Abstract
Deep neural networks provide a powerful driving force for breakthroughs in semantic segmentation technology. However, the current mainstream architecture generally falls into the “parameter redundancy trap” in pursuit of accuracy improvement, which brings a large number of calculations and model parameters, forcing researchers to seek a new structural paradigm balance between pixel-level parsing accuracy and the limited computing power of embedded devices. We propose a lightweight semantic segmentation network with multi-level feature fusion and dual attention coordination. In view of the large number of parameters in the traditional backbone network and the fact that it only outputs semantic features at the end of the network but lacks shallow feature information, it will cause significant information loss in the decoder stage, which may lead to fuzzy segmentation results and the misclassification of categories. We design a lightweight backbone network with multi-level feature fusion capability. The detail recovery capability is enhanced in the reconstruction process layer by constructing a cross-stage feature aggregation module system; secondly, in view of the lack of effective feature attention in previous methods, we propose a new DCA module in the proposed network and introduce CBAM in the multi-level special fusion network at a shallow level, which improves the model’s category discrimination ability with minimal parameter overhead, thereby optimizing feature expression and improving segmentation performance. The results show that in the Cityscapes dataset, the mIoU reaches 75.29% with only 5.82 M parameters. In the Pascal VOC 2012 dataset experiment, the proposed model achieves an mIoU of 74.24% with only 5.869 M parameters. Compared with DCN-Deeplabv3+ network, the parameters comprise 48% of it, but the accuracy is improved by 1.66%. Compared with the UNet and PSPNet models, the parameters are reduced by 86.63% and 87.44%, respectively.
1. Introduction
As a core technical difficulty in the field of computer vision [1], image semantic segmentation is committed to achieving pixel-level analysis to complete image understanding. The goal of image semantic segmentation is to segment the input image into multiple regions and assign a semantic category label to each pixel to indicate which object or region in the image the pixel belongs to. This technology has been widely used in unmanned driving [2,3], medical and biological image segmentation [4,5], remote sensing image analysis [6,7], robot vision [8,9], and augmented reality [10].
Traditional semantic segmentation methods are mainly based on threshold segmentation (such as Otsu’s method [11]) and edge detection (such as Canny operator [12]), which have significant limitations: the threshold method is sensitive to lighting, and the global strategy is prone to losing details (such as tissue overlap in medical images), edge detection has poor noise resistance and contour breaks (such as industrial reflective artifacts), and both lack semantic understanding capabilities and cannot distinguish between similar instances (such as street scene vehicle adhesion). In the era of deep learning, although the end-to-end architecture represented by FCN [13] has achieved paradigm innovation, the problem of spatial detail loss in the feature recovery process has become a key bottleneck restricting accuracy. Subsequent research continues to evolve in two directions. First, encoder–decoder structures (such as SegNet [14] and UNet [15]) are used to enhance the feature reconstruction capability, but there are still defects. SegNet still relies on the fully convolutional network structure, the upsampled feature channels are high, and the amount of calculation is still large. Compared with the lightweight network, the computational efficiency is still not ideal. UNet uses cross-layer jumps to achieve feature fusion, but the dense splicing operation causes the expansion of parameters (the number of parameters reaches 43.9 M), and there is a semantic gap in cross-level features. The second direction is to enhance context perception with the help of multi-scale modeling (such as PSPNet [16] and DeepLab series [17,18,19,20]). The Deeplab series is limited by its own overly complex backbone network design, which leads to a large amount of calculation (the number of parameters of the Deeplabv3+ network reaches 54.714 M), and there is a defect that only deep semantic features are extracted at the end of the network, but the spatial detail information in the shallow features is not fully utilized. PSPNet performs pooling operations on the input features at multiple scales and then splices the results back into the original feature map, which also brings the problem of too many parameters, resulting in too much computational overhead and difficult deployment. In the process of feature extraction and reconstruction, the above two methods make it difficult for the network to effectively focus on the areas with strong category discrimination and suppress redundant or irrelevant features.
In the semantic segmentation task, the core challenge of lightweighting is to maintain high accuracy while reducing computational costs. Traditional lightweight methods usually rely on reducing network depth or the number of convolution kernels to reduce the number of parameters, but this leads to limitations in capturing multi-scale information and fine-grained features. In addition, existing lightweight networks are relatively rough in feature fusion and lack the effective modeling of features at different levels, resulting in insufficient complementarity between shallow local information and deep semantic information.
With the continuous development of applications such as robot vision and autonomous driving, a semantic segmentation network with a low parameter count and high computational efficiency is urgently needed for resource-limited embedded platforms. However, the current mainstream semantic segmentation architectures such as DeepLabv3+, PSPNet and HRNet, although superior in accuracy, usually rely on deep stacking, complex decoder structures, or large-scale feature pyramids, resulting in large model parameters, high computational cost, and significant inference delay, which makes it difficult to meet the performance requirements of embedded real-time deployment. In addition, these networks often focus more on semantic information modeling rather than structural compression optimization and lack efficient modeling mechanisms for shallow features and local details. To address the above challenges, we propose a lightweight semantic segmentation network with multi-level feature fusion and dual attention coordination. Through the simplification of structural design and the guidance of an attention mechanism, the model has good semantic understanding and detail recovery capabilities while maintaining a low computational cost, taking into account both the accuracy and practicality of embedded deployment. In order to solve the problem of the excessive number of parameters in mainstream semantic segmentation networks, we designed a lightweight backbone network with multi-level feature fusion capabilities. Traditional multi-level fusion is mostly based on serial or single fusion, whereas we adopt a branch-fusion-enhancement structure, which allows shallow and deep features to converge and interact in parallel at different semantic levels before being fused. This network can efficiently extract feature information from four different levels, shallow and deep, respectively. While significantly reducing the overall number of parameters and computational overhead, it effectively makes up for the limitation of traditional backbone networks that lack multi-level feature fusion. Compared with traditional methods that rely only on deep semantic features, our design retains more shallow local boundaries and fine-grained structural information in the encoding stage, avoiding problems such as blurred boundaries, reduced spatial resolution, and category confusion caused by the lack of shallow features in the decoding stage, thereby improving the model’s feature reconstruction capabilities and segmentation accuracy. In view of the lack of ability of previous methods to focus on effective features, we propose a position-aware multi-level collaborative attention mechanism, which introduces a dual attention collaborative mechanism of lightweight attention modules ECA [21] and CBAM [22] before and after the fusion of features at different scales. This enhances the model’s ability to effectively focus on areas with strong category discrimination during the feature extraction and reconstruction processes at the cost of a very small number of parameters and brings about performance improvements. In short, our main contributions are as follows.
