Abstract
Real-time industrial inspection is a crucial component of production automation, with key challenges lying in enhancing detection accuracy for specific tasks and effectively mitigating the adverse impacts of complex production environments. Addressing these issues, this paper proposes an innovative solution. We introduce the Head_DySnake module in the detection head to significantly bolster the capture and recognition capabilities of defect texture features. Concurrently, at the initial stage of the backbone network, we integrate the Attention Denoising Module(ADConv) module, which employs an attention-guided mechanism for effective noise reduction in production environments, thereby eliminating high-level noise caused by high background similarity. Through these optimizations, our research achieves a 6.3% mAP improvement on the NEU-DET dataset with a computational demand of merely 9.8 GFLOPs, and a 5.9% mAP improvement on the GC10-DET dataset. This study thoroughly explores the impact of steel defect-specific textures on recognition performance and validates the positive role of attention-guided environmental denoising strategies in enhancing model robustness. These findings offer new perspectives for lightweight model design and performance optimization in industrial production inspection and are expected to provide valuable insights for the detection of other types of defects in related research fields.
1. Introduction
Steel surface defect detection is a pivotal task in modern industrial quality control, where undetected micro-scale imperfections can propagate into structural failures across automotive, aerospace, and civil infrastructure domains [1]. While deep-learning-based visual inspection [2,3] has demonstrated remarkable progress, its practical deployment in real production environments remains constrained by two fundamental challenges that are rarely addressed in concert:
Texture-ambiguous defects: Industrial flaws such as hairline cracks, inclusions, and mill-scale patches possess heterogeneous textures that often merge with legitimate surface patterns. Conventional backbones, optimized for natural-image statistics, struggle to isolate these high-frequency cues from background clutter, forcing a trade-off between texture fidelity and noise amplification.
Environmental noise interference: Steel production environments present a complex interplay of physical and optical disturbances that collectively degrade image fidelity and confound defect recognition. These disturbances manifest as three interrelated degradation pathways: optical degradation caused by particulate scattering and non-uniform illumination, mechanical degradation arising from vibration-induced motion blur, and thermal degradation resulting from infrared radiation interference. Existing methods lack explicit mechanisms to disentangle these environmental disturbances from genuine defect signatures.
The cumulative effect of these degradation pathways is a systematic reduction in the distinguishability of defect features, forcing detection models to operate under conditions where true positives are statistically scarce events. Existing approaches typically employ generic feature extractors coupled with standard detection heads, which lack explicit mechanisms to disentangle defect textures from environmental noise. While recent advances in attention mechanisms and deformable convolutions have shown incremental improvements, their computational overhead and indiscriminate noise suppression often fail to preserve critical defect signatures [4,5].
Our proposed YOLO-RSD model is specifically designed to address the challenges of achieving high accuracy and facilitating lightweight edge deployment in steel surface defect detection. This research holds significant potential for applications such as surface defect detection in urban infrastructure. The key innovations of our work are primarily threefold:
- Robust Environmental Denoising: We introduce a novel module dedicated to effectively mitigating noise from complex industrial environments. This enhancement significantly improves the model’s ability to discern defects amid challenging visual interference, leading to more reliable detection.
- Enhanced Contextual Understanding for Clustered Defects: To precisely identify defects that frequently appear in groups, our model incorporates a mechanism designed to acquire a larger receptive field. This enables a more comprehensive understanding of contextual information, thereby boosting the detection accuracy of such aggregated imperfections.
- Head_DySnake for Adaptive Texture Structure Recognition: Our model integrates the unique Head_DySnake component, which is engineered to adaptively capture and refine texture structures. This innovation drastically improves the recognition capability for defects defined by distinct textural patterns, ensuring high precision even for subtle or intricate structural variations.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 provides an overview of related work concerning defect detection tasks in industrial and infrastructural applications. Section 3 delves into the detailed principles behind the three core modules of YOLO-RSD. Subsequently, Section 4 presents and analyzes the comprehensive experimental results of YOLO-RSD across multiple datasets. Building upon these findings, Section 5 discusses the identified limitations of YOLO-RSD from Section 4 and outlines strategies for addressing them in future work. Finally, Section 6 concludes the paper by summarizing the contributions of YOLO-RSD.
2. Related Work
2.1. YOLO
The pursuit of real-time object detection has been fundamentally reshaped by the YOLO (You Only Look Once) family [6], whose architectural evolution reflects a systematic addressing of computational efficiency versus accuracy trade-offs. Originating with YOLOv1’s [7] groundbreaking regression-based paradigm that unified localization and classification into a single network pass, the subsequent iterations have introduced targeted innovations: YOLOv2 [8] (Darknet-19 backbone, anchor boxes, and dimension clusters) significantly improved multi-scale detection through prior-based bounding box estimation; YOLOv3’s [9] residual connections and feature pyramid network (FPN) enhanced hierarchical feature extraction; YOLOv4/v7’s [10,11] PANet (Path Aggregation Network) and CSPDarknet53 optimized cross-scale feature fusion; while YOLOv8’s [12] decoupled head and anchor-free design further streamlined inference pipelines.
However, these advancements primarily target generic object detection scenarios, exhibiting critical limitations when applied to industrial defect inspection: (1) Standard convolutions struggle to capture anisotropic texture patterns prevalent in linear steel defects (e.g., scratches, seams); (2) Fixed receptive fields in conventional architectures struggle to adapt to the highly variable defect densities in steel surfaces—from isolated pitting to clustered slag inclusions—often resulting in missed detections or merged predictions [13].
