Deep Learning Assisted Diagnosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on a Local-to-Global Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Previous studies selected some CT images from the whole CT sequence for COPD diagnosis, which cannot well capture the contextual details from successive CT slices. To this end, all the images of the CT sequence are analyzed for COPD CAD by a designed local-to-global deep framework with group attentions.
- To reveal the contextual information submerged in the CT images and among the CT slices, two types of group attentions are designed, involving GLAB for local image feature extraction and GGAB for long-range dependency extraction.
- Since the number of CT slices for a COPD patient influences the model’s prediction performance, a slice-aware loss is designed to adapt the model to the CT sequence with various numbers of CT images, which integrates a normalized function into the cross-entropy loss.
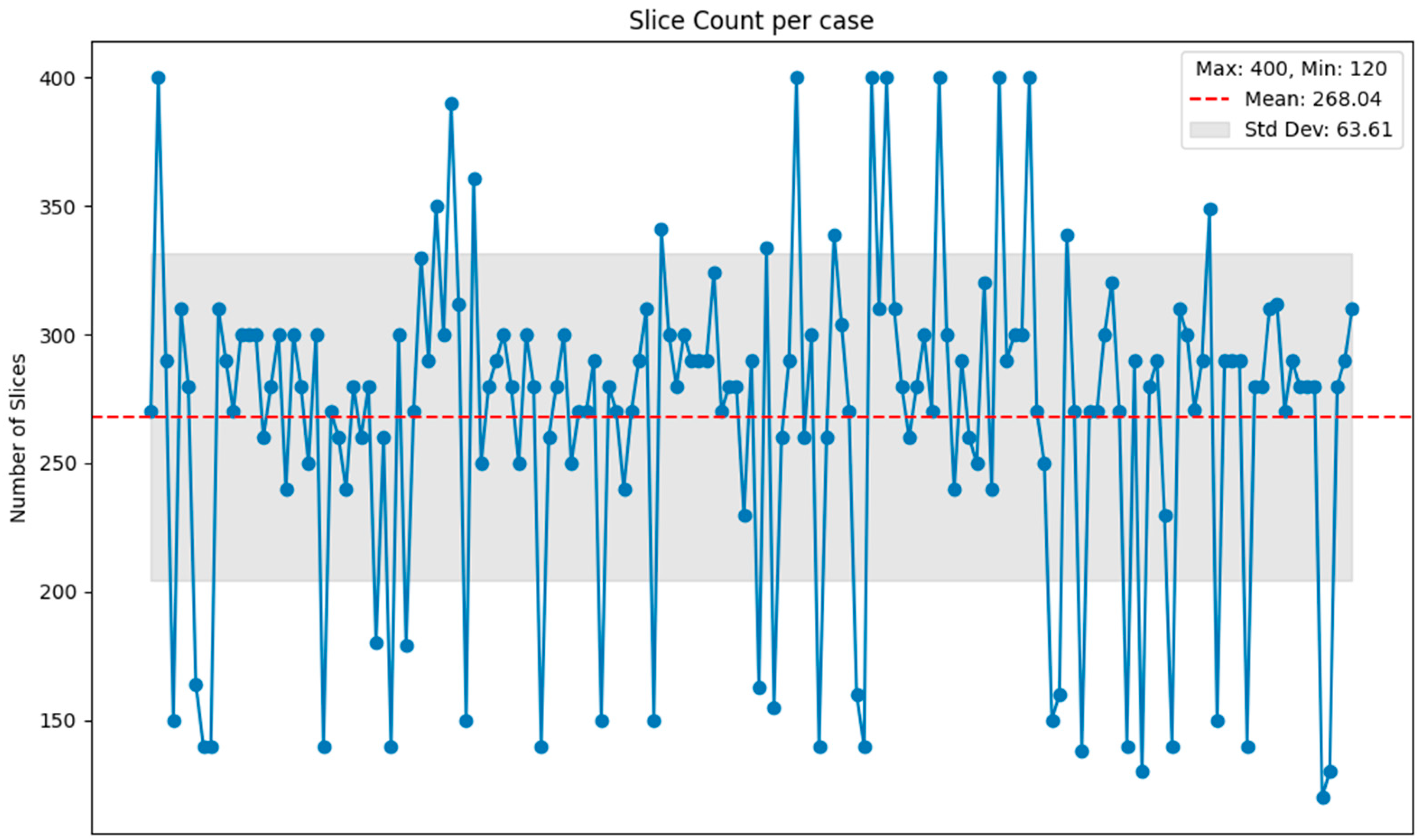
2. Materials
3. Methods
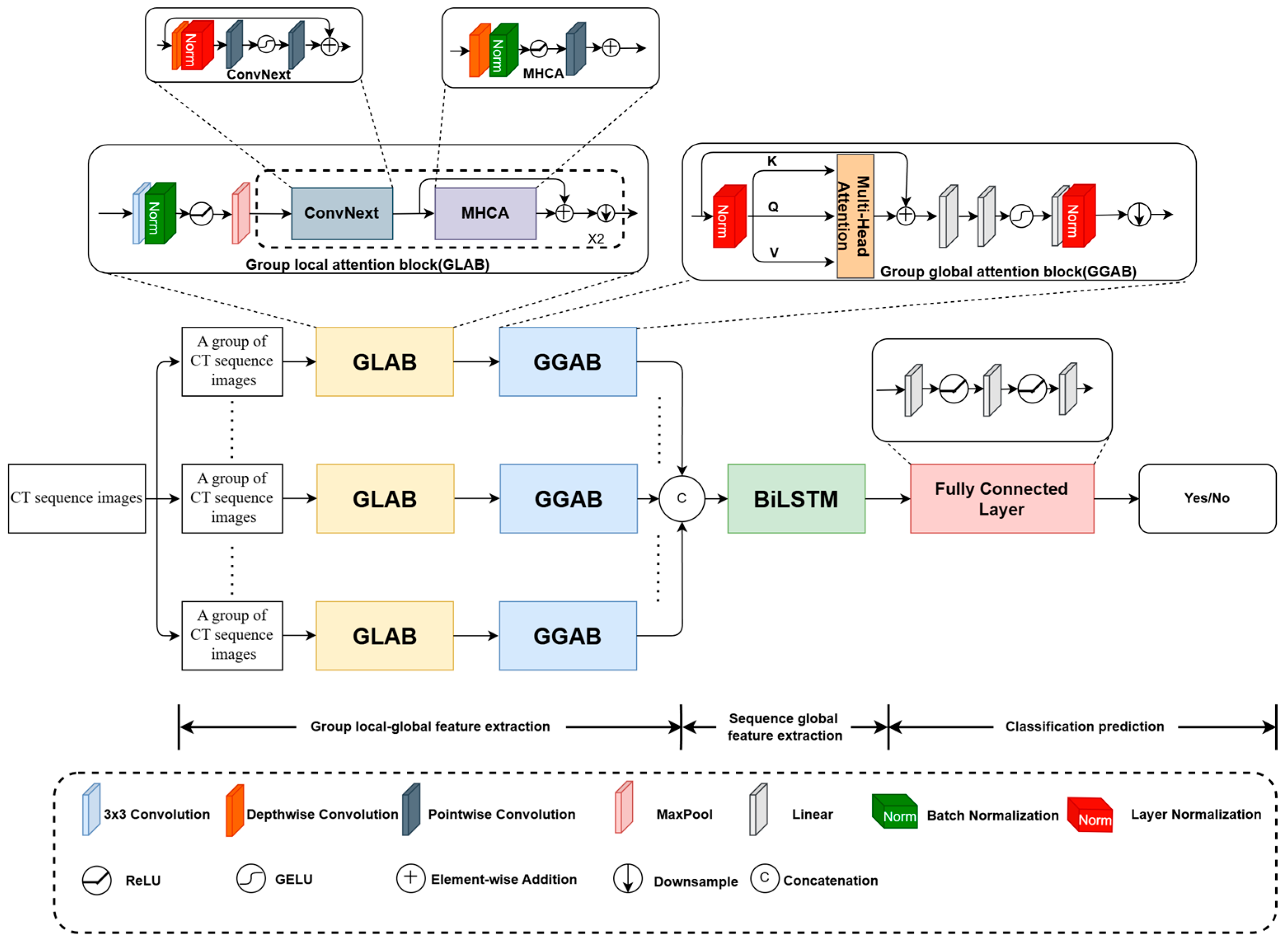
3.1. Architecture of the Designed Local-to-Global Deep Framework
3.2. GLAB
3.3. GGAB
3.4. BiLSTM
3.5. Slice-Aware Loss
4. Results
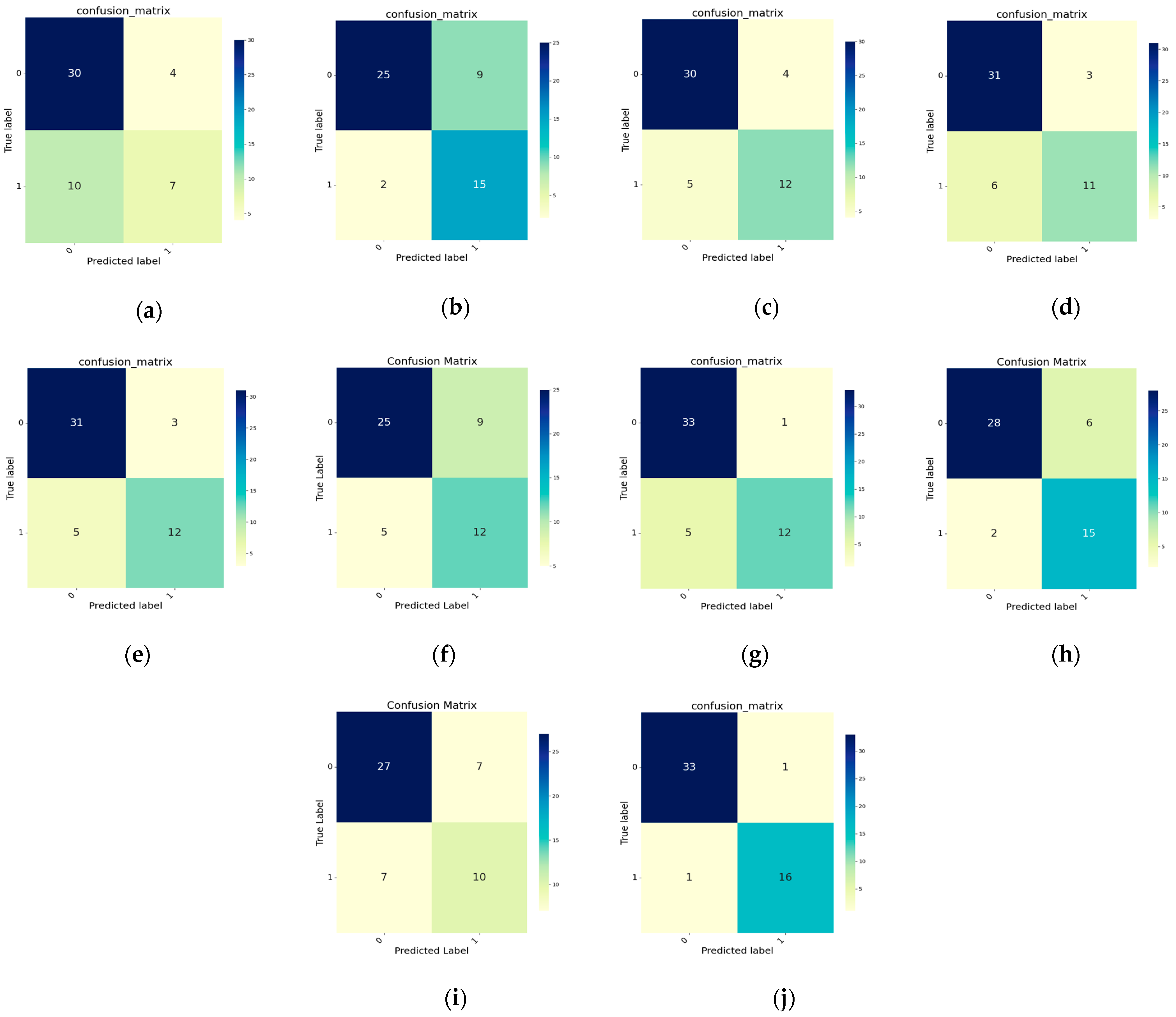
4.1. Comparison Experiments
4.2. Ablation Experiments
4.2.1. Influences of Different Modules
4.2.2. Influence of the Number of CT Slices in Each Group
4.2.3. Discussion on Loss Function
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagdonas, E.; Raudoniute, J.; Bruzauskaite, I.; Aldonyte, R. Novel aspects of pathogenesis and regeneration mechanisms in COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2015, 10, 995–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, F.W.; Chan, K.P.; Hui, D.S.; Goddard, J.R.; Shaw, J.G.; Reid, D.W.; Yang, I.A. Acute exacerbation of COPD. Respirology 2016, 21, 1152–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, T.Y.; Mac Aogáin, M.; Chan, A.K.; Yii, A.C.; Yong, V.F.; Tiew, P.Y.; Koh, M.S.; Chotirmall, S.H. Understanding COPD-overlap syndromes. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2017, 11, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, S. The effects and pathogenesis of PM2. 