Depth Estimation of an Underwater Moving Source Based on the Acoustic Interference Pattern Stream
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory and Method
2.1. Acoustic Interference Structure in Deep-Sea
2.2. Generalized Fourier Transform
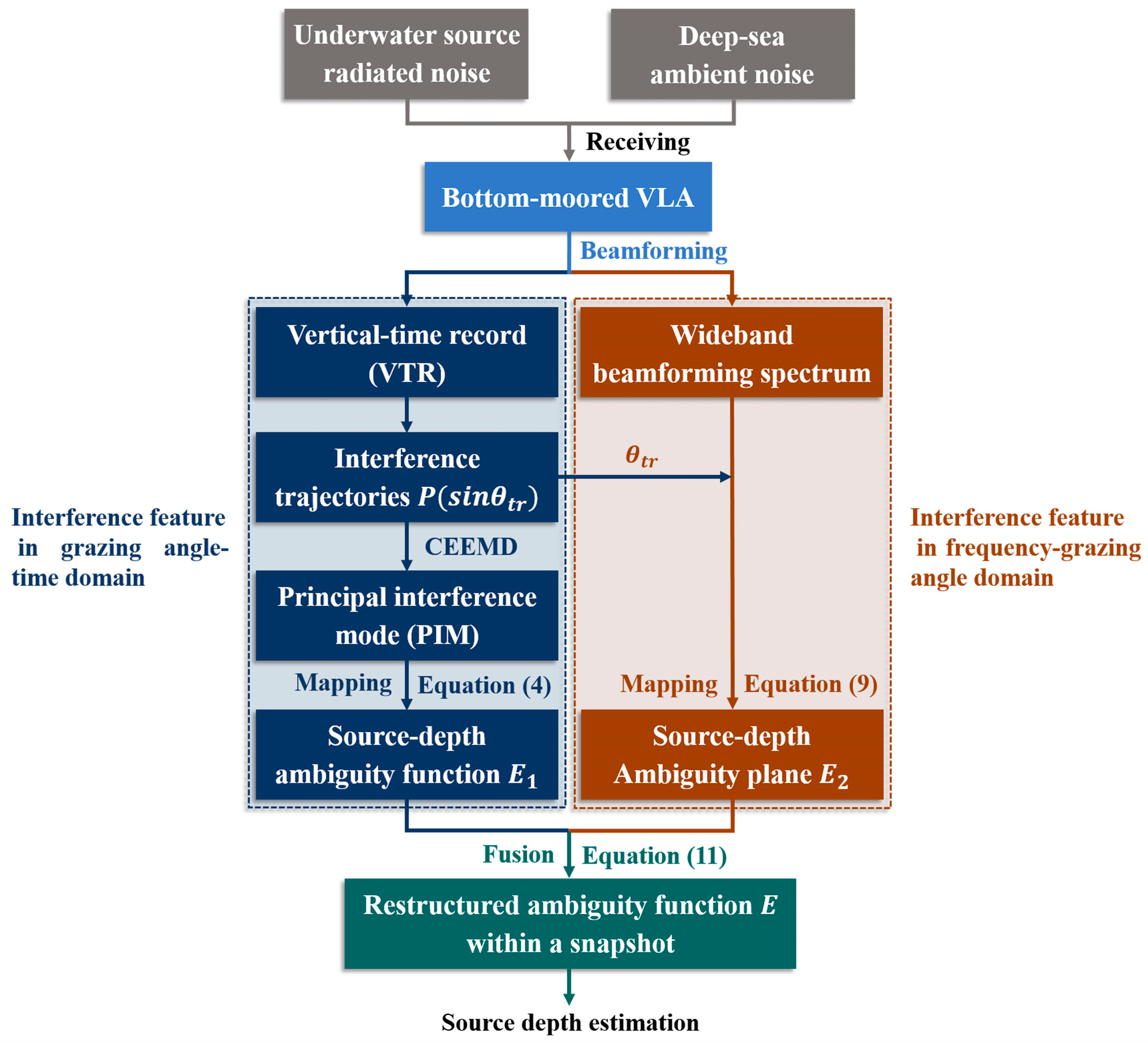
2.3. Interference Feature Fusion in Space–Time–Frequency Domain for Depth Estimation
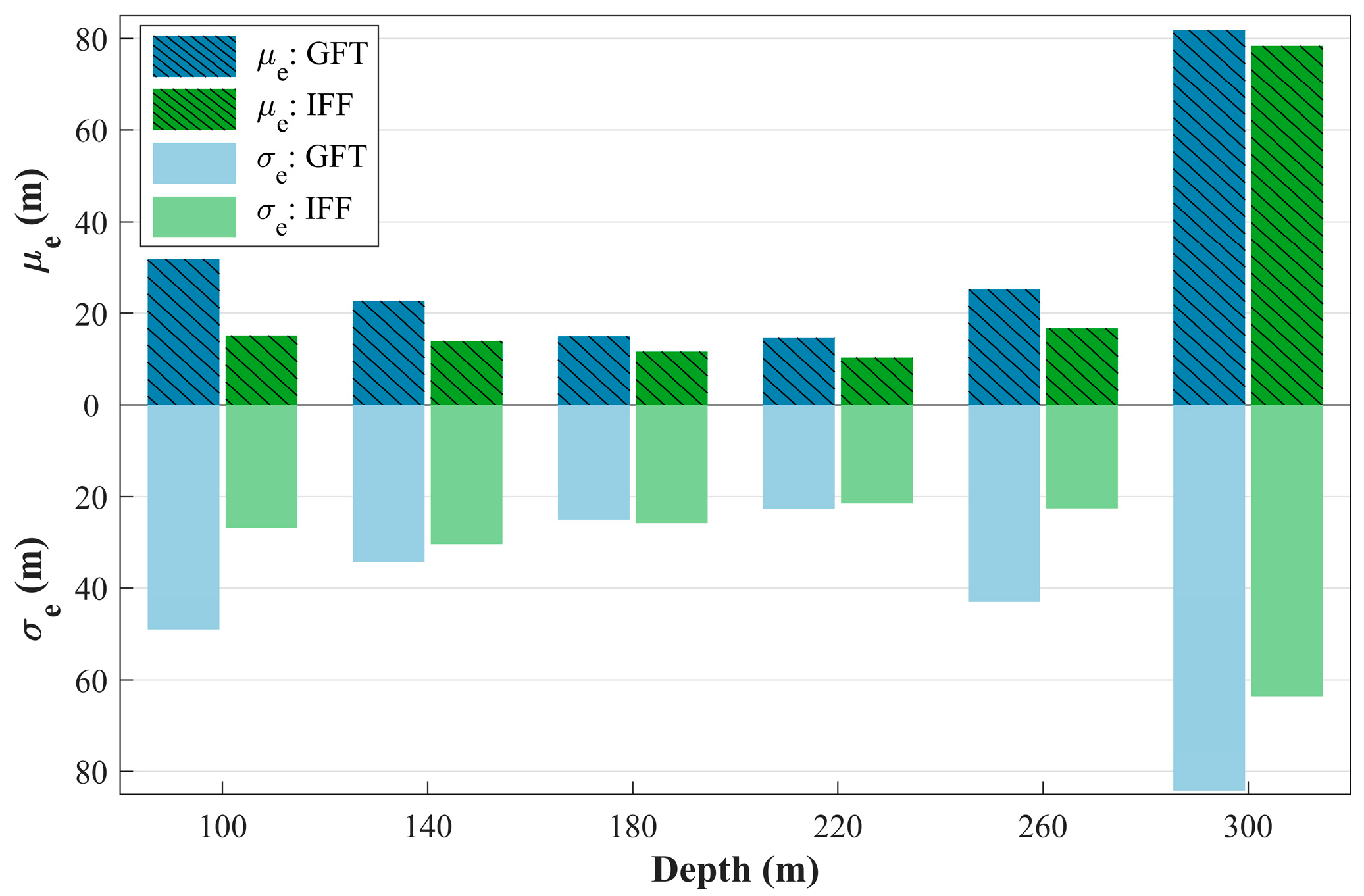
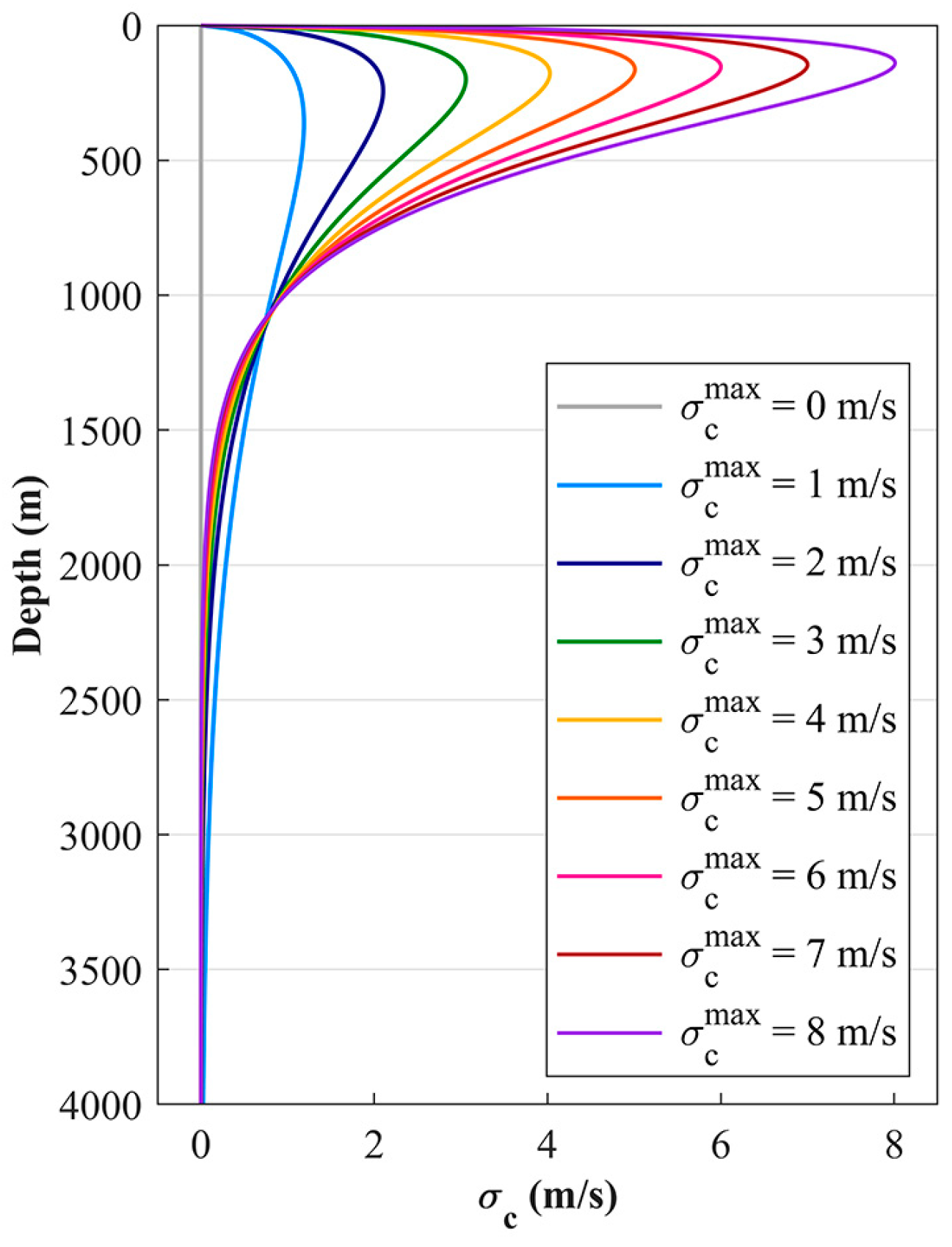
3. Simulation and Analysis
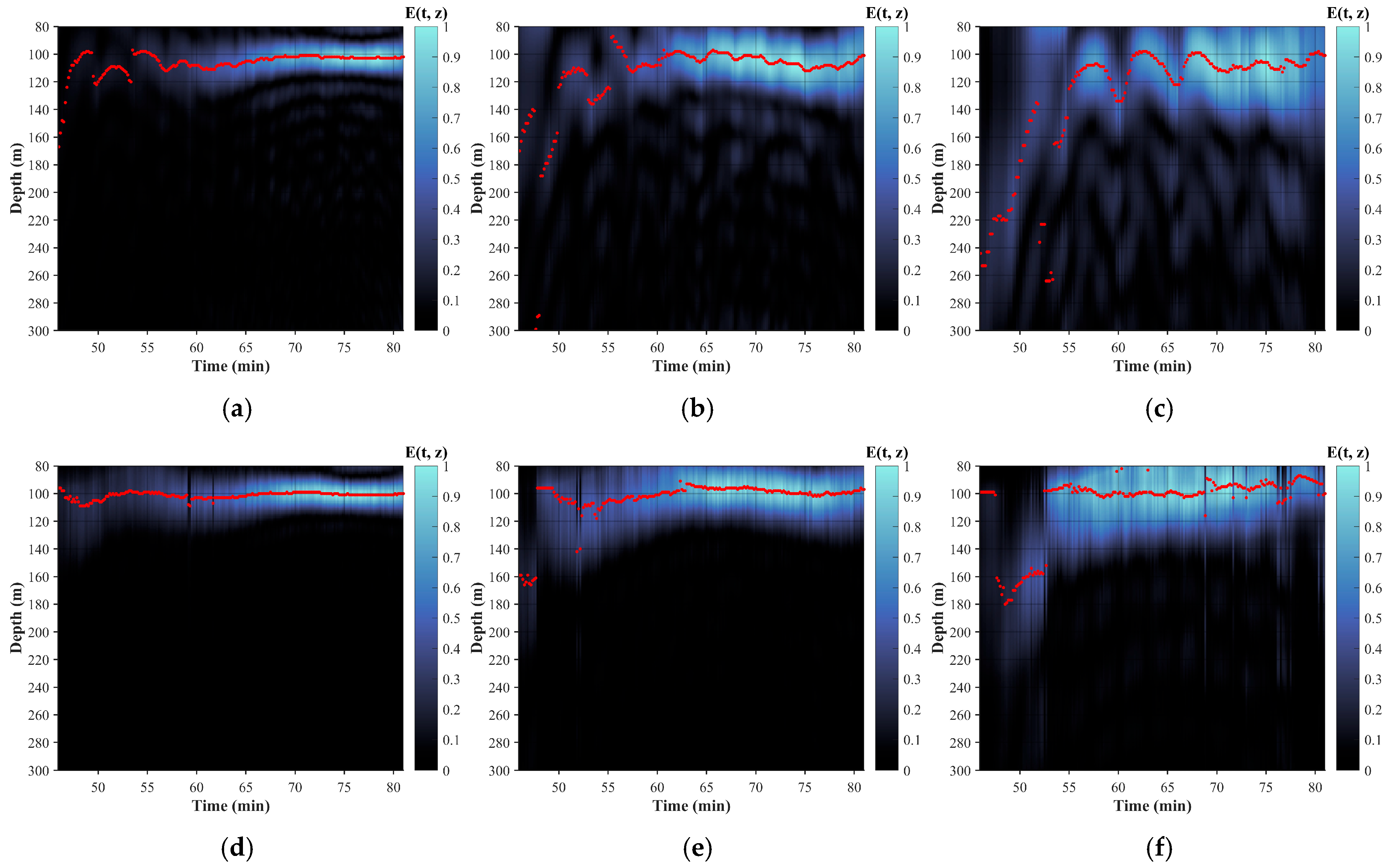
3.1. Depth Estimation for Single Source
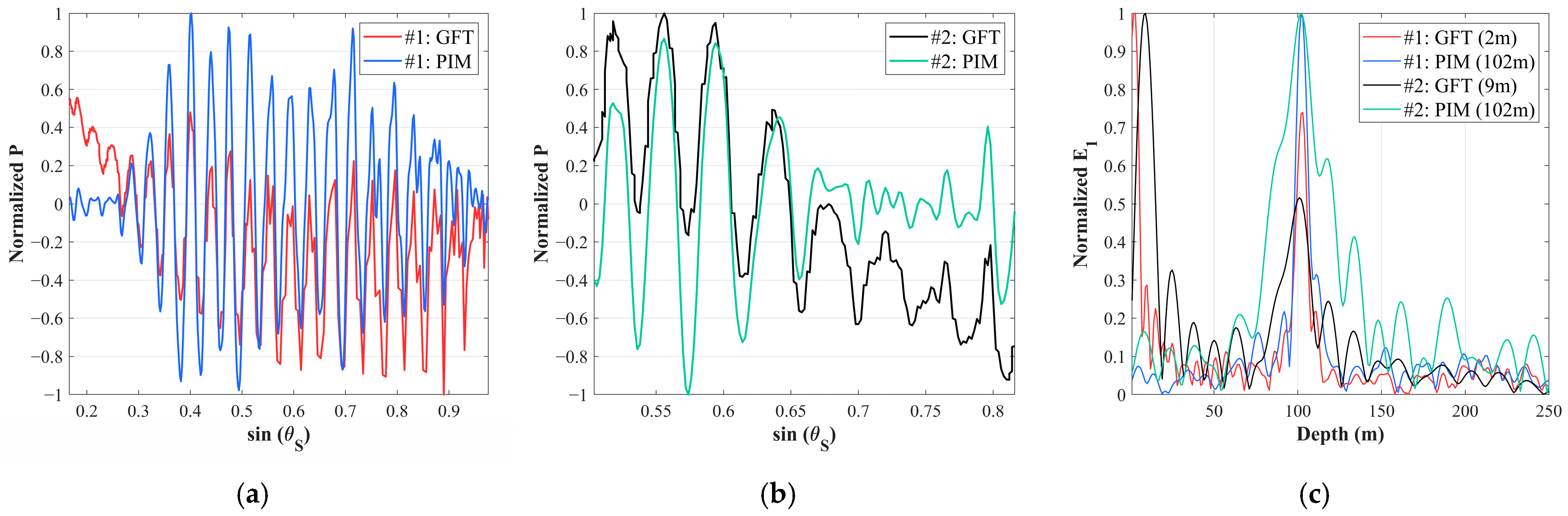
3.2. Depth Estimation for Multiple Sources
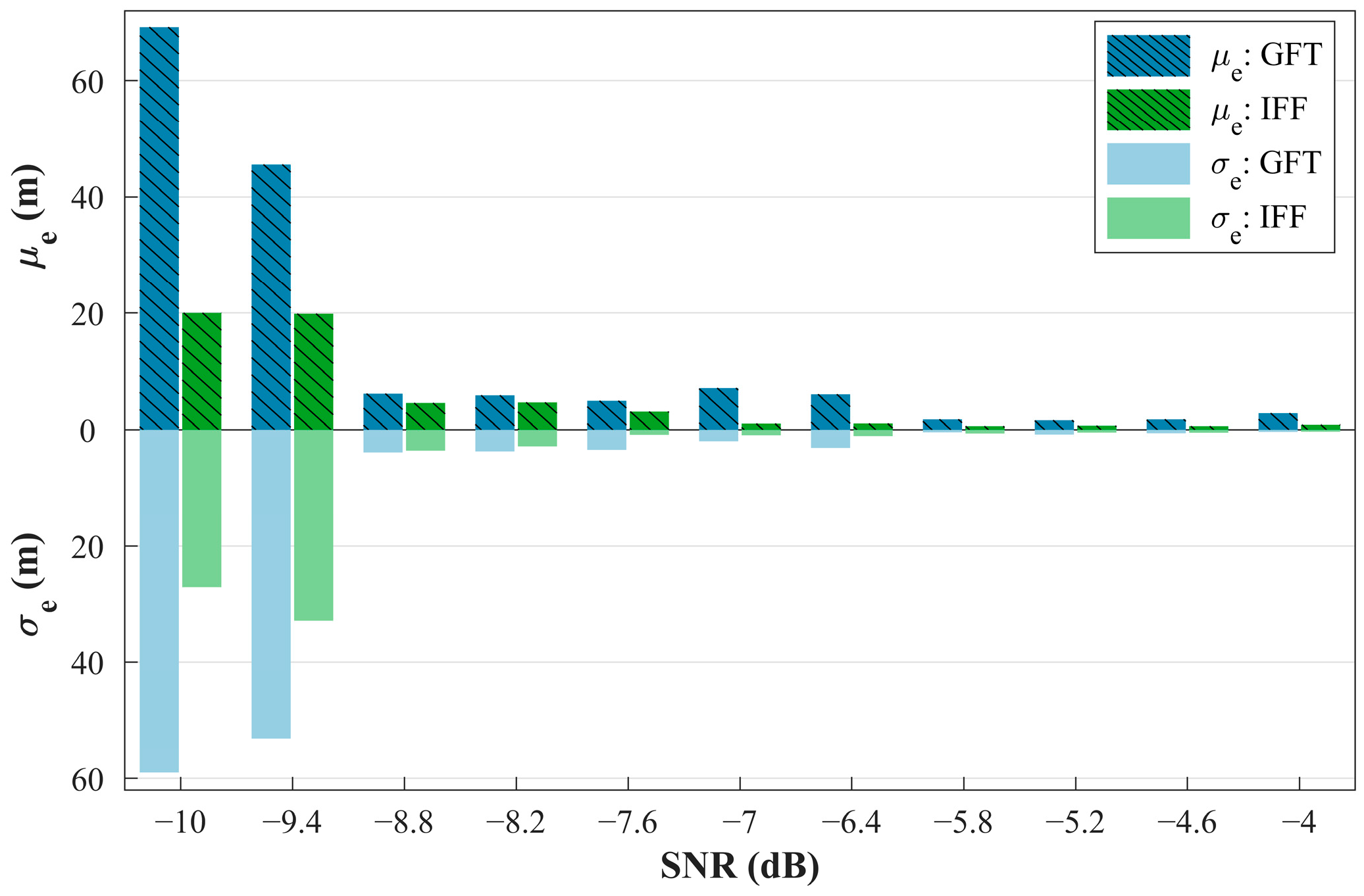
3.3. Robustness Analysis
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VTR | vertical-time record |
| IFF | interference feature fusion |
| RAP | reliable acoustic path |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
| VLA | vertical line array |
| GFT | generalized Fourier transform |
| D-path | direct path |
| SR-path | surface-reflected path |
| MVDR | Minimum Variance Distortionless Response |
| BSR | bottom–surface-reflected |
| SBSR | surface–bottom–surface-reflected |
| CEEMD | complete-ensemble empirical mode decomposition |
