A Two-Stage Sub-Threshold Voltage Reference Generator Using Body Bias Curvature Compensation for Improved Temperature Coefficient
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dibl Effect Compensation
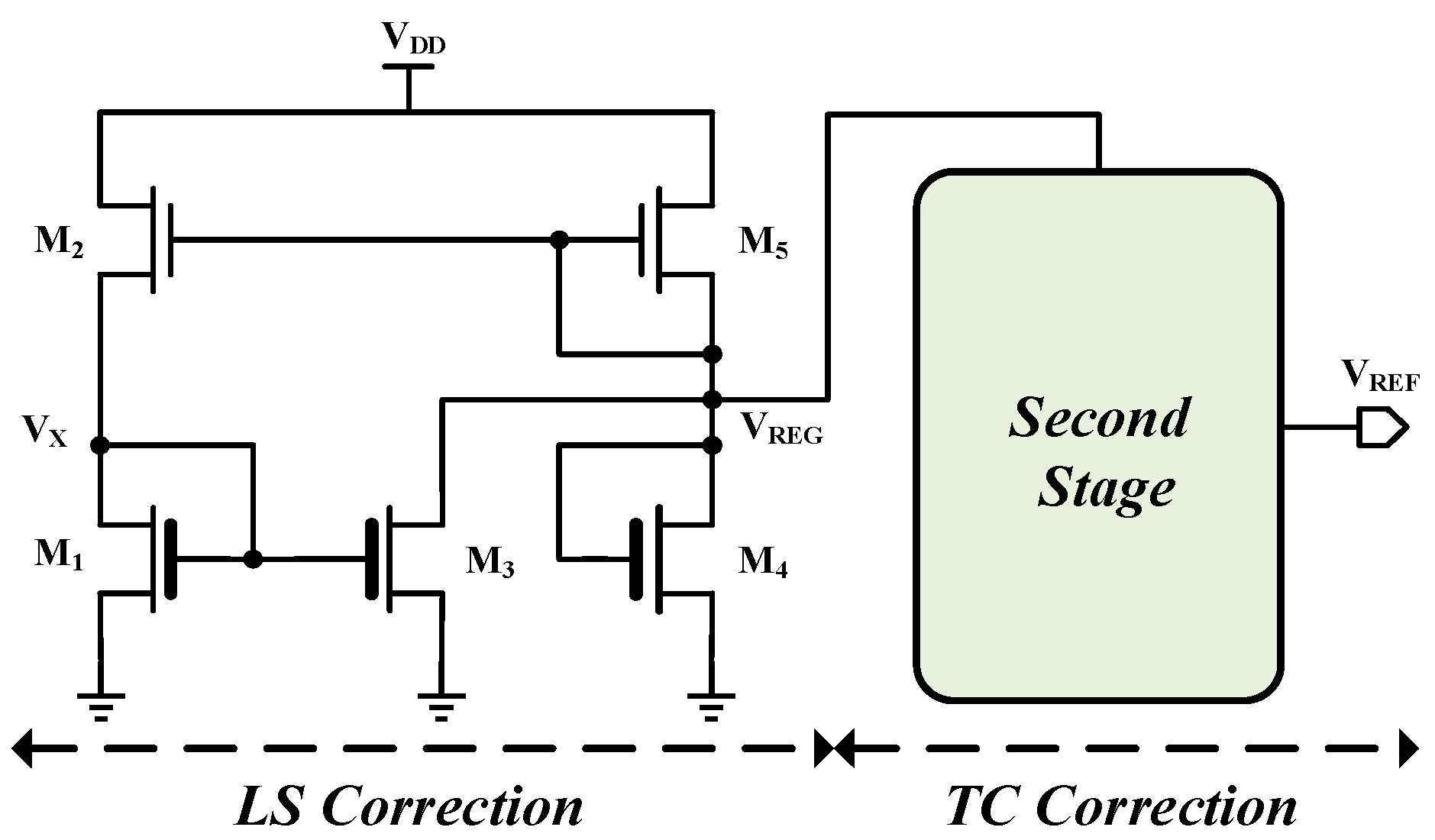
3. Proposed Voltage Reference Generator
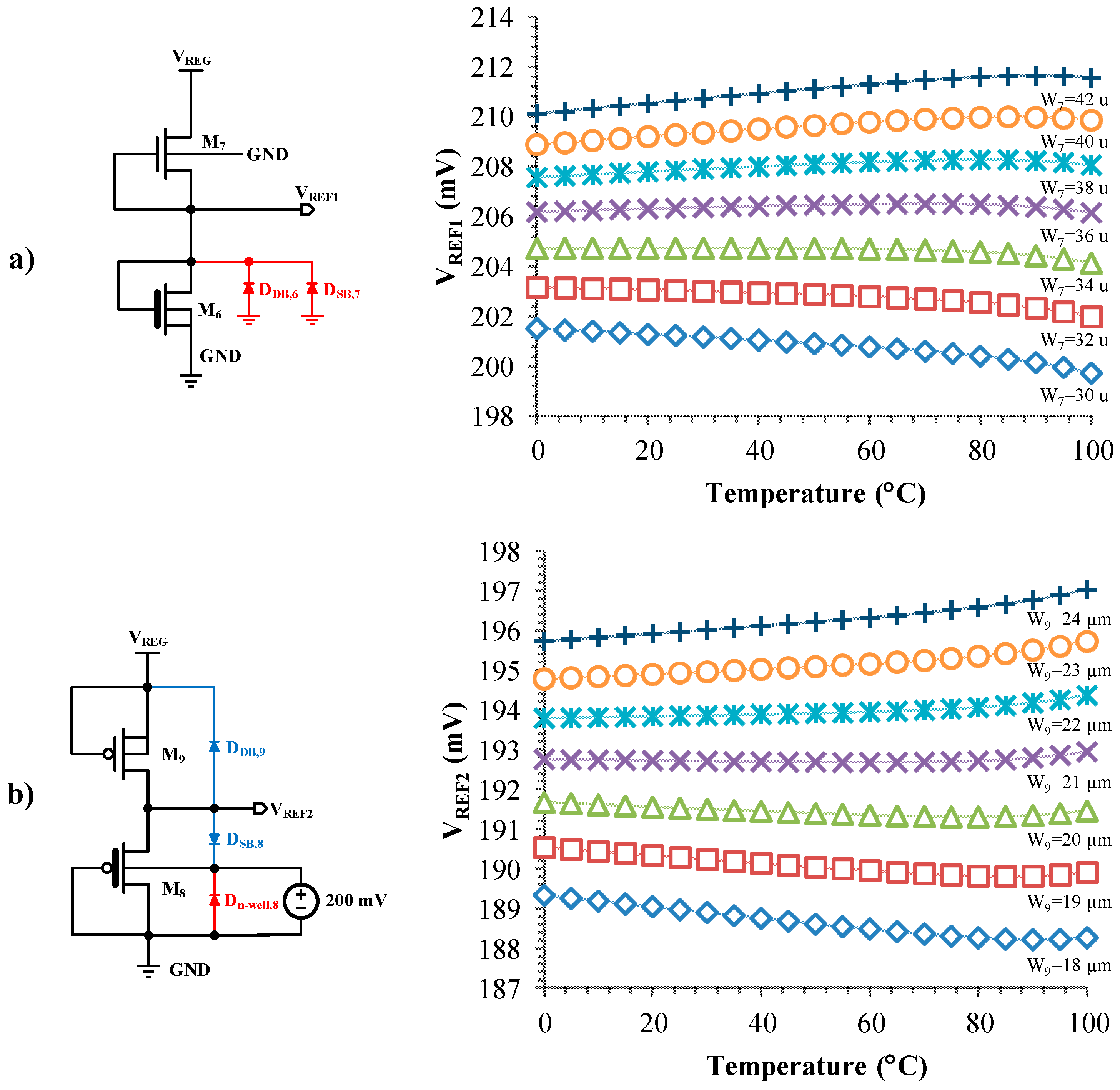
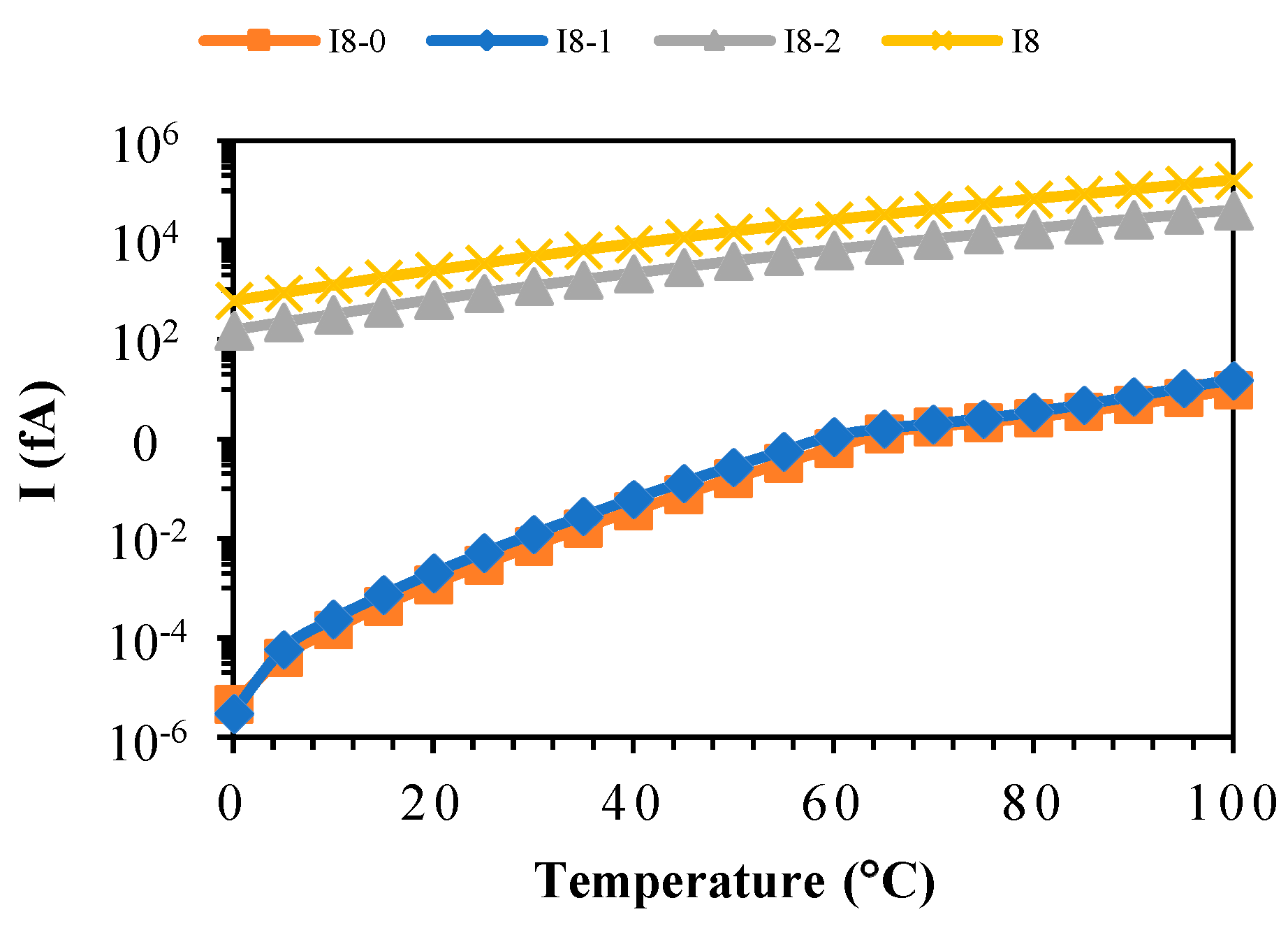
3.1. Effects of Parasitic Diodes Leakage Current in 2T n-Type and p-Type Voltage Reference Generators
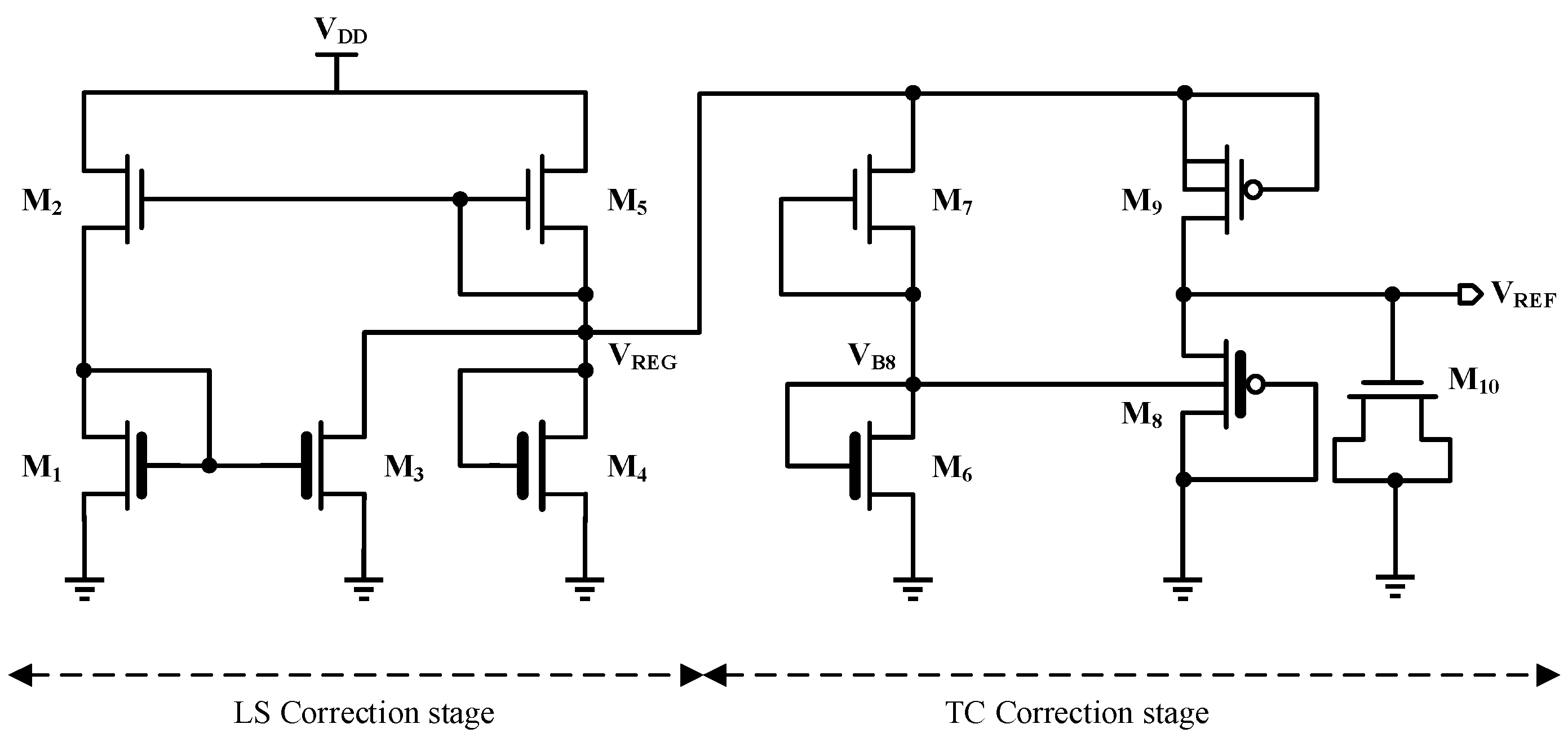
3.2. Proposed Circuit
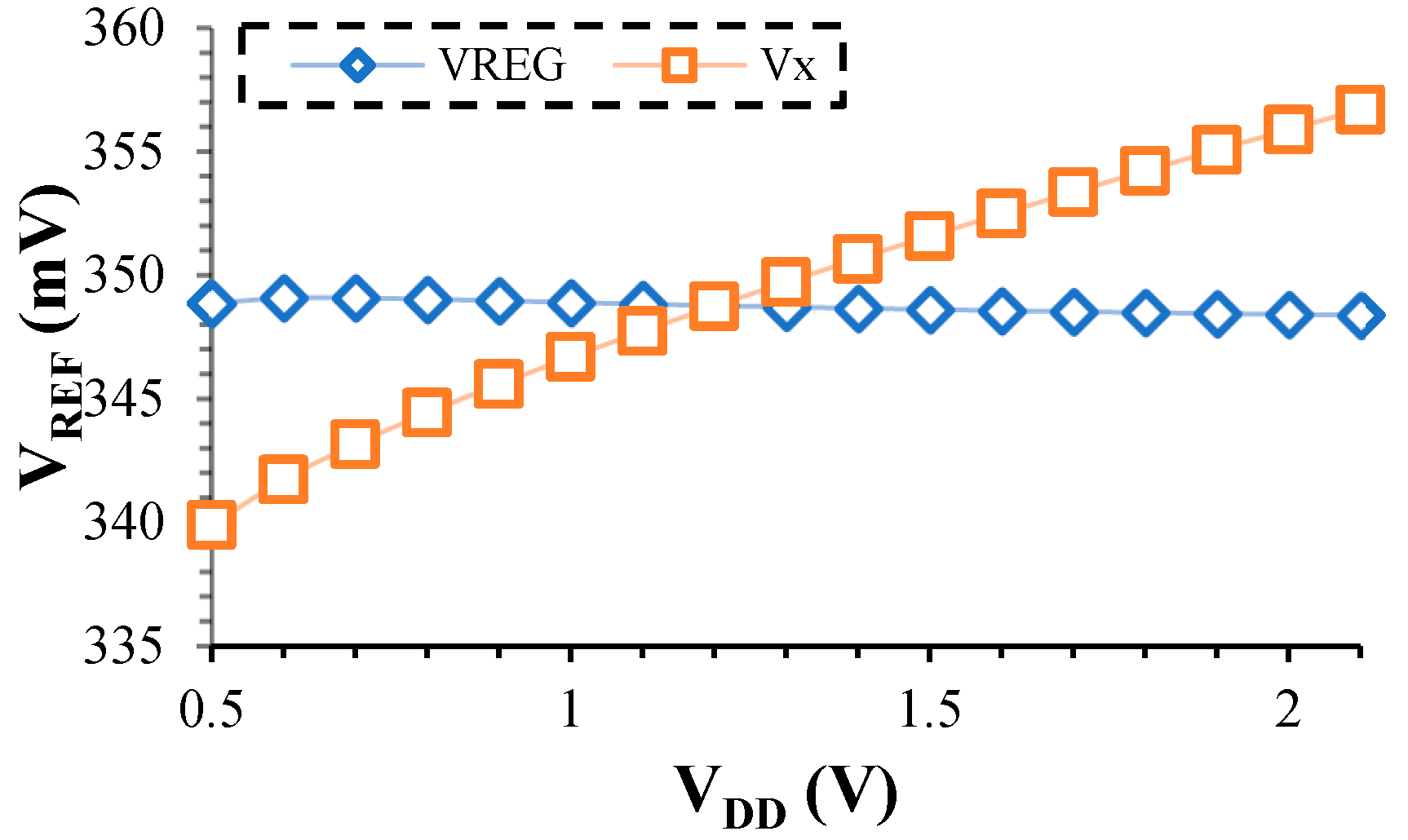
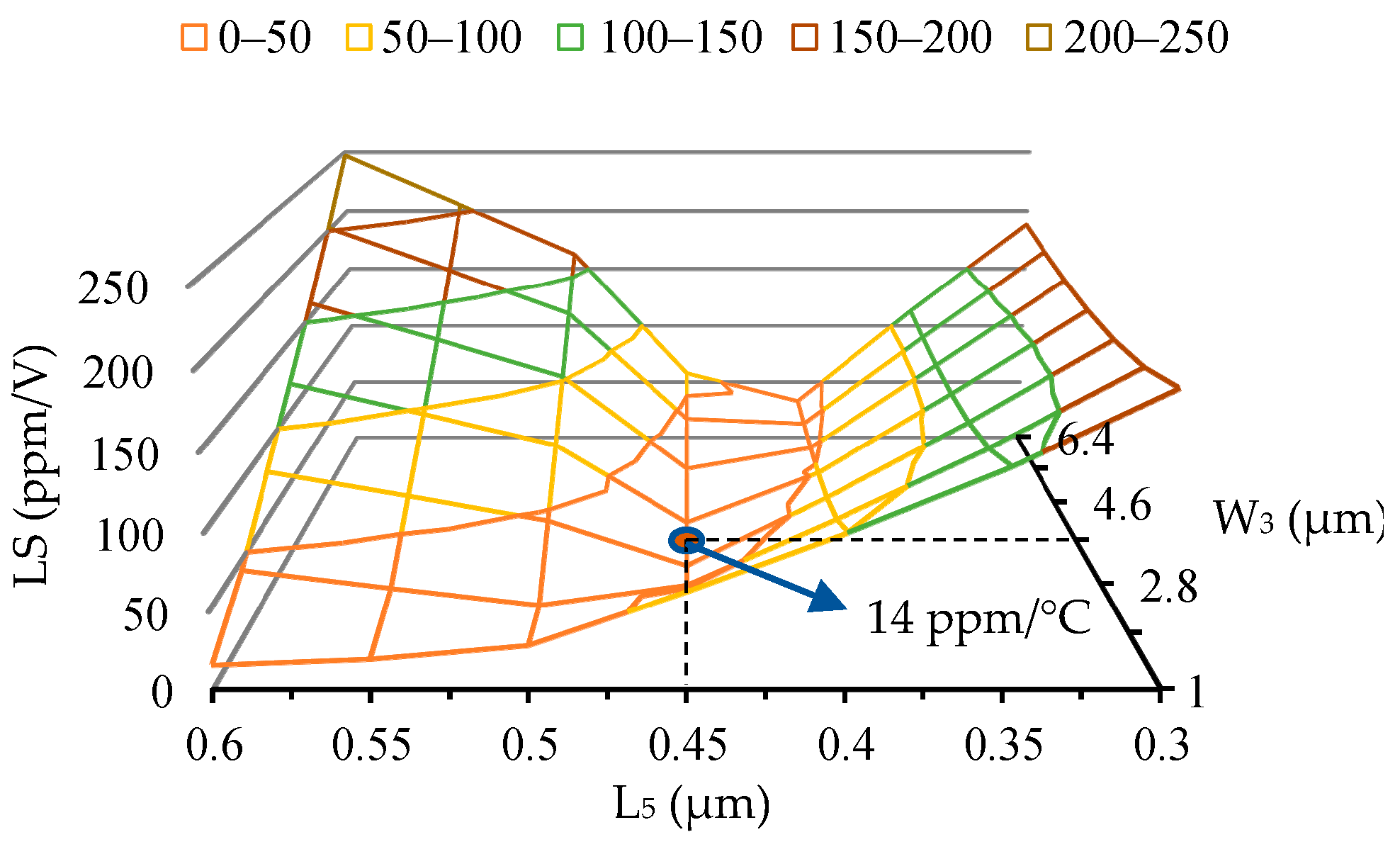
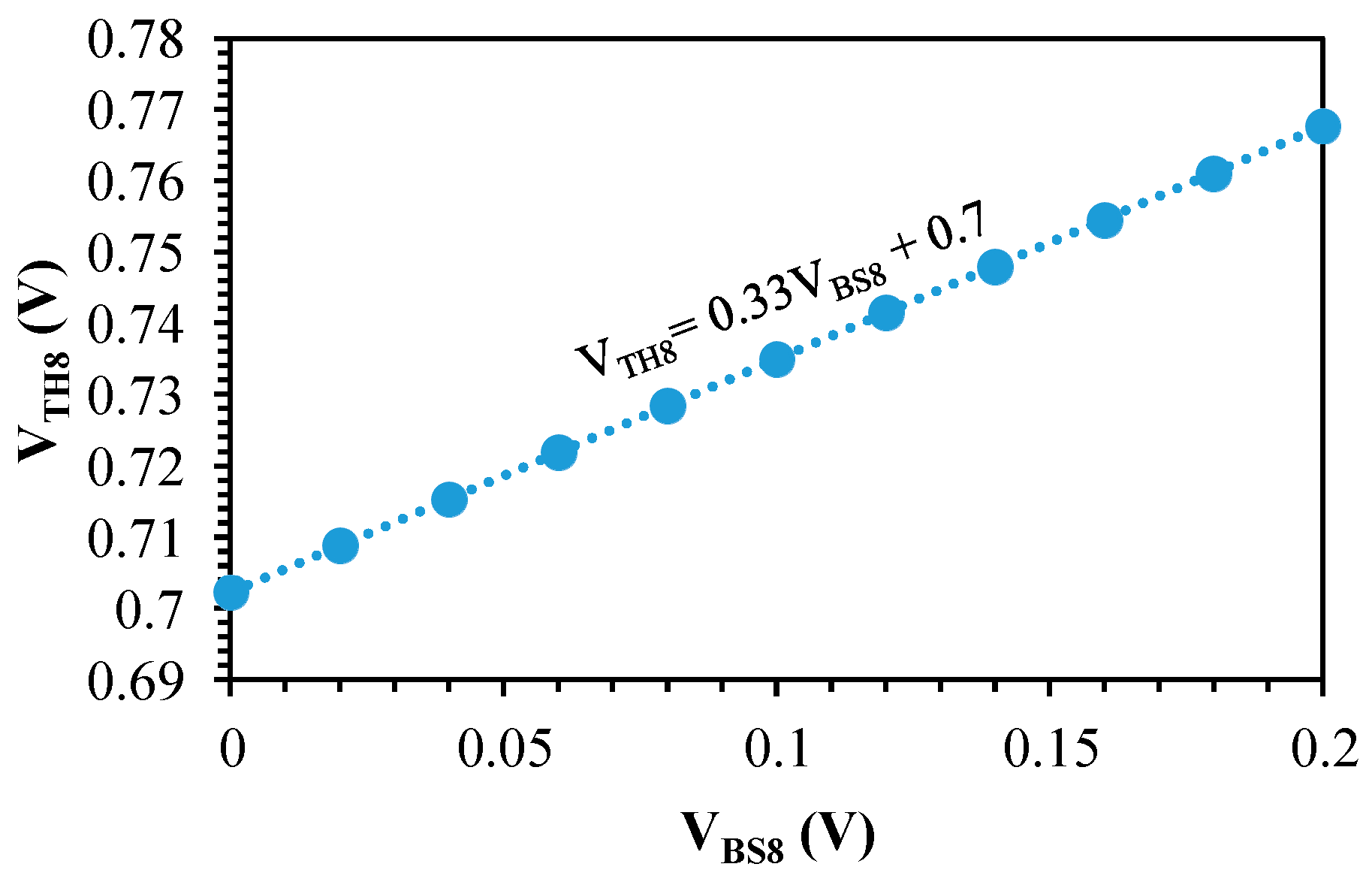
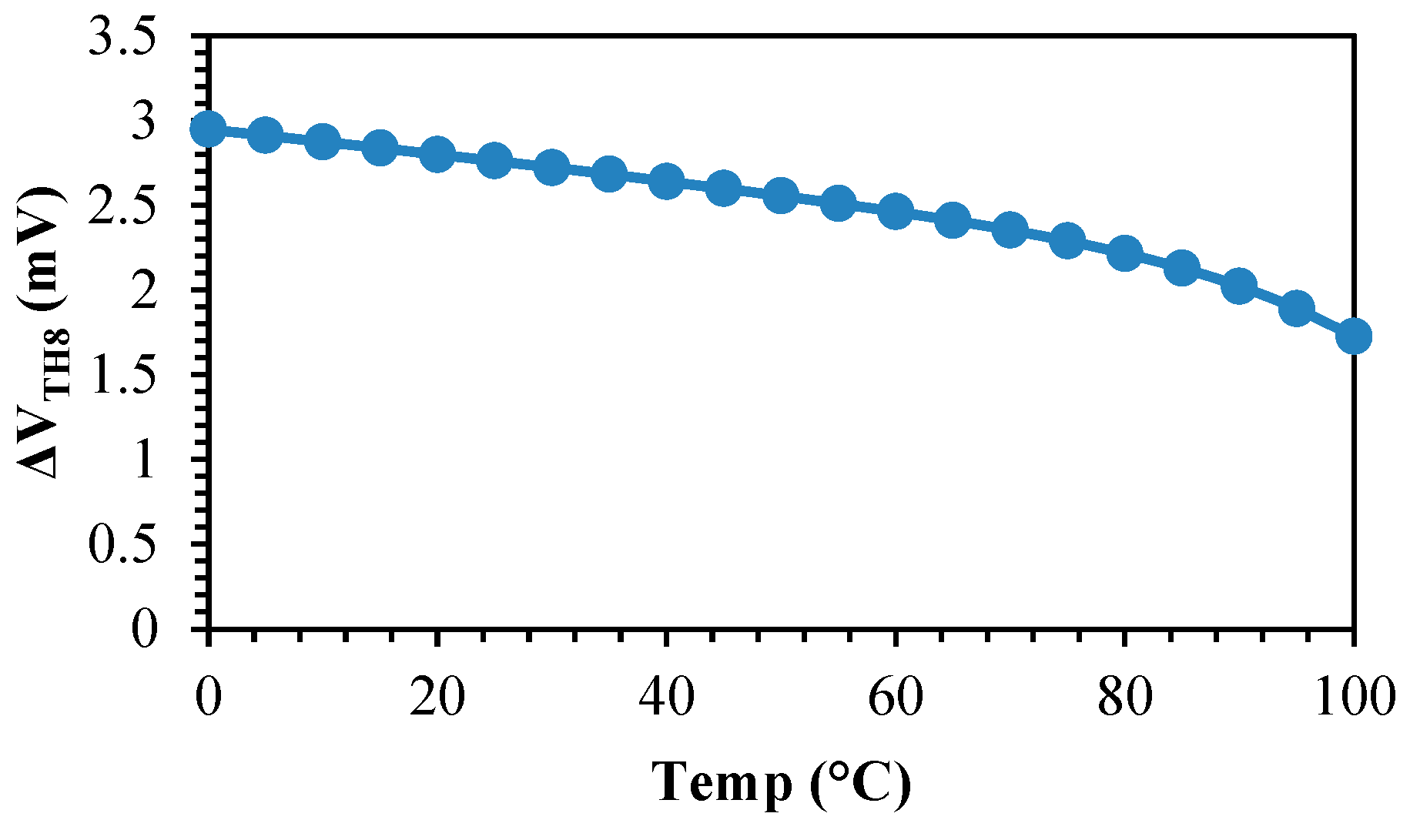
4. TC Optimization
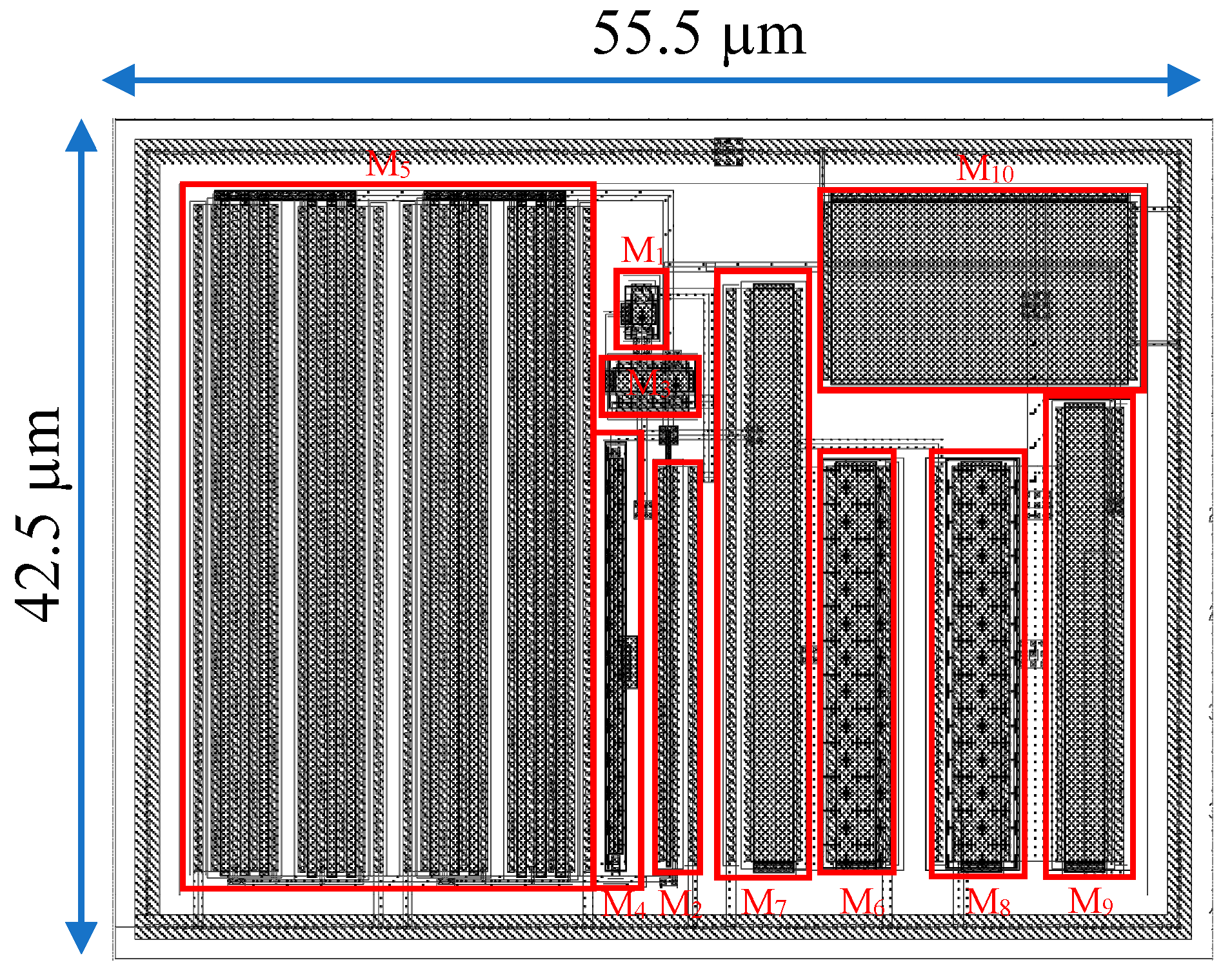
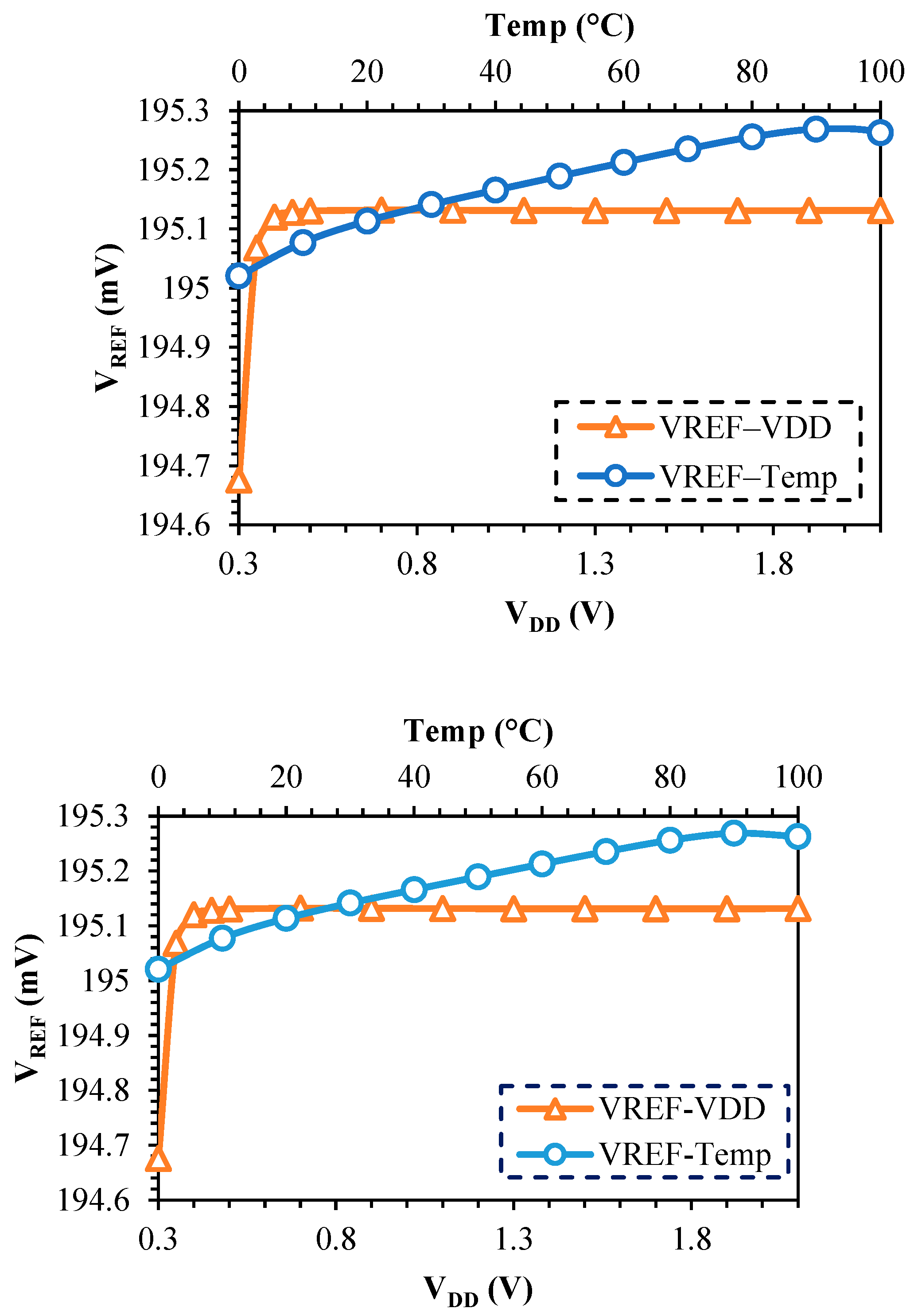
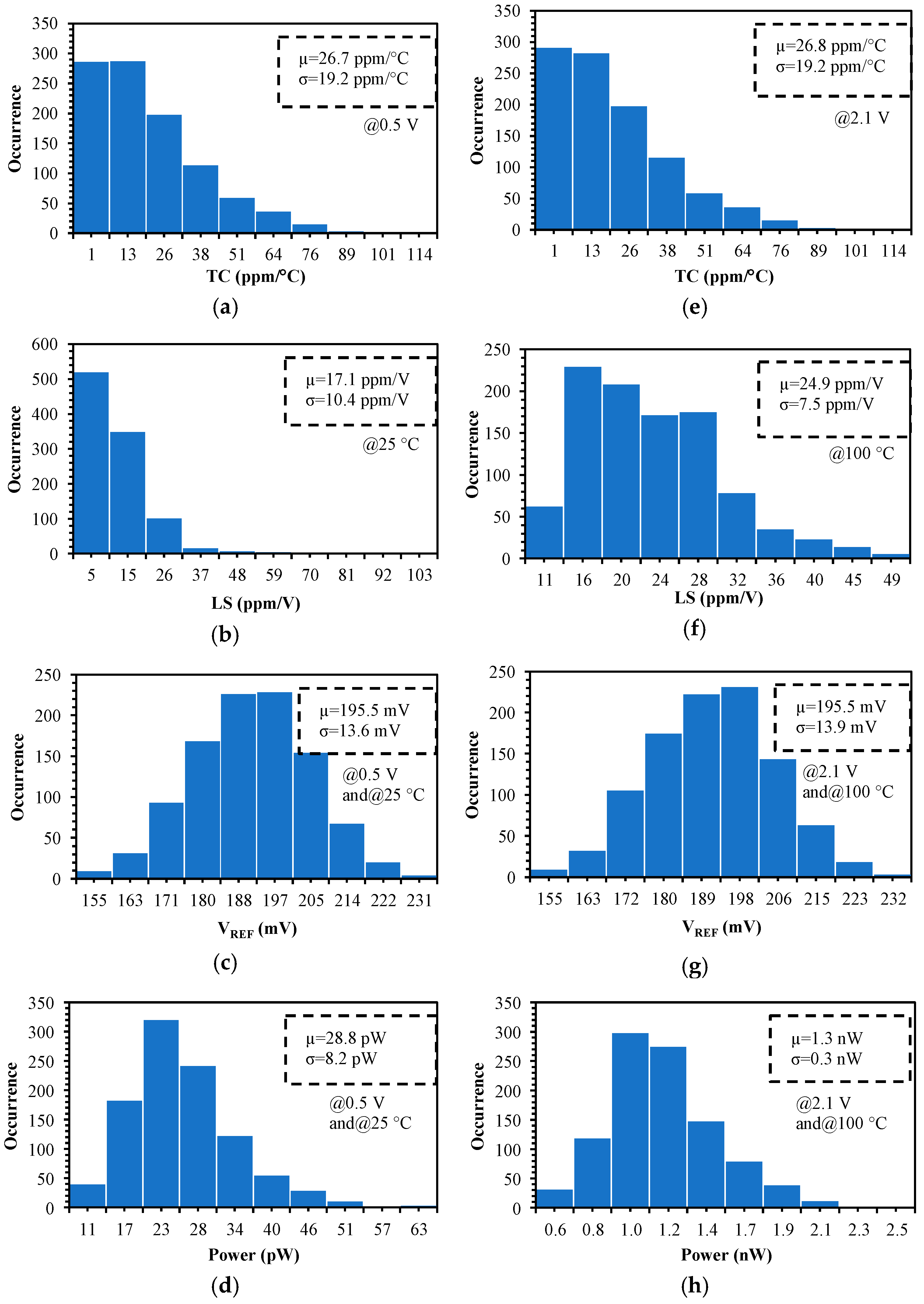
