Reactive Elements Control in LC Series Resonant Inverters by Current-Controlled Variable-Transformer and Magnetic Energy Recovery Switch for Induction Heating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. LC Series Resonant Converter Topology
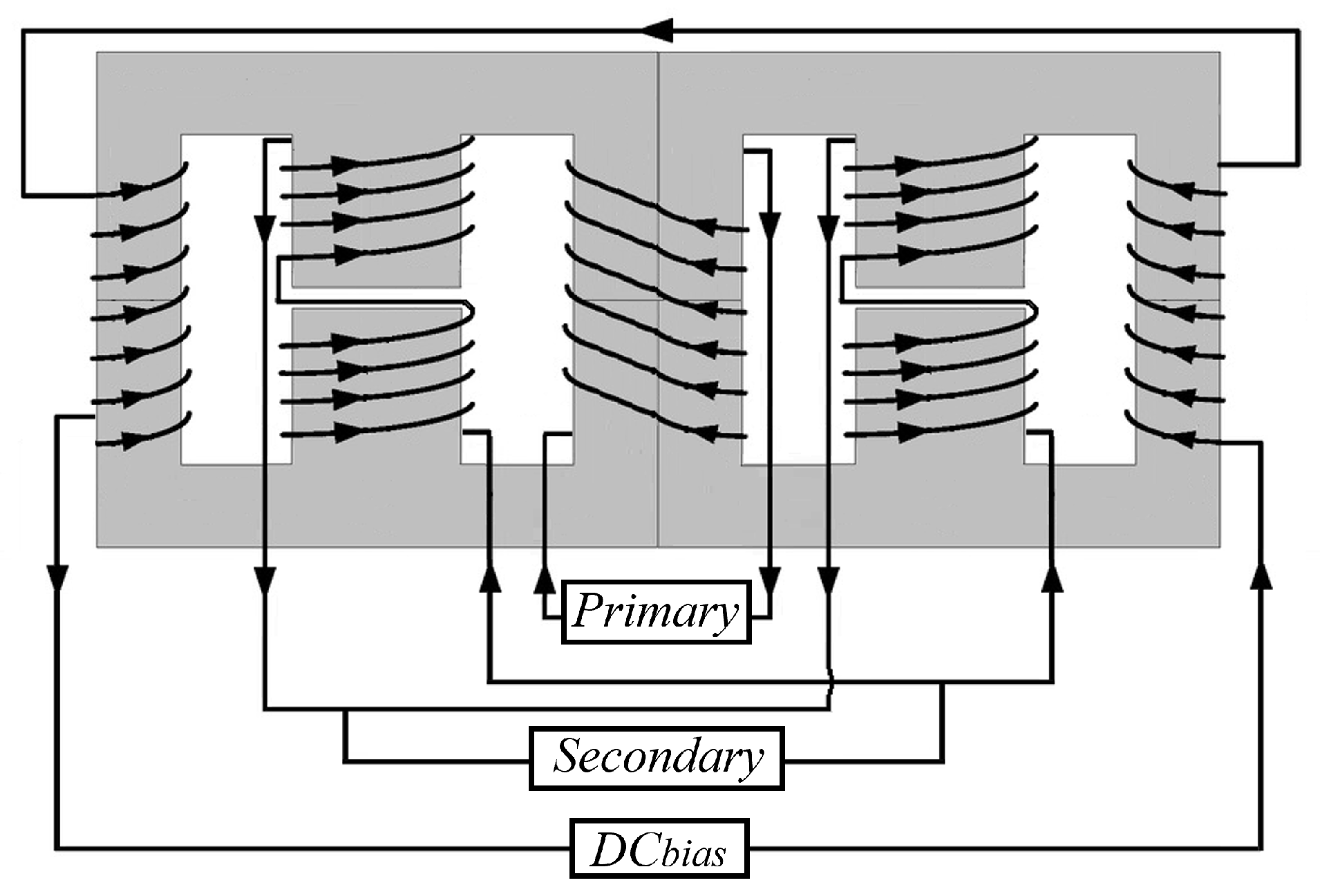
3. Analysis and Design of Current-Controlled Variable Transformer
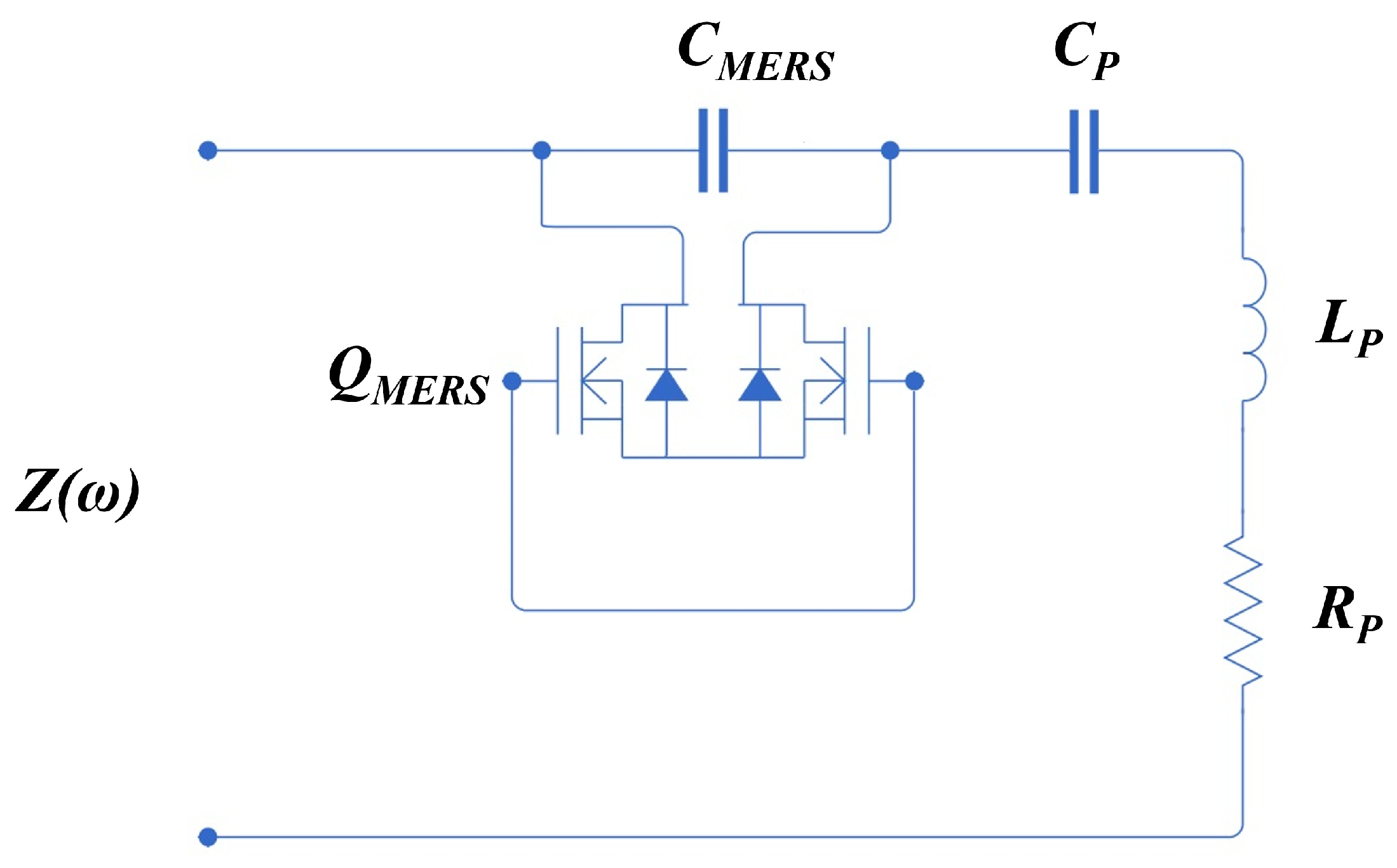
4. Analysis of Magnetic Energy Recovery Switch
5. Reactive Elements Control Inverter Design, Control and Efficiency
5.1. Design Procedure
- Bmax corresponds to the maximum flux density (T).
- J corresponds to the maximum current density (A/m2).
- K is a constant defined between 0.5 and 0.9, indicating the capacity of the winding.
- Hbias is the continuous magnetic field intensity.
- ldc is the length of the dc control branch from center to center of the core (m).
5.2. Control Operation Principle
5.3. Losses Analysis
6. Experimental Results
- (1)
- Induction heating inverter with six SiC NTH4L022N120M3S.
- (2)
- MERS capacitor.
- (3)
- Series capacitor (Cp).
- (4)
- Variable transformer.
- (5)
- Series inductor (Ls).
- (6)
- Set of workpieces.
- (7)
- 300 MHz bandwidth DSO.
- (8)
- Rogowski current probe.
- (9)
- Differential voltage probe.
