COVID-ResNet: COVID-19 Recognition Based on Improved Attention ResNet
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
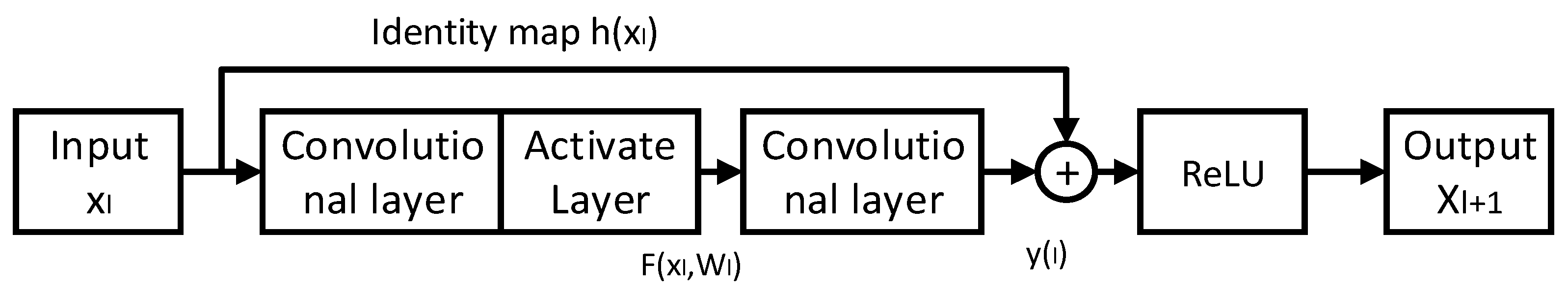
2.1. ResNet
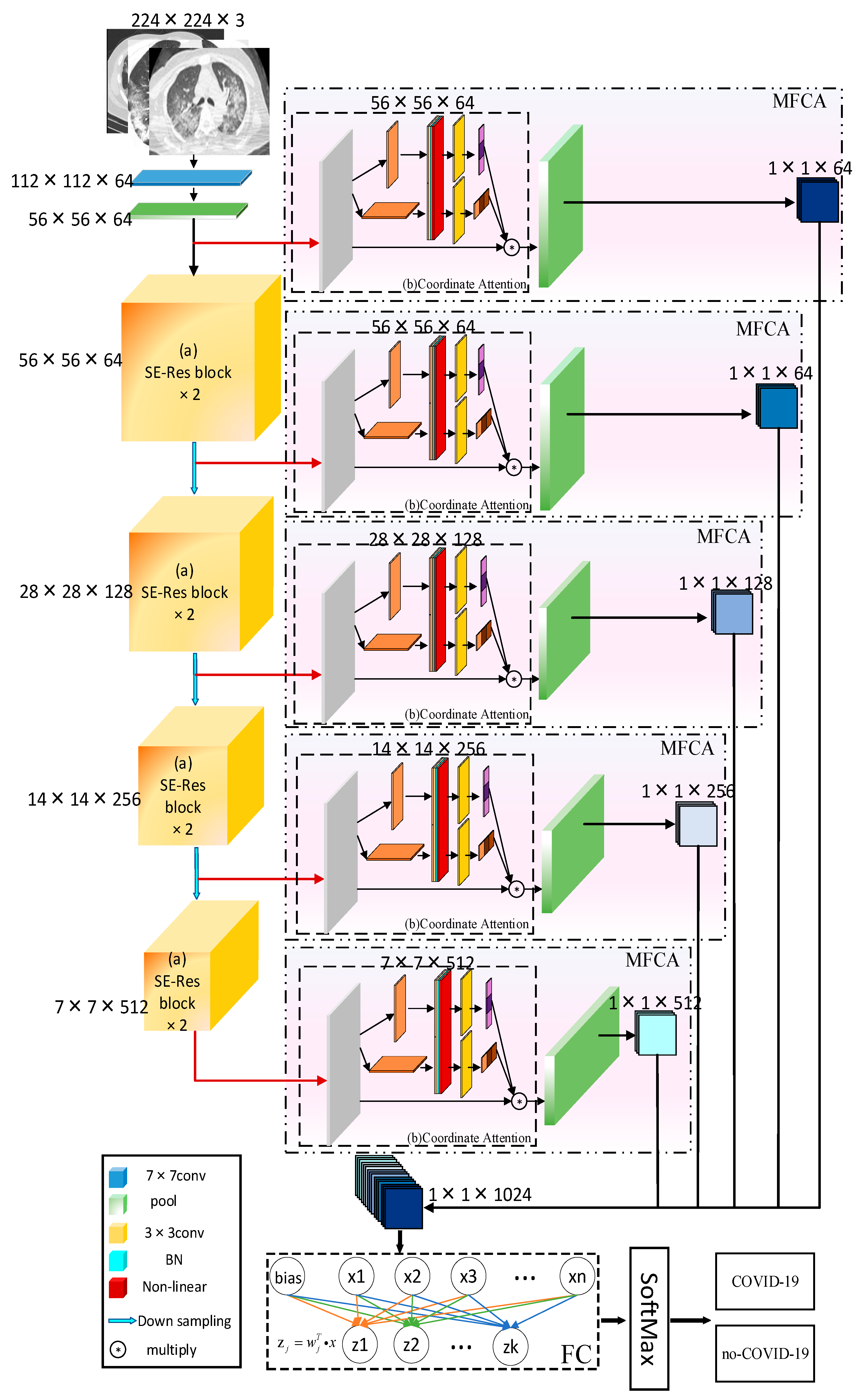
