Abstract
Hydrogen fuel cell water-thermal management systems suffer from slow response time, system vibration, and large temperature fluctuations of load current changes. In this paper, Logistic chaotic mapping, adaptively adjusted inertia weight and asymmetric learning factors are integrated to enhance the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm and combine it with fuzzy control to propose an innovative improved particle swarm optimization-Fuzzy control strategy. The use of chaotic mapping to initialize the particle population effectively enhances the variety within the population, which subsequently improves the ability to search globally and prevents the algorithm from converging to a local optimum solution prematurely; by improving the parameters of learning coefficients and inertia weight, the global and local search abilities are balanced at different stages of the algorithm, so as to strengthen the algorithm’s convergence certainty while reducing the dependency on expert experience in fuzzy control. In this article, a fuel cell experimental platform is constructed to confirm the validity and efficiency of the recommended strategy, and the analysis reveals that the improved particle swarm optimization (IPSO) algorithm demonstrates better convergence performance than the standard PSO algorithm. The IPSO-Fuzzy-PID management approach is capable of providing a swift response and significantly diminishing the overshoot in the system’s performance, to maintain the system’s safe and stable execution.
1. Introduction
Due to the severity of environmental problems and the energy crisis, a plethora of research efforts have been aimed at the development of cleaner technologies to replace traditional fuels [1,2]. Hydrogen energy is an important form of energy storage, with rich sources, wide range of uses, no pollution, etc., and is gradually becoming the focus of emerging energy sources [3]. Proton Exchange Membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is an electrochemical device that converts the chemical energy of hydrogen and oxygen directly into electricity. It is considered a clean energy technology, producing only water and heat as by-products. PEMFC is regarded as one of the most promising sources of alternative energy [4].
Managing the temperature of the electric stack is essential for the effective energy conversion of the fuel cell, as it has a direct impact on the efficiency of the electrochemical process and the general stability of the fuel cell. At the appropriate operational temperature, the catalyst can maintain a high activity, which promotes the electrochemical reaction of hydrogen and oxygen and generates more electrical energy. Ensuring the electric stack’s temperature stability is crucial to the level of performance exhibited by the fuel cell, since it has a direct impact on the effectiveness of the electrochemical reaction and the overall stability. At a suitable operating temperature, the catalyst can maintain a high activity, which promotes the electrochemical reaction and generates more electrical energy. However, when the reactor’s temperature is not up to the required standard, the catalyst activity decreases significantly, which hinders the quickness of the electrochemical reaction and leads to a decrease in conductivity [5].
Focusing on the temperature control strategies for hydrothermal management systems, Gürsel Sefkat et al. employed a fuzzy inference controller to regulate the ideal temperature for the battery assembly. The data revealed that the combined energy consumption for the propulsion, thermal management, and fuel supply systems dropped by 9.1% at 18 °C [6]. Lu Xing et al. put forward a PID control strategy for managing the coolant flow, which successfully stabilized the temperature of the electric stack at 350 K under real driving conditions, and the constant and relatively low inlet temperature of the coolant (340 K) improved the regulating capability of the PID control [7]. D. Zhu et al. offered a plan for temperature control, using PID control to reduce the loss of PEMFC and extend its service life [8]. Bo Deng introduced a thermal management control model for power reactors that utilizes a particle swarm optimization algorithm alongside an artificial neural network. This model was tested and compared against the traditional PID algorithm. The simulation results indicate that the time taken to regulate the coolant inlet temperature is decreased by over 74%, and the overshoot is minimized by more than 50% when there are changes in current [9]. Yan-Yun Shi introduced a fuzzy proportional–integral–derivative (PID) controller aimed at improving fan-side control, along with an enhanced whale optimization algorithm to establish dynamic operating conditions based on a fundamental energy management system. The effectiveness of the IWOA-FPID for temperature regulation was validated, resulting in a notable reduction in tuning time and a minimization of temperature overshoot to approximately 0.5 K [10]. Chen and colleagues created a controller based on fuzzy logic capable of handling multiple inputs and outputs, aimed at controlling the temperature and humidity of a fuel cell in real-time, thereby enhancing the fuel cell’s output efficiency [11]. Most of the control methods proposed in the above literature invoke fuzzy control to handle the hysteresis and indeterminacy in the fuel cell temperature regulation. However, the fuzzy control method depends largely on the selection of control parameters, and the expert experience has a large impact on the control accuracy and cannot be given to adaptive adjustment according to the system operation. Therefore, this paper considers the introduction of a particle swarm algorithm for iterative optimization of parameters.
In the research of particle swarm algorithm, Jiang et al. established a two-stratum particle swarm optimization algorithm to eliminate the difficulty associated with slow convergence of particle swarm optimization algorithm, which classifies the particle population, boosts the particle count within the swarm, with the goal of boosting the particle swarm’s diversity and expediting its search process [12]. Liu et al. aimed to improve the balance between the global exploration and local exploitation abilities of particle swarms. They found that non-linear inertia weights can better improve the performance of the algorithm, and suggested a non-linear inertia weight along with a method for updating the inertia weight that utilizes Logistic Chaos Mapping [13].
In the field of intelligent fuel cell control, Yuan designed an optimization strategy based on the deer hunting algorithm for PEMFC control parameter tuning, and the experiments proved that the proposed optimization algorithm has good effect on parameter tuning [14]. Zhao et al. proposed a new deep reinforcement learning algorithm, namely, the classified replay twin delayed Bayesian deep deterministic policy gradient (CTDB-DDPG) algorithm. The design of this algorithm introduces the Bayesian neural network, classification experience playback, and other techniques to improve the performance of the controller. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm can control the temperature of the PEMFC stack more effectively, which has certain practical significance [15].
With reference to the previously discussed literature, this paper improves the standard particle swarm algorithm and presents Logistic Chaos mapping as a method to initialize the particle swarm, which improves the diversity of the population. Furthermore, this paper adaptively modifies the inertia weight and learning parameters to enhance the convergence efficiency of PSO, which is implemented to discover the optimal elements of the fuzzy PID temperature controller, reduce the dependence on the experts’ experience, and heighten the control system’s precision. The control exactness is improved by reducing the dependence on experts’ experience. Based on a 3 kW PEMFC experimental system, the proposed control strategy is verified to have better dynamic response and robustness.
