Abstract
This paper concentrates on bipartite formation control for nonlinear leader-following multi-agent systems (MASs) with fixed and switching topologies under aperiodic Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks. Firstly, distributed control protocols are proposed under the aperiodic DoS attacks based on fixed and switching topologies. Then, considering control gains, as well as attack frequency and attack length ratio of the aperiodic DoS attacks, using algebraic graph theory and the Lyapunov stability method, some criteria are acquired to ensure that the nonlinear leader-following MASs with either fixed or switching topologies can realize bipartite formation under aperiodic DoS attacks. Finally, numerical simulations are carried out to validate the correctness of the theoretical results.
1. Introduction
Multi-agent systems (MASs) have become a significant research direction and have obtained a widespread application in many fields recently, such as modern robotics technology and modern engineering control. MASs offer numerous advantages compared to a single agent, including more efficient and complicated task execution, robustness in the event of agent failure, scalability, adaptability, and so on. As a result of the development of MASs, distributed cooperative control for MASs, including power sharing in sensor networks, the collaborative control mechanism of unmanned surface vehicles, and the formation control of satellites and so on, has attracted significant attention [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15], where the researchers design various control protocols to complete these intricate tasks.
Formation control is a critical aspect of distributed cooperative control of MASs, and its primary objective is to enable agents to accomplish and preserve desired geometric shapes through the formulation of suitable distributed cooperative control protocols. For example, Djamari [16] studied the formation control problem of MASs through scaling factors based on state estimators. Ranjbar et al. [17] investigated the formation control by using complex Laplacian combined with event-triggered strategies under directed graphs. Applying the center of gravity coordinate control method, Yang et al. [18] proposed a distributed planar master-slave formation control strategy. For a class of quadrotors, Liu et al. [19] explored the robust formation control issue. The authors designed a distributed robust control protocol, which includes an attitude controller to manage the rotational motion and a position controller to control the translational motion for the expected formation of each quadrotor. In global positioning system-denied situations, Guo et al. [20] provided a cooperative relative localization infrastructure-free method to achieve formation control. Each agent executes a consensus-based fusion cooperatively without any external infrastructures prepared. Based on a novel high-order finite-time sliding mode consensus control strategy, Li et al. [21] solved the problem of leader-following finite-time robust formation control with time-varying perturbations and parameter uncertainties. Using the asynchronous sampled-data mechanism, He et al. [22] focused on the issue of formation control through output feedback. The authors for linear MASs designed a formation control protocol where each agent estimates its state with a matched state observer by utilizing the asynchronously sampled outputs. Based on the proposed adaptive distributed event-triggered model predictive control strategy by using the information of the adjacent vehicles, Zhu et al. [23] investigated the trajectory tracking and formation control problem of unmanned aerial vehicles. Considering collision avoidance limitations and constraint communication ranges of MASs, Huang et al. [24] proposed a collision-free and connectivity preservation distributed control method to solve the formation control issue. In summary, as a main and important research direction, formation control has attracted much attention from many researchers. However, it is worth noting that the research results above only concentrate on the construction of strategies and consider ideal scenarios relatively: considering that the relationship between agents is only cooperative in the system, resulting in the strategies investigated more valuable theoretically but reducing their engineering applicability.
In social systems, as well as natural and engineering situations, competitive relationships frequently coexist with cooperative relationships. It is more common for MASs to participate in competition-cooperation relationships. Compared with the traditional formation control problem, bipartite formation enables agents to achieve two formation structures in opposite directions. Zhang et al. [25] explored the multi-group formation for nonlinear MASs based on a neural network approximator. Utilizing signed directed topology, Yang et al. [26] explored the bipartite leader-following consensus issues. Wang et al. [27] analyzed the adaptive bipartite formation with hybrid impulses based on the state-feedback method. For MASs with heterogeneous groups, Li et al. [28] investigated the issue of hybrid bipartite formation tracking based on the leading-following method. The authors designed a new control strategy using leader dynamics and neighbor information, where the second-order agents in the first group have unknown input to track their leader, and a velocity estimator is designed for the first-order agents in the other group. Considering limited communication resources for uncertain linear MASs, Cai et al. [29] explored the bipartite time-varying formation control by proposing a static bipartite control strategy and a fully adaptive event-triggered bipartite control scheme, respectively. For heterogeneous MASs with multiple leaders, Cai et al. [30] addressed the problem of fixed-time bipartite time-varying output formation-containment tracking based on the bipartite fixed-time compensator. Based on an unknown input observer and an interval observer for heterogeneous MASs with external disturbances, Zhao et al. [31] investigated the problem of bipartite formation containment tracking. Based on a semi-signed directed graph, Du et al. [32] addressed the issue of bipartite formation group containment for MASs with unknown input leaders and multi-layer networks. The authors designed different control protocols for the containment layer and formation layer, respectively. Considering time-varying linear MASs with matched uncertainties and multiple leaders, Li et al. [33] explored the problem of bipartite output formation tracking. Based on the event-triggered strategy and relative information between the neighboring agents, the authors designed an independent, asynchronous, fully controlled scheme.
