Physical Layer Authentication Exploiting Antenna Mutual Coupling Effects in mmWave Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To demonstrate the authentication feasibility of the MC feature, we first utilize the generalized Gaussian and Laplace distributions to precisely characterize the statistical model of amplitude and phase of MC, respectively.
- To further enhance the device distinguishability, we leverage two unique hardware-specific fingerprints in terms of the amplitude and phase of MC to design a kernel-based identity authentication scheme tailored for the mmWave communication systems.
- Based on the knowledge of statistical signal processing and hypothesis testing, we analytically derive expressions for the false alarm and detection probabilities, providing a theoretical characterization of the authentication performance of the proposed authentication scheme.
- Finally, we resort to a series of experiments to verify the reliability, effectiveness of the proposed authentication scheme under various settings. The results also validate the correctness of the proposed theoretical performance metrics and demonstrate the satisfactory detection performance even in the low signal–noise ratio scenario.
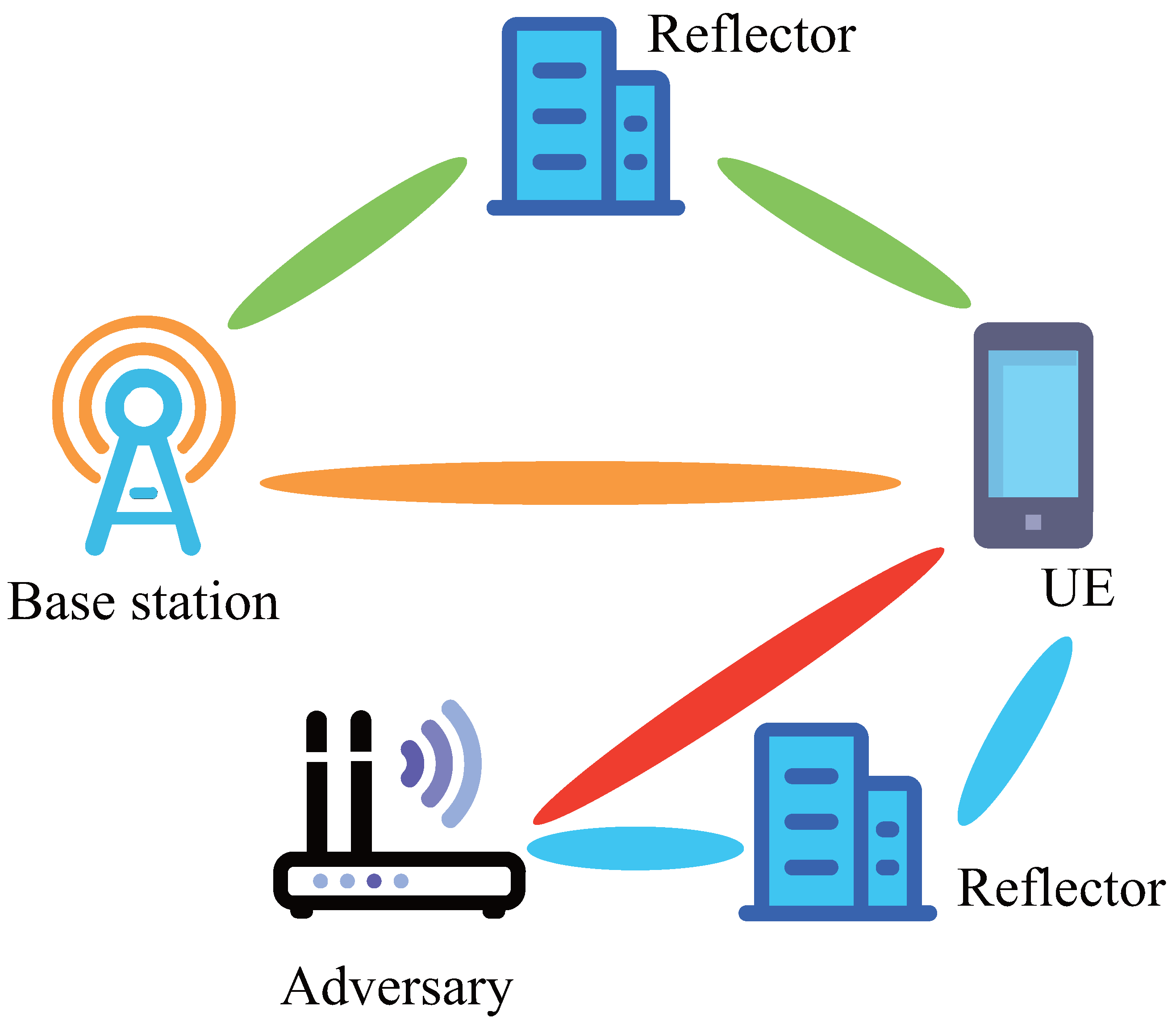
2. Problem Formulation and System Model
2.1. Problem Formulation
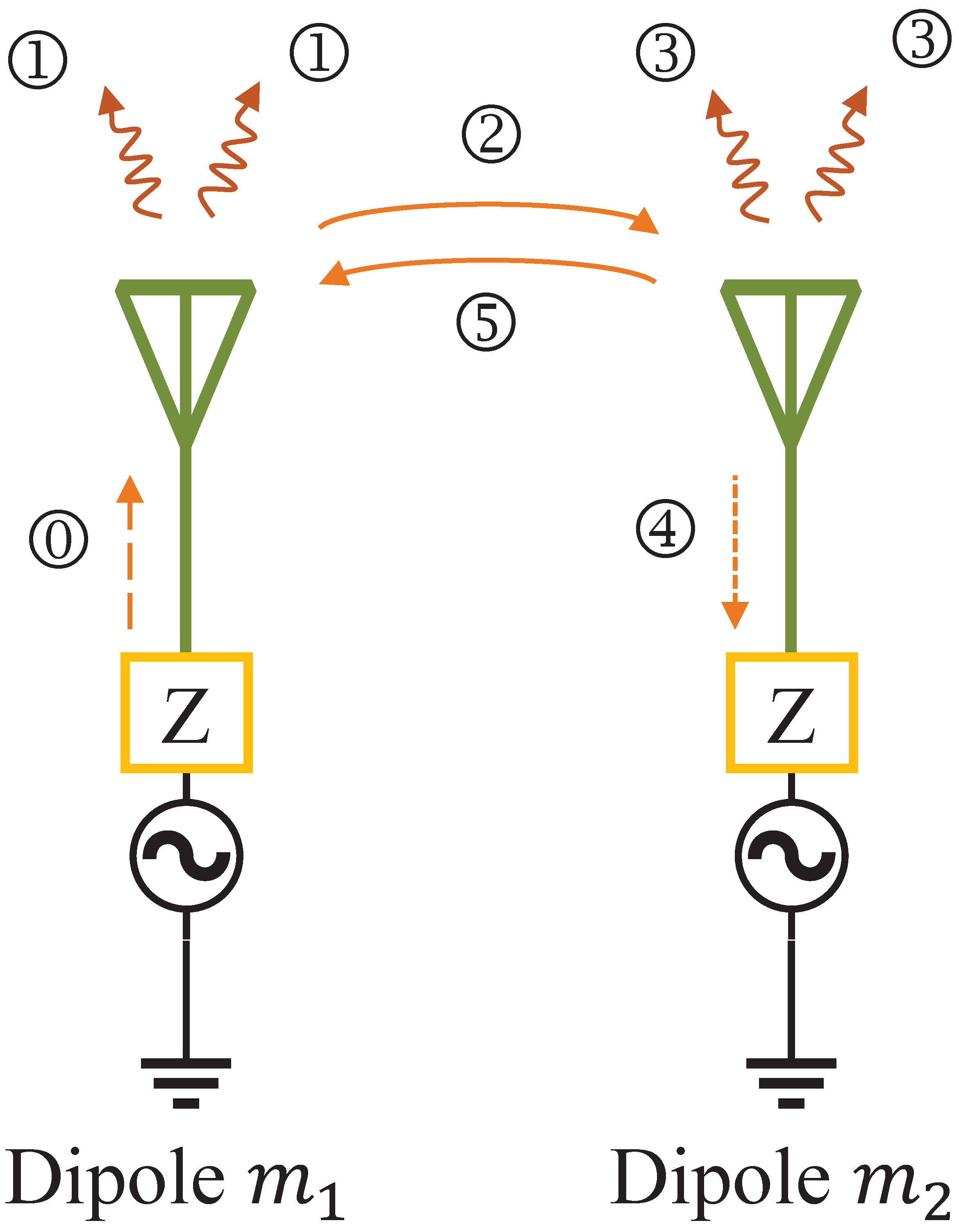
2.2. Antenna MC Model
2.3. Signal Model
3. Proposed Kernel-Based Authentication Scheme
3.1. Estimate MC
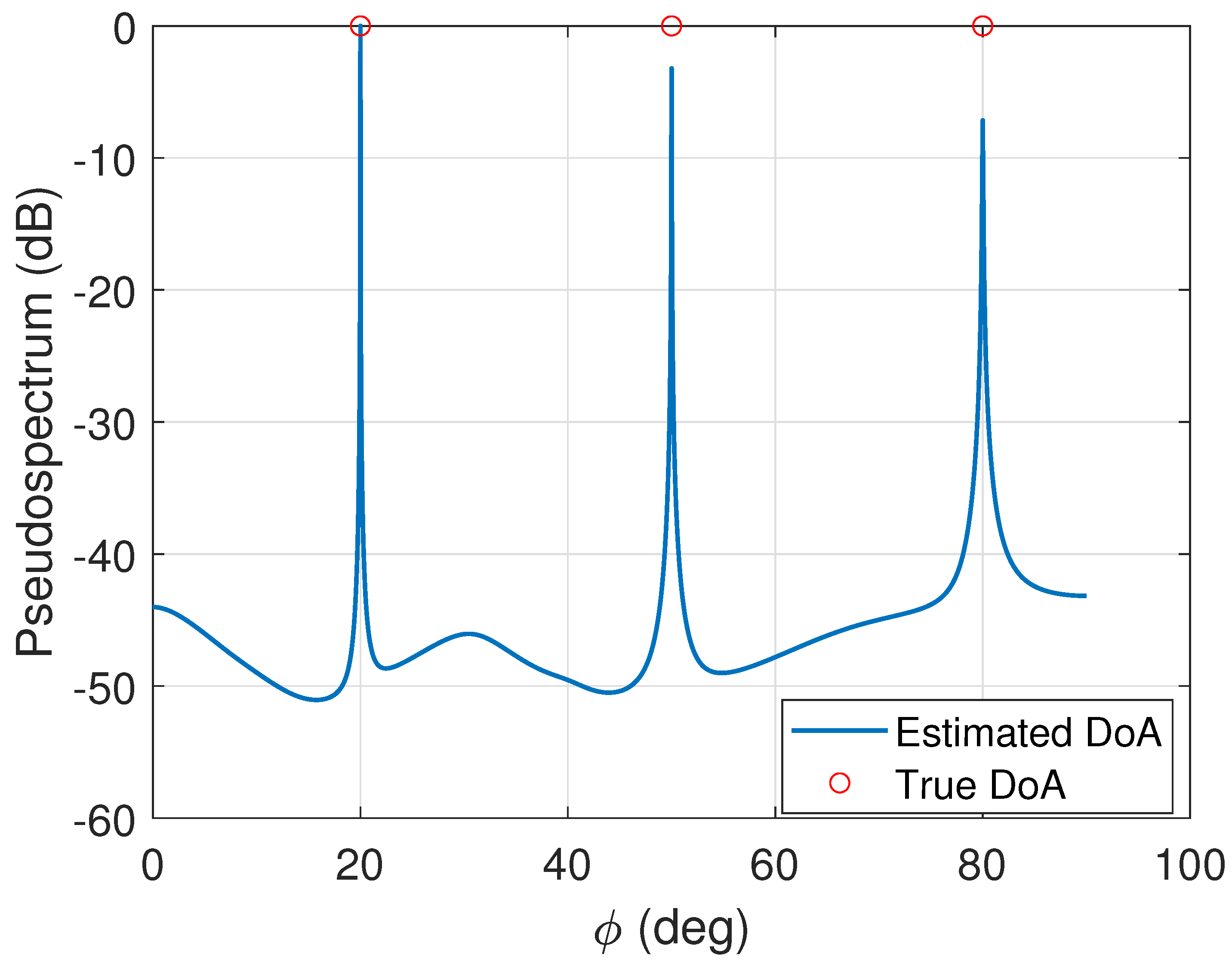
- MC compensation: In this subsection, the goal is to extract MC. It is noticed that we first need to jointly estimate DoD and DoA with unknown MC. To facilitate the joint accurate DoD and DoA estimation, it is necessary to implement MC compensation. In particular, the first and last () transmit (receiving) antenna elements are designated as auxiliary elements. The remaining elements are renumbered from 1 to and from 1 to , respectively. We denote by the virtual received data matrix obtained from the non-auxiliary elements. To mitigate the effect of mutual coupling, the data from the auxiliary elements is discarded, and is directly used for angle estimation. More specifically, define the matrices and and then the received data can be obtained by left multiplying on both sides of in (12) as
- Angle estimation applying the complex matrix method: Here a complex matrix method is employed to estimate the DoD and DoA. Observing (13), we find that the subspace spanned by is identical to the subspace spanned by the column eigenvectors in matrix . Then, it should have a unique nonsingular matrix to satisfy
- Mutual coupling coefficients estimation: So far we have obtained DoD and DoA estimation and then we can perform MC estimation via the received data of the full virtual array.
