A Multi-Hop Graph Neural Network for Event Detection via a Stacked Module and a Feedback Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Studies
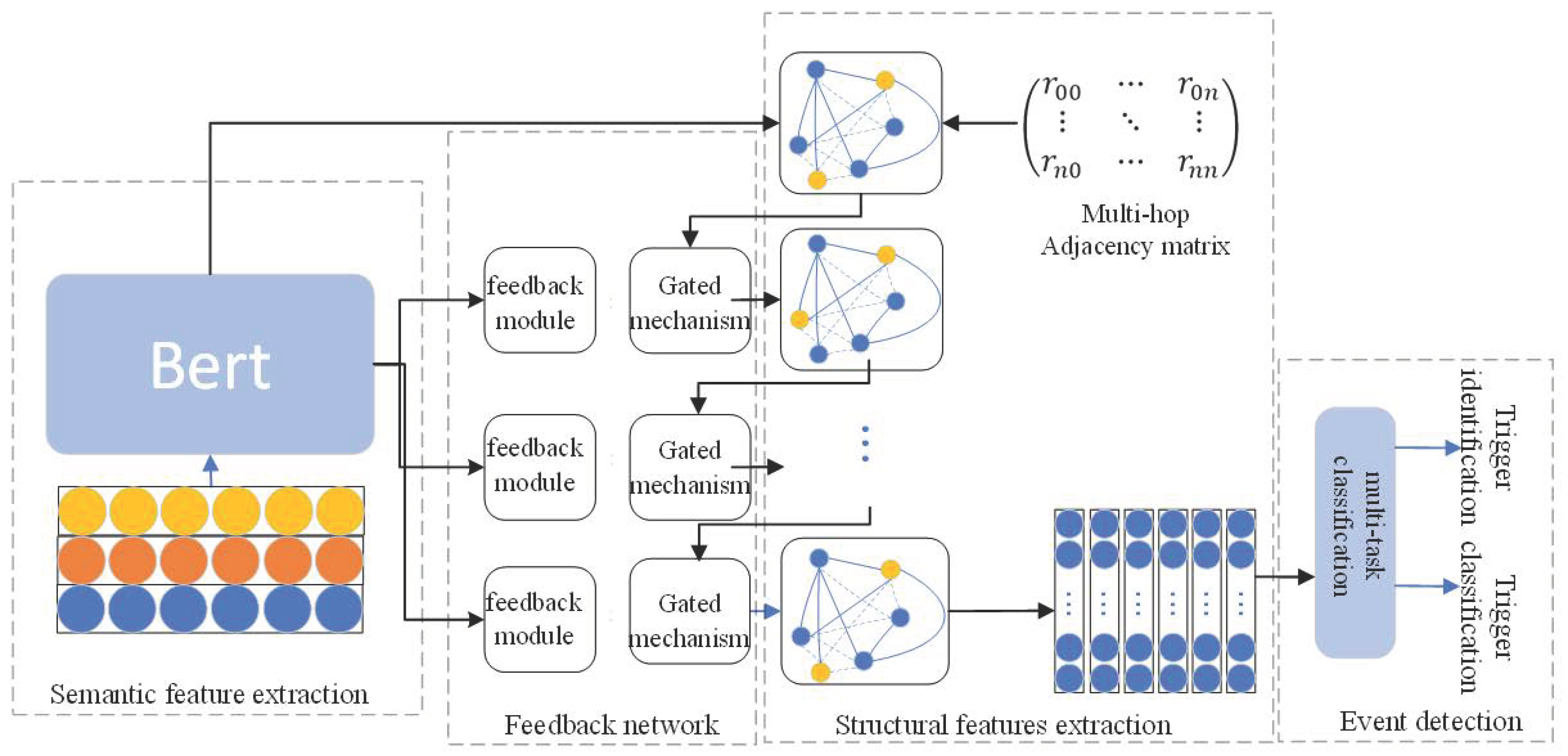
3. Event Detection Model
3.1. Semantic Features
3.2. Structural Features
3.2.1. Syntactic Analysis
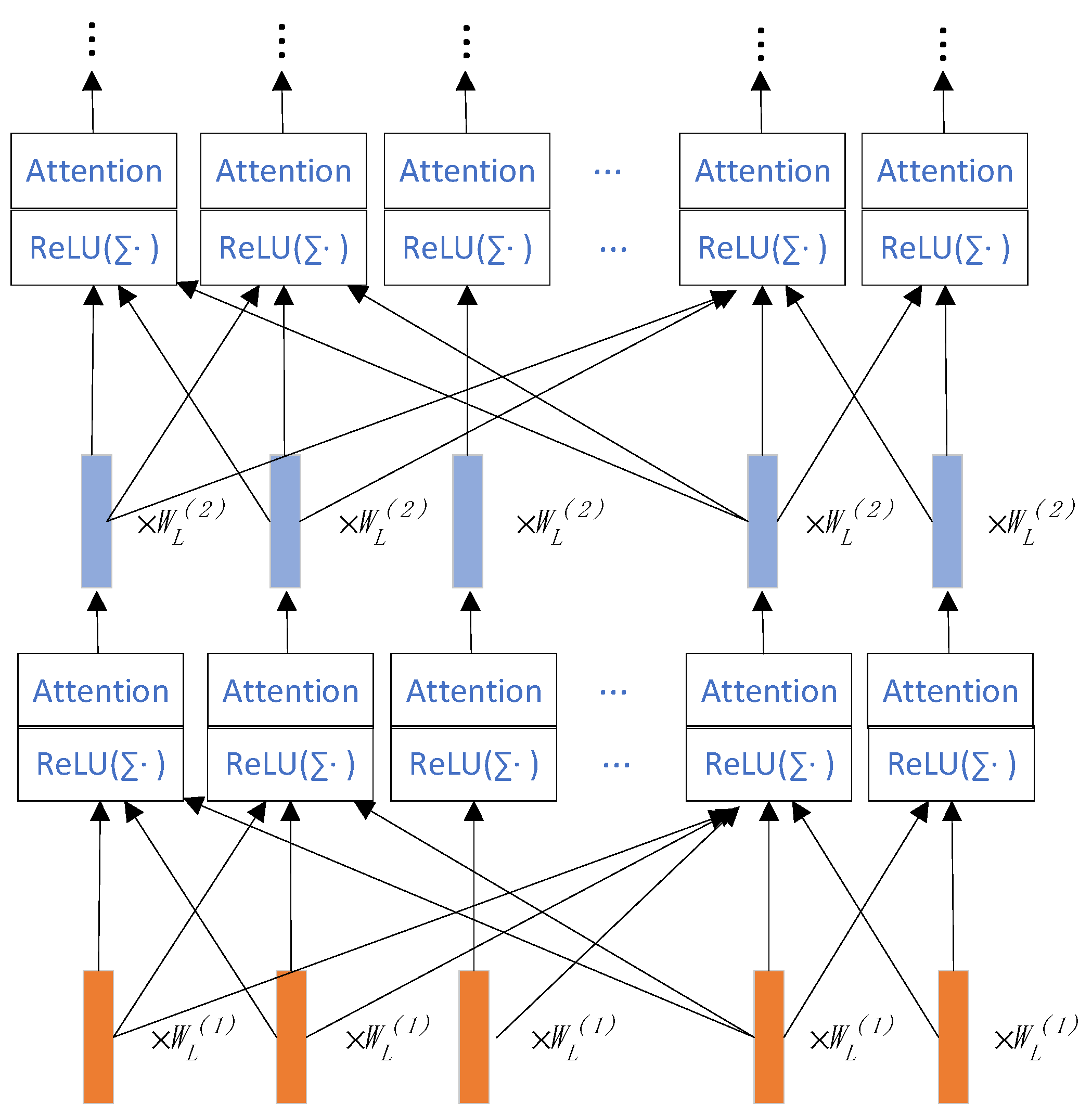
