Digital Image Identification and Verification Using Maximum and Preliminary Score Approach with Watermarking for Security and Validation Enhancement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Maximum and Preliminary Score Approach
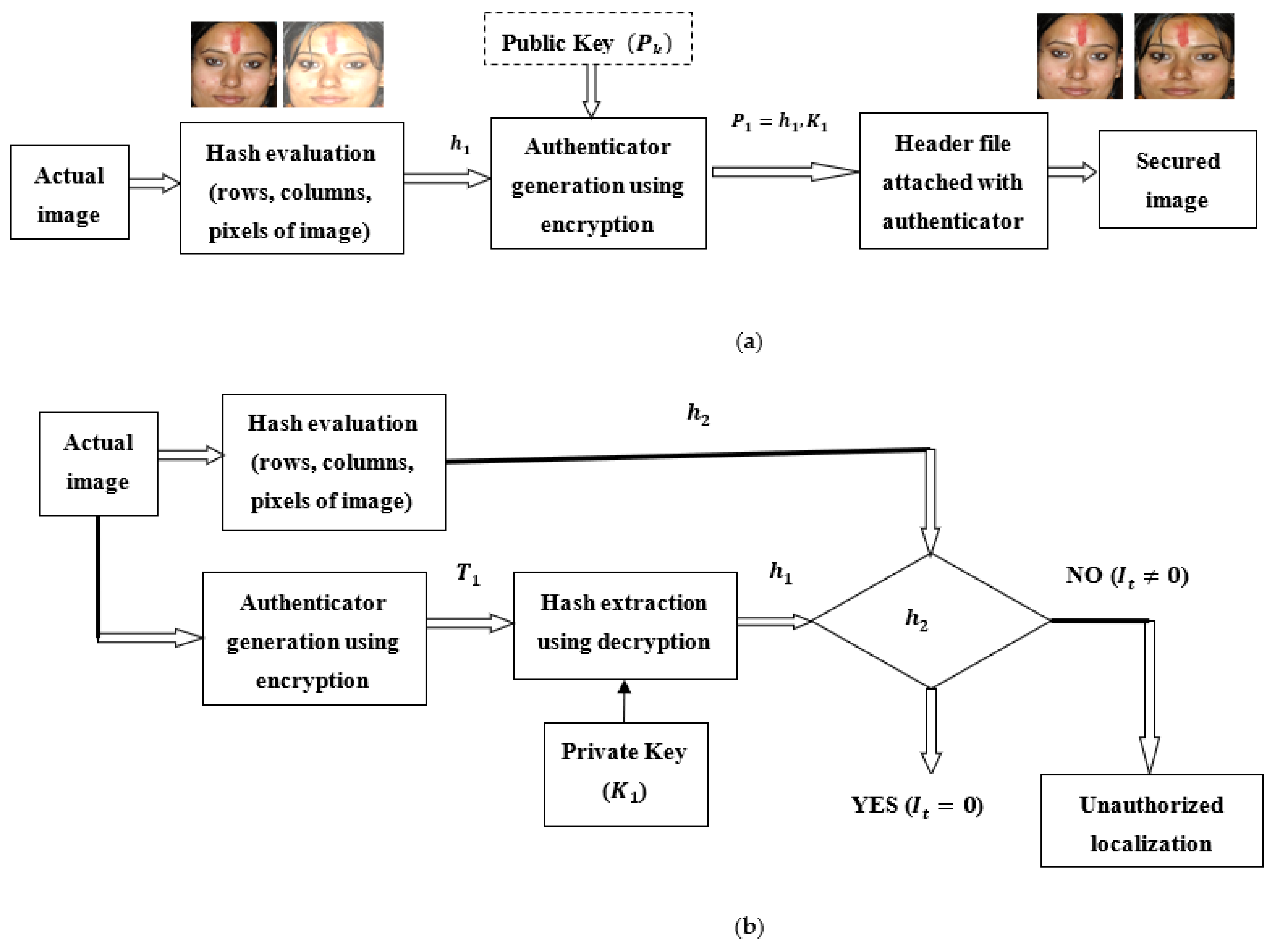
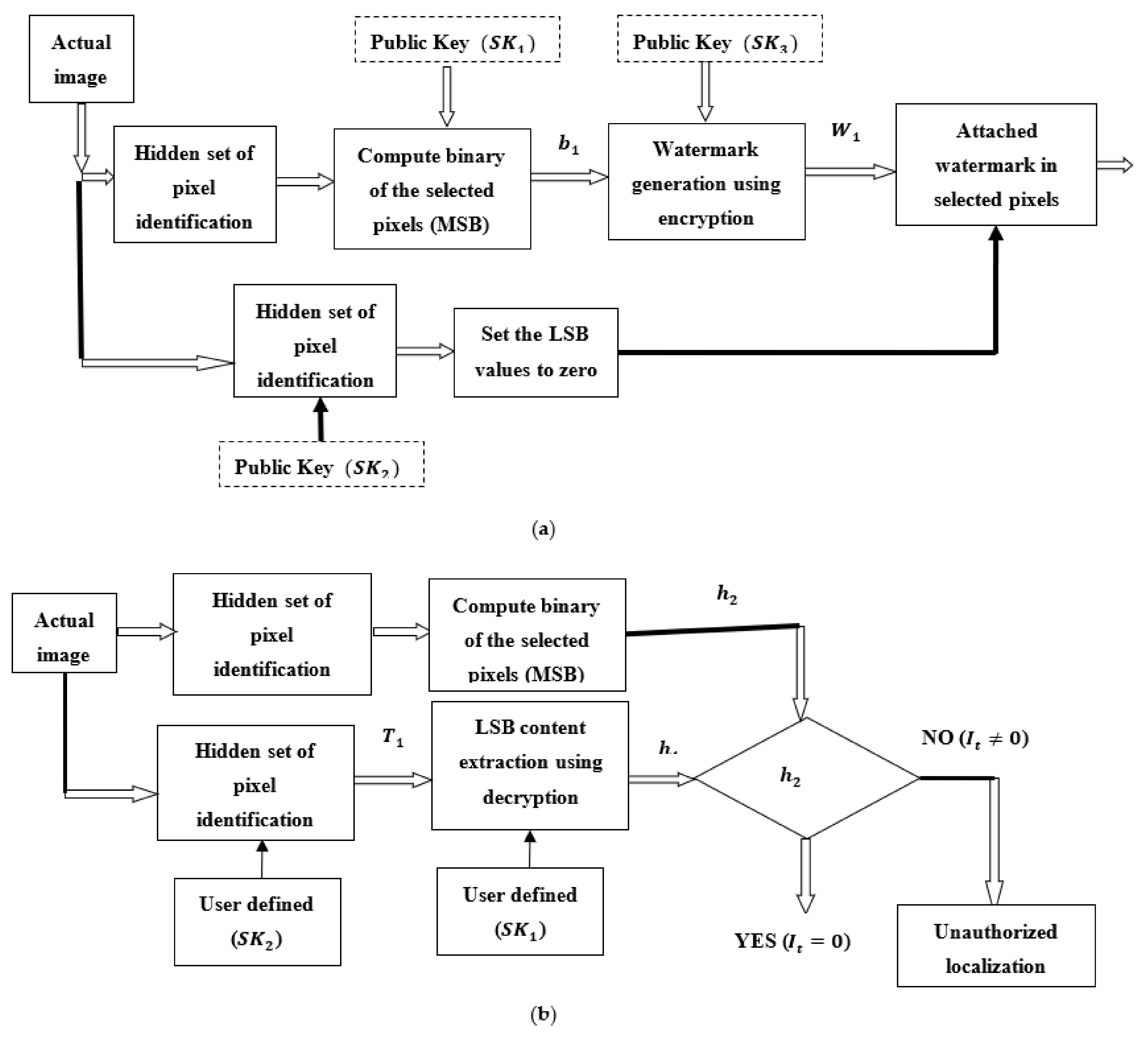
4. Image Authentication
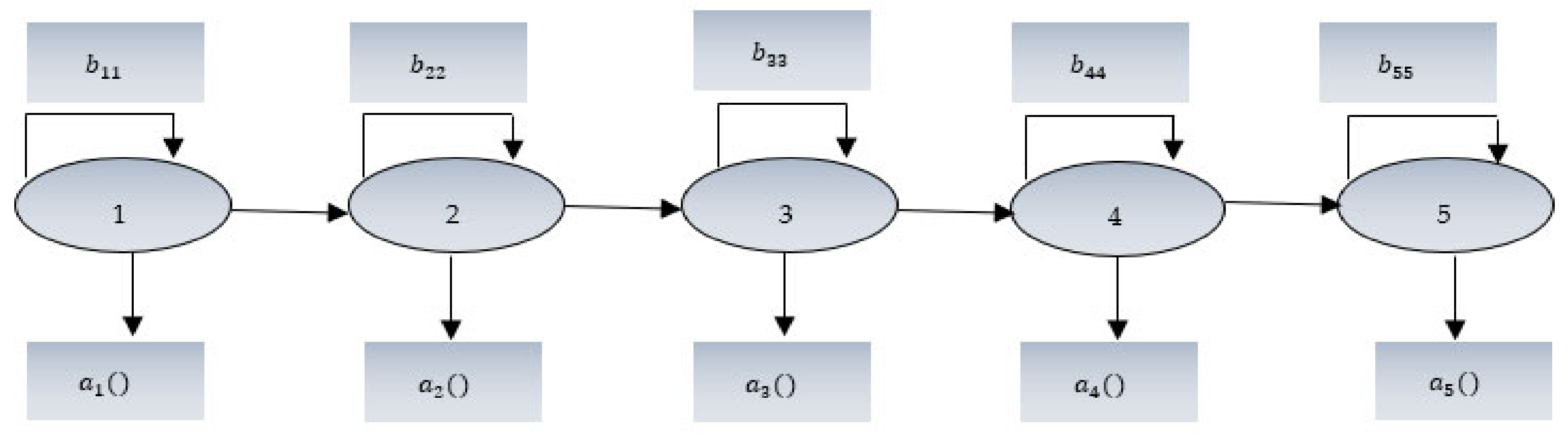
5. Frame Selection and Average Score Algorithm
- 1.
- Video frame selection based on average using discrete wavelet transform method which firstly identifies the first given input image which may be evaluated as:where represents the estimated coefficients of the image, contains coefficient details of vertical, horizontal and verticals sidebands.
- 2.
- Filtering process will be applied using high pass and low pass for decomposition of parents wavelets.
- 3.
- Next level of DWT now applied to first approximation achieved in first step approximation band.where, , denotes second level estimation of input image .
- 4.
- Average of every DWT band is evaluated by dividing image in windows being captured.where, is the likelihood majority function which indicates pixel values in probability form reflecting in locality and is the complete pixels.
- 5.
- If window size is thenwhere, denotes number of pixels in windows.