2.2. COVID-ResNet
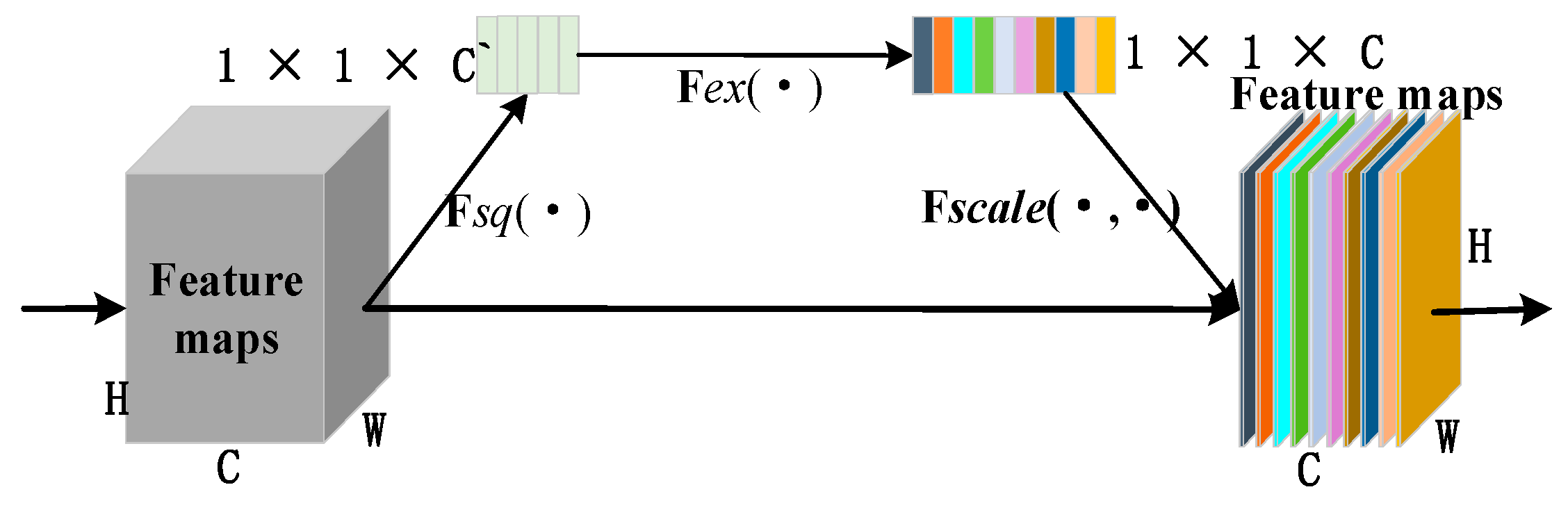
2.2.1. Squeeze-and-Excitation
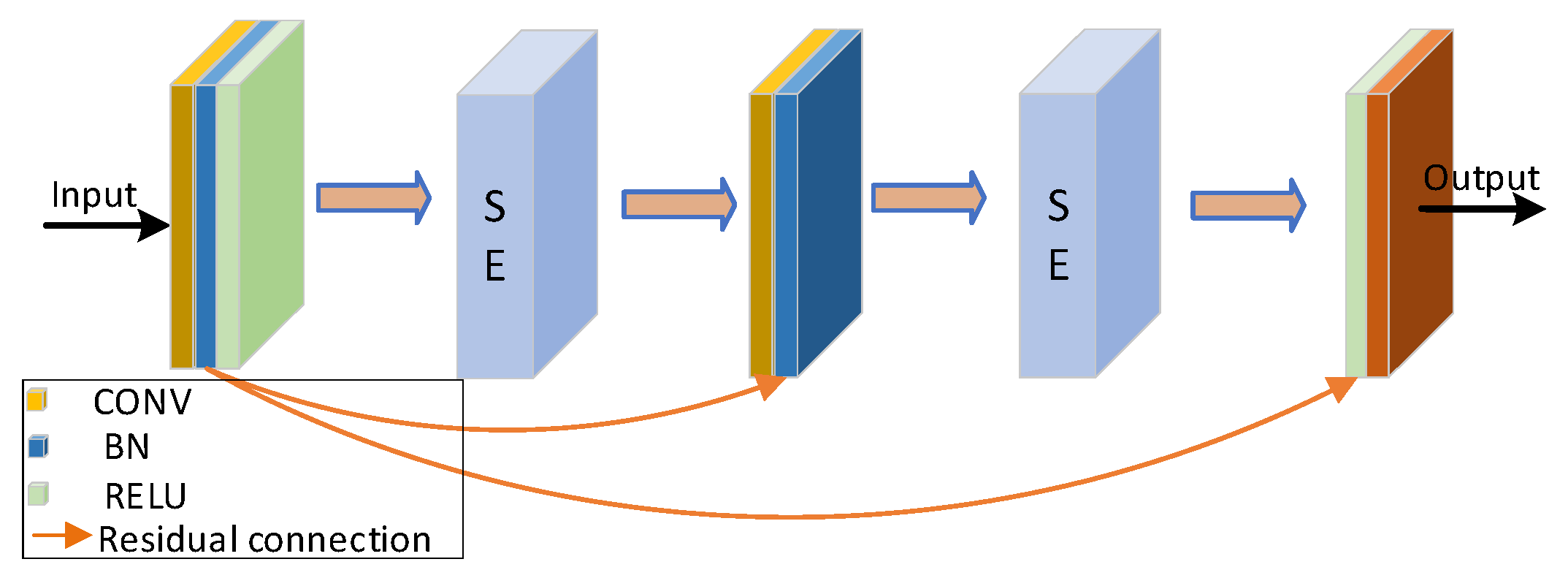
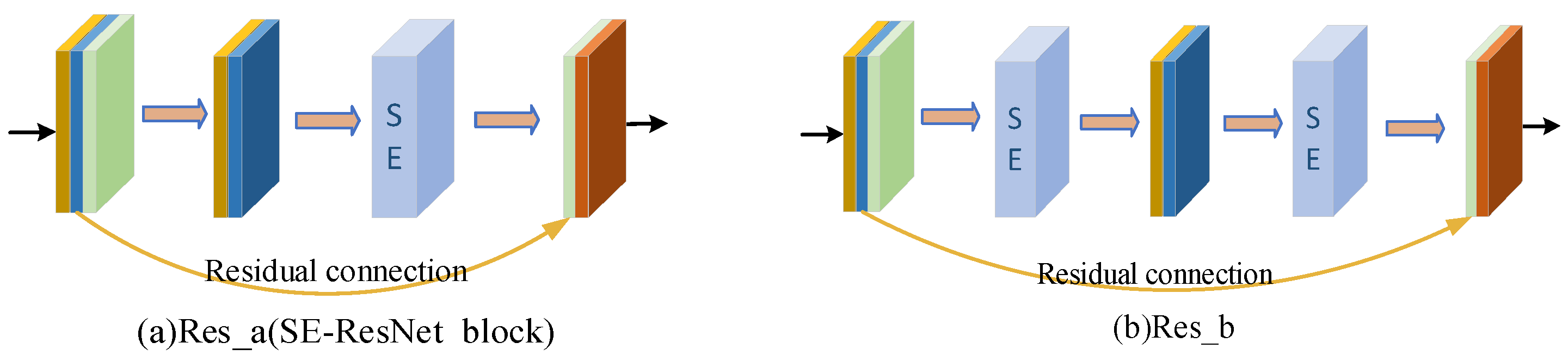
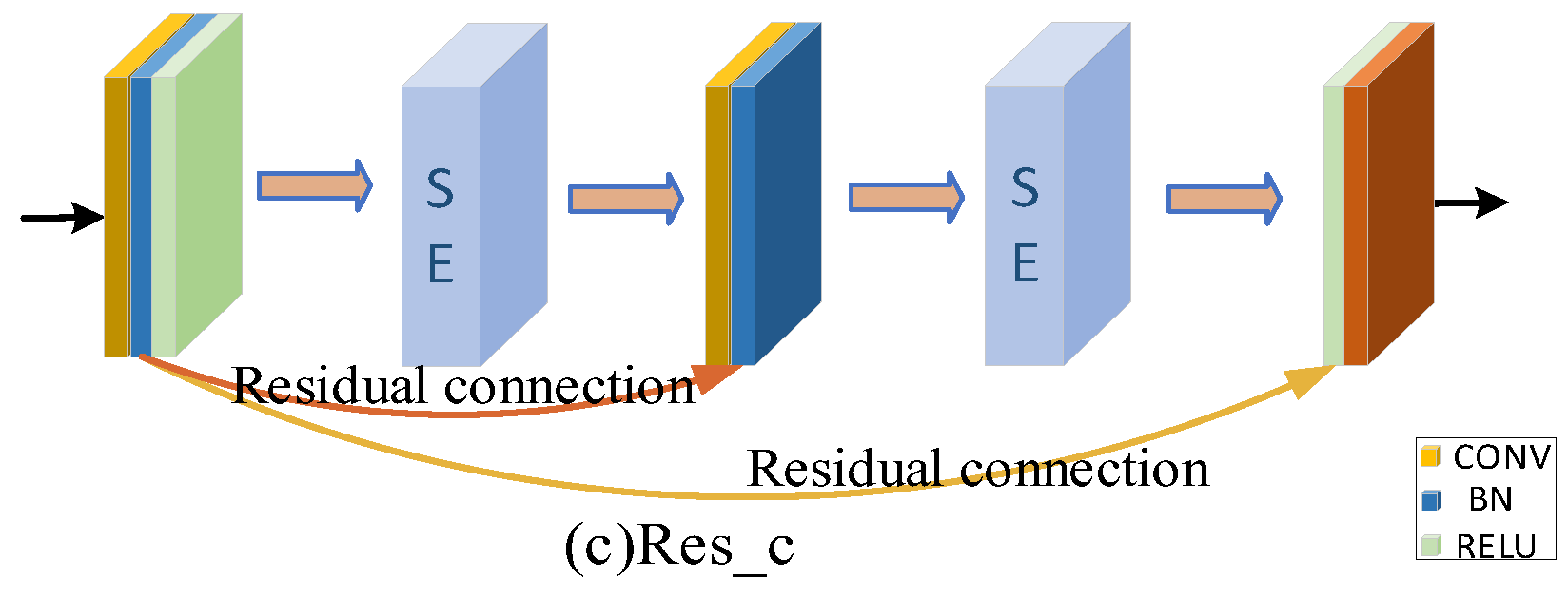
