Attention Mechanism Trained with Small Datasets for Biomedical Image Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Feature Fusion Works
1.1.1. Multilayer Feature Fusion
1.1.2. Multibranch Feature Fusion
1.2. Related Attention Mechanisms
1.2.1. Spatial Attention
1.2.2. Channel Attention
2. Methods
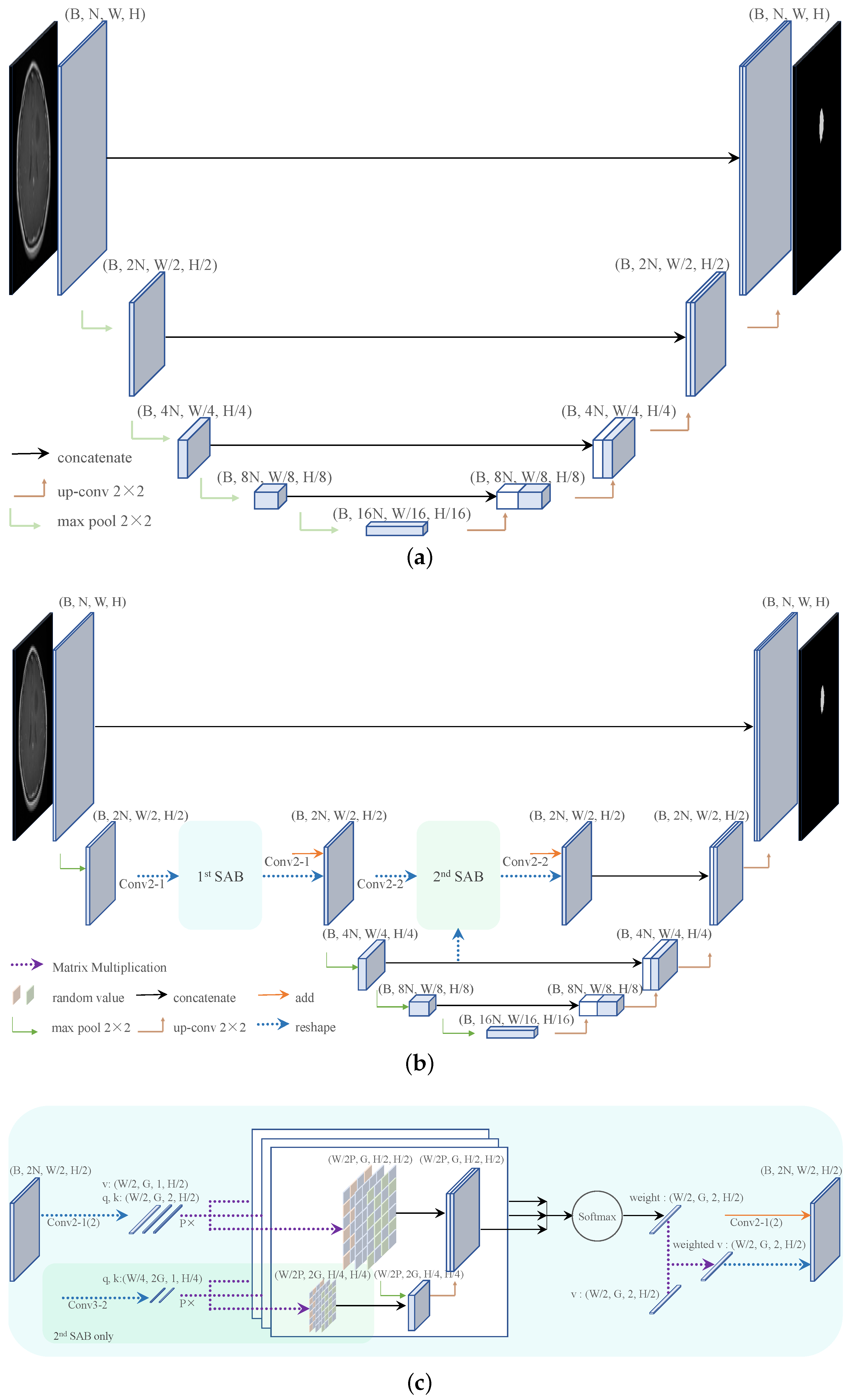
2.1. Network Architecture
2.2. Smooth Attention Branch
2.2.1. Convolutions within SABs
2.2.2. Position Blurring
2.2.3. Inner Cropping
2.3. Datasets
2.4. Implementation Details
3. Results
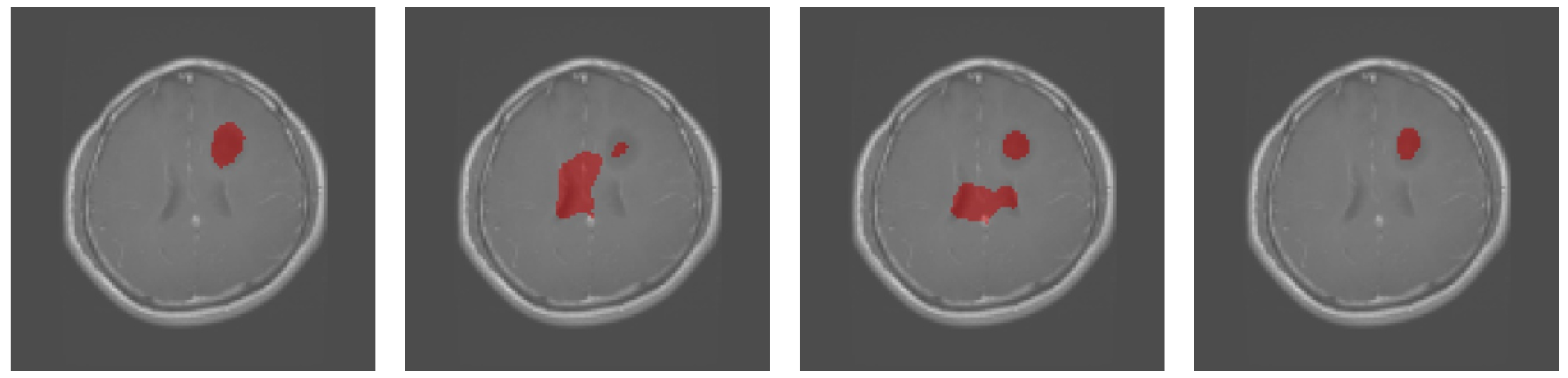
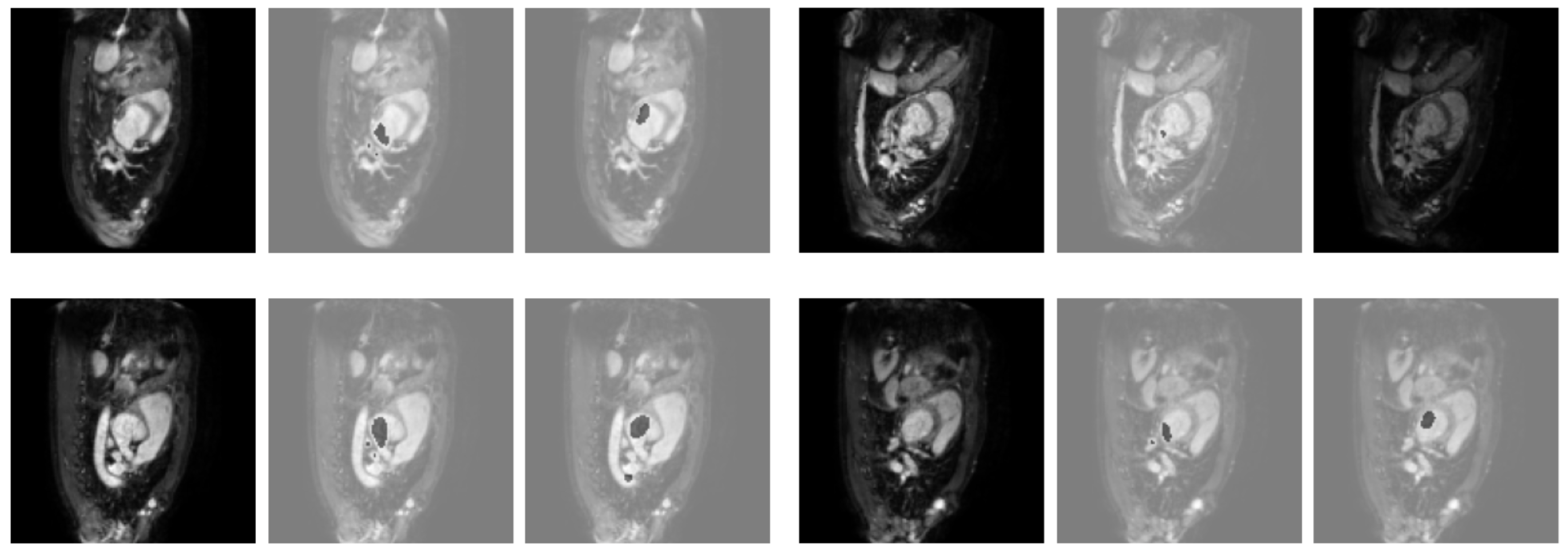
3.1. Results Obtained on the Brain MRI Dataset
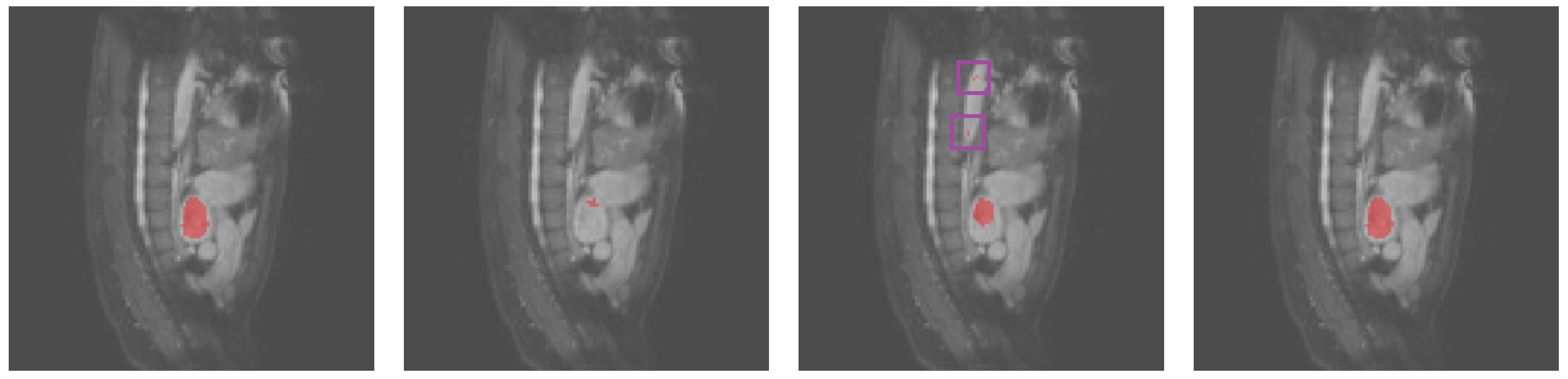
3.2. Results Obtained on the Heart MRI Dataset
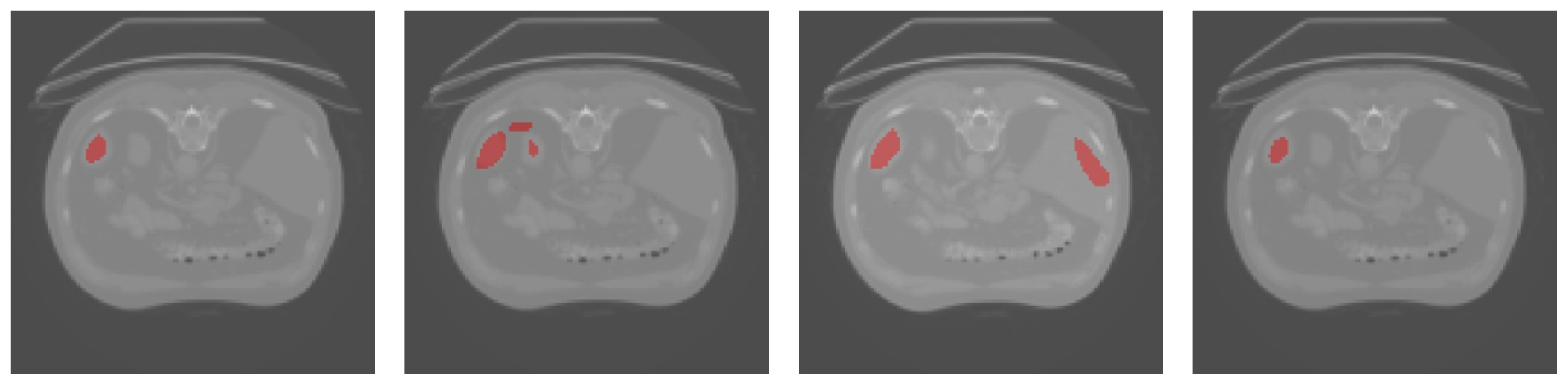
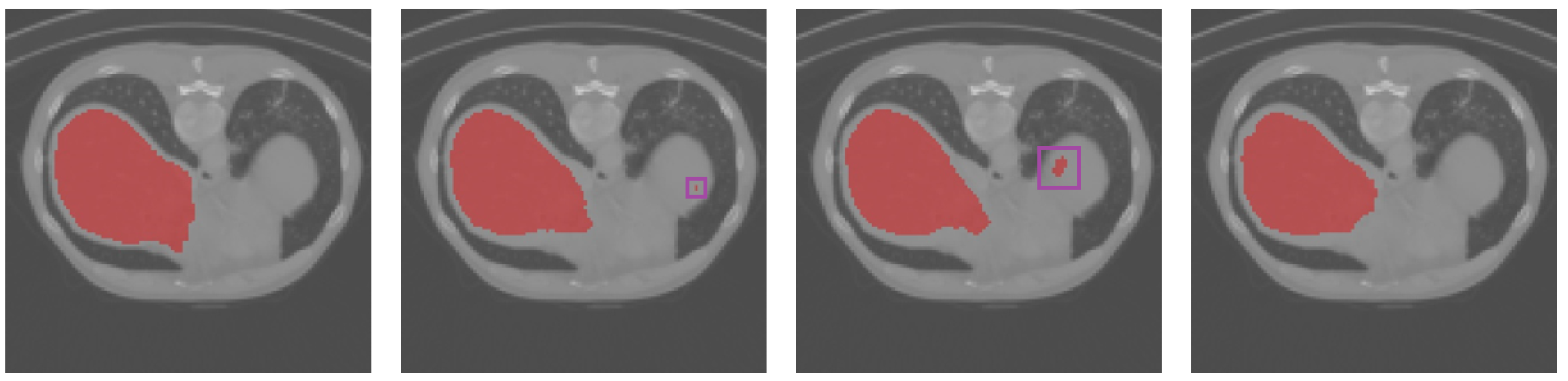
3.3. Results Obtained on the Spleen and Liver CT Datasets
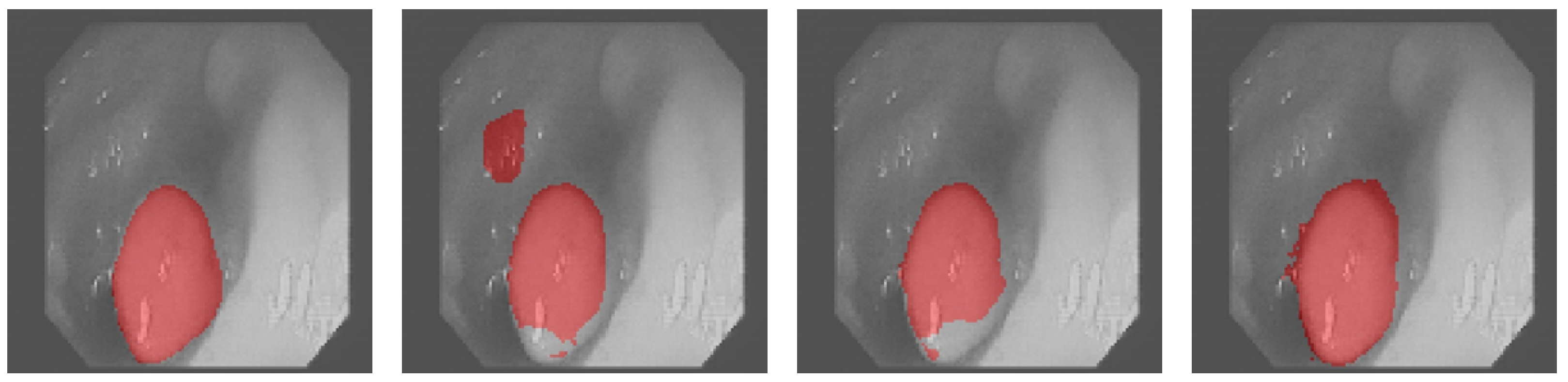
3.4. Results Obtained on the Colonoscopy Dataset
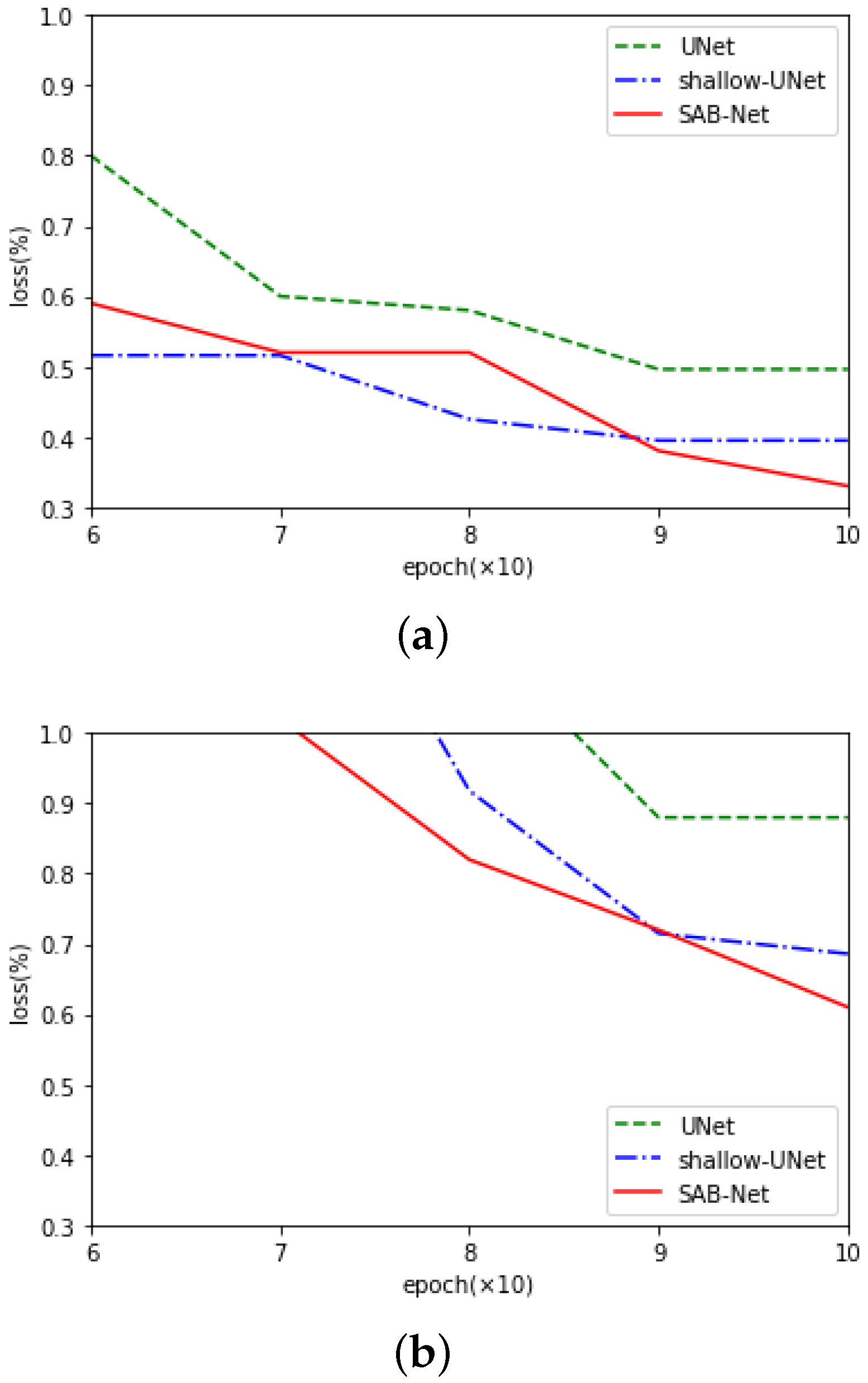
4. Discussion
4.1. Residual Learning Framework and Comparison with the U-Net Family
4.2. Comparison with Recent Self-Attentions
4.3. Position Blurring and Inner Cropping
4.4. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Song, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. A review of deep-learning-based medical image segmentation methods. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Q.; Alazab, M.; Zhao, H.; Su, C. DEEP-FEL: Decentralized, Efficient and Privacy-Enhanced Federated Edge Learning for Healthcare Cyber Physical Systems. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 3558–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Drozdzal, M.; Vorontsov, E.; Chartrand, G.; Kadoury, S.; Pal, C. The importance of skip connections in biomedical image segmentation. In Deep Learning and Data Labeling for Medical Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Gegundez-Arias, M.E.; Marin-Santos, D.; Perez-Borrero, I.; Vasallo-Vazquez, M.J. A new deep learning method for blood vessel segmentation in retinal images based on convolutional kernels and modified U-Net model. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 205, 106081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibtehaz, N.; Rahman, M.S. MultiResUNet: Rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. 2020, 121, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Rahardja, S. BSEResU-Net: An attention-based before-activation residual U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 205, 106070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lv, P.; Wang, H.; Shi, C. SAR-U-Net: Squeeze-and-excitation block and atrous spatial pyramid pooling based residual U-Net for automatic liver segmentation in Computed Tomography. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Yuwen, C.; Jiang, L.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Y. Multiscale attention guided U-Net architecture for cardiac segmentation in short-axis MRI images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 206, 106142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Fan, Q.; Feris, R.S.; Vasconcelos, N. A unified multi-scale deep convolutional neural network for fast object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 354–370. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Sun, J. Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7103–7112. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Cheng, L. Dilated densely connected U-Net with uncertainty focus loss for 3D ABUS mass segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 209, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jégou, S.; Drozdzal, M.; Vazquez, D.; Romero, A.; Bengio, Y. The one hundred layers tiramisu: Fully convolutional densenets for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.; Zhou, T.; Li, Y.; Qiu, X. NAS-Unet: Neural Architecture Search for Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44247–44257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoph, B.; Le, Q.V. Neural architecture search with reinforcement learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.01578. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Sheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cai, L.; Ling, H. M2det: A single-shot object detector based on multi-level feature pyramid network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January 27–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 9259–9266. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.; Li, Y.; Urtasun, R.; Zemel, R. Understanding the effective receptive field in deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 4898–4906. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A.A. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, G.; Luo, G.; Sun, J. Large kernel matters–improve semantic segmentation by global convolutional network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4353–4361. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; Liu, S. Attention guided U-Net with atrous convolution for accurate retinal vessels segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 32826–32839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28 (NIPS 2015), Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, Q. Transfuse: Fusing transformers and cnns for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, D.; Vasylechko, S.D.; Gholipour, A. Convolution-free