Recent YOLO adaptations like GC-YOLO [14] (global context attention) and ASFF-YOLO [15] (adaptive spatial feature fusion) partially address scale variance but fail to jointly optimize for directional texture modeling and environmental robustness. Our YOLO-RSD bridges these gaps through a co-designed architecture where Receptive Field Attention (RFA) dynamically adjusts spatial focus regions for clustered defects, Dynamic Snake Convolution (DySnake) employs deformable kernels to track anisotropic textures, and Attention-guided Denoising (ADConv) suppresses irrelevant background patterns—forming an integrated solution for industrial-grade steel inspection.
2.2. Steel Defect Detection
Steel defect detection technology has undergone significant evolution, transitioning from reliance on manual expertise to automated computer vision solutions. Early approaches primarily employed handcrafted feature extractors (such as Gabor filters and Local Binary Patterns—LBP) combined with classifiers like Support Vector Machines (SVM). While these methods established an automation foundation, their generalization capability for complex and variable defect types, particularly those with irregular textures and diverse morphologies, exhibited notable limitations [16]. The application of deep learning has become a prominent approach in industrial steel defect detection, showcasing promising results in real-world scenarios [17,18].
In recent years, deep learning models have demonstrated significant advantages and have become mainstream [19]. Fully Convolutional Neural Network (FCNN [20])-based segmentation methods enable precise pixel-level defect annotation, yet their high computational cost restricts real-time application in industrial settings. Region-based detection frameworks, such as Faster R-CNN [21] and its variants, offer high accuracy but often suffer from inference speeds insufficient for high-throughput production line demands. Currently, the field faces two core challenges: (1) Accurate Detection of Texture-Sensitive Defects: Standard isotropic convolution operations struggle to effectively capture directional features inherent to steel surface defects, such as elongated scratches; (2) Robustness in Complex Production Environments: Background noise like rust-resembling textures frequently causes interference, leading to increased false positives [22].
To simultaneously maintain detection accuracy and elevate inference speed, recent efforts have focused on refining the lightweight yet efficient YOLO family. Wang et al. proposed YOLOv5-CD [23], which integrates Coordinate Attention (CoordAtt) into the backbone. By explicitly encoding horizontal and vertical positional information into the channel-attention map, the method markedly suppresses high-frequency background noise. Additionally, a decoupled head disentangles classification and regression, rendering the model less sensitive to directional variations of scratches. Nevertheless, CoordAtt still relies on regular-grid pooling, constraining its adaptability to defects exhibiting extreme geometric deformation. Additionally, Li et al. introduced DEW-YOLO [24]. They replace the standard C2f block with a C2f_DCN module that embeds DCNv2 into the YOLOv8 backbone, thereby enabling dynamic, deformation-aware receptive fields. This yields superior performance on irregular defects such as rust spots and pits. Empirical results reveal, however, that under TEMCoil high-frequency texture scenarios, the DCN offset fields are susceptible to noise perturbations, while the orientation-agnostic sampling strategy inadequately preserves the boundaries of slender scratches.
In summary, existing YOLO-based optimized solutions still exhibit limitations in key areas: texture pattern modeling (especially for directional features), suppression of complex background noise, and balanced adaptability to diverse defect morphologies (linear vs. irregular shapes). In contrast to these approaches, the proposed YOLO-RSD framework in this paper aims for synergistic innovation across three dimensions—feature modeling capability, environmental robustness, and computational efficiency—to systematically address these critical challenges.
3. Proposed Method
To enhance the performance of real-time steel surface defect detection, we propose YOLO-RSD, a nano-scale object detection model developed as an improvement upon the YOLOv8 framework. Our modifications primarily concentrate on refining the feature extraction capabilities within the backbone and the defect classification prowess of the head sections, incorporating three novel modules: ADConv [25], RFAConv [26], and Head_DySnake [27].
As illustrated in Figure 1, in the backbone section, the input image first passes through the ADConv module. This module is designed to perform attention-guided denoising, effectively mitigating the influence of complex industrial environmental noise on the critical texture structures of defects. Subsequently, within the backbone, RFAConv layers are introduced. These layers leverage large receptive fields to adapt to the common clustering characteristic of steel defects. By broadening the perception area, RFAConv can search for and integrate relevant texture information from surrounding regions, thereby significantly enhancing the feature representation of local areas. Furthermore, in the detection head, the Head_DySnake module is integrated. This module is specifically engineered to learn and leverage intricate texture-specific knowledge, enabling more accurate discovery and identification of defects based on these refined textural patterns. Through these targeted enhancements, YOLO-RSD aims to achieve superior performance in challenging industrial settings.
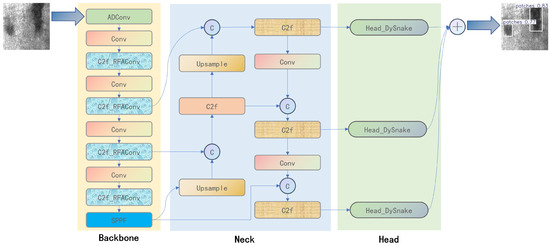
Figure 1.
Overview of the YOLO-RSD architecture. The model is distinctly divided into three functional components, indicated by their respective background colors: the Backbone (yellow), the Neck (blue), and the Head (green). Upon input, images first pass through the ADConv module within the Backbone, which performs crucial denoising to mitigate the impact of complex environments on texture feature recognition. Following this, RFAConv modules are strategically placed to leverage large receptive fields, enabling the model to search for relevant texture structures within surrounding receptive fields based on the common clustered nature of defects, thereby enhancing the recognition of current regions. Finally, the Head_DySnake module in the Detection Head is designed to learn and extract intricate texture knowledge, facilitating the precise discovery and identification of defects from these learned textural patterns.
