Abstract
Despite the rapid advancement of smart-grid technologies, automated pointer meter reading in power substations remains a persistent challenge due to complex electromagnetic interference and dynamic field conditions. Traditional computer vision methods, typically designed for ideal imaging environments, exhibit limited robustness against real-world perturbations such as illumination fluctuations, partial occlusions, and motion artifacts. To address this gap, we propose PriKMet (Prior-Guided Pointer Meter Reader), a novel meter reading algorithm that integrates deep learning with domain-specific priors through three key contributions: (1) a unified hierarchical framework for joint meter detection and keypoint localization, (2) an intelligent meter reading method that fuses the predefined inspection route information with perception results, and (3) an adaptive offset correction mechanism for UAV-based inspections. Extensive experiments on a comprehensive dataset of 3237 substation meter images demonstrate the superior performance of PriKMet, achieving state-of-the-art meter detection results of 99.4% AP50 and 85.5% for meter reading accuracy. The real-time processing capability of the method offers a practical solution for modernizing power infrastructure monitoring. This approach effectively reduces reliance on manual inspections in complex operational environments while enhancing the intelligence of power maintenance operations.
1. Introduction
In the digital era, the integration of digital meters in industrial systems has revolutionized the monitoring of equipment due to their superior signal transmission capabilities [1]. Digital meters offer enhanced data accuracy, real-time monitoring, and ease of integration into automated systems. However, in critical power transmission and transformation scenarios, especially those involving high magnetic interference and challenging environmental conditions, traditional pointer meters still play an essential role [2]. These meters are renowned for their resilience, providing stable readings in environments where digital meters often struggle due to electromagnetic noise, variable lighting, and other environmental disturbances. As smart grid technologies advance, the demand for automated condition monitoring solutions has grown significantly. However, despite progress in automated meter reading technologies, accurate and reliable pointer meter recognition in real-world industrial settings remains a formidable challenge.
In real-world applications, cameras used in power station inspections are required to cover large areas, and they frequently encounter dynamic environmental changes, which complicate meter recognition tasks. These challenges, such as lighting fluctuations, partial occlusions, motion artifacts, and varying angles, limit the effectiveness of many existing methods [3]. Furthermore, the performance of most existing algorithms significantly drops when these factors come into play, thus failing to meet the real-time and reliability requirements of industrial power systems. For instance, traditional computer vision approaches like the improved Hough circle transform and edge detection algorithms [4,5] struggle with noise interference in complex backgrounds, while template matching techniques remain sensitive to viewpoint variations. Wang et al. [6] developed a multi-scale template matching algorithm that leveraged prior knowledge of dial scales to improve positioning accuracy. Deep learning-based solutions, such as Mask R-CNN for pointer segmentation [7] or keypoint detection frameworks [8], have demonstrated remarkable capability in accurately localizing pointers. However, existing approaches exhibit performance degradation under low illumination or motion blur conditions and fail to utilize structured prior knowledge specific to power scenarios fully.
The integration of UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) in smart-grid systems has revolutionized power equipment inspection methodologies. However, as illustrated in Figure 1a, UAV-based substation inspections introduce unique challenges for meter reading: while providing unprecedented operational flexibility, UAVs are susceptible to positional deviations during flight operations (shown in Figure 1b), potentially compromising reading accuracy. To address this limitation, recent research has explored the fusion of inspection systems with prior knowledge. Multi-camera collaborative calibration systems [9] improve meter positioning accuracy through 3D reconstruction, while SLAM-based UAV navigation frameworks [10] achieve centimeter-level hovering precision. Knowledge graph-driven detection algorithms [11] encode equipment topological relationships into networks, and advanced OCR techniques [12] enhance scale information extraction. However, these approaches often target isolated interference factors, demonstrating limited applicability in UAV-assisted power equipment inspection scenarios where complex, coupled environmental conditions are prevalent.
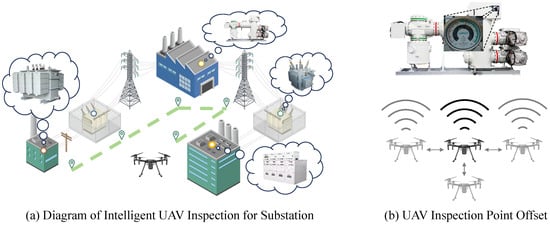
Figure 1.
UAV inspection system for substation meters: (a) planned inspection route with predefined measurement points; (b) positional offset occurring during actual UAV operation.