medical image segmentation using transformers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Ding, M.; Yu, H.; Zha, S.; Li, J. Transbts: Multimodal brain tumor segmentation using transformer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Dong, L.; Lapata, M. Long short-term memory-networks for machine reading. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1601.06733. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Residual attention network for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3156–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Jia, J.; Koltun, V. Exploring self-attention for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10076–10085. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.; Xiong, K.; Pang, Y.; Li, X. Video summarization with attention-based encoder–decoder networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2019, 30, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H.; Hirakawa, T.; Yamashita, T.; Fujiyoshi, H. Attention branch network: Learning of attention mechanism for visual explanation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 10705–10714. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Lin, S. Local relation networks for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3464–3473. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, W.; Cao, S.; Yang, R.; Yang, W.; Yun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q. Enhanced performance of brain tumor classification via tumor region augmentation and partition. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, A.L.; Antonelli, M.; Bakas, S.; Bilello, M.; Farahani, K.; Van Ginneken, B.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Landman, B.A.; Litjens, G.; Menze, B.; et al. A large annotated medical image dataset for the development and evaluation of segmentation algorithms. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.09063. [Google Scholar]
- Bilic, P.; Christ, P.F.; Vorontsov, E.; Chlebus, G.; Chen, H.; Dou, Q.; Fu, C.W.; Han, X.; Heng, P.A.; Hesser, J.; et al. The liver tumor segmentation benchmark (lits). arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.04056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, J.; Tajkbaksh, N.; Sánchez, F.J.; Matuszewski, B.J.; Chen, H.; Yu, L.; Angermann, Q.; Romain, O.; Rustad, B.; Balasingham, I.; et al. Comparative validation of polyp detection methods in video colonoscopy: Results from the MICCAI 2015 endoscopic vision challenge. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2017, 36, 1231–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Yeung, M.; Sala, E.; Schönlieb, C.B.; Rundo, L. Focus U-Net: A novel dual attention-gated CNN for polyp segmentation during colonoscopy. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 137, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Warde-Farley, D.; Mirza, M.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Maxout networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; pp. 1319–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Greff, K.; Schmidhuber, J. Highway networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00387. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1492–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Hu, Y.C.; Liu, C.J.; Halpenny, D.; Hellmann, M.D.; Deasy, J.O.; Mageras, G.; Veeraraghavan, H. Multiple resolution residually connected feature streams for automatic lung tumor segmentation from CT images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, M.H. Optimization, Learning, and Control for Interdependent Complex Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 1123. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, D.; Zhang, X.; Shi, W.; Li, L. Neural Architecture Search for a Highly Efficient Network with Random Skip Connections. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Conv | PB | Crop | Plus | Dice | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 54.35% | ||||
| AB-UNet | 49.85% | ||||
| SAB-1-Net | ✓ | 54.95% | |||
| SAB-1-Net | ✓ | 48.08% | |||
| SAB-1-Net | 49.83% | ||||
| SAB-1-Net | 49.86% | ||||
| SAB-1-Net | ✓ | 53.51% | |||
| SAB-2-Net | ✓ | ✓ | 56.41% | ||
| SAB-2-Net | ✓ | 54.28% | |||
| SAB-2-Net | ✓ | 55.17% | |||
| SAB-2-Net | ✓ | ✓ | 59.23% | ||
| SAB-3-Net | ✓ | ✓ | 57.40% | ||
| SAB-3-Net | ✓ | ✓ | 58.21% | ||
| SAB-3-Net | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 60.89% | |
| SAB-3-Net | ✓ | ✓ | 58.81% | ||
| SAB-3-Net | ✓ | ✓ | 60.80% | ||
| SAB-Net | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 62.37% | |
| SAB-Net | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 61.83% |
| Dice | TPR | TNR | HD95 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 54.35% | 45.23% | 99.80% | 9.22 |
| UNet++ | 56.45% | 48.35% | 99.76% | 8.06 |
| Att-UNet | 58.06% | 46.87% | 99.86% | 8.35 |
| Focus-UNet | 48.59% | 37.34% | 99.85% | 9.43 |
| SAB-Net | 61.83% | 55.15% | 99.78% | 8.06 |
| Dice | TPR | TNR | HD95 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 73.94% | 80.71% | 98.24% | 24.28 |
| UNet++ | 74.06% | 90.25% | 97.50% | 28.33 |
| Att-UNet | 72.82% | 83.74% | 97.84% | 27.39 |
| Focus-UNet | 68.03% | 87.79% | 96.72% | 39.92 |
| SAB-Net | 78.27% | 82.63% | 98.67% | 21.21 |
| Dice | TPR | TNR | HD95 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 42.36% | 27.46% | 99.99% | 5.60 |
