Multispectral Pedestrian Detection Based on Prior-Saliency Attention and Image Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
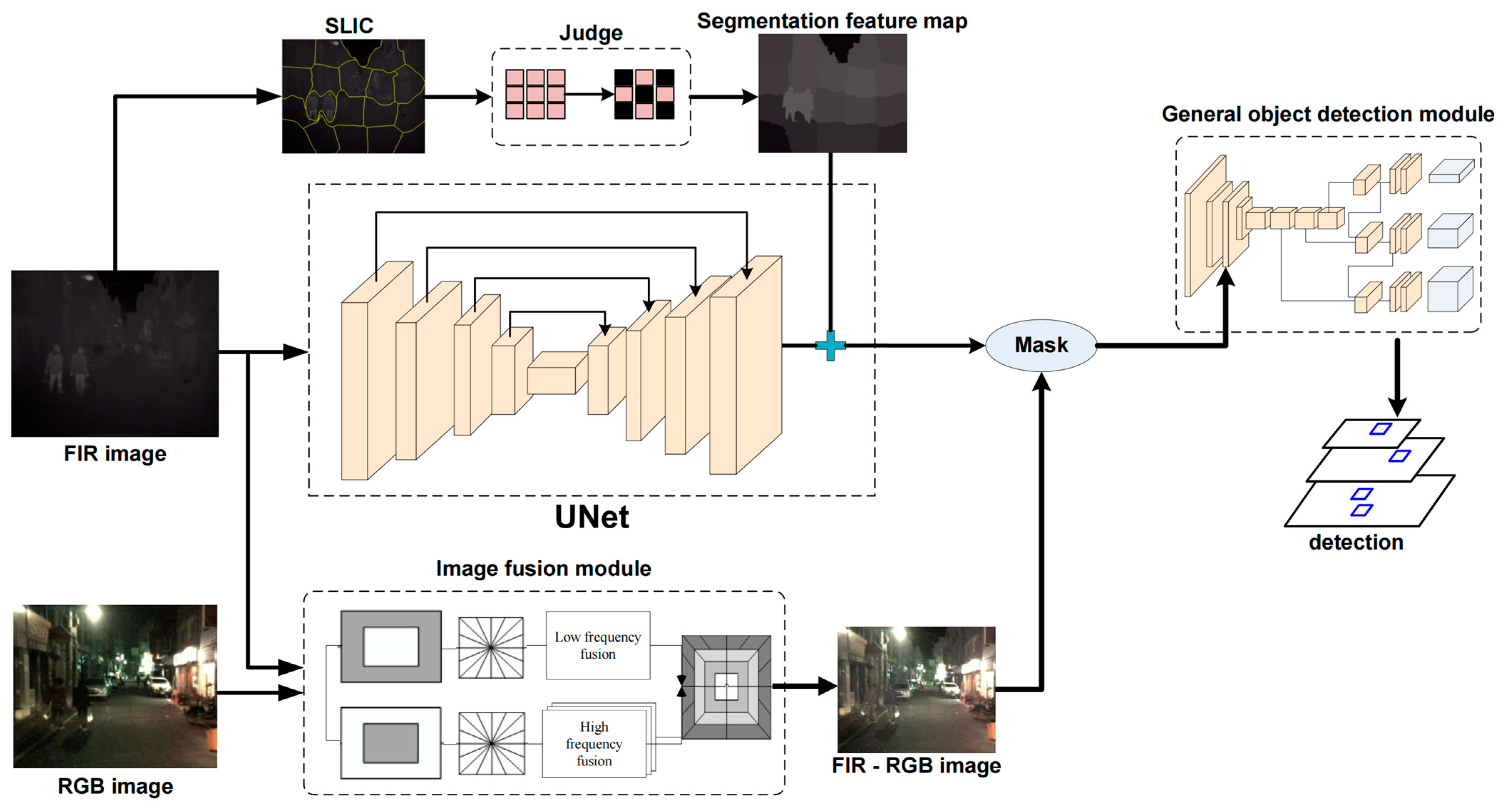
3.1. Network Structure
3.2. Prior-Attention Module
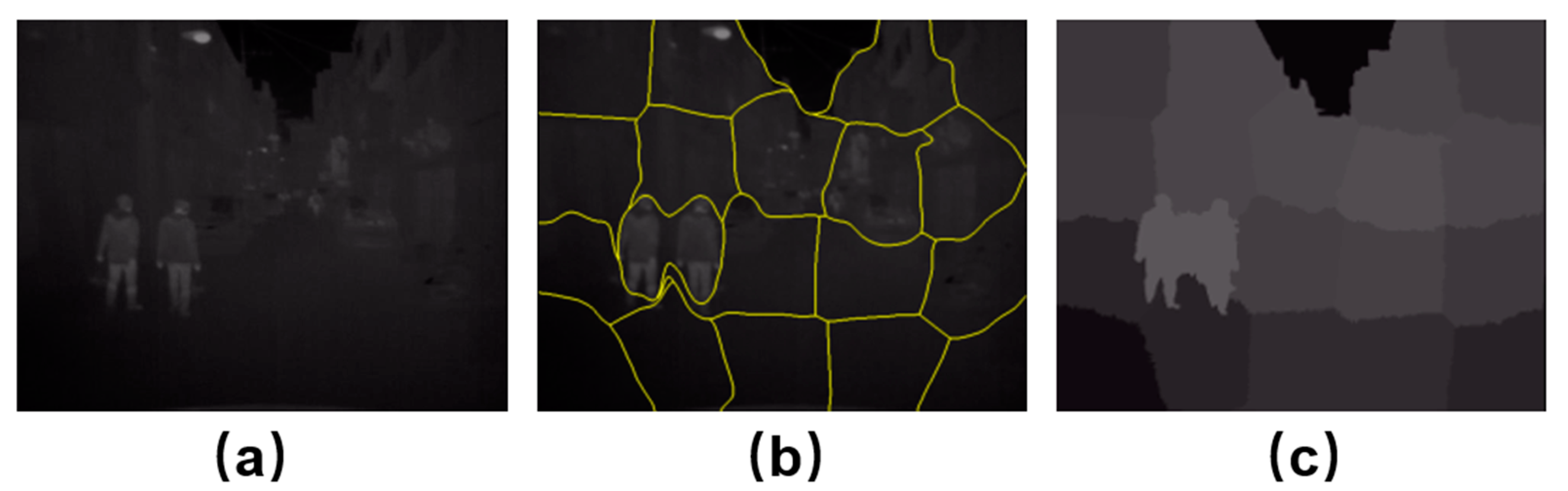
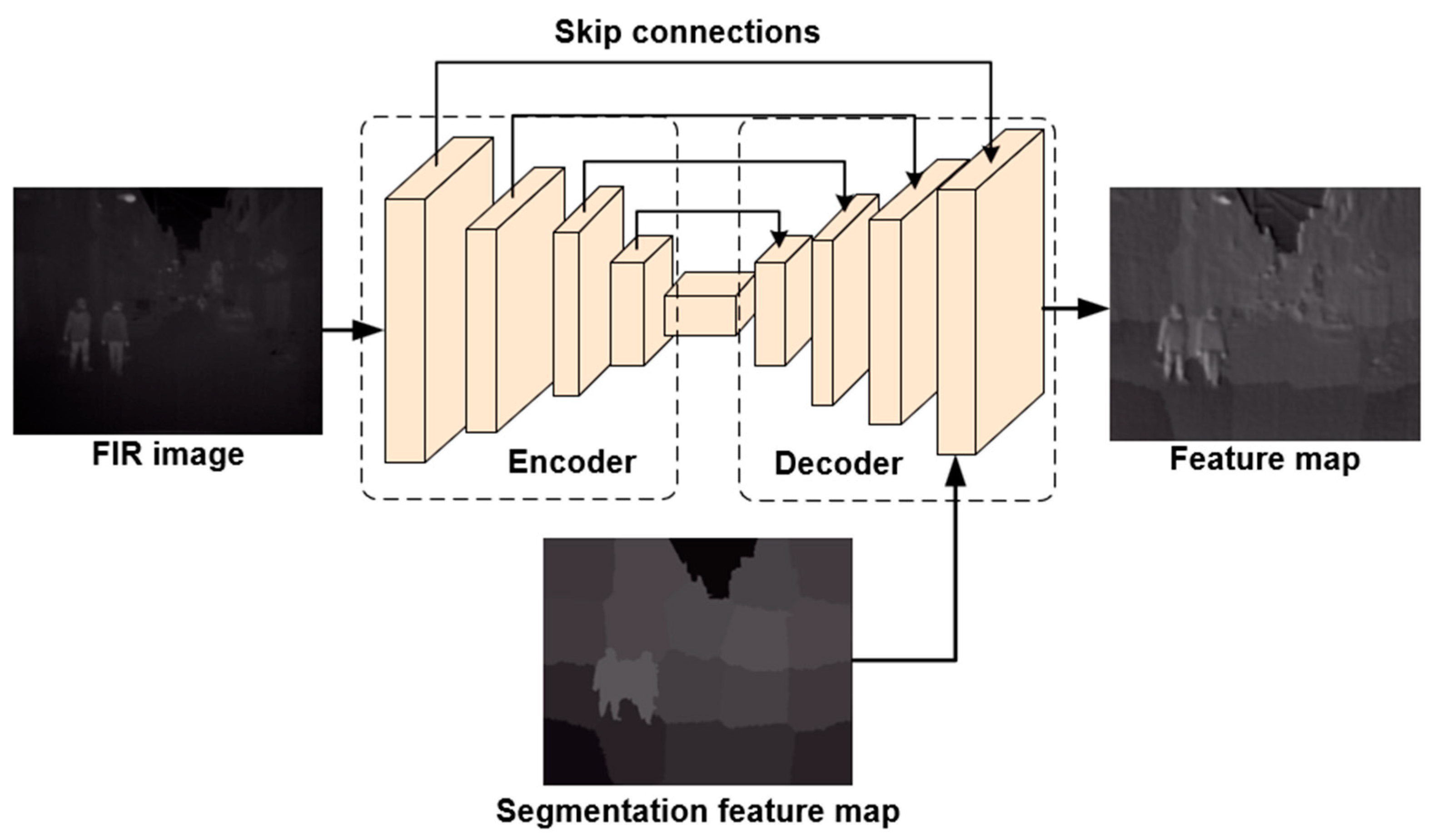
3.2.1. Segmentation Feature Extraction Module
3.2.2. Prior-Based Saliency Attention
3.3. Image Fusion Module
3.4. Complexity and Running Time
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Training Setting
4.3. Evaluation Metric
4.4. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Multispectral Pedestrian Detection Methods
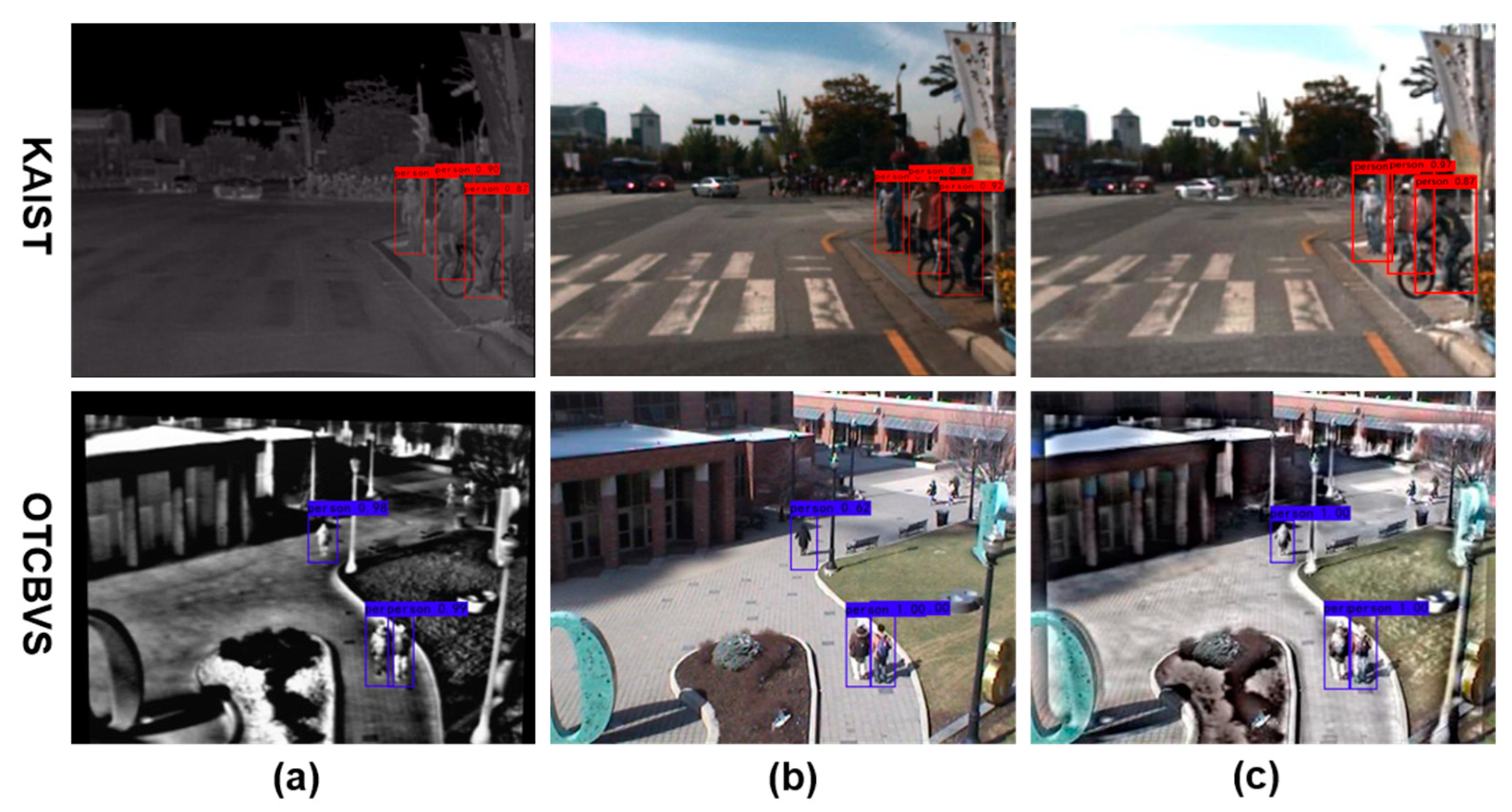
4.4.1. KAIST Dataset
4.4.2. OTCBVS Dataset
4.4.3. CVC-14 Dataset
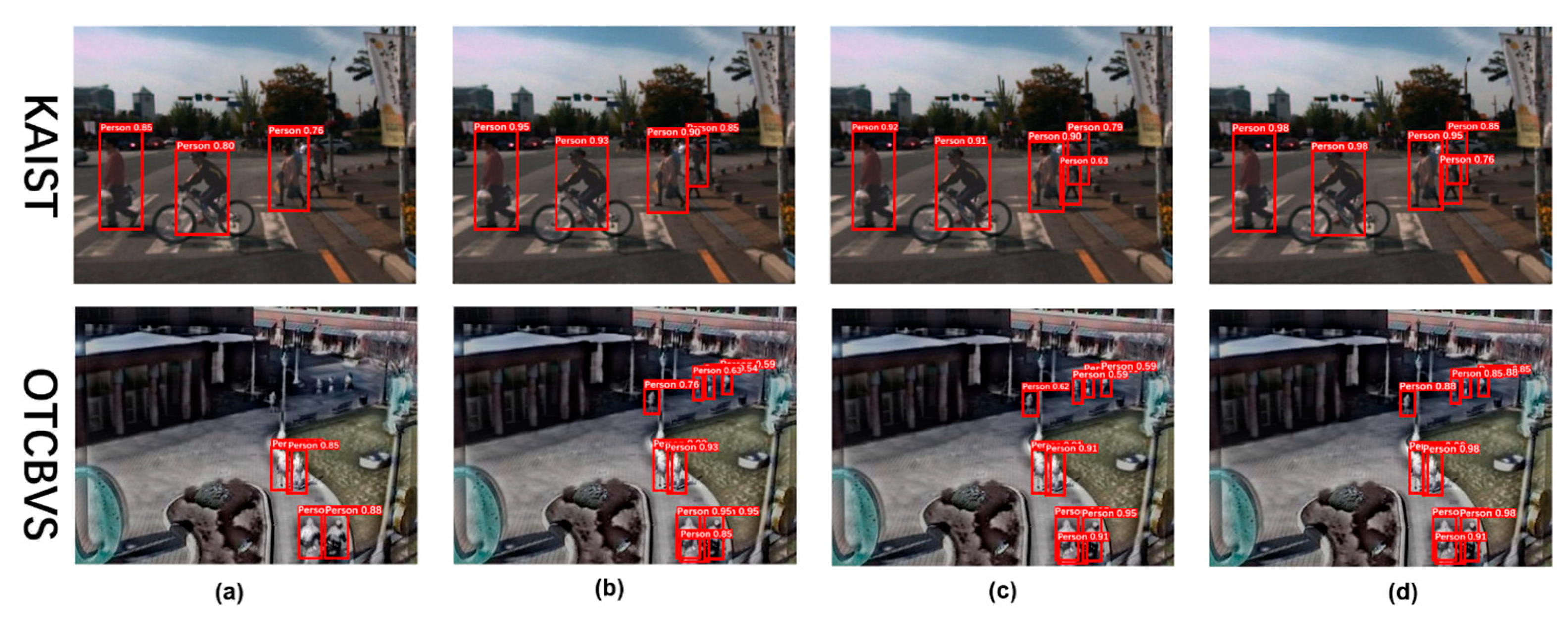
4.5. Ablation Study
4.5.1. Effect of FIR-RGB Fusion Module
4.5.2. Effect of Prior-Attention Module
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, G.; Qin, H. Class-discriminative focal loss for extreme imbalanced multiclass object detection towards autonomous driving. Vis. Comput. 2022, 38, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao HY, M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Shit, S.; Das, D.K.; Ray, D.N.; Roy, B. An encoder-decoder based CNN architecture using end to end dehaze and detection network for proper image visualization and detection. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 2023, 34, e2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavirisetti, D.P.; Xiao, G.; Liu, G. Multi-sensor image fusion based on fourth order partial differential equations. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion), Xi’an, China, 10–13 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dogra, A.; Goyal, B.; Agrawal, S. From multi-scale decomposition to non-multi-scale decomposition methods: A comprehensive survey of image fusion techniques and its applications. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 16040–16067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, P.J.; Adelson, E.H. The laplacian pyramid as a compact image code. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1983, 31, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toet, A. Image fusion by a ratio of low-pass pyramid. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1989, 9, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Manjunath, B.S.; Mitra, S.K. Multisensor image fusion using the wavelet transform. Graph. Models Image Process 1995, 57, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencini, F.; Garzelli, A.; Baronti, S.; Alparone, L. Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, B.L. Multifocus image fusion using the non sub sampled contourlet transform. Signal Process. 2009, 89, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; He, K.; Xu, D.; Yue, Y.; Luo, Y. Adaptive low light visual enhancement and high-significant target detection for infrared and visible image fusion. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 6723–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Hui, B.; Sun, S.; Ma, Y. Infrared image super-resolution method based on dual-branch deep neural network. Vis. Comput. 2023, 40, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Chen, L.; Cao, X. Improving multispectral pedestrian detection by addressing modality imbalance problems. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 787–803. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, D.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, M.Y. Fusion of multispectral data through illuminance-aware deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Park, J.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.; So Kweon, I. Multispectral pedestrian detection: Benchmark dataset and baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Y.; Leykin, A.; Hammoud, R. Thermal-visible video fusion for moving target tracking and pedestrian motion analysis and classification. In Augmented Vision Perception in Infrared: Algorithms and Applied Systems; Springer: London, UK, 2007; pp. 349–369. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Estrada, F.; Wils, P.; Süsstrunk, S. Salient region detection and segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision Systems: 6th International Conference, ICVS 2008, Santorini, Greece, 12–15 May 2008; Proceedings 6. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- González, A.; Fang, Z.; Socarras, Y.; Serrat, J.; Vázquez, D.; Xu, J.; López, A.M. Pedestrian detection at day/night time with visible and FIR cameras: A comparison. Sensors 2016, 16, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St-Charles, P.L.; Bilodeau, G.A.; Bergevin, R. SuBSENSE: A universal change detection method with local adaptive sensitivity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 24, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, L.A.; Keles, H.Y. Foreground segmentation using a triplet convolutional neural network for multiscale feature encoding. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2018, 112, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kim, Y. Background subtraction using illuminance invariant structural complexity. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 634–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W. Moving object detection using edges of residuals under varying illuminances. Multimed. Syst. 2019, 25, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Singh, S. Neural style transfer combined with EfficientDet for thermal surveillance. Vis. Comput. 