The works mentioned above were acquired in a secure information transmission environment, which is unrealistic because communication networks may suffer from complex malicious attacks [34,35]. For example, denial of service (DoS) is a class of typical internet attacks and has received significant attention in recent studies for multi-agent systems. DoS attacks can disrupt communication between two agents, resulting in potential instability of the system. The various types of DoS attacks can be categorized into two primary classes: periodic attacks and aperiodic attacks. Periodic DoS attacks take into account the attacker’s limited energy, allowing them to have certain windows of time for action and rest, and usually conform to a certain distribution (such as the Bernoulli distribution) or satisfy a certain periodicity to simplify model analysis. The aperiodic DoS attacks launched for each agent of MASs are random. Considering DoS attacks, Zhao et al. [36] studied the fault-tolerant control for MASs based on state feedback methods. Wang et al. [37] studied the elastic formation control based on the event-triggered mechanism with periodic DoS attacks. Utilizing state observers, Ren et al. [38] studied the consensus control of nonlinear MASs under DoS attacks. Based on complex Laplacian and event-triggered methods, Wang et al. [37] investigated the problem of attack-resilient formation control for MASs under DoS attacks formulated as Bernoulli distribution. The designed attack-resilient mechanism is used to solve formation shape problems. Considering DoS attacks and parameter uncertainties, Wang et al. [39] investigated the problem of consensus for time-varying MASs based on an event-triggered control method. Utilizing state-dependent thresholds, a novel event-driven mechanism is designed, and the complementary linearization algorithm is proposed. Liu et al. [40] explored the problem of bounded consensus for leader-following MASs with DoS attacks by means of event-triggered schemes and an optimization approach. Considering the situation of communication interruption, Ma et al. [41] addressed the problem of impulsive consensus of T-S fuzzy MASs with nonlinear dynamics under DoS attacks by designing a discontinuous Lyapunov function. Wang et al. [42] explored the problem of event-triggered resilience for cyber-physical systems under periodic DoS attacks. An event-triggered strategy without Zeno behaviors is designed to eliminate the occurrence of invalid events and save network resources during periodic DoS attacks by formulating an event-triggered predictor-based control framework. Considering periodic DoS attacks and packet dropout modeling by two independent Bernoulli distributions. Su et al. [43] explored the problem of observer-based output feedback control for cyber-physical systems. It is necessary to consider the type of DoS attack to be aperiodic, which is more extensive and general in practical situations than periodic DoS attacks.
Furthermore, it is practical in the article to consider a mathematical nonlinear term further owing to the intricate nonlinear dynamics of each agent [44,45,46]. Meanwhile, considering the practical situation of information transmission, the communication topology of MASs may be switched. Switching topology may affect system performance, causing unpredictable instability and even destroying the stability of systems. Therefore, it is significant and challenging to explore the bipartite formation issue of nonlinear leader-following MASs further with fixed and switching topologies under aperiodic DoS attacks.
Inspired by the discussions above, addressing the problem of leader-following bipartite formation control under DoS attacks, the paper designs distributed bipartite formation control protocols based on the position and velocity error between agents to achieve bipartite formation for MASs under both the situation of fixed and switching topologies. The main contribution points are shown as follows:
- This paper investigates the formation control problem considering the competitive relationship in MASs, and our study is more extensive.
- The distributed control protocols are proposed considering the situations of both fixed and switching topologies for nonlinear MASs with aperiodic DoS attacks, which is more practical and general.
- Sufficient conditions are obtained and proved in detail to ensure that nonlinear leader-following MASs with either fixed or switching topologies can realize bipartite formation under aperiodic DoS attacks.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 gives some preliminaries and presents the studied model. Section 3 investigates the bipartite formation based on fixed and switching topologies under aperiodic DoS attacks. Section 4 provides simulations to illustrate the feasibility of the designed control strategies. We conclude the results in Section 5.