2.2.2. SE-Res Block (Squeeze-and-Excitation ResNet Block)
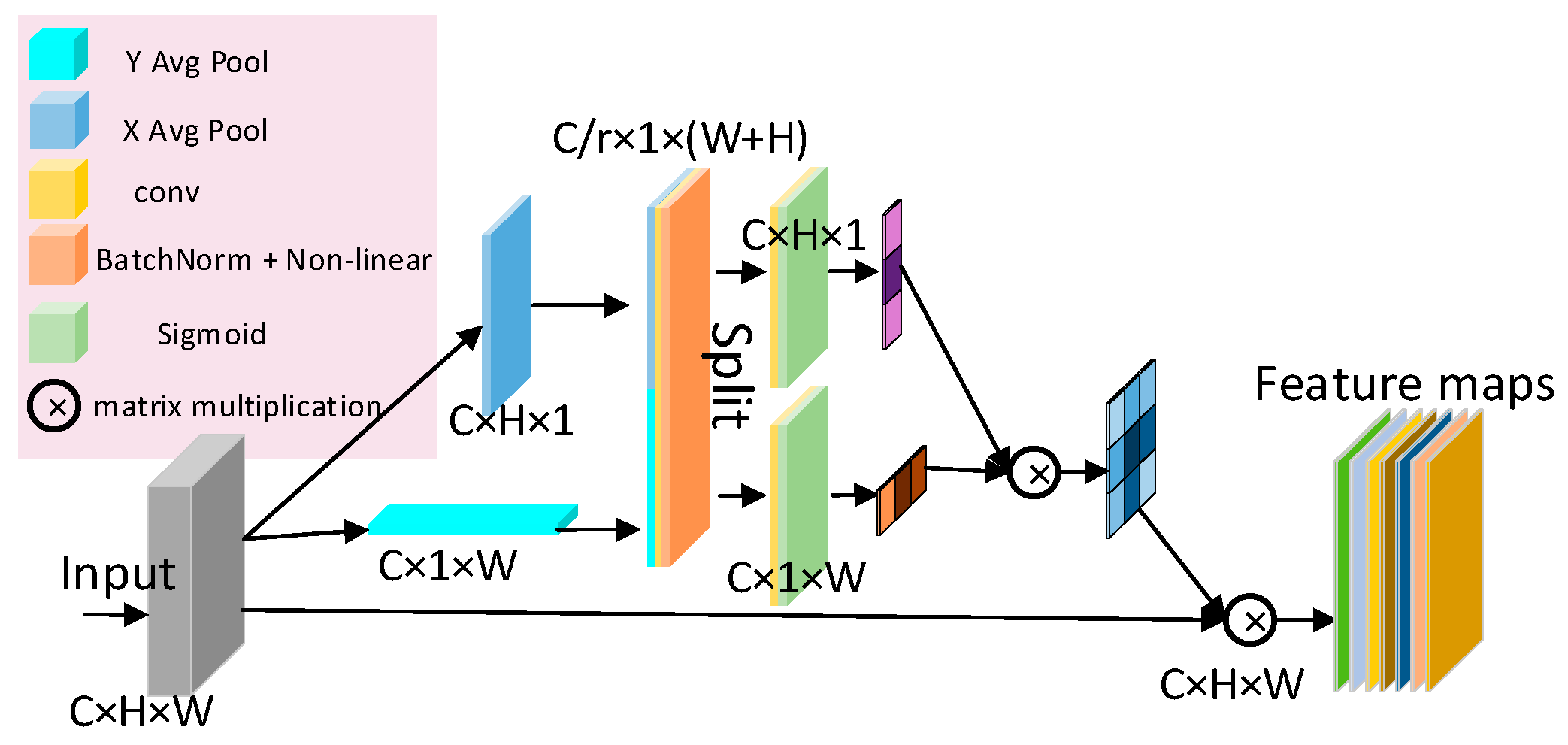
2.2.3. Coordinate Attention
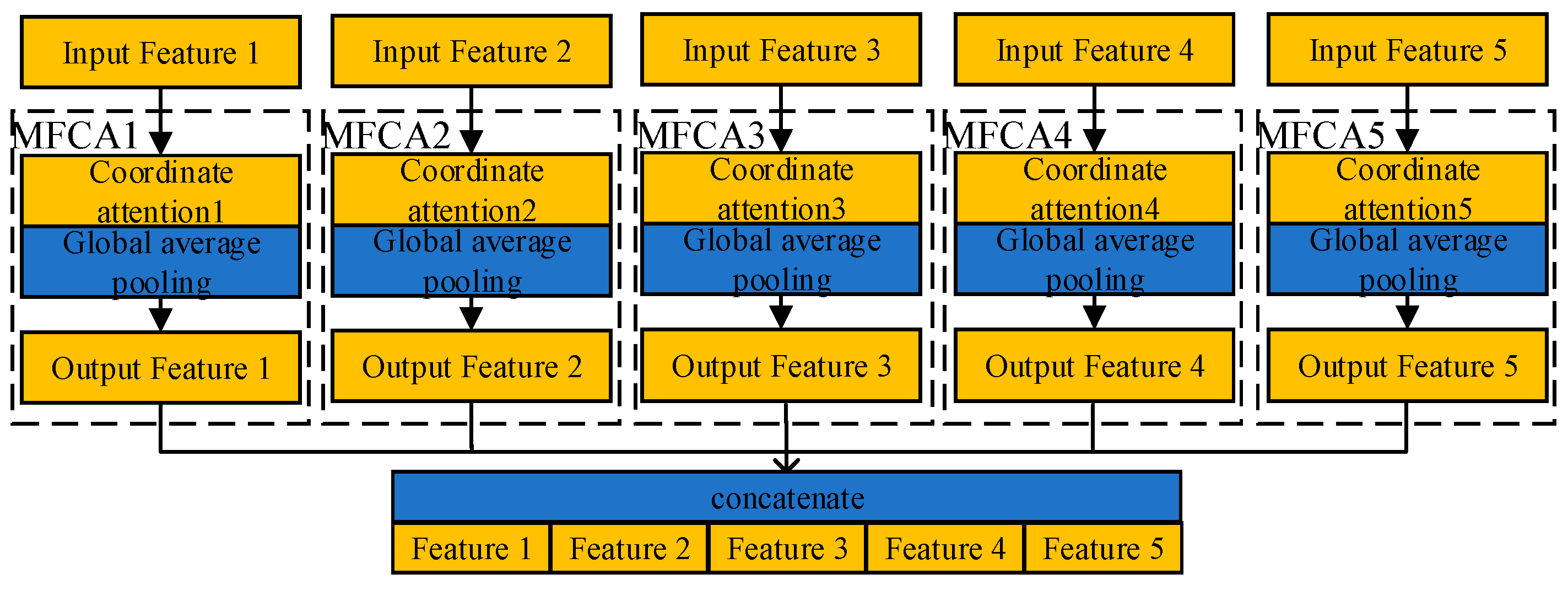
2.2.4. MFCA (Multi-Layer Feature Converge Attention)
