A Power Analysis Method for Self-Interference Signal Components in Full-Duplex Transceivers Under Constant/Nonconstant Modulus Signal Stimulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A theoretical analysis tool for PA nonlinearities is proposed, which is capable of observing in-band nonlinearities. While conventional communication and radar systems tend to focus on adjacent-band nonlinearities, in-band nonlinearities also do matter.
- It offers a theoretical basis for simplifying the design of SIC methods. As indicated in this paper, full-duplex devices in different application scenarios have different performance requirements for the SIC method, and thus their realization difficulties vary.
- The system-level power analysis methods can be employed to assess the effectiveness of all types of SICs. A verification of whether the SI has been suppressed below the receiver noise level can be conducted according to the system-level power model.
2. Signal Model
3. Power Analysis Method
3.1. Quantitative Analysis of PA Nonlinear Component
| Algorithm 1 Separate analysis of linear and nonlinear components |
|
3.2. The System-Level Power Model
4. Simulation Analysis and Verification
4.1. The PA Nonlinear Component
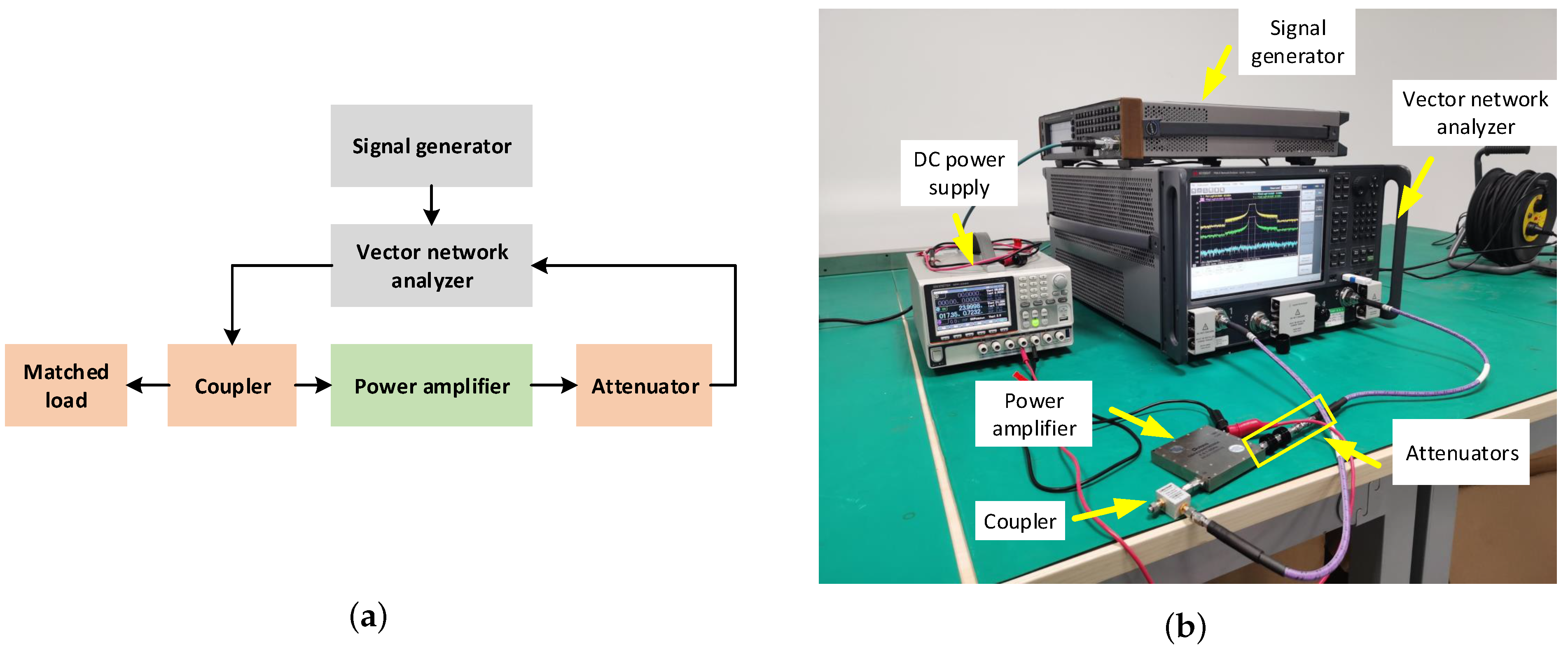
4.1.1. Signal Parameter and Experimental Setup
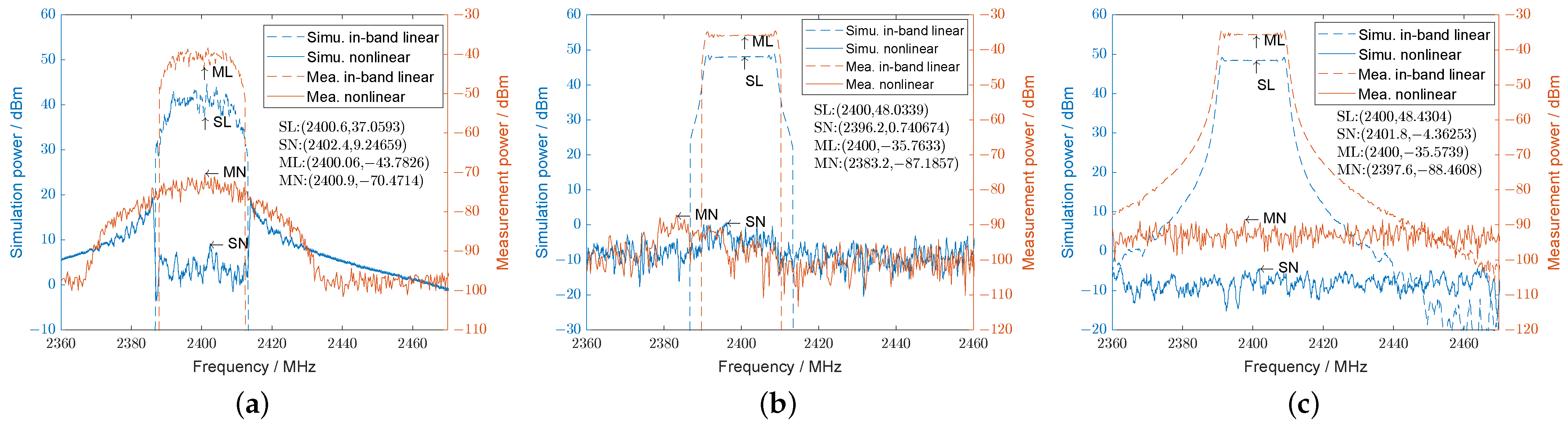
4.1.2. Simulation and Measurement Analysis
- The method of analyzing PA output signal components through behavioral models is universally significant for analysis in different application scenarios.
- Regardless of the state in which the PA operates, it does not generate nonlinear distortion when excited by the LFMCW signal.
- If the constant modulus signal contains rectangular window modulation in the time domain, in-band nonlinear distortion will be introduced by the PA but will be smaller than the nonconstant modulus signal.
4.2. The System-Level Power Model
4.2.1. The Transceiver Parameter Setup
4.2.2. Transceiver Platform Establishment
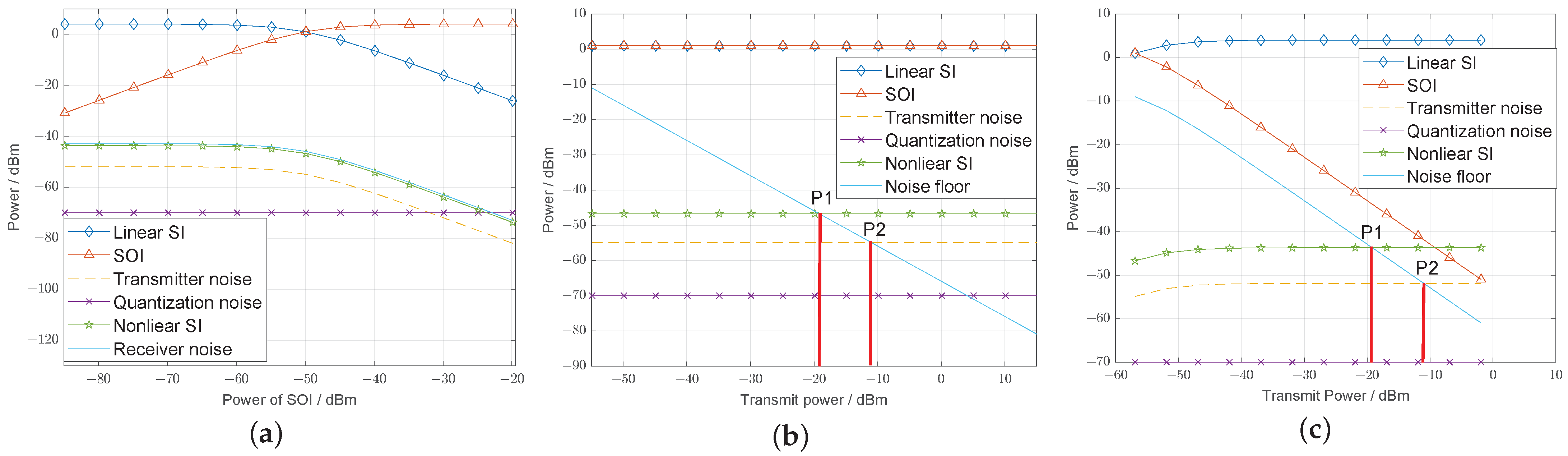
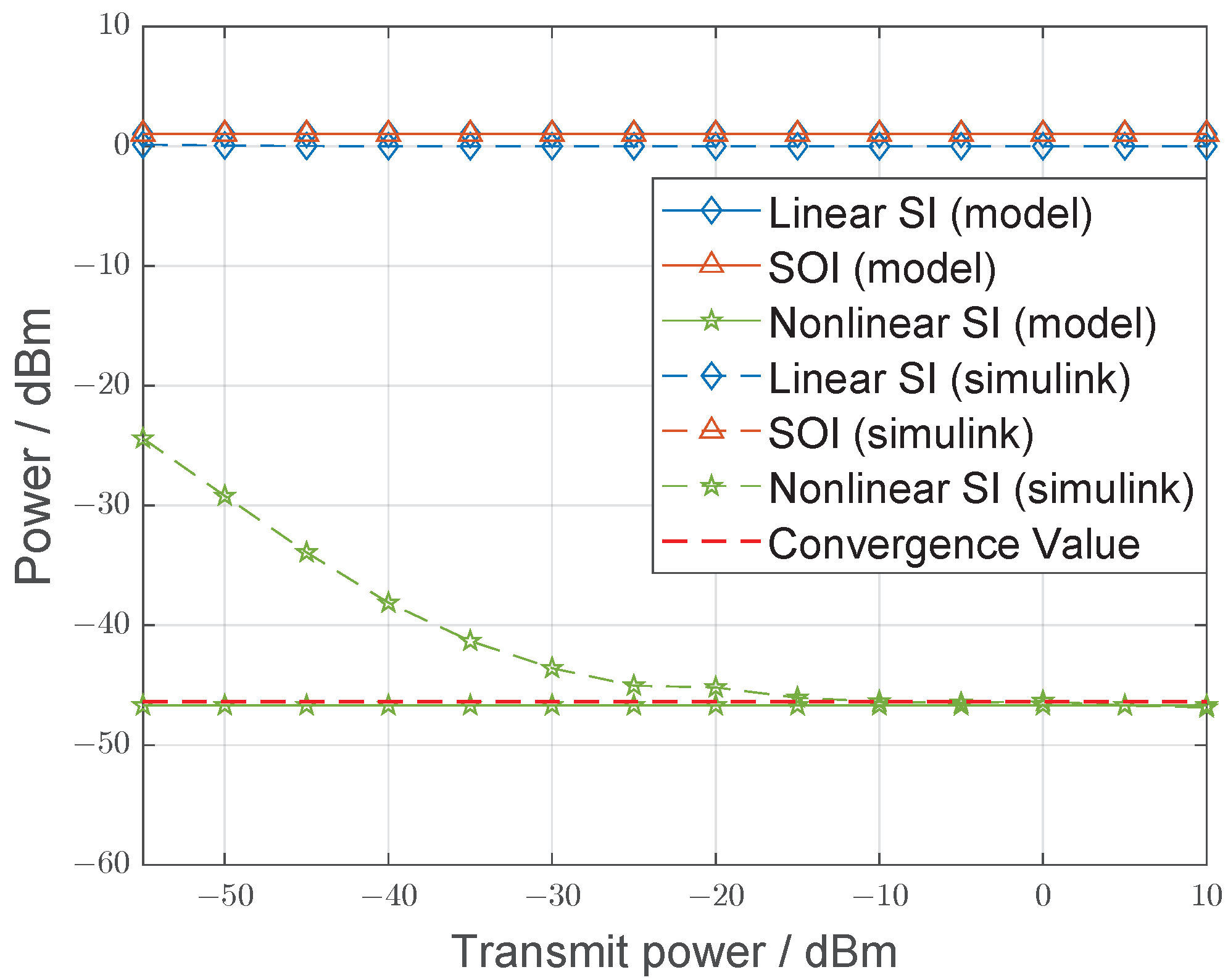
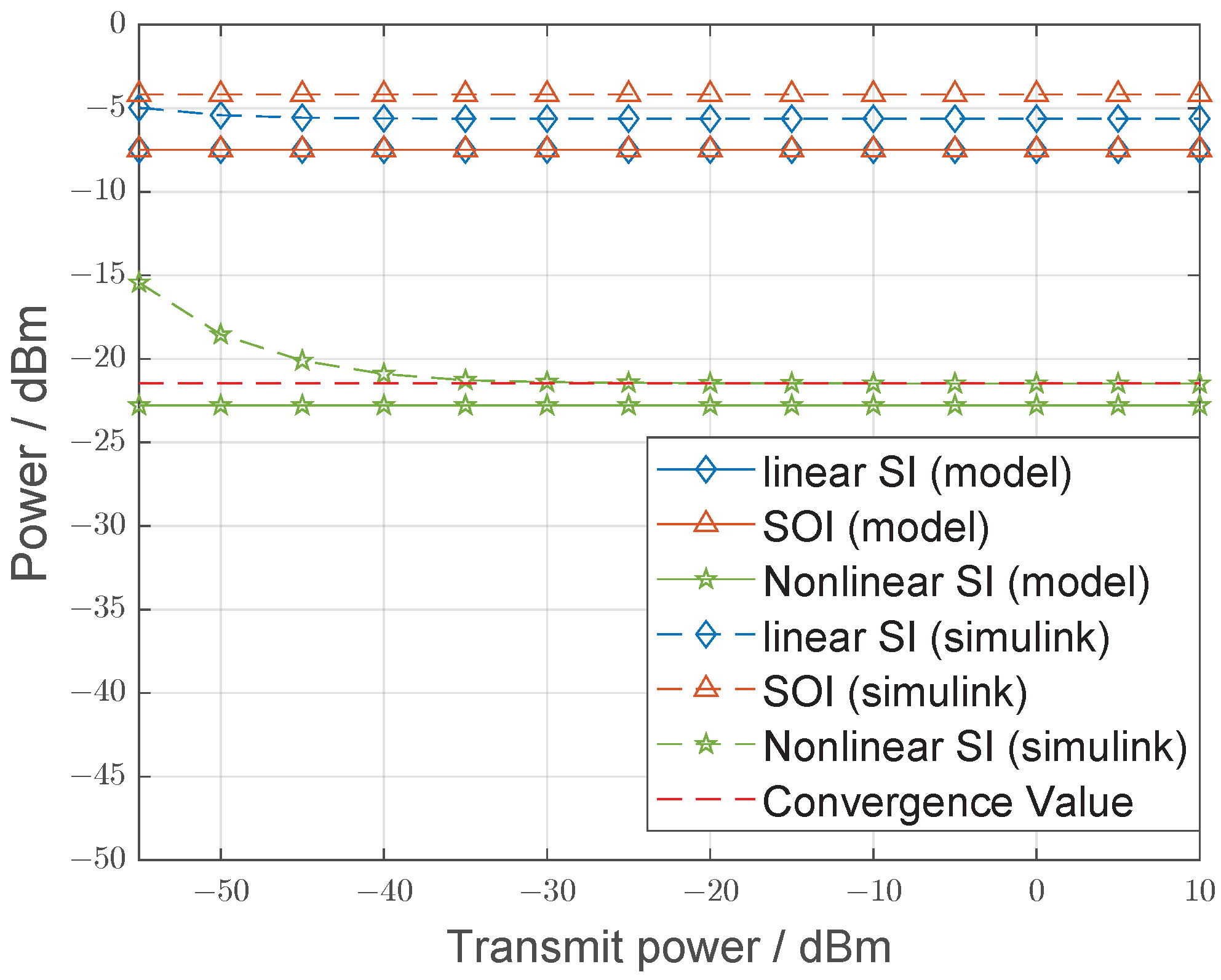
4.2.3. Constant Modulus Signal Stimulation
