Unstructured Document Information Extraction Method with Multi-Faceted Domain Knowledge Graph Assistance for M2M Customs Risk Prevention and Screening Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We constructed a dataset of unstructured customs documents based on real customs business scenarios and proposed optimization methods for OCR models, HMLKD, and post-OCR text recognition correction methods, iCDKG-PostOCR.
- We evaluated the recognition accuracy of public OCR models on the CUSD-RBS dataset and selected a benchmark model that balances performance and inference speed. The effectiveness of the HMLKD and iCDKG-PostOCR methods was validated on this model, and the advantages and disadvantages of the methods were analyzed. The study achieved an accuracy of over 94% for three types of fields.
- We proposed a new perspective on the intelligent processing of documents and offered ideas and a framework for handling customs unstructured accompanying documents, which is a topic that has received less research attention. This can serve as a reference for other researchers.
2. Related Works
2.1. OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
2.2. Text Correction
2.3. Knowledge Distillation
3. Methodology
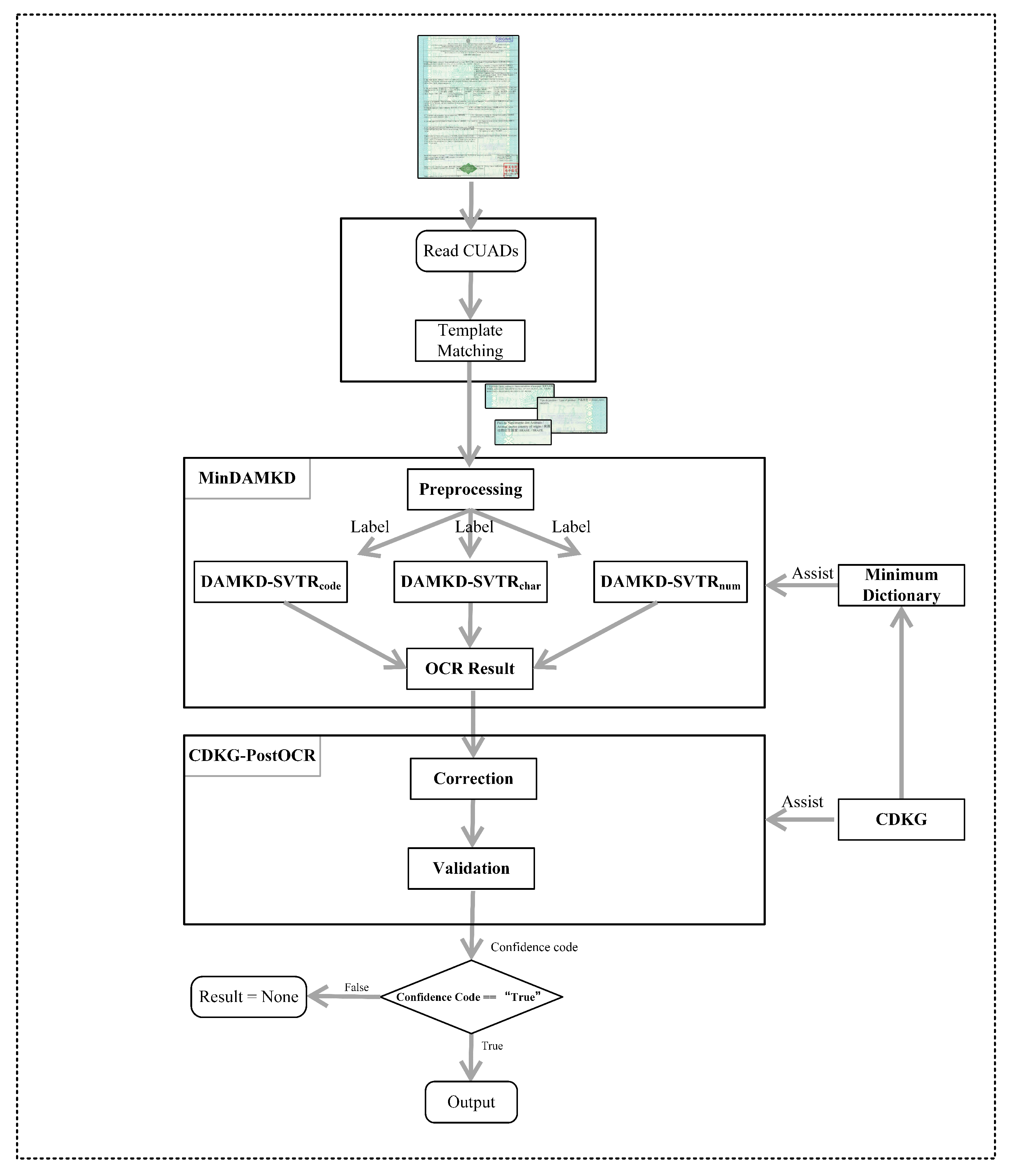
3.1. Overall Process of CUAD Information Extraction
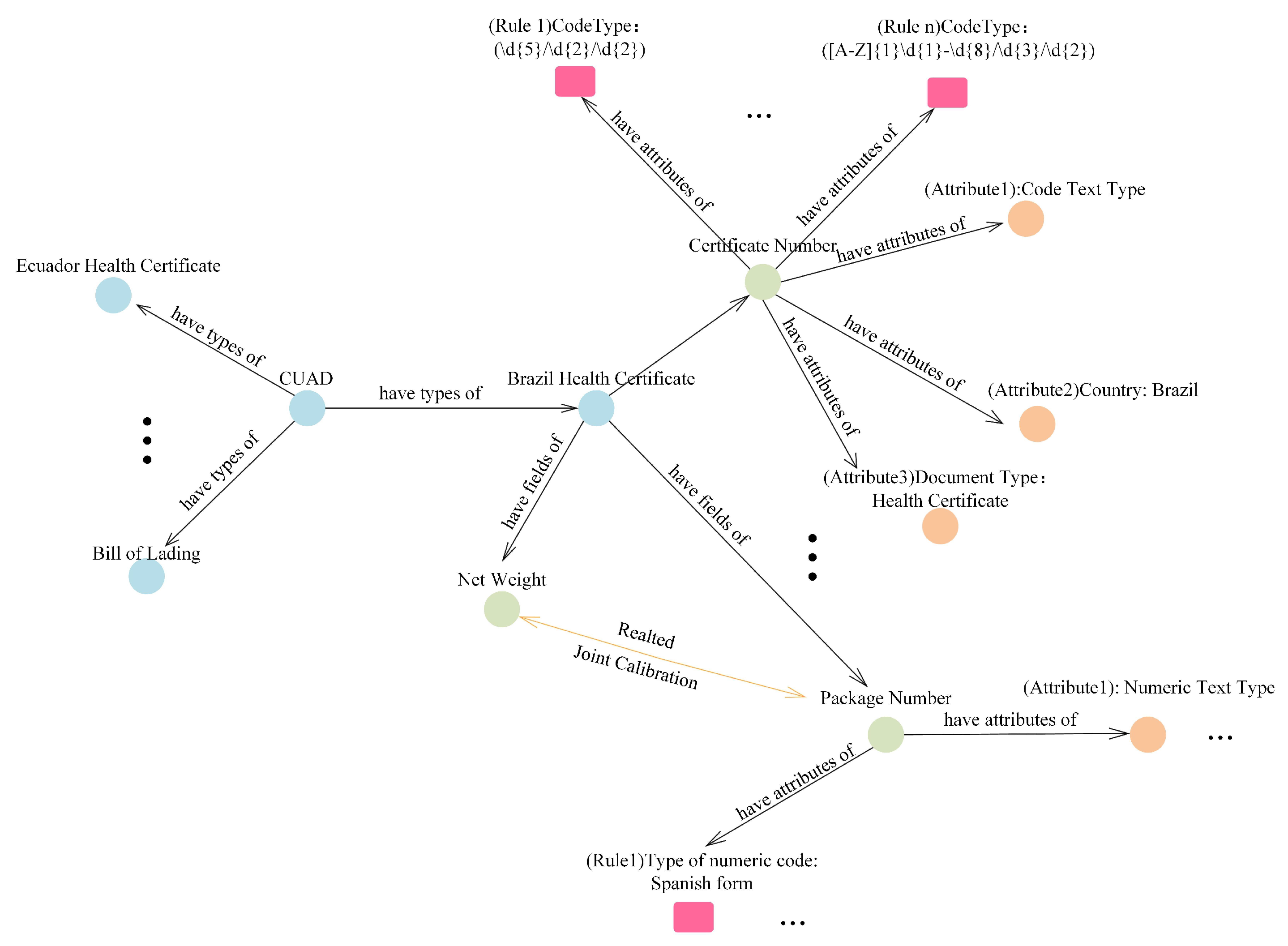
3.2. Customs Domain Knowledge Graph
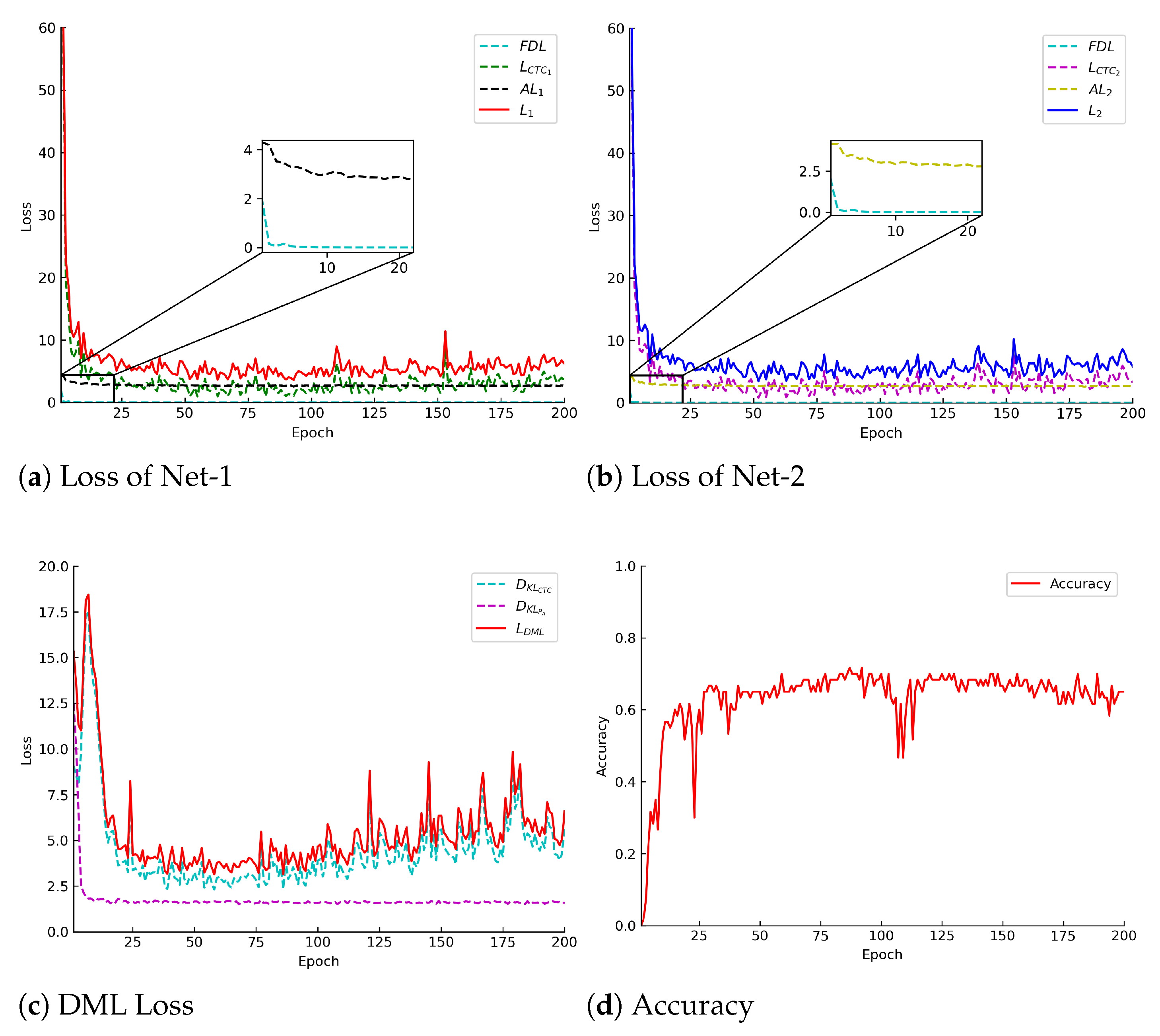
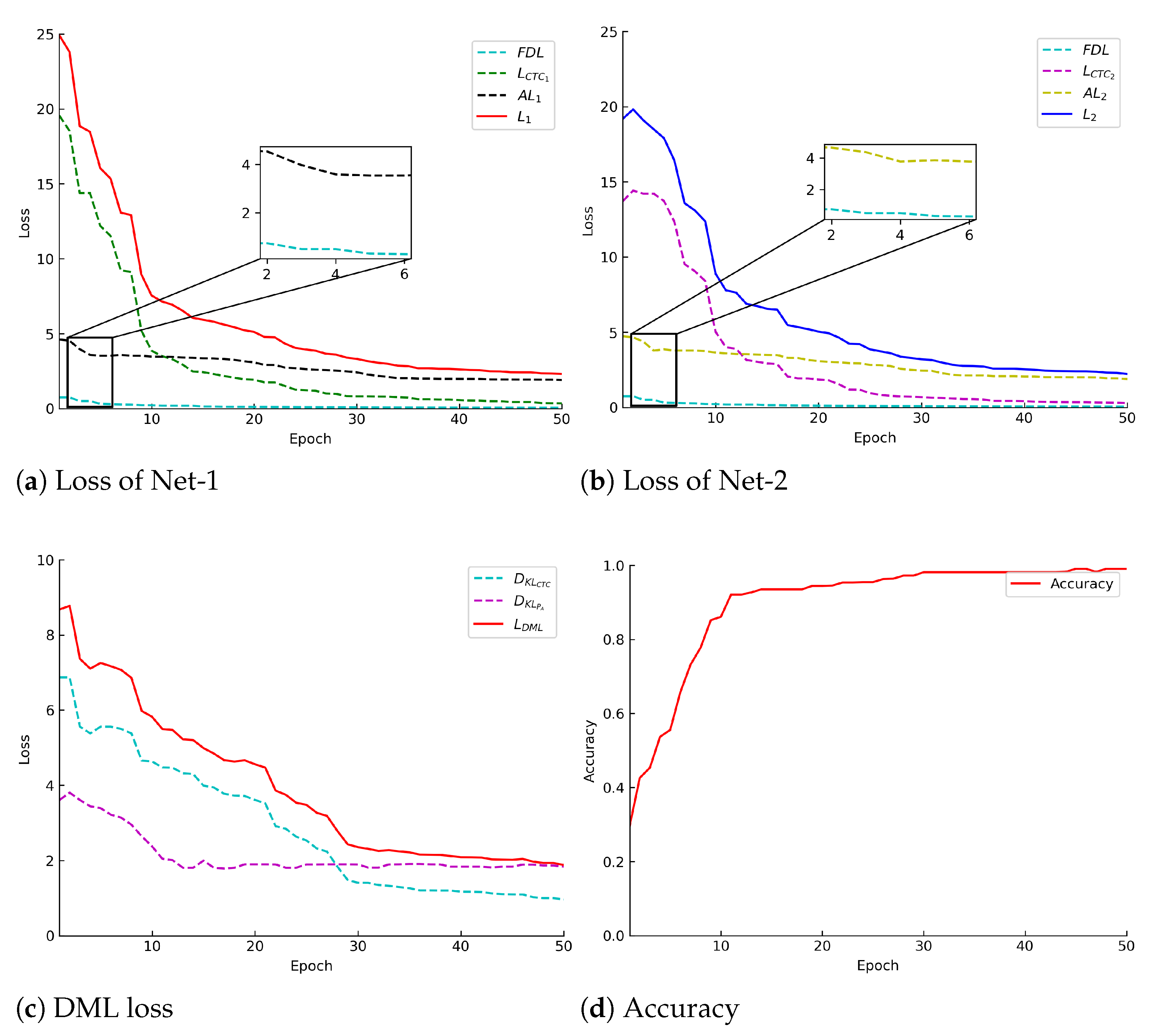
3.3. Hybrid Mutual Learning Knowledge Distillation Method
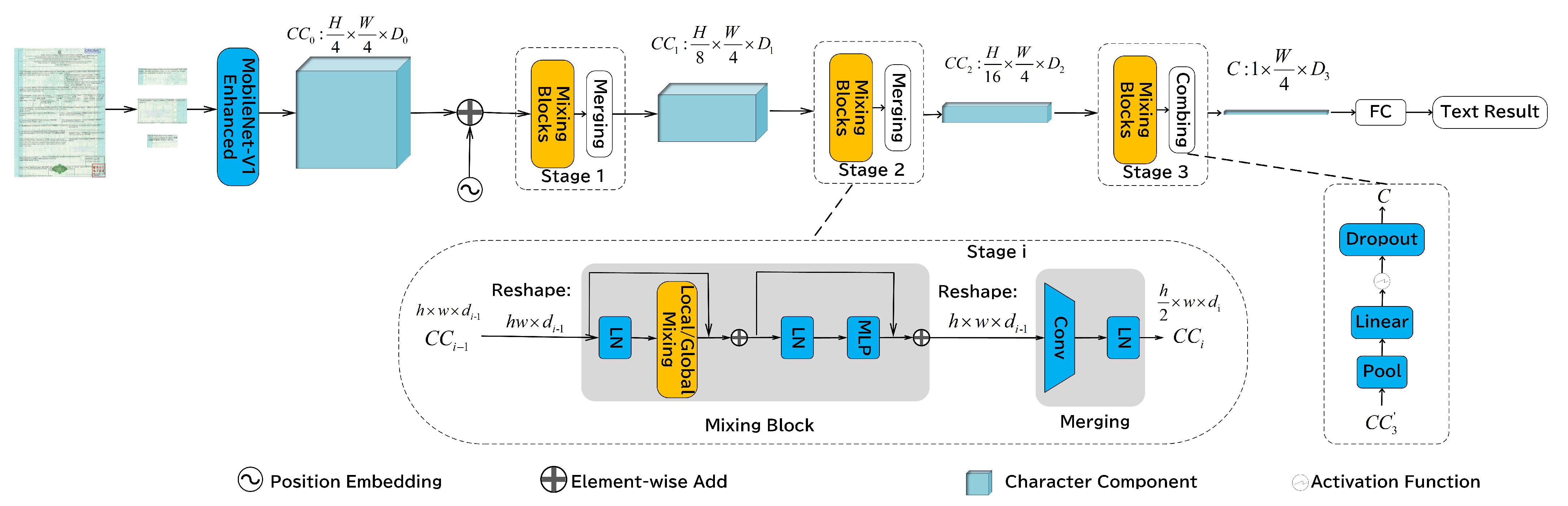
3.3.1. Baseline
3.3.2. GTC Strategy
3.3.3. Minimal Dictionary
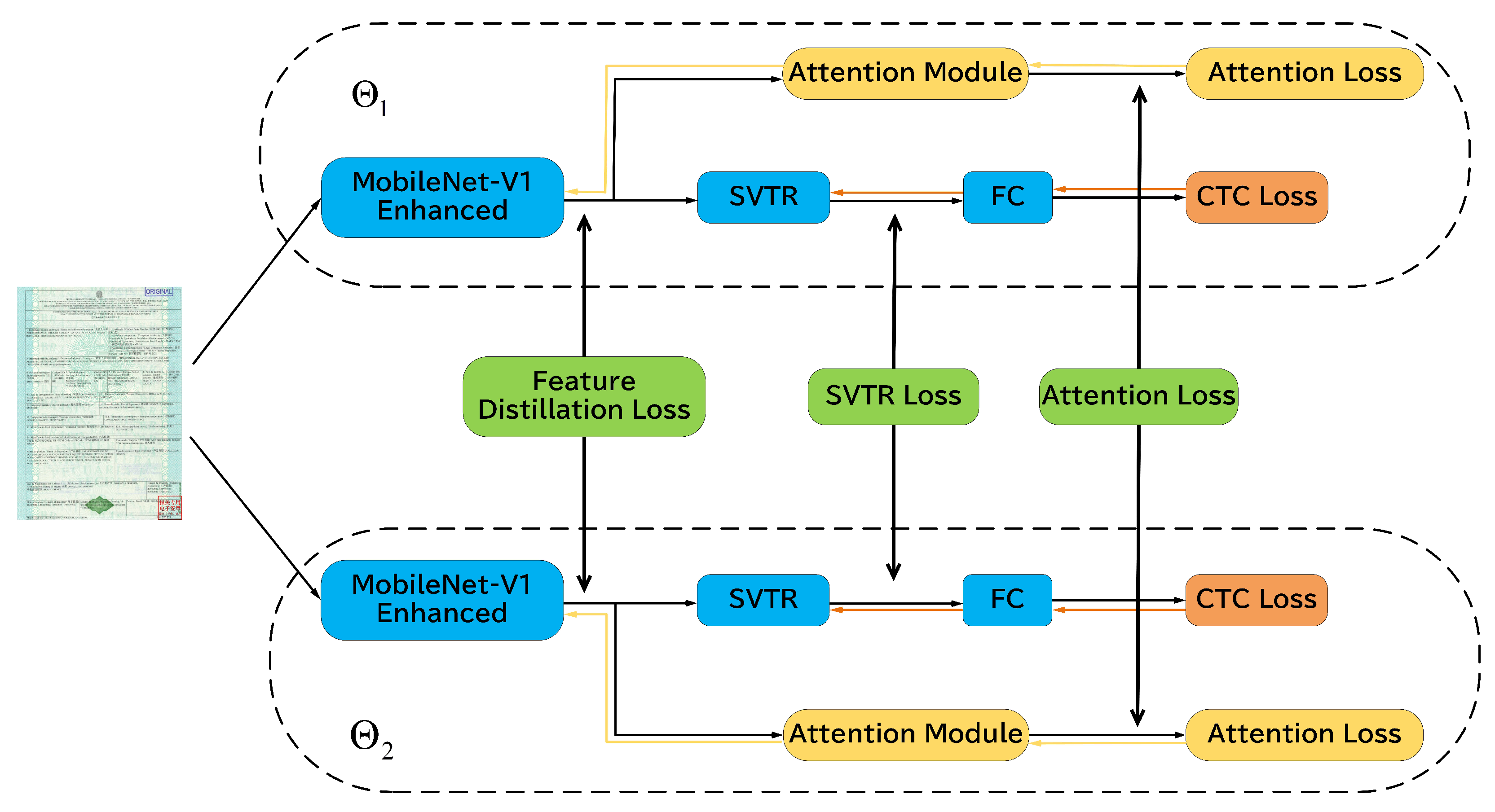
3.3.4. Mutual Learning Distillation
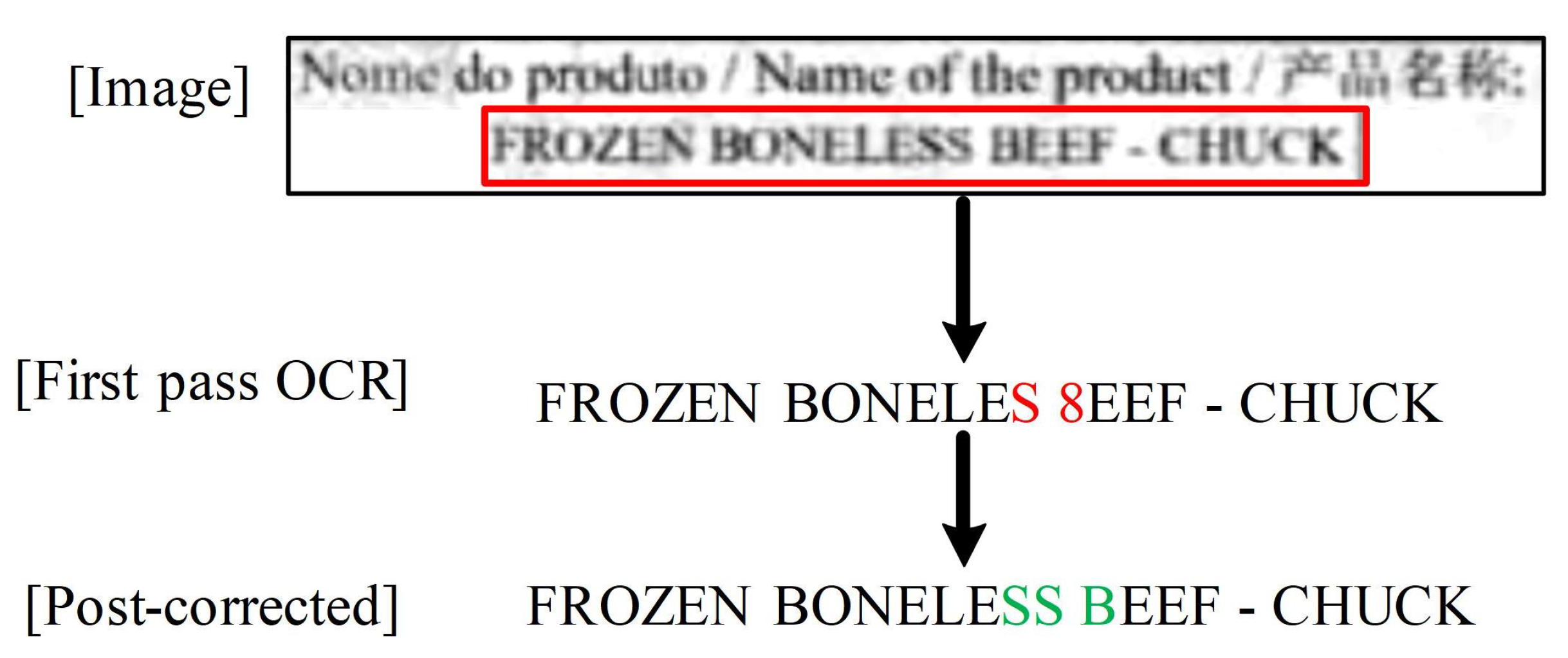
3.4. iCDKG-PostOCR Methodology
| Algorithm 1: The Training Procedure of HMLKD |
 |
4. Evaluation Experiments
4.1. Benchmark Dataset
4.2. Metrics
4.3. Image Pre-Processing
4.4. Evaluation Experiments and Results
4.4.1. OCR Performance Evaluation
4.4.2. Code Text Type
4.4.3. Character Text Type
4.4.4. Numeric Text Type
4.5. Post-OCR