2022, 38, 4111–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q.; Duan, J.; Cai, H.; Liu, G.W. Electronics, Communications and Networks IV, 1st ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, K. Compressed fusion of infrared and visible images combining robust principal component analysis and non-subsampled contour transform. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2020, 57, 041005. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, J.; Fischer, V.; Herman, M.; Behnke, S. Multispectral pedestrian detection using deep fusion convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 24th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning (ESANN), Bruges, Belgium, 27–29 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Laganière, R.; Huang, D.; Luo, X.; Zhang, H. A robust and fast multispectral pedestrian detection deep network. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 227, 106990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Metaxas, D.N. Multispectral deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.02644. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, L.; Liang, X.; He, K. Is faster R-CNN doing well for pedestrian detection? In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part II 14. Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Konig, D.; Adam, M.; Jarvers, C.; Layher, G.; Neumann, H.; Teutsch, M. Fully convolutional region proposal networks for multispectral person detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Song, D.; Tong, R.; Tang, M. Multispectral pedestrian detection via simultaneous detection and segmentation. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), Newcastle, UK, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 225.1–225.12. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Song, D.; Tong, R.; Tang, M. Illumination-aware faster R-CNN for robust multispectral pedestrian detection. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 85, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ouyang, W.; Ricci, E.; Wang, X.; Sebe, N. Learning cross-modal deep representations for robust pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Qiao, H.; Huang, K.; Hussain, A. Cross-modality interactive attention network for multispectral pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Lei, Z.; Liu, Z. Weakly aligned cross-modal learning for multispectral pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5127–5137. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.; Kim, S.; Sohn, K. Unified multi-spectral pedestrian detection based on probabilistic fusion networks. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 80, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, H.; Qi, X.; Dou, Q.; Fu, C.W.; Heng, P.A. H-DenseUNet: Hybrid densely connected UNet for liver and tumor segmentation from CT volumes. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2663–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, N.; Hwang, S.; Park, K.; Yoon, J.S.; An, K.; Kweon, I.S. KAIST multi-spectral day/night data set for autonomous and assisted driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 934–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.W.; Sharma, V. Background-subtraction using contour-based fusion of thermal and visible imagery. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2007, 106, 162–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollar, P.; Wojek, C.; Schiele, B.; Perona, P. Pedestrian detection: An evaluation of the state of the art. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 34, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Fan, H.; Yang, W. ICAFusion: Iterative cross-attention guided feature fusion for multispectral object detection. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 145, 109913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Datasets | Day | Night | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | Validation | Training | Validation | |