- (10)
- Hall effect probe.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esteve, V.; Bellido, J.L.; Jordán, J. State of the Art and Future Trends in Monitoring for Industrial Induction Heating Applications. Electronics 2024, 13, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgraja, J. Dual-Frequency Induction Heating Generator with Adjustable Impedance Matching. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 8308–8317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frania, K.; Kierepka, K.; Kasprzak, M.; Zimoch, P. Single Three-Phase Inverter for Dual-Frequency Induction Heating. Energies 2024, 17, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve, V.; Jordan, J.; Sanchis-Kilders, E.; Dede, E.J.; Maset, E.; Ejea, J.B.; Ferreres, A. Comparative Study of a Single Inverter Bridge for Dual-Frequency Induction Heating Using Si and SiC MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 1440–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JAcero, J.M.; Burdio, L.A.; Barragan, L.; Navarro, D.; Llorente, S. EMI improvements using the switching frequency modulation in a resonant inverter for domestic induction heating appliances. In Proceedings of the IEEE 35th Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Aachen, Germany, 20–25 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Esteve, V.; Bellido, J.L.; Jordán, J.; Dede, E.J. Improving the Efficiency of an Isolated Bidirectional Dual Active Bridge DC–DC Converter Using Variable Frequency. Electronics 2024, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajales, L.; Lee, F.C. Control system design and small-signal analysis of a phase-shift controlled series-resonant inverter for induction heating. In Proceedings of the PESC ‘95—Power Electronics Specialist Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 18–22 June 1995; pp. 450–456. [Google Scholar]
- Esteve, V.; Jordán, J.; Dede, E.J.; Martinez, P.J.; Ferrara, K.J.; Bellido, J.L. Comparative analysis and improved design of LLC inverters for induction heating. IET Power Electron. 2023, 16, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajales, L.; Sabaté, J.A.; Wang, K.R.; Tabisz, W.A.; Lee, F.C. Design of a 10 kW, 500 kHz phase-shift controlled series-resonant inverter for induction heating. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1993 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Twenty-Eighth IAS Annual Meeting, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–8 October 1993; pp. 843–849. [Google Scholar]
- Dudrik, J.; Trip, N.-D. Soft-switching PS-PWM DC–DC converter for full-load range applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2807–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellido, J.L.; Esteve, V.; Jordán, J. Efficiency Optimization in Parallel LLC Resonant Inverters with Current-Controlled Variable-Inductor and Phase Shift for Induction Heating. Electronics 2024, 13, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellido, J.L.; Esteve, V.; Jordán, J. Performance Enhancement in LC Series Resonant Inverters with Current-Controlled Variable-Transformer and Phase Shift for Induction Heating. Electronics 2024, 13, 2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia, O.; Maussion, P.; Dede, E.J.; Burdio, J.M. Induction heating technology and its applications: Past developments, current technology, and future challenges. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Chen, D.Y.; Lee, F.C.; Gradzki, P.M.; Knights, M.A. Forward Converter Regulator Using Controlled Transformer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1996, 11, 356–364. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, C.; Bernal, D.; Martinez, W. Analysis and Validation of Variable Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 30th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE), Kyoto, Japan, 20–23 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Medini, D.; Ben-Yaakov, S. A Current-Controlled Variable-Inductor for High Frequency Resonant Power Circuits. In Proceedings of the IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference Exposition (ASPEC), Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 February 1994; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, C.; Gerardo, D.; Martinez, W.H. Magnetically Controlled Transformer with Variable Turns Ratio and Low Series-inductance: Analysis and Implementation towards Its Application in SMP. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 14360–14374. [Google Scholar]
