network components, and enhance autonomous operational capabilities. This evolution in AVEC not only bolsters network performance but also sets the stage for transformative developments in public safety, traffic management, and connectivity across both urban and remote environments.
2.3. Resource Allocation in AVEC
In an AVEC, optimizing resource allocation involves meticulously managing several key resources to ensure that the network operates efficiently under varying conditions and demands. Here, we break down the allocation of the three critical resources–transmission power, computational resources, and bandwidth–by incorporating basic conceptual equations to clarify the allocation process.
2.3.1. Transmission Power Allocation
Transmission power allocation plays a critical role in AVEC, particularly when offloading tasks to other computational platforms [31,32]. The transmission power required by an offloading node directly influences the energy consumed during the data transmission process. The transmission power has a direct impact on energy consumption. In the resource allocation problem, based on the objective function, researchers must design algorithms to allocate transmission power. Allocating an appropriate level of transmission power is essential for ensuring efficient communication while minimizing energy use. A higher transmission power increases the reach and strength of the signal, which can be particularly important in environments with high interference or long distances between the transmitter and receiver. However, this also results in higher energy consumption. Thus, it is crucial to balance the transmission power to optimize energy efficiency while ensuring reliable communication.
The transmission power must be set such that it meets the minimum required signal-to-noise ratio for reliable data transfer but does not exceed this requirement to avoid unnecessary energy expenditure. Transmission power allocation can often be adjusted dynamically based on the communication channel’s condition and distance to the receiving node to minimize the overall energy consumption while maintaining a satisfactory quality of service [33]. Furthermore, the transmission power range can be maintained using constraints while allocating the transmission power. This approach helps to conserve the battery life of mobile devices within a vehicular network, thereby extending their operational duration and effectiveness.
2.3.2. Computational Resource Allocation
In AVEC, computational resource allocation plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient task execution by managing the distribution of computational workloads among available resources, including onboard vehicle units, RSUs, base stations, and aerial platforms such as UAVs, HAPs, and satellites. Proper allocation minimizes task-processing delays, while maintaining energy efficiency and system reliability [34]. The computational demand of a task is defined by parameters such as the task size, required computation cycles, and latency constraints, which are the common assumptions in the research field of computational resource allocation. The total workload for a task can be calculated by the product of the task data size (in bits or bytes) and the number of computation cycles required per unit of data.
The time required to complete the task using a computational resource with a processing speed (in cycles per second) is expressed as
where W is the total workload.
Efficient computational resource allocation aims to minimize , ensuring that tasks are executed within their deadlines while effectively utilizing the available resources. The key decision in computational resource allocation is determining the processing location for a task, which can be local (onboard the vehicle) or remote (offloaded to RSUs or UAVs). This decision depends on factors such as
- Processing capabilities: The computational capability of the available computing nodes.
- Task urgency: Tasks with stricter deadlines require faster processing resources.
- Energy efficiency: Balancing energy consumption for local execution and task offloading.
Task offloading decisions can be modeled as optimization problems, where the goal is to minimize the execution time, energy consumption, or a weighted combination of both. The total energy consumption can be expressed as
where represents the energy consumed during local processing and accounts for the energy used for transmitting the task and its remote execution.
The computational resource allocation process must consider constraints such as the limited processing capacity of the computation nodes, real-time variations in vehicular traffic and task demands, task latency, and energy consumption thresholds [35]. Dynamic resource-allocation strategies are particularly important in highly variable AVEC environments. In this regard, advanced techniques such as ML and RL are increasingly being used to predict task demands and adaptively allocate resources in real-time.
By optimizing the distribution of computational workload, resource allocation reduces latency, improves energy efficiency, and ensures the reliability of VEC systems. Future research should explore more adaptive and intelligent approaches to computational resource management, focusing on real-time decision-making and resource optimization in dynamic vehicular networks.
2.3.3. Bandwidth Allocation
In AVEC, bandwidth allocation is essential for ensuring efficient data transmission between vehicles, RSUs, and aerial platforms. With the increasing number of connected vehicles and data-intensive applications, the bandwidth must be dynamically managed to prevent network congestion, minimize latency, and maintain QoS [36].
The bandwidth required for transmission depends on factors such as data size, transmission time, and channel conditions. Efficient bandwidth allocation in VEC must address the following challenges:
- Dynamic vehicular environments: Rapid changes in network topologies owing to vehicle mobility require adaptive bandwidth allocation strategies.
- Competing resource demands: Vehicles and edge devices compete for limited bandwidth, necessitating prioritization based on application needs, such as safety-critical versus noncritical tasks.
- Interference management: High vehicular density can lead to interference, further complicating bandwidth allocation.
Bandwidth allocation strategies often aim to maximize the data throughput while minimizing latency and ensuring fairness among users [37]. The allocation process can be modeled as an optimization problem, where the objective is to maximize the total utility of the system, which is defined as
where is the utility of bandwidth allocated to user and is the total number of users or vehicles in the system.
Utility functions are typically designed to reflect the priority of an application, with a higher utility assigned to tasks requiring low latency or high reliability. The sensitivity of system performance to the utility function design, especially under varying vehicular densities, depends on how the utility functions prioritize factors such as fairness and interference management in high-density environments. This sensitivity is typically managed by adjusting the resource allocation strategies or the parameters within the utility functions based on real-time network conditions [38]. Researchers need to design utility functions based on their specific network architecture, objectives, and models to ensure optimal performance under varying conditions.
- Static allocation: Predefined bandwidth allocation based on fixed priorities. This method is simple but lacks adaptability to dynamic conditions.
- Dynamic allocation: Adaptive methods that adjust the bandwidth allocation in real-time based on traffic demands, channel conditions, and application requirements. Machine learning (ML) and optimization algorithms are increasingly used to predict bandwidth requirements and allocate resources efficiently.
A key consideration in bandwidth allocation is the management of interference in high-density environments. Techniques such as channel reuse, interference coordination, and spectrum sharing are often employed to enhance bandwidth efficiency [39]. Moreover, bandwidth slicing, supported by technologies such as SDN, enables the division of the available bandwidth into virtual channels tailored to specific applications or user groups.
By optimizing bandwidth allocation, AVEC systems can reduce data transmission delays, improve throughput, and enhance overall network performance. Future research directions include developing intelligent bandwidth management algorithms capable of learning from network conditions, integrating advanced wireless communication technologies, such as 5G and beyond, and addressing the challenges of ultra-reliable low-latency communication in vehicular environments.
2.3.4. Basic System Model in AVEC
The basic system model in AVEC integrates vehicles, RSUs, and aerial platforms into a unified framework to support the computational and communication requirements of transportation systems. This system aims to address challenges such as latency, resource constraints, and mobility by leveraging edge-computing resources. Below, the key components and their interactions are outlined.
In a typical VEC system, vehicles are equipped with sensors, cameras, and communication modules that generate data for various applications such as real-time navigation, collision avoidance, and in-car entertainment [40]. These applications require low-latency data processing, which the traditional cloud model cannot efficiently provide owing to high transmission delays. VEC overcomes this limitation by bringing computational and storage resources closer to vehicles, thereby enabling real-time data processing and decision-making.
The core components of the AVEC system model include the following:
- Vehicles as mobile nodes: Vehicles act as both data sources and edge devices, capable of processing tasks locally or offloading them to nearby RSUs, base stations (BSs), or aerial platforms. They are equipped with onboard units that perform computational, storage, and communication tasks [41].
- RSUs: RSUs are deployed along roads to provide localized computational support and communication infrastructure. They act as fixed-edge nodes that enable vehicles within their range to offload computational tasks and access edge services [42].
- Aerial platforms: UAVs and HAPs serve as mobile edge nodes, dynamically extending the reach of a VEC system [43,44]. They are particularly effective in areas with sparse RSU deployments or peak network loads. Satellites can also act as cloud servers with high coverage and computational capacity [45].
- Base stations: BSs are fixed-edge nodes in an AVEC system that provide stable computational and communication support. They ensure seamless connectivity within coverage areas and facilitate task offloading from vehicles. BSs are critical in high-density urban regions and offer consistent low-latency services. They also act as intermediaries between vehicles, RSUs, and aerial platforms, ensuring efficient resource allocation and system stability [46,47].
In a basic VEC system, tasks generated by vehicles can be either processed locally or offloaded to nearby edge nodes based on factors such as task complexity, available resources, and latency constraints. To achieve efficient task execution, a VEC system relies on dynamic resource allocation and task scheduling strategies. These strategies aim to optimize key performance metrics such as latency, throughput, and energy consumption under the constraints of a highly dynamic vehicular environment.
The basic system model also incorporates advanced communication technologies like vehicle-to-everything (V2X) protocols, which enable seamless communication between vehicles, RSUs, and aerial platforms. These technologies ensure reliable data exchange and coordination, even in high-density or high-mobility scenarios.
VEC systems significantly enhance the responsiveness and reliability of transportation applications by integrating computational resources at the network edge. However, challenges, such as managing mobility, maintaining connectivity, and optimizing resource allocation, remain areas of active research and development.
3. Key Design Considerations
Designing an efficient RA framework for AVEC requires the careful consideration of several critical elements. These include task offloading strategies, mobility management, and handling of diverse network characteristics, all of which are essential for maintaining optimal system performance under dynamic conditions. The placement and movement planning of the aerial platforms, efficient cache utilization, and grouping of vehicles further enhanced the system’s adaptability and efficiency. Addressing these considerations ensures low latency (in association with allowable delay for task completion), reduced energy consumption (in association with dynamic mobility and charging capability), and reliable service delivery even in scenarios with high mobility and varying traffic loads.
3.1. Task Offloading Strategy
Task offloading is a crucial aspect of RA in AVEC systems. It involves transferring computational tasks from vehicles to nearby edge nodes, such as BSs, RSUs, or aerial platforms (UAVs, HAPs, and satellites), to optimize processing efficiency and reduce latency. Effective offloading strategies are essential to ensure low energy consumption and satisfy stringent QoS requirements in dynamic vehicular environments. Three primary task offloading strategies are considered in the AVEC.
3.1.1. Binary Offloading
In binary offloading, tasks are executed either locally on the vehicle’s onboard unit or remotely on an edge server or aerial platform [48]. Therefore, this approach simplifies the decision-making process but may not be efficient for all tasks because some may benefit from partial distribution to balance workload and energy consumption. Most studies on binary offloading have used binary decision-making parameters. Binary offloading is suitable for tasks with uniform resource requirements and fixed execution constraints.