| KAIST | 2254 | 225 | 3500 | 350 |
| OTCBVS | 1054 | 105 | 400 | 106 |
| CVC-14 | 706 | 71 | 1386 | 139 |
| Detector | Backbone | Training Epoch | Batch Size | Learning Rate | Weight Attenuation | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5 | CSPDarknet53 | 100 | 4 | 10−3 | 10−4 | 0.5 |
| Method | Low Illuminance (Night) | High Illuminance (Day) |
|---|---|---|
| RF HOG+LBP [18] | 29.4 | 28.7 |
| LateFusion CNN [26] | 37.0 | 46.2 |
| EarlyFusion CNN [26] | 51.8 | 50.9 |
| CMT-CNN [33] | 54.8 | 47.3 |
| Halfway fusion [28] | 26.59 | 24.88 |
| MSDS-RCNN [31] | 10.60 | 13.73 |
| CIAN [34] | 11.13 | 14.77 |
| AR-CNN [35] | 8.38 | 9.94 |
| MBNet [13] | 7.86 | 8.28 |
| ICAFusion [41] | 6.82 | 7.85 |
| Ours | 6.13 | 7.04 |
| Method | F1 Score | mAP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SuBSENSE [19] | 0.638 | - | ||||
| IISC [21] | 0.674 | - | ||||
| Kim’s method [22] | 0.569 | - | ||||
| FgSegNet [20] | 0.077 | - | ||||
| SRCNN+EDM [23] | - | 65.45 | ||||
| EDSR+EDM [23] | - | 76.01 | ||||
| STEIM+EDM [23] | - | 87.51 | ||||
| Ours | all | day | night | all | day | night |
| 0.678 | 0.699 | 0.639 | 94.54 | 97.65 | 92.62 | |
| Method | Low Illuminance (Night) | High Illuminance (Day) |
|---|---|---|
| RF HOG+LBP [18] | 26.6 (RGB) 16.7 (FIR) | 81.2 (RGB) 24.8 (FIR) |
| Halfway fusion [28] | 34.4 | 38.1 |
| AR-CNN [35] | 18.1 | 24.7 |
| MBNet [13] | 13.5 | 24.7 |
| Ours | 17.6 | 11.0 |
| Mode | Night (Low Illuminance) | Day (High Illuminance) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR | mAP | MR | mAP | |
| FIR | 9.76 | 75.6 | 17.61 | 91.5 |
| RGB | 10.87 | 78.5 | 12.55 | 93.2 |
| FIR-RGB | 7.89 | 87.0 | 13.52 | 93.5 |