2. Preliminaries and Model Formulation
2.1. Preliminaries
- (1)
- Notations
represents the Euclidean space of dimension and denotes a set of matrices. Let be a real matrix with minimum eigenvalue and maximum eigenvalue . The transpose of a matrix is represented by . denotes the diagonal matrix. represents the absolute value of a number. represents the Euclidean norm of a vector. denotes the standard signum function.
- (2)
- Graph Theory
We discuss a MAS comprising a leader numbered and followers numbered . The interactive topology among the followers is represented by a weighted signed graph , where denotes the vertex set, the edge set, and denotes the weighted adjacency matrix. If , then ; , otherwise. For an undirected graph, implies . and denote the competitive and collaborative relationship between two agents. Then, represents the set of neighbors of the agent . is the degree matrix where . is the adjacency matrix of the unsigned graph . Correspondingly, define the Laplacian matrix of the signed graph and unsigned graph as and , respectively. Under leader-following topology, define , where indicates the leader can transmit information to the th agent, otherwise . shows the interactive topology of the MAS, and the corresponding Laplacian matrix is .
Definition 1 ([47]).
If the signed graph is structurally balanced, then
satisfy the conditions as follows:
- (i)
- , .
- (ii)
- , for all , .
- (iii)
- , for all , , , .
Remark 1.
The node bipartition of a structurally balanced graph is characterized by a diagonal matrix , where for
and
for
.
Assumption 1.
is structurally balanced.
Assumption 2.
contains a spanning tree, and the leader is the root node.
Lemma 1 ([47]).
There exists such that
has all nonnegative entries if and only if corresponding signed graph
is structurally balanced.
Lemma 2 ([48]).
Under Assumption 2, the unsigned Laplacian matrix satisfies the following conditions:
- (i)
- The matrix is positive definite.
- (ii)
- for all .
- (3)
- Aperiodic DoS Attacks
This part briefly introduces the aperiodic DoS attacks. Figure 1 depicts the aperiodic DoS attack sequence. Define and as the aperiodic DoS attack sequences and the duration of the th aperiodic DoS attack, respectively. There are and . The th DoS attack is represented by the time interval of . For , define
and
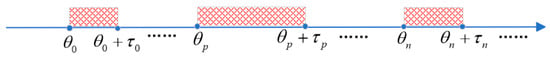
Figure 1.
The aperiodic DoS attacks model.
Note that and are the time intervals for successful information transmission and communication interruption during , respectively.
Definition 2 ([49]).
Let represent the total number of attacks on the system during time period
, then the aperiodic DoS attack frequency is defined as
Definition 3 ([49])
Let represent the total duration of the aperiodic DoS attack on interval
; the attack length ratio is defined as
Remark 2.
Compared with [34,37], the DoS attack considered for MASs is aperiodic in the paper. The systems under aperiodic attacks are more extensive in practical situations.
2.2. Model Formulation
Consider a MAS with followers and a leader. The dynamic equations of the followers are modeled by
where and represent the position and velocity of the th agent, respectively; denotes the th agent control input(acceleration-level) that needs to be designed; models the nonlinear dynamics of the th agent. The leader’s dynamic equation is given as
where the corresponding variables are similar to the definition of follower.
Assumption 3.
The function
satisfies the condition , which indicates that
is an odd function of .
Assumption 4.
satisfies the following Lipschitz condition
where
is a positive constant.
Definition 4 ([27]).
Define as the formation position error between the agent
and , the MAS (5) and (6) can realize bipartite formation control if
where
if
,
if
,
is the desired position.
3. Analysis of Model and Main Results
3.1. Bipartite Formation Control with Fixed Topology under Aperiodic DoS Attacks
The situation of fixed topology under aperiodic DoS attacks for the MAS (5) and (6) is addressed in this part. The distributed control protocol is proposed as
where and are control gains, represents the collaboration relationship or competition relationship between two agents.
Theorem 1.
Suppose Assumptions 1–4 hold. Under the control protocol (10), the bipartite formation can be realized for the MAS (5) and (6) with fixed topology under aperiodic DoS attacks if the gains and satisfy
and there exists a constant
such that the
and the
of the aperiodic DoS attacks satisfy
and
where , , , , .
Proof.
Under Assumption 1 and Lemma 1, there exists that makes has all nonnegative entries. Let , , . Notice that and for . By Assumption 3, the control protocol can be rewritten as follows
Then, the dynamic equation of the follower can be written as
Let , , . When , the Equation (15) can be rewritten as
For the system (16), choose a Lyapunov function candidate as
Since Assumption 2 holds, Lemma 2 is satisfied. We can get that is positive definite and its time derivative along the trajectory of system (16) is
According to Assumption 4, we can get
Finally, we can obtain
Obviously, if the control gains satisfy , we can get . Using Lyapunov theory, the system (16) is stable when .
