Lightweight Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Adaptive DenseNet with Knowledge Distillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We introduce an adaptive knowledge distillation network for infrared and visible image fusion tasks, which can be trained by leveraging the knowledge from pre-existing large fusion models and achieves a comparable performance with smaller model parameters and a more simplified model structure.
- (2)
- The devised knowledge distillation network exhibits the capability of adaptively tuning hyperparameters and can be trained by various categories of pre-existing fusion models, encompassing CNN-based, transformer-based, and high-vision-level-based models.
- (3)
- The newly created dataset comprises 3288 pairs of infrared and visible images captured from multiple typical scenes, such as city roads, pedestrian crossings, parking lots, mountain forests, and buildings in the background. The images were meticulously selected to offer a broad representation of real-world scenarios, making the dataset suitable for training and evaluating models for infrared and visible image fusion tasks.
2. Related Works
2.1. Knowledge Distillation
2.2. Adaptive Mechanisms
2.3. Typical Image Fusion Model
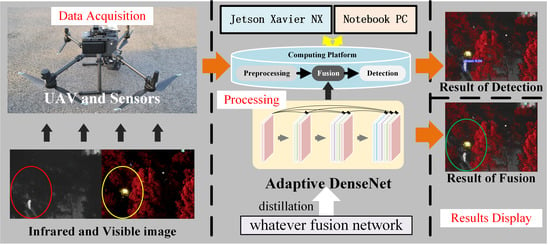
3. Framework and Methodology
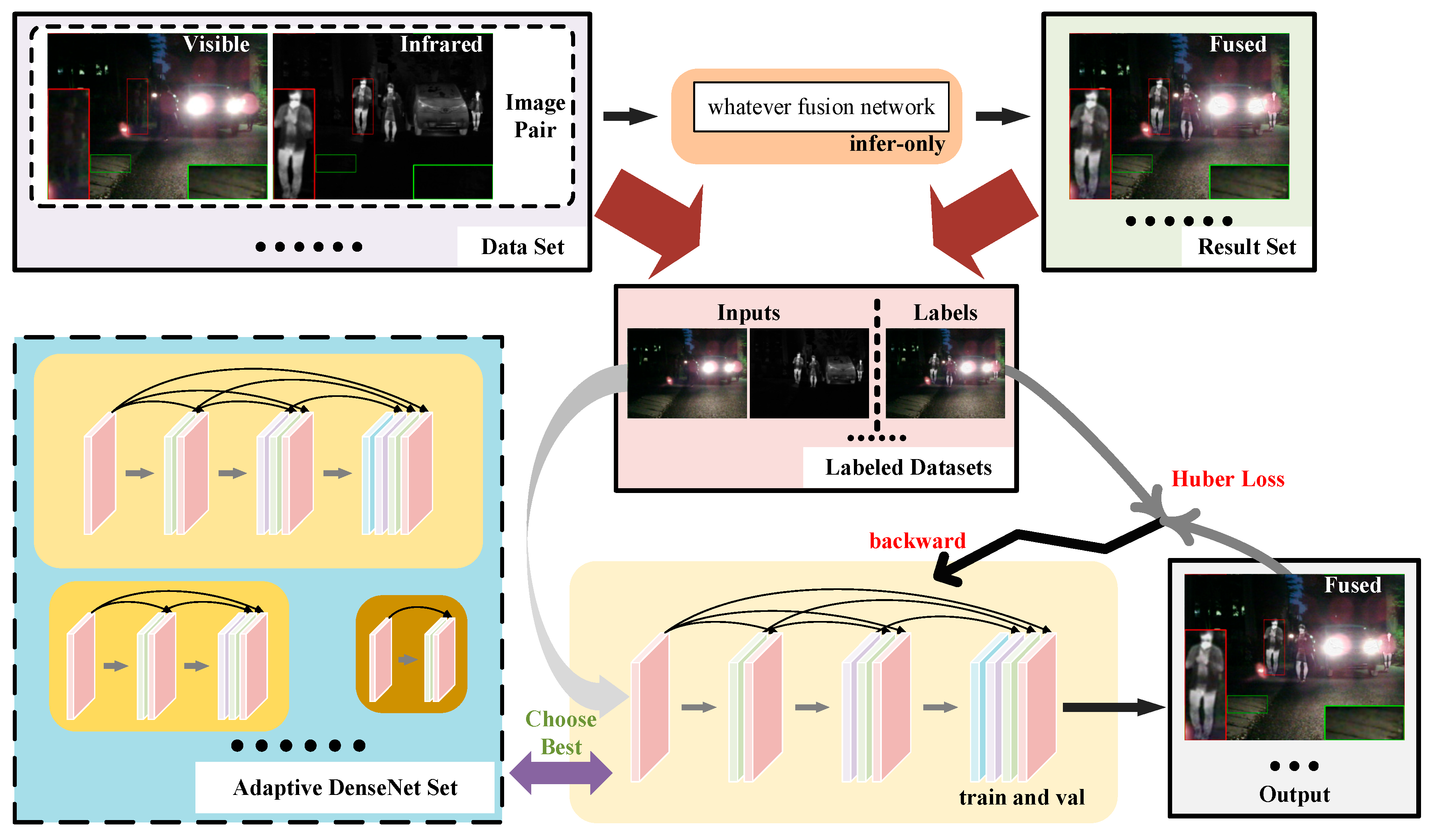
3.1. The Framework of Fusion Network
- (1)
- Construct a paired dataset of visible light and infrared images.