2. PEMFC Hydrothermal Management System
2.1. System Structure
The hydrothermal management system of the PEMFC consists of temperature sensors, heat sinks, circulating water pumps, and thermostatic water tanks, as shown in Figure 1. The system achieves temperature control via water cooling techniques. The electronic water pump drives the coolant to circulate in the system. While the coolant is pumped through the fuel cell, it takes in the heat produced by the chemical reaction occurring, resulting in an increase in temperature. With the coolant filtering through the radiator, it communicates with the atmospheric air to release heat, thus lowering the coolant temperature. This process effectively regulates the temperature and ensures keeping it within the correct operational bounds.
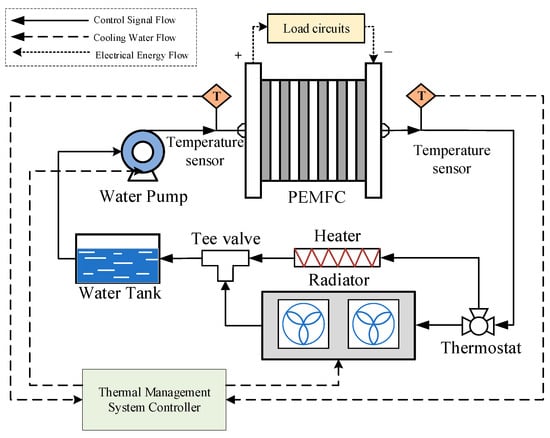
Figure 1.
Structure of fuel cell thermal management system.
2.2. Modeling of the Output Voltage of the Stack
The output voltage of the fuel cell is the voltage that the fuel cell can provide to the external circuits under actual operating conditions. The operational voltage is generally less than the theoretical voltage, due to various kinds of voltage losses that occur while the fuel cell is functioning. The Uout of PEMFC is shown as follows [16]:
where Ncell is the number of single cells in the fuel cell; Enerest indicates the Nernst open-circuit electromotive force; Uact, Uohm and Ucon are the activation polarization loss, ohmic polarization loss and concentration polarization loss, respectively.
Enernst represents the conceptual electrical potential of a single cell under open-circuit conditions without any load:
where F is Faraday’s constant; R represents the universal gas constant; PH2 represents the effective partial pressure of hydrogen; while PO2 denotes the effective partial pressure of oxygen; Tst refers to the operating temperature of the power stack.
The activation polarization voltage Uact can be expressed as:
where CO2 is the concentration of oxygen involved in the cathodic reaction; Ist is the loading current; CH2 is the concentration of hydrogen involved in the anodic reaction; Am is the effective activation area for proton exchange; ξ1, ξ2, ξ3, ξ4 are empirical coefficients, which are indeed taken as reasonable values after experiments with reference to the range of values of empirical coefficients proposed by J.C. Amphlett.
The concentration polarization overvoltage loss Ucon is expressed as:
where Ilim is the ultimate current density.
The ohmic polarization overvoltage Uohm is a voltage drop due to the internal impedance of the cell and can be expressed as:
where RM is the equivalent membrane impedance; rm is the resistivity of the proton exchange membrane; and lm is the thickness of the proton exchange membrane.
2.3. Heat Production Modeling
The primary source of energy for energy transfer, material warming, and power output comes from the chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, assuming that all of this chemical energy is transformed into electrical and thermal energy.
Essentially, the energy is derived from the energy enthalpy difference between the reactants and products during the redox reaction:
The enthalpy of hydrogen is ∆H = 285.8 kJ/mol. Therefore, the aggregate chemical energy (Qtot) from the hydrogen reaction per unit time can be calculated using the expression:
where qrec represents the mass flow rate of the molar reactants.
The output electric power Pst can be formulated as:
where Ust denotes the voltage output from the fuel cell; Ist is used to express the current.
From the analysis, the heat produced by the fuel cell, denoted as Qgen, can be represented as:
2.4. Thermal Modeling
It is assumed that the hydrogen tail gas not involved in the reaction has no effect on the system. Heat transfer within the fuel cell system takes into account only the heat released by the gas, the water produced, and the heat removed by the condensation water.
The fuel cell system’s heat dissipation power per unit time is:
Qcool signifies the heat extracted by the coolant while flowing through the stack, denoted by:
where Cw denotes the specific heat capacity of the coolant; Mw stands for the mass of the coolant; Tst,out is the temperature of the coolant out of the reactor; Tst,in is the temperature of the coolant into the reactor.
Qgas represents the heat transported by hydrogen and oxygen to and from the fuel cell stack, expressed as:
where qrec,O2 is the oxygen flux involved in the reaction at the cathode; qrec,H2 is the hydrogen flux involved in the reaction at the anode; CO2 signifies the heat capacity per unit mass of oxygen, and CH2 does the same for hydrogen; CH2O refers to the specific heat capacity of water vapor, while Tatm denotes the temperature of the surrounding environment.
Qamb refers to the heat released by the thermal radiation of the electric pile into the surrounding environment [17]:
From the above analysis, the PEMFC heat balance equation can be expressed as:
where Cst is the specific heat capacity of the fuel cell stack, Mst represents the stack mass.
The heat sink is modeled and the heat dissipated by the heat sink is expressed as:
where A represents the heat dissipation area of the heat sink; K is the heat dissipation coefficient of the heat sink; Trad is the temperature of the heat sink.
The radiator temperature can be expressed as:
where Trad,out is the radiator outlet temperature; Trad,in is the radiator inlet temperature.
3. Improved Particle Swarm Algorithm
3.1. Standard Particle Swarm Algorithm
The Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm is a heuristic intelligent optimization approach, adapting the foraging techniques observed in bird herds. In the course of the flock’s foraging, each individual records the location of the richest food source it has found, which is called the individual optimal location. Also, the entire flock records the optimal one of the food sources found by all individuals, noted as the global optimal position. By sharing this information, each flying bird in the flock continuously adjusts its flight path in order to move closer to these optimal positions [18].