3.2. Validation Decision
- : the signal frame is from Alice,
- : the signal frame is not from Alice,
4. Performance Analysis
4.1. Representation for and
4.2. Representation for and
4.3. Representation for and
5. Numerical Results
5.1. Parameter Settings
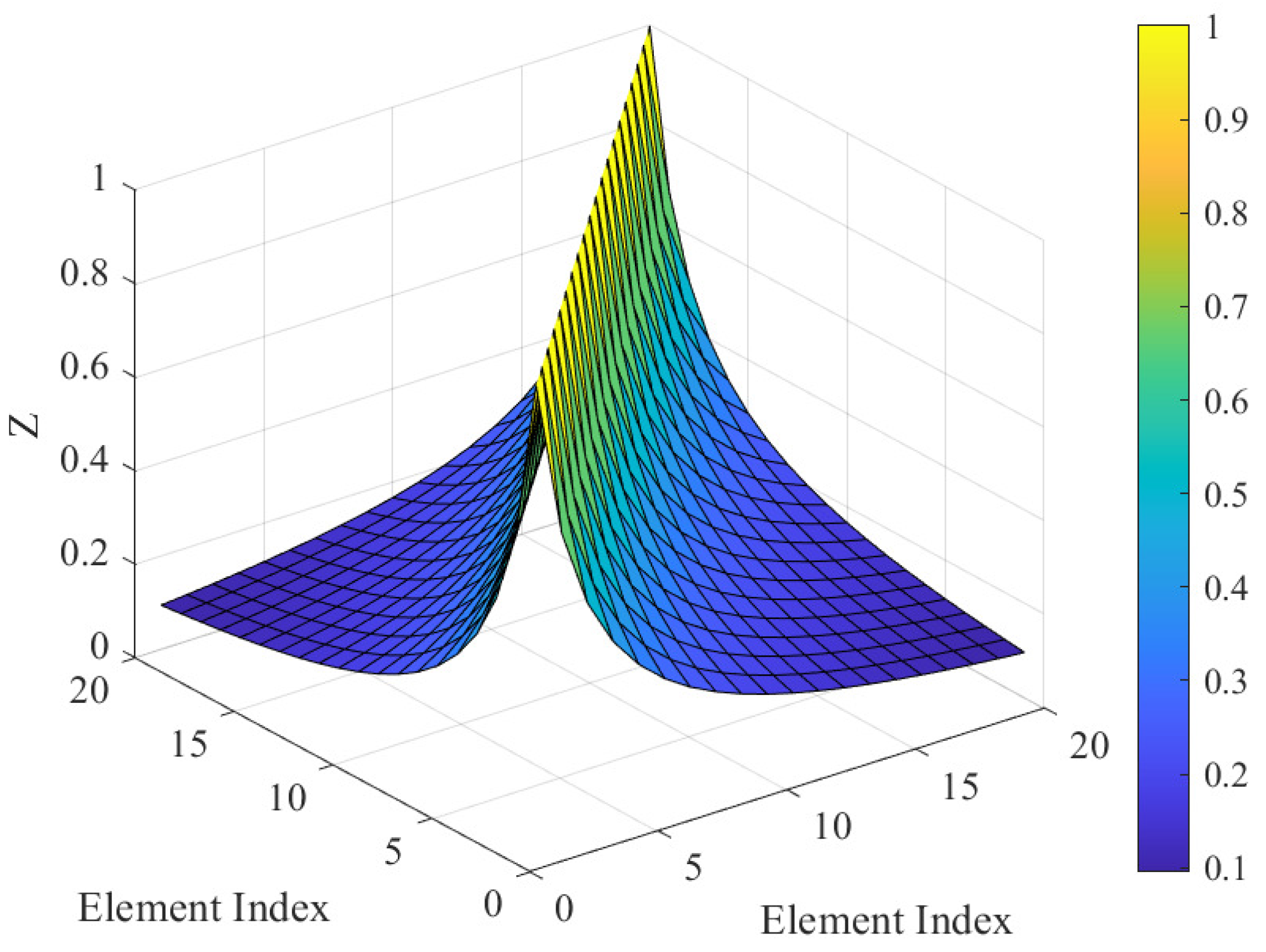
5.2. Performance Illustration of Feature Extraction
5.3. Model Validation
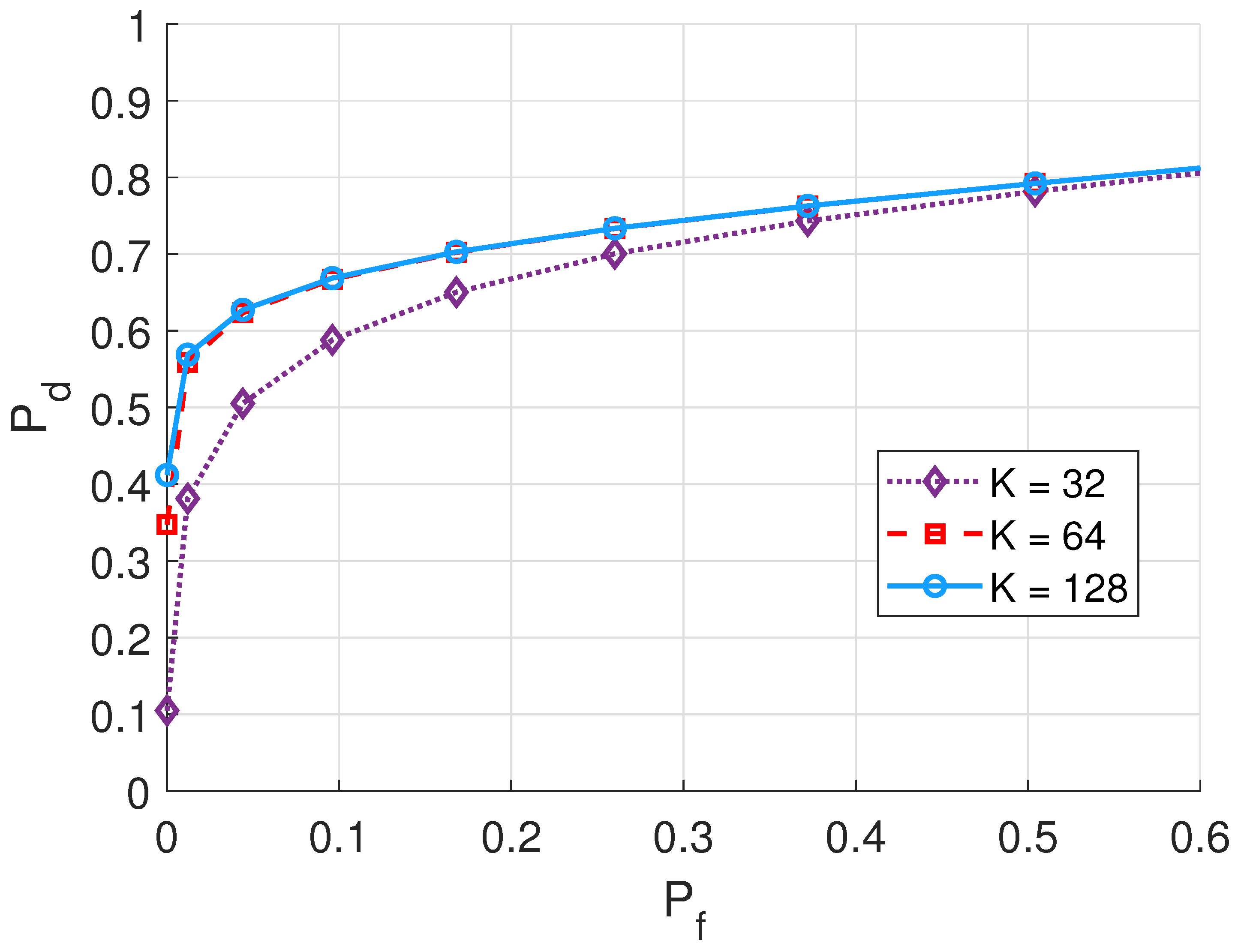
5.4. Impacts of System Parameters on Authentication Performance
5.5. Performance Comparison
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Alouzi, M.; Yanikomeroglu, H.; Kurt, G.K. Adaptive Phase Shifters for Hybrid Beamforming in mmWave Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2025, 24, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Fang, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, H. Hybrid Precoding and Combining for Millimeter Wave/Sub-THz MIMO-OFDM Systems With Beam Squint Effects. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 8314–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Qi, C.; Wang, C.; Li, G.Y. Beam Training and Tracking for Extremely Large-Scale MIMO Communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 5048–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luo, X.; Chen, M.; Xu, C.; Mao, S.; Liu, Y. Contextual Combinatorial Beam Management via Online Probing for Multiple Access mmWave Wireless Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2025, 43, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Gao, F.; Tao, X.; Zhang, J.; Alkhateeb, A. Computer Vision Aided mmWave Beam Alignment in V2X Communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 2699–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Balakrishnan, S.; Su, L.; Bhuyan, A.; Wang, P.; Qiao, C. Who Is in Control? Practical Physical Layer Attack and Defense for mmWave-Based Sensing in Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Wen, Y.; Liu, H.; Ju, Y.; Wang, H.; Wong, K.; Yuan, J. Physical-Layer Security of Uplink mmWave Transmissions in Cellular V2X Networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 9818–9833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ju, Y.; Zhang, N.; Pei, Q.; Liu, L.; Dong, M.; Leung, V.C.M. Resisting Malicious Eavesdropping: Physical Layer Security of mmWave MIMO Communications in Presence of Random Blockage. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 16372–16385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Kang, M.; Teoh, A.B.J.; Gao, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y. A Dual-Level Cancelable Framework for Palmprint Verification and Hack-Proof Data Storage. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 8587–8599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Bian, W.; Xie, D.; Xu, D.; Xu, Z. Secure and Efficient Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks Protocol Based on Cancelable Biometrics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 13580–13590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, H.; Liu, A.X.; Niyato, D. Hybrid Physical-Layer Authentication. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 1295–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Xie, N.; Li, H. Privacy-Preserving Physical-Layer Authentication Under Cooperative Attacks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2024, 32, 1171–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sha, M.; Xiong, W.; Xie, N.; Mao, R.; Zhang, P.; Huang, L. Blind Tag-Based Physical-Layer Authentication. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2024, 32, 4735–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xu, A.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, H.; Zhang, T. MmWave MIMO Physical layer Authentication by Using Channel Sparsity. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Information Systems (ICAIIS), Dalian, China, 20–22 March 2020; pp. 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Greenstein, L.J.; Mandayam, N.B.; Trappe, W. Channel-based detection of sybil attacks in wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2009, 4, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, X. End-to-End Physical Layer Authentication for Dual-Hop Wireless Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 38322–38336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, A.; Laurenti, N.; Masiero, C.; Pavon, M.; Tomasin, S. On the Error Region for Channel Estimation-Based Physical Layer Authentication Over Rayleigh Fading. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jiao, L.; Alipour-Fanid, A.; Dabaghchian, M.; Zeng, K. Pilot Contamination Attack Detection for NOMA in 5G mm-Wave Massive MIMO Networks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 1363–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jiao, L.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Zeng, K. Exploiting beam features for spoofing attack detection in mmWave 60-GHz IEEE 802.11 ad networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 3321–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Woods, R.; Sandell, M.; Valkama, M.; Marshall, A.; Cavallaro, J. Radio Frequency Fingerprint Identification for Narrowband Systems, Modelling and Classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 3974–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Huang, M.; Huang, L.; Du, X.; Guizani, M. A robust authentication scheme based on physical-layer phase noise fingerprint for emerging wireless networks. Comput. Netw. 2017, 128, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, A.C.; Goeckel, D.L. Wireless Device Identification Based on RF Oscillator Imperfections. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 2492–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, S.J.; Yapici, Y.; Güvenç, I.; Dai, H.; Bhuyan, A. Power Allocation for Fingerprint-Based PHY-Layer Authentication with mmWave UAV Networks. In Proceedings of the ICC 2021—IEEE International Conference on Communications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–23 June 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Jensen, M.A. Improved Radiometric Identification of Wireless Devices Using MIMO Transmission. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2011, 6, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Qian, S.; Wang, W. Influence of Random Errors in Element Positions on Performance of Antenna Arrays Considering Mutual Coupling Effect. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2023, 22, 2215–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, M.A.; Dutta, A.K.; Mukherjee, A. Performance Analysis of Dipole Antenna Based Planar Arrays With Mutual Coupling and Antenna Position Error in mmWave Hybrid System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 10209–10221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Song, H.J. Accurate Statistical Model of Radiation Patterns in Analog Beamforming Including Random Error, Quantization Error, and Mutual Coupling. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2021, 69, 3886–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. Off-Grid DOA Estimation Using Sparse Bayesian Learning in MIMO Radar With Unknown Mutual Coupling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemadeh, I.A.; Satyanarayana, K.; El-Hajjar, M.; Hanzo, L. Millimeter-Wave Communications: Physical Channel Models, Design Considerations, Antenna Constructions, and Link-Budget. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 870–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Gao, F.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhong, Z.; Nallanathan, A. Angle Domain Channel Estimation in Hybrid Millimeter Wave Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 8165–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint DOD and DOA estimation of bistatic MIMO radar in the presence of unknown mutual coupling. Signal Process. 2012, 92, 3039–3048. [CrossRef]
- Baracca, P.; Laurenti, N.; Tomasin, S. Physical layer authentication over MIMO fading wiretap channels. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 2564–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margoosian, A.; Abouei, J.; Plataniotis, K.N. An Accurate Kernelized Energy Detection in Gaussian and non-Gaussian/Impulsive Noises. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 5621–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serfling, R.J. Approximation Theorems of Mathematical Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Trees, H.L.V.; Bell, K.L.; Tian, Z. Detection, Estimation, and Modulation Theory, Part I: Detection, Estimation, and Filtering Theory, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Z.; Chen, H.; Xu, P.; Li, Y.; Vucetic, B. Physical Layer Authentication for non-Coherent Massive SIMO-Enabled Industrial IoT Communications. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2020, 15, 3722–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Chen, C.; Ming, Z. Security Model of Authentication at the Physical Layer and Performance Analysis over Fading Channels. IEEE Trans. Depend. Sec. Comput. 2021, 18, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Pang, Z.; Wen, H.; Lei, W.; Xu, X. Weighted Voting in Physical Layer Authentication for Industrial Wireless Edge Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 2796–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Wu, Q.; Yao, Y.D.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Kernel-Based Learning for Statistical Signal Processing in Cognitive Radio Networks: Theoretical Foundations, Example Applications, and Future Directions. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2013, 30, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradshteĭn, I.S.; Ryzhik, I.M.; Jeffrey, A. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products, 7th ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nadarajah, S.; Kotz, S. On the linear combination, product and ratio of normal and Laplace random variables. J. Frankl. Inst. 2011, 348, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Kernel Name | Expression |
|---|---|
| Gaussian | |
| Laplacian |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, M.; Nuertai, A.; Wang, R.; Zhang, P. Physical Layer Authentication Exploiting Antenna Mutual Coupling Effects in mmWave Systems. Electronics 2025, 14, 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102055
Niu M, Nuertai A, Wang R, Zhang P. Physical Layer Authentication Exploiting Antenna Mutual Coupling Effects in mmWave Systems. Electronics. 2025; 14(10):2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102055
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Mu, Ayinuer Nuertai, Runqing Wang, and Pinchang Zhang. 2025. "Physical Layer Authentication Exploiting Antenna Mutual Coupling Effects in mmWave Systems" Electronics 14, no. 10: 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102055
APA StyleNiu, M., Nuertai, A., Wang, R., & Zhang, P. (2025). Physical Layer Authentication Exploiting Antenna Mutual Coupling Effects in mmWave Systems. Electronics, 14(10), 2055. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14102055