Denote . We consider following the Lyapunov function candidate when for the system(16) as
The derivative of along the trajectory in the system (16) is that
By comparing and combing Equations (20) and (22), when and , we define and , respectively. Then, we can obtain
and
respectively. According to Definitions 2 and 3, for and for . Since , we can obtain for
Denote . We can get
which implies that when . Hence, both and hold. Thus, under the protocol (10), the bipartite formation for the MAS (5) and (6) with fixed topology under aperiodic DoS attack is realized. □
3.2. Bipartite Formation Control with Switching Topology under Aperiodic DoS Attacks
The situation of switching topology for MAS (5) and (6) under aperiodic DoS attacks is addressed in this section.
Define a set of graphs with possible topologies and its index set . Denote indicates different switching topologies of the system. Define an infinite time intervals series , , with and as . At time , the communication topology of the system is represented by . Different from the fixed topology, the communication weights and signed Laplacian matrix are time-varying owing to the switching bipartite graph . During the interval , suppose the interaction topology is time-invariant. Therefore, there is an assumption throughout this section.
Assumption 5.
There is at least one follower who can communicate with the leader for the MAS (5) and (6) with switching topology under the aperiodic DoS attacks, which indicates .
The distributed control protocol with switching topology under the aperiodic DoS attacks is designed as
where is the group of neighbors of the agent in the situation of switching topology.
Theorem 2.
Suppose Assumptions 1–5 hold. Under the control strategy (27), the bipartite formation can be achieved for the MAS (5) and (6) with switching topology under the aperiodic DoS attacks if the gains and satisfy
and there exists a constant
such that the
and the
satisfy
and
where , , , , .
Proof.
The equations of the MAS (5) and (6) are simply written as
under the distributed protocol (27). According to the analysis of Theorem 1, we can conclude
when , and introduce a Lyapunov function candidate as
Analogically, if is satisfied, it implies . When , we choose the same Lyapunov candidate function as Theorem 1. Since the next proof procedure is similar to Theorem 1, it is therefore omitted. Thus, we can conclude that bipartite formation can be achieved for the MAS (5) and (6) with switching topology under the aperiodic DoS attacks. □
Remark 3.
In the situation of switching communication topologies, it can be seen that the minimum eigenvalue of all corresponding Laplacian matrices is significant for MASs to achieve bipartite formation. If the control gain is selected based on the minimum eigenvalue, and the attack frequency and attack length ratio of DoS attacks meet the theorem conditions, the bipartite formation control for MASs with switching topology under DoS attacks can be realized.
4. Simulation
Simulations are shown in this section to validate the feasibility of the theoretical results.
Example 1.
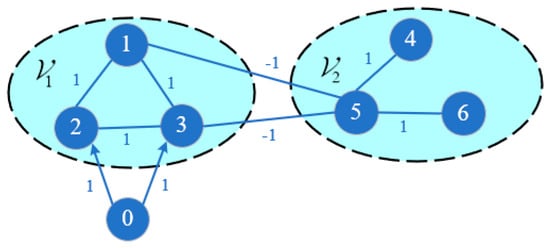
We analyze the MAS (5) and (6), where the followers are numbered from 1–6, and the leader is numbered by 0. According to Definition 1, Figure 2 illustrates the fixed structurally balanced communication topology. Furthermore, two node sets and can be obtained from Figure 2, respectively. The corresponding matrix , and associated with is given by

Figure 2.
The fixed communication topology .
The initial positions of all agents are randomly distributed near the origin of the coordinates. Select the nonlinear dynamics for the followers and leader as , which guarantees that Assumptions 2 and 3 hold. Let the gain , , and choose . Suppose that the time intervals in which aperiodic DoS attacks occur are , , , and .
Figure 3 illustrates the trajectories of all agents of the MAS (5) and (6) with fixed topology under aperiodic DoS attacks. Based on the structurally balanced communication topology, the agents are divided into two subgroups. The followers in set form a desired triangular formation, moving to the right along the x-axis, with the leader positioned inside. The remaining followers in set move in the opposite direction, maintaining the same desired formation. Figure 4 shows the evolutions of the norms of followers’ formation position error states with fixed topology under aperiodic DoS attacks. It can be seen that all the formation position errors converge to zero. Figure 5 depicts the evolutions of the followers’ velocity states with fixed topology under aperiodic DoS attacks. It can be observed that agents within the same node set converge to the same velocity, while agents in different node sets have the same velocity magnitude but opposite signs. Thus, from Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5, it is not difficult to verify that the bipartite formation for the MAS (5) and (6) with fixed topology under aperiodic DoS attacks is accomplished.