3.1. ADConv
To address the issue of contextual noise originating from complex production environments, which significantly impacts the auxiliary information present in steel surface images (primarily derived from the clustered characteristics of defects), we introduce the ADConv module for effective noise reduction (Figure 2).
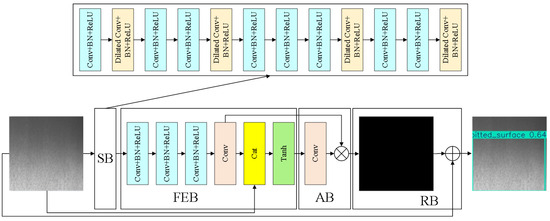
Figure 2.
Architecture of the ADConv. This module is designed with four key components: a Sparse Feature Block (SB) to capture contextual understanding for clustered defects; a Feature Enhancement Block (FEB) to strengthen fine-grained details; an Attention Denoising Block (AB) which fuses intermediate features, suppresses environmental interference, and focuses on crucial texture structures; and a Reconstruction Block (RB) to preserve the original structural characteristics.
Firstly, the SB enhances image context understanding by leveraging the concentrated nature of steel defects. It combines dilated convolutions for global context perception and small-kernel convolutions to preserve crucial textural details, as expressed in Equation (1).
where represents the input feature map to the ADConv module.
Next, the FEB uses residual connections to integrate environmental features and local texture structures from FSB, significantly enhancing image detail. A dedicated branch within FEB generates enhanced detail features, as shown in Equation (2).
Following this, the AB processes multi-level information via an attention mechanism for effective denoising. As defined in Equation (3), AB fuses intermediate results, suppresses environmental interference, and focuses on critical texture structures.
Finally, the RB performs multi-level reconstruction of image detail features. Its core function, described in Equation (4), is to ensure that defect texture structure details are completely preserved after denoising and feature extraction, providing high-quality input for subsequent tasks.
where represents the final output feature map of the ADConv module.
3.2. RFAConv
Leveraging the inherent clustered nature of defects, YOLO-RSD integrates large convolution kernels to capture broader contextual information. To further enhance the YOLO-RSD’s representational capacity for varied regional content, we introduce an attention mechanism branch. This new branch, in conjunction with conventional convolutions, dynamically re-weights and generates novel regional convolution kernels (Figure 3), thereby significantly improving the YOLO-RSD’s ability to characterize diverse defect patterns.
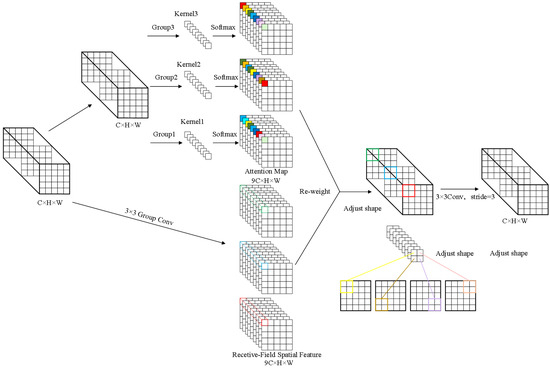
Figure 3.
Detailed architecture of the RFAConv. RFAConv processes the input image through multiple branches: one branch extracts convolutional kernel content, while parallel branches generate attention maps. These are then combined to re-weight and produce new convolutional kernels. This multi-branch approach, by generating distinct kernels for different receptive field regions, effectively mitigates the issue of weak feature representation caused by shared parameters. The image in the bottom right provides a macroscopic representation of the RFAConv’s overall operation.
Equation (5) illustrates how the attention mechanism generates to form the basis for constructing the new convolutional kernel . The subscript is used to distinguish between different convolutional kernels and attention maps. It denotes the independent operation of each branch or head within a multi-branch or multi-head attention mechanism. This process significantly aids the model in comprehending auxiliary environmental information within large receptive fields. Through the attention-guided re-weighting, the model can dynamically focus on distinct features across different regions. For instance, in manufacturing environments, various areas often present unique characteristics, such as lower regions being prone to water interference or edge areas being susceptible to chipping. By employing this dual-path re-weighting of convolutional kernels, RFAConv substantially enhances YOLO-RSD’s capacity for extracting environmental auxiliary information and consequently improves its recognition accuracy.
3.3. Head_DySnake
The detection head is endowed with the capability for texture-specific linear structural sampling. By incorporating DySnake Conv (Figure 4), YOLO-RSD effectively controls the content of the offset matrix, enabling the model to comprehend the corresponding features.
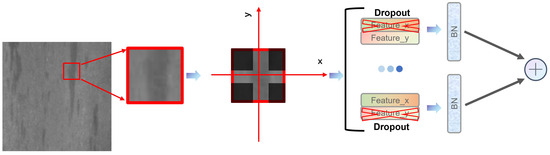
Figure 4.
Conceptual architecture of the Head_DySnake module. This module enhances the receptive field by performing individual convolutions that ensure linear sampling along a single direction (e.g., x or y-axis). The results from these multi-directional sampling convolutions are then fused to capture comprehensive texture structure information across various orientations.
To enhance the YOLO-RSD’s understanding of defect texture structures, which often manifest as either singular linear patterns (e.g., crease-like textures) or complex stacked linear textures (e.g., snowflake-like structures), our detection head incorporates multi-directional DySnake sampling. These diverse texture structures are characterized by performing focused sampling along multiple directions. The results from these multi-directional convolutions are subsequently fused to form a comprehensive representation. Specifically, the unique texture-aware convolutional kernels are obtained through specialized sampling formulas focusing on the x-axis, as presented in Equation (6), and the y-axis, as detailed in Equation (7). This approach significantly augments the model’s capacity for intricate texture structure comprehension.