4.5.1. Code Text Type
4.5.2. Character Text Type
4.5.3. Numeric Text Type
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CUAD | Customs Unstructured Accompanying Document |
| M2M | Machine-to-Machine |
| M2H | Machine-to-Human |
| OCR | Optical Character Recognition |
| HMLKD | Hybrid Mutual Learning Knowledge Distillation |
| CDKG | Customs Domain Knowledge Graph |
| CUSD-RBS | Customs Unstructured Documents based on Real-world Business Scenarios |
| FER | Field Error Rate |
| CR | Confidence Rate |
References
- Chakraborty, S.; Harit, G.; Ghosh, S. TransDocAnalyser: A framework for semi-structured offline handwritten documents analysis with an application to legal domain. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, San Jose, CA, USA, 21–26 August 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 45–62. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.; Priyadarshini, J.; Gopal, S.; Gupta, S.; Dayal, H.S. Optical character recognition on bank cheques using 2D convolution neural network. In Proceedings of the Applications of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Engineering: SIGMA 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 2, pp. 589–596. [Google Scholar]
- Pradipta, D.J.; Handayani, P.W.; Shihab, M.R. Evaluation of the customs document lane system effectiveness: A case study in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd East Indonesia Conference on Computer and Information Technology (EIConCIT), Surabaya, Indonesia, 9–11 April 2021; pp. 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Basir, A.; Satyadini, A.E.; Barata, A. Modern Customs Risk Management Framework: Improvement towards Institutional Reform. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 2019, 4, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, S.; Suen, C.Y.; Yamamoto, K. Historical review of OCR research and development. Proc. IEEE 1992, 80, 1029–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, N.; Matton, A.; Greaves, M.; Lam, A. A survey of deep learning approaches for ocr and document understanding. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.13534. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.Y.; Osindero, S. Recursive recurrent nets with attention modeling for ocr in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2231–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Wang, C.; Su, J.; Taylor, C. An elevator button recognition method combining YOLOv5 and OCR. CMC Comput. Mater. Cont. 2023, 75, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Wan, Z.; Yao, C.; Chen, K.; Bai, X. Real-time scene text detection with differentiable binarization. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11474–11481. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Bai, X.; Yao, C. An end-to-end trainable neural network for image-based sequence recognition and its application to scene text recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 2298–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisyuk, F.; Gordo, A.; Sivakumar, V. Rosetta: Large scale system for text detection and recognition in images. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, London, UK, 19–23 August 2018; pp. 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Atienza, R. Vision transformer for fast and efficient scene text recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Lausanne, Switzerland, 5–10 September 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 319–334. [Google Scholar]
- Santamaría, G.; Domínguez, C.; Heras, J.; Mata, E.; Pascual, V. Combining image processing techniques, OCR, and OMR for the digitization of musical books. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems, La Rochelle, France, 21–28 February 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 553–567. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jia, C.; Yin, X.; Zheng, T.; Li, C.; Du, Y.; Jiang, Y.G. SVTR: Scene text recognition with a single visual model. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.00159. [Google Scholar]