4.2.4. Nonconstant Modulus Signal Stimulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Hara, F.; Moore, G. A high performance CW receiver using feedthrough nulling. Microw. J. 1963, 6, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Henson, B.; Shen, L.; Zakharov, Y. Full-duplex UAC receiver with two-sensor transducer. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2022, 69, 4764–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, H.; Riihonen, T.; Suraweera, H.A. Full-Duplex Communications for Future Wireless Networks; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, C.; Hu, W.; Yuan, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X. Multi-domain self-interference cancellation methods considering RF imperfections. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 8668–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Self-interference digital cancellation algorithm in simultaneous transceiver system based on deep neural network. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2022, 44, 4229–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Luo, J. The research on digital cancellation in simultaneous transmission and reception technology. J. Signal. Pro. 2017, 33, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.; Bernhardt, M.; Riihonen, T. Full-duplex constant-envelope jamceiver and self-interference suppression by highpass filter: Experimental validation for WI-FI security. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2023, 41, 2937–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.; Bernhardt, M.; Riihonen, T. Full-duplex multifunction transceiver with joint constant envelope transmission and wideband reception. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 8258–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayar, H.; Gurbuz, O. Switched radio architecture with non-Linear frequency-domain estimation for in-band full-duplex Communication. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 1651–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayati, S.-A.; Alizadeh, A.; Kiaei, S. CMOS full-duplex mixer-first receiver with adaptive self-interference cancellation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. 2021, 68, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej, K.E. In-Band Full-Duplex Wireless Systems Handbook; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J. A foreground wide-band receiver I/Q mismatch calibration method in FDD transceiver. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ye, F.