A Multi-Task Classification Method for Application Traffic Classification Using Task Relationships
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (i).
- Improved classification accuracy: improved classification performance considering relationships between multiple tasks (browsers, HTTP protocols, applications, services);
- (ii).
- Generalizability and portability of the four multitask classification methods: the generalized classification model for multiple classifications improves classification performance across diverse backbone networks;
- (iii).
- Possibility to monitor and analyze from multiple perspectives: network administrators can gain more detailed information and insights into the traffic occurring on the networks under their jurisdiction when monitoring and analyzing their networks.
2. Related Works
2.1. Task Description
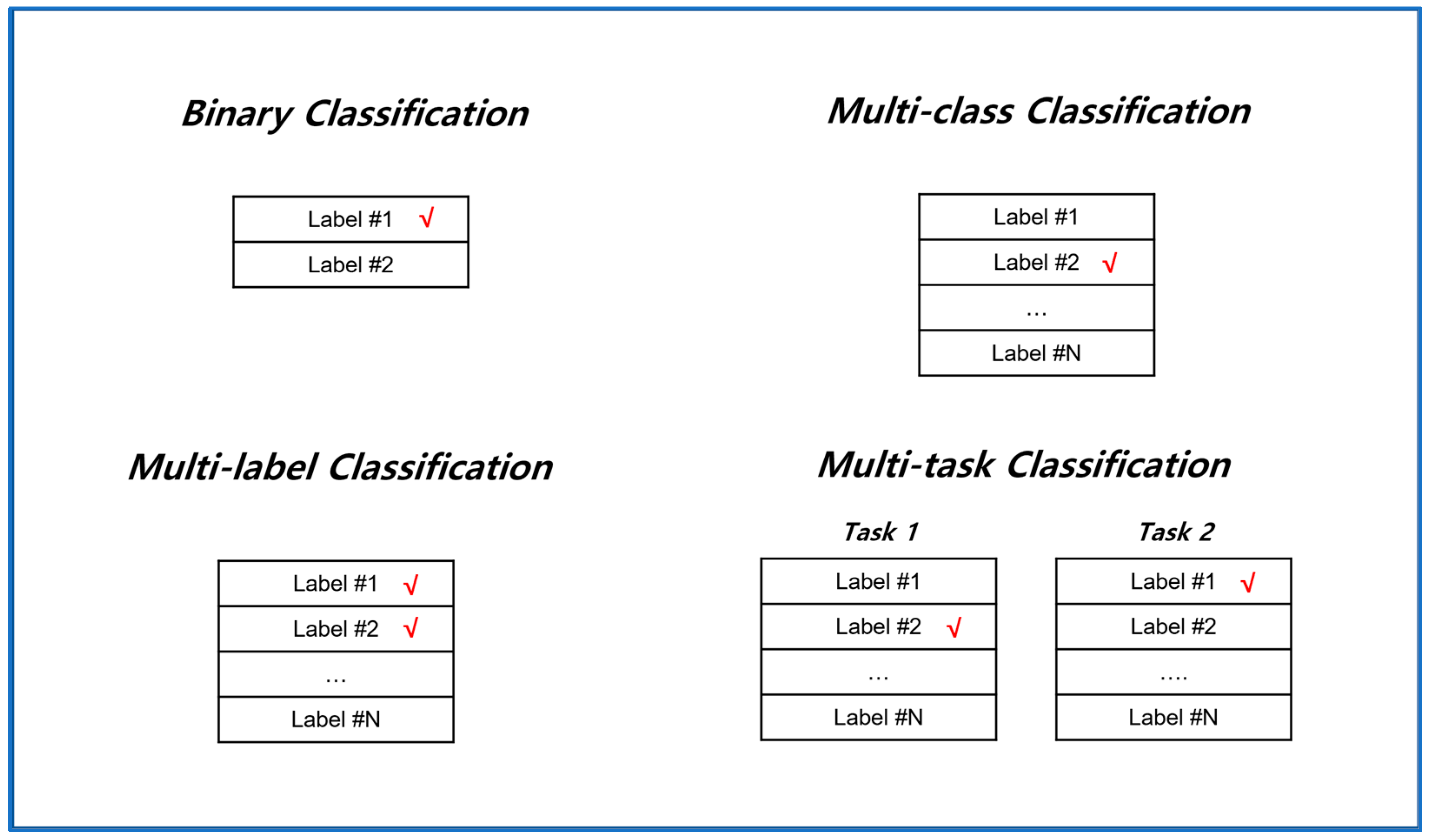
2.2. Classification Type
2.3. Structured Inference Neural Network
2.4. DL-Based Spatial-Temporal Feature Extraction
2.5. MTC-Based Traffic Classification
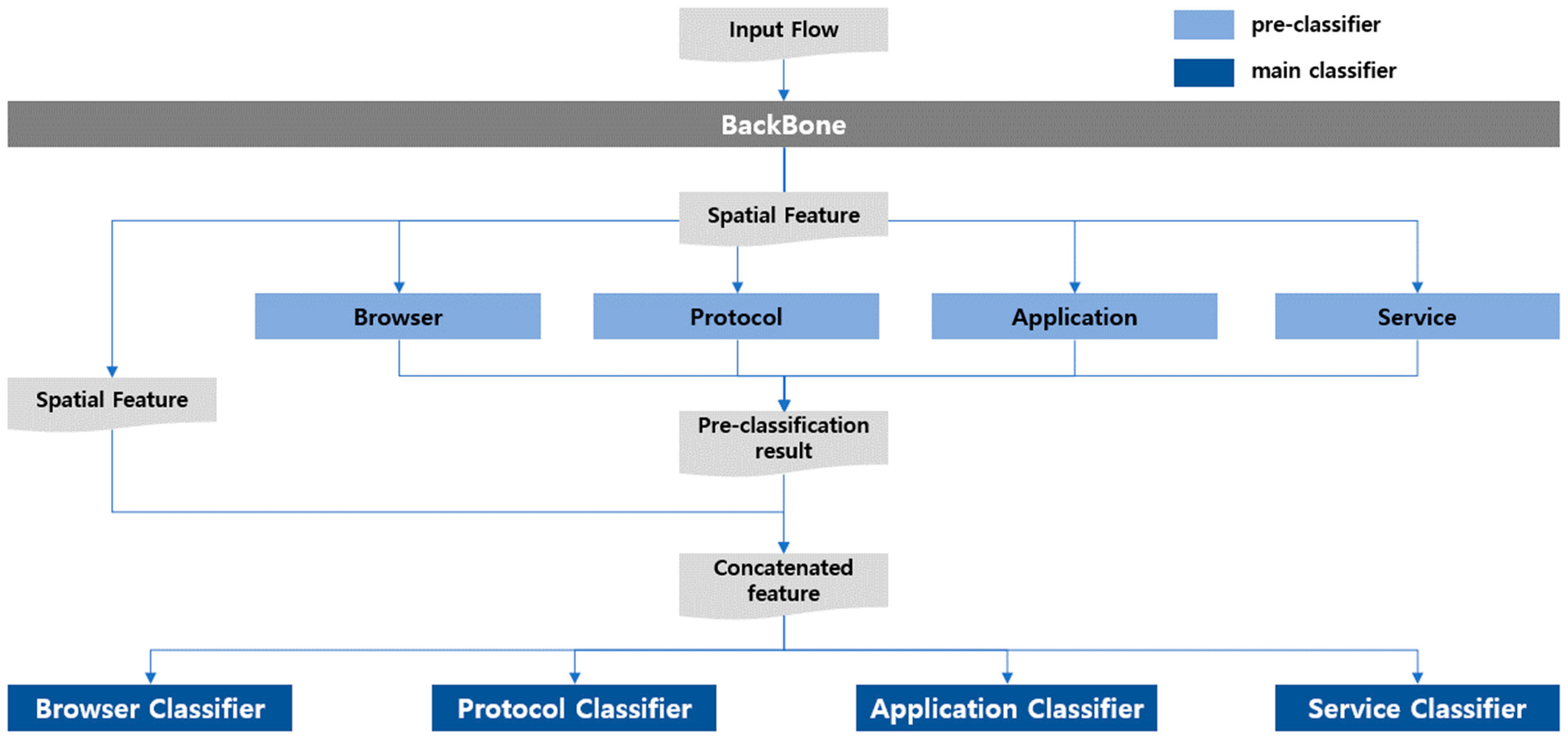
3. Proposed Method
3.1. MTC-Based Traffic Classification
3.1.1. Single Task Single Inference
3.1.2. Multitask
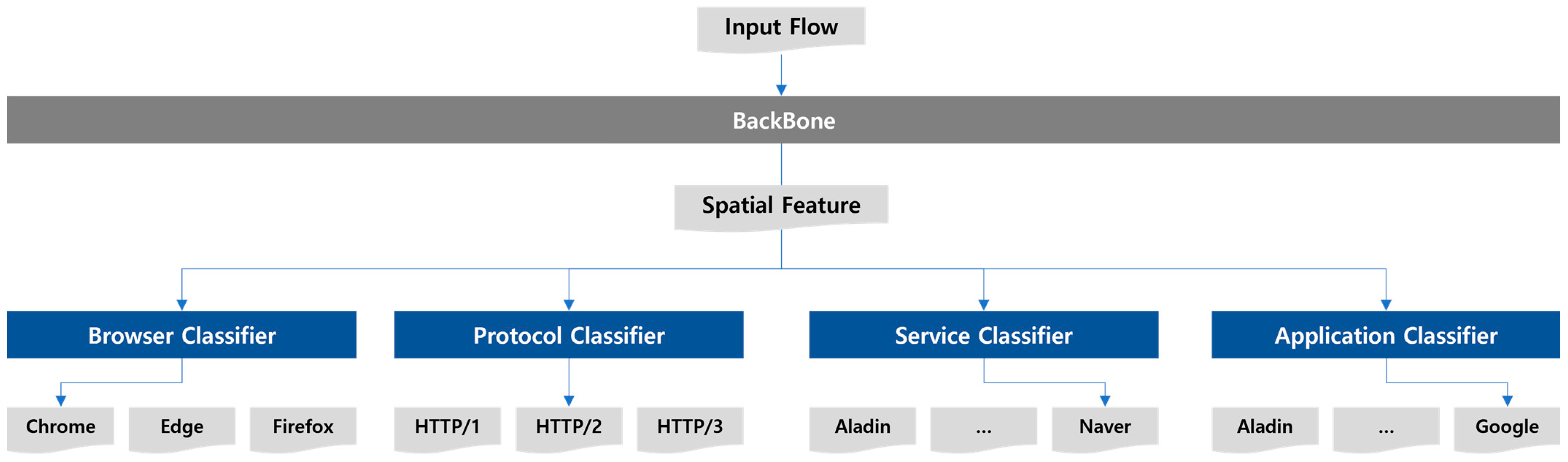
3.1.3. Multitask Single Inference