- A lightweight backbone network with multi-level feature fusion capability using a branch-fusion-enhancement structure is proposed. This greatly reduces the number of parameters and computational cost of the overall network while overcoming the defect that the traditional backbone network lacks a multi-level feature fusion design, resulting in high-level semantic information dominating the encoding process, while the local boundaries and fine-grained structural information in the low-level features are not effectively preserved.
- A multi-level collaborative attention mechanism with position awareness was introduced, and attention modules were introduced before and after the fusion of features of different scales. The model’s adaptive feature selection capability in the process of feature extraction and reconstruction was enhanced with extremely low parameter overhead, and the problem of partial information loss in the process of obtaining multi-scale information was alleviated, ultimately achieving an improvement in segmentation performance.
- Our method achieves 74.24% mIOU on the PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset with only 5.869 M parameters and an average pixel accuracy of 83.08%. On the Cityscapes dataset, it achieves 75.29% mIoU with only 5.82 M parameters, achieving a good balance between segmentation accuracy and model lightweightness.
2. Related Work
This section focuses on the development and optimization of deep learning technology in the field of semantic segmentation. First, Section 2.1 reviews the evolution of high-precision semantic segmentation methods and analyzes the key technologies from FCN to multi-scale feature fusion and high-resolution feature learning. Second, Section 2.2 discusses the research progress of lightweight semantic segmentation, including efficient network structure, optimized decoding strategy, and model compression technology, Section 2.3 discusses some of the latest semantic segmentation research methods.
2.1. High-Accuracy Semantic Segmentation
FCN [13] is the first semantic segmentation model that improves the traditional classification network to make it a fully convolutional architecture. It uses convolutional layers instead of fully connected layers to achieve pixel-level prediction. PSPNet [16] proposes a pyramid pooling module that extracts multi-scale global context information through pooling layers of different scales to enhance the model’s perception of large-scale targets. For refined tasks such as medical image segmentation, UNet [15] gradually extracts deep semantic features during the encoding process through a symmetrical U-shaped structure and uses jump connections to fuse low-level detail information during the decoding process. In addition, HRNet [23] maintains high-resolution feature representation throughout the network process and interacts with features through multi-scale parallel branches. RefineNet [24] gradually refines the prediction results by using information at different scales. CE-Net [25] enhances the ability to recover local details by combining global context information. Although the above methods have achieved remarkable segmentation performance on multiple benchmark datasets, they generally rely on deep network stacking, complex module design or a large number of feature channels, which brings about problems such as a large number of model parameters, a high computational overhead, and a slow inference speed. They are difficult to directly apply to resource-constrained scenarios such as edge computing and mobile devices.
Therefore, reducing the computational and storage costs while ensuring segmentation accuracy has become an important direction for the current semantic segmentation model design. To address the above issues, this paper proposes a lightweight semantic segmentation network for resource-constrained environments. Through the collaborative modeling of multi-level feature fusion and dual attention mechanisms, while enhancing the model’s multi-scale perception and spatial detail expression capabilities, it effectively controls the parameter scale and computational complexity, providing a more feasible solution for actual deployment.
2.2. Lightweight Semantic Segmentation
The core goal of lightweight semantic segmentation networks is to reduce the amount of computation and parameter size while maintaining good segmentation accuracy as much as possible. To achieve this goal, researchers have proposed a variety of optimization strategies, including designing lightweight backbone networks, optimizing decoding structures, and using pruning and quantization techniques.
In terms of lightweight backbone networks, MobileNetV2 [26] uses deep separable convolution and inverted residual structures to effectively reduce the amount of computation. ShuffleNetV2 [27] improves computational efficiency through grouped convolution and channel mixing strategies, making it suitable for resource-constrained devices. In addition, EfficientNet [28] uses neural architecture search (NAS) to automatically optimize the network structure to achieve better computing performance.
In terms of decoding structure optimization, ESPNet [29] proposes an efficient spatial pyramid module, which reduces the amount of computation through layered convolution. BiSeNet [30] adopts a dual-path architecture to extract spatial information and semantic information, respectively, thereby reducing the amount of computation while maintaining high accuracy. Fast-SCNN [31] uses a lightweight encoder and a fast decoding structure with jump connections, which improves real-time performance while reducing computing costs.
In addition, model compression technology also plays an important role in lightweight semantic segmentation tasks. Channel pruning [32] reduces the amount of computation by removing redundant channels, and its effectiveness has been verified on networks such as ResNet [33]. Quantization-aware training uses low-bit quantization (such as 8-bit integer calculations) to accelerate the inference process, allowing lightweight models to further reduce storage and computing overhead while maintaining a certain degree of accuracy.