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Environment
3.2. Datasets
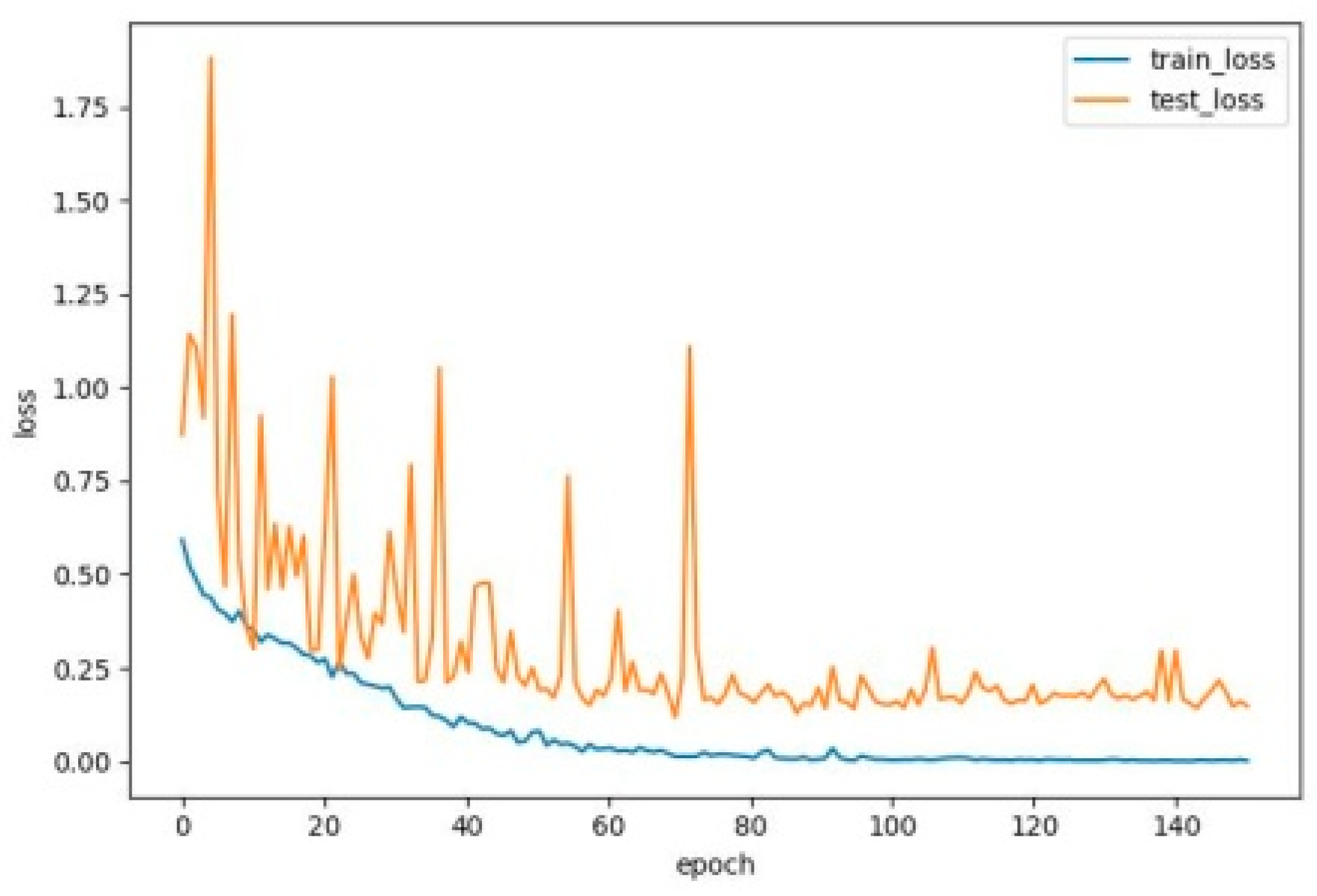
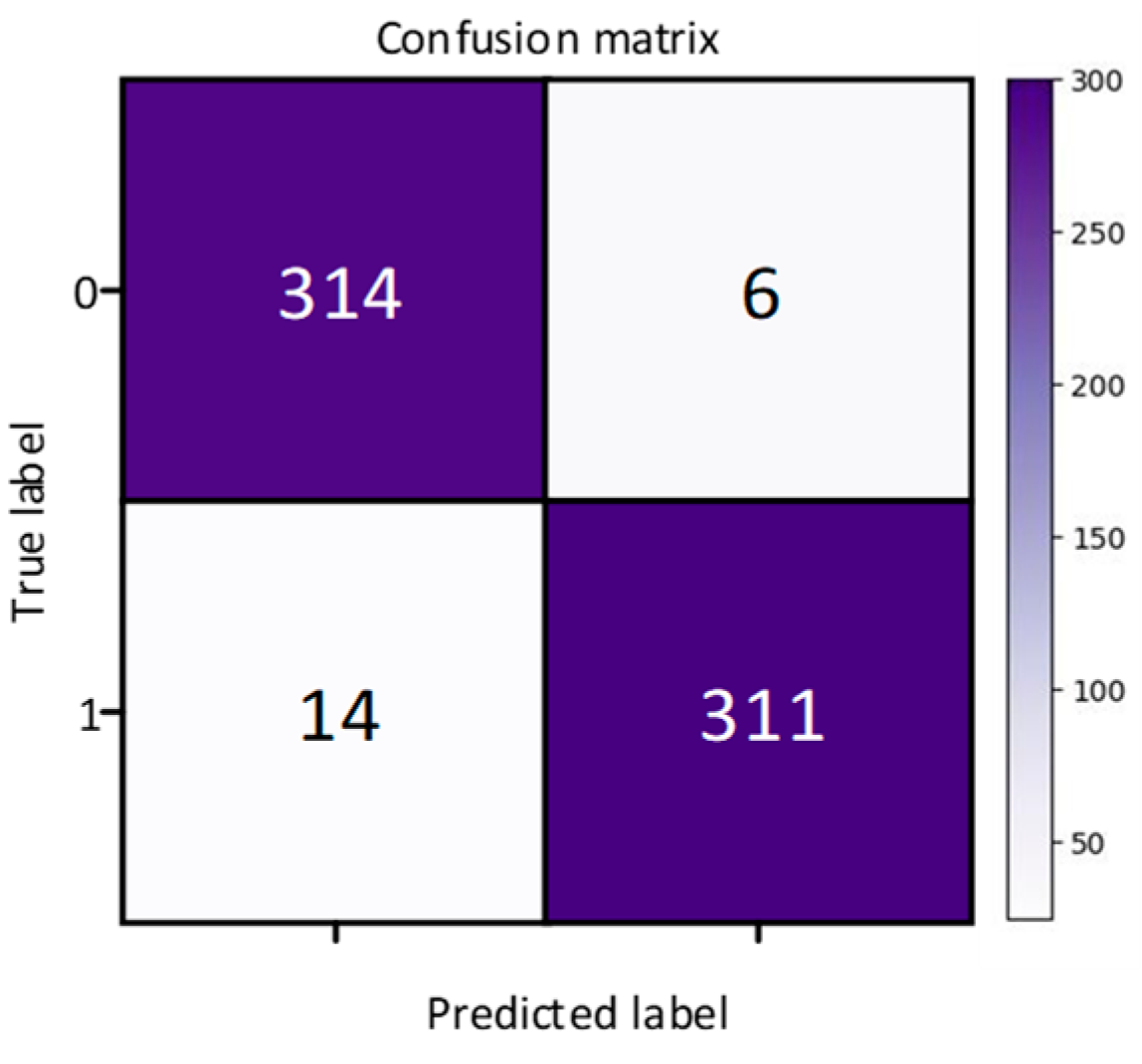
3.3. Experimental Results
3.4. Ablation Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- COVID-ResNet achieved good results in the classification of COVID-19 CT images. In this study, the dataset of COVID-19 included COVID-19 and no COVID-19. There were other diseases in the lung, including lung cancer, tuberculosis, and so on. Applying the networks to more types and multi-source datasets is the direction for future research tasks.