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Environment and Parameters
To validate the robustness of YOLO-RSD’s performance improvements, extensive experiments were conducted across multiple datasets, including NEU-DET [28,29,30] and GC10-DET [31]. The specific specifications for each dataset are detailed in Table 1. Additionally, a visual representation of the NEU-DET dataset’s distribution can be found in Figure 5.

Table 1.
Summary of Datasets Used for Experiments.
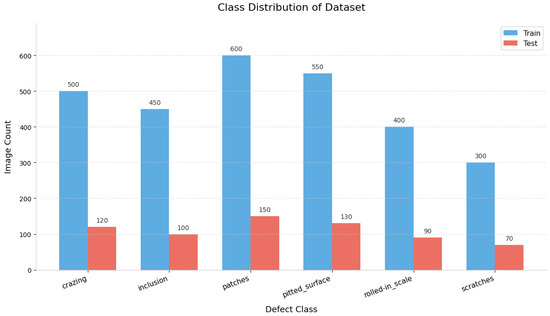
Figure 5.
Distribution of the NEU-DET dataset, showing the division between training and testing sets. This dataset comprises images of six typical steel surface defect types: Crazing (CR), Inclusion (IN), Patches (PA), Pitted-surface (PS), Rolled-in scale (RS), and Scratches (SC). The dataset is randomly split into a 4:1 ratio, allocating 80% of images for training and 20% for testing.
The experimental environment and training parameters for this study are detailed in Table 2. All models were trained and evaluated under a unified configuration. To ensure a fair comparison across different datasets with varying resolutions (as detailed in Table 1), all input images were resized to a consistent 200 × 200-pixel resolution.

Table 2.
Experimental Setup and Hyperparameters.
Regarding data augmentation, this study adopted the same Mosaic data augmentation strategy as the YOLOv4 model [10]. This technique splices four training images into one, thereby enhancing the model’s generalization capabilities and its performance in detecting small objects.
4.2. Model Performance Analysis Across Datasets
To rigorously assess the efficacy of the proposed methodology and facilitate comprehensive comparisons, two primary evaluation metrics were employed. Overall model efficacy and granular per-defect performance were quantified using the mean Average Precision at an Intersection over Union (IoU) threshold of 0.5 (). This metric provides a balanced assessment of both object localization and classification accuracy. For a given class, Average Precision (AP) is calculated as the area under its Precision-Recall curve. The then represents the average of these AP values across all detected classes at the specified IoU threshold.
Furthermore, the Giga Floating-Point Operations per Second (GFLOPs) metric was utilized to gauge the computational expenditure of models. This measure is crucial for evaluating a model’s suitability for industrial lightweight deployment, as it directly reflects the processing demands during inference. A lower GFLOPs value signifies a more computationally efficient architecture, which is highly desirable for real-time applications and resource-constrained environments.
As presented in Table 3, the efficacy of the YOLO-RSD’s strategy for enhancing texture structure recognition is clearly evident, as it achieves the highest overall . This superior performance extends to several specific defect categories, notably RS and SC.

Table 3.
Comparison of and GFLOPs on the NEU-DET dataset. The bold values indicate the best performance in each column. The bold values indicate the best performance in each column.
The Head_DySnake module, with its specialized texture structure recognition capabilities, played a pivotal role in elevating the accuracy for SC defects to an exceptionally high level. Its performance on SC not only surpassed 90% but approached 95%, marking a significant improvement, particularly when contrasted with the comparatively weaker performance of the YOLOv11l on this specific defect. Furthermore, for RS defects, the RFAConv module effectively enhanced recognition by leveraging large receptive fields to acquire and optimize contextual information. A similar approach is observed in the DDN, which utilizes a Region Proposal Network (RPN) to acquire Regions of Interest (ROIs) for defect content, also yielding commendable results on this defect type. The comprehensive improvement across multiple defect categories is largely attributed to the ADConv module’s robust denoising capabilities, underscoring its high generalizability as a module improvement.
However, the model does exhibit certain limitations. For instance, YOLO-RSD shows some shortcomings in detecting defects like PA and CR when compared to models like MSFT-YOLO. Considering that MSFT-YOLO primarily employs an attention mechanism and global feature extraction for recognition, it suggests that these particular defect types may not be effectively detected solely through texture-based structural analysis. Instead, they might necessitate multi-scale representations facilitated by attention mechanisms, highlighting an area for future research and optimization.
The bolded values in each column of Table 4 highlight the best performance achieved by a model for that specific defect category. Our proposed YOLO-RSD demonstrates superior overall performance, achieving the highest mAP50 among all compared methods, indicating its robust capability across diverse defect types.

Table 4.
Multi-defect evaluation of various object detection models on the GC10-DET dataset, quantified by their mAP50 performance. Defect abbreviations are PU (Punching), WL (Weld line), CG (Crescent gap), WS (Water spot), OS (Oil spot), SS (Scratches), IN (Inclusion), RP (Rolled pit), CR (Crease), and WF (Wrinkle). The bold values indicate the best performance in each column.
Beyond the overall mAP, YOLO-RSD also exhibits competitive or leading performance in several specific defect categories. Notably, for defects such as WL, YOLO-RSD achieved the best recognition accuracy. This can be attributed to the effectiveness of the Head_DySnake module, which excels at learning and exploiting the distinct texture structures characteristic of WL defects. Furthermore, for OS defects, which often appear in clusters, the RFAConv module, with its ability to leverage large receptive fields, significantly enhanced the model’s recognition capability, resulting in a performance improvement of nearly 10% compared to the YOLOv8n. Similarly, RP defects are highly susceptible to complex environmental noise, and the integrated ADConv module successfully performed denoising, leading to a substantial improvement in recognition accuracy by approximately 15 percentage points.