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y. Multi-head self-attention mechanism combined with feedforward network for time-varying nonlinear digital self-interference cancellation. Digit. Signal Prog. 2024, 155, 104699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, K.M.; Cosmas, J.P.; Bard, M.; Gledhill, J. Performance of an echo canceller and channel estimator for on-channel repeaters in DVB-T/H networks. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2007, 53, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, M.S.; Chung, M.; Kim, D.; Chung, J.; Kim, D.K.; Chae, C. Nonlinear self-interference cancellation for full-duplex radios: From link-level and system-level performance perspectives. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannouchi, F.M.; Hammi, O.; Helaoui, M. Behavioral Modeling and Predistortion of Wideband Wireless Transmitters; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, D.; Ma, Z.; Kim, J.; Zierdt, M.; Pastalan, J. A generalized memory polynomial model for digital predistortion of RF power amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 3852–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kang, Z.; Sellathurai, M.; Chen, N. Joint time domain nonlinear post-distortion scheme for reconstruction of distorted signals. Signal Process. 2024, 215, 104487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H. A memory polynomial-based iterative orthogonal least square algorithm for reconstructing self-interferences in full-duplex communications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs. 2024, 71, 2494–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motz, C.; Paireder, T.; Pretl, H.; Huemer, M. A survey on self-interference cancellation in mobile LTE-A/5G FDD transceivers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2021, 68, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Yao, H.; Wei, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, D. Co-aperture dual-circular-polarized patch antenna for simultaneous transmit and receive. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2023, 22, 2745–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Wei, X.; Tang, Y.; Hu, D. A parasitic decoupling structure for dual-polarized patch antenna arrays. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2023, 22, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziej, K.E.; Janice, B.A.; Sands, A.I.; Perry, B.T. Scalable in-band full-duplex phased arrays: Complexity reduction and distributed processing. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2023, 41, 2808–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Sun, J.; Xie, M. Isolation enhancement of dual-circularly-polarized antenna using hierarchical decoupling scheme. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2024, 23, 2391–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, J.C.; Sarkar, D. A co-Linearly polarized shared radiator-based full-duplex antenna with high Tx-Rx isolation using vias and stub resonator. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2023, 70, 2400–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Mobini, Z.; Galappaththige, D.; Tellambura, C. A comprehensive survey on full-duplex communication: Current solutions, future trends, and open issues. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2023, 25, 2190–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgenstern, C.W.; Rong, Y.; Herschfelt, A.; Molnar, A.C.; Apsel, A.B.; Landon, D.G.; Bliss, D.W. Analog-domain self-interference cancellation for practical multi-tap full-duplex system: Theory, modeling, and algorithm. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2023, 41, 2796–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Weifeng, M.; Chu, J.; Wei, X. Digital self-interference cancellation based on bounded component analysis for in-band full-duplex. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2023, 45, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.H.; Kil, Y.-S.; Kim, S.-H. Neural network aided digital self-interference cancellation for full-duplex communication over time-varying channels. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 6201–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Q. An imporved NLMS algorithm for interference cancellation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 3rd Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC), Chongqing, China, 11–13 October 2019; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Quan, H.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Y. Digital self-interference cancellation based on iterative variable step-size LMS. Acta Electron. Sin. 2016, 44, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpi, D.; Anttila, L.; Syrjälä, V.; Valkama, M. Widely linear digital self-interference cancellation in direct-conversion full-duplex transceiver. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 1674–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Guo, W.; Shao, S.; Tang, Y. A time-robust digital self-interference cancellation in full-duplex radios: Receiver design and performance analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 185021–185031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, J.P.; Kolodziej, K.E.; Perry, B.T. Simultaneous transmit and receive performance of an 8-channel digital phased array. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA, 9–14 July 2017; pp. 1043–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.T.; Huang, X.; Ding, C.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.J. An in-band full-duplex prototype with joint self-interference cancellation in antenna, analog, and digital domains. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2024, 72, 5540–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Le, A.T.; Guo, Y.J. Joint analog and digital self-interference cancellation for full duplex transceiver With frequency-dependent I/Q imbalance. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 2364–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, S. A multi-stage self-interference canceller for full-duplex wireless communications. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 December 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, I.T.; Doane, J.P.; Schulz, T.J.; Havens, T.C. Aperture-level simultaneous transmit and receive with digital phased arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 1243–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpi, D.; Riihonen, T.; Syrjälä, V.; Anttila, L.; Valkama, M.; Wichman, R. Full-duplex transceiver system calculations: Analysis of ADC and linearity challenges. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 3821–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, R.; Yeary, M.; Sigmarsson, H.; Rincon, R. Adaptive digital predistortion for radar applications using convex optimization. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Washington, DC, USA, 28–30 April 2020; pp. 816–820. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, L.; Zhu, A. Optimized low-complexity implementation of least squares based model extraction for digital predistortion of RF power amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, K.; Harada, H. Quantization noise reduction by digital signal processing-assisted analog-to-digital converter for in-band full-duplex systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 6643–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DBPA3500700300A_V8.pdf. Available online: https://www.qotana.com/p/pdf.html?name=%2Fuploads%2F20241128%2FDBPA3500700300A_V8.