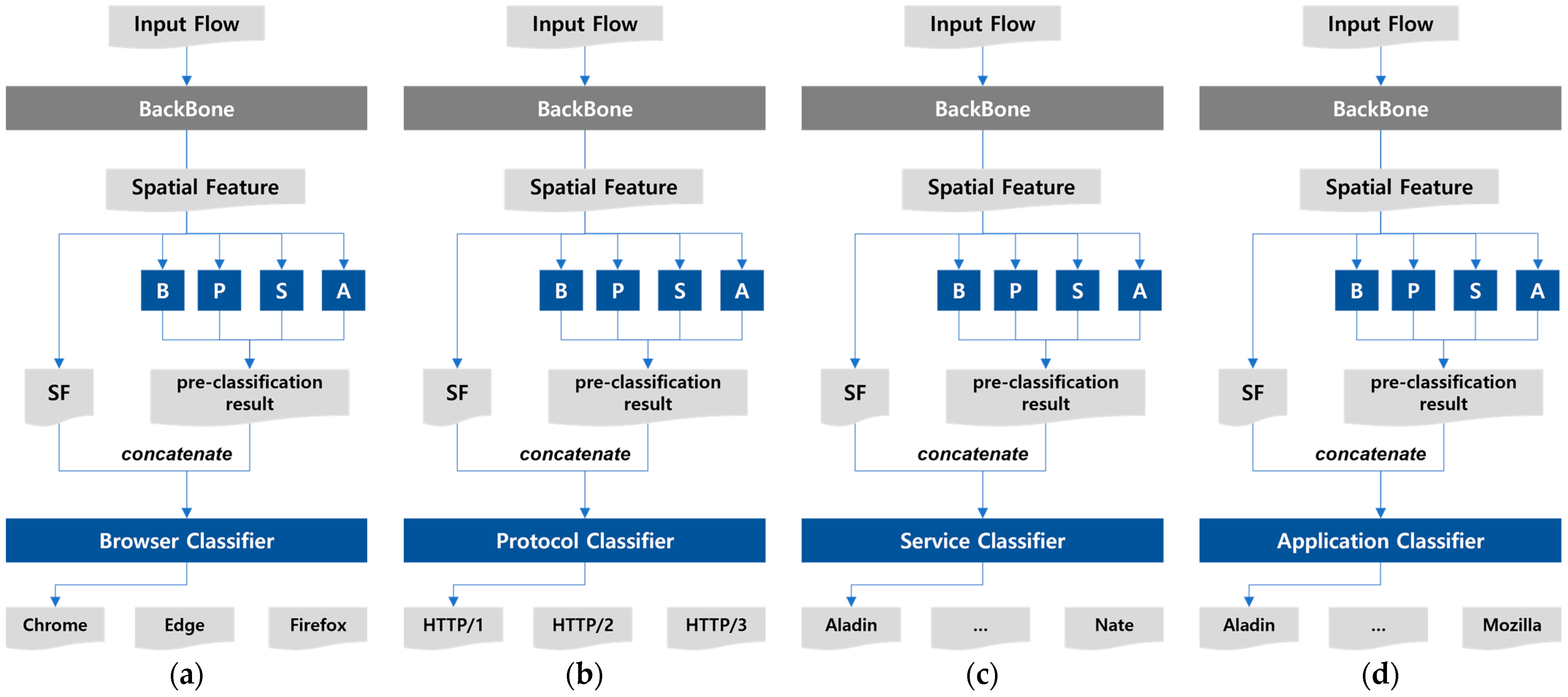
3.1.4. Multitask Multi Inference
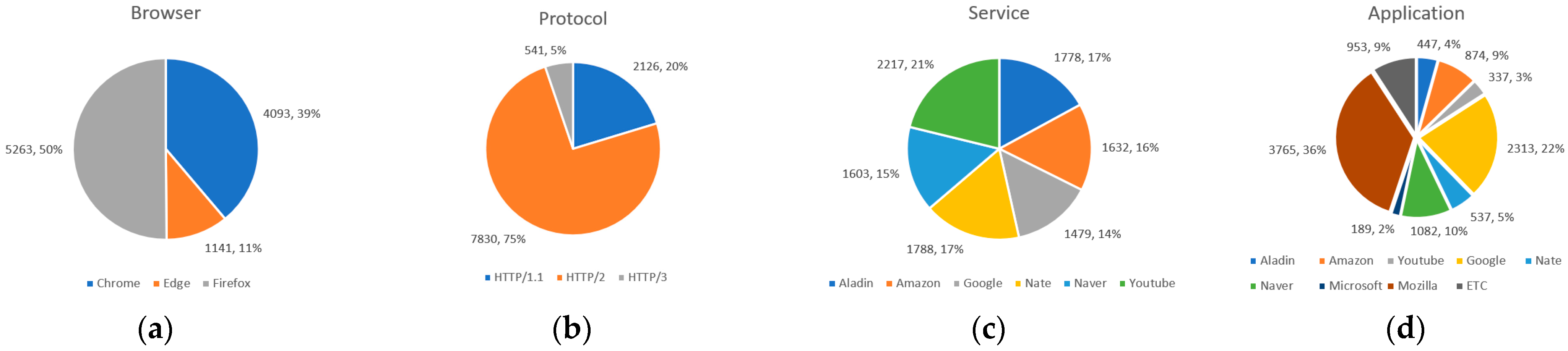
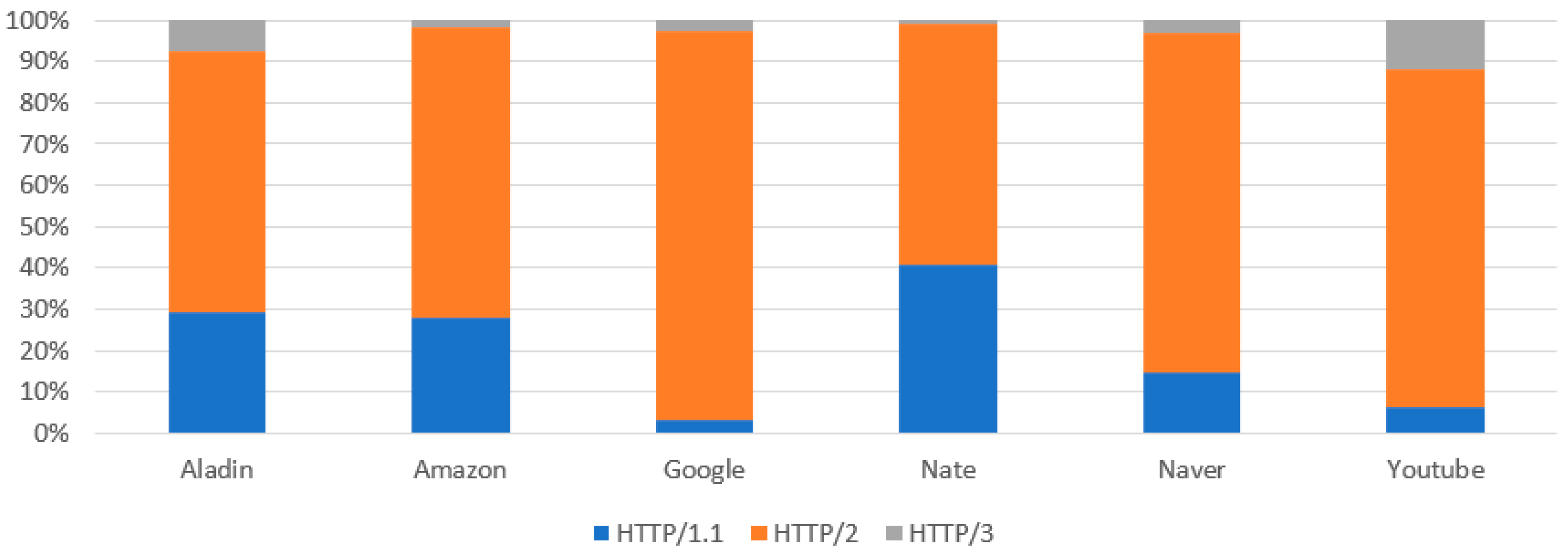
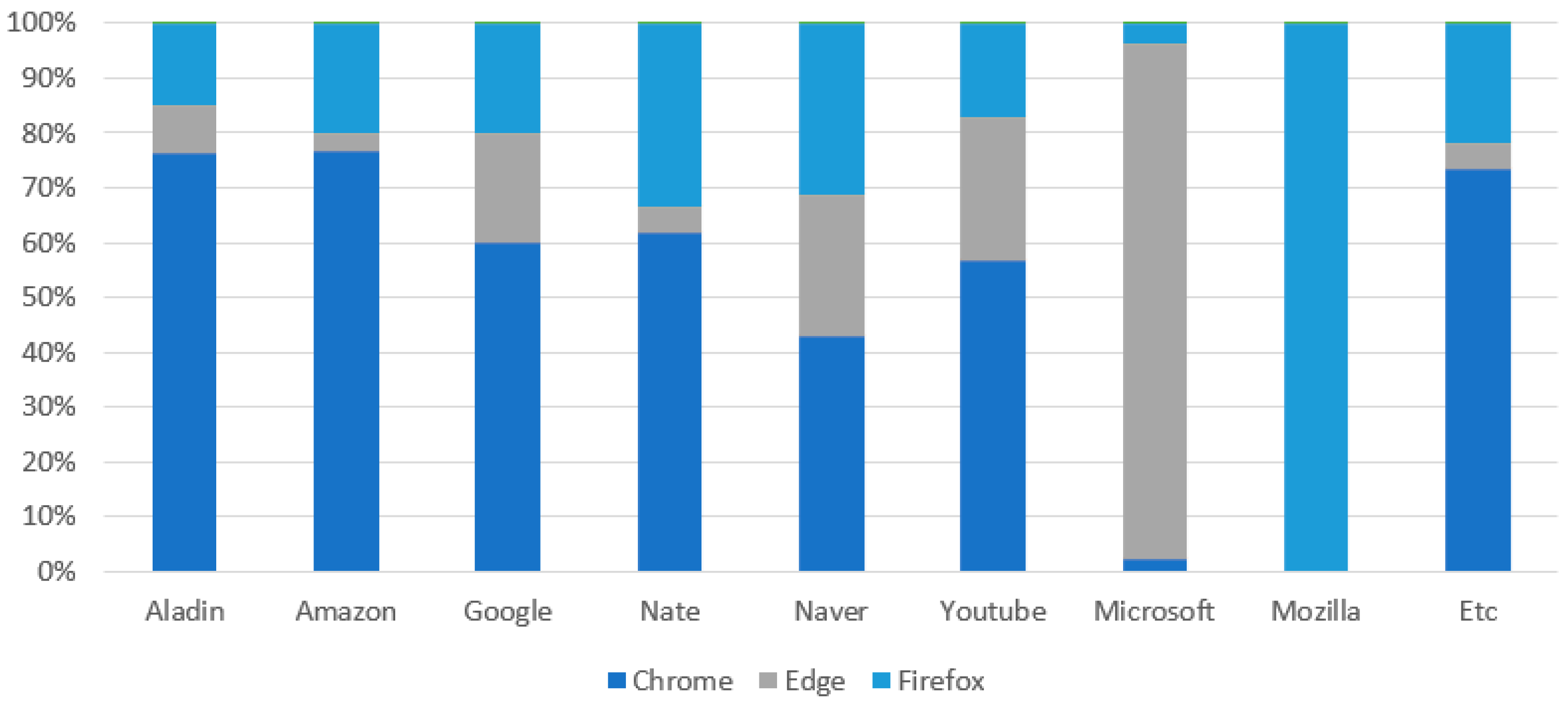
3.2. Dataset Description
- Service: labeled at the time of collection;
- Browser: labeled at the time of collection;
- HTTP protocol: check the HTTP version of the GET or POST method response header when the protocol of the traffic flow is HTTP (perform the same process after decryption in the case of HTTPS);
- Application: check the Request URL for HTTP or the Service name indicator (SNI) in the Transport Layer Security (TLS) layer for HTTPS.