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palumbo, G. Voltage references: From diodes to precision high-order bandgap circuits [Book Review]. IEEE Circuits Devices Mag. 2002, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.; Hussein, S.M.; Hashim, Y.; Tang, K.-T. An enhanced input differential pair for low-voltage bulk-driven amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2021, 29, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, A.; Torkzadeh, P.; Dousti, M. A 6-bit 1.5-GS/s SAR ADC with smart speculative two-tap embedded DFE in 130-nm CMOS for wireline receiver applications. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2021, 29, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdary, G.; Aashish, T.; Chatterjee, S. A 99% Current Efficient Three-Transistor Regulator With Built-In 80 ppm/° C Reference, for 0–10 mA Loads. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Lett. 2018, 1, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, A.C.; Cordova, D.; Klimach, H.; Bampi, S. A 0.12–0.4 V, versatile 3-transistor CMOS voltage reference for ultra-low power systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2018, 65, 3790–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, F.; da Silva, L.S.; Petraglia, A. A 120 mV Supply, Triode-Regulated Femto-Watt CMOS Voltage Reference Design. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 68, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. Voltage reference with linear-temperature-dependent power consumption. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2020, 28, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, M.; Kim, G.; Blaauw, D.; Sylvester, D. A portable 2-transistor picowatt temperature-compensated voltage reference operating at 0.5 V. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 2534–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.C.; Cordova, D.; Klimach, H.; Bampi, S. Picowatt, 0.45–0.6 V self-biased subthreshold CMOS voltage reference. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 64, 3036–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, M.; Habibi, M.; Crovetti, P. pMOS-only pW-power voltage reference with sub-10 ppm/°C trimmed temperature coefficient and sub-100 ppm/V line sensitivity. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2023, 51, 2638–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgerdi, M.A.; Habibi, M.; Dolatshahi, M. A novel two stage cross coupled architecture for low voltage low power voltage reference generator. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2019, 99, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Luo, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H. A 48 pW, 0.34 V, 0.019%/V line sensitivity self-biased subthreshold voltage reference with DIBL effect compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2019, 67, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.; Park, H.-J.; Sim, J.-Y. A 192-pW Voltage Reference Generating Bandgap–Vth With Process and Temperature Dependence Compensation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 3281–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Yang, K.; Blaauw, D.; Sylvester, D. A 114-pW PMOS-only, trim-free voltage reference with 0.26% within-wafer inaccuracy for nW systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits (VLSI-Circuits), Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–17 June 2016; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, I.; Chowdary, G. A 0.3 nW, 0.093%/V Line Sensitivity, Temperature Compensated Bulk-Programmable Voltage Reference for Wireless Sensor Nodes. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2022, 30, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Zhan, C.; Chen, Y. A− 40 °C to 140 °C Picowatt CMOS Voltage Reference With 0.25-V Power Supply. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 3118–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-M.; Lee, C.-C.; Jheng, S.-H.; Chen, W.-C.; Lee, B.-Y. A sub-1 ppm/° C precision bandgap reference with adjusted-temperature-curvature compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 64, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnelli, L.; Crupi, F.; Corsonello, P.; Iannaccone, G. A sub-1 V nanopower temperature-compensated sub-threshold CMOS voltage reference with 0.065%/V line sensitivity. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2015, 43, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnelli, L.; Crupi, F.; Corsonello, P.; Pace, C.; Iannaccone, G. A 2.6 nW, 0.45 V temperature-compensated subthreshold CMOS voltage reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 46, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, M.; Habibi, M.; Karimi-Alavijeh, H.R. A 0.4 V, 19 pW subthreshold voltage reference generator using separate line sensitivity and temperature coefficient correction stages. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2021, 140, 153949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B. Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits, 2nd ed. McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2017.