Although these lightweight strategies effectively reduce the amount of computation, lightweight backbone networks may reduce the ability to express features while reducing parameters, which can easily lead to a loss of accuracy when dealing with complex scenes or recognizing small targets. Secondly, optimizing the decoding structure often means reducing the recovery process of high-resolution features, which may lead to insufficient semantic information, especially in boundary processing and fine-grained segmentation tasks, where the model may find it difficult to accurately distinguish similar categories. Finally, although model compression techniques such as pruning and quantization can reduce storage and computing requirements, they usually require additional training or fine-tuning steps; otherwise, the model performance may deteriorate. In addition, these methods are usually optimized for specific hardware or tasks, lack versatility, and may need to be readjusted and redesigned in different application scenarios, limiting their wide applicability.
2.3. Emerging Research Paradigms in Semantic Segmentation
In recent years, with the continuous advancement of foundation models and contrastive learning in the field of vision, semantic segmentation methods are gradually shifting from the traditional architecture optimization paradigm to a new development path centered on large-scale pre-training, cross-task generalization, and few-sample adaptability. The Segment Anything Model [34] proposes a general segmentation framework driven by prompts, which has good cross-domain migration capabilities and shows significant advantages in zero-sample and few-sample scenarios. Prototype-based Semantic Segmentation [35] uses a non-parametric prototype representation method to replace a large number of model parameters to be learned with the average vector of each type of training sample features, thereby achieving a more generalized semantic representation. PiCo [36] is based on a pixel-level contrastive learning mechanism. By enhancing the semantic consistency between pixels of the same type and the discriminability between different classes, it effectively improves boundary recognition and intra-class aggregation capabilities and promotes the implementation of the metric learning paradigm in supervised semantic segmentation. Furthermore, the review study “Image segmentation in foundation model era: A survey” [37] systematically summarizes the evolution trends of current image segmentation methods in the context of basic models, covering multimodal perception, unified task modeling, and generalization techniques driven by large-scale data.
3. Methods
3.1. Lightweight Semantic Segmentation Network with Multi-Level Feature Fusion and Dual Attention Collaboration
This study proposes a lightweight semantic segmentation network with multi-level feature fusion and dual attention coordination. Its overall structure adopts an encoder–decoder architecture to improve feature expression capabilities while ensuring computational efficiency. In the encoder part, we designed an improved lightweight multi-level feature fusion backbone network that can extract feature information at four different levels while maintaining computational efficiency and further enhance the complementarity of shallow and deep features through structural optimization, thereby improving the multi-scale perception ability of the model. Unlikke the existing multi-level fusion structure, we introduced a more targeted feature fusion strategy and carefully designed the fusion method and feature interaction to alleviate the problem of information redundancy. The deepest features are introduced into the DCA Module, in which we combine the dilated convolution with the efficient channel attention mechanism ECA for joint modeling. The ECA module improves feature selectivity through lightweight adaptive channel weight allocation, so that the dilated convolution can compensate for its lack of ability to obtain local structural information while modeling large-scale contexts, thereby enhancing the recognition of deep semantic features. Subsequently, the features extracted at different voiding rates are fused and sent to our improved SAM (Spatial Attention Model) module. This module optimizes the weight generation structure based on the classic spatial attention mechanism, making it more focused on discriminative spatial regions, further promoting the deep fusion of global semantic information and local details.
In terms of shallow feature processing, we introduced the CBAM module and customized it to address the problems of traditional methods, which often ignore local details and blurred boundaries during the extraction process. This allows the first three layers of shallow features to be jointly modeled in the channel and spatial dimensions, improving the model’s ability to focus on key details. Different from the conventional use of CBAM, we introduced a layer-by-layer attention fusion mechanism in the shallow branch, allowing the model to dynamically select edge information from different scales, thereby effectively enhancing the response strength of the boundary area. The introduction of CBAM not only improves the shallow features’ ability to depict structural details but also improves the entire model’s accuracy in discriminating category boundaries, significantly alleviating the category confusion problem caused by insufficient shallow information.
In the decoding stage, we first fuse the enhanced shallow features in the channel dimension through 1 × 1 convolution to make them work more closely together. Subsequently, the deep features processed by the DCA module are finely fused with the shallow features through 4× upsampling to ensure effective alignment of high-level semantic information with low-level detail information. Finally, the fused features are further optimized through a 1 × 1 convolution and upsampled again by 4× to restore the original image resolution and generate the final segmentation result. Overall, this design greatly reduces the computational complexity while enhancing the feature extraction and fusion capabilities, providing an innovative solution for lightweight and high-precision semantic segmentation. The structure is shown in Figure 1.
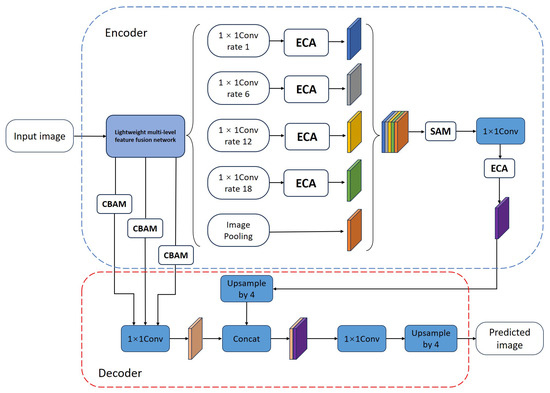
Figure 1.
The structure of the lightweight semantic segmentation network with multi-level feature fusion and dual attention.