4. Experiments
5. Experiment Results
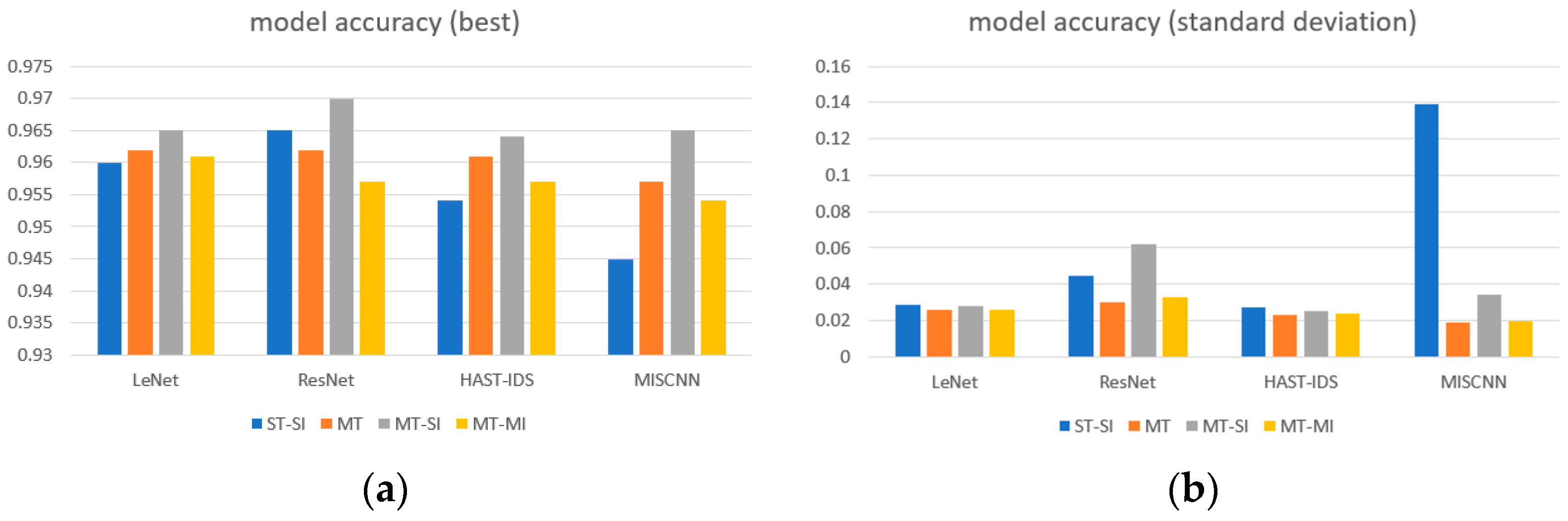
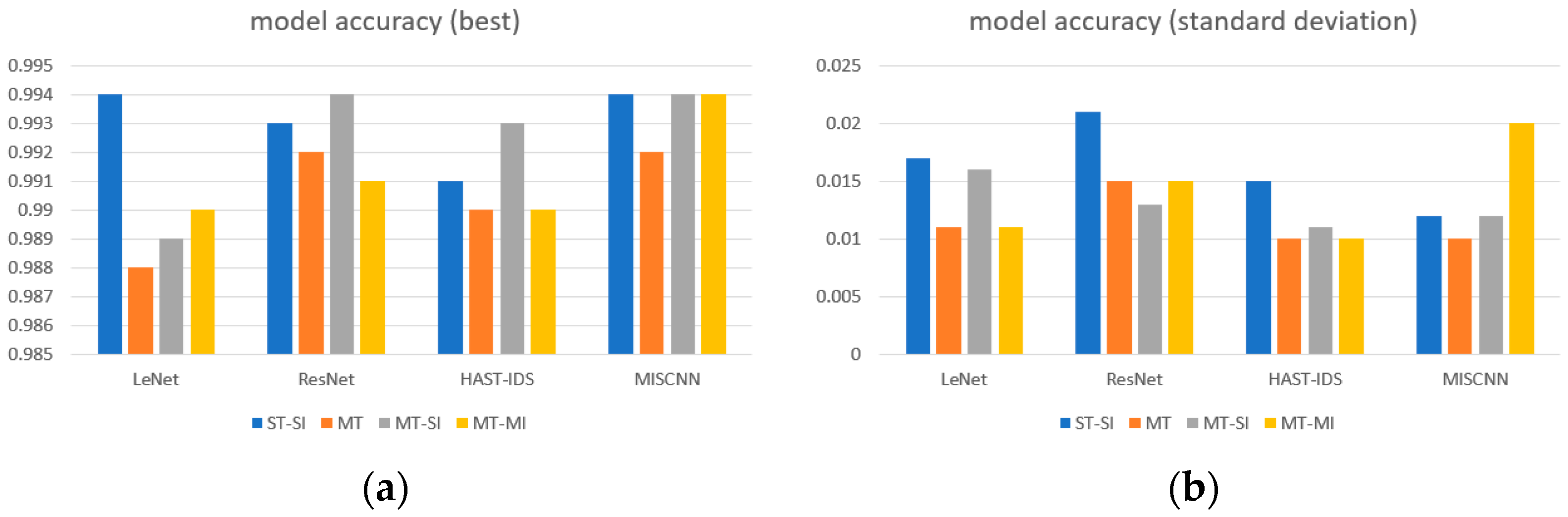
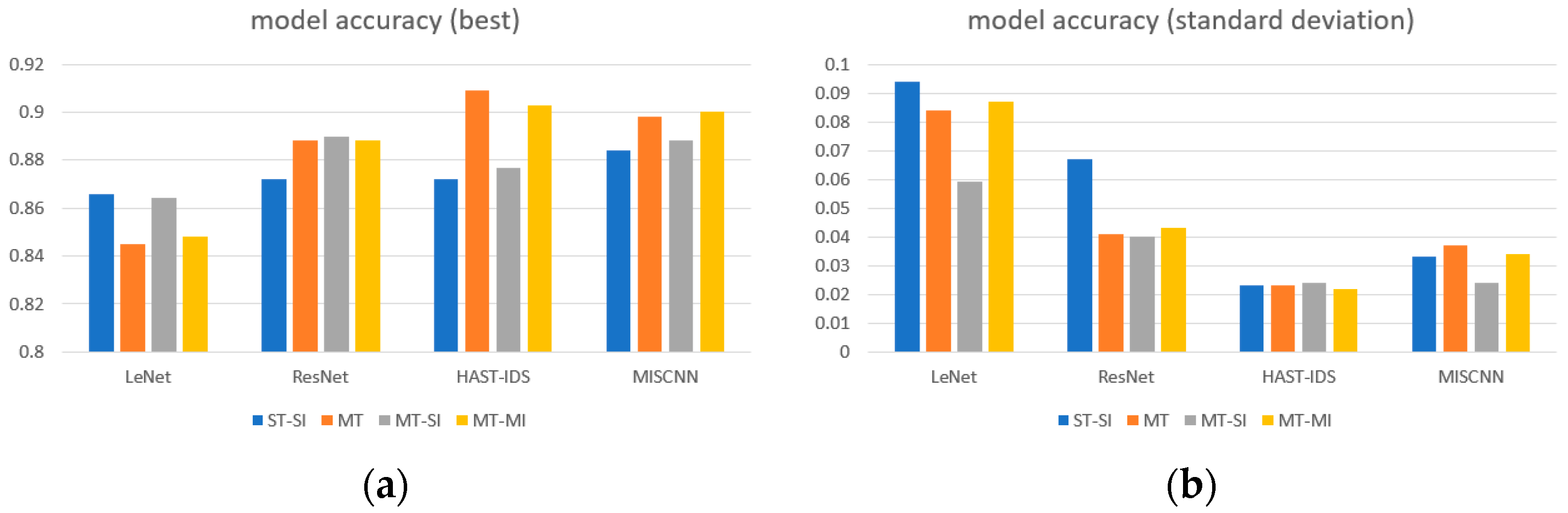
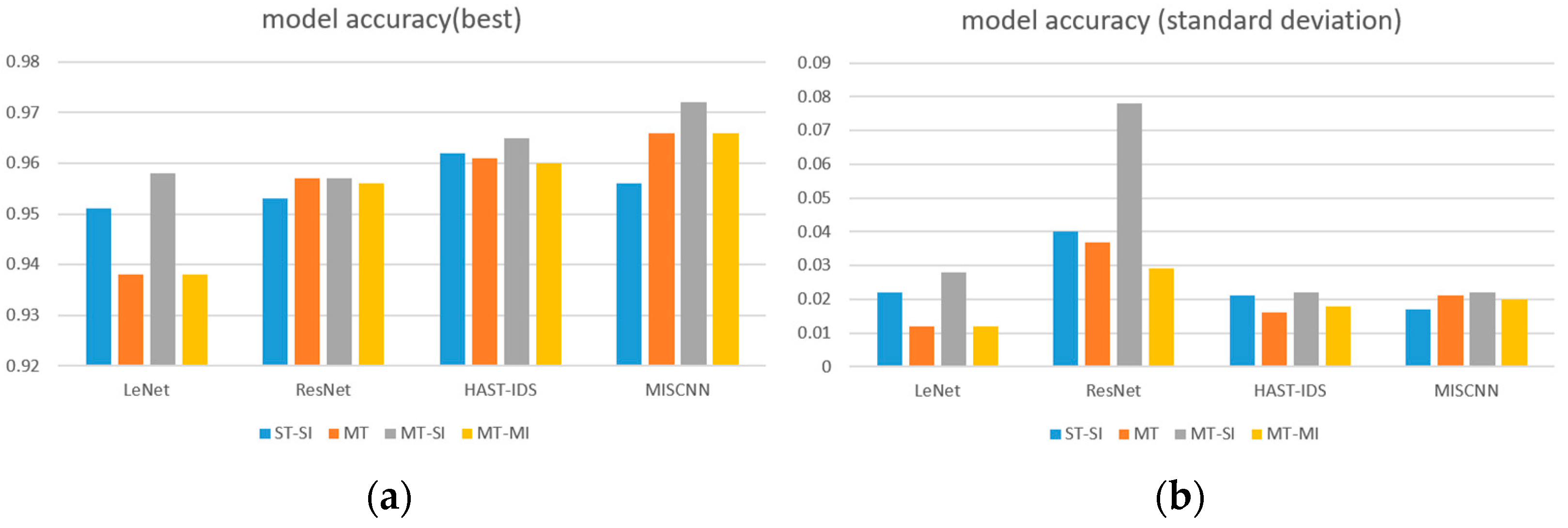
5.1. Comparison of Task Performance According to Parameters