3.1.2. Partial Offloading
Partial offloading allows the tasks to be broken down into smaller segments. In this approach, some parts are processed locally, while others are sent to remote servers for execution. This method ensures more effective use of available computational resources and adapts to different task complexities. For example, tasks requiring significant computational power can be offloaded, whereas simpler parts can be processed locally, leading to improved energy efficiency and reduced delays. Many studies have used task-splitting ratios as decision-making parameters, where tasks are divided into two parts: one for local execution and the other for offloading to remote nodes [36]. The allocation of computational and communication resources depends on the portion of the task that is offloaded. Therefore, the task offloading ratio plays a critical role in the resource allocation.
3.1.3. Hybrid Offloading
Hybrid offloading combines the features of both binary and partial offloading [49]. It dynamically adapts the offloading strategy based on the current network conditions, resource availability, and task requirements. This approach maximizes the advantages of both strategies, offering higher adaptability and efficiency in managing diverse workloads in AVEC systems. Hybrid offloading is particularly useful in scenarios in which network stability and computational resources fluctuate frequently.
These offloading strategies are fundamental for achieving optimal performance in AVEC. They not only reduce the computational burden on vehicles but also improve the overall responsiveness and scalability of systems. As the decision-making of task division ratio in both partial and hybrid offloading methods is an optimization problem, according to recent research, the decision is based on system model, objective, and the constraints of the optimization problem [50,51]. For instance, if the optimization objective is energy consumption reduction, the decision is made to minimize energy usage. If the objective is different, such as latency reduction or task completion rate maximization, the decision is made accordingly. This task division ensures that the offloading strategy aligns with the system’s performance objectives and optimizes the overall system efficiency.
3.2. Mobility Management
Vehicles in AVEC systems are highly mobile, which introduces significant challenges to maintaining stable and efficient communication. The movement of vehicles causes frequent changes in communication channel conditions and alters the distance between vehicles and edge nodes, thereby providing computational services [52]. These dynamic factors lead to constant fluctuations in the network status, making resource allocation and task offloading more complex.
The high mobility of vehicles can result in intermittent connections and variations in signal strength, thereby affecting the QoS. Additionally, rapid changes in network topology require adaptive mechanisms to ensure that tasks are seamlessly offloaded and executed without delays or interruptions [53]. Effective mobility management strategies are crucial to address these issues. Such strategies must consider real-time vehicle locations, predict movement patterns, and dynamically adapt the allocation of resources to maintain reliable connectivity and minimize latency.
By efficiently managing mobility, AVEC systems can overcome the challenges posed by dynamic vehicular environments, ensuring consistent service quality and the optimal utilization of available computational resources.
3.3. Heterogeneous Network Model
In AVEC, the edge-computing infrastructure comprises a variety of nodes, including BSs, RSUs, and aerial platforms such as UAVs, HAPs, and satellites [8]. These components form a heterogeneous network with diverse attributes and capabilities that significantly influence the performance and design of resource allocation strategies.
Each type of edge node offers distinct advantages and has specific constraints. As terrestrial nodes, the BSs and RSUs provide relatively stable connections and high computational capacities; however, their coverage is limited by their fixed locations. In contrast, aerial platforms, such as UAVs and HAPs, are mobile and can dynamically adjust their positions to address coverage gaps or meet increased demand [44]. UAVs are highly flexible and can serve specific areas on demand, whereas HAPs offer broader and more stable coverage over larger regions. Satellites provide the most extensive coverage and are essential for connecting remote areas; however, their communication latency is higher than that of other edge nodes.
The diversity among these edge nodes directly influences real-time task offloading decisions. Since each node has varying computational capacities, energy limitations, and latency characteristics, the selection of the most suitable node for task offloading becomes a complex decision. For instance, tasks requiring high computational power and low latency may be offloaded to BSs or RSUs, while tasks requiring mobility and flexibility may be better suited for UAVs. HAPs may be chosen for tasks needing broader coverage, and satellites may be selected for tasks in remote areas despite higher latency [54]. This diversity means that real-time task offloading strategies must dynamically evaluate factors such as the current load of each node, its proximity to the task, its available energy, and its communication capabilities [16]. The decision-making process for task offloading thus becomes highly context-dependent, requiring adaptive algorithms that consider these factors to ensure efficient resource usage, low latency, and minimal energy consumption.
The heterogeneity of network elements creates challenges for their integration into a unified framework. Differences in communication protocols, computational capacities, energy limitations, and latency characteristics must be carefully managed to ensure a seamless operation. Resource allocation strategies must account for these variations by dynamically assigning tasks to the most appropriate nodes based on real-time network conditions, task requirements, and node capabilities.
Heterogeneous network models in AVEC systems can enhance their flexibility, scalability, and reliability by leveraging the strengths of each type of node and addressing their limitations. Future research should focus on designing adaptive algorithms that efficiently coordinate diverse network components to achieve optimal performance in dynamic vehicular environments.
3.4. Task Model
The task model is a critical component of AVEC because it defines the characteristics of computational tasks and their influence on resource allocation. Tasks in AVEC are typically described by attributes such as task size, task complexity, and task latency requirements. These attributes play vital roles in determining how resources are allocated to ensure efficient and timely execution.
3.4.1. Task Size
Task size refers to the amount of data associated with a computational task, usually measured in bits or bytes. Larger tasks require more transmission bandwidth and computational resources, resulting in higher energy consumption and potential delays. Efficient resource allocation strategies must account for task size to optimize the use of communication channels and processing nodes [55]. For example, tasks with smaller sizes are often more suitable for immediate offloading to aerial platforms or nearby edge nodes, whereas tasks with larger sizes may require splitting or selective offloading.
3.4.2. Task Complexity
Task complexity represents the number of computation cycles required to process a task [56,57]. Highly complex tasks require greater computational power and specialized hardware or extended processing times. This attribute directly affects the choice of processing nodes, because high-complexity tasks may be better suited for edge servers with higher processing capabilities, such as satellites or HAPs. On the other hand, simpler tasks can often be processed locally on the vehicle or offloaded to nearby RSUs or UAVs to minimize energy consumption and latency.
3.4.3. Task Latency Requirements
Latency requirements specify the maximum allowable delay for task completion. Time-sensitive tasks, such as those supporting real-time decision-making in autonomous driving or emergency responses, require low-latency processing [58,59,60]. These tasks must be prioritized during resource allocation to ensure that they are executed within given time constraints. By contrast, tasks with more relaxed latency requirements can be scheduled for processing during periods of lower network congestion or offloading to distant nodes.
Researchers typically define a range for each task attribute to simulate and evaluate resource-allocation strategies in an AVEC. The task size, complexity, and latency requirements are assigned values within these ranges and are often chosen randomly during task generation to mimic real-world conditions. For example, the task size may be set within a range of 500 KB to 10 MB, task complexity within 200 to 700 CPU cycles/bit, and latency requirements within 10 to 100 ms. This approach allows researchers to create diverse task scenarios that test the adaptability and efficiency of resource allocation algorithms.
The combination of these task attributes influences resource allocation decisions. Larger tasks with high complexity and strict latency requirements pose significant challenges, requiring careful selection of offloading strategies and resource allocation to meet the performance goals. In contrast, less demanding tasks can be processed locally or offloaded to nodes with limited resources, helping balance the overall system load. By accurately modeling tasks and considering their attributes during simulations, researchers can design and evaluate resource allocation strategies that are robust, adaptable, and capable of satisfying the diverse demands of AVEC systems.
In AVEC systems, task attributes such as task size, complexity, and latency requirements are crucial for effective resource allocation. Task size, which refers to the amount of data involved, impacts the required transmission bandwidth and computational resources, with larger tasks often requiring more complex offloading strategies [4]. Task complexity, represented by the number of computation cycles, determines the choice of processing node, with more complex tasks being suited for powerful edge servers like satellites or HAPs, while simpler tasks can be processed locally or offloaded to UAVs or RSUs. Task latency requirements specify the maximum allowable delay, with time-sensitive tasks prioritized for low-latency processing. Researchers simulate these attributes within specific ranges to evaluate and optimize resource allocation strategies. The combination of these task characteristics guides resource allocation decisions, ensuring that the system can efficiently handle diverse tasks, from high-complexity, low-latency demands to less demanding ones that can be processed with minimal resources.
3.5. Trajectory and Deployment of Aerial Platforms
The trajectory and deployment of aerial platforms play a vital role in improving the efficiency and reliability of AVEC systems. Proper trajectory planning and deployment strategies ensure that aerial platforms can effectively support computational and communication tasks, particularly in dynamic high-density vehicular environments.
3.5.1. Trajectory Planning
Trajectory planning involves determining the optimal flight path for aerial platforms to maximize the coverage and efficiency [61]. A well-planned trajectory ensures that the UAVs can dynamically adjust their positions to serve areas with high task density or network demand. For example, during peak traffic hours or in areas with frequent accidents, UAVs can move to regions where vehicles generate a high volume of computational tasks, thereby providing localized edge-computing support. Additionally, trajectory planning helps minimize energy consumption by optimizing flight paths and ensuring that UAVs conserve power while maximizing their operational time [62,63]. Trajectory planning also affects communication reliability. UAVs must maintain line-of-sight communication with vehicles and ground stations while avoiding interference from obstacles, such as buildings or terrain. A carefully designed trajectory minimizes disruptions in connectivity, reduces latency, and enhances the QoS in AVEC systems.
3.5.2. Deployment Locations
Finding the optimal deployment locations for aerial platforms is critical. The placement of UAVs and HAPs determines the coverage area and the availability of edge-computing resources for vehicles [64,65,66]. Deploying aerial platforms near areas with high task densities ensures that computational and communication needs are met effectively. For example, urban intersections with heavy traffic or remote regions with limited terrestrial infrastructure may require strategic deployment of UAVs to fill coverage gaps and provide reliable services [67]. The deployment locations must also consider the capabilities of the aerial platforms. UAVs with limited battery lives and computational resources are best suited for short-term operations in high-demand areas, whereas HAPs with greater endurance and broader coverage are better suited for long-term deployment over larger regions. Satellites can provide overarching coverage but are less responsive to localized changes in task demand.