| PIM | principal interference mode |
| HYCOM | hybrid coordinate ocean model |
| CPA | closest point of approach |
| SOFAR | sound fixing and ranging |
References
- Qiu, C.; Ma, S.; Chen, Y.; Meng, Z.; Wang, J. Reliable acoustic path and directed-arrival zone spatial gain analysis for a vertical line array. Sensors 2018, 18, 3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Feng, X. Investigating the reliable acoustic path properties in a global scale. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1213002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhou, S. Complex acoustic intensity with deep receiver in the direct-arrival zone in deep water and sound-ray-arrival-angle estimation. Acta Phys Sin. 2016, 65, 164302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zurk, L.M.; Ma, B. Vertical arrival structure of shipping noise in deep water channels. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2010 MTS/IEEE SEATTLE, Seattle, WA, USA, 20–23 September 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Chen, Y.; Ma, S.; Meng, Z. Spatial gain analysis for vertical linear array in the direct-arrival zone. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Qingdao, China, 14–16 September 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y. Passive localization in the deep ocean based on cross-correlation function matching. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, EL196–EL201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Yang, K.; Yang, Q.; Chen, P.; Sun, Q.; Xue, R. Localization of two sound sources based on compressed matched field processing with a short hydrophone array in the deep ocean. Sensors 2019, 19, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Lü, L.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z. Source localization by matching sound intensity with a vertical array in the deep ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, EL477–EL481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geroski, D.J.; Dowling, D.R. Robust long-range source localization in the deep ocean using phase-only matched autoproduct processing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 150, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, E.; Wang, Y. Environmental mismatching effects on source localization processing in mode space. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 89, 2285–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, Y.; Dosso, S.E.; Socheleau, F.X.; Bonnel, J. Bayesian source localization with uncertain Green’s function in an uncertain shallow water ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, J.M.Q.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Matched-field processing of 200-Hz continuous wave (cw) signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1991, 89, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Yang, Y. A passive source range and depth estimation method by single hydrophone in shadow zone of deep water. Acta Acust. 2018, 43, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCargar, R.; Zurk, L.M. Depth-based signal separation with vertical line arrays in the deep ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, EL320–EL325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurk, L.M.; Boyle, J.K.; Shibley, J. Depth-based passive tracking of submerged sources in the deep ocean using a vertical line array. In Proceedings of the 2013 Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 2130–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniffin, G.P.; Boyle, J.K.; Zurk, L.M.; Siderius, M. Performance metrics for depth-based signal separation using deep vertical line arrays. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Zheng, G.; Liu, F. A matched beam intensity processing method for estimating source depth using vertical linear array in deep water. In Proceedings of the 2021 OES China Ocean Acoustics (COA), Harbin, China, 14–17 July 2021; pp. 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Yang, K.; Li, H.; Ma, Y. Acoustic-intensity striations below the critical depth: Interpretation and modeling. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, EL245–EL250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Duan, R. Striation-based source depth estimation with a vertical line array in the deep ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, EL8–EL12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Yang, T.C.; Ma, Q.; Du, S. Matched beam-intensity processing for a deep vertical line array. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zheng, G.; Yang, T.C. Target depth estimation by frequency interference matching for a deep vertical array. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 186, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, C. Sources depth estimation for a tonal source by matching the interference structure in the arrival angle domain. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 154, 2800–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, P.; Guo, W.; Zhang, B.; Hu, Z. Passive source depth estimation using beam intensity striations of a horizontal linear array in deep water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 154, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Niu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhai, D.; Chen, D. Source depth estimation based on Gaussian processes using a deep vertical line array. Appl Acoust. 2024, 215, 109684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Su, L.; Hu, T.; Ren, Q.; Gerstoff, P.; Ma, L. Source depth estimation using spectral transformations and convolutional neural network in a deep-sea environment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2020, 148, 3633–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, F.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Porter, M.B.; Schmidt, H.; Tolstoy, A. Computational Ocean Acoustics, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.R.; Shieh, J.S.; Huang, N.E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data. Anal. 2010, 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.; Wu, M.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.A.; Nai-Chyuan, Y.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassignet, E.P.; Hurlburt, H.E.; Smedstad, O.M.; Halliwell, G.R.; Hogan, P.J.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Baraille, R.; Bleck, R. The HYCOM (hybrid coordinate ocean model) data assimilative system. J. Mar. Syst. 2007, 65, 60–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Experimental and numerical study on underwater radiated noise of AUV. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 201, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, W. Self-noise characteristic analysis of a type of UUV. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Xi’an, China, 25–27 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yang, K.; Cao, R.; Duan, S. Spatial vertical directionality and correlation of low-frequency ambient noise in deep ocean direct-arrival zones. Sensors 2018, 18, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Nolte, L.W. Effects of environmental uncertainties on sonar detection performance prediction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, M. Modeling of time-varying characteristics of deep-sea sound velocity profile based on layered EOF. Coast. Eng. 2022, 41, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