5.1.1. MT Method and Backbone Network
5.1.2. Performance Comparison by the Number of Tasks
5.2. Ablation Study
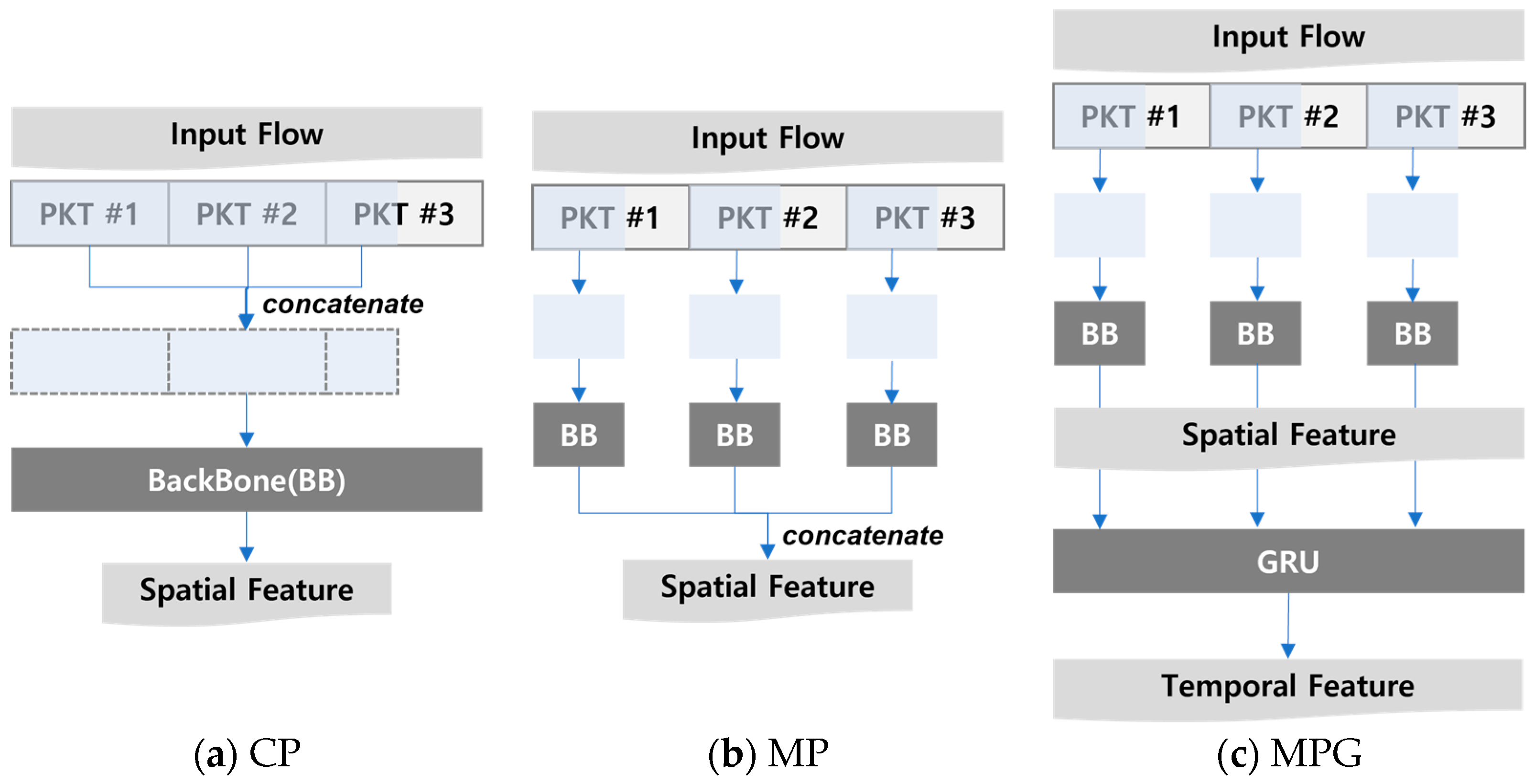
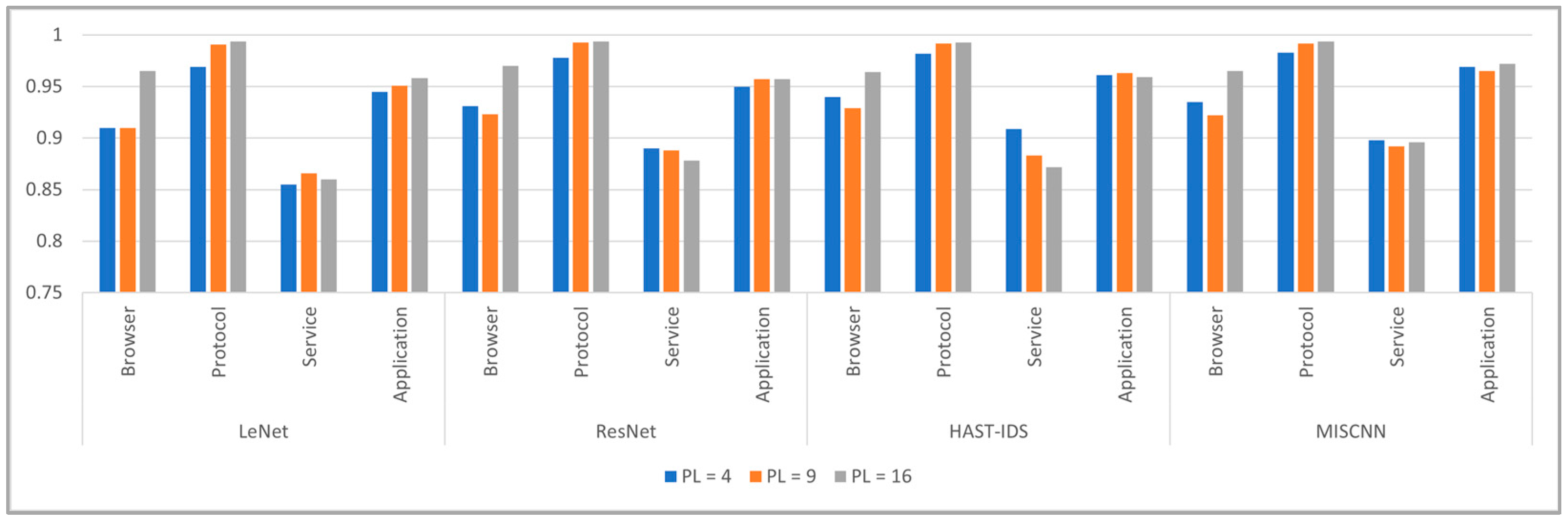
5.2.1. Number of Packets and Backbone Network