In the implementation of the particle swarm algorithm, every particle symbolizes a possible solution to the optimization issue. In each iteration, the N particles within the D-dimensional solution space adjust their velocities and locations according to the best past positions of individual particles and the best past positions of the entire group. And this process persists until certain predetermined stopping conditions are satisfied, like reaching the maximum number of iterations or achieving a solution quality that meets specific standards.
The formula for updating particle velocity is [19]:
The formula for updating the position of a particle is:
where Vi,j(t) represents the velocity value of particle i in the jth dimension at generation t; Xi,j(t) denotes the positional value of the jth dimension of particle i at generation t; ω represents the inertia weight coefficient, which regulates the rate at which the particle’s influence diminishes; c1 denotes the personal learning component that indicates how much particles favor their own best value; c2 is the social learning component that indicates how much particles favor the optimal value of the group [20]; rand1() and rand2() are mutually non-interfering stochastic functions taking values between [0,1]; Pi,j(t) is the optimal fitness value experienced by particle i, named the individual historical optimal value; Gi,j(t) represents the most advantageous location that has been encountered by the entire swarm of particles, which is referred to as the global best position.
From Equation (21), it is evident that the individual learning component (c1), the social learning component (c2), and the inertia weighting coefficient (ω) are three key parameters, which will directly affect the effectiveness and outcomes of the model.
Therefore, this research optimizes and improves the standard particle swarm algorithm for these three parameters.
3.2. Initializing Particle Populations Based on Logistic Chaotic Mapping
The elementary particle swarm optimization algorithm usually determines the position of the initial population by means of random initialization, relying on the rand function to generate random numbers to set the starting point of each particle. The formula is as follows:
where X denotes the location of the produced particle; rand represents the generated random number, considering a value range from 0 to 1; ub, lb denote the upper and lower boundaries of the solution space, respectively.
The random initialization method ensures diversity in the initial population each time the algorithm is run, but it has some drawbacks. The main problem is that the distribution of particles in the solution space may not be uniform enough, sometimes certain localized regions will have too many particles concentrated while other regions are too sparse. This unequal distribution negatively impacts the algorithm’s ability to converge quickly, especially for those population optimization algorithms that are prone to getting stuck in local optima, which may lead to a reduction in the convergence speed, or even fail to achieve convergence.
To address the issue, this paper utilizes chaotic mapping to initialize the particle swarm. This method has good randomness, traversal, and regularity, and can traverse the search space within a specific range based on its own rules without duplicating efforts. The starting population generated by chaotic initialization shows significant improvement in both solution accuracy and convergence rate [21]. It enhances the variety of the particle population and assists the algorithm in escaping the confines of local optimization, thus enhancing the ability of global optimization. In this paper, we have chosen Logistic Chaos Mapping as the method for chaos initialization, which is formulated as follows [22]:
where ξ is the chaotic model mapping parameter.
3.3. Dynamic Regulation of Learning Factors
In the elementary particle swarm optimization algorithm, the components c1 and c2 serve a significant purpose. Specifically, the individual learning components c1 denotes the particle’s dependence on its own historical optimal position, demonstrating the particle’s capacity to gain knowledge from its personal experiences, while the social learning component c2 embodies the particle’s social interactivity, characterizing the particle’s behavior of learning and converging to the optimal solution in the group.
During the execution of the algorithm, the goal of the initial phase is to achieve a broad search to improve the variety of the particles and their capacity to navigate the solution space. As the algorithm advances, the emphasis slowly transitions towards enhancing its convergence efficiency. This shift requires that the weights of the learning components c1 and c2 can be adjusted accordingly rather than remaining fixed.
As a result, this document suggests a plan for dynamically adjusting the learning factors by designing c1 as a function that monotonically diminishes as the number of iterations rises, and c2 as a function that monotonically increases. This design seeks to strike a balance between exploring and utilizing the particle swarm algorithm to ensure that the algorithm is capable of conducting a thorough search in the beginning and then rapidly reaching the best solution as it progresses.
The specific function expression is shown below:
where t represents the count of current iteration, while Tmax denotes the highest iteration count.
Through this dynamic adjustment mechanism, the algorithm can effectively guide the particle swarm to converge to the optimal solution while maintaining diversity.
3.4. Adaptive Adjustment of the Inertia Weighting Factor
The inertia weight factor is a key parameter in particle swarm optimization algorithms, which controls the exploration behavior and convergence characteristics of particles within the area of exploration. Higher inertia weights are beneficial for exploring the global search space, while lower inertia weights are better suited for focusing on local search, while a particle swarm with constant inertia weights is likely to get stuck in local optima with low solution accuracy [23].
To achieve a balance between the global search capability and local optimization ability of the PSO algorithm, this paper adopts the coefficient of non-linear dynamic inertia weight, which are dynamically adjusted with the adjustment of the particle’s objective function value to align with the various phases of the algorithm and the requirements of the search process, and its expression is:
where f represents the current objective function value of the particles, favg denotes the average value of the current particle, while fmin indicates the minimum target value.
3.5. Flow of the Improved PSO Algorithm
The particle swarm algorithm’s process is founded on Logistic chaotic mapping initializing particles. The learning factors and inertia weight factor dynamic adjustment are described as follows.
Step 1: Initialization of particle swarm parameters. Use Logistic chaotic mapping to generate the initial particle swarm. Set the particle swarm’s velocity and position, and specify the maximum iteration count and the size of the particle swarm;
Step 2: Assess the fitness score for every particle. Identify the best overall particle position, and record the best historical position for each individual particle;
Step 3: According to the optimization strategy, revise the inertia weight and learning factors, then adjust the position of each particle accordingly;
Step 4: Revise the personal best value and the overall best value for the current particle;
Step 5: Verify whether the designated number of iterations has been finished. If it has not, return to Step 2 and repeat the process; if it has, proceed to Step 6;
Step 6: Assess if the output criteria are met. If they are not, revert to Step 2; if they are, provide the current best value.