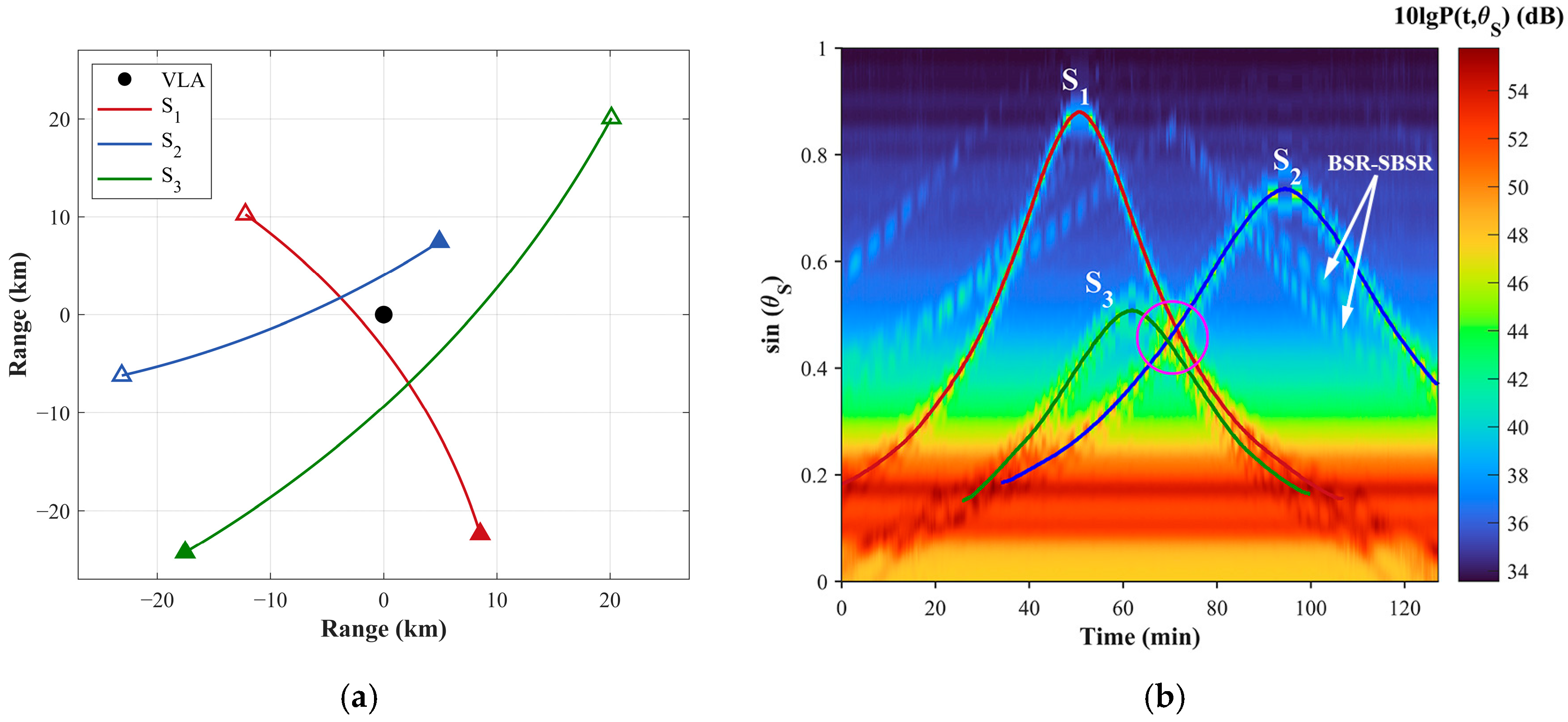
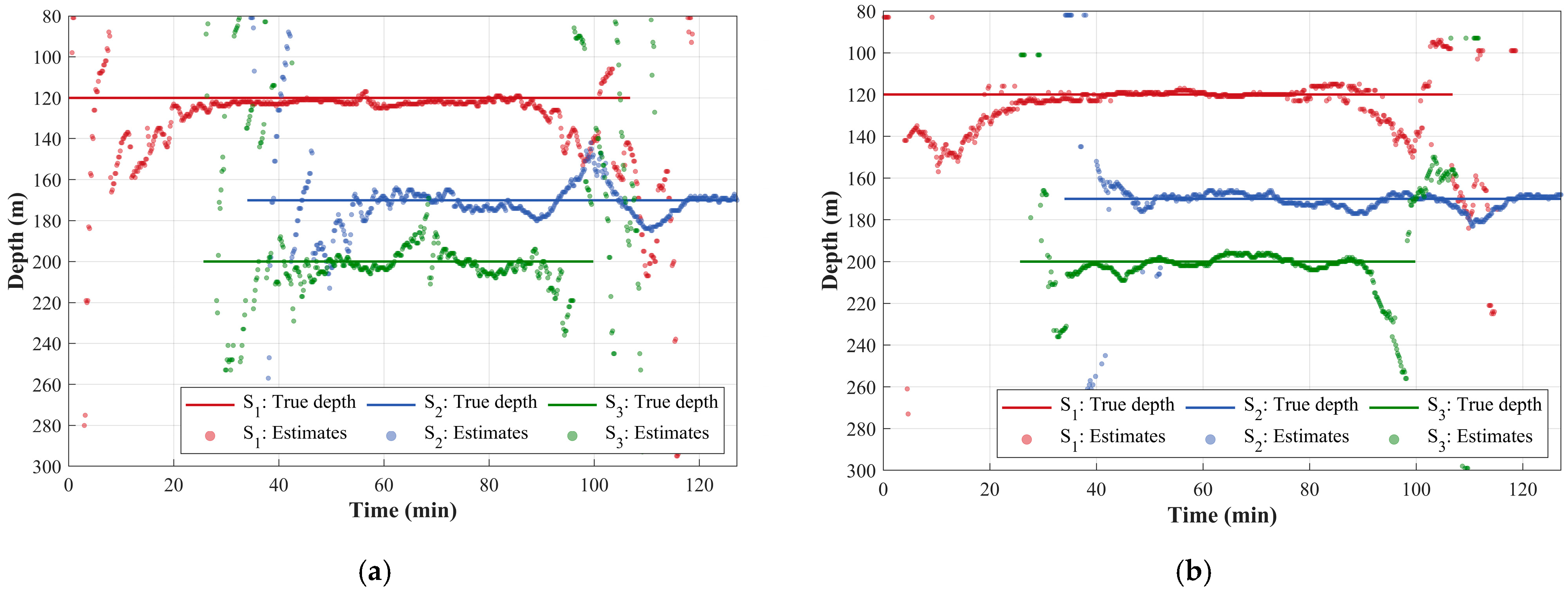


| Source | Depth (m) | CPA (km) | Speed (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 120 | 1.96 | 10 |
| S2 | 170 | 3.43 | 8 |
| S3 | 200 | 6.24 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rong, L.; Lei, B.; Gu, T.; He, Z. Depth Estimation of an Underwater Moving Source Based on the Acoustic Interference Pattern Stream. Electronics 2025, 14, 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112228
Rong L, Lei B, Gu T, He Z. Depth Estimation of an Underwater Moving Source Based on the Acoustic Interference Pattern Stream. Electronics. 2025; 14(11):2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112228
Chicago/Turabian StyleRong, Lintai, Bo Lei, Tiantian Gu, and Zhaoyang He. 2025. "Depth Estimation of an Underwater Moving Source Based on the Acoustic Interference Pattern Stream" Electronics 14, no. 11: 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112228
APA StyleRong, L., Lei, B., Gu, T., & He, Z. (2025). Depth Estimation of an Underwater Moving Source Based on the Acoustic Interference Pattern Stream. Electronics, 14(11), 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14112228