To address these challenges, we introduce PriKMet (Prior-Guided Pointer Meter Reader), a robust algorithm that synergizes deep learning with domain-specific prior knowledge to achieve accurate meter readings in challenging field environments. By leveraging predefined inspection routes and meter specifications, PriKMet mitigates environmental uncertainties. Additionally, our novel UAV pose correction mechanism compensates for operational deviations, ensuring reliable readings even during dynamic inspections. The main contributions of this paper include the following:
- Innovative Meter Dial Detection and Keypoint Localization: We present a novel approach to meter dial detection, coupled with keypoint localization, that enhances the generalization of the model. This technique is robust to environmental challenges such as poor lighting, occlusion, and blurring, which are often encountered in real-world power equipment inspections.
- Effective Use of Prior Information: Our algorithm makes use of predefined information, such as inspection routes and meter range data, to interpret meter readings accurately. This use of prior information reduces the uncertainty caused by environmental interference and enhances the accuracy of the readings.
- UAV Inspection Error Correction: We introduce a correction mechanism that compensates for any deviations in the UAV position during inspections. This adjustment ensures that the meter readings are accurate despite any operational inconsistencies, thus making the algorithm suitable for real-time, field-deployed systems.
Comprehensive evaluation on a 3237-image dataset collected from five operational substations demonstrates the superiority of PriKMet over state-of-the-art methods, achieving 99.4% AP50 in detection and 85.5% reading accuracy. The system maintains real-time performance (30.9 FPS on server-grade GPUs) while significantly outperforming existing approaches in challenging scenarios involving occlusion, glare, and motion blur.
2. PriKMet: Prior-Guided Pointer Meter Reader
In this section, we introduce the PriKMet algorithm. The overall pipeline of PriKMet is summarized in Figure 2. The process begins with meter detection, followed by pointer keypoint localization. Once the pointer is localized, the angle calculation and offset correction mechanisms are applied to derive the accurate meter reading. Finally, the system leverages prior knowledge of inspection routes and meter scales to refine the reading and ensure robustness under diverse environmental conditions.

Figure 2.
Overall pipeline of our PriKMet system showing the four-stage processing from input image to final meter reading.
2.1. PriKMet Network
As shown in Figure 3, the framework of the PriKMet model begins with the detection of the meter dial from an input image. Once the meter dial is localized, the algorithm proceeds to identify the keypoints of the pointer. The predictions of the model provide the information source for the subsequent reading calculation.
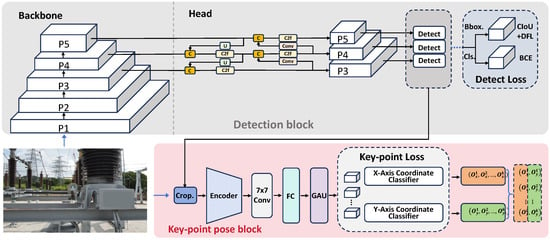
Figure 3.
Two-stage pipeline of PriKMet: (1) Detection block localizes meter dials in input images using efficient feature extraction, (2) Key-point pose block precisely identifies pointer positions within detected dial regions.
2.1.1. Detection Module
The detection module architecture, as shown in Figure 3, consists of two main parts: the backbone network and the head network. The backbone network is constructed using CSPNet (Cross-Stage Partial Network). The CSPNet Backbone extracts image features, and the P3, P4, and P5 feature layers are input into the Head network for further processing of the dial region. In the Head stage, image features are processed using concatenation (Concat), upsampling (Upsample), convolution (Conv), and C2f modules [13]. Inspired by [13], we adopt the Cross-Stage Partial feature-Fusion module (C2F), which enriches gradient pathways with minimal overhead, keeping the network lightweight yet markedly enhancing its fine-grained feature capture. The detailed structure of the Head section is shown in Figure 4. Concat, Split, Bottleneck, Conv2d, BatchNorm2d, and SiLU denote the standard PyTorch v1.11.0 operations for channel-wise concatenation, channel splitting, residual bottleneck block, 2D convolution, batch normalization, and SiLU activation, respectively. The C2f module is defined as follows:
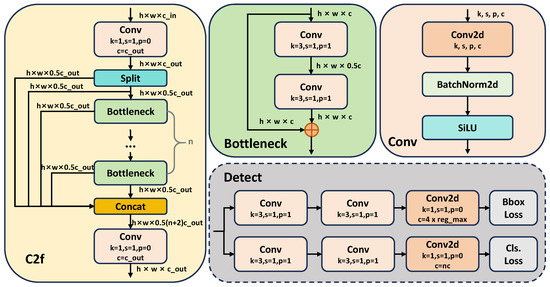
Figure 4.
