DFANet: Denoising Frequency Attention Network for Building Footprint Extraction in Very-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (a)
- In optical remote-sensing images, buildings have small inter-class variance and large intra-class variance [7]. For example, non-buildings such as roads, playgrounds, and parking lots have similar characteristics (such as spectrum, shape, size, structure, etc.), which are easy to confuse the extraction method [8].
- (b)
- Due to the different imaging angles of sensors, high-rise buildings often produce different degrees of geometric distortion, which increases the difficulty of algorithm recognition [9].
- (c)
- Due to the difference in the sun’s altitude angle when shooting, buildings tend to produce shadow areas at different angles, which not only interferes with the coverage area of the building itself, but also easily conceals the characteristics of other buildings covered by shadows [10].
- (1)
- We propose a novel denoising frequency attention network (DFANet) for building footprint extraction in VHR images. It contributes to the enhancement of the frequency details of the building while filtering out the background noise interference, which in turn greatly improves the building extraction capability.
- (2)
- We specifically design the denoising frequency attention block and pyramid pooling module to enable better extraction of building footprints by refining the feature mapping of different layers and constructing multi-scale fusion feature maps with adaptive average pooling layers of different sizes.
- (3)
- Numerous experiments on public datasets demonstrate the advanced performance achieved by our method. In addition, both visualization analysis and ablation experiments confirm that our proposed DFAB and PPM have a positive effect on the improvement results.
2. Related Works
2.1. Conventional Building Footprint Extraction Methods
2.2. Deep-Learning-Based Building Footprint Extraction Methods
3. Methodology
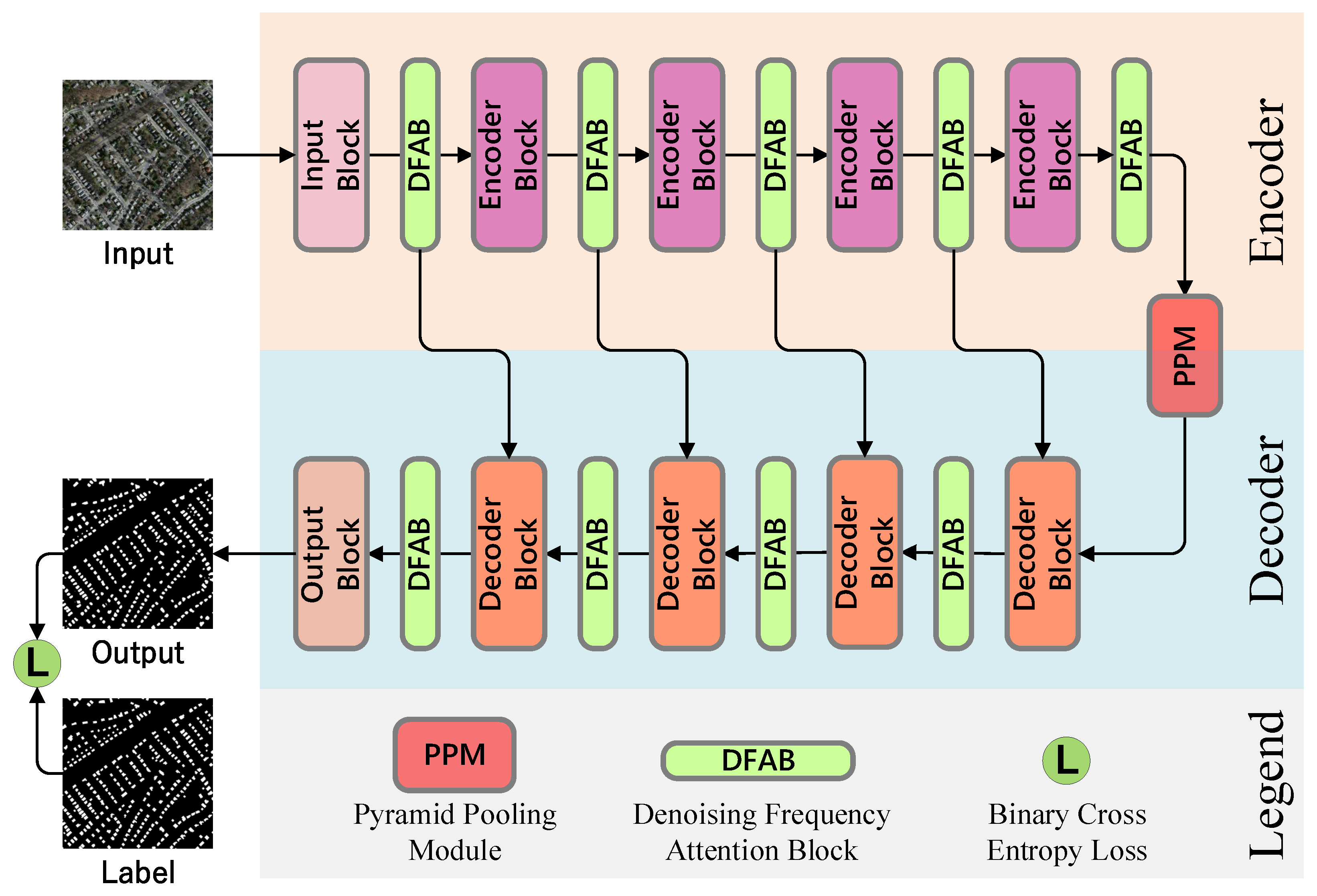
3.1. Overview
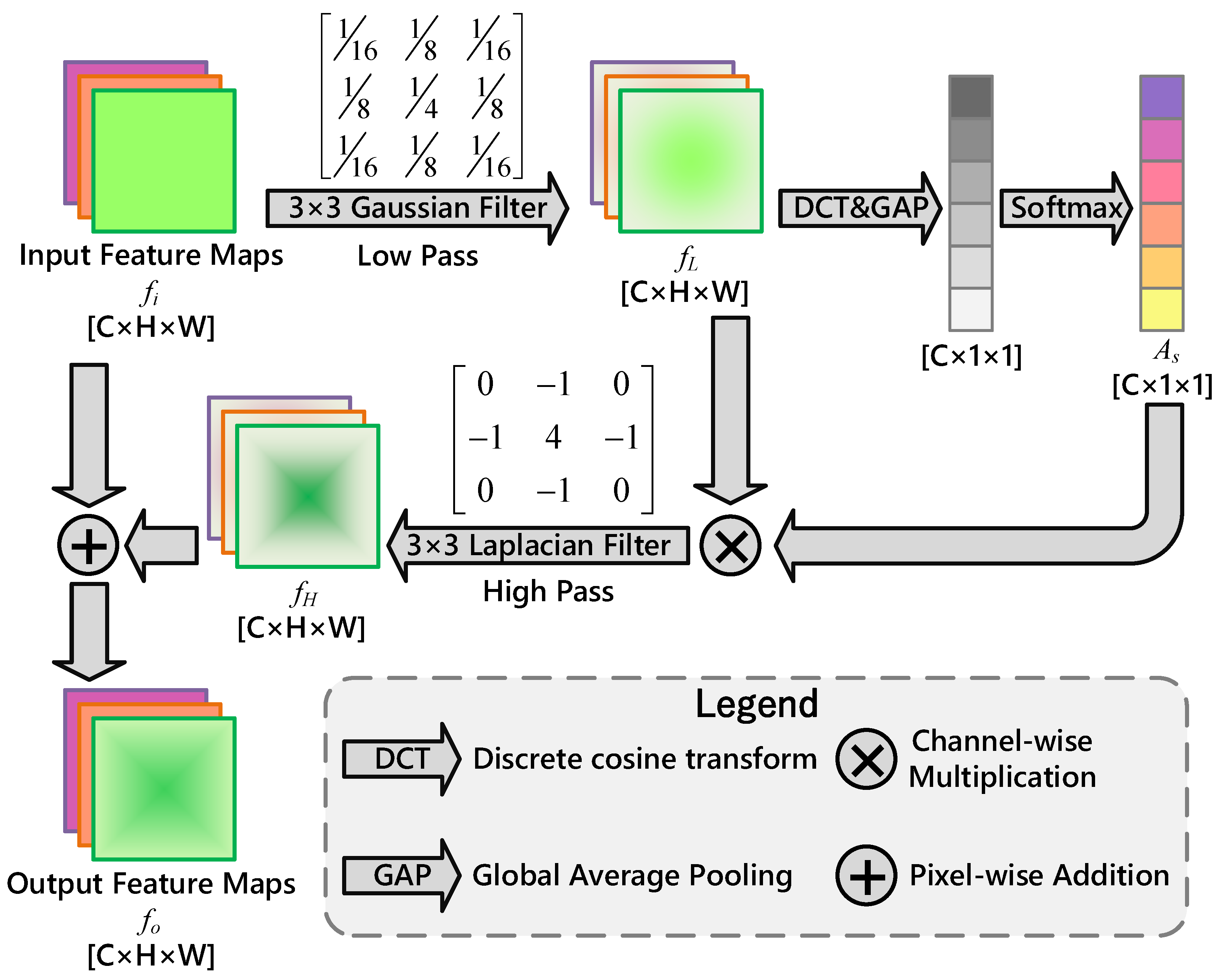
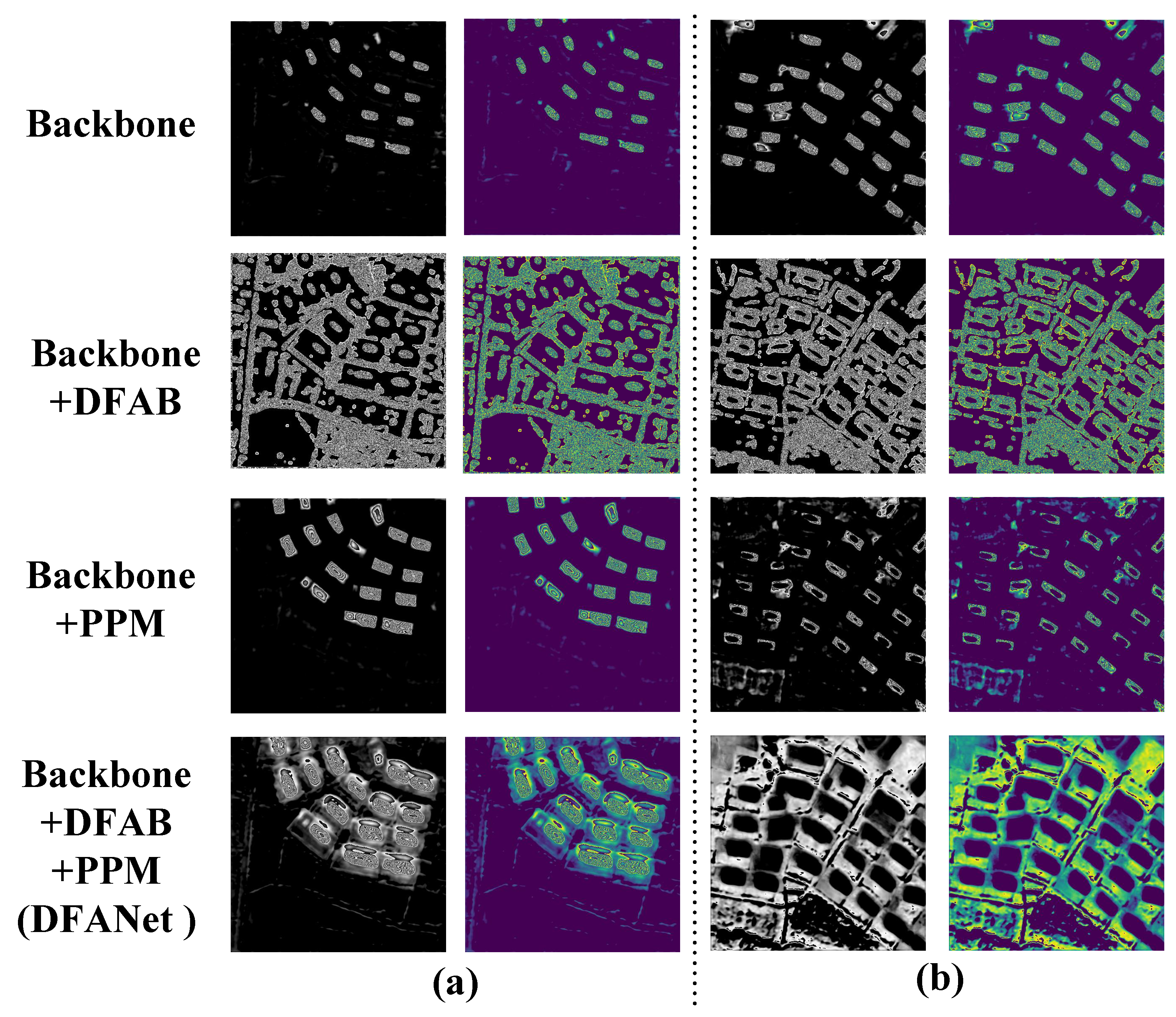
3.2. Denoising Frequency Attention Block
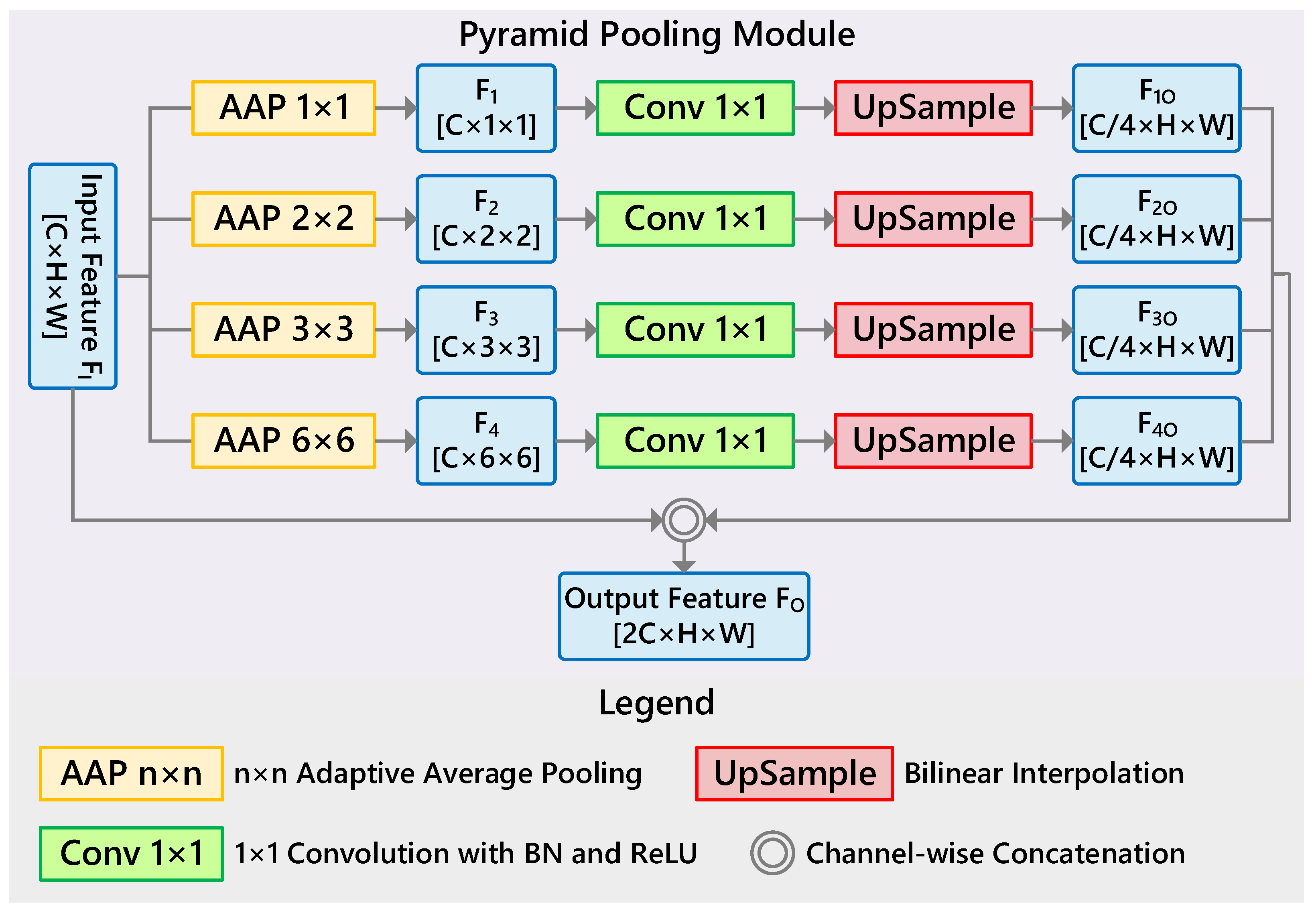
3.3. Pyramid Pooling Module
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Implementation Details
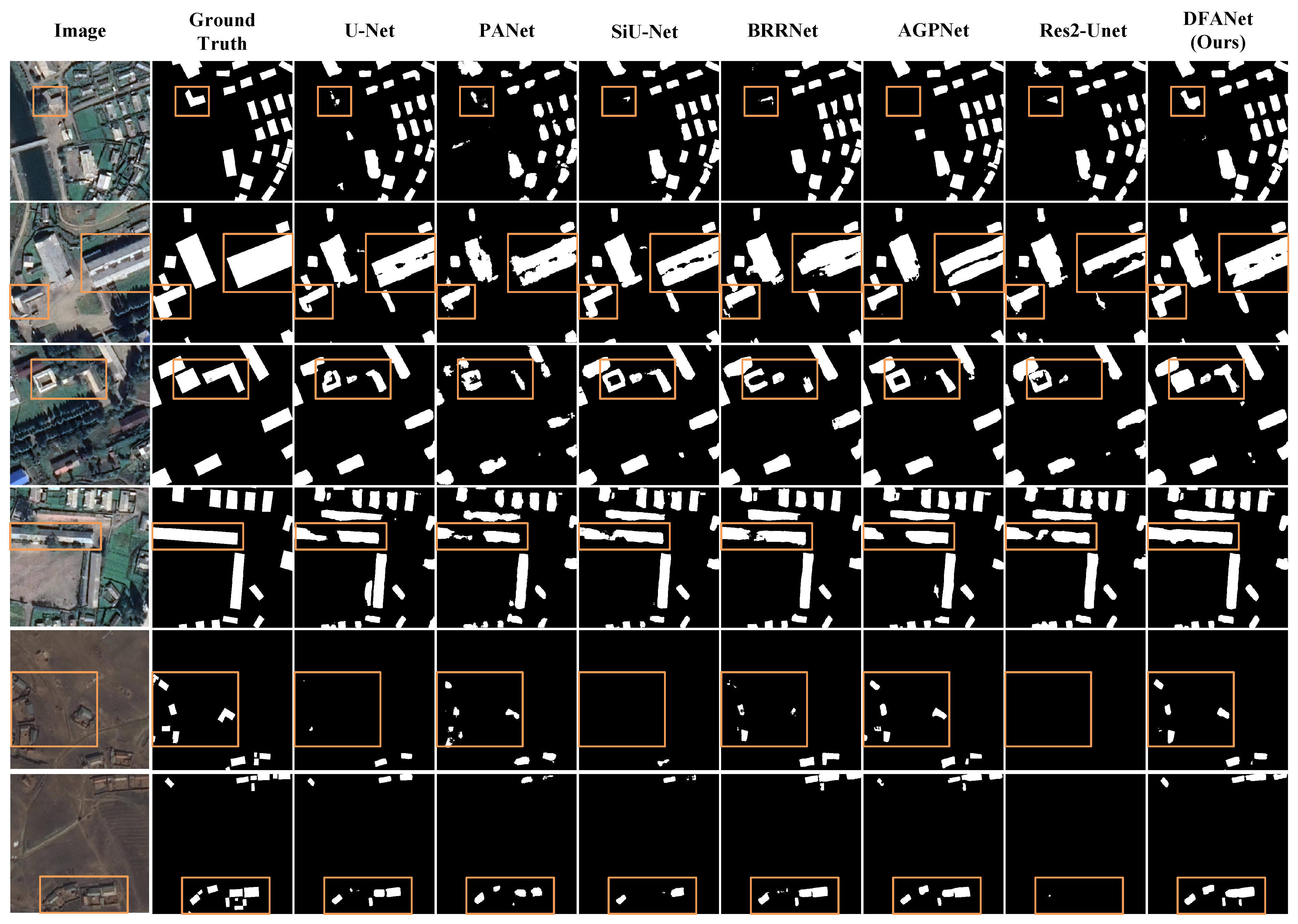
4.3. Comparison with Other Methods
4.3.1. Comparative Algorithms
- (1)
- (2)
- PANet [72] proposed a pyramid attention network to exploit the influence of global context information in semantic segmentation, and introduced feature pyramid attention and global attention upsampling to overcome the loss of localization information.
- (3)