- Aminzadeh, H. Subthreshold reference circuit with curvature compensation based on the channel length modulation of MOS devices. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2022, 50, 1082–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsividis, Y. Operation and Modeling of the MOS Transistor; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Haartman, M.V.; Östling, M.; Haartman, M.v.; Östling, M. 1/F Noise in Mosfets: Origins and modeling. In Low-Frequency Noise In Advanced Mos Devices; 2007; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 53–102. [Google Scholar]
- Fassio, L.; Lin, L.; De Rose, R.; Lanuzza, M.; Crupi, F.; Alioto, M. Trimming-less voltage reference for highly uncertain harvesting down to 0.25 V, 5.4 pW. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 3134–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Transistor | Type | Size |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | Thick oxide | 1 µm/1 µm |
| M2 | Thin oxide | 20 µm/0.18 µm |
| M3 | Thick oxide | 3.7 µm/1 µm |
| M4 | Thick oxide | 0.22 µm/20 µm |
| M5 | Thin oxide | (101.1 µm/0.45 µm) × 4 |
| M6 | Thick oxide | 20 µm/2 µm |
| M7 | Thin oxide | 29 µm/2 µm |
| M8 | Thick oxide | 20 µm/2 µm |
| M9 | Thin oxide | 23 µm/2 µm |
| M10 | Thin oxide | 9 µm/15 µm |
| Parameters | µ | σ | σ/µ |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC (ppm/°C) @0.5 V | 26.7 | 19.2 | 71.9% |
| @2.1 V | 26.8 | 19.2 | 71.6% |
| LS (ppm/V) @25 °C | 17.1 | 10.4 | 60.8% |
| @100 °C | 24.9 | 7.5 | 30.1% |
| VREF (mV) @0.5 V and 25 °C | 195.5 | 13.6 | 7% |
| @2.1 V and 100 °C | 195.5 | 13.9 | 7.1% |
| Power (pW) @0.5 V and 25 °C | 28.8 | 8.2 | 28.5% |
| @2.1 V and 100 °C | 1308 | 305 | 23.3% |
| Design | This Work * | [6] * | [12] | [20] * | [16] | [8] | [25] | [9] | [10] * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tech (µm) | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| Min supply (V) | 0.5 | 0.12 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| LS (ppm/V) | |||||||||
| µ | 17.1 | 2200 † | 190 | 143.8 | 3000 | 330 | 1600 | 1100 | 51.7 |
| 360 T | 51.5 T | ||||||||
| σ | 10.4 | - | 60 | 17.3 | - | - | 500 | - | 10.8 |
| 10 T | |||||||||
| Power (pW) | 28.8 | 0.25 | 48 | 19.1 | 113 | 2.2 29.5 T | 5.4 | 664 | 25.9 25.9 T |
| Temp range (°C) | 0–100 | −40–120 | 0–100 | 0–80 | −40–140 | −20–80 | 0–120 | 0–120 | −20–80 |
| TC (ppm/°C) | |||||||||
| µ | 26.7 | 89.81 | 52 | 39.2 | 73.5 | 62 | 265 | 495 | 34.3 |
| 10.1 T | - | 29 T | 11.6 T | 4.4 T | |||||
| σ | 19.2 | 11.7 | 19 | 28 | 11.7 | 41 | 45 | - | 26.5 |
| 1.5 T | - | 11 | 1.4 T | 7 T | |||||
| PSR (dB) | |||||||||
| @10 Hz | −72 C | −78 C | −62.7 C | −90.9 | - | −50.5 C | −70 | −45 C | −41.2 |
| @10 KHz | −33.3 C | −96 C | −50.2 C | −78 | - | −58.5 C | −83.5 | −55 C | −25.6 |
| VREF (mV) | 195.5 | 65.7 | 147.9 T | 119.2 | 118.1 | 176 | 91.4 | 457.1 T | 206 T |
| Area (µm2) | 2358.8 | 70 | 33,200 | 2183 | 924 | 9300 | 2200 | 1700 | 10,208 |
| FoM (°C·V/W) | |||||||||
| Before trim | 7.61 | 5.18 | 0.22 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 2.22 | 0.06 | 0.001 | 2.18 |
| After trim | - | - | 1.08 | - | - | 0.32 | - | 0.02 | 16.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azimi, M.; Habibi, M.; Crovetti, P. A Two-Stage Sub-Threshold Voltage Reference Generator Using Body Bias Curvature Compensation for Improved Temperature Coefficient. Electronics 2024, 13, 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13071390
Azimi M, Habibi M, Crovetti P. A Two-Stage Sub-Threshold Voltage Reference Generator Using Body Bias Curvature Compensation for Improved Temperature Coefficient. Electronics. 2024; 13(7):1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13071390
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzimi, Mohammad, Mehdi Habibi, and Paolo Crovetti. 2024. "A Two-Stage Sub-Threshold Voltage Reference Generator Using Body Bias Curvature Compensation for Improved Temperature Coefficient" Electronics 13, no. 7: 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13071390
APA StyleAzimi, M., Habibi, M., & Crovetti, P. (2024). A Two-Stage Sub-Threshold Voltage Reference Generator Using Body Bias Curvature Compensation for Improved Temperature Coefficient. Electronics, 13(7), 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13071390