Below is the flow chart for the enhanced particle swarm algorithm (Figure 2):
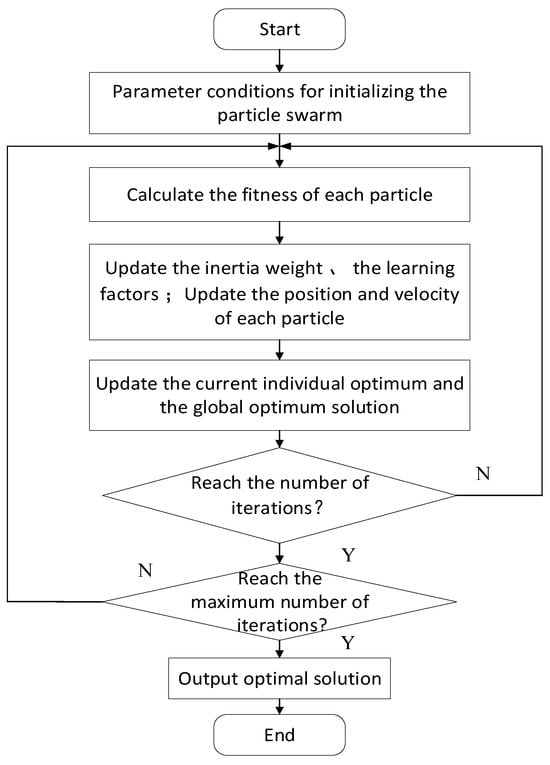
Figure 2.
Flow chart of improved particle swarm algorithm.
4. Design of PEMFC Temperature Controller Based on IPSO-Fuzzy-PID
4.1. Fuzzy-PID Control
To address the hysteresis and nonlinearity in temperature regulation, fuzzy-PID control is employed to offset the delay, enhancing the control accuracy [24]. In this paper, a dual-input three-output fuzzy controller is selected to self-tune the PID parameters. The structure is shown below (Figure 3):
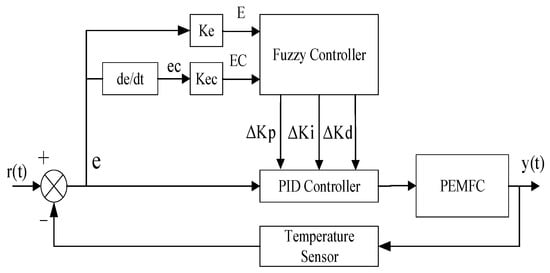
Figure 3.
Structure of the Fuzzy-PID controller.
The controller inputs are e and ec, both with fuzzy domains [−6, 6]; the outputs are ΔKp, ΔKi, ΔKd, with fuzzy domains [−1, 1]; the fuzzy languages of the input and output variables are {NB, NM, NS, ZO, PS, PM, PB}; and the fuzzy language corresponding to the degree of affiliation functions are all trigonometric functions, as shown in Figure 4.
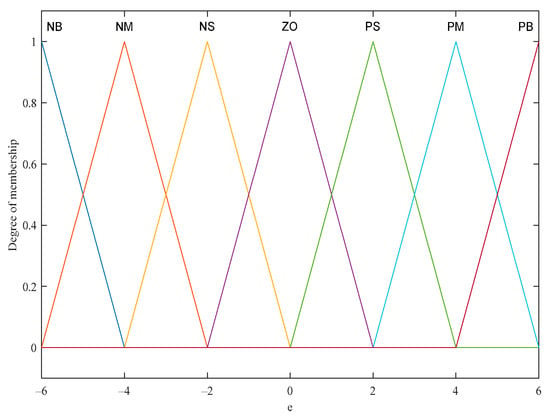
Figure 4.
Plot of error e affiliation function.

Table 1.
∆Kp fuzzy control rules.

Table 2.
∆Ki fuzzy control rules.

Table 3.
∆Kd fuzzy control rules.
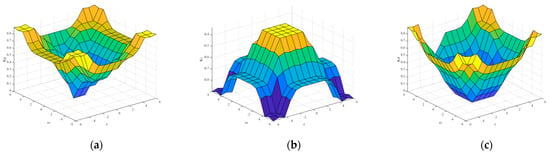
Figure 5.
(a) ∆Kp, (b) ∆Ki, (c) ∆Kd Surface Plot.
4.2. Optimization of Fuzzy-PID Controller Parameters Based on IPSO
In fuzzy control logic, the choice of quantization and proportionality factors, along with the fuzzy control rules, is essential in assessing how well the control performance works. The quantization factor determines the degree of fuzzification of the input mistake and the rate at which the error changes, while the proportionality factor influences the strength of the fuzzy control output to adjust the PID parameters. However, in conventional fuzzy PID controllers, once these parameters are set, they are fixed, which limits the ability of the controller to adapt to dynamically changing environments. Therefore, in this paper, the second part of the IPSO algorithm is introduced to dynamically adjust the quantization and scaling factors, and iteratively seek the optimization of the parameters for PID control to enhance control accuracy. Figure 6 illustrates the configuration of the IPSO-Fuzzy-PID controller:
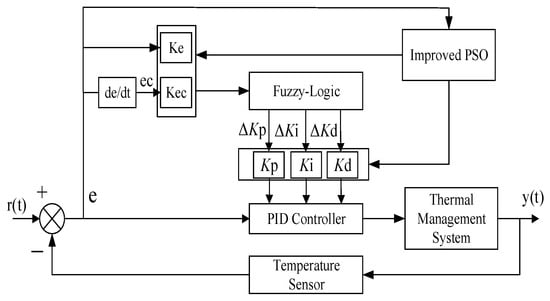
Figure 6.
Structure of IPSO-Fuzzy-PID controller.
According to the controller structure design, this paper adopts the ITAE index as the objective function, and determines the degree of adaptation by calculating the integral of the product of the time and the temperature deviation of the stack, and conducts a comprehensive assessment of the system control performance to ensure that the attraction system meets the overshooting amplitude and time requirements, and the ITAE expression is:
where t is the time; e(t) is the temperature control deviation value of the fuel cell electric stack.
According to the analysis provided above, this experiment uses MATLAB to test the effective feasibility of the optimization effect of the particle swarm algorithm, and builds the IPSO-Fuzzy-PID controller model by Simulink as illustrated in Figure 7.