- Semkovych, V.; Shymanskyi, V. Combining OCR methods to improve handwritten text recognition with low system technical requirements. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Computer Science, Digital Economy and Intelligent Systems, Wuhan, China, 11–13 November 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 693–702. [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, S.; de Herrera, A.G.S.; Doctor, F.; Mirza, A. An OCR post-correction approach using deep learning for processing medical reports. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 2574–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo-Nguyen, T.A.; Nguyen, P.; Le, H.S. An efficient method to extract data from bank statements based on image-based table detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 15th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Applications (ACOMP), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 24–26 November 2021; pp. 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, P.; Chaudhary, D.; Madaan, V.; Zabrovskiy, A.; Prodan, R.; Kimovski, D.; Timmerer, C. Automated bank cheque verification using image processing and deep learning methods. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 5319–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wang, B.; Lai, X. Research on the construction of intelligent customs clearance information system for cross-border road cargo between Guangdong and Hong Kong. In Proceedings of the International Conference on AI-Generated Content, Shanghai, China, 25–26 August 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 181–190. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Yun, J. M2M service platforms: Survey, issues, and enabling technologies. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2013, 16, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, R.; Altrjman, C.; Al-Turjman, F. An overview of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine to Machine (M2M) Communications. NEU J. Artif. Intell. Internet Things 2023, 2, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Jiang, T.; Han, Z. A survey of emerging M2M systems: Context, task, and objective. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 1246–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barki, A.; Bouabdallah, A.; Gharout, S.; Traore, J. M2M security: Challenges and solutions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2016, 18, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Jatowt, A.; Coustaty, M.; Doucet, A. Survey of post-OCR processing approaches. ACM Comput. Surv. CSUR 2021, 54, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damerau, F.J. A technique for computer detection and correction of spelling errors. Commun. ACM 1964, 7, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijhwani, S.; Anastasopoulos, A.; Neubig, G. OCR post correction for endangered language texts. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.05402. [Google Scholar]
- Francois, M.; Eglin, V.; Biou, M. Text detection and post-OCR correction in engineering documents. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems, La Rochelle, France, 22–25 May 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 726–740. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, T.; Hospedales, T.M.; Lu, H. Deep mutual learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4320–4328. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Ji, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, L.; Liu, L.; Sun, M.; Liu, Q.; Yang, R. Construction and application of a knowledge graph. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Salih, B. Domain-specific knowledge graphs: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 185, 103076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubauer, T.; Lamparter, S.; Haase, P.; Herzig, D.M. Use cases of the industrial knowledge graph at siemens. In Proceedings of the ISWC (P&D/Industry/BlueSky), Monterey, CA, USA, 8–12 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, C.; Pu, H. Domain knowledge graph-based research progress of knowledge representation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Fernández, S.; Gomez, F.; Schmidhuber, J. Connectionist temporal classification: Labelling unsegmented sequence data