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Gu, Q. RF System Design of Transceivers for Wireless Communications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]






| Parameter | OFDM | LFM | LFMCW |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal bandwidth | 20 MHz | 20 MHz | 20 MHz |
| Signal duration | 32 μs | 10 μs | 10 μs |
| Subcarriers | 64 | - | - |
| Modulation type | QPSK | LFM | LFM |
| Pulse repetition interval | - | 70.8 μs | - |
| Parameter | Symbol | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal bandwidth | B | MHz | 20 |
| Receiver noise figure | F | dB | 4.1 |
| Antenna isolation | dB | 30 | |
| Receiver sensitivity | s | dBm | −86.9 |
| Receiver dynamic range | dB | 70 | |
| Minimum SNR | dB | 10 | |
| Transmitter SNR | dB | 60 | |
| ADC max input voltage | V | 4.5 | |
| ADC bit | b | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X.; Lai, J.; Xiao, J. A Power Analysis Method for Self-Interference Signal Components in Full-Duplex Transceivers Under Constant/Nonconstant Modulus Signal Stimulation. Electronics 2024, 13, 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13244961
Sun J, Huang J, Liu Y, Wei X, Lai J, Xiao J. A Power Analysis Method for Self-Interference Signal Components in Full-Duplex Transceivers Under Constant/Nonconstant Modulus Signal Stimulation. Electronics. 2024; 13(24):4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13244961
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jia, Jinping Huang, Yonghong Liu, Xizhang Wei, Jingtong Lai, and Jie Xiao. 2024. "A Power Analysis Method for Self-Interference Signal Components in Full-Duplex Transceivers Under Constant/Nonconstant Modulus Signal Stimulation" Electronics 13, no. 24: 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13244961
APA StyleSun, J., Huang, J., Liu, Y., Wei, X., Lai, J., & Xiao, J. (2024). A Power Analysis Method for Self-Interference Signal Components in Full-Duplex Transceivers Under Constant/Nonconstant Modulus Signal Stimulation. Electronics, 13(24), 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13244961