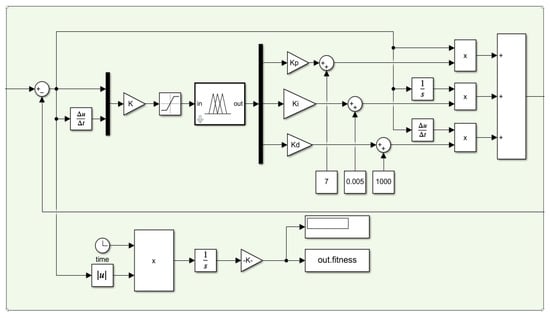
Figure 7.
IPSO-Fuzzy-PID Simulink model diagram.
5. Analysis of Experiment Results
5.1. Experimental System
For the experiments conducted in this paper, we utilized the 3 kW hydrogen fuel cell testing system with water cooling created by our group. And the experimental testing setup consists of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack and a TC275 system controller, host computer, air compressor, constant temperature water tank, circulating water pump, humidification tank, mass flow meter, gas safety cabinet, various types of valves and pipelines, as well as temperature and pressure sensors.
To attain precise management of this complex system, independent research and development focused on designing a system controller utilizing the Infineon TC275 processor, which was based on the configuration software Kingview 6.55 development of fuel cell experimental monitoring system. The test system in kind as shown in Figure 8.
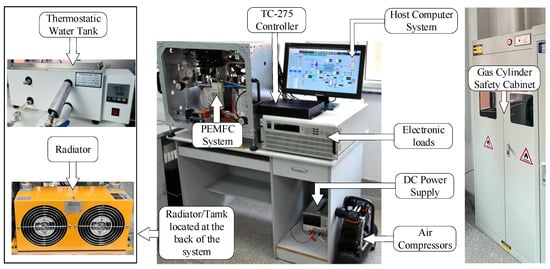
Figure 8.
Physical diagram of the fuel cell test system.
The controller gathers information and tracks the operational status of every subsystem in real-time, assists the management personnel in executing the operation instructions, and warns the key parameters. Once the parameter exceeds the limit, the system will alarm and stop the system in an emergency, to ensure the fuel cell system operates safely and stably in order to fulfill the experiment’s requirements.
5.2. Analysis of the Polarization Curve of the Stack
In the course of the simulation and experiment, the parameters for the system’s operating conditions are established as follows: the surrounding temperature is maintained at 27 °C, while the stack operates at a temperature of 70 °C. The pressure difference between the stack’s cathode and anode is established at 20 kPa (with anode pressure at 0.17 MPa and the cathode pressure at 0.15 MPa). The pressure on the anode side is modified according to the pressure on the cathode side, and the load current varies from 0 to 48 A.
Figure 9 shows the polarization curve of the stack:
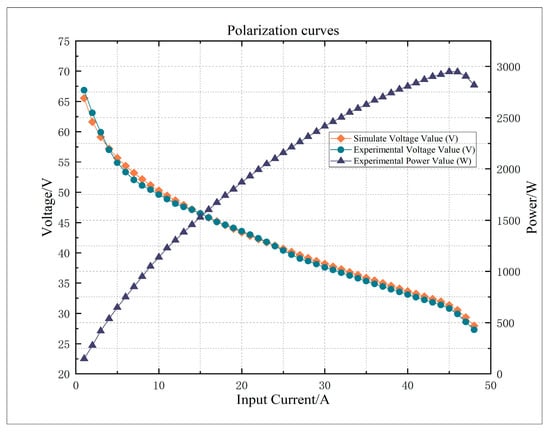
Figure 9.
Comparison of simulated and experimental values of polarization curves of the stack.
The figure indicates that there is a noticeable difference between the results obtained from experiments and those generated by simulations during the low current density phase. This discrepancy is primarily because the system is in its initial phase, leading to an uneven temperature distribution in the fuel cell, and inadequate wetting of the proton exchange membrane. A corresponding current density also rises within the fuel cell’s internal resistance. As the current density rises and enters the medium current density range, there is a notable enhancement in the alignment between the data points from the experiments and the curves generated by the simulations. This leads to a reduction in error and an increase in the model’s accuracy. In the area of high current density, the water produced during system operation cannot be expelled quickly enough, leading to water buildup within the power stack. This causes the experimental data to typically show some discrepancies compared to the simulation values, although these discrepancies remain within acceptable limits. In conclusion, the overall experimental data are somewhat lower than the simulation results, but it exhibits a comparable trend to the simulation curve. This suggests that the model that has been created can more accurately represent the performance of the fuel cell during actual operation.
5.3. Analysis of the IPSO Algorithm
Within the particle swarm optimization method, initializing the population is a crucial step that significantly impacts both the algorithm’s search efficiency and the ultimate optimization outcome. The comparison of particle distribution using Logistic Chaos Mapping and random initialization is shown in Figure 10:
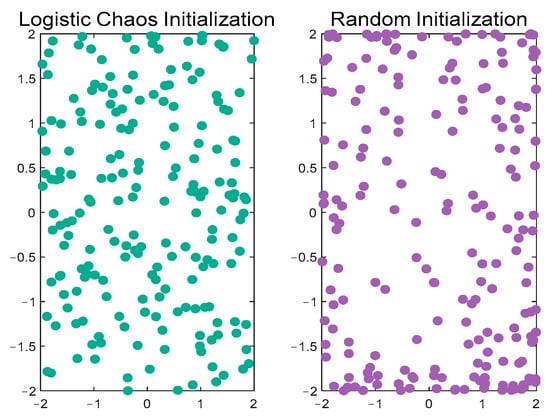
Figure 10.
Comparison of initialized particle distribution.
The comparison of the particle distribution between Logistic Chaos Mapping and random initialization can be visualized in Figure 10. In the case of random initialization, particles appear to pile up significantly in the boundary regions of the solution space, resulting in over-densification of particles in these regions. In contrast, the particle distribution initialized with Logistic Chaos Mapping shows a more balanced character.