with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Cai, X.; Hou, J.; Yi, S.; Lin, Z. GTC: Guided training of ctc towards efficient and accurate scene text recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 11005–11012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, P.; Shen, C.; Zhang, G. Show, attend and read: A simple and strong baseline for irregular text recognition. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 8610–8617. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Liu, W.; Guo, R.; Yin, X.; Jiang, K.; Du, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhu, L.; Lai, B.; Hu, X.; et al. PP-OCRv3: More Attempts for the Improvement of Ultra Lightweight OCR System. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.03001. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco, R.C. An open-source OCR evaluation tool. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Digital Access to Textual Cultural Heritage, Madrid, Spain, 19–20 May 2014; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, F.; Chen, Z.; Xu, B. NRTR: A no-recurrence sequence-to-sequence model for scene text recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), Sydney, Australia, 20–25 September 2019; pp. 781–786. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Lyu, P.; Yao, C.; Bai, X. ASTER: An attentional scene text recognizer with flexible rectification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 2035–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, S.; Baek, J.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, H. On recognizing texts of arbitrary shapes with 2D self-attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 546–547. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.; Alahari, K.; Jawahar, C. Scene text recognition using higher order language priors. In Proceedings of the BMVC—British Machine Vision Conference, Glasgow, UK, 25–28 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Babenko, B.; Belongie, S. End-to-end scene text recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 1457–1464. [Google Scholar]