| Mode | Night (Low Illuminance) | Day (High Illuminance) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR | mAP | MR | mAP | |
| FIR | 17.98 | 84.4 | 19.30 | 94.2 |
| RGB | 20.97 | 86.8 | 17.86 | 95.2 |
| FIR-RGB | 19.53 | 89.4 | 17.60 | 97.8 |
| Mode | Night (Low Illuminance) | Day (High Illuminance) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR | mAP | MR | mAP | |
| FIR-RGB | 7.89 | 87.00 | 13.52 | 93.50 |
| FIR-RGB + Saliency Attention | 6.62 | 92.10 | 8.73 | 95.53 |
| FIR-RGB + Segmentation | 6.26 | 97.31 | 8.14 | 97.74 |
| FIR-RGB + Prior-Attention | 6.13 | 97.56 | 7.04 | 98.12 |
| Mode | Night (Low Illuminance) | Day (High Illuminance) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MR | mAP | MR | mAP | |
| FIR-RGB | 19.53 | 89.42 | 17.60 | 97.80 |
| FIR-RGB + Saliency Attention | 16.73 | 92.61 | 12.73 | 95.70 |
| FIR-RGB + Segmentation | 8.00 | 97.86 | 8.00 | 98.62 |
| FIR-RGB + Prior-Attention | 5.00 | 98.32 | 5.00 | 99.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Huang, Z.; Tao, Y. Multispectral Pedestrian Detection Based on Prior-Saliency Attention and Image Fusion. Electronics 2024, 13, 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13091770
Guo J, Huang Z, Tao Y. Multispectral Pedestrian Detection Based on Prior-Saliency Attention and Image Fusion. Electronics. 2024; 13(9):1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13091770
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jiaren, Zihao Huang, and Yanyun Tao. 2024. "Multispectral Pedestrian Detection Based on Prior-Saliency Attention and Image Fusion" Electronics 13, no. 9: 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13091770
APA StyleGuo, J., Huang, Z., & Tao, Y. (2024). Multispectral Pedestrian Detection Based on Prior-Saliency Attention and Image Fusion. Electronics, 13(9), 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13091770