The learning component in the PSO algorithm is a key parameter affecting the performance of the algorithm, and the individual learning component and the social learning component determine the degree of influence of the personal experience and the collective experience of the particles on their position update during the search process. The improved dynamic learning factor transformation is analyzed through simulation experiments. The curve is illustrated in Figure 11:
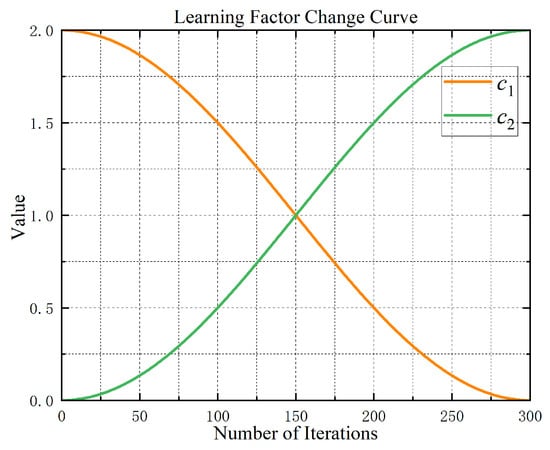
Figure 11.
Graph of learning factor dynamics.
From the above figure, in order to avoid the particles converging too rapidly towards the local optimal solution during the initial phase of evolution, thus limiting the scope of global search, a higher value of c1 is given in the early stage to encourage the particles to explore based on their own experience, while a lower value of c2 is given to reduce the dependence on the globally optimal particles. During the final stages of the particle search iterations, to improve the rapid and precise convergence of the particles towards the global optimal solution, as well as to boost the rate at which the algorithm converges and its precision, the value of c1 is reduced while the value of c2 is increased to strengthen the learning process and ensure that the particles converge towards the optimal solution for the population.
In the research and practice of intelligent optimization algorithms, convergence performance is a key index, which is directly related to whether the algorithm can find the best solution to the problem within a limited number of cycles (Figure 12).
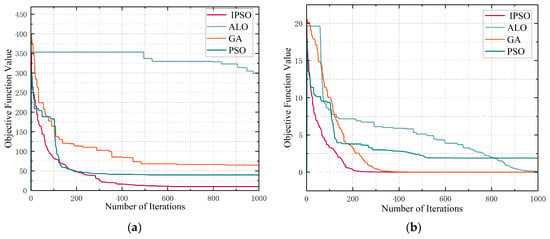
Figure 12.
Convergence comparison curves, (a) F9 Objective function value curve, (b) F10 Objective function value curve.
In this paper, F9 and F10 in the test function set CE2005 are used as the target test functions, the number of populations is set to 200, and the maximum number of iterations is set to 1000, and the convergence performance of four intelligent optimization algorithms, namely, PSO, IPSO, Ant-Lion Optimizer (ALO), and Genetic Algorithm (GA), are compared, respectively (Table 4).

Table 4.
Performance comparison of different control methods for scene 1.
F9 test function is:
where the F10 test function is:
As illustrated in the figure above, the curve obtained by the IPSO approaches the horizontal direction faster than the curve of the basic algorithm. This indicates that the IPSO algorithm has the ability to get close to the optimal solution at a faster rate during the iteration process and is able to stabilize quickly without further fluctuations after reaching the optimal solution. The fitness value curve illustrates that the IPSO algorithm has significantly improved its search efficiency. It can not only find a solution closer to the optimal solution in a short time, but also successfully steer clear of local optima, improving the algorithm’s ability to search globally and its robustness.
5.4. Analysis of IPSO-Fuzzy-PID Experimental Results
This study confirms the effectiveness of the proposed strategy by constructing an experimental system for hydrogen fuel cells, burning the control algorithm into the TC275 controller. The actuator device controls each sub-system device to execute the algorithmic commands. The hydrogen fuel cell system replicates real operating conditions using the IT8902E-1200-80 electronic load (ITECH ELECTRONIC Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China), which is configured to operate in constant current mode. The system also includes the HU0854 integrated temperature transmitter as sensors.
Firstly, the convergence of the IPSO algorithm on the optimization of the control parameters is verified: the maximum limit for simulation iterations is established at 100, along with the iterative adjustments of the three control parameters, Kp, Ki, and Kd are shown in Figure 13:
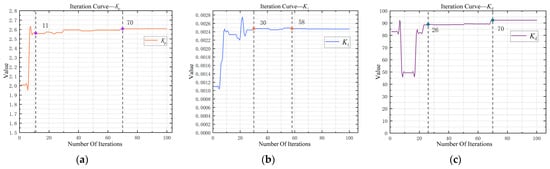
Figure 13.
Iterative optimization curve, (a) Kp iterative optimization curve, (b) Ki iterative optimization curve, (c) Kd iterative optimization curve.
Upon examining the figure above, it becomes clear that: Kp in the algorithm iteration to the 11th generation when the output is gradually stable, in the 70th generation when the output of the final value of the steady state 2.6082; Ki in the algorithm iteration to the 30th generation of the output is stable, in the 58th generation of the output value is not fluctuating for 0.0025; Kd in the algorithm iteration to the 26th generation of the output is stable, in the 70th generation of the output value no longer fluctuates for 92.3192. The overall change in the ISPO algorithm introduced in this document demonstrates a quicker optimization speed, stable output, and meets the system control requirements.
Simulation verification is carried out in MATLAB/Simulink (R2022a) as a reference for the actual system experiments, and the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed control strategy are verified by setting different simulation scenarios to simulate the whole process of system operation.
Simulation experiment scene 1 and scene 2 are setup to verify the robustness and dynamic response capability of the proposed strategy by evaluating the control performance of IPSO-Fuzzy-PID in comparison to standard PID control and fuzzy PID control, regarding temperature regulation of the fuel cell. For the two particle swarm algorithms in the experiment, the parameters of the algorithms are reset considering the simulation running time: the number of populations is 100, the maximum number of iterations is 20, the maximum velocity of the particles is 0.1, the minimum velocity is −0.1, the upper limit of the outputs is [10 50 0.01 100], and the lower limit of the outputs is [0 0 0 0].