The density of tasks generated by vehicles is a critical factor that influences both trajectory planning and deployment strategies. High-task-density regions, such as congested highways or urban centers, require aerial platforms to concentrate their resources in these areas to handle the increased demand. Conversely, in regions with a low task density, aerial platforms can adopt broader trajectories or higher altitudes to conserve energy while maintaining sufficient coverage [62]. Dynamic task density also requires adaptive strategies. As vehicular traffic patterns change over time, the trajectory and deployment of aerial platforms must be adjusted in real time to ensure optimal resource allocation. ML and optimization algorithms are often employed to predict task density and dynamically reconfigure the deployment and movement of aerial platforms.
By carefully planning trajectories and selecting the optimal deployment locations, AVEC systems can improve coverage, reduce latency, and enhance resource utilization. These strategies ensure that aerial platforms provide efficient and reliable support for various vehicular applications in both urban and remote environments.
3.6. Cache Management
Cache management is a vital component of AVEC systems [68]. By caching data and services at edge nodes such as UAVs, HAPs, and satellites, AVEC systems can significantly reduce task-completion delays and alleviate bandwidth consumption. These aerial platforms complement terrestrial infrastructure, providing enhanced computational and storage capabilities, particularly in dynamic and resource-constrained vehicular environments.
3.6.1. Key Consideration in Cache Management
Aerial platforms have a limited storage capacity, making efficient caching strategies essential. Content caching involves storing frequently requested data, whereas service caching focuses on storing programs or resources required for processing computational tasks. A hybrid approach that combines content and service caching is often utilized to optimize resource usage and adapt to the dynamic demands of vehicular networks [65]. This approach minimizes unnecessary data transmissions and ensures timely task execution by storing only the most relevant data or services.
3.6.2. Dynamic Caching Strategies
Aerial platforms operate in dynamic environments with constantly changing user demands and task requirements. Adaptive caching strategies are critical in addressing these challenges. ML techniques, including deep RL and federated learning, have been employed to optimize caching by dynamically predicting content popularity and updating cache data dynamically [68]. These methods ensure high cache hit ratios and reduced latency while responding to varying network conditions. In addition, collaborative caching among multiple aerial platforms supported by advanced algorithms helps to balance workloads and enhance system efficiency.
3.6.3. Challenges in Cache Management
Effective cache management in AVEC systems must overcome several challenges:
- Limited storage resources: Aerial platforms have constrained storage capacities and require intelligent selection of cached content or services to maximize utility.
- Mobility and dynamic network topology: The movement of vehicles and aerial platforms introduces variability into data access patterns. Collaborative and predictive caching strategies can help maintain a seamless service delivery.
- Real-time adaptation: Rapidly changing user demands necessitate continuous updates to the cached data. Leveraging real-time data analytics and ML enables proactive cache adjustments to satisfy emerging requirements.
Efficient cache management directly enhances performance metrics, including reduced latency, improved energy efficiency, and better QoS. By relying on the localized processing capabilities of aerial platforms and reducing dependency on remote cloud resources, caching strategies can decrease communication overhead and enhance system responsiveness. Aerial platforms, whether operating independently or collaboratively, are particularly effective in high-demand scenarios such as urban traffic congestion, where timely computational support is critical. In conclusion, cache management in aerially assisted VEC systems is crucial for maintaining efficient and reliable service delivery. Future research should focus on advanced caching algorithms, multiplatform collaboration frameworks, and adaptive strategies to optimize system performance in diverse vehicular environments.
3.7. Vehicle Clustering
Vehicle clustering is an essential technique in aerial-assisted vehicular networks for enhancing communication, computation, and resource allocation efficiency. Clustering enables the better management of network resources and reduces the overall system overhead by grouping vehicles into clusters based on proximity or task similarity [35]. Each cluster typically has a leader who can communicate with aerial platforms such as UAVs, HAPs, or satellites to relay information and distribute computational tasks among member vehicles.
Clustering helps to maintain robust communication links, particularly in high-density traffic or dynamic environments [64,69]. Clustering minimizes communication latency and bandwidth usage by reducing the number of direct connections required between individual vehicles and aerial platforms. Additionally, it supports efficient resource sharing, as clustered vehicles can offload tasks collaboratively with local leaders or nearby edge nodes, thereby improving system responsiveness and reducing energy consumption. Task density and vehicular mobility significantly affect the clustering strategies. High task densities in urban areas may necessitate smaller clusters with more frequent interactions with aerial platforms, whereas low-density rural areas may support larger clusters with less frequent updates. The mobility patterns of vehicles also play a critical role, requiring dynamic adjustments to cluster configurations to maintain connectivity and ensure service continuity.
Through clustering, aerial-assisted networks achieve greater scalability and adaptability, enabling efficient handling of vehicular communication and computational requirements in diverse environments.
3.8. Security and Trust Management in AVEC
In the context of AVEC, security and trust management are essential to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the network. As AVEC systems involve a range of heterogeneous devices including vehicles, UAVs, HAPs, and edge nodes, securing data communication, protecting user privacy, and ensuring the integrity of the system are critical considerations. The dynamic and decentralized nature of AVEC introduces additional complexities in managing security and trust.
3.8.1. Security Challenges
AVEC systems face several security challenges including data confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. Because data is transmitted across various aerial and terrestrial platforms, ensuring secure communication channels is paramount to prevent unauthorized access or tampering [70]. Furthermore, protecting sensitive information such as vehicular data, user behavior, and task-related information is crucial to maintaining privacy in autonomous driving and other real-time applications.
3.8.2. Trust Management
Trust management is vital for ensuring reliable interactions between different nodes in AVEC systems. Since UAVs and other aerial platforms are highly mobile, ensuring that they follow the predefined network protocols and securely interact with vehicles and edge nodes is essential. Dynamic trust models can be implemented to evaluate and establish trust relationships based on node behavior, historical performance, and compliance with security policies [71]. These models help mitigate the risk of malicious nodes or compromised UAVs disrupting the system.
3.8.3. Techniques for Security and Trust Management
Several techniques can be employed to address security and trust management challenges in AVEC systems:
- Encryption and Authentication: Secure communication channels can be established through advanced encryption techniques such as end-to-end encryption and blockchain-based authentication, ensuring data confidentiality and authenticity [72,73,74].
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS can monitor traffic patterns and node behaviors to detect and prevent any unauthorized or malicious activities within the AVEC network [75].
- Blockchain for Trust: Blockchain technology can be used to establish a decentralized and immutable record of trust, ensuring that each node’s activities and reputation are transparently tracked and verified [76].
Security and trust management are crucial in AVEC systems to ensure secure communication, data protection, and reliable interactions among heterogeneous nodes. Techniques such as encryption, authentication, intrusion detection, and blockchain-based trust models help address security challenges and maintain system integrity in dynamic AVEC environments.
3.9. Energy Constraints and Integration with 5G/6G
Energy efficiency is a critical factor for UAVs in AVEC systems, as limited battery capacity directly affects their operational time, coverage, and computational support capabilities [77]. Efficient energy management strategies are essential to balance flight duration, task offloading, and communication requirements, particularly in high-demand scenarios such as urban traffic congestion or disaster response.
The integration of AVEC with advanced wireless networks like 5G and emerging 6G provides opportunities to enhance system performance while mitigating energy constraints [78]. High-bandwidth, low-latency communication enables UAVs to offload computation tasks efficiently, reducing onboard energy consumption. Network slicing and edge-assisted computing further allow UAVs to dynamically allocate communication and computational resources while maintaining energy-efficient operations.
By addressing energy constraints and leveraging 5G/6G capabilities, AVEC systems can achieve longer operational times, reliable connectivity, and improved resource allocation across aerial and vehicular nodes.
4. Resource Allocation Techniques in Aerial-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing
Efficient resource allocation is critical to the performance and reliability of AVEC systems. These systems must address the challenges of dynamic vehicular environments including high mobility, fluctuating network demands, and limited resources on aerial platforms. Resource allocation techniques aim to optimize key resources, such as computational power, bandwidth, and energy, to ensure low latency, high throughput, and reliable service delivery. This section explores the major techniques used in AVEC for resource allocation. Figure 3 presents the classification of the techniques used for RA in AVEC based on recent studies. In this figure, traditional algorithms used in AVEC are categorized under heuristics (i.e., game theory and alternative optimization) and optimization techniques (i.e., successive convex approximation, P-norm and convex optimization, dynamic programming, and Lagrangian gradient descent). Reinforcement learning-based algorithms are classified into value-based RL (i.e., DQN, DDQN, and multi-agent Q-learning) and policy-based RL (i.e., PPO and MADDPG). Additionally, hybrid methods like federated learning are also included.
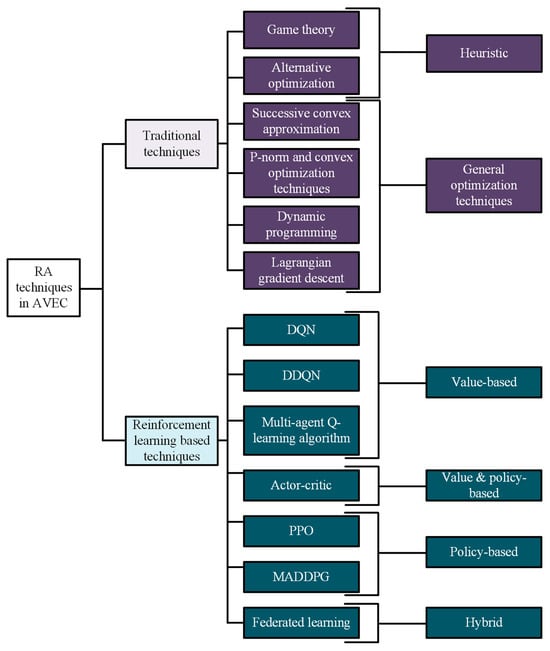
Figure 3.
Classification of the RA techniques used in AVEC.
4.1. Traditional Techniques
Traditional AVEC techniques focus on optimizing resource allocation using deterministic methods. These methods simplify complex problems into structured models, enabling the efficient allocation of resources such as bandwidth, computation, and transmission power. Although they are effective in static environments, they often lack adaptability to highly dynamic AVEC systems.