- (2)
- With the development of COVID-19, COVID-19 does not only infect the lungs, but also the upper respiratory tract. It is not enough to check the lungs. Other images can be used for screening in the future.
- (3)
- In the future, other networks of deep learning can be used for auxiliary diagnosis. For example, DenseNet, Capsule Network, Googlenet, etc.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Means | |
|---|---|
| features map of input | |
| features map of output | |
| residual function | |
| identity map | |
| X | features map of input about SE block |
| Conversion operation | |
| Features after conversion operation | |
| number of channels | |
| features map of output about SE block | |
| feature vector | |
| weight matrix | |
| σ | Sigmoid |
| δ | ReLU |
| excitation operation | |
| concat operation | |
| f | the intermediate feature mapping of spatial information in coding |
| F | 1 × 1 convolution |
| g | weight |
Appendix B
- Confusion Matrix
| Predicted as Positive Sample | Predicted as Negative Sample | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Label as positive sample | TP (True Positive) | FN (False Negative) | TP + FN |
| Label as negative sample | FP (False Positive) | TN (True Negative) | FP + TN |
| Total | TP + FP | FN + TN | TP + TN + FP + FN |
- 2.
- Accuracy
- 3.
- Precision
- 4.
- Recall
- 5.
- F1 score
- 6.
- AUC (Area under Curve)
References
- Watson, J.; Whiting, P.F.; Brush, J.E. Interpreting a COVID-19 test result. BMJ 2020, 369, m1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abumalloh, R.A.; Nilashi, M.; Ismail, M.Y.; Alhargan, A.; Alghamdi, A.; Alzahrani, A.O.; Saraireh, L.; Osman, R.; Asadi, S. Medical image processing and COVID-19: A literature review and bibliometric analysis. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 15, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famiglini, L.; Campagner, A.; Carobene, A.; Cabitza, F. A robust and parsimonious machine learning method to predict ICU admission of COVID-19 patients. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raihan, M.; Hassan, M.; Hasan, T.; Bulbul, A.A.-M.; Hasan, K.; Hossain, S.; Roy, D.S.; Awal, A. Development of a Smartphone-Based Expert System for COVID-19 Risk Prediction at Early Stage. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, A.; Navimipour, N.J.; Unal, M.; Toumaj, S. Machine learning applications for COVID-19 outbreak management. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 15313–15348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassif, A.B.; Shahin, I.; Bader, M.; Hassan, A.; Werghi, N. COVID-19 Detection Systems Using Deep-Learning Algorithms Based on Speech and Image Data. Mathematics 2022, 10, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Chen, X.Z. Research progress of deep learning in lioblastoma. Chin. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 13, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Gao, Y.; Ding, W.; Niu, Z.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.; Fang, E.F.; Menpes-Smith, W.; Xia, J.; et al. Robust weakly supervised learning for COVID-19 recognition using multi-center CT images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 116, 108291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Muhammad, K.; Bhattacharyya, S. A deep fuzzy model for diagnosis of COVID-19 from CT images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 122, 108883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.; Guo, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, B.; Meng, X.F. Supercomputing-supported COVID-l9 CT image comprehensive analysis assistant system. J. Image Graph. 2020, 25, 2142–2150. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Lu, H.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Huo, B.; Dong, Y. The ensemble deep learning model for novel COVID-19 on CT images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 98, 106885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamalakis, M.; Swift, A.J.; Vorselaars, B.; Ray, S.; Weeks, S.; Ding, W.; Clayton, R.H.; Mackenzie, L.S.; Banerjee, A. DenResCov-19: A deep transfer learning network for robust automatic classification of COVID-19, pneumonia, and tuberculosis from X-rays. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 94, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Kafieh, R.; Sonka, M.; Yazdani, S.; Soufi, G.J. Deep-COVID: Predicting COVID-19 from chest X-ray images using deep transfer learning. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 65, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ye, X.; Lu, H.; Zheng, X.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y. Dense Convolutional Network and Its Application in Medical Image Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 2384830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Sheikh, K.H.; Cuevas, E.; Sarkar, R. COVID-19 detection from CT scans using a two-stage framework. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 193, 116377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L. Handwritten digit recognition with a back-propagation network. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1990, 2, 396–404. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. Comput. Sci. 2015, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual Conference, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 13708–13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Chang, X.Y.; Lu, H.L.; Ye, X.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Zheng, X.M. Pooling Operations in Deep Learning: From “Invariable” to “Variable”. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, E.; Angelov, P.; Biaso, S.; Froes, M.H.; Abe, D.K. SARS-CoV-2 CT-Scan Dataset: A Large Dataset of Real Patients CT Scans for SARS-CoV-2 Identification; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.4842 (accessed on 30 December 2015).