- SiU-Net [15] is designed based on a Siamese fully convolutional network, where the two branches of the network share weights, and the original image and its downsampled counterpart are used as input.
- (4)
- BRRNet [49] consists of a prediction module and a residual refinement module. The prediction module obtains a larger receptive field by introducing dilated convolutions with different dilation rates, while the residual refinement module takes the output of the prediction module as input to improve the accuracy of building segmentation.
- (5)
- AGPNet [55] is one of the state-of-the-art methods designed for architectural segmentation. It is an encoder–decoder structure that combines a grid-based attention gate and an atrous-space pyramid pooling module.
- (6)
- Res2-Unet [73] is an end-to-end building detection network that employs granular-level multi-scale learning to expand the receptive field size of each bottleneck layer, focusing on pixels in complex background boundary regions.
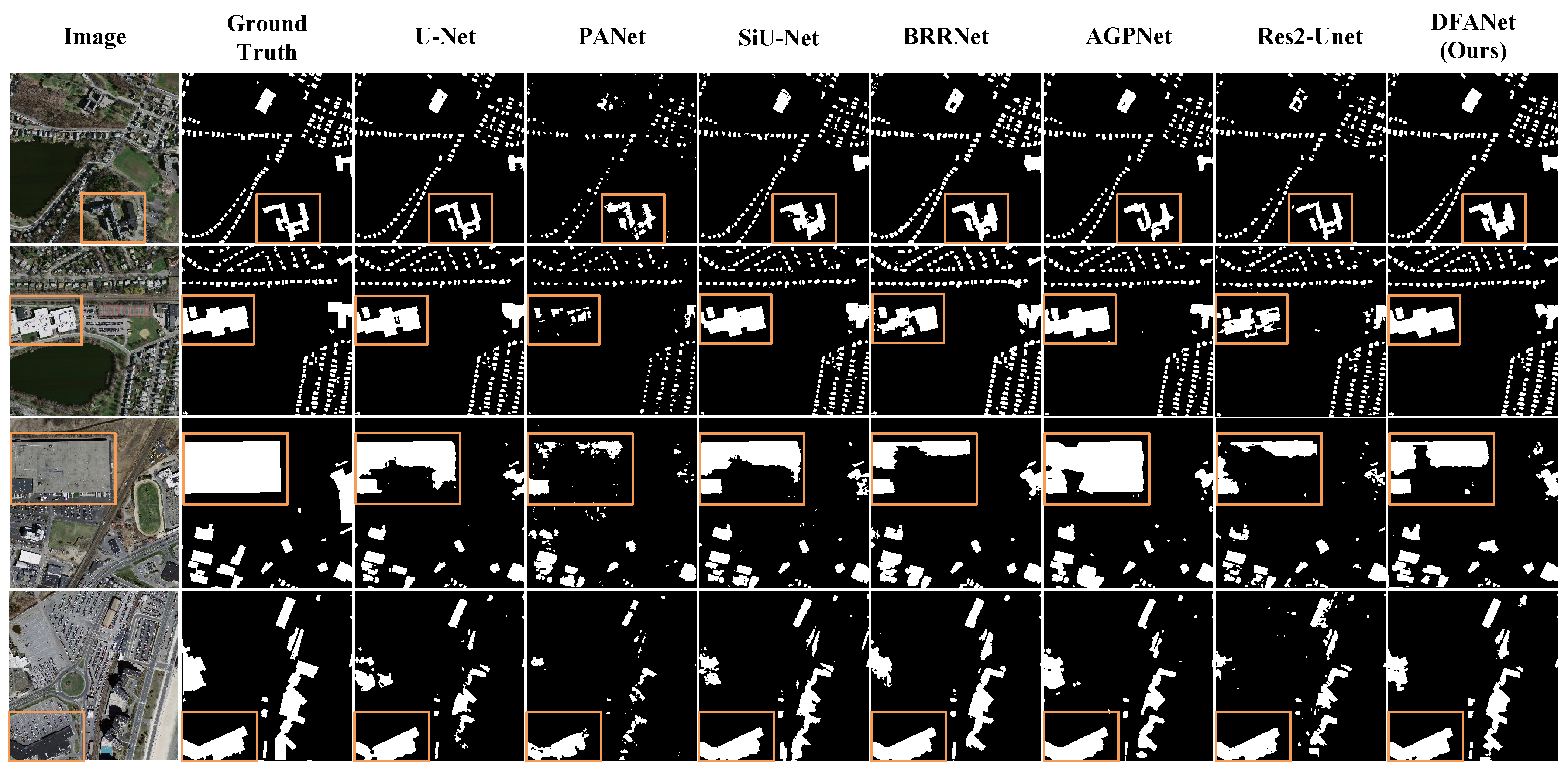
4.3.2. Results on the Massachusetts Dataset
4.3.3. Results of the East Asia Dataset
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, Z.; Liu, T.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Falco, N. Land cover change detection techniques: Very-high-resolution optical images: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Mag. 2021, 10, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M. Two-path aggregation attention network with quad-patch data augmentation for few-shot scene classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2022, 60, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Tan, X.; Sui, H.; Xu, C.; Duan, H.; Li, D. Context-aware convolutional neural network for object detection in VHR remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2019, 58, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Gong, M.; Zheng, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J. Self-Supervised Global-Local Contrastive Learning for Fine-Grained Change Detection in VHR Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2023, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Shi, Q.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y. Building footprint extraction from high-resolution images via spatial residual inception convolutional neural network. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, F.; Zhao, H. Self-supervised monocular depth estimation with multiscale perception. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 3251–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Hu, H.; Mei, X.; Li, H. MAP-Net: Multiple attending path neural network for building footprint extraction from remote sensed imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2020, 59, 6169–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Gong, M.; Lu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, M. Building change detection for VHR remote sensing images via local–global pyramid network and cross-task transfer learning strategy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2021, 60, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hua, Y.; Mou, L.; Zhu, X.X. CG-Net: Conditional GIS-aware network for individual building segmentation in VHR SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2021, 60, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, N.; Mourshed, M. A shadow-overlapping algorithm for estimating building heights from VHR satellite images. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2017, 15, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Gong, M.; Gong, P.; Fan, X.; Qin, A.; Miao, Q.; Ma, W. Self-Supervised Intra-Modal and Cross-Modal Contrastive Learning for Point Cloud Understanding. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Qin, A.; Xing, L.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Deep Fuzzy Variable C-Means Clustering Incorporated with Curriculum Learning. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, M.; Zhang, M.; Li, J. Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation With Self-Perceptual Anomaly Handling. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Qin, A.; Miao, Q.G.; Gong, M.G. Commonality autoencoder: Learning common features for change detection from heterogeneous images. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 4257–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, M. Fully convolutional networks for multisource building extraction from an open aerial and satellite imagery data set. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2018, 57, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, M.; Li, J.; Feng, K.; Zhang, M. Autonomous perception and adaptive standardization for few-shot learning. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 277, 110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J. Learning building extraction in aerial scenes with convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 2793–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Gong, M.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Landslide inventory mapping method based on adaptive histogram-mean distance with bitemporal VHR aerial images. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, X.; Fan, X.; Tu, K.; Gong, M.; Miao, Q.; Ma, W. Correspondence-Free Point Cloud Registration Via Feature Interaction and Dual Branch [Application Notes]. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2023, 18, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhong, P.; Wang, W.; You, Z.; Shi, C. Novel Piecewise Distance based on Adaptive Region Key-points Extraction for LCCD with VHR Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2023, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Gong, M. Multi-fidelity evolutionary multitasking optimization for hyperspectral endmember extraction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 111, 107713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhang, P.; Sun, W.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Li, J.; Wang, W. Novel Adaptive Region Spectral-Spatial Features for Land Cover Classification with High Spatial Resolution Remotely Sensed Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2023, 61, 5609412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahar, L.; Muthukumar, S.; French, S.P. Using aerial imagery and GIS in automated building footprint extraction and shape recognition for earthquake risk assessment of urban inventories. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2010, 48, 3511–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Etten, A.; Hogan, D.; Manso, J.M.; Shermeyer, J.; Weir, N.; Lewis, R. The multi-temporal urban development spacenet dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 6398–6407. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Yu, J. Detection of collapsed buildings in post-earthquake remote sensing images based on the improved YOLOv3. Remote. Sens. 2019, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T. Cost-sensitive self-paced learning with adaptive regularization for classification of image time series. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2021, 14, 11713–11727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Haithcoat, T.L. Development of comprehensive accuracy assessment indexes for building footprint extraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2005, 43, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, A.K.; Davis, C.H.; Wang, X. Automated 2-D building footprint extraction from high-resolution satellite multispectral imagery. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 3, pp. 1996–1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, O.; Lodha, S.K.; Helmbold, D.P. A bayesian approach to building footprint extraction from aerial lidar data. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on 3D Data Processing, Visualization, and Transmission (3DPVT’06), Washington, DC, USA, 14–16 June 2006; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Zabuawala, S.; Nguyen, H.; Wei, H.; Yadegar, J. Fusion of LiDAR and aerial imagery for accurate building footprint extraction. In Image Processing: Machine Vision Applications II; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7251, pp. 337–347. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, C.; Lehrbass, B. Building extraction from LiDAR and aerial images and its accuracy evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, X.; Huang, B.; Li, P. A pixel shape index coupled with spectral information for classification of high spatial resolution remotely sensed imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2006, 44, 2950–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L. A Multidirectional and Multiscale Morphological Index for Automatic Building Extraction from Multispectral GeoEye-1 Imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote. Sens. 2011, 77, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Morphological building/shadow index for building extraction from high-resolution imagery over urban areas. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2011, 5, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M. An automatic morphological attribute building extraction approach for satellite high spatial resolution imagery. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, J.; Feyissa, M.E.; Yang, X. Automatic building detection from very high-resolution images using multiscale morphological attribute profiles. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2020, 11, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, H.; Gong, M.; Qin, A.; Ma, W.; Miao, Q.; Tan, K.C. Evolutionary multiform optimization with two-stage bidirectional knowledge transfer strategy for point cloud registration. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2022, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Gong, M.; Fan, X.; Zhang, M.; Qin, A.; Miao, Q. Rornet: Partial-to-partial registration network with reliable overlapping representations. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gong, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y. Multiform Ensemble Self-Supervised Learning for Few-Shot Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2023, 61, 4500416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Shi, J.; Gu, L. A review of deep learning methods for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 169, 114417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeser, T.; Kuenzer, C. Object detection and image segmentation with deep learning on earth observation data: A review-part I: Evolution and recent trends. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeser, T.; Bachofer, F.; Kuenzer, C. Object detection and image segmentation with deep learning on Earth observation data: A review—Part II: Applications. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, P.; Yan, X. Deep learning-based building extraction from remote sensing images: A comprehensive review. Energies 2021, 14, 7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, M.; Liu, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, D.; Zheng, H.; Jiang, F. Context-content collaborative network for building extraction from high-resolution imagery. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 263, 110283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Tang, P.; Wang, Z.; Saleem, N.; Yam, S.; Sommai, C. BRRNet: A fully convolutional neural network for automatic building extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yan, X. A context feature enhancement network for building extraction from high-resolution remote sensing imagery. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wu, L.; Tang, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Jiao, L. Building extraction of aerial images by a global and multi-scale encoder-decoder network. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, M. A scale robust convolutional neural network for automatic building extraction from aerial and satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2019, 40, 3308–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y. Building extraction based on U-Net with an attention block and multiple losses. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Shi, Q.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Ding, H. Scene-driven multitask parallel attention network for building extraction in high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2020, 59, 4287–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Shi, Q.; Li, J. Attention-gate-based encoder–decoder network for automatical building extraction. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2021, 14, 2611–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, P.; Yao, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y. Building extraction in very high resolution imagery by dense-attention networks. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Xu, W. MSST-Net: A multi-scale adaptive network for building extraction from remote sensing images based on swin transformer. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Qin, K. Multiscale building extraction with refined attention pyramid networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, G.; He, G.; Long, T.; Yin, R.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Luo, B. Robust building extraction for high spatial resolution remote sensing images with self-attention network. Sensors 2020, 20, 7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Gong, M.; Liu, T.; Jiang, F.; Zhan, T.; Lu, D.; Zhang, M. HFA-Net: High frequency attention siamese network for building change detection in VHR remote sensing images. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 129, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Yan, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, X. ED-Net: Automatic building extraction from high-resolution aerial images with boundary information. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2021, 14, 4595–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Chen, F.; Wang, N.; Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, L. MSFTrans: A multi-task frequency-spatial learning transformer for building extraction from high spatial resolution remote sensing images. GISci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1978–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, X. A multiscale attention-guided UNet++ with edge constraint for building extraction from high spatial resolution imagery. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Choi, H.S.; Kang, M. Boundary enhancement semantic segmentation for building extraction from remote sensed image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2021, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Xu, C.; Cui, Z.; Zheng, X.; Yang, J. CVNet: Contour Vibration Network for Building Extraction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1383–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Shi, W.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, M.; Xuan, Z. CGSANet: A Contour-Guided and Local Structure-Aware Encoder–Decoder Network for Accurate Building Extraction From Very High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2021, 15, 1526–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fang, S.; Meng, X.; Li, R. Building extraction with vision transformer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y. PolyBuilding: Polygon transformer for building extraction. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2023, 199, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.; Chu, H.; Zheng, L. Frequency Spectrum Intensity Attention Network for Building Detection from High-Resolution Imagery. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V. Machine Learning for Aerial Image Labeling; University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xiong, P.; An, J.; Wang, L. Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10180. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Wang, N.; Yu, B.; Wang, L. Res2-Unet, a New Deep Architecture for Building Detection from High Spatial Resolution Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2022, 15, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Methods | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | IOU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net [47] (2015) | 88.66 | 72.19 | 79.58 | 66.09 |