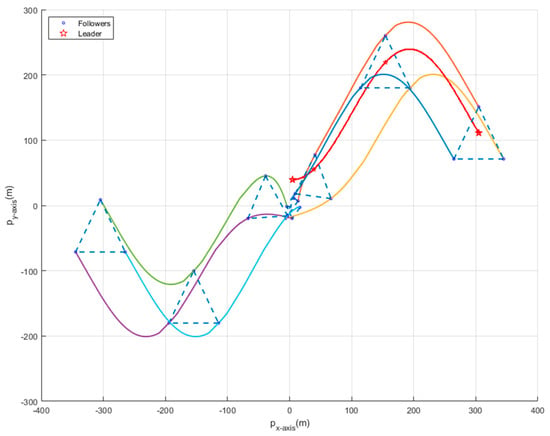
Figure 3.
Trajectories of all agents with fixed topology under aperiodic DoS attacks.
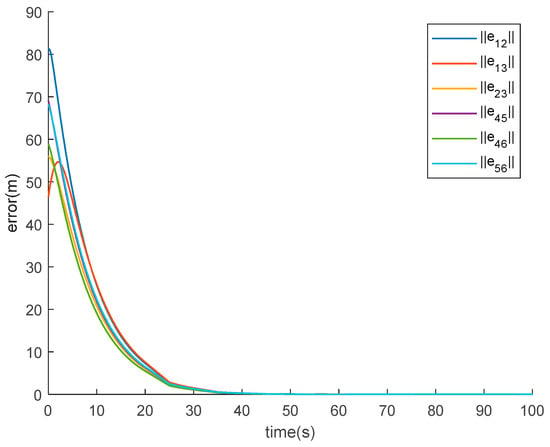
Figure 4.
The norm of followers’ position errors with fixed topology under aperiodic DoS attacks.
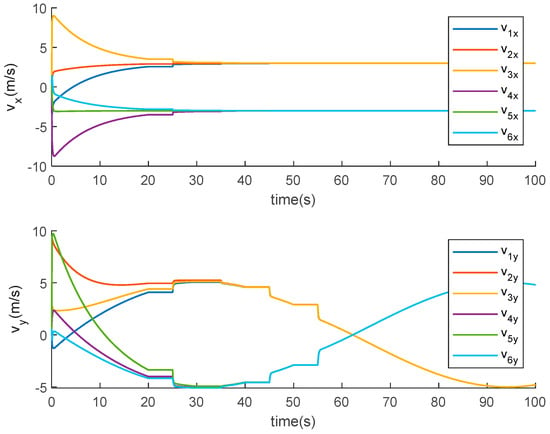
Figure 5.
Evolutions of followers’ velocity states with fixed topology under aperiodic DoS attacks.
Example 2.
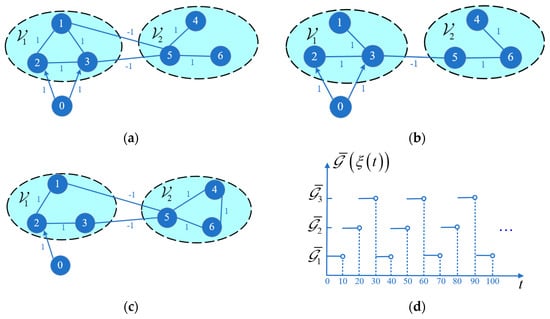
In the example of switching topology, the followers are divided in the same way as in Example 1. The switching communication topologies that switches as with a switching period of 10 s are shown in Figure 6. The corresponding matrix , and associated with , and is shown by
respectively. Obviously, and . The matrix is the same as in Example 1. The initial positions of all agents are also randomly distributed near the origin of the coordinates, as in Example 1. The nonlinear terms are selected using the same criteria as in Example 1. Select , and . Suppose that the time intervals in which aperiodic DoS attacks occur are , , under switching topology.

Figure 6.
The switching topologies and switching periodic signals (a–c) represent the topology , , and , respectively. (d) represents the switching periodic signals.