4.1.1. Game Theory
Game theory offers a robust framework for analyzing interactions and decision-making among multiple agents, enabling the optimal allocation of resources in competitive or cooperative scenarios. In the context of AVEC systems, game theory has been utilized to address resource allocation challenges such as task offloading, channel access, and computation resource management. This approach models the interactions between vehicles and edge nodes as strategic games in which each agent aims to optimize its utility under system constraints. In [79], a game-theoretic approach was proposed to minimize the age of information (AoI) in UAV-assisted VEC networks. The problem was framed as a channel-access game, in which vehicles competed for limited wireless resources. A distributed stochastic learning algorithm was designed to achieve Nash equilibrium and ensure efficient and timely data transmission. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the algorithm in reducing the AoI compared with traditional methods. Similarly, Li et al. [44] employed a coalition game approach to optimize task offloading and multidimensional resource allocation in an air–ground integrated VEC network. Their method addresses challenges such as UAV trajectory design and bandwidth allocation. The proposed scheme minimizes task-offloading delays by considering the cooperative behavior among vehicles and UAVs.
Lesson Learned: Game theory provides a powerful tool for modeling complex resource allocation problems in VEC systems. This will facilitate the development of distributed, scalable, and efficient algorithms to ensure improved system performance and fairness among multiple users. However, the careful consideration of real-time constraints and dynamic network conditions is crucial for practical implementation. For instance, when multiple vehicles compete for the same edge server, a game-theoretic mechanism can guide them to make balanced decisions that reduce delays and prevent monopolization, ensuring both individual benefit and system-wide efficiency.
4.1.2. Alternative Optimization
Alternative optimization is a systematic method that addresses complex, nonconvex problems by breaking them into simpler subproblems. These sub-problems are solved iteratively, with the solution of one sub-problem influencing the next. This approach ensures convergence to a high-quality solution by refining each variable while keeping the others fixed, thereby holistically optimizing the system. In [80], an alternative optimization technique was utilized to maximize the computational efficiency of a UAV-aided VEC system. The authors formulated a mixed-integer nonconvex problem involving communication scheduling, UAV trajectory design, and computational resource allocation. To address this, they decomposed the problem into two subproblems: (1) optimizing communication scheduling using a Lagrangian dual decomposition method, and (2) optimizing UAV trajectories and computing resources using a successive convex approximation (SCA) technique. The optimized resources include the communication bandwidth, UAV trajectory, and computational power allocation for IoT devices.
Lesson Learned: Alternative optimization is a versatile method for solving resource allocation challenges in complex VEC systems. The iterative refinement process ensures a balance between computational efficiency and system constraints, making it a practical solution for real-world applications under dynamic operational conditions. In practice, this approach allows large problems to be divided into smaller, manageable parts, which makes system optimization more flexible and easier to implement.
4.1.3. Successive Convex Approximation
SCA is an iterative optimization method designed to address nonconvex problems by approximating them with a series of convex subproblems. In each iteration, the method linearizing or approximates the nonconvex parts of the objective function or constraints around the current solution, solving the resulting convex problem to obtain an updated solution. This process ensures convergence toward a locally optimal solution under appropriate conditions. In [37], the SCA was utilized as part of a comprehensive algorithm for resource allocation and UAV positioning in a UAV-assisted VEC system. The authors aimed to minimize the maximum delay and energy consumption of the system, which poses a mixed-integer nonlinear programming challenge. The SCA was specifically applied to optimize UAV positioning by transforming a nonconvex trajectory optimization problem into a series of solvable convex problems. This optimization directly influences the allocation of computational resources, bandwidth, and UAV trajectories, ensuring fairness among vehicular user devices and enhancing system efficiency. Similarly, Ren et al. [36] employed the SCA to address the delay minimization problem in HAP-assisted vehicular networks. Their framework optimizes task-splitting ratios, bandwidth distribution, and computational resource allocation while accounting for network dynamics and handoff conditions. By iteratively solving convex sub-problems, the SCA-based approach ensures that tasks are processed efficiently, even in highly dynamic vehicular environments.
Lesson Learned: SCA is a versatile tool for solving nonconvex optimization problems in AVEC systems. It enables the iterative refinement of resource allocation strategies, ensuring scalability and effectiveness under dynamic network conditions. However, careful initialization and parameter tuning are critical for achieving optimal performance. In practice, its success depends on designing suitable convex approximation and ensuring that the iterative process converges within reasonable complexity limit.
4.1.4. P-Norm and Convex Optimization Techniques
P-norm and convex optimization techniques are effective methods for addressing complex resource allocation problems by converting nonconvex objectives into solvable convex problems. The p-norm approximates the maximum value in a dataset by aggregating values with a controllable degree of emphasis on larger elements, whereas convex optimization ensures computational efficiency and guarantees convergence to a globally optimal solution. Liwang et al. [81] employed p-norm and convex optimization techniques to solve the resource allocation problem in air-ground integrated vehicular networks. The authors aimed to optimize the mapping of computation-intensive graph tasks carried out by UAVs to available vehicular resources, considering energy consumption, task completion time, and communication costs. They formulated a nonconvex mixed-integer optimization problem and applied a two-stage decoupled approach. The P-norm is used to approximate the maximum data transmission delay and convert it into a convex formulation. Convex optimization was then applied to efficiently allocate the UAV transmission power across service providers, ensuring that the constraints on energy consumption and data exchange costs were met. The allocated resources include the UAV transmission power, task scheduling, and data transmission bandwidth.
Lesson Learned: The combination of the p-norm and convex optimization provides a robust framework for handling nonconvex optimization problems in VEC systems. These methods enable efficient resource allocation, but their success depends on precise problem decomposition and parameter tuning to balance computational complexity and solution quality. In real-world deployments, their effectiveness also relies on adaptability to dynamic network conditions and scalability to large-scale systems, which may introduce additional challenges for convergence and stability.
4.1.5. Dynamic Programming
Dynamic programming (DP) is an optimization approach that solves complex problems by breaking them into smaller subproblems, solving each subproblem only once, and storing their solutions. DP is particularly effective in solving sequential decision-making problems, in which decisions at each stage affect future outcomes. It is widely applied in time-dependent optimization scenarios by leveraging deterministic or stochastic models to determine optimal policies. In [82], DP was applied to optimize resource allocation in a UAV-RIS-assisted vehicular communication system. The authors aimed to minimize the total power consumption while maintaining the QoS and energy constraints. They formulated the problem as a multi-slot power allocation and optimization task for a discrete-time dynamic system. DP was employed to schedule the transmit power of the UAV and the number of active reflecting elements (REs) in the reflective intelligent surface (RIS) over finite time horizons. The offline deterministic DP algorithm addresses cases with predictable environmental dynamics, whereas the stochastic DP algorithm addresses both uncertain and dynamic conditions. This allowed for the efficient allocation of transmit power and active REs under varying channel conditions, significantly improving energy efficiency and reducing transmission failures.
Lesson Learned: Dynamic programming is a powerful tool for addressing sequential resource allocation problems in both dynamic and constrained environments. Its adaptability to both deterministic and stochastic scenarios ensures optimal performance but requires careful modeling to balance computational complexity and scalability. In practice, its effectiveness depends on accurate system state estimation and efficient state-space representation to manage the trade-off between precision and feasibility in large-scale deployments.
4.1.6. Lagrangian Gradient Descent
Lagrangian gradient descent is a powerful optimization technique for solving constrained optimization problems. It operates by constructing a Lagrangian function that incorporates an objective function and constraints with associated multipliers. The gradients of this function are iteratively computed and updated to minimize the objective while ensuring that the constraints are satisfied. This method is particularly effective in addressing coupled problems in resource allocation. Liu et al. [83] applied Lagrangian gradient descent to minimize the outage probability in a UAV-assisted vehicular network. The authors addressed the coupled subproblems of vehicle clustering, UAV trajectory optimization, and power allocation. They used an improved k-means algorithm to cluster vehicles and select cluster heads. Subsequently, the Lagrangian gradient descent method was employed to jointly optimize the UAV trajectory and power distribution among the cluster vehicles and the UAV itself. This iterative optimization allocates transmission power resources to vehicles and UAVs, while dynamically adapting the UAV’s position to minimize the outage probability under energy and mobility constraints.
Lesson Learned: Lagrangian gradient descent effectively handles complex coupled optimization problems, enabling scalable and precise resource allocation in vehicular edge networks. Its iterative nature ensures adaptability to dynamic conditions; however, careful parameter tuning is crucial to avoid convergence issues. In practical deployments, its performance depends on accurate modeling of system constraints and efficient decomposition of subproblems, which ensures both feasibility and real-time applicability.
4.2. Reinforcement Learning-Based Techniques
RL-based techniques address AVEC’s dynamic challenges of AVECs by enabling adaptive decision-making through environmental interactions. RL-based techniques handle complex decentralized systems while maintaining scalability and privacy.
In comparison to the traditional techniques, the RL-based techniques can be effectively used to design the optimized solutions for task offloading, mobility management, path planning, cache control, and vehicle clustering [68]. They provides an effective solution for decentralized resource allocation in AVEC, which are particularly suitable for large-scale systems. Such advantages are thanks to the dynamic decision-making capabilities and real-time environmental interactions of RL-based resource allocation. In summary, while the traditional techniques are suitable for problems with predictable conditions and structured constraints, the RA-based methods offer flexibility and adaptability in dynamic and complex AVEC scenarios, resulting in the improved performance of recent state-of-the-art applications.
4.2.1. Deep Q-Network
Deep Q-network (DQN) is an RL algorithm that extends Q-learning using neural networks to approximate the Q-value function, enabling it to handle large state-action spaces effectively. In a DQN, the Q-value function predicts the expected cumulative reward for taking a particular action in a given state, and the neural network iteratively updates its parameters based on the observed rewards and transitions. This algorithm employs experience replay and target networks to stabilize the training and improve the learning efficiency. Yang et al. [84] applied a DQN to optimize the channel allocation and task offloading in temporary UAV-assisted VEC networks. The authors formulated the problem as a Markov decision process (MDP) to minimize service costs while ensuring that task deadlines were met. The UAV acted as both a relay and an edge-computing node, supporting tasks from vehicles via the LTE-V2X and TDMA communication protocols. Using a DQN, the system dynamically selects optimal channel allocation and task processing modes based on real-time environmental factors, such as task size and channel conditions. The allocated resources include communication bandwidth and UAV computational capacity. The simulation results demonstrated significant improvements in transmission efficiency and cost-effectiveness compared with conventional methods.