- 6.
- Average of every opening now integrated to evaluate the attribute merit of line.
- 7.
- Final total score of images , was obtained by averaging the feature value of each band individually:
- 8.
- For a video image , feature score of frames is denoted by and obtained max-min normalization usingwhere, denotes all feature scores for and ), denotes the denotes the minimum and maximum value of .
- 9.
- Formerly the outcome of individual structure is evaluated compatible process for structure nomination is carry out to identity best deposit frame [36].where, denote mean appropriate for the feature value and represents the standard deviation.
- 10.
- Testing performed for the rich feature frame from the database and verified with the matched score for its perfect authentication.
6. Proposed Model for Identification and Verification
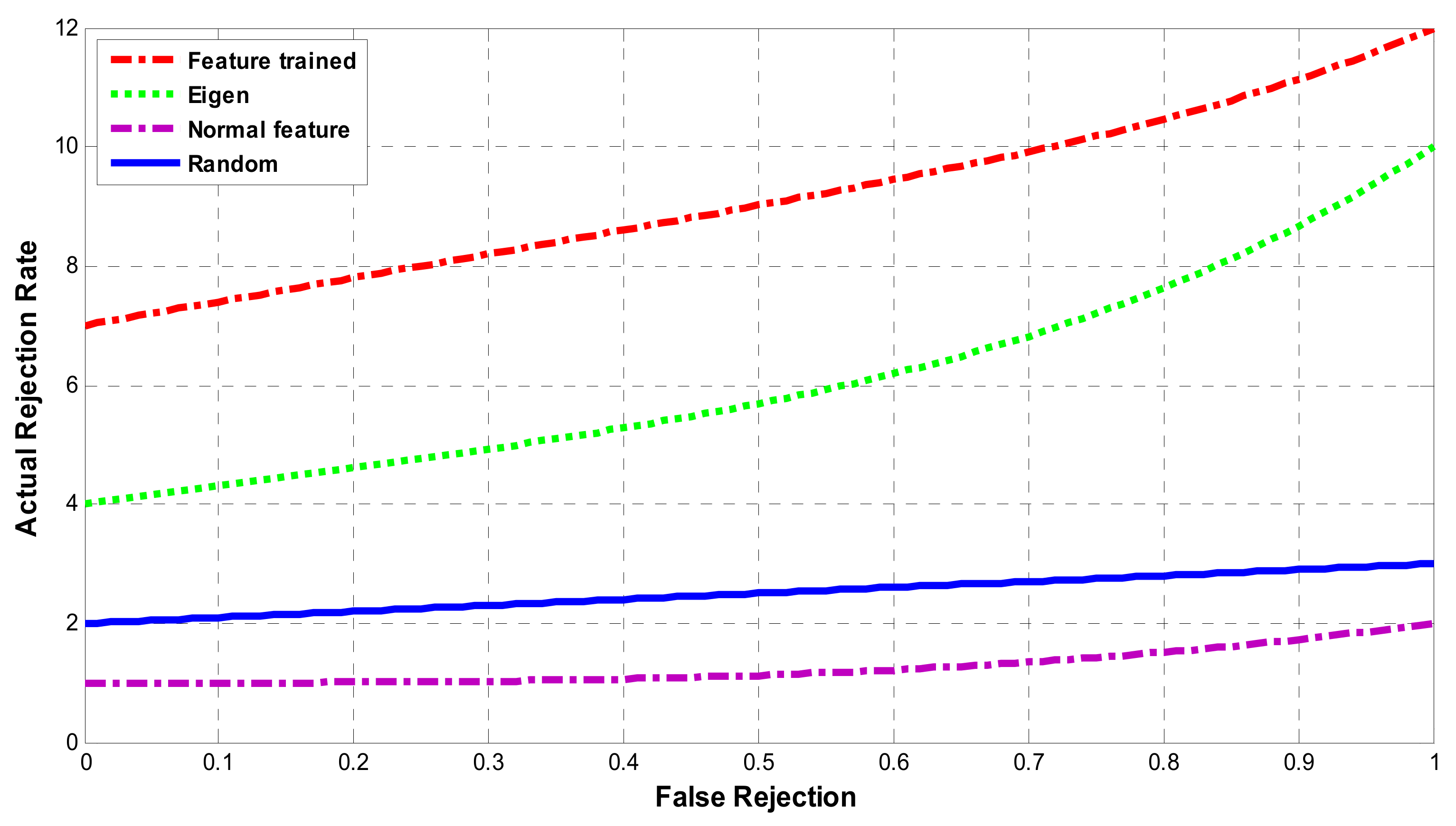
7. Results & Discussions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Upadhyay, A.; Sharma, S. Robust Feature Extraction using Embedded HMM for Face Identification & Verification. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2017, 12, 15729–15777. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, H.; Singh, R. On recognizing faces in videos using clustering-based re-ranking and fusion. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2014, 9, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, M.; Uddin, M.S. Digital image watermarking techniques: A review. Information 2020, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Paul, V. An imperceptible spatial domain color image water scheme. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2019, 31, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, S.; Liu, R.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Z. Secure and robust digital image watermarking scheme using logistic and RSA encryption. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018, 97, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsawwaf, M.; Chaczko, Z.; Kulbacki, M. In your face: Person identification through ratios and distances between facial features. Vietnam J. Comput. Sci. 2022, 9, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Kadhim Farhan, A. A novel improvement with an effective expansion to enhance the MD5 hash function for verification of a secure E-Document. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 80290–80304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambino, L.L.; Silva, J.S.; Bernardino, A. Multispectral facial recognition: A review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 80290–80304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Shi, B.; Zhong, T. Research on recognition method of electrical components based on YOLO v3. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 157818–157829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.; Khan, M.; Aslam, M.; Fiaz, M.J. Weapon detection in real-time CCTV videos using deep learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 34366–34382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Wnag, L.; Ren, P. Tinier-YOLO: A real-time object detection method for constrained environments. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 1935–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, J.; Yu, J.; Wu, Q. UFaceNet: Research on multitask face recognition algorithm based on CNN. Algorithms 2021, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Verma, S.; Kavita; Khan, M.S.; Wozniak, M.; Shafi, J.; Ijaz, M.F. A Hybrid Method to Enhance Thick and Thin Vessels for Blood Vessel Segmentation. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenvi, D.; Shet, K. CNN based COVID-19 prevention system. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Systems (ICAIS), Coimbatore, India, 25–27 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 873–878. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Raju, K.S.; Kumar, D.; Goyal, N.; Verma, S.; Singh, A. An efficient framework using visual recognition for IoT based smart city surveillance. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 31277–31295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Jan, M.A.; Rehman, A.U.; Babar, M.; Aimal, M.M.; Verma, S. Interoperability and Data Storage in Internet of Multimedia Things: Investigating Current Trends, Research Challenges and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 124382–124401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jain, A. Handbook of Face Recognition; Springer: Secaucus, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.P.; Li, J. Implement of Face Recognition System Based on Hidden Markov Model. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Natural Computation (ICNC), Yantai, China, 10–12 August 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, D.; Touqir, I.; Siddiqui, A.M.; Malik, J.; Imran, M. Face Recognition System Based on Four State Hidden Markov Model. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 74436–74448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, V.; Verma, S.; Kavita; Chatterjee, P.; Shafi, J.; Choi, J.; Ijaz, M.F. A Complete Process of Text Classification System Using State-of-the-Art NLP Models. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1883698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Kavita; Verma, S.; Rawat, D.B.; Dash, S. Mitigation of black hole attacks using firefly and artificial neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 15101–15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, J.T.; Liao, P. Maximum confidence hidden Markov modelling for face recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Verma, S.; Kumar, A.; Ijaz, M.F.; Rawat, D.B. ANAF-IoMT: A Novel Architectural Framework for IoMT-Enabled Smart Healthcare System by Enhancing Security Based on RECC-VC. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 8936–8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, N.R.; Singh, A.P.; Verma, S.; Wozniak, M.; Shafi, J.; Ijaz, M.F. A blockchain based lightweight peer-to-peer energy trading framework for secured high throughput micro-transactions. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Mukherjee, P.; Verma, S.; Kaur, M.; Singh, S.; Kobielnik, M.; Woźniak, M.; Shafi, J.; Ijaz, M.F. BBNSF: Blockchain-Based Novel Secure Framework Using RP2-RSA and ASR-ANN Technique for IoT Enabled Healthcare Systems. Sensors 2022, 22, 9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvel, L.M.; Hartwig, G.W. Compression compatible fragile and semi fragile tamper detection. In Proceedings of the SPIE International Conference on Security and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents, San Jose, CA, USA, 9 May 2000; Volume 2, pp. 3971–3981. [Google Scholar]
- Fridrich, J.; Goljan, M.; Du, R. Invertible authentication. In Proceedings of the SPIE, Security and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–26 January 2001; pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, H.; Han, K. Design for access control system based on voice recognition for infectious disease prevention. J. Korea Converg. Soc. 2020, 11, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.; Mun, H. Comparison analysis and case study for deep learning-based object detection algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Converg. 2020, 2, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Verma, E.S.; Kavita, E. Solving ipv4 (32 bits) address shortage problem using ipv6 (128 bits). IJREISS 2012, 2, 58–68. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, M.; Shah, J.H.; Mohsin, S.; Raza, M. Sub-Holistic Hidden Markov Model for Face Recognition. Res. J. Recent Sci. 2013, 2, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, D.; Akhtar, M.A.K. A modified GA-based load balanced clustering algorithm for WSN: MGALBC. Int. J. Embed. Real-Time Commun. Syst. (IJERTCS) 