3.2.2. Stacked Graph Neural Network
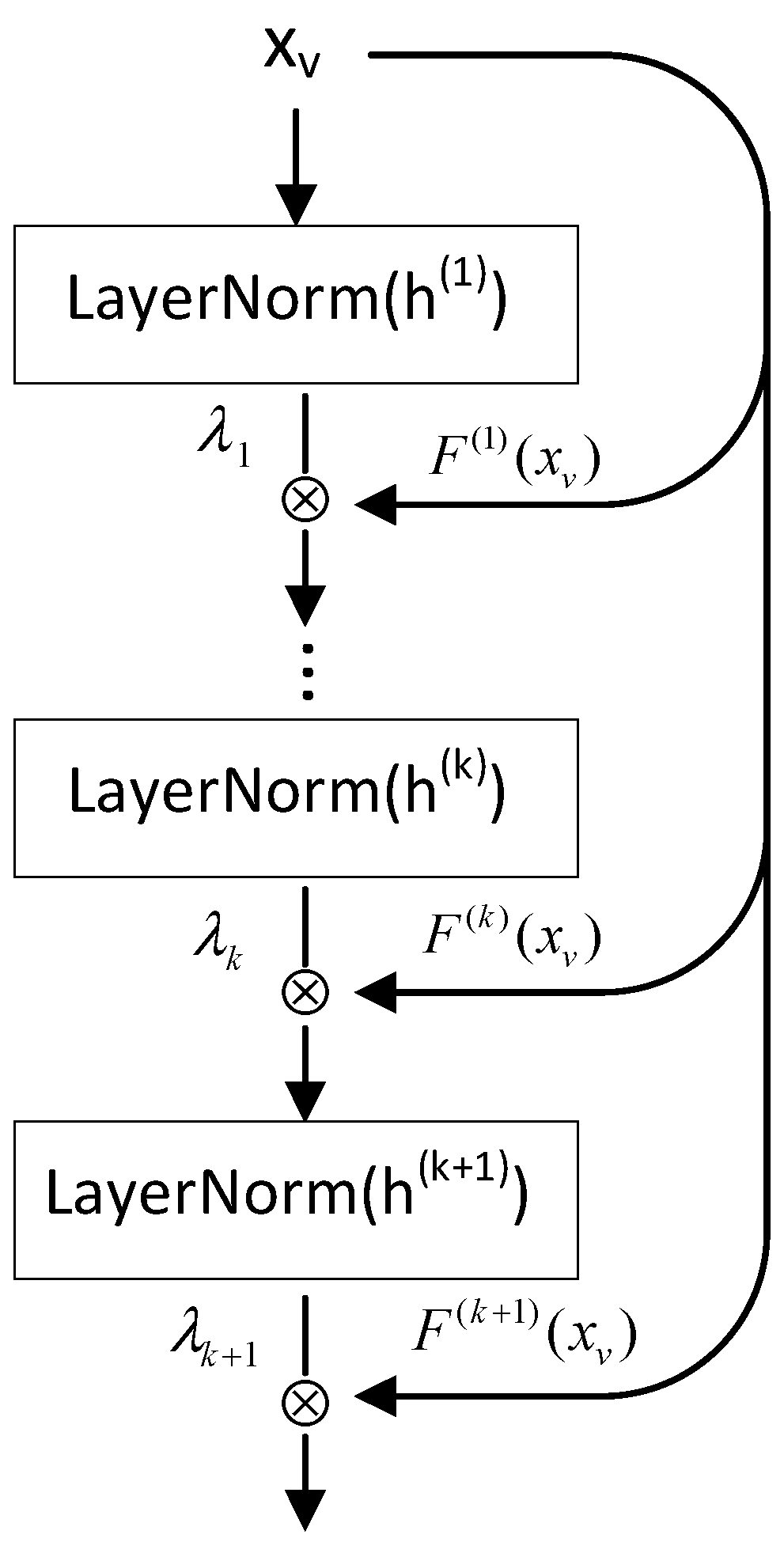
3.3. Feedback Network
3.4. Event Detection
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Data and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Experimental Environment and Model Training Parameters
4.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.3.1. Comparison Experiments
4.3.2. Ablation Study
4.3.3. Influence of the Model Depth
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linguistic Data Consortium. ACE (Automatic Content Extraction) English Annotation Guidelines for Events Version 5.4. 3. Available online: https://www.ldc.upenn.edu/ (accessed on 18 June 2020).