- Pajnić, M.; Pejović, P.; Aleksić, O. Design and Analysis of a Novel Coupled Inductor Structure with Variable Coupling Coefficient. IET Power Electron. 2018, 11, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TIsobe, Y.; Miyaji, T.; Kitahara; Fukutani, K.; Shimada, R. Soft-switching inverter for variable frequency induction heating using magnetic energy recovery switch (MERS). In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Barcelona, Spain, 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Isobe, T.; Shimada, R. New power supply topologies enabling high performance induction heating by using MERS. In Proceedings of the IECON 2013—39th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Vienna, Austria, 10–13 November 2013; pp. 5046–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, F.D.; Watanabe, E.H.; de Souza, L.F.W.; Alves, J.E.R. SSR and Power Oscillation Damping Using Gate-Controlled Series Capacitors (GCSC). IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2007, 22, 1806–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, L.; Watanabe, E.; Alves, J.; Pilotto, L. Thyristor and gate controlled series capacitors: Comparison of components rating. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37491), Toronto, ON, Canada, 13–17 July 2003; Volume 4, pp. 2542–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, H.A. Inductance formulas for circular and square coils. Proc. IEEE 1982, 70, 1449–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.R. Modelling and Simulation of Magnetic Components in Electric Circuits. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Electronics and Computer Science, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Esteve, V.; Jordan, J.; Sanchis, E.; Dede, E.J.; Maset, E.; Ejea, J.B.; Ferreres, A. Improving the reliability of series resonant inverters for induction heating applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J. Multivariable Control for Industrial Applications; Peter Peregrinus Ltd.: London, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport, E.; Pleshivteva, Y. Optimal Control of Induction Heating Process; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, J.M.; Perdigão, M.S.; Vaquero, D.G.; Calleja, A.J.; Saraiva, E.S. Analysis, Design, and Experimentation on Constant Frequency DC-DC Resonant Converters with Magnetic Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Scan Step | Workpiece Diameter (mm) | Penetration Depth (mm) | Frequency (kHz) | Quality Factor | Maximum Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23.5 | 0.7 | 67 | 10 | 6 |
| 2 | 30.2 | 0.6 | 77.5 | 8 | 9 |
| 3 | 25.5 | 0.55 | 89 | 9 | 10 |
| 4 | 35 | 0.5 | 100 | 6 | 10 |
| 5 | 32 | 0.65 | 72 | 7 | 10 |
| Scan Step | Workpiece Diameter (mm) | Inductor Current (Arms) | Transformer Ratio | Equivalent Capacitor (μF) | MERS Capacitance (μF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23.5 | 567 | 4.7 | 0.65 | 3.58 |
| 2 | 30.2 | 608 | 4.77 | 0.48 | 1.73 |
| 3 | 25.5 | 634 | 4.98 | 0.33 | 0.66 |
| 4 | 35 | 488 | 3.84 | 0.45 | 1.4 |
| 5 | 32 | 622 | 4.88 | 0.53 | 2.73 |
| Control Current | Theoretical Inductance (μH) | Measured Inductance (μH) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Circuit | Short Circuit | Open Circuit | Short Circuit | |||||
| 0 | 1103.1 | 79.37 | 1.22 | 0.793 | 1124.9 | 82.7 | 1.14 | 0.816 |
| 1 | 227.3 | 34.89 | 0.544 | 0.236 | 232.4 | 29.53 | 0.489 | 0.256 |
| Control Current | Theoretical | Measured | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR | TR | |||||
| 0 | 1103.1 | 79.37 | 2 | 1124.9 | 82.7 | 1.82 |
| 0.25 | 478.06 | 60.45 | 3 | 472.89 | 58.16 | 3.1 |
| 0.5 | 333.12 | 42.79 | 4 | 327.93 | 41.68 | 4.34 |
| 0.75 | 258.32 | 35.43 | 5.5 | 275.5 | 35.01 | 5.36 |
| 1 | 227.3 | 34.89 | 7 | 232.4 | 29.53 | 6.58 |
| Scan Step | Power (kW) | Frequency (kHz) | Phase Shift (°) | Transformer Ratio | Equivalent Capacitor (μF) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theor. | Meas. | Theor. | Meas. | Theor. | Meas. | Theor. | Meas. | ||
| 1 | 5 | 67 | 66.98 | 79.3 | 80.46 | 4.7 | 4.87 | 0.66 | 0.6 |
| 6 | 67.24 | 74.4 | 76.01 | 4.65 | 0.65 | ||||
| 2 | 5 | 77.5 | 77.62 | 66.7 | 67.11 | 4.77 | 4.7 | 0.48 | 0.47 |
| 9 | 77.48 | 38 | 38.84 | 4.76 | 0.47 | ||||
| 3 | 5 | 89 | 89.43 | 60 | 59.58 | 4.98 | 5.11 | 0.33 | 0.3 |
| 10 | 89.57 | 25.4 | 26.82 | 5.03 | 0.31 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 100 | 101.71 | 76.6 | 76.3 | 3.84 | 3.71 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| 10 | 102.3 | 54 | 53.89 | 3.82 | 0.42 | ||||
| 5 | 5 | 72 | 72.17 | 61.7 | 63.18 | 4.88 | 4.95 | 0.53 | 0.5 |
| 10 | 72.65 | 28 | 30.58 | 4.78 | 0.52 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellido, J.L.; Esteve, V.; Jordán, J. Reactive Elements Control in LC Series Resonant Inverters by Current-Controlled Variable-Transformer and Magnetic Energy Recovery Switch for Induction Heating. Electronics 2024, 13, 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13234666
Bellido JL, Esteve V, Jordán J. Reactive Elements Control in LC Series Resonant Inverters by Current-Controlled Variable-Transformer and Magnetic Energy Recovery Switch for Induction Heating. Electronics. 2024; 13(23):4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13234666
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellido, Juan L., Vicente Esteve, and José Jordán. 2024. "Reactive Elements Control in LC Series Resonant Inverters by Current-Controlled Variable-Transformer and Magnetic Energy Recovery Switch for Induction Heating" Electronics 13, no. 23: 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13234666
APA StyleBellido, J. L., Esteve, V., & Jordán, J. (2024). Reactive Elements Control in LC Series Resonant Inverters by Current-Controlled Variable-Transformer and Magnetic Energy Recovery Switch for Induction Heating. Electronics, 13(23), 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13234666