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated Residual Transformations for Deep Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5987–5995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07261 (accessed on 30 December 2015).
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]






| ResNet Structural [11] | COVID-ResNet Structural | COVID-ResNet18 | Input Size | Output Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convolutional layer | Convolutional layer | |||
| Maxpooling layer | Maxpooling layer | |||
| MFCA block | ||||
| Res block | SE-Res block | |||
| MFCA block | ||||
| Res block | SE-Res block | |||
| MFCA block | ||||
| Res block | SE-Res block | |||
| MFCA block | ||||
| Res block | SE-Res block | |||
| MFCA block | ||||
| Classification layer | Classification layer | Full connection |
| Dataset | Train | Validation | Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 | No-COVID-19 | COVID-19 | No-COVID-19 | COVID-19 | No-COVID-19 | |
| SARS-CoV-2 | 752 | 737 | 250 | 246 | 250 | 246 |
| COVID-19 CT | 209 | 239 | 70 | 79 | 70 | 79 |
| Model Parameter Quantity (MB) | ACC | PRE | RC | F1 | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 [11] | 85.28 | 0.9379 | 0.9228 | 0.9569 | 0.9396 | 0.9788 |
| DenseNet [15] | 53.07 | 0.9519 | 0.9537 | 0.9508 | 0.9560 | 0.9868 |
| Googlenet [25] | 48.08 | 0.9473 | 0.9318 | 0.9662 | 0.9482 | 0.9871 |
| ResNext50 [26] | 175.35 | 0.9457 | 0.9394 | 0.9538 | 0.9466 | 0.9863 |
| SE-ResNet18 [20] | 85.96 | 0.9519 | 0.9324 | 0.9754 | 0.9534 | 0.9803 |
| Xception [27] | 158.78 | 0.9426 | 0.9472 | 0.9385 | 0.9428 | 0.9799 |
| Inceptionv3 [28] | 168.74 | 0.9302 | 0.9403 | 0.9200 | 0.9300 | 0.9562 |
| Inceptionv4 [29] | 313.92 | 0.9581 | 0.9656 | 0.9508 | 0.9581 | 0.9811 |
| EiffcienNetb0 [30] | 30.59 | 0.9395 | 0.9359 | 0.9446 | 0.9403 | 0.9802 |
| COVID-ResNet | 86.94 | 0.9689 | 0.9579 | 0.9815 | 0.9696 | 0.9904 |
| Parameter Quantity (MB) | ACC | PRE | RC | F1 | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment 1 | 85.28 | 0.9379 | 0.9429 | 0.9662 | 0.9444 | 0.9825 |
| Experiment 2 | 85.58 | 0.9535 | 0.9429 | 0.9662 | 0.9544 | 0.9867 |
| Experiment 3 | 85.96 | 0.9519 | 0.9324 | 0.9754 | 0.9534 | 0.9803 |
| Experiment 4 | 86.26 | 0.9550 | 0.9405 | 0.9723 | 0.9561 | 0.9857 |
| Experiment 5 | 86.64 | 0.9535 | 0.9456 | 0.9631 | 0.9543 | 0.9875 |
| Experiment 6 | 86.94 | 0.9628 | 0.9574 | 0.9692 | 0.9633 | 0.9935 |
| Experiment 7 | 86.64 | 0.9597 | 0.9572 | 0.9631 | 0.9601 | 0.9910 |
| Experiment 8 | 86.94 | 0.9689 | 0.9579 | 0.9815 | 0.9696 | 0.9904 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, T.; Chang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ye, X.; Lu, H.; Hu, F. COVID-ResNet: COVID-19 Recognition Based on Improved Attention ResNet. Electronics 2023, 12, 1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12061413
Zhou T, Chang X, Liu Y, Ye X, Lu H, Hu F. COVID-ResNet: COVID-19 Recognition Based on Improved Attention ResNet. Electronics. 2023; 12(6):1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12061413
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Tao, Xiaoyu Chang, Yuncan Liu, Xinyu Ye, Huiling Lu, and Fuyuan Hu. 2023. "COVID-ResNet: COVID-19 Recognition Based on Improved Attention ResNet" Electronics 12, no. 6: 1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12061413
APA StyleZhou, T., Chang, X., Liu, Y., Ye, X., Lu, H., & Hu, F. (2023). COVID-ResNet: COVID-19 Recognition Based on Improved Attention ResNet. Electronics, 12(6), 1413. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12061413