- Li, Q.; Peng, H.; Li, J.; Xia, C.; Yang, R.; Sun, L.; Yu, P.S.; He, L. A survey on text classification: From traditional to deep learning. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2022, 13, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, D.W.; Medina, J.R.; Kalita, J.K. A survey of the usages of deep learning for natural language processing. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 604–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Mallik, A.; Khetarpal, A.; Panda, B.S. Influence maximization in social networks using graph embedding and graph neural network. Inf. Sci. 2022, 607, 1617–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jia, S.; Xiang, Y. A review: Knowledge reasoning over knowledge graph. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 141, 112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, C.; Huang, F.; Fu, H.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, W. GraphCDR. A graph neural network method with contrastive learning for cancer drug response prediction. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbab457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, M.E.; Neumann, M.; Iyyer, M.; Gardner, M. Deep contextualized word representations. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; pp. 2227–2237. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving language understanding by generative pre-training. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.07157. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, P.; Manning, C.D. Graph convolution over pruned dependency trees improves relation extraction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.10185. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, K.; Lan, H.; Guo, J. Event detection from text using path-aware graph convolutional network. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 4987–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Grishman, R. Graph convolutional networks with argument-aware pooling for event detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 5900–5907. [Google Scholar]
- Scarselli, F.; Gori, M.; Tsoi, A.C.; Hagenbuchner, M.; Monfardini, G. The graph neural network model. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2008, 20, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Xu, N.; Liu, H. Self-Attention Graph Residual Convolutional Networks for Event Detection with dependency relations. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2021, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 16–20 November 2021; pp. 302–311. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Lin, Y.; Li, W.; Li, P.; Zhou, J.; Sun, X. Measuring and relieving the over-smoothing problem for graph neural networks from the topological view. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 3438–3445. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Liu, K.; Zeng, D.; Zhao, J. Event extraction via dynamic multi-pooling convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Grishman, R. Modeling skip-grams for event detection with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–4 November 2016; pp. 886–891. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Cho, K.; Grishman, R. Joint event extraction via recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–17 June 2016; pp. 300–309. [Google Scholar]
- Jagannatha, A.N.; Yu, H. Bidirectional RNN for medical event detection in electronic health records. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; p. 473. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, Q. Self-regulation: Employing a generative adversarial network to improve event detection. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Melbourne, Australia, 15–20 July 2018; pp. 515–526. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, X.; Yang, T. Event detection without triggers. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 735–744. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Feng, D.; Qiao, L.; Kan, Z.; Li, D. Exploring pre-trained language models for event extraction and generation. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 29–31 July 2019; pp. 5284–5294. [Google Scholar]
- Wadden, D.; Wennberg, U.; Luan, Y.; Hajishirzi, H. Entity, relation, and event extraction with contextualized span representations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.03546. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, K.; Bi, W.; Liu, X. Event extraction as machine reading comprehension. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 1641–1651. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.; Cardie, C. Event extraction by answering (almost) natural questions. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.13625. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Chen, Y.; Shen, K.; Guo, X.; Gao, H.; Li, S.; Pei, J.; Long, B. Graph neural networks for natural language processing: A survey. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.06090. [Google Scholar]