Model details of PriKMet: This figure illustrates the detailed components within the Detection block, including the C2f [13], Bottleneck, Conv, and Detect modules. Each module is expanded and marked with consistent colors for clarity.
Here, the Split operation divides the input tensor x into two parts, and Concat represents the concatenation operation, while Bottleneck refers to a series of convolutional layers that form the bottleneck structure.
The Bottleneck module, as shown in Figure 4, includes one or more depthwise separable convolution layers, which reduce the number of parameters and computational complexity. Let the input tensor x have dimensions , where H, W, and C represent the height, width, and channels, respectively. After the Split operation, each sub-tensor has dimensions . The output dimensions of each layer in the Bottleneck remain unchanged, i.e., .
In the Conv module, depthwise separable convolutions replace traditional convolution operations. Depthwise separable convolution consists of two steps: depthwise convolution (Depthwise Convolution) and pointwise convolution (Pointwise Convolution). For a given input tensor x, depthwise convolution applies a convolutional kernel to each input channel independently, and pointwise convolution uses a kernel to combine the outputs. Specifically, the Conv operation is expressed as:
Compared to traditional convolution, depthwise separable convolution significantly reduces the number of parameters and computational cost while maintaining competitive expressive power.
To locate the dial position and category, the Head network uses the Anchor-Free mechanism of YOLO-v8 to handle classification and regression tasks. The detection module loss function includes classification loss , localization loss , and confidence loss . The overall loss function is:
where and are hyperparameters used to adjust the weight of each loss term. For the localization loss, the model uses CIoU Loss, which considers the overlap between the predicted and ground truth boxes, along with the center distance and aspect ratio differences:
Here, d represents the Euclidean distance between the center points of the predicted and true boxes, c is the diagonal length of the smallest enclosing rectangle around both boxes, and is a balancing factor.
For the classification loss, the model uses the Varifocal Loss (VFL) function, which handles class imbalance via an asymmetrical weighted loss function:
where p is the predicted probability, q is the ground truth label, and is the adjustment factor.
2.1.2. Pointer Keypoint Localization Module
Building on the meter dial region localized in the inspection image, the PriKMet network further performs keypoint localization for the pointer. Referring to the RTMPose method [14], PriKMet utilizes a feature encoder (CSPNeXt) network to extract features from the local dial image. The decoder then refines these features, integrating context from the entire image to improve keypoint prediction accuracy.
To better capture spatial relationships in the image, the pointer keypoint localization module uses a 7 × 7 convolution layer to generate feature maps that describe low-level structures. By applying multiple convolution layers, the model can learn more abstract and complex patterns.
The network introduces Graph Attention Units (GAUs) to enhance pose estimation accuracy. GAUs allow the model to dynamically adjust the attention of different parts based on the dependencies between nodes. Specifically, compute the initial attention score for each node pair i and j:
where and are the feature vectors for nodes i and j, W is the weight matrix, and a is the attention parameter vector. ∥ represents vector concatenation.
Normalize the attention scores:
where denotes the set of neighbors of node i.
Update the node features based on the normalized attention scores:
where is typically the ReLU activation function.
The pointer keypoint localization module uses two loss functions to optimize the model: keypoint loss and confidence loss. Keypoint loss: Encourages the model to accurately predict keypoint locations:
where and are the predicted and actual keypoint coordinates and N is the total number of keypoints.
Confidence loss: Ensures the model assigns high confidence scores to correct keypoints:
where and represent the predicted and actual confidence scores and is the sigmoid function.
2.2. Angle Calculation and Offset Correction
After locating the pointer, PriKMet calculates the pointer’s orientation angles and relative to the dial scale, as shown in Figure 2.
Angle Calculation: The angle is calculated using the positions of the center, starting, and ending points relative to the center and the scale markings of the dial. The formula for angle calculation is:
where are coordinates of the starting points of the dial scale markings, are coordinates of the dial center points, and are coordinates of the ending points of the dial scale markings. Note that these coordinate parameters can be predetermined based on prior knowledge.
where are the prediction coordinates of the pointer tip, are coordinates of the dial center points, and are coordinates of the ending points of the dial scale markings.