5 and its components on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2023, 18, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negewo, N.A.; Gibson, P.G.; McDonald, V.M. COPD and its comorbidities: Impact, measurement and mechanisms. Respirology 2015, 20, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Luo, C.; Ouyang, L.; Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhou, M.; et al. The burden of COPD in China and its provinces: Findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 859499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhvi, D.; Bon, J. CT imaging and comorbidities in COPD: Beyond lung cancer screening. Chest 2021, 159, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budoff, M.J.; Nasir, K.; Kinney, G.L.; Hokanson, J.E.; Barr, R.G.; Steiner, R.; Nath, H.; Lopez-Garcia, C.; Black-Shinn, J.; Casaburi, R. Coronary artery and thoracic calcium on noncontrast thoracic CT scans: Comparison of ungated and gated examinations in patients from the COPDGene cohort. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2011, 5, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.A.; Austin, J.H.; Hogg, J.C.; Grenier, P.A.; Kauczor, H.U.; Bankier, A.A.; Barr, R.G.; Colby, T.V.; Galvin, J.R.; Gevenois, P.A.; et al. CT-definable subtypes of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A statement of the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2015, 277, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.A.; Moore, C.M.; Wilson, C.; Nevrekar, D.; Jennermann, T.; Humphries, S.M.; Austin, J.H.M.; Grenier, P.A.; Kauczor, H.U.; Han, M.K.; et al. CT-based visual classification of emphysema: Association with mortality in the COPDGene study. Radiology 2018, 288, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Wu, G.; Suk, H.I. Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 19, 221–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadoss, R.; Vimala, C. Classification of Pulmonary Emphysema using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electronic Systems and Intelligent Computing (ICESIC), Chennai, India, 22–23 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Parui, S.; Parbat, D.; Chakraborty, M. A deep learning paradigm for computer aided diagnosis of emphysema from lung HRCT images. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Computing in Engineering & Technology (ICCET), Lonere, India, 12–13 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Polat, Ö.; Şalk, İ.; Doğan, Ö.T. Determination of COPD severity from chest CT images using deep transfer learning network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 21903–21917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Qi, S.; Feng, J.; Xia, S.; Kang, Y.; Qian, W.; Yao, Y. Identification of COPD from multi-view snapshots of 3D lung airway tree via deep CNN. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 38907–38919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Du, R.; Feng, J.; Qi, S.; Pang, H.; Xia, S.; Qian, W. Deep CNN for COPD identification by Multi-View snapshot integration of 3D airway tree and lung field. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 79, 104162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.T.; Kim, T.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, C.H.; Chae, K.J.; Bak, S.H.; Kwon, S.; Jin, G.; Park, E.; Choi, S.; et al. A 3D-CNN model with CT-based parametric response mapping for classifying COPD subjects. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Vesal, S.; Durlak, F.; Kaergel, R.; Ravikumar, N.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Maier, A. COPD classification in CT images using a 3D convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2020: Algorithmen–Systeme–Anwendungen, Berlin, Germany, 15–17 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, M.; Jia, S.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Yu, L.; Zhu, W. CT-based COPD identification using multiple instance learning with two-stage attention. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 230, 107356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Qi, S.; Feng, J.; Xia, S.; Kang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Qian, W. DCT-MIL: Deep CNN transferred multiple instance learning for COPD identification using CT images. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 145011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, S.M.; Notary, A.M.; Centeno, J.P.; Strand, M.J.; Crapo, J.D.; Silverman, E.K.; Lynch, D.A. Deep learning enables automatic classification of emphysema pattern at CT. Radiology 2020, 294, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ren, L.; Wang, G. LGI Net: Enhancing local-global information interaction for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 167, 107627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Shi, W.; Tian, J.; Qi, B.; Li, B.; Hao, H.; Xu, B. Attention-based bidirectional long short-term memory networks for relation classification. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Berlin, Germany, 7–12 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Z. TriConvUNeXt: A Pure CNN-Based Lightweight Symmetrical Network for Biomedical Image Segmentation. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2024, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A convnet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xia, X.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Wang, R.; Zhen, M. Next-vit: Next generation vision transformer for efficient deployment in realistic industrial scenarios. arXiv 2022, arXiv:220705501. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, V.; Keniya, R.; Shridharani, A.; Punjabi, M.; Shah, J.; Mehendale, N. Diagnosis of COVID-19 using CT scan images and deep learning techniques. Emerg. Radiol. 2021, 28, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollias, D.; Arsenos, A.; Soukissian, L.; Kollias, S. MIA-COV19D: COVID-19 detection through 3-D chest CT image analysis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Varchagall, M.; Nethravathi, N.; Chandramma, R.; Nagashree, N.; Athreya, S.M. Using deep learning techniques to evaluate lung cancer using CT images. SN Comput. Sci. 2023, 4, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienzle, D.; Lorenz, J.; Schön, R.; Ludwig, K.; Lienhart, R. COVID detection and severity prediction with 3D-ConvNeXt and custom pretrainings. In Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Jacobs, C.; Charbonnier, J.P.; Slebos, D.J.; van Ginneken, B. Emphysema subtyping on thoracic computed tomography scans using deep neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, K.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Leader, J.; Pu, J. BeyondCT: A deep learning model for predicting pulmonary function from chest CT scans. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.05645. [Google Scholar]

| Methods | ACC | SEN | SPE | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shah et al. [28] (2021) | 72.55% | 41.18% | 88.24% | 63.14% |
| Ahmed et al. [19] (2020) | 78.43% | 88.24% | 73.53% | 81.49% |
| Xu et al. [21] (2020) | 82.35% | 70.59% | 88.24% | 82.52% |
| Kolias et al. [29] (2021) | 82.35% | 64.71% | 91.18% | 87.37% |
| Humphries et al. [22] (2020) | 84.31% | 70.59% | 91.18% | 83.22% |
| Varchagall et al. [30] (2023) | 72.55% | 70.59% | 73.53% | 79.93% |
| Kienzle et al. [31] (2022) | 88.24% | 70.59% | 97.06% | 92.90% |
| Xie et al. [32] (2023) | 84.31% | 88.24% | 82.35% | 89.62% |
| Geng et al. [33] (2024) | 72.55% | 58.82% | 79.41% | 72.32% |