Figure 7 shows the trajectories of all agents of the MAS (5) and (6) with switching topology under DoS attacks. The agents form two desired triangular formations and move in opposite directions. Figure 8 describes the evolutions of the norms of followers’ formation position error states with switching topology under aperiodic DoS attacks. We can see that all the formation position errors converge to zero. Figure 9 depicts the evolutions of the followers’ velocity states. We can get that for the MAS (5) and (6) with switching topology under aperiodic DoS attacks, the followers’ velocity states achieve bipartite consensus, similar to in Example 1. Thus, from Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9, we can see that the MAS (5) and (6) can realize the bipartite formation with switching topology under aperiodic DoS attacks.
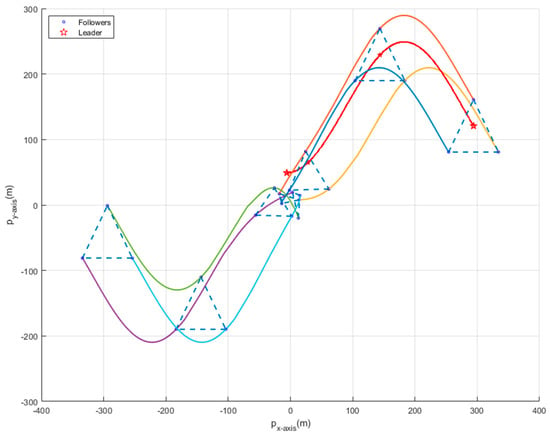
Figure 7.
Trajectories of all agents with switching topology under aperiodic DoS attacks.
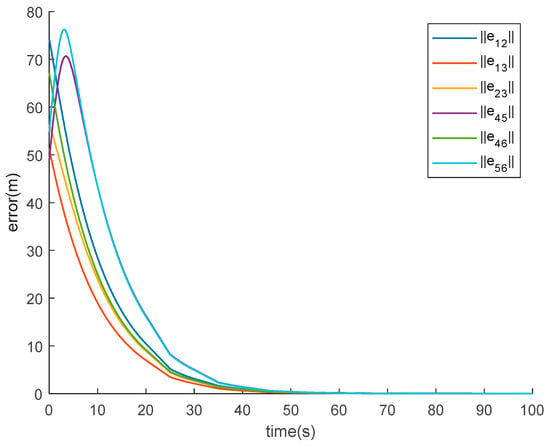
Figure 8.
The norm of followers’ position errors with switching topology under aperiodic DoS attacks.
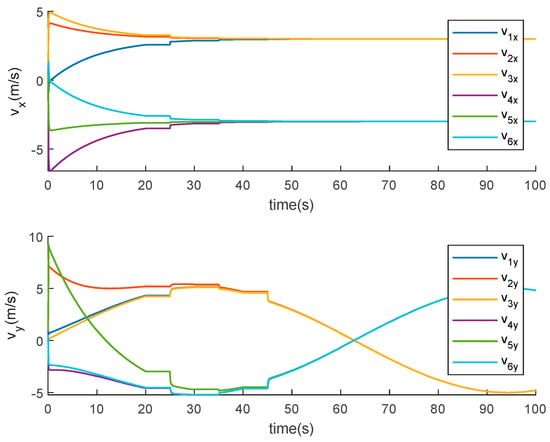
Figure 9.
Evolutions of followers’ velocity states with switching topology under aperiodic DoS attacks.
5. Conclusions
This paper explored the bipartite formation problem for nonlinear leader-following MASs with fixed and switching topologies under aperiodic DoS attacks. The distributed bipartite formation control strategies were designed and analyzed in detail. By employing algebraic graph theory and the Lyapunov stability method, some criteria are derived such that the nonlinear leader-following MASs with fixed and switching topologies under aperiodic DoS attacks were proven to realize the bipartite formation control using the designed control protocols, i.e., the followers are capable of achieving and upholding desired bipartite formations. Finally, two simulations were given to verify the correctness of the theoretical results. From the numerical simulations of the MASs with either fixed topology or switching topology under aperiodic DoS attacks, one can see that all agents with arbitrary initial positions achieve the desired triangle formation and move in opposite directions.
This paper represents an effective endeavor in the research direction of distributed bipartite formation control for MASs with fixed topology and switching topology under aperiodic DoS attacks. It offers theoretical value and practical application prospects. However, the control protocols proposed in this study also have certain limitations. For example, it is hard to solve the case where MASs suffer from finite communication bandwidth, restricted communication range, or sensor measurement noise.