5.2.2. Packet Length and Backbone Network
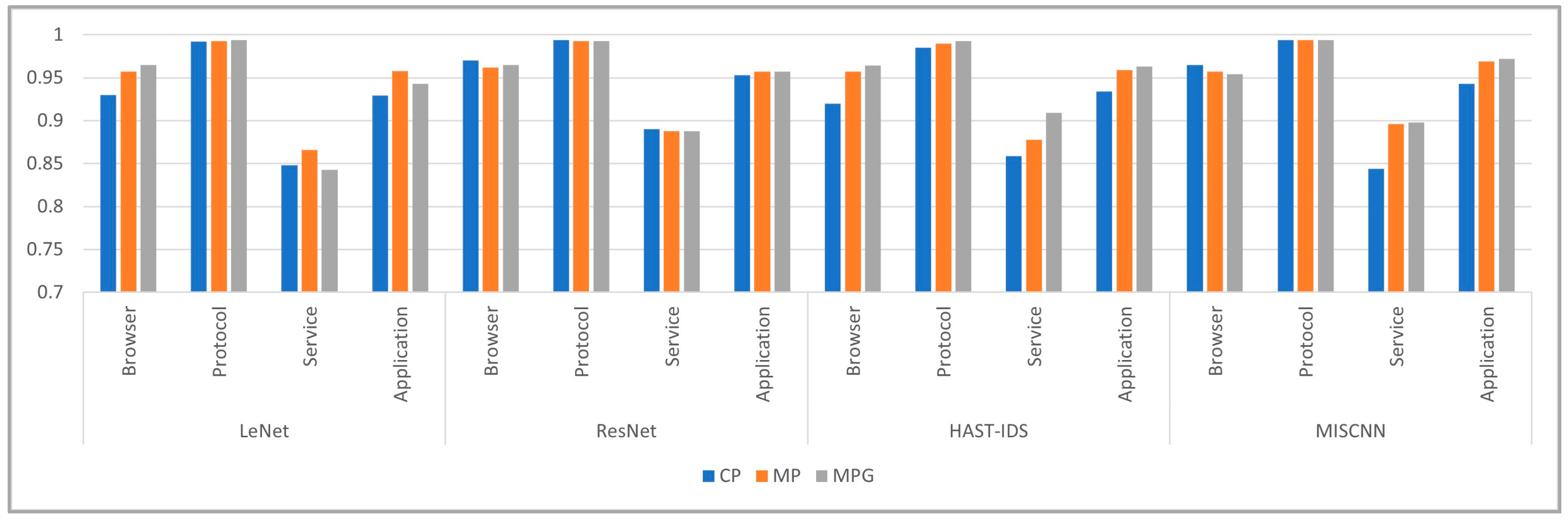
5.2.3. Input Type and Backbone Network
5.2.4. Overall
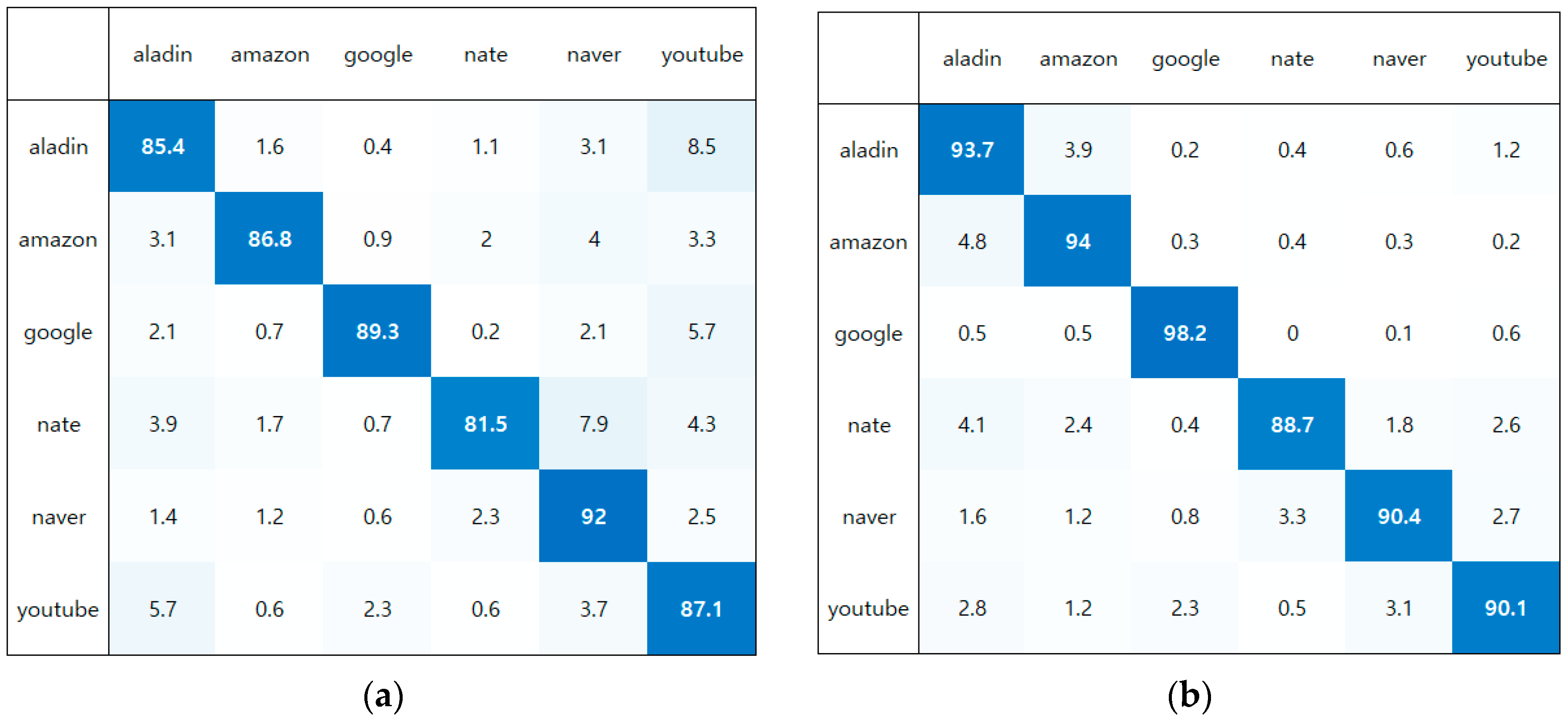
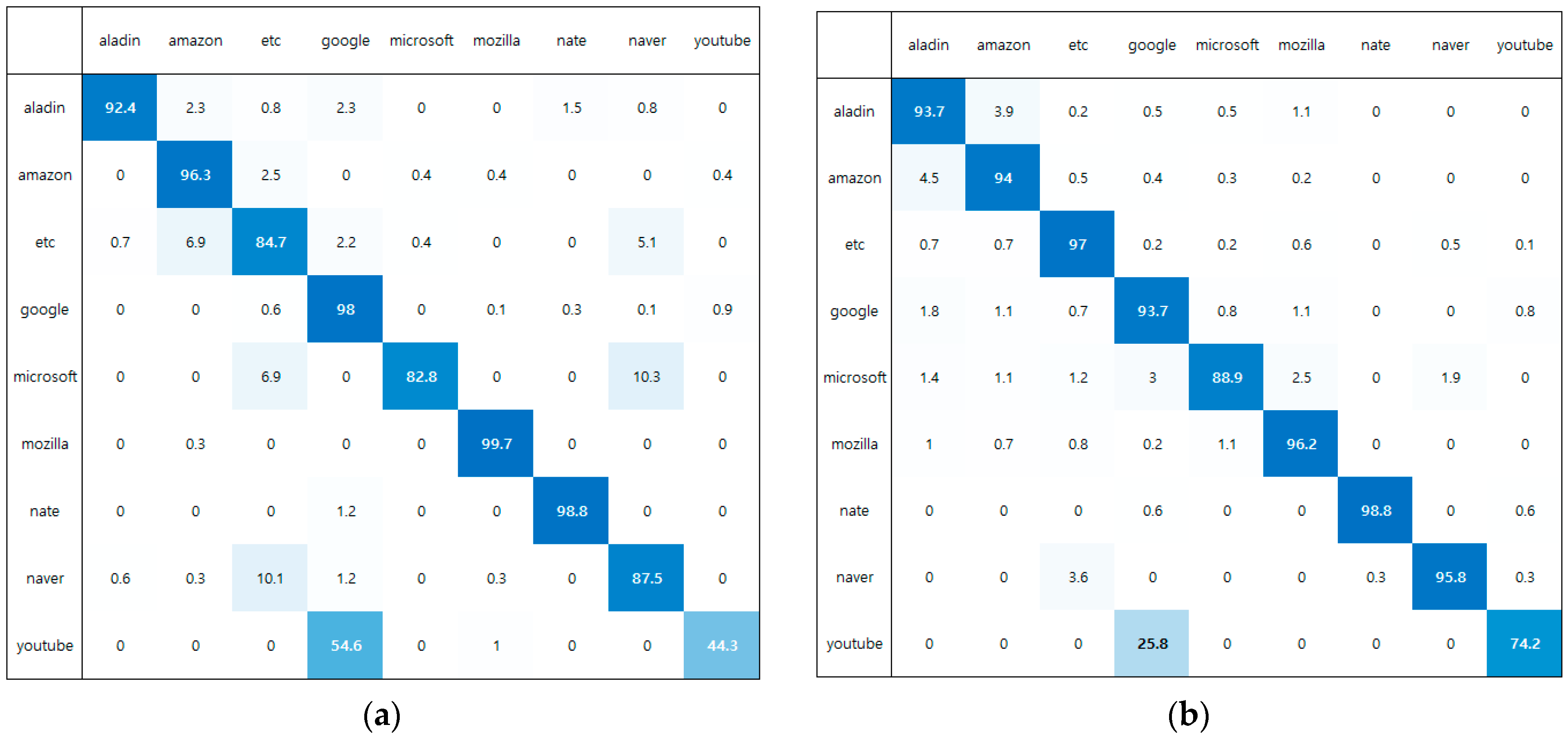
5.2.5. Confusion Matrix for the Service Task
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GITNUX. Internet Traffic Statistics And Trends in 2023. Available online: https://blog.gitnux.com/internet-traffic-statistics/ (accessed on 7 August 2023).