Experimental Scenario 1: The starting temperature of the experiment is set at 333 K, and the electronic load generates a step change in current when running for 20 s, simulating the rise in fuel cell power output and the abrupt variation in load power, and the temperature data are recorded and analyzed under the three control strategies from 0 to 1000 s in the experiment;
Experimental Scenario 2: The starting temperature of the experiment is set at 300.15 K, and load current increases suddenly when the system is running for 50 s, and the load current decreases abruptly at 800 s and 1600 s. Record the temperature data under the three control strategies from 0 to 2000 s.
The response curves corresponding to the different control methods in Scene 1 are shown in Figure 14.
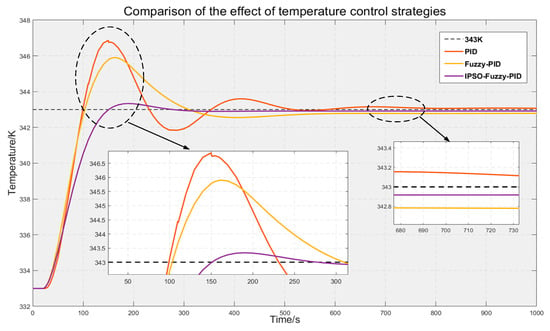
Figure 14.
Iterative optimization curve.
Comparative analysis of the above graph indicates that: the step change in the load occurs, the output power of the heap changes abruptly, and the internal temperature changes accordingly, and the target temperature of the heap is set to be 343 K. The three control strategies are aimed at controlling the sudden change in the temperature when the system is running for 20 s. The IPSO-Fuzzy-PID strategy has a better performance than the other two strategies. According to the curve changes, it can be seen that the control performance of the IPSO-Fuzzy-PID strategy proposed in this paper is better than that of the other two strategies, with smaller overshooting, faster oscillation suppression, and stabilization value closer to the target value.
The quantitative analysis for Figure 14 is as follows:
The typical PID control system exhibits a sluggish response time, a large overshoot, 1.1075%, and an extended period to achieve equilibrium. The regulation time needs 691.32 s, and is accompanied by a slight oscillation phenomenon, the peak time of 150.033 s, the constant value of 343.1 K. The fuzzy PID control system can significantly enhance the system’s response time, a slight reduction in the overshoot, 0.9043%, system oscillation is reduced, reduce the time to achieve steady state, 553.030 s, the constant value of 342.8 K, and the peak time of 162.398 s. However, the fuzzy PID controller has a blindness due to the adjustment of the weight factor by the expert, and it cannot be used for the tracking adjustment of the parameters, and the control effect is not ideal. The improved particle swarm algorithm optimized fuzzy PID parameters control approach utilized in this study has the fastest response speed, and the smallest overshooting amount of 0.1167%. The steady state value is nearer to the target value, resulting in increased stability and a reduced regulation time of 293.478 s. And the system reaches the steady state in the shortest time, and with better robustness.
Table 5 displays the comparison of performance among various methods.

Table 5.
Performance comparison of different control methods for scene 1.
The response curves corresponding to the different control methods for Scenario 2 are shown in Figure 15.
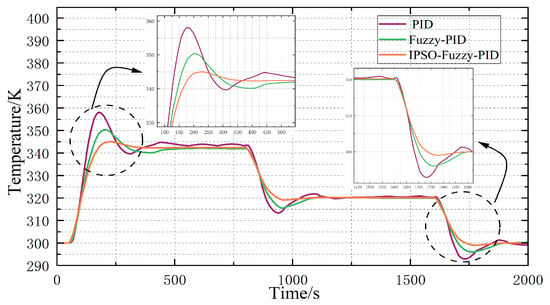
Figure 15.
Iterative optimization curve.
The analysis of the above curves shows that: Scenario 2 simulates multiple changes in fuel cell power to verify the control performance of each control strategy. After 50 s of operation, the system starts to run, the chemical reaction occurs inside the fuel cell, and the output power increases. The temperature of the electric pile also rises, and the control strategy is adjusted accordingly for the sudden temperature change at 50 s startup. When the system runs smoothly to 800 s, the power demand decreases, simulating the scenarios such as fuel cell vehicle deceleration, and each control strategy is adjusted according to the temperature change in the electric pile. When the system runs to 1600 s, the power demand of the system decreases again, simulating the shutdown state of the system, and the control strategies are adjusted to prevent the damage to the interior of the electric stack caused by the sudden temperature drop.
Comparison of the curve changes shows that the overshoot in standard PID control is the highest, and there are still oscillations once the steady state is achieved. Although the overshoot of the fuzzy PID is reduced, the time taken to achieve a steady state remains lengthy, while the IPSO-Fuzzy-PID control suggested in this document is effective in minimizing the overshoot in the two experimental scenarios of the temperature increasing and decreasing, which is robust; and the response is rapid, and the regulation time is significantly reduced in comparison to the other two, which has good dynamic performance. The response is fast. The regulation time is significantly reduced in comparison to the other two, and the dynamic performance is strong.
The economic value of the proposed control strategy is reflected in the following: by optimizing the temperature control strategy, the performance and lifetime of the fuel cell stack can be significantly improved, and the maintenance cost and replacement frequency can be reduced, thus bringing about economic savings. Also, the fuel cell system can be operated with high efficiency under various operating conditions. This improved efficiency directly translates into increased economic value of the system; reduced performance degradation and potential failures due to temperature fluctuations, further reducing operating costs.
Overall, the IPSO-Fuzzy-PID control method proposed in this paper is more effective than the other two control techniques for the temperature variations brought about by sudden changes in power demand in different scenarios, thus providing better economic value and application value.