In our future work, we will further explore the fixed-time or described-time bipartite formation control problem for the heterogeneous MASs under aperiodic DoS attacks with transmission delays and data packet loss, which is more extensive and feasible in practical engineering applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.L. and S.L.; methodology, funding acquisition, project administration, T.L.; software, writing-original draft preparation, S.L.; methodology, formal analysis, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, Y.H.; validation, J.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61873287.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zeng, X.; Hui, Q. Energy-Event-Triggered Hybrid Supervisory Control for Cyber-Physical Network Systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 3083–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Cao, H.; Fu, Y. Decentralized Adaptive Flocking Control Algorithm with Avoiding Collision and Preserving Connectivity for Crowded UUV Swarm with Uncertainties and Input Saturation. Ocean Eng. 2021, 237, 109545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Tian, S.; Zhou, B.; Han, Q.; Tian, Y.; Weng, T.; Mamut, T. Consensus of Fixed and Adaptive Coupled Multi-Agent Systems with Communication Delays. Electronics 2023, 12, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zong, G.; Zhao, X.; Huo, X. Observed-Based Adaptive Finite-Time Tracking Control for a Class of Nonstrict-Feedback Nonlinear Systems with Input Saturation. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 11518–11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Xia, X.; Sun, X. Formation Control with Collision Avoidance for Underactuated Surface Vehicles. Asian J. Control 2022, 24, 2244–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwe, M.; Schubert, K.; Vermet, F. Multi-Group Binary Choice with Social Interaction and a Random Communication Structure—A Random Graph Approach. Phys. Stat. Mech. Appl. 2020, 556, 124735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Shi, J.; Wen, F. Phase Compensation-based 2D-DOA estimation for EMVS-MIMO radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gao, Z. A Distributed Flocking Control Strategy for UAV Groups. Comput. Commun. 2020, 153, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Wang, H.; Gui, G.; Sari, H.; Adachi, F. Polarized intelligent reflecting surface aided 2D-DOA estimation for NLoS sources. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, S. Collaboration of Multiple SCARA Robots with Guaranteed Safety Using Recurrent Neural Networks. Neurocomputing 2021, 456, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, B. Distributed Adaptive Fault-Tolerant Control for Leaderless/Leader–Follower Multi-Agent Systems against Actuator and Sensor Faults. Electronics 2023, 12, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Guan, Z.-H.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, D.-F.; Zhang, X.-H.; Xiao, J.-W. Three-Dimensional Containment Control for Multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. J. Frankl. Inst. 2016, 353, 2929–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zhang, W. Trajectory Tracking Control of AUVs via Adaptive Fast Nonsingular Integral Terminal Sliding Mode Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 1248–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Guo, W.; Wang, L.; Bekiros, S.; Alsubaie, H.; Alotaibi, A.; Jahanshahi, H. Stochastic Fixed-Time Tracking Control for the Chaotic Multi-Agent-Based Supply Chain Networks with Nonlinear Communication. Electronics 2022, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Esa, Y.; Mohamed, A. Applications of Complex Network Analysis in Electric Power Systems. Energies 2018, 11, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamari, D.W. Distributed Position Estimation Approach for Multiagent Formation with Size Scaling. Asian J. Control 2022, 24, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, M.; Beheshti, M.T.H.; Bolouki, S. Event-Based Formation Control of Networked Multi-Agent Systems Using Complex Laplacian Under Directed Topology. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2021, 5, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, D.; Duan, H. Distributed Planar Formation Maneuvering of Leader-Follower Networked Systems via a Barycentric Coordinate-Based Approach. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, T.; Lewis, F.L.; Wan, Y. Robust Formation Control for Multiple Quadrotors with Nonlinearities and Disturbances. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Li, X.; Xie, L. Ultra-Wideband and Odometry-Based Cooperative Relative Localization with Application to Multi-UAV Formation Control. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 50, 2590–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Gao, J.; Liu, P.X. Finite-Time Robust Formation Control of Multiple Aerial Robotic Vehicles with Uncertainties and Time-Varying Complex Perturbations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2024, 129, 107672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Liu, W. Formation Control for Linear Multi-Agent Systems with Asynchronously Sampled Outputs. Inf. Sci. 2024, 658, 119992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, S.; Guo, G.; Yuan, P.; Bai, J. Formation Control of UAV–USV Based on Distributed Event-Triggered Adaptive MPC with Virtual Trajectory Restriction. Ocean Eng. 2024, 294, 116850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Meng, Z.; Dimarogonas, D.V. Prescribed Performance Formation Control for Second-Order Multi-Agent Systems with Connectivity and Collision Constraints. Automatica 2024, 160, 111412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, T.; Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Xue, B. Multi-Group Formation Tracking Control for Second-Order Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems Using Adaptive Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 168207–168215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Peng, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, F. Bipartite Consensus of Linear Multi-Agent Systems by Distributed Event-Triggered Control. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2021, 34, 955–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, C.; Huang, C.; Cao, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, L. Bipartite Formation Problem of Second-Order Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with Hybrid Impulses. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 370, 124926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Du, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, L. Bipartite Hybrid Formation Tracking Control for Heterogeneous Multi-Agent Systems in Multi-Group Cooperative-Competitive Networks. Appl. Math. Comput. 2023, 456, 128133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xi, R.; He, Q. Fully Distributed Bipartite Time-varying Formation Control for Uncertain Linear Multi-agent Systems under Event-triggered Mechanism. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2021, 31, 5165–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Z.; He, Q. Adaptive Bipartite Fixed-Time Time-Varying Output Formation-Containment Tracking of Heterogeneous Linear Multiagent Systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 4688–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhu, F.; Xu, D. Self-Triggered Bipartite Formation-Containment Control for Heterogeneous Multi-Agent Systems with Disturbances. Neurocomputing 2023, 548, 126382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, W.; Xiao, J.; Chen, Z. Bipartite Time-Varying Formation Group Containment Control for Multi-Agent Systems Based on Multi-Layer Network and Semi-Signed Directed Graph. J. Frankl. Inst. 2023, 360, 1929–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Y. Fully Distributed Event-Triggered Bipartite Formation Tracking for Multi-Agent Systems with Multiple Leaders and Matched Uncertainties. Inf. Sci. 2022, 596, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Sun, H.; Hou, L. Decentralized Event-Triggered Adaptive Neural Network Control for Nonstrict-Feedback Nonlinear Interconnected Systems with External Disturbances against Intermittent DoS Attacks. Neurocomputing 2023, 517, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadpour, A.; Ja’fari, F.; Taleb, T.; Shojafar, M.; Yang, B. SCEMA: An SDN-Oriented Cost-Effective Edge-Based MTD Approach. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2023, 18, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, G.-H. Adaptive Fault-Tolerant Control for Nonlinear Multi-Agent Systems with DoS Attacks. Inf. Sci. 2020, 526, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Wu, P. Attack-Resilient Event-Triggered Formation Control of Multi-Agent Systems under Periodic DoS Attacks Using Complex Laplacian. ISA Trans. 2022, 128, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.-E.; Li, R. Switched Observer-Based Dynamic Event-Triggered Consensus of Multi-Agent Systems under DoS Attacks. J. Frankl. Inst. 2023, 360, 4331–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Y. Event-Triggered Based Security Consensus Control for Multi-Agent Systems with DoS Attacks. Neurocomputing 2022, 505, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Event-Triggering-Based Leader-Following Bounded Consensus of Multi-Agent Systems under DoS Attacks. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2020, 89, 105342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, B. Impulsive Consensus of Nonlinear Fuzzy Multi-Agent Systems under DoS Attack. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 2022, 44, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.-B.; Ren, X.-M.; Zheng, D.-D. Event-Triggered Resilient Control for Cyber-Physical Systems under Periodic DoS Jamming Attacks. Inf. Sci. 2021, 577, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Ye, D. Reprint of: Observer-Based Output Feedback H ∞ Control for Cyber–Physical Systems under Randomly Occurring Packet Dropout and Periodic DoS Attacks. ISA Trans. 2020, 104, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschelli, M.; Pisano, A.; Giua, A.; Usai, E. Finite-Time Consensus with Disturbance Rejection by Discontinuous Local Interactions in Directed Graphs. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Deng, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, Z.; Cao, H.; Wei, Z. Fast Integral Terminal Sliding Mode Control with a Novel Disturbance Observer Based on Iterative Learning for Speed Control of PMSM. ISA Trans. 2023, 134, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.-Z.; Li, Y.-X.; Hou, Z.-S. Distributed Model-Free Adaptive Control for Multi-Agent Systems with External Disturbances and DoS Attacks. Inf. Sci. 2022, 613, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altafini, C. Consensus Problems on Networks with Antagonistic Interactions. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olfati-Saber, R.; Murray, R.M. Consensus Problems in Networks of Agents with Switching Topology and Time-Delays. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2004, 49, 1520–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Gong, Y. Leader-Following Secure Consensus for Second-Order Multi-Agent Systems with Nonlinear Dynamics and Event-Triggered Control Strategy under DoS Attack. Neurocomputing 2020, 416, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).