3.2. Lightweight Multi-Level Feature Fusion Backbone Network
Inspired by the MobileNetV2 network, MobileNetV2, as an efficient and lightweight deep convolutional neural network, introduces an inverted residual structure and a linear bottleneck design, which can maintain strong feature extraction capabilities under limited computing resources. The mathematical expression of the inverted residual structure is shown in Formulas (1) and (2):
where x is the input feature map, is the nonlinear mapping that transforms the input feature x, and y is the output feature map. When the step size is 1, the input x and output y have the same spatial size and can be jump-connected. is the weight matrix of the expanded convolution. Depthwiseconv uses depthwise separable convolution to reduce the amount of calculation, and reduces the channel dimension through linear transformation. However, MobileNetV2 still has certain limitations in feature expression, which is mainly reflected in the weak multi-scale feature extraction capability; in particular, the shallow local boundary information and fine-grained structure information are easily lost in the encoding stage, which makes it difficult to reconstruct fine segmentation results in the decoding stage. In response to the above limitations, as shown in Figure 2, we propose a lightweight backbone network with multi-level feature fusion capabilities. The backbone consists of four stages, which extract multi-scale features , , and from shallow to deep layers. Among them, and maintain high spatial resolution and are mainly responsible for capturing fine-grained boundaries and texture information. and improve semantic abstraction capabilities while reducing resolution. Spatial compression is performed between each stage through a specific downsampling rate (such as 2× or 4×) so that high-level features have a stronger receptive field. Specifically, as shown in Formula (3).
where represents features of different scales. Shallow features , , and contain rich boundaries and fine-grained features, and deep features have higher semantic expression capabilities. The network extracts features from multiple different levels and integrates shallow structural detail information with deep high-order semantic features through a fusion strategy so that the network can improve the ability to depict the target boundary and retain spatial details while maintaining lightweight. In order to enhance cross-layer information interaction, we designed a cross-stage connection path in the backbone structure to spatially align shallow features with adjacent deep features through upsampling and then use channel splicing and 1 × 1 convolution fusion to further compress redundant channels and unify feature dimensions. Finally, as shown in Formula (4),
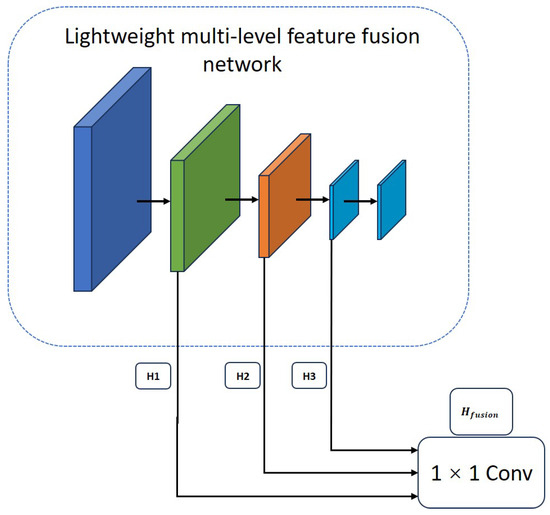
Figure 2.
The structure of the lightweight multi-level feature fusion network.
All shallow-level features are processed by a unified 1 × 1 convolution and integrated with the deep-level output for subsequent segmentation prediction branches. This fusion method not only retains the shallow structural information but also enhances the contextual correlation between features, effectively improves the recognition ability of boundary areas, and improves the recognition performance of small targets. This structural design achieves efficient feature utilization and expression capabilities while ensuring the overall light weight of the model, providing a more practical solution for the application of semantic segmentation tasks in resource-constrained environments. Its structure is shown in Figure 2.
3.3. Multi-Channel Feature Aggregation with CBAM
In the design of the lightweight backbone network, we constructed four layers of feature representation at different levels to enhance the model’s perception of multi-scale information. Considering that shallow features mainly capture fine-grained local structural information, while deep features carry more abstract high-semantic information, achieving effective fusion while ensuring computational efficiency and avoiding semantic conflicts and information redundancy is a key issue in our design. In response to the semantic interference problem caused by the simple concatenation of shallow and deep features commonly seen in existing methods, we proposed a shallow layer enhancement fusion strategy based on attention guidance. Specifically, a customized CBAM module is introduced in each layer except the deepest layer, which not only uses its joint attention mechanism of channel and spatial dimensions to improve the feature screening ability but also makes the attention mechanism more targeted to focus on discriminative local structural areas through structural coordination with the backbone fusion path. Unlike traditional CBAM, which is only an additional module, we deeply embed it into the feature fusion process and adjust its attention weights in combination with the semantic levels of features at different scales so as to enhance key features with minimal parameter overhead. This strategy effectively improves the expression quality of fused features while maintaining the light weight of the network and enhancing the model’s discrimination and detail reconstruction capabilities, reflecting certain structural design innovation and practical value. Figure 3 shows its structure.
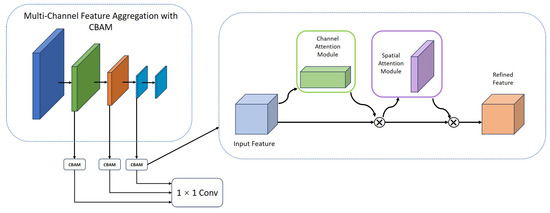
Figure 3.
The structure of Multi-Channel Feature Aggregation with CBAM.
CBAM has the characteristics of taking into account both channel attention and spatial attention, which enables the model to be adaptively adjusted in feature representations of different scales and levels. Specifically, in the channel dimension, different channels in the feature map often represent different visual patterns and semantic information. However, the contributions of different channels are not balanced. Some channels contribute more to the final classification or segmentation task, while others may contain redundant or noisy information. To this end, CBAM uses global pooling (including average pooling and maximum pooling) to extract global information between channels and learns the importance distribution of different channels through a fully connected network to obtain the channel attention weight, as shown in Figure 4. The formula is shown in (5).
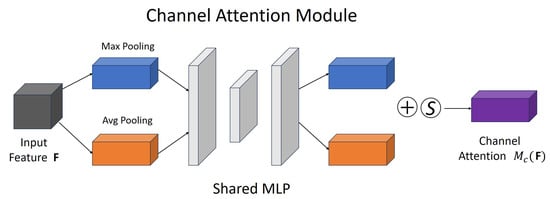
Figure 4.