| Ours | 96.08% | 94.12% | 97.06% | 95.32% |
| GLAB | GGAB | BiLSTM | ACC | SEN | SPE | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76.47% | 94.12% | 67.65% | 89.10% | |||
| √ | 82.35% | 70.59% | 88.24% | 91.18% | ||
| √ | 80.39% | 94.12% | 73.53% | 90.83% | ||
| √ | 82.35% | 76.47% | 85.29% | 90.83% | ||
| √ | √ | 88.24% | 70.59% | 97.06% | 94.81% | |
| √ | √ | 86.27% | 82.35% | 88.24% | 91.70% | |
| √ | √ | 86.27% | 94.12% | 82.35% | 92.91% | |
| √ | √ | √ | 96.08% | 94.12% | 97.06% | 95.32% |
| Number of Group Slices | ACC | SEN | SPE | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 90.20% | 76.47% | 97.06% | 91.52% |
| 10 | 96.08% | 94.12% | 97.06% | 95.32% |
| 15 | 90.20% | 82.35% | 94.12% | 94.46% |
| 20 | 90.20% | 76.47% | 97.06% | 92.56% |
| Input | Loss Functions | ACC | SEN | SPE | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Slices | cross entropy loss (120) | 82.35% | 76.47% | 85.29% | 89.27% |
| cross entropy loss (268) | 88.24% | 82.35% | 91.18% | 91.52% | |
| cross entropy loss (400) | 80.39% | 64.71% | 88.24% | 88.58% | |
| Variable Slices | cross entropy loss | 92.16% | 88.24% | 94.12% | 95.16% |
| slice-aware loss | 96.08% | 94.12% | 97.06% | 95.32% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, N.; Xie, Y.; Cai, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, P. Deep Learning Assisted Diagnosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on a Local-to-Global Framework. Electronics 2024, 13, 4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13224443
Cai N, Xie Y, Cai Z, Liang Y, Zhou Y, Wang P. Deep Learning Assisted Diagnosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on a Local-to-Global Framework. Electronics. 2024; 13(22):4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13224443
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Nian, Yiying Xie, Zijie Cai, Yuchen Liang, Yinghong Zhou, and Ping Wang. 2024. "Deep Learning Assisted Diagnosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on a Local-to-Global Framework" Electronics 13, no. 22: 4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13224443
APA StyleCai, N., Xie, Y., Cai, Z., Liang, Y., Zhou, Y., & Wang, P. (2024). Deep Learning Assisted Diagnosis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Based on a Local-to-Global Framework. Electronics, 13(22), 4443. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13224443