2021, 12, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londhe, A.; Rao, P.V.R.D.; Upadhyay, S.; Jain, R. Extracting behavior identification features for monitoring and managing speech dependent smart mental illness healthcare systems. Comput. Intell. Neuro Sci. 2022, 2022, 8579640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Verma, S.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Talib, M.N. Secure Surveillance System Using Chaotic Image Encryption Technique. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 993, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, J.; Bowyer, K.; Flynn, P. Effective and ineffective digital watermarks. Commun. ACM 1998, 41, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Verma, S.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Ghoniem, R.M. Vbswp-CeaH: Vigorous Buyer-Seller Watermarking Protocol without Trusted Certificate Authority for Copyright Protection in Cloud Environment through Additive Homomorphism. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
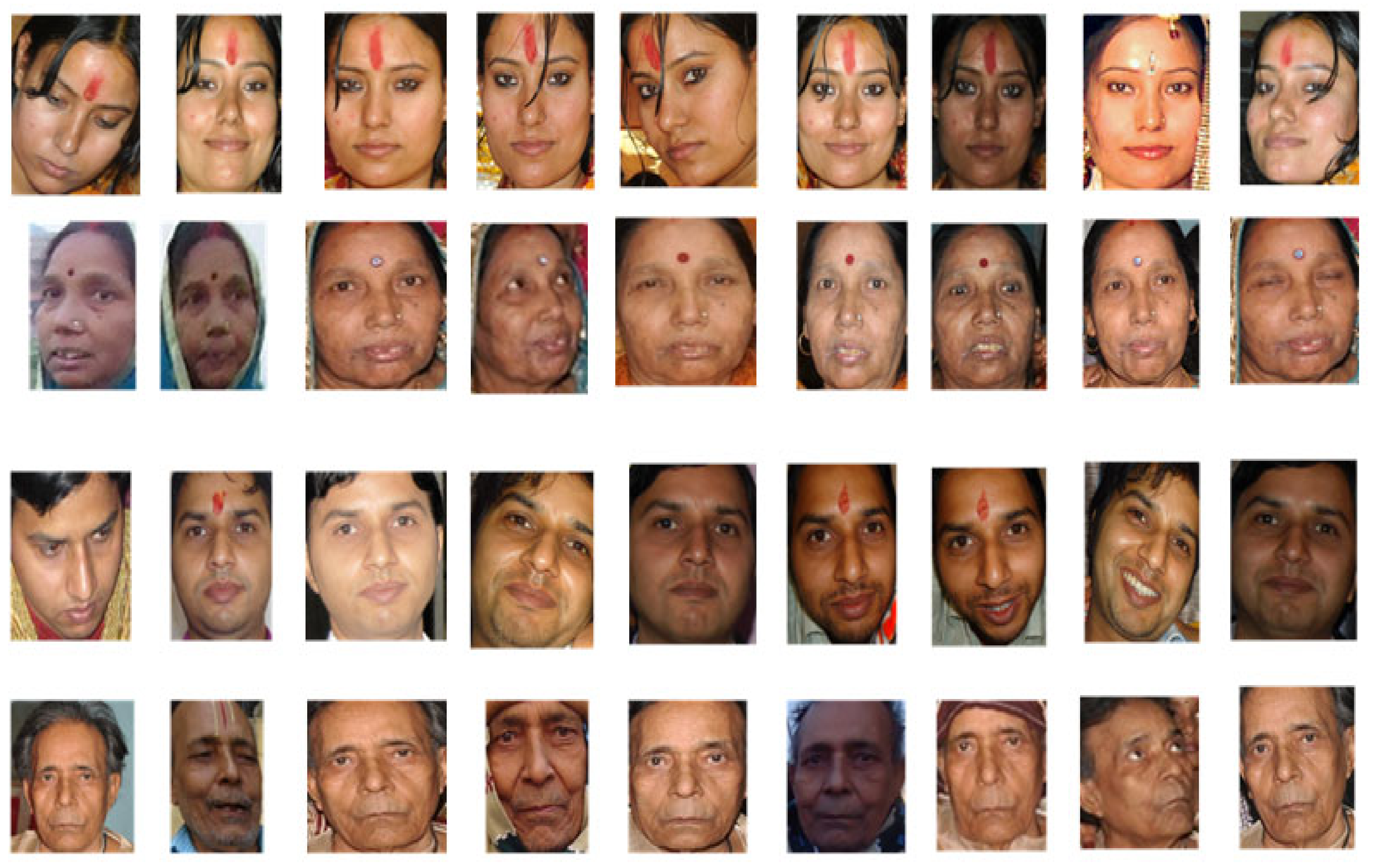






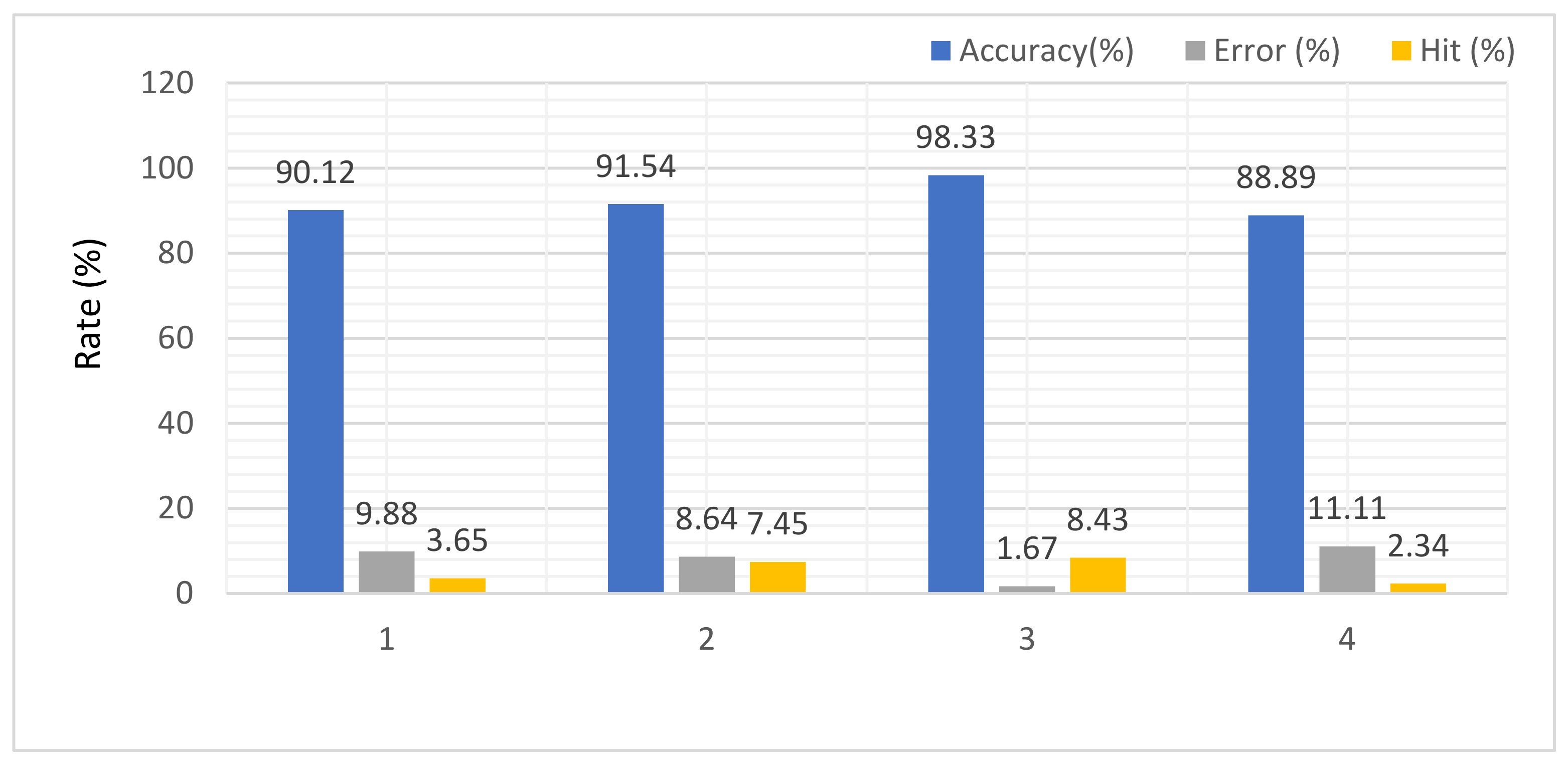
| Image Type | Identification Accuracy Rate (%) | Verification | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Error (%) | Hit (%) | ||
| 1. Random | 90.12 | 9.88 | 3.65 |
| 2. Eigen | 91.54 | 8.64 | 7.45 |
| 3. Feature trained | 98.33 | 1.67 | 8.43 |
| 4. Normal feature | 88.89 | 11.11 | 2.34 |
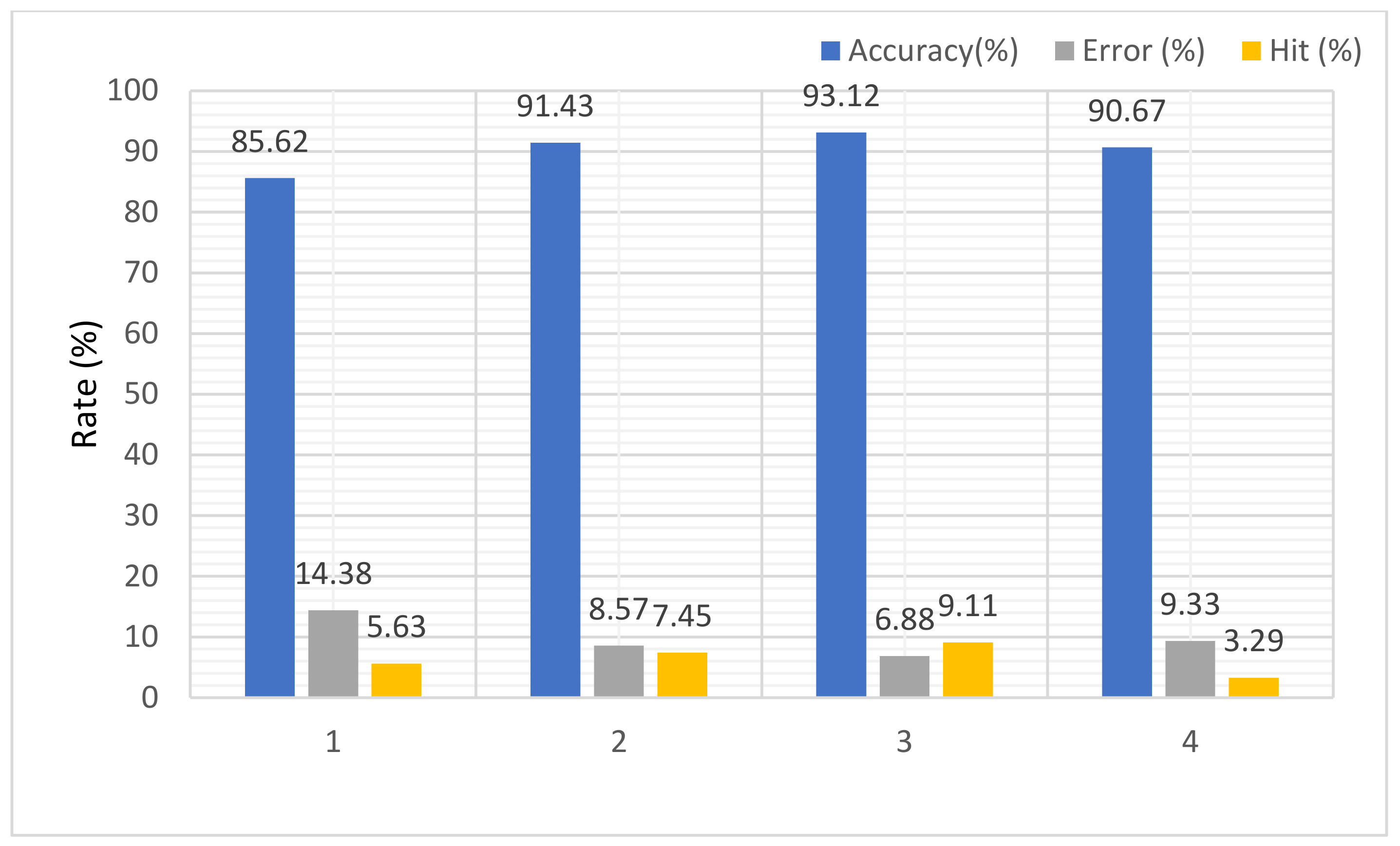
| Image Type | Identification Accuracy Rate (%) | Verification | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Error (%) | Hit (%) | ||
| 1. Random | 85.62 | 14.38 | 5.63 |
| 2. Eigen | 91.43 | 8.57 | 7.45 |
| 3. Feature trained | 93.12 | 6.88 | 9.11 |
| 4. Normal feature | 90.67 | 9.33 | 3.29 |
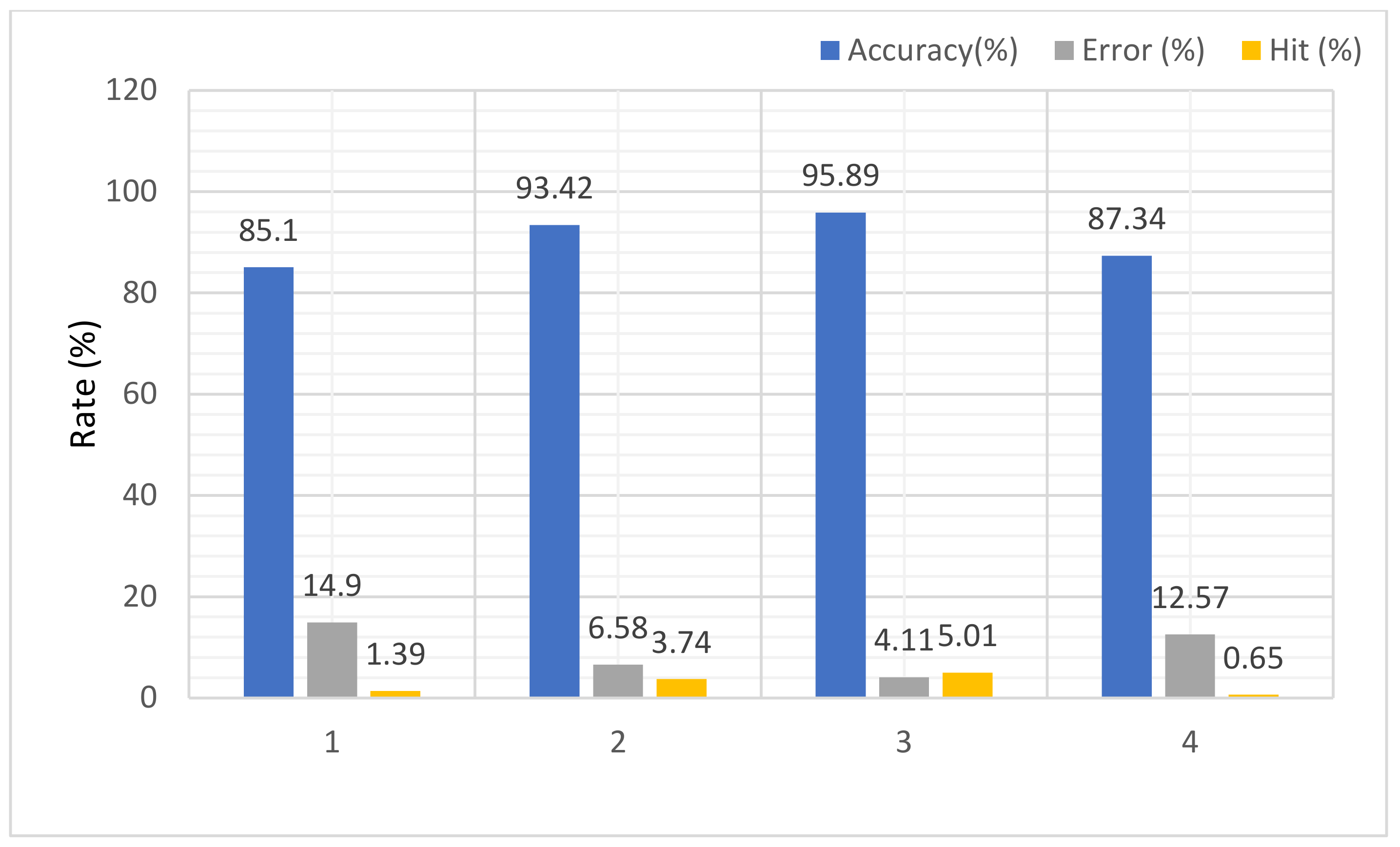
| Image Type | Identification Accuracy Rate (%) | Verification | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Error (%) | Hit (%) | ||