Offset Correction: UAV inspections often introduce tilt or positional errors. PriKMet compensates for this by calculating the deflection angle , which adjusts for the deviation in UAV position. As shown in Figure 5, we apply OpenCV for the segmentation of the dial of the meters and the fitting of and measurement of the deflection. The deflection angle is calculated as:
where l and d are the lengths of the major and minor axes of the dial ellipse of the meter.
The corrected pointer angle is then computed as:
where is the initially calculated pointer angle.
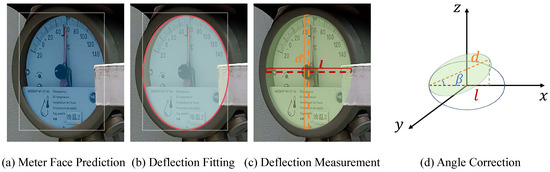
Figure 5.
Visualization of deflection analysis and correction in PriKMet: (a) Meter face prediction identifies the dial region; (b) Deflection fitting estimates the pointer’s angular displacement; (c) Deflection measurement calculates the precise tilt angle; (d) Angle correction adjusts the reading based on UAV positional offsets during inspections.
Meter Reading Calculation: The final step is to calculate the meter reading X by combining the corrected pointer angle with the predefined meter scale. The meter reading is given by:
where and are the minimum and maximum values of the meter’s scale, is the corrected pointer angle, and is the deflection angle that accounts for UAV positional deviations.
By using this prior information, PriKMet ensures real-time accuracy in diverse environmental conditions, reducing uncertainty and improving the overall robustness of the system.
3. Experiment Results
3.1. Benchmark
3.1.1. Training and Test Dataset
To verify the effectiveness of PriKMet proposed in this paper, we collected meter inspection data from substations and created training and test datasets to conduct thorough experimental validations of the algorithm models. Specifically, we conducted UAV-based inspections using five DJI Mavic 2 Pro UAVs (DJI, Shenzhen, China) equipped with their own onboard 20-megapixel Hasselblad camera (5472 × 3648 px). The drone was flown along eight pre-planned flight routes per site across five geographically distinct substations, yielding 3037 valid meter images that spanned a wide range of lighting, viewpoint, and occlusive conditions for model training. Based on the raw data, a total of 2199 partial meter images were extracted, including multiple types of meters such as oil level gauges, lightning arresters, SF6 meters, etc., shown in Figure 6b. To evaluate the performance of the model algorithm, we simultaneously collected 200 substation images as the test dataset, each containing one meter, totaling 200 partially annotated images, summarized in Table 1.
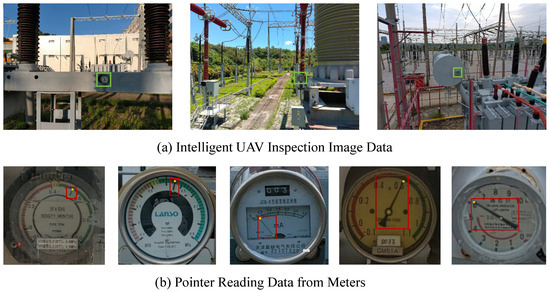
Figure 6.
Dataset composition and sample visualization: (a) UAV inspection images collected from substations across five regions, covering diverse scenarios, lighting conditions, and angles, with green boxes indicating the locations of meters; (b) Extracted partial meter images, including oil level gauges, lightning arresters, and SF6 meters, annotated for model training and evaluation, with red boxes indicating the positions of pointers.

Table 1.
Dataset composition and statistical details. The training set includes 3037 UAV inspection images and 2199 partial meter images. The test set contains 200 UAV inspection images with corresponding partial meter images, covering diverse scenarios, lighting conditions, and meter types.
3.1.2. Evaluation Metric
To compare the performance of different models, we evaluated the final trained model on the validation set using standard detection metrics such as mAP, Recall, and Accuracy for meter box detection. We also compared the accuracy of key point detection for meter pointers. For assessing meter reading accuracy, we calculated the deviation between actual and predicted readings, deeming a reading correct if the error was within ±5%, and incorrect otherwise. Reading accuracy was determined by the proportion of meters that were correctly read. Additionally, model inference speed was assessed based on inference time and frame rate.