However, the model’s performance on certain defect types, such as PU, shows a slight regression compared to the best-performing baseline. This is likely due to the more complex and less texture-dependent structural characteristics exhibited by these defects, which cannot be adequately captured or distinguished by features primarily focused on texture patterns. These specific challenges will be a key focus for future optimization efforts to further enhance YOLO-RSD’s robustness across all defect categories.
In Figure 6, the visualization reveals that the YOLO-RSD generally exhibits improved overall recognition accuracy and prediction confidence. For instance, in the detection of PA and SC defects, the YOLO-RSD not only accurately localizes the defects but also demonstrates higher prediction confidence compared to the baseline, indicating a more resolute identification of these defect types. Notably, for CR defects, the YOLO-RSD successfully identifies and boxes defect content that the YOLOv8n previously missed, highlighting the model’s enhanced capability in capturing complex, irregular defects that are often hidden by background similarity and characterized by diverse texture fusions.
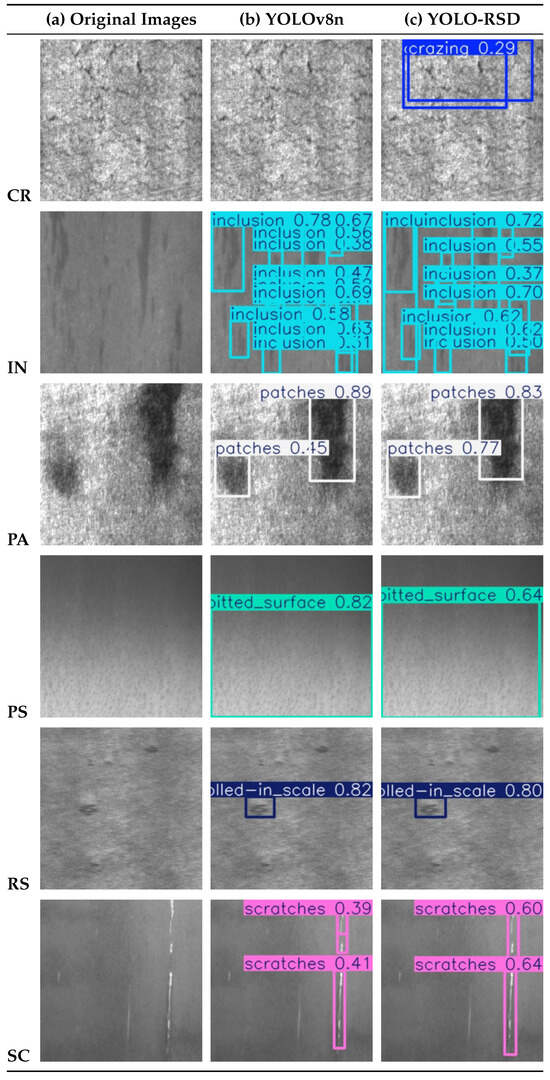
Figure 6.
Comparison of detection results for YOLOv8n and YOLO-RSD. This figure visually illustrates the models’ ability to accurately localize and classify defects in real-world scenarios.
However, the model still presents certain limitations when dealing with specific defect types. For PS defects, while the model is capable of detection, its prediction confidence appears to decrease. Furthermore, in the predictions for CR defects, we observed instances of overlapping detection boxes, which could potentially impact the precision of quantitative measurements such as defect count or area. Crazing defects present a challenge due to their nonlinear, diffusive crack-like features and confusing environmental backgrounds, which are difficult for the model to effectively capture.
Comparing the two figures, Figure 7 and Figure 8, we can see that the YOLO-RSD model reaches a peak F1 score of 0.70 on all categories, corresponding to an optimal confidence threshold of 0.321. Compared with YOLOv8n’s 0.64 F1 peak at 0.295 confidence, YOLO-RSD has achieved significant performance improvements.
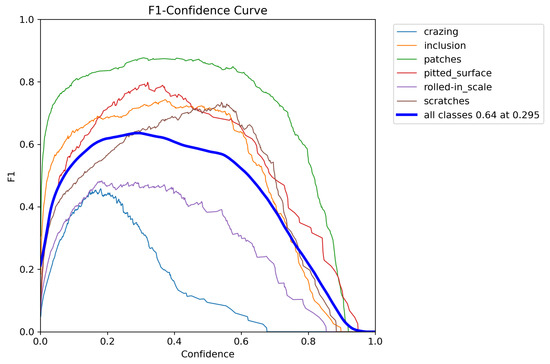
Figure 7.
F1-Confidence curves for the YOLOv8n, illustrating its detection performance across various confidence thresholds.
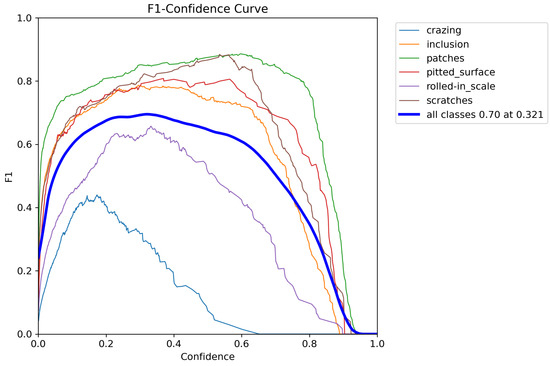
Figure 8.