- Azab, A.; Khasawneh, M.; Alrabaee, S.; Choo, K.-K.R.; Sarsour, M. Network traffic classification: Techniques, datasets, and challenges. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruana, R. Multitask learning. Mach. Learn. 1997, 28, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thung, K.-H.; Wee, C.-Y. A brief review on multi-task learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 29705–29725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, D.; Teng, J.; Yu, S. Multi-Task Network Anomaly Detection Using Federated Learning. In Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology, Hanoi, Vietnam, 4–6 December 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Sharafaldin, I.; Lashkari, A.H.; Ghorbani, A.A. Toward generating a new intrusion detection dataset and intrusion traffic characterization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy, Funchal, Portugal, 22–24 January 2018; Volume 1, pp. 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Draper-Gil, G.; Lashkari, A.H.; Mamun MS, I.; Ghorbani, A.A. Characterization of Encrypted and VPN Traffic Using Time-Related Features. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy, Rome, Italy, 19–21 February 2016; SCITEPRESS—Science and and Technology Publications: Rome, Italy, 2016; pp. 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- Lashkari, A.H.; Gil, G.D.; Mamun MS, I.; Ghorbani, A.A. Characterization of tor traffic using time based features. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy, Porto, Portugal, 19–21 February 2017; SciTePress: Setúbal, Portugal, 2017; pp. 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Aceto, G.; Ciuonzo, D.; Montieri, A.; Pescapé, A. DISTILLER: Encrypted Traffic Classification via Multimodal Multitask Deep Learning. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 183–184, 102985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Liu, X. Multitask Learning for Network Traffic Classification. In Proceedings of the 2020 29th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–6 August 2020; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Husák, M.; Čermák, M.; Jirsík, T.; Čeleda, P. HTTPS Traffic Analysis and Client Identification Using Passive SSL/TLS Fingerprinting. Eurasip J. Info. Secur. 2016, 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Lang, B.; Liu, H.; Chen, S. SSL/TLS Encrypted Traffic Application Layer Protocol and Service Classification. In Proceedings of the Embedded Systems and Applications, Academy and Industry Research Collaboration Center (AIRCC), Vienna, Austria, 26 March 2022; pp. 237–252. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, R.-H.; Peng, M.-C.; Huang, C.-W.; Lin, P.-C.; Nguyen, V.-L. An Unsupervised Deep Learning Model for Early Network Traffic Anomaly Detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 30387–30399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Mahmoud, Q.H. Design and Development of a Deep Learning-Based Model for Anomaly Detection in IoT Networks. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 103906–103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Sun, H.; Zhu, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Y. BAT: Deep Learning Methods on Network Intrusion Detection Using NSL-KDD Dataset. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 29575–29585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhou, G.-T.; Deng, Z.; Liao, Z.; Mori, G. Learning Structured Inference Neural Networks with Label Relations. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016; pp. 2960–2968. [Google Scholar]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, U.; Kim, B.; Park, J.; Choi, J.; Kim, M. MISCNN: A Novel Learning Scheme for CNN-Based Network Traffic Classification. In Proceedings of the 2022 23rd Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Takamatsu, Japan, 28–30 September 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.; Ye, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, M. HAST-IDS: Learning Hierarchical Spatial-Temporal Features Using Deep Neural Networks to Improve Intrusion Detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 1792–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors|Nature. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/323533a0 (accessed on 16 July 2023).
- Cho, K.; van Merrienboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations Using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.1078. [Google Scholar]
- Aceto, G.; Ciuonzo, D.; Montieri, A.; Pescapè, A. MIMETIC: Mobile Encrypted Traffic Classification Using Multimodal Deep Learning. Comput. Netw. 2019, 165, 106944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Jin, X.; Stone, P.; Liu, Q. Conflict-averse gradient descent for multi-task learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 18878–18890. [Google Scholar]


| Service | Aladin | Amazon | Nate | Naver | YouTube | Microsoft | Mozilla | Etc | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aladin | 1778 | 447 | 364 | 50 | 5 | 1 | 660 | 251 | ||
| 100% | 25.1% | 20.5% | 2.8% | 0.3% | 0.1% | 37.1% | 14.1% | |||
| Amazon | 1632 | 873 | 27 | 4 | 2 | 612 | 114 | |||
| 100% | 53.5% | 1.7% | 0.2% | 0.1% | 37.5% | 7 | ||||
| 1479 | 707 | 102 | 2 | 668 | ||||||
| 100% | 47.8% | 6.9% | 0.1% | 45.2% | ||||||
| Nate | 1788 | 1 | 76 | 537 | 10 | 2 | 597 | 565 | ||
| 100% | 0.1% | 4.2% | 30% | 0.6% | 0.1% | 33.4% | 31.6% | |||
| Naver | 1603 | 17 | 1022 | 101 | 451 | 12 | ||||
| 100% | 1.1% | 63.8% | 6.3% | 28.1% | 0.7% | |||||
| YouTube | 2217 | 1122 | 226 | 81 | 777 | 11 | ||||
| 100% | 50.6% | 10.2% | 3.7% | 35% | 0.5% | |||||
| Task | Accuracy (Service) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service | Browser | Protocol | Application | |
| √ | 86.124% ± 0.541% | |||
| √ | √ | 88.698% ± 0.723% | ||
| √ | √ | 89.028% ± 0.613% | ||
| √ | √ | 90.357% ± 0.568% | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 89.52% ± 1.195% | |
| √ | √ | √ | 89.81% ± 0.733% | |
| √ | √ | √ | 90.286% ± 0.735% | |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 90.512% ± 0.827% |
| Browser | Protocol | Service | Application | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LN | RN | HI | MC | LN | RN | HI | MC | LN | RN | HI | MC | LN | RN | HI | MC | |
| NP | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 16 | 9 or 16 | 9 | 16 |
| PL | 576 | 576 | 484 | 324 | 400 | 400 | 324 | 576 | 484 | 576 | 576 | 324 | 484 | 400 or 576 | 484 | 400 |
| IT | MPG | CP | MPG | CP | MPG | CP | MPG | CP | MP | CP | MPG | MPG | MP | MP or MPG | MPG | MPG |
| MT | MTSI | MTSI | MTSI | MTSI | STSI | MTSI | MTSI | MTSI | STSI | MTSI | MT | MT | MTSI | MT or MTSI | MTSI | MTSI |
| Acc | 0.965 | 0.97 | 0.964 | 0.965 | 0.994 | 0.994 | 0.993 | 0.994 | 0.866 | 0.89 | 0.909 | 0.898 | 0.958 | 0.957 | 0.965 | 0.972 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, U.-J.; Kim, B.; Park, J.-T.; Choi, J.-W.; Kim, M.-S. A Multi-Task Classification Method for Application Traffic Classification Using Task Relationships. Electronics 2023, 12, 3597. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173597
Baek U-J, Kim B, Park J-T, Choi J-W, Kim M-S. A Multi-Task Classification Method for Application Traffic Classification Using Task Relationships. Electronics. 2023; 12(17):3597. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173597
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Ui-Jun, Boseon Kim, Jee-Tae Park, Jeong-Woo Choi, and Myung-Sup Kim. 2023. "A Multi-Task Classification Method for Application Traffic Classification Using Task Relationships" Electronics 12, no. 17: 3597. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173597
APA StyleBaek, U.-J., Kim, B., Park, J.-T., Choi, J.-W., & Kim, M.-S. (2023). A Multi-Task Classification Method for Application Traffic Classification Using Task Relationships. Electronics, 12(17), 3597. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12173597