Channel attention module.
is the channel attention weight, and are the shared fully connected layer parameters, and and are the features after global average pooling and global maximum pooling, respectively. is the activation function.
In the spatial dimension, since different areas of the image contribute differently to the semantic segmentation task, traditional convolution operations cannot accurately focus on key areas, which easily leads to the interference of irrelevant background information with respect to the target features. CBAM further introduces the spatial attention mechanism after channel attention. It also calculates the global response in the spatial dimension based on average pooling and maximum pooling and learns spatial weights through convolution operations so that the network can focus on the salient features of the target area while suppressing background noise. In this way, shallow features can focus more on local key structures, while deep features can also focus more accurately on the target area at a high semantic level, thereby avoiding information redundancy and noise interference that may be introduced by direct splicing. The spatial dimension processing is shown in Figure 5.
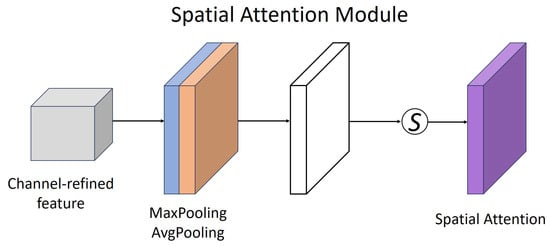
Figure 5.
Spatial attention module.
Finally, the shallow features strengthened by the CBAM module are spliced with the deep features so that the model can more fully integrate local details and global semantic information while being lightweight, thereby improving the performance of the model in semantic segmentation tasks. We provide a more targeted feature screening strategy at the cost of extremely low parameter overhead so that features at different levels can retain the most discriminative information when fused while suppressing unnecessary interference. Overall, this design not only improves the network’s adaptive perception of multi-scale features but also enhances the model’s generalization ability for complex scenes while ensuring computational efficiency, providing an effective optimization solution for lightweight semantic segmentation networks.
3.4. DCA Module
Although deep features contain rich semantic information after multiple downsampling, their spatial resolution is significantly reduced. It is difficult to effectively model the contextual associations of objects of different sizes by directly using a single-scale convolution operation. To this end, we adopt a parallel dilated convolution structure in our design and construct a multi-scale receptive field by setting different dilation rates (such as 1, 6, 12, and 18), so as to capture the contextual information of objects of different sizes without adding additional parameters or downsampling times. Smaller dilation rates help to preserve local details and boundary structures, while larger dilation rates help to model broader global dependencies. This multi-scale parallel strategy enables the network to take into account both details and semantic expression in the feature extraction process. However, since dilated convolution skips some neighborhood pixels during the dilation sampling process, it may cause sparse responses in the feature map. Especially when dealing with boundary areas and small objects, there is a certain risk of information loss, which in turn affects the accuracy of the final segmentation result.
To make up for this shortcoming, we introduce the ECA (efficient channel attention) attention mechanism after the dilated convolution so that the network can adaptively adjust the weights according to the importance of different channel features. ECA uses local one-dimensional convolution to model cross-channel dependencies without introducing a fully connected layer, which not only reduces the computational cost but also avoids the information loss caused by channel compression. Specifically, ECA can capture the complementarity between channels and guide the network to prioritize the discriminative channel responses when integrating multi-scale dilated features, thereby effectively alleviating the feature sparsity problem caused by dilated convolution. In this way, ECA not only improves the expression integrity of deep features but also enhances the model’s ability to adapt to situations such as blurred boundaries and changes in target size in complex scenarios. Its structure is shown in Figure 6.
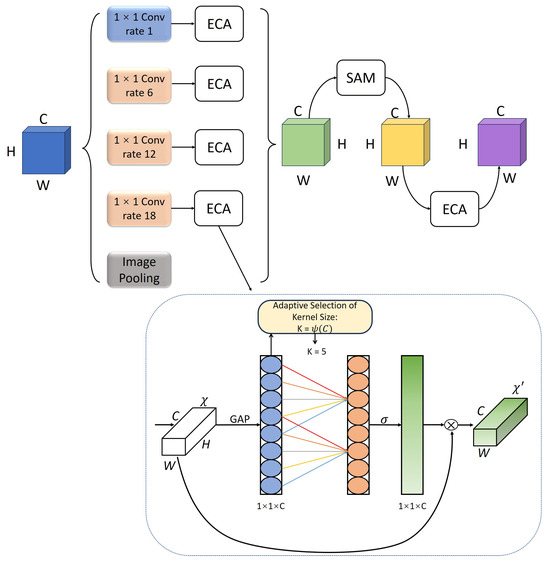
Figure 6.
The structure of the DCA Module.
The ECA module first performs global average pooling (GAP) on each channel of the input feature to obtain a global description vector , as shown in Formula (6).
A local 1D convolution is performed on the global description vector Z to obtain the convolution output , as shown in Formula (7).
The number of channels C determines the convolution kernel size k in an adaptive way. The convolution output S is converted into the channel attention weight through the function, as shown in Formula (8).
The input feature map is weighted using the calculated channel attention weight to obtain the enhanced feature map, as shown in Formula (9).
This operation can effectively compensate for the feature information imbalance caused by the dilated convolution, allowing features of different scales to interact more reasonably and avoiding the weakening of the expression ability of local information due to the introduction of long-distance receptive fields. Ultimately, the features adjusted by ECA form a closer dependency between different channels, optimizing the overall feature expression effect while maintaining a low amount of computation, thereby improving the model’s adaptability to complex scenes and enhancing the integrity of the target structure.