| PANet [72] (2018) | 85.05 | 42.02 | 56.25 | 39.13 |
| SiU-Net [15] (2019) | 84.82 | 75.80 | 80.06 | 66.74 |
| BRRNet [49] (2020) | 79.48 | 81.46 | 80.46 | 67.31 |
| AGPNet [55] (2021) | 84.72 | 74.86 | 79.48 | 65.95 |
| Res2-Unet [73] (2022) | 81.04 | 65.65 | 72.64 | 56.91 |
| DFANet (Ours) | 83.42 | 79.71 | 81.52 | 68.81 |
| Methods | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | IOU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net [47] (2015) | 88.41 | 71.22 | 78.89 | 65.14 |
| PANet [72] (2018) | 86.29 | 66.60 | 75.18 | 60.23 |
| SiU-Net [15] (2019 | 88.29 | 70.85 | 78.62 | 64.77 |
| BRRNet [49] (2020) | 84.06 | 78.02 | 80.93 | 67.97 |
| AGPNet [55] (2021) | 86.37 | 76.59 | 81.19 | 68.34 |
| Res2-Unet [73] (2022) | 84.07 | 69.14 | 75.88 | 61.14 |
| DFANet (Ours) | 81.93 | 80.82 | 81.37 | 68.59 |
| Methods | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | IOU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backbone | 80.63 | 77.74 | 79.16 | 65.51 |
| Backbone + DFAB | 81.48 | 79.39 | 80.42 | 67.26 |
| Backbone + PPM | 84.20 | 75.90 | 79.84 | 66.44 |
| Backbone + DFAB + PPM (DFANet) | 83.42 | 79.71 | 81.52 | 68.81 |
| Methods | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) | IOU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backbone | 86.68 | 75.02 | 80.51 | 67.37 |
| Backbone + DFAB | 84.73 | 77.31 | 80.85 | 67.86 |
| Backbone + PPM | 83.83 | 78.93 | 81.30 | 68.50 |
| Backbone + DFAB + PPM (DFANet) | 81.93 | 80.82 | 81.37 | 68.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, L.; Liu, T.; Jiang, F.; Han, B.; Zhao, P.; Wang, G. DFANet: Denoising Frequency Attention Network for Building Footprint Extraction in Very-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Electronics 2023, 12, 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224592
Lu L, Liu T, Jiang F, Han B, Zhao P, Wang G. DFANet: Denoising Frequency Attention Network for Building Footprint Extraction in Very-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Electronics. 2023; 12(22):4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224592
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Lei, Tongfei Liu, Fenlong Jiang, Bei Han, Peng Zhao, and Guoqiang Wang. 2023. "DFANet: Denoising Frequency Attention Network for Building Footprint Extraction in Very-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images" Electronics 12, no. 22: 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224592
APA StyleLu, L., Liu, T., Jiang, F., Han, B., Zhao, P., & Wang, G. (2023). DFANet: Denoising Frequency Attention Network for Building Footprint Extraction in Very-High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Electronics, 12(22), 4592. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224592