F1-Confidence curves for the proposed YOLO-RSD model, showcasing its enhanced detection capabilities.
It is worth noting that defect categories with significant differences in geometric structure, such as patches and scratches, have achieved significant F1 score improvements in the YOLO-RSD model. This fully demonstrates the robustness of our model, indicating that it can not only effectively identify linear texture features, but also show excellent recognition effects on other nonlinear complex texture structures. This ability is mainly due to the RFAConv module. Through its large receptive field design, RFAConv can capture a wide range of texture features of defects, so as to better adapt to and understand a variety of texture structures. In particular, the recognition accuracy of scratch defects has increased most significantly, which can be attributed to our knowledge-oriented special design in the module optimization stage, and deep optimization for linear textures that appear more frequently in defects, thereby achieving a higher recognition accuracy.
Although the overall performance of the YOLO-RSD model has been significantly improved, there are still challenges in the identification of specific defect categories. For example, the F1 score of the crazing defect has dropped slightly compared to the baseline model. The reason for this is that crazing defects usually appear as crack-like lines that spread in all directions. This nonlinear and diffusive geometric feature makes it difficult to be effectively captured by linear features or texture information obtained through the large receptive field of RFAConv. In addition, crazing defects are often accompanied by obvious black and gray stain-like environmental backgrounds, which also bring additional recognition difficulties to the ADConv module designed to suppress high background similarity noise. These characteristics together constitute the complexity of crazing defect recognition. Future work will focus on exploring more robust feature extraction methods and more sophisticated environmental noise modeling strategies, in order to effectively improve the model’s recognition performance for such complex defects. While overlapping detection boxes for IN defects persist, our method has effectively reduced their number compared to the baseline model, which provides a promising avenue for future optimization to enhance localization accuracy.
By comparing Figure 9 and Figure 10, it is evident that the YOLO-RSD significantly reduces the proportion of defects erroneously identified as background (i.e., values in the “background” row corresponding to defect columns) across most defect categories. For instance, the misclassification of rolled-in_scale as background decreased from 0.37 to 0.25. This improvement is primarily attributed to the powerful denoising capability of the ADConv module, which enables the model to more clearly distinguish between defect content and boundary features, thereby substantially reducing the incidence of false positives. Furthermore, for defects with prominent texture features, such as scratches, the increase in recognition accuracy is particularly notable. This benefit largely stems from our detection head, Head_DySnake, which is endowed with texture discrimination capabilities, effectively enhancing the model’s ability to discern such features.
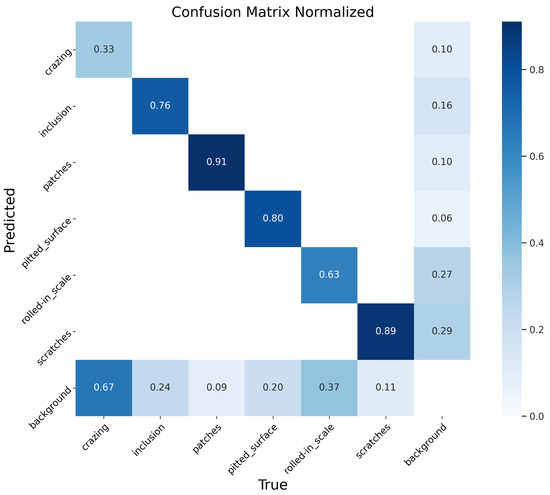
Figure 9.
Normalized confusion matrix for the YOLOv8n. The color bar on the right indicates the normalized value scale, aiding in the interpretation of prediction probabilities.
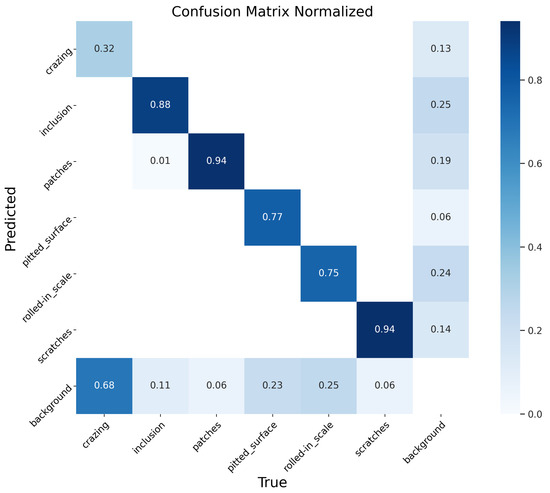
Figure 10.
Normalized confusion matrix for the YOLO-RSD.
Further analysis of inter-class confusion reveals that both the YOLOv8n and the YOLO-RSD exhibit minimal misclassification between different defect types. This suggests that the various defect categories generally possess sufficiently distinct features, and the primary task for the model is to accurately differentiate them from the background. However, in the YOLO-RSD, we observed that 0.01 of inclusion samples were incorrectly identified as patches. This particular cross-classification may arise because, in certain instances, the unique textural features of some inclusions bear a resemblance to those of patches, leading to ambiguous judgments by the model.
As observed in Figure 11, the YOLO-RSD model demonstrates a significantly stronger focus on defect features and notably reduced attention on background regions [36,37]. For instance, in the detection of RS defects, compared to the YOLOv8n, YOLO-RSD’s Grad-CAM heatmaps are more concentrated on the defect itself, with background areas appearing more predominantly blue (indicating lower attention). This clearly illustrates that the background denoising operation performed by the ADConv module has effectively contributed to the model’s ability to focus more precisely on targets rather than environmental interference. Furthermore, while the F1 curve for CR defects showed only a modest overall performance improvement, the Grad-CAM heatmaps reveal that YOLO-RSD successfully detected and focused on parts of the defect that the YOLOv8n baseline model originally missed, showcasing the model’s potential advancements in complex defect recognition.