Lesson Learned: The DQN offers a robust framework for solving dynamic resource allocation problems in UAV-assisted vehicular edge networks. Its ability to adapt to changing network conditions and optimize resource usage makes it a valuable tool, although the computational overhead and convergence speed require careful consideration in practical deployments.
4.2.2. Double Deep Q-Network
Double deep Q-network (DDQN) is an advanced RL technique that improves upon the traditional DQN by addressing the overestimation bias. In the DDQN, two separate neural networks are employed: one for action selection and the other for action evaluation. This separation allows for more accurate and stable learning, making the DDQN particularly effective in dynamic and complex environments. In [85], a DDQN was applied to optimize the joint spectrum allocation and configuration design in an RIS-assisted vehicular communication system. The authors formulated the problem of maximizing the data rates for vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) users while meeting the reliability and latency requirements of vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) pairs. By modeling the control variables as an MDP, they utilized a DDQN with an attention mechanism to focus on relevant inputs, thereby reducing computational redundancy. The resources allocated through this approach include spectrum assignment, STAR-RIS amplitude and phase-shift coefficients, and transmission power for V2V communication.
Lesson Learned: A DDQN effectively handles dynamic resource allocation problems in complex communication networks. Its attention mechanism enhances decision-making by focusing on critical parameters; however, its performance relies on careful tuning of the learning process to adapt to varying network conditions.
4.2.3. Multi-Agent Q-Learning Algorithm
Multi-Agent Q-learning is an RL technique designed to handle optimization problems involving multiple autonomous agents operating in shared environments. Each agent independently learns the optimal strategy by interacting with its local environment. Through iterative updates of the Q-values in a Q-table, the algorithm enables agents to make resource allocation decisions that maximize cumulative rewards while meeting predefined constraints. Unlike single-agent Q-learning, the multi-agent variant incorporates strategies to address the decentralized nature of the system and potential conflicts between agents. In [86], a multi-agent Q-learning algorithm was implemented for resource allocation in a UAV-enabled MEC network. The authors modeled the system as a multi-UAV network, where each UAV acted as an independent agent responsible for managing the computational and communication resources. The objective was to minimize total energy and computational resource consumption while satisfying the latency requirements of mobile users. The algorithm allows UAVs to allocate resources such as transmission power and computational capacity without requiring information exchange among agents. Each UAV independently observes its environment and updates its Q-table using local state information, action decisions, and reward functions. This decentralized approach reduces complexity and ensures scalability.
Lesson Learned: Multi-agent Q-learning provides an effective solution for decentralized resource allocation in UAV-enabled MEC networks. Its adaptability to dynamic conditions and ability to operate without centralized control makes it particularly suitable for large-scale multi-UAV systems. However, managing the interactions between agents remains a challenge that requires careful consideration.
4.2.4. Actor-Critic
Actor-Critic method is an RL framework combining policy- and value-based approaches. It consists of two main components: the actor, who decides the actions to take based on the current policy, and the critic, who evaluates the actions by estimating the value function. The Actor updates the policy directionally based on feedback from the critic, whereas the critic updates the value function to improve the evaluations over time. This interplay enables the algorithm to handle continuous action spaces efficiently and adapt to complex and dynamic environments. In [87], the actor–critic approach was implemented using the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm to optimize resource allocation and UAV speed in an energy-harvesting-based UAV-assisted VEC framework. The authors modeled the problem as a time-coupled long-term optimization task aimed at maximizing the amount of data offloaded to UAVs for computation. The actor–critic framework was employed to jointly optimize three key resources: computational resource allocation, power splitting for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer, and UAV flight speed. The Actor proposed actions to allocate resources and control UAV mobility, whereas the critic evaluated the cumulative rewards associated with these actions. Simulation results demonstrated that this approach effectively enhanced the data offloading efficiency while adhering to energy and latency constraints.
Lesson Learned: The actor–critic method is well-suited for solving multi-dimensional optimization problems in UAV-assisted VEC systems. Its ability to balance exploration and exploitation ensures efficient resource utilization; however, its reliance on modeling and training can affect its practical performance, requiring accurate modeling and sufficient training.
4.2.5. Proximal Policy Optimization
Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) is an RL algorithm that balances policy exploration and exploitation using a clipped surrogate objective function to limit updates. This ensured stable training and efficient learning in dynamic environments. PPO is particularly suitable for optimizing complex resource allocation tasks in the AVEC. Li et al. [88] used PPO to optimize task offloading and UAV trajectories in a digital twin-enabled UAV-assisted VEC network. The optimization aimed to minimize energy consumption while adhering to the latency constraints. By modeling the problem as an MDP, the PPO dynamically allocates the UAV computational resources, communication bandwidth, and trajectory paths based on real-time network states. This approach significantly improves the energy efficiency and reduces the latency compared with traditional methods. Similarly, Shen et al. [23] employed the PPO in an asynchronous federated learning framework for UAV-assisted VEC systems. Their method optimized task offloading while considering the task dependencies and priorities. The PPO facilitates the allocation of vehicle computational resources, UAV resources, and bandwidth, thereby reducing both task execution delay and energy consumption. The asynchronous federated learning mechanism enhances scalability by leveraging data from multiple UAVs while ensuring data privacy.
Lesson Learned: PPO is an effective algorithm for resource allocation in dynamic VEC environments, enabling real-time optimization and integration with advanced frameworks such as digital twins and federated learning. However, its success depends on precise system modeling and careful parameter tuning.
4.2.6. Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient
Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (MADDPG) is an RL algorithm designed to optimize resource allocation in multi-agent environments. It combines centralized training with distributed execution, allowing agents to make independent decisions based on local observations while benefiting from global information during training. This approach ensures cooperation among agents and is particularly effective for handling dynamic and continuous action spaces. In [89], MADDPG was applied to optimize spectrum, computing, and caching resource allocation in MEC- and UAV-assisted vehicular networks. By modeling MEC servers and UAVs as independent agents, they improved task offloading efficiency and reduced delays compared with traditional allocation strategies. Qin et al. [90] employed MADDPG in air-ground vehicular cooperative computing networks (AVC2N) to address challenges such as global state information uncertainty and long-term queuing constraints. Their framework optimized task offloading decisions, spectrum allocation, and UAV trajectories, achieving lower system costs and meeting the URLLC requirements. Wang et al. [91] introduced MADDPG with an attention mechanism in a security-constrained multi-UAV network. The framework jointly optimizes spectrum efficiency, computing resources, and bandwidth allocation, prioritizing vehicle safety and delay constraints while improving resource utilization under strict conditions. In [92], extended MADDPG to collaborative multi-UAV networks, focusing on UAV trajectory planning, spectrum resource allocation, and task offloading. Their approach was adapted to vehicular mobility and task dynamics, enhancing task completion times and maintaining QoS for vehicles.
Lesson Learned: MADDPG effectively manages complex resource allocation and optimization in multi-agent systems. The cooperative strategies and centralized training framework ensure adaptability in dynamic vehicular edge networks. However, high computational requirements and accurate modeling remain the key challenges for practical implementation.
4.2.7. Federated Reinforcement Learning
Federated Reinforcement Learning (FRL) combines the decentralized model training of federated learning with the dynamic decision-making capabilities of reinforcement learning. It enables collaborative learning among distributed agents without sharing raw data, preserves privacy, and reduces communication costs. The FRL is particularly effective in dynamic environments, such as vehicular networks, where agents independently train local models and periodically synchronize them with a global model hosted on a central server. In [93], the FRL was applied to optimize resource allocation in UAV-aided vehicular platooning networks. Their approach jointly managed the CPU/GPU frequency, transmission power, and platoon control to minimize energy consumption. By leveraging FRL, vehicles and UAVs collaboratively update models using local training data, reducing computational and communication overheads, while improving system efficiency. Song et al. [94] introduced a federated upgraded dueling double deep Q-network for hybrid air-ground multi-server computation offloading. Their FRL-based algorithm optimized the UAV trajectories, communication resources, and computation tasks. This approach improves delay and energy efficiency by leveraging federated learning to enhance the privacy and scalability of model training. Zhao et al. [95] focused on reliable client selection and resource scheduling in UAV-assisted vehicular networks. They proposed a reputation-based mechanism to select trustworthy clients and optimized the bandwidth allocation, local training rounds, and transmission power using FRL. This method improves the global model accuracy and reduces delay and energy costs.
Lesson Learned: FRL is a robust framework for dynamic resource management in UAV-assisted vehicular networks, enabling collaborative optimization while ensuring privacy and scalability. Success depends on effective client selection, reliable communication, and computational efficiency.
In this section, we explore the key RL techniques used for RA in VEC based on recent research. We discuss various RL-based approaches, their objectives, and their suitability for addressing the unique challenges of VEC environments. Understanding these techniques is essential for developing efficient and adaptive resource management solutions.
5. Comparison
Resource allocation techniques in AVEC encompass a diverse range of traditional and reinforcement learning-based methods, each with distinct advantages and limitations. Table 2 shows the comparison of resource allocation algorithms developed so far for AVEC in terms of main idea and target applications. Every algorithm has its own inherent characteristics and emerging target applications. This table can provide helpful idea to researchers and practitioners who will design a new algorithm or apply one of the existing algorithms to an application under consideration.

Table 2.
Comparison of resource allocation algorithms in AVEC in terms of main idea and target applications.
The comparison provided in Table 3 evaluates traditional techniques and RL-based approaches in terms of major features and characteristics, by focusing on their performance objectives, advantages, and limitations. This table shows the additional qualitative information of algorithm comparison for six traditional techniques and seven reinforcement learning-based techniques, which is also useful to researchers and practitioners in association with Table 2.

Table 3.
Comparison of resource allocation algorithms in AVEC in terms of major features and characteristics.
Table 4 summarizes the system and simulation parameters used in the performance study for the 13 resource allocation algorithms in AVEC. This table gives the comparative data of performance evaluation for different resource allocation techniques, which includes simulation tool, the number of UAVs, the number of vehicles, simulation area, and the performance metrics evaluated. Therefore, it will be technically useful to researchers and engineers.

Table 4.