3.5. Loss Function
The cross-entropy loss function is widely used in semantic segmentation [38]. It can be used to measure the difference between the predicted distribution and the true distribution of each pixel to guide the training of the model. However, in the semantic segmentation task, the background category usually occupies a large number of pixels, while the target category accounts for a small proportion. This imbalance will cause the model to pay more attention to the common category and ignore the target category. Therefore, this paper adopts the loss function [39]. Because the loss function focuses on the overlapping area of the segmentation results, it is more suitable for dealing with the problem of category imbalance and can better optimize the classification effect of minority classes. The coefficient is an indicator to measure the similarity between two sets. The larger the value, the higher the similarity. The expression of the Dice coefficient is shown in Formula (10).
and represent the number of elements in sets A and B, respectively. The function expression is shown in Formula (11).
In semantic segmentation, A and B represent the pixel sets of the predicted segmentation and the true segmentation, respectively. They are the sum of the dot products between the pixels of the predicted segmentation image and the pixels of the true segmentation image, and their sum is approximately the sum of the pixels in their corresponding images.
4. Results
4.1. Dataset
4.1.1. Pascal VOC 2012
The PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset was used in this study, which is a commonly used dataset for image classification, image segmentation, and object detection. It includes 21 categories such as people, animals, vehicles, and backgrounds. A total of 10,582 images are adopted as training datasets and 1449 as validation datasets.
4.1.2. Cityscapes
Cityscapes is a large-scale semantic segmentation dataset designed for understanding tasks for urban street scenes, and it is widely used in fields such as autonomous driving and intelligent transportation. The dataset was collected from 50 cities in Germany and its neighboring countries. There are 19 main categories, covering scenes such as buildings, traffic lights, pedestrians, and vehicles. A total of 2975 images are used as training sets and 500 images are used as validation sets.
4.2. Implementation Details
During the experiment, batch training was used, with the batchsize set to 8, and the SGD algorithm was used for optimization. The specific parameters of the network model are that the downsampling multiple is set to 16, the initial learning rate is set to , the minimum learning rate is set to , the momentum parameter is 0.9, the weight decay parameter is set to , and the cos category learning rate reduction method is used. For some application scenarios, especially when the dataset is small, data augmentation can effectively expand the diversity of the dataset without actually adding data. We preprocess the dataset by randomly cropping, flipping, rotating, and applying other data augmentation techniques on the input images. By generating different versions of the same image, the diversity of the data is increased, which helps the model learn more robust features, reduce dependence on specific training data, and reduce the risk of overfitting.
4.3. Experimental Evaluation Indicators
In order to verify the performance of the improved model, mean intersection over union (mIoU) was selected to measure the model performance, and floating point operations (FLOPs), parameters, and frames per second (FPS) were selected to measure the network calculation amount, calculation complexity, and model efficiency.
The intersection over union (IoU) is an indicator to measure the overlap between the predicted result and the true label. The mean intersection over union (mIoU) is the mean of the intersection over union of all categories. The larger the mIoU value, the higher the segmentation accuracy. The expression is shown in Formula (12).
where represents the number of samples whose true group is i but predicted as j and represents the number of correct samples whose category is i but predicted as i. k+1 represents the total number of categories.
4.4. Performance on Pascal VOC 2012 Dataset
The proposed model is compared with semantic segmentation models such as PSPNet, Unet, Deeplabv3+, DCN-Deeplabv3+ [40], MCTformer [41], AMN [42], and BiseNet on the PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset. The specific experimental comparison results are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of performance on the Pascal VOC 2012 dataset.
As can be seen from Table 1, the proposed method achieved the highest value of 89.6 in terms of frame rate (FPS), which fully demonstrates its significant advantages in model lightweight design and real-time processing capabilities. Although the mIoU value of PSPNet is the best in the experiment, the floating-point calculation amount and parameter amount are much larger than those of the algorithm proposed in this paper, and the model’s lightweight and computational efficiency are not as good as the algorithm proposed in this paper; the floating-point calculation amount and parameter amount of the UNet algorithm are 184.737 Gflops and 43.934 M, respectively, and the mIoU is 70.34%. The algorithm proposed in this paper is worse than UNet in model calculation amount, computational efficiency, and segmentation accuracy; the floating-point calculation amount of the algorithm proposed in this paper is about 1/3 of that of the Deeplabv3+ algorithm, and the parameter amount is about 1/9 of Deeplabv3+, but the mIoU only decreases by 3.79%, which further highlights that the algorithm has achieved a good balance between model lightweightness, computational efficiency and segmentation accuracy; compared with the lightweight semantic segmentation model BiseNet and DCN-Deeplabv3+ algorithm, the parameter amount of the algorithm proposed in this paper is reduced by 88% and 52%, respectively, and the mIoU is increased by 8.96% and 1.86%, respectively. Compared with MCTformer, our method reduces the number of parameters by 72.9% and improves the mIoU by 2.34%. The number of parameters is only 1/25 of that of AMN, while mIoU is improved by 3.54%. This highlights the segmentation performance advantage of this algorithm in lightweight networks.
4.4.1. Ablation Study on Pascal VOC 2012
The ablation experiment was carried out on the algorithm proposed in this paper, and the experimental results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Ablation study on the Pascal VOC 2012 dataset.
From the comparison results of Model0 and Model1 in Table 2, it can be seen that the addition of the DCA module to the algorithm improves mIoU by 1.05 percentage points; comparing the results of Model1 and Model2, it can be seen that the addition of multi-level feature fusion improves mIoU by 0.25 percentage points; comparing the results of Model2 and Model3, using Dice loss as the loss function improves mIoU by 0.3 percentage points. By comparing the experimental results of Model0 and Model3, it can be found that the algorithm proposed in this paper hardly increases the number of model parameters, and the FPS only decreases slightly, compared with the case without multi-level feature fusion and dual attention mechanism collaboration, but it still achieves an improvement of 1.6 percentage points in the mIoU indicator. As can be seen from Figure 7, Model3 (ours) achieves more refined effects on the tail of the aircraft, the edge of the vehicle, the outline of the person, the bicycle, and the edge details of the animal.