6. Conclusions
Addressing the issues of sluggish response time, system instability, and significant temperature variations in the thermal management system of the PEMFC power pile, this paper presents a control strategy that utilizes an enhanced particle swarm algorithm to optimize the fuzzy PID controller. The proposed method enhances the convergence performance of the PSO by incorporating Logistic chaotic mapping, an inertia weight factor, and a dynamic adjustment of the learning factor, and reduces the reliance on the experience of the experts, so that the controller is capable of functioning effectively. The experimental system of 3 kW water-cooled PEMFC is constructed, and the consistency and correctness of the constructed model and the experimental system are confirmed by contrasting the experimental data with the simulation data. According to the experimental configuration and the Simulink model, the control performance of the IPSO-Fuzzy-PID strategy suggested in this paper is validated by contrasting it with the PID control and Fuzzy-PID control methods. Due to the abrupt shift in temperature of the power reactor, the IPSO-Fuzzy-PID effectively reduces the amount of overshooting, which is only 0.1167%, and the duration for regulation is significantly less than that of the other approaches, and the occurrence of system oscillations is effectively suppressed. Although the improvement of the particle swarm algorithm in this paper greatly improves the iteration speed and control accuracy, there are some areas that need to be improved: the PSO algorithm itself needs to carry out a number of iterative operations for a large number of particles separately, which leads to a longer average computation time of the algorithm. This paper introduces adaptive inertia weights and other mechanisms to optimize the convergence performance of the algorithm, but accordingly also increases the algorithm’s complexity and the difficulty of expansion. The team will focus on breaking through these problems in the subsequent research.
In conclusion, the IPSO-Fuzzy-PID control method introduced in this paper demonstrates superior convergence performance compared to the traditional particle swarm algorithm. It can significantly reduce temperature swings and reduce the overshooting during the sudden change in the load current, with a good robustness to ensure a more efficient and stable operation of the system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L. and H.D.; methodology, Z.L.; software, Z.L.; validation, H.D.; formal analysis, Z.L.; investigation, Z.L.; resources, X.M. and H.D.; data curation, Z.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.L. and H.D; writing—review and editing, H.D and X.M.; visualization, Z.L.; supervision, H.D and X.M.; project administration, H.D and X.M.; funding acquisition, H.D and X.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by State Grid Corporation Limited Science and Technology Program, ≪Research on Intelligent Evaluation and Risk Traceability Technology of Distribution Grid Supply and Use System State Containing a High Percentage of Distributed Power Supplies Based on Graph Computing≫, grant number 52272223004H.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from Zenghui Liu (12222112@stu.lzjtu.edu.cn).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Xiping Ma was employed by the company State Grid Gansu Electric Power Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmad, S.; Ullah, A.; Samreen, A.; Qasim, M.; Nawaz, K.; Ahmad, W.; Alnaser, A.; Kanan, A.M.; Egilmez, M. Hydrogen production, storage, transportation and utilization for energy sector: A current status review. J. Energy Storage 2024, 101, 113733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Hu, T. Analysis of carbon emission status under the carbon neutral target in China for Earth’s atmospheric balance. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 804, p. 042082. [Google Scholar]
- Lebrouhi, B.E.; Djoupo, J.J.; Lamrani, B.; Benabdelaziz, K.; Kousksou, T. Global hydrogen development—A technological and geopolitical overview. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 7016–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Chai, T. Observer-Based Discrete Adaptive Neural Network Control for Automotive PEMFC Air-Feed Subsystem. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 3149–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, C.; Fan, R.; Bao, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Chin, C.S.; Li, C. Modelling and control of vehicle integrated thermal management system of PEM fuel cell vehicle. Energy 2020, 199, 117495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şefkat, G.; Özel, M.A. Experimental and numerical study of energy and thermal management system for a hydrogen fuel cell-battery hybrid electric vehicle. Energy 2020, 238, 121794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Chang, H.; Zhu, R.; Wang, T.; Zou, Q.; Xiang, W.; Tu, Z. Thermal analysis and management of proton exchange membrane fuel cell stacks for automotive vehicle. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 32665–32675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Ait-Amirat, Y.; Djerdir, A. Active thermal management between proton exchange membrane fuel cell and metal hydride hydrogen storage tank considering long-term operation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 202, 112187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Zhang, X.; Yin, C.; Luo, Y.; Tang, H. Improving a Fuel Cell System’s Thermal Management by Optimizing Thermal Control with the Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and an Artificial Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, M. Thermal Management of Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells with Enhanced Fuzzy Control via an Improved Whale Optimization Algorithm. Energy Technol. 2024, 12, 2400055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Fang, Y.; Li, W.; Ding, Y.; Wan, Z.; Wang, X.; Tu, Z. Temperature and humidity management of PEM fuel cell power system using multi-input and multi-output fuzzy method. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 203, 117865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wei, W.; Shao, W.; Liang, Y.; Qu, Y. Research on Large-Scale Bi-Level Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 56364–56375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Tu, L. A modified particle swarm optimization using adaptive strategy. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 152, 113353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Ashourian, M. Parameter identification of PEMFC based on Convolutional neural network optimized by balanced deer hunting optimization algorithm. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Pan, S.; Ma, L.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y. Control of Fuel Cell Temperature Based on Classified Replay Twin Delayed Bayesian Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2024, 13, 4240–4256. [Google Scholar]
- Souissi, A. Adaptive sliding mode control of a PEM fuel cell system based on the super twisting algorithm. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 3390–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Cao, G.; Zhu, X.; Hu, M. Coolant circuit modeling and temperature fuzzy control of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 9110–9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Zhang, J.; Yao, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. A Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Based on Improved Inertia Weight. Comput. Digit. Eng. 2022, 8, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, W. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm with Improved Inertia Weight. Mod. Inf. Technol. 2023, 20, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Ma, D.; Lu, J.; Xing, B.; Wang, K.; Gao, Y.; Han, B. In situ calibration of triaxial coils of a vector optically pumped magnetometers based on a particle swarm optimization algorithm. Measurement 2022, 202, 111878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Min, P.; Zhang, J. Research on MPPT of photovoltaic array based on improved PSO algorithm. Transducer Microsyst. Technol. 2024, 8, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y. Secure sharing of privacy data in the Internet of Things under attribute Logistic chaos mapping. Mod. Electron. Tech. 2024, 13, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Nayeem, G.M.; Fan, M.; Akhter, Y. A time-varying adaptive inertia weight based modified PSO algorithm for UAV path planning. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Robotics, Electrical and Signal Processing Techniques (ICREST), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 5–7 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, R.; Yang, J.; Yu, P.; Wang, J.; Kong, X. Temperature Control of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Based on Fuzzy Active Disturbance Rejection. J. Shandong Ind. Technol. 2022, 6, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