Comparison of resource allocation algorithms in AVEC in terms of parameters used in the performance study.
Traditional techniques such as game theory, alternative optimization, SCA, p-norm optimization, dynamic programming, and Lagrangian gradient descent offer structured approaches to resource allocation by addressing specific objectives such as minimizing delay, maximizing computational efficiency, and reducing power consumption. For example, game theory ensures fair resource distribution in competitive scenarios, while dynamic programming is particularly effective for solving sequential optimization problems. However, these techniques often fail in dynamic AVEC environments because of their reliance on static assumptions or high computational overhead, which limits their scalability and adaptability to real-time changes.
In contrast, reinforcement learning-based techniques provide more dynamic solutions by leveraging real-time environmental interactions to optimize resource allocation. That is, in comparison to the traditional techniques, the RA-based methods offer flexibility and adaptability in dynamic and complex AVEC scenarios without the requirement of predictable conditions and structured constraints, resulting in the improved performance of re-cent state-of-the-art applications.
DQN and DDQN excel at adapting to changing network conditions and improving transmission efficiency; however, they require significant computational resources and exhibit convergence challenges during training. Multi-agent RL approaches, such as MADDPG, enable decentralized agents, such as UAVs, to make collaborative resource allocation decisions. These methods are particularly effective in handling large-scale and decentralized systems but face challenges in terms of agent coordination and computational complexity. Actor–critic methods and PPO enhance continuous action optimization and stabilize policy updates, making them suitable for energy-efficient task offloading and UAV trajectory optimization. However, the computational intensity can limit the scalability of large AVEC networks. FRL introduces privacy-preserving distributed optimization, which is ideal for collaborative resource allocation in AVEC. Despite its potential, the FRL incurs high communication overhead, making it less practical in high-density vehicular environments.
Overall, traditional techniques are suitable for problems with predictable conditions and structured constraints, whereas reinforcement learning-based methods offer flexibility and adaptability in dynamic and complex AVEC scenarios. However, the computational and training requirements of learning-based approaches remain key barriers to their widespread adoption. Future research should focus on hybrid solutions that integrate the reliability of traditional methods with the adaptability of RL to effectively address the unique challenges of AVEC systems.
6. Challenging Issues and Future Research Directions
With the evolution of AVEC systems, addressing their unique challenges requires innovative approaches and forward-looking research. Below are six technically advanced and underexplored research challenges along with potential future directions.
6.1. Scalability in Heterogeneous Multi-Platform Networks
The integration of heterogeneous platforms such as UAVs, HAPs, satellites, and base stations enhances the flexibility of AVEC systems but also introduces significant scalability challenges. Each platform offers distinct advantages: UAVs provide mobility but have limited resources, HAPs deliver medium coverage with persistent energy supply, satellites ensure global reach but at the cost of higher latency, and base stations offer stable high computation capacity [96]. Coordinating resource allocation across these diverse platforms becomes exponentially complex as network size increases [97,98,99]. For example, in a metropolitan traffic management system, large fleets of UAVs may be deployed to monitor accidents or congestion hotspots, while HAPs provide persistent regional coverage and satellites support rural connectivity. Without efficient coordination, UAVs in urban areas may generate overlapping coverage and interference, while satellites may remain underutilized in the same system, leading to resource imbalance and degraded service quality.
Probable future direction: Hierarchical resource allocation models leveraging multi-agent RL can enable efficient platform-specific optimization while ensuring global coordination. By integrating GNNs to model the interdependencies among platforms, scalable solutions can be adaptive to dynamic topology changes and reduce the incurred control overhead.
6.2. Dynamic Inter-Platform Resource Sharing
The heterogeneous nature of AVEC systems creates inherent difficulties in sharing resources efficiently across platforms. UAVs, HAPs, satellites, and base stations operate with different latency, bandwidth, and computational constraints, which complicates coordination [54,100,101,102]. For instance, UAVs that offload tasks to satellites during peak hours may experience long transmission delays, while HAPs attempting to balance workloads between UAVs and satellites often lack real-time knowledge of network states, leading to suboptimal allocation. Static or semi-dynamic pooling mechanisms are insufficient in this context because they cannot adapt quickly to rapid fluctuations in vehicular traffic demand, resulting in congestion, idle resources, and degraded system performance [103].
Probable future direction: The adaptive resource-pooling systems that incorporate predictive resource state estimations using ML can be developed. These systems enable platforms to allocate bandwidth, computations, and storage dynamically to ensure balanced resource utilization. SDN can further enhance inter-platform orchestration in a real-time basis.
6.3. Integration of Quantum Computing for Optimization
Real-time optimization tasks, such as UAV trajectory planning, multiplatform task offloading, and joint resource allocation, are inherently nonconvex and involve high-dimensional decision spaces. For example, simultaneously optimizing the trajectory and power allocation for multiple UAVs while minimizing energy and latency constraints leads to computational bottlenecks when using classical algorithms.
Probable future direction: Quantum computing offers a promising approach to overcoming the bottlenecks by exploiting quantum parallelism to search high-dimensional solution spaces more efficiently than classical methods [78]. Hybrid quantum-classical algorithms, such as quantum annealing and variational quantum eigen solvers, can be applied to resource scheduling and trajectory optimization problems, providing faster convergence to near-optimal solutions [104]. In an AVEC context, quantum-enabled optimization could allow UAV swarms to jointly determine energy-efficient trajectories and task allocations in real time, even under highly dynamic traffic and communication conditions. By integrating quantum optimization techniques with classical reinforcement learning frameworks, future AVEC systems could achieve both scalability and low-latency responsiveness, which are currently difficult to realize with conventional algorithms alone. Specific hybrid quantum-classical algorithms such as the quantum approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA) could be explored for solving combinatorial optimization problems in AVEC, while tools like IBM’s Qiskit and Google’s Cirq could be used to simulate quantum-enhanced solutions [78,105]. However, practical deployment of quantum computing in AVEC faces hardware challenges including limited quantum processor capabilities and the need for low-latency stable hybrid systems. These limitations must be addressed for quantum computing to be effective in real-world AVEC applications.
6.4. Proactive Task Prediction and Offloading
Most task-offloading frameworks are reactive, relying only on current network and resource states without anticipating upcoming workloads [106]. For instance, a UAV may become overloaded when several vehicles simultaneously offload computationally intensive tasks, leading to delays or request drops. Proactive task prediction addresses this issue by forecasting workload patterns in advance and pre-allocating resources accordingly [107,108]. Techniques such as machine learning-based demand forecasting, temporal workload modeling, and mobility-aware prediction enable UAVs and HAPs to anticipate task surges before they occur [109]. By integrating predictive models with offloading mechanisms, AVEC systems can reduce latency, prevent overload situations, and achieve more efficient task distribution across platforms.
Probable future direction: Transformer-based models can be used for time-series forecasting of both vehicular workload trends and peak demand periods. These predictions can be integrated into proactive task-offloading mechanisms, allowing UAVs, HAPs, and satellites to pre-allocate resources. Combining prediction with edge-cloud hybrid systems ensures that tasks are optimally distributed before resource contention occurs.
6.5. Tiny Machine Learning (TinyML) for AVEC
Edge devices in AVEC, such as UAVs and IoT sensors, face stringent constraints on computational power and energy [110]. Conventional resource-allocation algorithms, which are typically designed for cloud servers or high-performance edge devices, are often too complex and resource-intensive for these platforms. Tiny machine learning (TinyML) offers a lightweight alternative by enabling the deployment of optimized ML models directly on low-power devices [111]. Through techniques such as model quantization, pruning, and hardware-aware optimization, TinyML allows resource allocation, anomaly detection, and task scheduling to be executed locally without constant reliance on higher-tier nodes [112,113]. This enhances responsiveness, reduces communication overhead, and extends device lifetime, thereby improving the overall efficiency of AVEC operations.
Probable future direction: TinyML models optimized for ultra-lightweight execution can enable real-time decision-making on resource-constrained mobile devices. For instance, energy-efficient neural networks with hardware-aware training can be deployed on UAVs for localized resource allocation. TinyML can also support decentralized task scheduling, thereby reducing reliance on centralized systems while conserving energy. However, deploying TinyML in AVEC faces constraints such as limited processing power, memory, and the need for stable communication networks for real-time decision-making. Overcoming these challenges requires further advancements in hardware optimization and network reliability.
6.6. Adaptive Security and Privacy Mechanisms
AVEC systems are vulnerable to cyberattacks, including eavesdropping, jamming, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Decentralized frameworks, such as federated learning, also introduce privacy concerns since shared gradient updates may expose sensitive information [114,115]. Addressing these challenges requires adaptive mechanisms that can dynamically adjust to evolving threats. Techniques such as differential privacy, secure multiparty computation, and blockchain-based authentication can safeguard data integrity and confidentiality, while lightweight cryptographic schemes ensure feasibility for resource-constrained devices [116,117,118,119]. Furthermore, the integration of real-time intrusion detection powered by machine learning enhances resilience against malicious activities, ensuring reliable and secure operation of AVEC systems.
Probable future direction: Blockchain-based security frameworks can establish tamper-proof logs for task offloading and resource-sharing operations. Combining privacy-preserving RL with homomorphic encryption can enhance user security and privacy while maintaining the required learning efficiency. AI-driven intrusion detection systems can proactively identify and mitigate potential security threats in a real-time basis.
7. Conclusions
AVEC has established itself as a promising solution for the growing demand for vehicular networks by integrating UAVs, HAPs, and satellites to complement traditional VEC. This study analyzed resource allocation techniques in AVEC, examining traditional and reinforcement learning-based methods to address the key challenges in optimizing bandwidth, computational power, and energy utilization across heterogeneous platforms. Although existing methods have demonstrated substantial advancements, critical issues such as real-time adaptability, seamless interoperability, and efficient scalability in multiplatform environments remain unresolved. Addressing these gaps requires innovative technologies, including quantum computing, to solve complex optimization problems and TinyML to enable low-power intelligence. This survey not only consolidates the current advancements in AVEC, but also identifies specific opportunities for future research to enhance system efficiency, security, and resilience. By addressing these challenges, AVEC systems can transform intelligent transportation networks, enabling robust, adaptive, and sustainable connectivity for next-generation applications. This study provides a foundation for further innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration in this rapidly evolving field.