Figure 7.
Visual segmentation results of the ablation study on the Pascal VOC 2012 dataset.
4.4.2. Visualization Results on the Pascal VOC 2012 Dataset
This paper randomly selected five groups of images from the Pascal VOC 2012 dataset for testing, and the test image comparison is shown in Figure 8.

Figure 8.
Visual segmentation results of the Pascal VOC 2012 dataset.
From the comparison results in the first row of Figure 8, it can be seen that UNet failed to correctly segment the chair on the left, while the algorithm proposed in this paper successfully segmented the left chair part; in the comparison of the second and fourth rows of Figure 8, although our visualization results are slightly redundant in the frame part compared to the visualization results of Deeplabv3+, the segmentation map of the algorithm in this paper is more refined in the contours of the car and the aircraft and the details of the car chassis; from the comparison results in the third row of Figure 8, MCTformer and AMN segment the bicycle contour roughly. We can clearly observe that the segmentation results of the bicycle of the algorithm proposed in this paper are more accurate; from the comparison results in the fifth row of Figure 8, it can be seen that the segmentation of pedestrians and the rear vehicles by UNet is not accurate enough, while the Deeplabv3+ model failed to segment the rear car, and the algorithm proposed in this paper successfully segmented the rear part of the car.
Observing the comparison results in the first row of Figure 8, PSPNet failed to correctly segment the legs of the chair, BiseNet mistakenly took the ground as a table, and the algorithm proposed in this paper has been greatly improved; in the comparison of the second and fourth rows of Figure 8, the segmentation map of the algorithm proposed in this paper is more refined in the outlines of the car and the plane and the details such as the chassis of the car, while BiseNet failed to segment some parts of the car and the plane correctly; observing the third row of Figure 8, PSPNet’s segmentation of the bicycle wheel hub is not coherent enough, BiseNet failed to correctly segment some parts of the bicycle, and the algorithm proposed in this paper is more accurate in segmentation; from the comparison of the fifth row of Figure 8, it can be observed that neither PSPNet nor BiseNet segmented the car at the back, while the algorithm proposed in this paper successfully segmented the car at the back.
From Figure 8, we can see that the segmentation results of the algorithm proposed in this paper are closer to the real segmentation effect, which is mainly due to the DCA module improving the feature extraction ability of the model without losing the receptive field. At the same time, the backbone network extracts four different levels of feature information, enabling the model to obtain more levels of feature information and avoid the loss of some feature information at a single level. In the segmentation process, the algorithm proposed in this paper has achieved good improvements in the details and contours of the object.
4.5. Performance on the Cityscapes Dataset
To further verify the generalization and effectiveness of the model, we conducted comparative experiments with PSPNet, EncNet [43], DDRNet [44], STDC [45], RDRNet [46], and other models on the Cityscapes dataset. The experimental results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparison of performance on the Cityscapes dataset.
From Table 3, our method achieved the highest frame rate (FPS) of 90.1, further verifying its superiority in model lightweight and real-time performance. We can see that compared with PSPNet, EncNet and RDRNet, although RDRNet and PSPNet have the best mIoU values in the experimental results, reaching 78.6% and 78.5%, respectively, they are at the cost of the largest number of parameters and floating-point calculations. The mIoU value of our method is only slightly lower than that of PSPNet and RDRNet and is not much different from EncNet, but the numbers of parameters and floating-point calculations are much lower than those of PSPNet and EncNet. Compared with BiseNet, DCN-Deeplabv3+ and STDC, it is obvious that our method is better than them in segmentation effect, model lightweightness, and computational efficiency, reflecting the superior performance of our method in both segmentation accuracy and lightweightness. The mIoU value of DDRNet is only 2.53% higher than that of our method, but the numbers of parameters and Gflops are 3.5 times and 2.53 times those of our method, respectively, and it is not as good as our method in computational efficiency and model lightweight.
Visualization Results on Cityscapes
Figure 9 shows the visualization results of five groups of pictures randomly selected from the Cityscapes validation set. The red dotted box marks the part of the same image where the segmentation accuracy is more obvious. From the first and second rows of pictures, we can see that compared with other methods, our method has a more coherent segmentation effect on the traffic light poles. In the third row of pictures, the cars in the distance appear smaller in the picture, but our method can better segment the cars in the distance. In the fourth row of pictures, our method has a more refined segmentation effect on the pedestrian part of the picture. From the fifth row of pictures, we can see that the segmentation effect of other methods on the poles beside the road is either missing or incomplete, while our method better shows the integrity of this part.
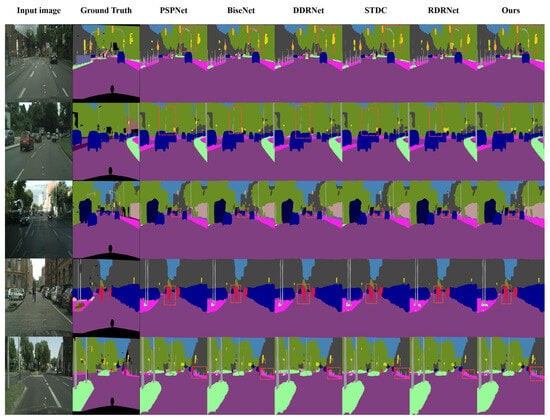
Figure 9.
Visual segmentation results of the Cityscapes dataset.