| 1. Random | 85.10 | 14.9 | 1.39 |
| 2. Eigen | 93.42 | 6.58 | 3.74 |
| 3. Feature trained | 95.89 | 4.11 | 5.01 |
| 4. Normal feature | 87.34 | 12.57 | 0.65 |
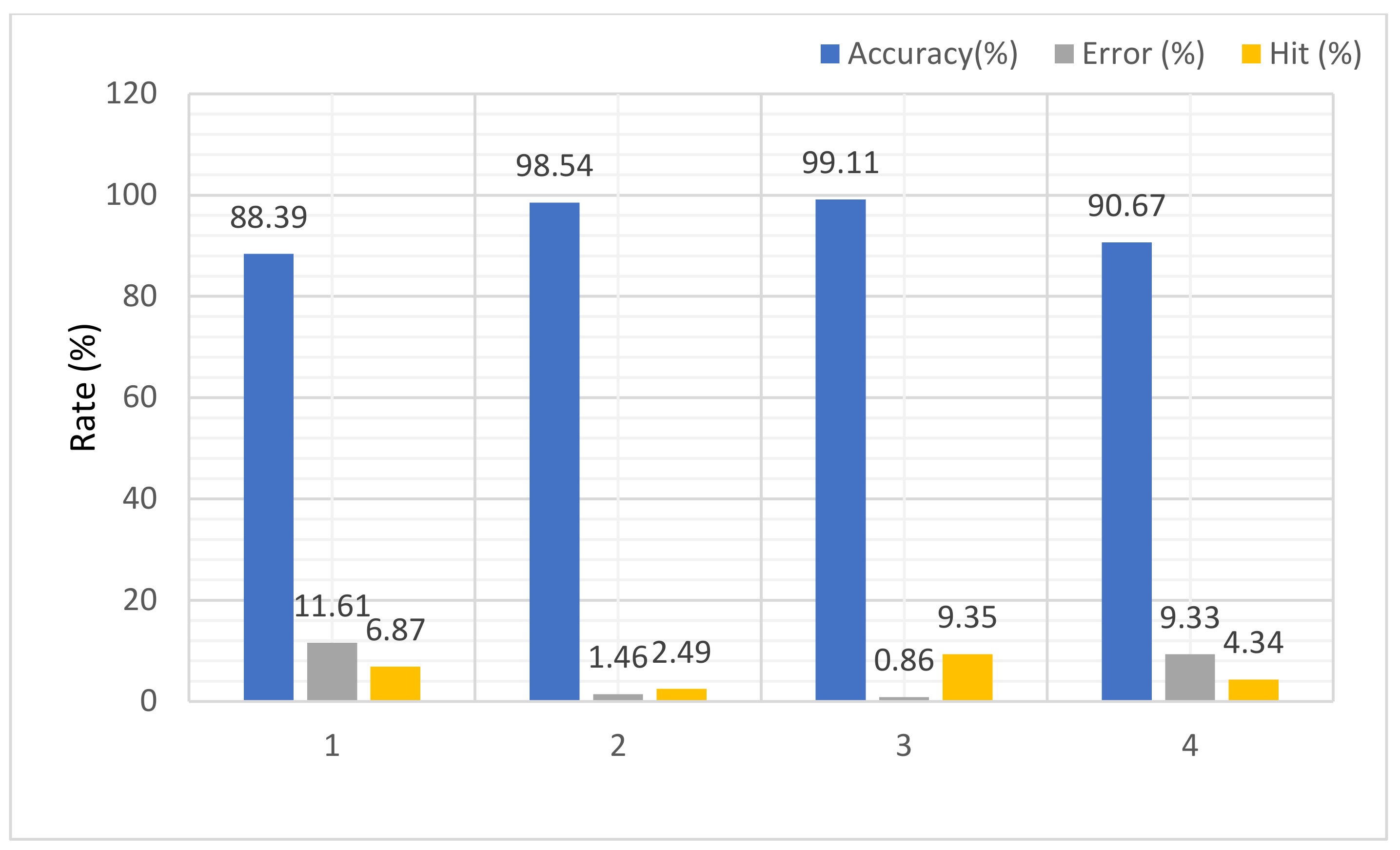
| Image Type | Identification AccuracyRate (%) | Verification | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Error (%) | Hit (%) | ||
| 1. Random | 88.39 | 11.61 | 6.87 |
| 2. Eigen | 98.54 | 1.46 | 2.49 |
| 3. Feature trained | 99.11 | 0.86 | 9.35 |
| 4. Normal feature | 90.67 | 9.33 | 4.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Upadhyay, S.; Kumar, M.; Upadhyay, A.; Verma, S.; Kavita; Hosen, A.S.M.S.; Ra, I.-H.; Kaur, M.; Singh, S. Digital Image Identification and Verification Using Maximum and Preliminary Score Approach with Watermarking for Security and Validation Enhancement. Electronics 2023, 12, 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12071609
Upadhyay S, Kumar M, Upadhyay A, Verma S, Kavita, Hosen ASMS, Ra I-H, Kaur M, Singh S. Digital Image Identification and Verification Using Maximum and Preliminary Score Approach with Watermarking for Security and Validation Enhancement. Electronics. 2023; 12(7):1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12071609
Chicago/Turabian StyleUpadhyay, Shrikant, Mohit Kumar, Aditi Upadhyay, Sahil Verma, Kavita, A. S. M. Sanwar Hosen, In-Ho Ra, Maninder Kaur, and Satnam Singh. 2023. "Digital Image Identification and Verification Using Maximum and Preliminary Score Approach with Watermarking for Security and Validation Enhancement" Electronics 12, no. 7: 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12071609
APA StyleUpadhyay, S., Kumar, M., Upadhyay, A., Verma, S., Kavita, Hosen, A. S. M. S., Ra, I.-H., Kaur, M., & Singh, S. (2023). Digital Image Identification and Verification Using Maximum and Preliminary Score Approach with Watermarking for Security and Validation Enhancement. Electronics, 12(7), 1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12071609