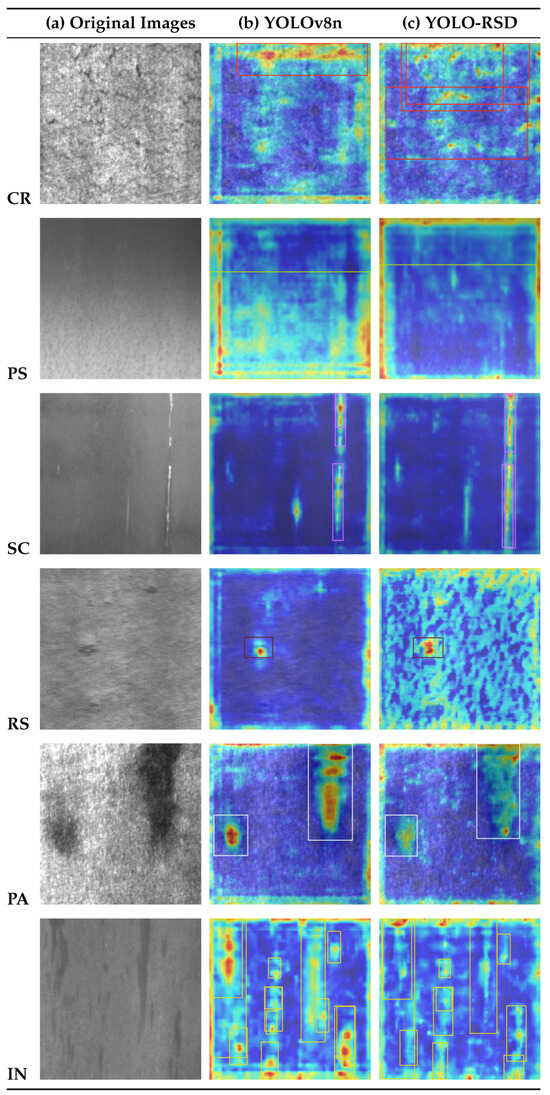
Figure 11.
Through Grad-CAM (Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping) heatmaps, we visually demonstrate the regions of an image most crucial for the models’ classification decisions [38], thereby providing a clear comparison of how YOLOv8n and YOLO-RSD localize predictions and allocate attention on various defect instances.
However, the model still exhibits certain limitations. Taking IN defects as an example, we observed overlapping detection boxes in YOLO-RSD, and the overall attention given to the defect was inferior to that of YOLOv8n. This issue primarily stems from the inherent lack of distinct texture features in IN defects, which hinders the effective functioning of texture-optimizing modules (such as Head_DySnake and RFAConv), and may even lead to a slight performance degradation for this category.
4.3. Module Ablation Analysis
In Table 5, the addition of RFAConv significantly improved the model’s receptive field capabilities, leading to a new high for mAP50 at 0.755. This indicates its strong ability to capture comprehensive contextual information crucial for accurately identifying defects. Following this, the integration of ADConv aimed to mitigate high noise levels caused by the similarity between environmental backgrounds and defect features. By leveraging an attention mechanism, ADConv successfully suppressed such noise, resulting in a new peak for P at 0.714. This highlights its efficacy in reducing false positives and enhancing the reliability of detections in complex industrial environments. Finally, the Head_DySnake module, specifically designed to focus on intricate texture structure features for defect detection, achieved the highest R of 0.722. This is attributed to its ability to recognize the unique textural mechanisms of steel defects, making the model less susceptible to various influencing factors. Furthermore, Head_DySnake also yielded the best mAP50-95 score of 0.449, underscoring its superior performance in precise localization and segmentation across a wide range of Intersection over Union thresholds, which is crucial for high-quality defect analysis.

Table 5.
Ablation Study Results of Proposed Modules(RFAConv, ADConv and Head_DySnake) on YOLOv8n. The bold values indicate the best performance in each column.
Table 5 unequivocally demonstrates that each proposed module (RFAConv, ADConv, and Head_DySnake) makes a distinct and vital contribution, collectively enhancing the robustness and accuracy of our steel defect detection system.
5. Discussion
The experimental results demonstrate that the YOLO-RSD model achieves the best overall mAP50 performance in comparative studies, showcasing its robust capabilities for steel surface defect detection. This robust performance suggests the methodology has potential for future exploration in diverse tasks involving other materials that exhibit distinct texture structures, particularly through the expansion of datasets to broader applications, opening avenues for enhancing task-specific model performance based on unique textural characteristics. Furthermore, the feasibility of using texture-based solutions for defect detection on various textured surfaces has been demonstrated in prior work [39].
Furthermore, with a lightweight computational demand of merely 9.8 GFLOPs, YOLO-RSD is highly suitable for edge deployment, highlighting its significant practical application potential.
Despite its strengths, the YOLO-RSD model does exhibit limitations in certain defect categories, such as PA and CR defects, where its precision shows a slight regression. A comparison with models like MSFT-YOLO, which leverage attention mechanisms and global feature extraction, reveals a potential avenue for improvement. The superior recognition accuracy achieved by attention mechanisms in those cases suggests a similar effect to how RFAConv learns clustered defect characteristics. Therefore, future work could explore integrating new optimization modules that incorporate attention mechanisms to provide multi-scale representations for these challenging defects, thereby further enhancing YOLO-RSD’s comprehensive detection capabilities.