3.2. Implementation Details
During the model training and testing process, we employed the PyTorch framework for both training and experimental inference. The experiments were conducted using 2 NVIDIA GTX 3090 GPUs by default. For model training, we used Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) as the optimization algorithm, with the following hyperparameters: 100 epochs, a batch size of 16, and an initial learning rate of 0.01.
3.3. Main Results
3.3.1. Meter Detection Results
As shown in Table 2, PriKMet achieves an AP50 of 99.4% in detection tasks, significantly outperforming models from the YOLO series and DETR-like models. In key point localization tasks (Table 3), PriKMet AP50kp reaches 90.7%, which is a 4.2 percentage points improvement over Mask R-CNN [15]. The reading accuracy increases to 85.5% when incorporating prior information with a correction mechanism (Table 3), demonstrating the algorithm’s robustness in complex scenarios.

Table 2.
Performance comparison of mainstream detection models. Our PriKMet outperforms the state-of-the-art YOLO detectors and DETRs in both AP, Recall, and Precision.

Table 3.
Comparison of keypoint detection performance. PriKMet achieves a keypoint AP50 of 90.7%, showing a 4.2% improvement over Mask R-CNN while maintaining high localization accuracy under occlusion and blur.
3.3.2. Analysis of Meter Reading Accuracy
Table 3 compares the performance of keypoint detection. By introducing Graph Attention Units (GAUs) to enhance spatial relationship modeling, PriKMet achieves an AP75kp of 72.8%, a 2.0% increase over baseline models. Various results show that the model can accurately locate pointer base and tip keypoints even under occlusion and blur conditions.
3.3.3. Inference Time Comparison
To evaluate the computational efficiency of PriKMet for real-time deployment in power inspection systems, we conducted comprehensive inference time comparisons with state-of-the-art methods under different hardware configurations. The experiments were designed to simulate both high-performance server and edge computing scenarios commonly found in power monitoring applications. Specifically, we employed NVIDIA GTX 3090 as server-grade hardware and used NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin as edge-computing and NVIDIA Jetson TX2 as an embedded device. Table 4 presents the detailed comparison with mainstream detection frameworks. PriKMet achieves 30.9 FPS on server-grade hardware and maintains 17.6 FPS on edge devices, meeting the minimum 15 FPS requirement for UAV real-time inspection systems. Compared to YOLOv8-L, our method shows 17% faster inference on AGX Orin with comparable accuracy, making it more suitable for field deployment. On embedded devices, PriKMet maintains <150 ms latency, which is critical for mobile inspection robots with limited computing resources.

Table 4.
Inference time comparison across hardware platforms . PriKMet achieves real-time performance compared with state-of-the-art methods, meeting real-world inspection requirements.
3.4. Ablation Study
3.4.1. Ablation Study on Meter Detection and Result Correction
To validate the effectiveness of each module, three groups of experiments were designed: (1) removing the dial detection module (relying solely on keypoint localization); (2) basic model (including detection and keypoint modules); (3) full model (adding tilt correction mechanisms). As shown in Table 5, without dial detection, the reading accuracy plummets to 43.2%, indicating the critical role of local dial positioning for subsequent tasks. The correction mechanism further improves accuracy by 1.8%, proving its efficacy in compensating for UAV pose offset errors.

Table 5.
Ablation experiments of PriKMet on key point localization and meter reading results.
3.4.2. Ablation Study on Different Backbones
To further evaluate the impact of different backbone networks on the performance of PriKMet, we conducted an ablation study comparing several popular backbone architectures. The backbones tested included CSPNet (used in the original PriKMet), ResNet-50, EfficientNet-B4, and Swin Transformer. The experiments were performed on the same dataset and training parameters to ensure a fair comparison. To fully evaluate the model, we used AP50 for detection tasks, for keypoint localization, and reading accuracy (error within ). The performance metrics for each backbone are summarized in Table 6. CSPNet achieves the highest performance across all metrics, demonstrating its suitability for the PriKMet framework. Its design, which combines cross-stage partial connections, effectively balances computational efficiency and feature extraction capability. ResNet-50 shows competitive results but slightly lagged behind CSPNet, particularly in keypoint localization. This may be due to its less efficient feature fusion mechanism compared to CSPNet. EfficientNet-B4 performs well in detection tasks but exhibited a marginal drop in keypoint localization accuracy, likely due to its focus on computational efficiency over fine-grained feature extraction. Swin Transformer delivers strong results, especially in detection tasks, but its performance in keypoint localization was slightly inferior to CSPNet. The transformer global attention mechanism may not be as effective for precise keypoint localization as CSPNet hierarchical feature extraction.