| Method | Code Text | Character Text | Numeric Text | Parameters (M) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FER | Inference Time * | FER | Inference Time * | FER | Inference Time * | ||
| CRNN [11] | 100% | 0.82 | 100% | 1.04 | 100% | 0.65 | 8.3 |
| NRTR [40] | 85.42% | 7.72 | 85.07% | 8.42 | 90.48% | 4.99 | 31.7 |
| ASTER [41] | 97.92% | 2.76 | 85.07% | 2.80 | 95.24% | 2.49 | 27.2 |
| SAR [37] | 95.83% | 3.60 | 91.04% | 3.77 | 66.67% | 3.25 | 57.5 |
| SATRN [42] | 87.50% | 7.40 | 85.07% | 7.86 | 61.90% | 5.22 | 48.6 |
| SVTR [15] | 55.57% | 1.13 | 86.67% | 1.51 | 30.56% | 0.83 | 20.2 |
| HMLKD-SVTR_code | 13.89% | 1.11 | - | - | - | - | 20.2 |
| HMLKD-SVTR_char | - | - | 28.34% | 1.25 | - | - | 16.9 |
| HMLKD-SVTR_num | - | - | - | - | 8.34% | 0.83 | 20.2 |
| Environment | Configuration | |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware | CPU: | AMD Ryzen 7 4800 H 2.90 GHz |
| GPU: | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2060 | |
| Memory: | 16 GB RAM | |
| Software | Operating System: | Microsoft Windows 10 |
| Development Platform: | PyCharm 2022.1.2 | |
| Language: | Python 3.8 | |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Learning rate decay strategy | Piecewise |
| Initial learning rate | |
| Batch size | 16 |
| 0.5 | |
| 1 |
| HMLKD-SVTR_Code | FER | Parameters (M) | Inference Speed (s/image) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMLKD with min-Dict | 41.70% | 16.9 | 1.10 |
| HMLKD without min-Dict | 13.89% | 20.2 | 1.11 |
| HMLKD-SVTR_Character | FER | Parameters (M) | Inference Speed (s/image) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMLKD with min-Dict | 28.34% | 16.9 | 1.25 |
| HMLKD without min-Dict | 31.70% | 20.2 | 1.49 |
| HMLKD-SVTR_Numeric | FER | Parameters (M) | Inference Speed (s/image) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HMLKD with min-Dict | 66.67% | 16.8 | 0.82 |
| HMLKD without min-Dict | 8.34% | 20.2 | 0.83 |
| FER | Parameters (M) | Inference Speed (s/image) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IIIT5K | SVT | IIIT5K | SVT | IIIT5K | SVT | |