- Zaratiana, U.; Tomeh, N.; Holat, P.; Charnois, T. GNNer: Reducing Overlapping in Span-based NER Using Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Student Research Workshop, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.; Yu, B.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shi, J. Edge-enhanced graph convolution networks for event detection with syntactic relation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.10757. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Jin, X.; Meng, X.; Guo, J.; Cheng, X. Event detection with multi-order graph convolution and aggregated attention. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 5766–5770. [Google Scholar]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Liò, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, L.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Xu, G.; Sun, X. Hgeed. Hierarchical graph enhanced event detection. Neurocomputing 2021, 453, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Schuster, M.; Chen, Z.; Le, Q.V.; Norouzi, M.; Macherey, W.; Krikun, M.; Cao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Macherey, K.; et al. Google’s neural machine translation system: Bridging the gap between human and machine translation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.08144. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Dong, Y.; Wang, K.; Lee, W.; Hooi, B.; Xu, H. Understanding and resolving performance degradation in deep graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 2728–2737. [Google Scholar]
- Doddington, G.; Mitchell, A.; Przybocki, M.; Ramshaw, L.; Strassel, S.; Weischedel, R. The automatic content extraction (ace) program-tasks, data, and evaluation. Lrec 2004, 2, 837–840. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Ji, H.; Sil, A. Joint entity and event extraction with generative adversarial imitation learning. Data Intell. 2019, 1, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ji, H.; Huang, L. Joint event extraction via structured prediction with global features. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Sofia, Bulgaria, 4–9 August 2013; pp. 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Yacouby, R.; Axman, D. Probabilistic extension of precision, recall, and f1 score for more thorough evaluation of classification models. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Evaluation and Comparison of NLP Systems, Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 20 November 2020; pp. 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, D.M.W. Evaluation: From precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.16061. [Google Scholar]
- Opitz, J.; Burst, S. Macro f1 and macro f1. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.03347. [Google Scholar]
- Izsak, P.; Berchansky, M.; Levy, O. How to train BERT with an academic budget. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.07705. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, M.; Liao, R.; Urtasun, R.; Sinz, F.H.; Zemel, R.S. Normalizing the normalizers: Comparing and extending network normalization schemes. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.04520. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Luo, Z.; Huang, H. Jointly multiple events extraction via attention-based graph information aggregation. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Nguyen, T.H. One for all: Neural joint modeling of entities and events. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January 2019; pp. 6851–6858. [Google Scholar]



| Event Type | Event Subtype |
|---|---|
| Life | Be-Born, Divorce, Marry, Injure, Die |
| Movement | Transport |
| Transaction | Transfer-Ownership, Transfer-Money |
| Business | Start-Org, Merge-Org, Declare-Bankruptcy, End-Org |
| Conflict | Attack, Demonstrate |
| Contact | Meeting, Phone-Write |
| Personnel | Start-Position, End-Position, Nominate, Elect |
| Justice | Arrest-Jail, Release-Parole, Trial-Hearing, Charge-Indict, Sue, Convict, Sentence, Fine, Execute, Extradite, Acquit, Appeal, Pardon |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Epoch | 10 |
| Batch size | 8 |
| Learning rate | 4 × 10−5 |
| Dropout | 0.2 |
| Warmup proportion | 0.1 |
| GCN layers | 5 |
| GCN input | 768 |
| Hidden size | 768 |
| Methods | Trigger Classification | Trigger Identification | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | R | F1 | P | R | F | |
| DMCNN [16] | 75.6 | 63.6 | 69.1 | 80.4 | 67.7 | 73.5 |
| TBNNAM [21] | 76.2 | 64.5 | 69.9 | - | - | - |
| BERT_QA [25] | 71.12 | 73.70 | 72.39 | 74.29 | 77.42 | 75.82 |
| GCN-ED [12] | 77.9 | 68.8 | 73.1 | - | - | - |
| JMEE [43] | 76.3 | 64.5 | 69.9 | 80.2 | 72.1 | 75.9 |
| Joint3EE [44] | 68.00 | 71.80 | 69.80 | 70.50 | 74.50 | 72.50 |
| HGEED [31] | 80.1 | 72.7 | 76.2 | - | - | - |
| Our model | 76.16 | 76.92 | 76.54 | 81.57 | 82.38 | 81.97 |
| Methods | Trigger Classification | Trigger Identification | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | R | F1 | P | R | F | |
| Our model | 76.16 | 76.92 | 76.54 | 81.57 | 82.38 | 81.97 |
| -attention | 73.98 | 76.92 | 75.42 | 79.23 | 82.38 | 80.77 |
| -fusion | 73.42 | 75.43 | 74.41 | 79.71 | 81.88 | 80.78 |
| -feedback | 72.79 | 71.71 | 72.2 | 78.58 | 77.41 | 78 |
| -gcn | 69.77 | 76.18 | 72.84 | 67.15 | 73.2 | 70.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Ding, K.; Liu, M.; Liu, S. A Multi-Hop Graph Neural Network for Event Detection via a Stacked Module and a Feedback Network. Electronics 2023, 12, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12061386
Liu L, Ding K, Liu M, Liu S. A Multi-Hop Graph Neural Network for Event Detection via a Stacked Module and a Feedback Network. Electronics. 2023; 12(6):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12061386
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Liu, Kun Ding, Ming Liu, and Shanshan Liu. 2023. "A Multi-Hop Graph Neural Network for Event Detection via a Stacked Module and a Feedback Network" Electronics 12, no. 6: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12061386
APA StyleLiu, L., Ding, K., Liu, M., & Liu, S. (2023). A Multi-Hop Graph Neural Network for Event Detection via a Stacked Module and a Feedback Network. Electronics, 12(6), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12061386