Table 6.
Performance comparison of PriKMet with different backbone networks. CSPNet outperforms ResNet, EfficientNet, and Swin Transformer in detection and reading accuracy, proving its architectural suitability.
The ablation study confirms that CSPNet is the optimal backbone for PriKMet, as it provides the best balance between detection accuracy, keypoint localization precision, and reading reliability. While other backbones like Swin Transformer and EfficientNet-B4 offer competitive performance, the CSPNet architecture is better suited for the specific challenges of meter reading in complex power scenarios. Future work could explore hybrid architectures or further optimizations of CSPNet to enhance performance.
3.5. Visualization
To validate the reliability of PriKMet in real-world substation inspections, we conducted a comprehensive visualization study under six representative challenging conditions: strong direct light, partial occlusion, geometric distortion, low-light conditions, blurred dial, and dust and stains. Figure 7 illustrates the method’s performance across all these scenarios. In the first case (Figure 7a), the model successfully locates the dial region under strong light reflections, maintaining precise pointer localization despite significant glare interference. The second scenario (Figure 7b) demonstrates the algorithm’s resilience to partial occlusions: the pointer tip and root keypoints are accurately localized, even when external objects partially obscure the pointer. The third example (Figure 7c) highlights the system’s capability to handle geometric distortions caused by UAV positional offsets. Here, the dial exhibits a light tilt due to UAV instability during inspection. PriKMet adaptively accounts for this spatial misalignment, preserving reliable keypoint detection and angle measurement without explicit post-correction. In the fourth example (Figure 7d), despite severely insufficient ambient lighting, PriKMet still accurately captures the dial contour and pointer position. In Figure 7e, the overall appearance of the dial and its scale marks are heavily blurred and nearly indistinguishable; nevertheless, our PriKMet still achieves precise pointer localization. For scenarios involving dials contaminated by stains, dust, or water droplets, we visualize the results in Figure 7f; the outcomes demonstrate that even when the dials are partially occluded by such contaminants, pointer localization remains unaffected. These visual results collectively validate the framework’s robustness against variable illumination, occlusion, blur, geometric distortion, surface contamination, and perspective distortions commonly encountered in power-substation environments.
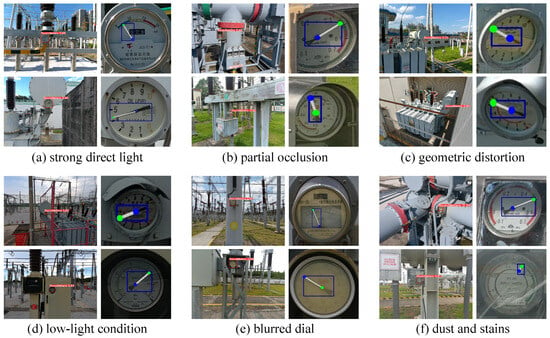
Figure 7.
Visualization of PriKMet performance under diverse challenging conditions: (a) Robust dial segmentation under intense light reflections, preserving precise boundary detection; (b) Accurate pointer keypoint localization despite partial occlusion; (c) Reliable angle measurement for geometric distortions caused by UAV positional offsets.
3.6. Limitations
The current PriKMet framework is trained and evaluated on standard clockwise, circular analogue meters with uniform scales. In practice, however, industrial plants may deploy instruments with counter-clockwise dials, non-uniform tick marks, or elliptical faces. Counter-clockwise rotation demands a reversed reading logic, non-linear scales require precise OCR-based tick recognition, and elliptical geometries impose stricter accuracy on the pointer-tip position. Extending PriKMet to handle these variations remains an open direction for future work.