| Without distillation | 51.26% | 38.84% | 20.24 | 20.24 | 0.499 | 0.148 |
| Distillation without min-Dict | 6.25% | 1.01% | 20.24 | 20.24 | 0.483 | 0.150 |
| Distillation with min-Dict | 6.25% | 3.13% | 16.99 | 16.96 | 0.099 | 0.137 |
| Method | FER | CR |
|---|---|---|
| HMLKD-SVTR without iCDKG-PostOCR | 13.89% | 98.36% |
| HMLKD-SVTR with iCDKG-PostOCR | 2.30% | 99.17% |
| Method | FER | CR |
|---|---|---|
| HMLKD-SVTR without iCDKG-PostOCR | 28.34% | 100% |
| HMLKD-SVTR with iCDKG-PostOCR | 3.45% | 100% |
| Method | FER | CR |
|---|---|---|
| HMLKD-SVTR without iCDKG-PostOCR | 8.34% | 99.38% |
| HMLKD-SVTR with iCDKG-PostOCR | 4.00% | 99.38% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, F.; Wang, H.; Wan, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, R.; Lv, D.; Lin, Y. Unstructured Document Information Extraction Method with Multi-Faceted Domain Knowledge Graph Assistance for M2M Customs Risk Prevention and Screening Application. Electronics 2024, 13, 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101941
Tian F, Wang H, Wan Z, Liu R, Liu R, Lv D, Lin Y. Unstructured Document Information Extraction Method with Multi-Faceted Domain Knowledge Graph Assistance for M2M Customs Risk Prevention and Screening Application. Electronics. 2024; 13(10):1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101941
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Fengchun, Haochen Wang, Zhenlong Wan, Ran Liu, Ruilong Liu, Di Lv, and Yingcheng Lin. 2024. "Unstructured Document Information Extraction Method with Multi-Faceted Domain Knowledge Graph Assistance for M2M Customs Risk Prevention and Screening Application" Electronics 13, no. 10: 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101941
APA StyleTian, F., Wang, H., Wan, Z., Liu, R., Liu, R., Lv, D., & Lin, Y. (2024). Unstructured Document Information Extraction Method with Multi-Faceted Domain Knowledge Graph Assistance for M2M Customs Risk Prevention and Screening Application. Electronics, 13(10), 1941. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13101941