Funding
This work was supported in part by research fund from Chosun University, 2025.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks Ahmadun Nabi for his contribution in establishing the fundamentals of the survey. The author also thanks the editor and anonymous referees for their comments, which helped to improve the quality of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huda, S.M.A.; Moh, S. Survey on Computation Offloading in UAV-Enabled Mobile Edge Computing. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2022, 201, 103341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziyauddin, R.A.; Niyato, D.; Luong, N.C.; Mohd Atan, A.A.A.; Mohd Izhar, M.A.; Azmi, M.H.; Mohd Daud, S. Computation Offloading and Content Caching and Delivery in Vehicular Edge Network: A Survey. Comput. Netw. 2021, 197, 108228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, C.; Pei, Q.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Vehicular Edge Computing and Networking: A Survey. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2021, 26, 1145–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, A.; Moh, S. Offloading Decision and Resource Allocation in Aerial Computing: A Comprehensive Survey. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2025, 56, 100734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEnroe, P.; Wang, S.; Liyanage, M. A Survey on the Convergence of Edge Computing and AI for UAVs: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 15435–15459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, M.; Berger, G.S.; Braun, J.; Mendes, J.A.; Bonzatto Junior, L.; Lima, J. Advance Reconnaissance of UGV Path Planning Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle to Carry Our Mission in Unknown Environment. In Robot 2023: Sixth Iberian Robotics Conference; Lino, M., Santos, C., Lima, J.L., Tardioli, D., Ferre, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 50–61. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Yu, F.R.; Huang, T. Collaborative Vehicular Edge Computing Networks: Architecture Design and Research Challenges. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 178942–178952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Gregory, M.A.; Li, S. A Survey of Multi-Access Edge Computing and Vehicular Networking. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 123436–123451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naren; Gaurav, A.K.; Sahu, N.; Dash, A.P.; Chalapathi, G.S.S.; Chamola, V. A Survey on Computation Resource Allocation in IoT Enabled Vehicular Edge Computing. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 3683–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor-A-Rahim, M.; Liu, Z.; Lee, H.; Ali, G.G.M.N.; Pesch, D.; Xiao, P. A Survey on Resource Allocation in Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 701–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Hu, S.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Shi, W. Resource Scheduling in Edge Computing: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 2131–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoud, A.; Sami, H.; Mourad, A.; Otrok, H.; Mizouni, R.; Bentahar, J. AI, Blockchain, and Vehicular Edge Computing for Smart and Secure IoV: Challenges and Directions. IEEE Internet Things Mag. 2020, 3, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djigal, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. Machine and Deep Learning for Resource Allocation in Multi-Access Edge Computing: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 2449–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, A.; Nencioni, G.; Khan, M.M.I. Resource Allocation in Multi-Access Edge Computing for 5G-and-beyond Networks. Comput. Netw. 2023, 227, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Debroy, S. Resource Management in Mobile Edge Computing: A Comprehensive Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi-Varzaneh, M.; Dakkak, O.; Habbal, A.; Kim, B.-S. Resource Scheduling in Edge Computing: Architecture, Taxonomy, Open Issues and Future Research Directions. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 25329–25350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, S. Energy-Latency Tradeoffs for Joint Optimization of Vehicle Selection and Resource Allocation in UAV-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2024, 2, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.P.; Hota, L.; Kumar, A.; Turuk, A.K.; Chong, P.H.J. Autonomous Vehicles: Resource Allocation, Security, and Data Privacy. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2022, 6, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Kim, D.K. Decentralized Multi-Agent DQN-Based Resource Allocation for Heterogeneous Traffic in V2X Communications. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 3070–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Lee, S. Resource Allocation for Vehicular Fog Computing Using Reinforcement Learning Combined with Heuristic Information. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 10450–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, B.; Li, H. UAVA: Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Assisted Vehicular Authentication Scheme in Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 22091–22106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Shen, Y. Air-Ground Integrated Mobile Edge Computing in Vehicular Visual Sensor Networks. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 24395–24405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Shen, G.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, K.; Kong, X.; Li, J. Asynchronous Federated Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Based Dependency Task Offloading for UAV-Assisted Vehicular Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 31561–31574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, A.; Baidya, T.; Moh, S. Comprehensive Survey on Reinforcement Learning-Based Task Offloading Techniques in Aerial Edge Computing. Internet Things 2024, 28, 101342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arani, A.H.; Hu, P.; Zhu, Y. HAPS-UAV-Enabled Heterogeneous Networks: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2023, 4, 1745–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqar, N.; Hassan, S.A.; Mahmood, A.; Dev, K.; Do, D.-T.; Gidlund, M. Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation in MEC-Enabled Integrated Aerial-Terrestrial Vehicular Networks: A Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 21478–21491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Naja, R.; Zeghlache, D. Adaptive Federated Reinforcement Learning for Critical Realtime Communications in UAV Assisted Vehicular Networks. Comput. Netw. 2024, 247, 110456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Yuan, C.; Zheng, B.; Tang, X. An Adaptive Deployment Scheme of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Dynamic Vehicle Networking for Complete Offloading. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 23509–23520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Xie, S. Cost-Efficient Deployment Optimization for Multi-UAV Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 6, 6158–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fei, W.; Bilal, M.; Xu, X. Adaptive Ubiquitous Learning for Server Deployment and Distributed Offloading in UAV-Enhanced IoV. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2024, 161, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, K.; Dai, P.; Han, Z. An Adaptive Q-Value Adjustment-Based Learning Model for Reliable Vehicle-to-UAV Computation Offloading. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 3699–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, D.; Huang, F.; Zhang, R. An MEC-Enabled Framework for Task Offloading and Power Allocation in NOMA Enhanced ABS-Assisted VANETs. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y. Joint Task Offloading Scheduling and Resource Allocation in Air–Ground Cooperation UAV-Enabled Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 5796–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhai, D.; Zhang, R.; Du, J.; Aujla, G.S.; Cao, H. A Mobile Edge Computing Framework for Task Offloading and Resource Allocation in UAV-Assisted VANETs. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2021-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–13 May 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tian, D.; Sheng, Z.; Duan, X.; Qu, G.; Leung, V.C.M. Joint Communication and Computation Resource Scheduling of a UAV-Assisted Mobile Edge Computing System for Platooning Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 8435–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Abbasi, O.; Kurt, G.K.; Yanikomeroglu, H.; Chen, J. Handoff-Aware Distributed Computing in High Altitude Platform Station (HAPS)–Assisted Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 8814–8827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lü, Z.; Ge, M.; Wang, L. UAV-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing System: Min-Max Fair Offloading and Position Optimization. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 7412–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, F.; Xiong, N. Utility Maximization Resource Allocation in Wireless Networks: Methods and Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Syst. 2015, 45, 1018–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseh, D.; Shinde, S.S.; Tarchi, D. Network Sliced Distributed Learning-as-a-Service for Internet of Vehicles Applications in 6G Non-Terrestrial Network Scenarios. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2024, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Bilal, M.; Khan, M.; Xing, Y. UAV-Assisted Content Caching for Human-Centric Consumer Applications in IoV. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, P.S.; Tun, Y.K.; Ei, N.N.; Hong, C.S. Energy-Efficient Offloading and User Association in UAV-Assisted Vehicular Ad Hoc Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 21st Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 22–25 September 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Jain, V.K.; Mishra, S. An Efficient Multi-Objective UAV Assisted RSU Deployment (MOURD) Scheme for VANET. Ad Hoc Netw. 2024, 163, 103598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, X.; Guo, D.; Xie, J.; Chen, H. Task Scheduling with UAV-Assisted Vehicular Cloud for Road Detection in Highway Scenario. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 7702–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ale, L.; Chen, H.; Tan, F.; Quek, T.Q.S.; Zhang, N.; Dong, M.; Ota, K. Joint Computation Offloading and Multidimensional Resource Allocation in Air–Ground Integrated Vehicular Edge Computing Network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 32687–32700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Singh, K.; Nguyen, M.-H.T.; Pan, C.; Li, C.-P. Digital Twin-Assisted Space-Air-Ground Integrated Networks for Vehicular Edge Computing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2024, 18, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Shen, X.S. DDPG-Based Resource Management for MEC/UAV-Assisted Vehicular Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Fall), Victoria, BC, Canada, 8 November–16 December 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Zhao, H.; Geng, L. An Offloading Algorithm Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning for UAV-Aided Vehicular Edge Computing Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 9th International Conference on Cyber Security and Cloud Computing (CSCloud)/2022 IEEE 8th International Conference on Edge Computing and Scalable Cloud (EdgeCom), Xi’an, China, 25–27 June 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Zhang, W.; Lei, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. UAV-Assisted Heterogeneous Multi-Server Computation Offloading with Enhanced Deep Reinforcement Learning in Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 5323–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Loo, J.; Yang, D.; Xiao, L. Completion Time Minimization for UAV-Assisted Mobile-Edge Computing Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 12253–12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, S.M.A.; Moh, S. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Computation Offloading in UAV Swarm-Enabled Edge Computing for Surveillance Applications. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 68269–68285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidya, T.; Nabi, A.; Moh, S. Trajectory-Aware Offloading Decision in UAV-Aided Edge Computing: A Comprehensive Survey. Sensors 2024, 24, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, S.; Nouri, N.; Abouei, J.; Avokh, A.; Plataniotis, K.N. Relaying Data with Joint Optimization of Energy and Delay in Cluster-Based UAV-Assisted VANETs. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 24541–24559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, M.; Xiong, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Han, L.; Niyato, D.; Tong, Y.; Xie, S. UAV-Assisted Dynamic Avatar Task Migration for Vehicular Metaverse Services: A Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2024, 11, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, A.; Moh, S. Joint Offloading Decision, User Association, and Resource Allocation in Hierarchical Aerial Computing: Collaboration of UAVs and HAP. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2025, 8, 7267–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Feng, L.; Lin, P.; Zhang, Y. Online Distributed Learning-Based Load-Aware Heterogeneous Vehicular Edge Computing. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 17350–17365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, P.A.; Fragkos, G.; Tsiropoulou, E.E.; Papavassiliou, S. Data Offloading in UAV-Assisted Multi-Access Edge Computing Systems Under Resource Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2023, 22, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Xiong, S.X.; Yang, J.; Mao, Y. Compound Model of Task Arrivals and Load-Aware Offloading for Vehicular Mobile Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 26631–26640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, H.; Long, K.; Leung, V.C.M. User Association, Subchannel and Power Allocation in Space-Air-Ground Integrated Vehicular Network with Delay Constraints. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Yin, J.; Guan, P.; Xiong, N.N.; Zhang, L.; Mumtaz, S. Intelligent Delay-Aware Partial Computing Task Offloading for Multiuser Industrial Internet of Things through Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 2954–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; He, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Li, F. Revenue and Energy Efficiency-Driven Delay-Constrained Computing Task Offloading and Resource Allocation in a Vehicular Edge Computing Network: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 8852–8868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, C. Joint Optimization of the Deployment and Resource Allocation of UAVs in Vehicular Edge Computing and Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Fall), Victoria, BC, Canada, 18 November–16 December 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, K.; Dai, P. Lyapunov-Based Joint Flight Trajectory and Computation Offloading Optimization for UAV-Assisted Vehicular Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 22243–22256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Xiong, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, C. Edge Computing Task Offloading Optimization for a UAV-Assisted Internet of Vehicles via Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 5647–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Kuang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Hou, F. Task Offloading and Resource Allocation in UAV-Assisted Vehicle Platoon System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 1, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.; Li, C.; Jiang, K.; Wan, S. Improved AFSA-Based Energy-Aware Content Caching Strategy for UAV-Assisted VEC. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2024, 10, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yang, C.; Lin, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X. Joint Deployment and Trajectory Optimization in UAV-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing Networks. J. Commun. Netw. 2022, 24, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, Z. Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Based Computation Offloading in UAV-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 19882–19897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wan, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, N. Joint Data Caching and Computation Offloading in UAV-Assisted Internet of Vehicles via Federated Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 17644–17656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, D.; Zhou, J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L. Joint Communication and Control Optimization of a UAV-Assisted Multi-Vehicle Platooning System in Uncertain Communication Environment. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 3177–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Chen, K.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Chen, Q.; Sahni, Y. Security-Sensitive Task Offloading in Integrated Satellite-Terrestrial Networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2025, 24, 2220–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Shi, L.; Liang, H.; Zhang, W. Trusted Mobile Edge Computing: DAG Blockchain-Aided Trust Management and Resource Allocation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 5006–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, T.; Cheng, Q.; Ma, S.; Ma, J. Smart Applications in Edge Computing: Overview on Authentication and Data Security. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 4063–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; You, L.; Hu, G.; Wang, S. Secure and Efficient Biometric-Based Anonymous Authentication Scheme for Mobile-Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 33604–33623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, A.; Elgendy, I.A.; Yu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H. Secure Task Offloading in Blockchain-Enabled Mobile Edge Computing with Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2022, 19, 4872–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kaur, A.; Aujla, G.S.; Batth, R.S.; Kanhere, S. DaaS: Dew Computing as a Service for Intelligent Intrusion Detection in Edge-of-Things Ecosystem. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 12569–12577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, T.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Blockchain-Aided Decentralized Trust Management of Edge Computing: Toward Reliable Off-Chain and On-Chain Trust. IEEE Netw. 2024, 38, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, B.; Liu, L. Mobile-Edge Computing in the Sky: Energy Optimization for Air–Ground Integrated Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 7443–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.O.; Waheed, N.; Duong, T.Q.; Ejaz, W. Quantum-Inspired Resource Optimization for 6G Networks: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, L.; Nguyen, T.N.; Su, C. Age Efficient Optimization in UAV-Aided VEC Network: A Game Theory Viewpoint. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 25287–25296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Yang, K.; Wang, K.; Zhang, G. UAV-Aided Vehicular Short-Packet Communication and Edge Computing System Under Time-Varying Channel. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 6625–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liwang, M.; Gao, Z.; Hosseinalipour, S.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, H. Graph-Represented Computation-Intensive Task Scheduling Over Air-Ground Integrated Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2023, 16, 3397–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, M. Digital Twin for UAV-RIS Assisted Vehicular Communication Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 7638–7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tian, Q.; Xie, Y.; Chan, K.Y. Outage Probability Minimization for Vehicular Networks via Joint Clustering, UAV Trajectory Optimization and Power Allocation. Ad Hoc Netw. 2023, 140, 103060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Xie, K.; Xie, S. Learning Based Channel Allocation and Task Offloading in Temporary UAV-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 9884–9895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, P.S.; Nguyen, L.X.; Tun, Y.K.; Han, Z.; Hong, C.S. Deep Reinforcement Learning-Based Joint Spectrum Allocation and Configuration Design for STAR-RIS-Assisted V2X Communications. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 11298–11311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shi, S.; Gu, S.; Zhang, N.; Gu, X. Intelligent Resource Allocation in UAV-Enabled Mobile Edge Computing Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Fall), Victoria, BC, Canada, 18 November–16 December 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, X.; Xu, C.; Wu, R. Energy Harvesting-Based UAV-Assisted Vehicular Edge Computing: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC Workshops), Foshan, China, 11–13 August 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Xie, W.; Ye, Y.; Liu, L.; Fei, Z. FlexEdge: Digital Twin-Enabled Task Offloading for UAV-Aided Vehicular Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 11086–11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Shen, X. Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Based Resource Management in MEC- and UAV-Assisted Vehicular Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, X. MADRL-Based URLLC-Aware Task Offloading for Air-Ground Vehicular Cooperative Computing Network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 6716–6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Yu, F.R.; Lin, Q.; Leung, V.C.M. Efficient Resource Allocation in Multi-UAV Assisted Vehicular Networks with Security Constraint and Attention Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 4802–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tan, L.; Huang, T.; Huang, X.; Huang, M.; Zhang, G. Resource Allocation and Trajectory Optimization in Multi-UAV Collaborative Vehicular Networks: An Extended Multi-Agent DRL Approach. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 8, 9391–9404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Richard Yu, F. A UAV-Aided Vehicular Integrated Platooning Network for Heterogeneous Resource Management. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2023, 7, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, S.; Song, T.; Xu, L. Hybrid Multi-Server Computation Offloading in Air–Ground Vehicular Networks Empowered by Federated Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 5175–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHAO, H.; GENG, L.; FENG, W.; ZHOU, C. Client Selection and Resource Scheduling in Reliable Federated Learning for UAV-Assisted Vehicular Networks. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2024, 37, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.-V.; Ruby, R.; Fang, F.; Nguyen, D.C.; Yang, Z.; Le, M.; Ding, Z.; Hwang, W.-J. Aerial Computing: A New Computing Paradigm, Applications, and Challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 8339–8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, F.; Han, Z.; Zhu, H. Joint Resource and Trajectory Optimization for Heterogeneous-UAVs Enabled Aerial-Ground Cooperative Computing Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 8812–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, W.; Fan, P.; Fan, Q.; Wang, J.; Letaief, K.B. URLLC-Awared Resource Allocation for Heterogeneous Vehicular Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 11789–11805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, N.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, F.; Shi, Q.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, M. A Task-Driven Sequential Overlapping Coalition Formation Game for Resource Allocation in Heterogeneous UAV Networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2023, 22, 4439–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Sheng, M.; Li, J.; Han, Z. Toward Data Collection and Transmission in 6G Space–Air–Ground Integrated Networks: Cooperative HAP and LEO Satellite Schemes. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 10516–10528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Yang, P.; Alzenad, M.; Xi, X.; Wu, D.; Yanikomeroglu, H. Airborne Communication Networks: A Survey. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2018, 36, 1907–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, B.; Marojevic, V.; Yi, Y.; Abdalla, A.S.; Liu, L. Spectrum Sharing for UAV Communications: Spatial Spectrum Sensing and Open Issues. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2020, 15, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Zhu, C. Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Vehicular Resource Allocation: A Comparison Study of Different Agent Cooperation Levels. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyama, T.; Kawamoto, Y.; Kato, N. Resource Allocation Optimization by Quantum Computing for Shared Use of Standalone IRS. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2023, 11, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, K.; Innan, N.; Behera, B.K.; Mumtaz, S.; Al-Kuwari, S.; Farouk, A. Optimizing Low-Energy Carbon IIoT Systems with Quantum Algorithms: Performance Evaluation and Noise Robustness. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 34653–34662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Liu, C.; Wen, F.; Han, G. Joint Optimization of Task Offloading and Resource Allocation for Cooperative Perception in Vehicular Edge Computing Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shi, J.; Sun, Y.; Men, A. Task Prediction Based Edge Computing Offloading of Satellite-HAP-Terrestrial Integrated Network. IEEE Netw. Lett. 2025, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Xu, K.; Xiang, S.; Dai, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zeng, L. Task Offloading and Resource Scheduling in Mobile Edge-Cloud Computing Based on Edge Competition and Task Prediction. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Dai, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, H.; Ma, Y.; Xia, Y. A Cloud-Edge-Vehicle Framework for Task Offloading with Trajectory Prediction Information. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C.N.; Prazeres, C.V.S. Tiny Federated Learning for Constrained Sensors: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Sens. Rev. 2025, 2, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, R.H.; Chi, H.R.; Wu, H. TinyML for Empowering Low-Power IoT Edge Consumer Devices. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 7318–7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, P.; Pan, S.; Zhong, L.; Deng, J. Giant Could Be Tiny: Efficient Inference of Giant Models on Resource-Constrained UAVs. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 21170–21179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Cheng, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Li, M.; Jiang, H. TinyFEL: Communication, Computation, and Memory Efficient Tiny Federated Edge Learning via Model Sparse Update. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 8247–8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, E.; Guizani, M.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Tan, L. Privacy-Preserving Task Offloading in Vehicular Edge Computing Using Federated Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gu, A.; Liang, Y. Federated Reinforcement Learning-Empowered Task Offloading for Large Models in Vehicular Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 74, 1979–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cao, P.; Zhang, F. A Secure Pairing-Free Certificateless Online/Offline Signcryption Scheme with Batch Verification for Edge Computing-Based VANETs. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 74, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Geng, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, H. A Differential Privacy Based Task Offloading Algorithm for Vehicular Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 30921–30932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y. Optimizing Resource Allocation and Energy Efficiency in Vehicle Mobile Edge Computing with Blockchain Integration. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 18, 36807–36818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Zhou, D.; Cui, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Bolodurina, I.; He, D. Security-Enhanced Data Sharing via Efficient Sanitization for VANETs. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2025, 24, 4925–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).