4. Conclusions
This paper proposes a prior-guided keypoint detection algorithm (PriKMet) for pointer meter reading in complex power scenarios, integrating deep learning with domain-specific priors to achieve unified solutions for dial detection, pointer localization, and reading calibration. The algorithm innovatively combines a robust detection framework, spatial relationship modeling, and dynamic error compensation mechanisms, demonstrating effectiveness and practicality under diverse environmental challenges. Extensive experiments on a comprehensive dataset of 3237 substation meter images demonstrate the superior performance of PriKMet, achieving state-of-the-art meter detection results of 99.4% AP50 and 85.5% for meter reading accuracy. Future work will focus on improving adaptability to extreme conditions, reducing reliance on predefined priors, and exploring multimodal collaborative perception to extend the algorithm’s generalization capabilities and deployment efficiency, thereby advancing intelligent industrial instrument inspection technologies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Y.; methodology, H.C.; validation, H.C.; investigation, H.C.; resources, J.F.; data curation, J.F., Y.W. and D.Q.; writing—original draft, Y.W.; writing—review & editing, W.H.; supervision, Y.Y.; project administration, D.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Co., Ltd. Technology Project grant number B311XT24006M.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in this study was collected within substations that form part of critical infrastructure. As the data may contain sensitive equipment and operational information, it cannot be made publicly available due to security considerations. Researchers who require access to the data may contact the corresponding author to discuss the possibility of collaborative use under appropriate confidentiality agreements.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Jun Feng and Yidan Wang were employed by the company State Grid Zhejiang Electric Power Co., Ltd. Information and Communication Branch. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Sala, A.; Barbetti, L.; Rosini, A. Green web meter: Structuring and implementing a Real-Time digital sustainability monitoring system. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, P.; Fischedick, M.; Viebahn, P. Holistic evaluation of digital applications in the energy sector—Evaluation framework development and application to the use case smart meter roll-out. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Yu, M.; Huang, Z. Lightweight Design of Vibration Control Devices for Offshore Substations Based on Inerters. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, L.; Zhang, D.; Ke, T.; Li, J. Pointer meter recognition method based on Yolov7 and hough transform. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Yen, S.Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Tsai, M.Y.; Chuang, T.H. Intelligent Casting Quality Inspection Method Integrating Anomaly Detection and Semantic Segmentation. Machines 2025, 13, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Cheng, R. Automatic reading system for analog instruments based on computer vision and inspection robot for power plant. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control (ICMIC), Guiyang, China, 2–4 July 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, M.; Anwar, H.; Tufail, M.; Khan, A.; Khan, M.; Ramli, D.A. Image-based automatic energy meter reading using deep learning. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 74, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, J.; Kang, B.; Wang, Y. A Keypoint Driven Robust Pointer Meter Reading Method with Enhanced Structure for Complex Environments. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 5023116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yuan, H.; Bian, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, B.; Chen, Z.; Basit, M.A. Multi-camera vision-based synchronous positioning and mapping for green construction of electric substations. Front. Energy Res. 2024, 12, 1370873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Li, Y.; Yi, Z.; Wang, K.; Yu, P.; Zhao, K.; Yang, T. Review of autonomous inspection technology for power lines using UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Mechatronics Technology (ICEEMT), Qingdao, China, 2–4 July 2021; pp. 481–484. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, Y.; Niu, G.; Yang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Han, Y.; Sun, B. Knowledge-aware design of high-strength aviation aluminum alloys via machine learning. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 346–361. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, J.; Ma, X.; Li, R. SC-ViT: Semantic Contrast Vision Transformer for Scene Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Yokohama, Japan, 30 June–5 July 2024; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, J. Yolov8. 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Jiang, T.; Lu, P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, N.; Han, R.; Lyu, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, K. Rtmpose: Real-time multi-person pose estimation based on mmpose. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.07399. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, J. Yolov5 Release v7.0. 2022. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/v7.0 (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Lv, W.; Bai, X.; Long, X.; Deng, K.; Dang, Q.; Han, S.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X.; et al. PP-YOLOE: An evolved version of PP-YOLO towards real-time object detection with higher precision. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.10419. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Geng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, B.; Ke, Z.; Xu, X.; Chu, X. YOLOv6 v3.0: A full-scale reloading. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2301.05586v1. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, T.; Sun, J. Anchor DETR: Query design for transformer-based object detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.07401. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, D.; Chen, X.; Fan, Z.; Zeng, G.; Li, H.; Yuan, Y. Conditional DETR for Fast Training Convergence. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Maican, M. Efficient DETR: Improving end-to-end object detector with dense prior. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.06493. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Zheng, M.; Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Li, H. Fast convergence of DETR with spatially modulated co-attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3621–3630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable DETR: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Qi, X.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L. DAB-DETR: Dynamic anchor boxes are better queries for DETR. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.12329. [Google Scholar]
- Duburcq, A.; Schramm, F.; Boéris, G.; Bredeche, N.; Chevaleyre, Y. DN-DETR: Accelerate DETR training by introducing denoising. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.01148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; Ni, L.M.; Shum, H. DINO: DETR with improved denoising anchor boxes for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.01148. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).