| UNet++ | 50.36% | 37.14% | 99.96% | 5.00 |
| Att-UNet | 53.15% | 50.20% | 99.88% | 7.00 |
| Focus-UNet | 35.19% | 27.42% | 99.91% | 14.46 |
| SAB-Net | 57.32% | 58.40% | 99.89% | 5.10 |
| Dice | TPR | TNR | HD95 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 55.88% | 42.11% | 99.15% | 8.77 |
| UNet++ | 58.78% | 46.28% | 98.90% | 8.00 |
| Att-UNet | 60.16% | 50.82% | 98.21% | 6.40 |
| Focus-UNet | 46.10% | 38.36% | 97.24% | 8.06 |
| SAB-Net | 61.13% | 50.27% | 98.60% | 7.07 |
| Dice | TPR | TNR | HD95 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 60.12% | 56.72% | 99.93% | 4.99 |
| UNet++ | 68.93% | 59.93% | 99.97% | 6.32 |
| Att-UNet | 72.37% | 61.77% | 99.98% | 5.74 |
| Focus-UNet | 68.13% | 55.16% | 99.97% | 7.01 |
| SAB-Net | 74.31% | 63.05% | 99.98% | 4.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weng, W.; Zhu, X.; Jing, L.; Dong, M. Attention Mechanism Trained with Small Datasets for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Electronics 2023, 12, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030682
Weng W, Zhu X, Jing L, Dong M. Attention Mechanism Trained with Small Datasets for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Electronics. 2023; 12(3):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030682
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeng, Weihao, Xin Zhu, Lei Jing, and Mianxiong Dong. 2023. "Attention Mechanism Trained with Small Datasets for Biomedical Image Segmentation" Electronics 12, no. 3: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030682
APA StyleWeng, W., Zhu, X., Jing, L., & Dong, M. (2023). Attention Mechanism Trained with Small Datasets for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Electronics, 12(3), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030682