5. Conclusions
In order to reduce the number of parameters and computational complexity of the model and make it more suitable for mobile devices and various embedded devices, this paper proposes a lightweight semantic segmentation network with multi-level feature fusion and dual attention collaboration. The backbone network of the model can generate four different levels of features as the input of the decoder so that the network can obtain more levels of feature information. Except for the fourth layer, the feature information of each layer is added to the CBAM module, and the shallow feature information is finally spliced. In the DCA module, the ECA module is added after each dilated convolution, and the SAM module is introduced after the DCA feature fusion, which effectively balances the relationship between a larger receptive field and multi-scale information extraction. Finally, the shallow features and deep features are spliced through 1 × 1 convolution blocks. In the experiments on the PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset and the Cityscapes dataset, the average intersection-over-union ratio of the model reached 74.24% and 75.29%, respectively. The experimental results show that the algorithm proposed in this paper has fewer parameters and good computational efficiency, and the effectiveness of the segmentation results has been verified in the experiments.
Although the proposed algorithm has made great improvements in model lightweighting and segmentation effect, due to factors such as the diversity of scenes, irregular shapes of objects, background interference, etc., the proposed algorithm still needs to be improved in more complex scenes and on the segmentation effect of object edge details. In the future, more adaptive feature fusion strategies and the use of multi-scale convolutional attention modules to replace traditional CNN-based structures can be further explored. Currently, a separate Dice loss function is used, but in the future, the cross entropy loss function and the Dice loss function adaptive loss function weight mechanism can be further explored to give full play to their respective advantages and further improve the segmentation performance of the model under an imbalanced distribution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.M., X.W. and Y.Y.; methodology, Y.M., X.W. and B.D.; software, Y.M.; validation, Y.M. and Y.Y.; formal analysis, B.D.; resources, X.W.; writing—original draft, Y.M.; writing—review & editing, X.W. and B.D.; visualization, Y.M.; supervision, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in this article is a publicly available dataset. The link to the Pascal VOC 2012 dataset is http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/voc2012/ (accessed on 18 April 2024) and the link to the Cityscapes dataset is www.cityscapes-dataset.com (accessed on 16 May 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Fu, Q.; Kou, R.; Huang, F.; Yang, B.; Yang, T.; Gao, M. Techniques and challenges of image segmentation: A review. Electronics 2023, 12, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Shen, X.; Peng, Y.; Shao, Y.; Yuan, W.; Ji, Z.; Bai, J. A real-time semantic segmentation approach for autonomous driving scenes. J. Comput. Aided Des. Comput. Graph. 2021, 33, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.; Chang, C.C.; Li, T. Autonomous driving control based on the technique of semantic segmentation. Sensors 2023, 23, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Wang, T.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. A review of deep learning based methods for medical image multi-organ segmentation. Phys. Medica 2021, 85, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Zhang, R.; Diao, S.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Cai, J.; Shao, L.; Li, S.; Qin, W. Dual domain distribution disruption with semantics preservation: Unsupervised domain adaptation for medical image segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 97, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zheng, G.; Yao, X. Semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images with improved U-Net based on transfer learning. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2023, 16, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jiang, B.; Lv, S.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y. Deep-learning-based semantic segmentation of remote sensing images: A survey. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 17, 8370–8396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Song, K.; Tian, H.; Man, Y.; Yan, Y.; Meng, Q. SG-grasp: Semantic segmentation guided robotic grasp oriented to weakly textured objects based on visual perception sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 28430–28441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainetter, S.; Fraundorfer, F. End-to-end trainable deep neural network for robotic grasp detection and semantic segmentation from rgb. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 13452–13458. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Rasti, S.; Dev, S.; Campbell, A.G. On the use of a semantic segmentation micro-service in ar devices for ui placement. In Proceedings of the IEEE Games, Entertainment, Media Conference (GEM), Bridgetown, Barbados, 27–30 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. Automatica 1975, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canny, J. A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, 6, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder–decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected crfs. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.7062. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder–decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Milan, A.; Shen, C.; Reid, I. Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1925–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Zhou, K.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. Ce-net: Context encoder network for 2D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.T.; Sun, J. Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 July 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M.; Caspi, A.; Shapiro, L.; Hajishirzi, H. Espnet: Efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 552–568. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Poudel, R.P.; Liwicki, S.; Cipolla, R. Fast-scnn: Fast semantic segmentation network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.04502. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Kadav, A.; Durdanovic, I.; Samet, H.; Graf, H.P. Pruning filters for efficient convnets. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1608.08710. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27 June–2 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.; et al. Segment Anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 3992–4003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, W. Prototype-Based Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 6858–6872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, W. Cross-Image Pixel Contrasting for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 5398–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, F.; Chang, B.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Konukoglu, E.; Cremers, D. Image Segmentation in Foundation Model Era: A Survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.12957. [Google Scholar]
- Chern, W.C.; Nguyen, T.V.; Asari, V.K.; Kim, H. Impact of loss functions on semantic segmentation in far-field monitoring. Comput. Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2023, 38, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Xiang, S.; Chen, M.; Li, H.; Su, Q. DCN-Deeplabv3+: A novel road segmentation algorithm based on improved Deeplabv3+. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 87397–87406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ouyang, W.; Bennamoun, M.; Boussaid, F.; Xu, D. Multi-class Token Transformer for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 4300–4309. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Kim, D.; Shim, H. Threshold Matters in WSSS: Manipulating the Activation for the Robust and Accurate Segmentation Model Against Thresholds. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 4320–4329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Dana, K.J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Tyagi, A.; Agrawal, A. Context Encoding for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2022; pp. 7151–7160. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Hong, Y.; Sun, W.; Jia, Y. Deep Dual-Resolution Networks for Real-Time and Accurate Semantic Segmentation of Traffic Scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 3448–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Lai, S.; Huang, J.; Wei, X.; Chai, Z.; Luo, J.; Wei, X. Rethinking BiSeNet For Real-time Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 9711–9720. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Shi, D. Reparameterizable Dual-Resolution Network for Real-time Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.12496. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).