6. Conclusions
This paper introduced YOLO-RSD, a novel lightweight object detection model (9.8 GFLOPs) for steel surface defect detection. Extensive multi-dataset experiments affirmed YOLO-RSD’s robustness to diverse environmental noise, primarily due to the ADConv module, making it suitable for complex industrial and urban infrastructure settings. Our research achieved a 6.3% mAP improvement on the NEU-DET dataset, and a 5.9% mAP improvement on the GC10-DET dataset. The Head_DySnake module’s texture-specific enhancement and the RFAConv module’s focus on clustered defect characteristics were empirically validated, yielding significant accuracy improvements. Beyond steel inspection, the principles of texture structure enhancement and defect characteristic-oriented module optimization within YOLO-RSD offer promising potential for adaptation in broader cross-domain visual inspection tasks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.P. and Y.Z.; methodology, H.P.; software, H.P. and J.S.; validation, J.S. and H.X.; formal analysis, J.S.; investigation, H.P.; resources, H.X. and Y.Z.; data curation, H.P.; writing—original draft preparation, H.P. and J.S.; writing—review and editing, H.P., J.S., H.X., and Y.Z.; visualization, J.S. and Y.Z.; supervision, H.X. and Y.Z.; project administration, H.X. and J.S.; funding acquisition, H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Special Technology Mission Team Project, Zhejiang Institute of Economics and Trade under Grant no. 22KJTPY10.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Luo, Q.; Fang, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y. Automated visual defect detection for flat steel surface: A survey. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 626–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordia, R.; Verma, A.K. Visual techniques for defects detection in steel products: A comparative study. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 134, 106047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wei, X.; Hassaballah, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. A deep learning model for steel surface defect detection. Complex Intell. Syst. 2024, 10, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Chen, J.; Lu, Z.; Li, F.; Liu, Y. Steel Surface Defect Detection via Deformable Convolution and Background Suppression. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Lv, Z.; Zhou, C.; Gu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, K.; Li, Z. Mixed Receptive Fields Augmented YOLO with Multi-Path Spatial Pyramid Pooling for Steel Surface Defect Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultralytics. Ultralytics YOLO. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/ (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.02640. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.02696. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, R.; M, S. YOLOv8: A Novel Object Detection Algorithm with Enhanced Performance and Robustness. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Advances in Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing Systems (ADICS), Chennai, India, 18–19 April 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M. YOLO-v1 to YOLO-v8, the Rise of YOLO and Its Complementary Nature toward Digital Manufacturing and Industrial Defect Detection. Machines 2023, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singlor, T.; Thawatdamrongkit, P.; Techa-Angkoon, P.; Suwannajak, C.; Bootkrajang, J. Globular Cluster Detection in M33 Using Multiple Views Representation Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning, Évora, Portugal, 22–24 November 2023; pp. 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Learning Spatial Fusion for Single-Shot Object Detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.09516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.; Hu, H.; Ahmad, A.; Wang, K. A Review of Metal Surface Defect Detection Technologies in Industrial Applications. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 48380–48400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.L.; Chiu, Y.Y.; Lin, B.H.; Wang, C.C.; Wu, Y.T.; You, C.Y.; Chien, Y.R. Integration of deep learning network and robot arm system for rim defect inspection application. Sensors 2022, 22, 3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semitela, Â.; Pereira, M.; Completo, A.; Lau, N.; Santos, J.P. Improving Industrial Quality Control: A Transfer Learning Approach to Surface Defect Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberironaghi, A.; Ren, J.; El-Gindy, M. Defect Detection Methods for Industrial Products Using Deep Learning Techniques: A Review. Algorithms 2023, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, T.; Liu, C.; Dong, W. FCNN: Simple neural networks for complex code tasks. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2024, 36, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yin, J.; Huang, F.; Li, Q. Surface defect inspection of industrial products with object detection deep networks: A systematic review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, M.; Yang, J.; Luo, H. YOLOv5-CD: Strip steel surface defect detection method based on coordinate attention and a decoupled head. Meas. Sens. 2023, 30, 100909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, M. DEW-YOLO: An Efficient Algorithm for Steel Surface Defect Detection. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zuo, W.; Fei, L.; Liu, H. Attention-guided CNN for image denoising. Neural Netw. 2020, 124, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Song, T.; Ye, Y.; Li, K.; Song, Y. RFAConv: Innovating spatial attention and standard convolutional operation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03198. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; He, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G. Dynamic snake convolution based on topological geometric constraints for tubular structure segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 6070–6079. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Song, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, X. Triplet-graph reasoning network for few-shot metal generic surface defect segmentation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Yan, Y. A noise robust method based on completed local binary patterns for hot-rolled steel strip surface defects. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 285, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Song, K.; Meng, Q.; Yan, Y. An end-to-end steel surface defect detection approach via fusing multiple hierarchical features. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Duan, F.; Jiang, J.j.; Fu, X.; Gan, L. Deep metallic surface defect detection: The new benchmark and detection network. Sensors 2020, 20, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Huang, Z.; Li, G. Msft-yolo: Improved yolov5 based on transformer for detecting defects of steel surface. Sensors 2022, 22, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, C.; Yang, G.; Xue, T.; Ma, J.; Liu, L.; Ren, J. Siamese-RCNet: Defect Detection Model for Complex Textured Surfaces with Few Annotations. Electronics 2024, 13, 4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Lipton, Z.C. The mythos of model interpretability: In machine learning, the concept of interpretability is both important and slippery. Queue 2018, 16, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, D. Automatic defect detection of texture surface with an efficient texture removal network. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 53, 101672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).