- (2)
- Select a teacher model (SeAFusion in this case) and use its pre-trained weights to infer the visible light and infrared images in the dataset to obtain a collection of fused images.
- (3)
- Combine the fused images obtained in step 2 with the original dataset to form a new dataset with visible light and infrared images as inputs and corresponding fusion images as labels.
- (4)
- Use the labeled dataset from step 3 to train a student model, which is described in detail in Section 3.3 of the manuscript. This step is the actual knowledge distillation process, as the student model is trained to capture the information in the labeled dataset using the fusion images obtained from the teacher model as soft labels.
- (5)
- Obtain the student model, which is a self-adaptive DenseNet with weights trained in step 4. The student model has similar fusion effects to the teacher model SeAFusion, but is far superior in terms of inference speed and model size.
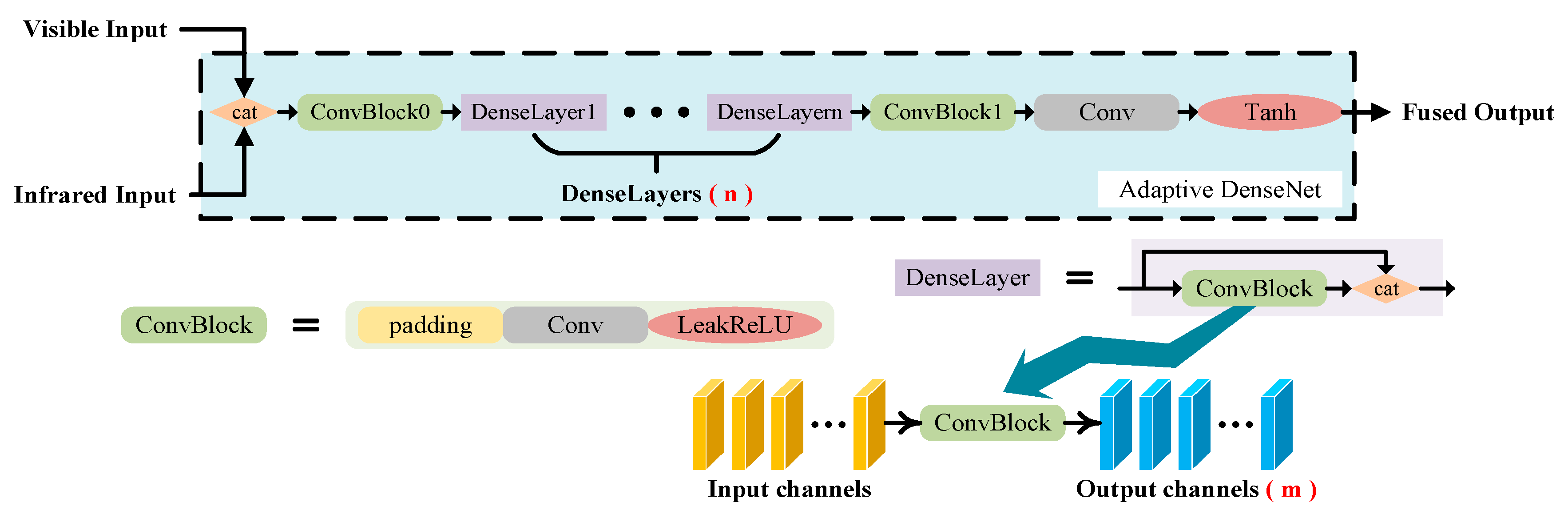
3.2. Adaptive DenseNet and Loss Function
3.3. Adaptive Optimal Strategy for DenseNet
| Algorithm 1: Adaptive Optimal Search |
| Input: train set , val set } |
| Output: s→ |
| Begin |
| 1. Calculate f(n0, m0) and σ |
| 2. = 1 → |
| 3. = 16 → |
| 4. )//2 = 8 → |
| 5. While do |
| 6. | < σ do |
| 7. |
| 8. )//2 |
| 9. else do |
| 10. + 1 |
| 11. )//2 |
| 12. |
| end |
4. Offline Experimental Setup and Comparative Analysis
4.1. Dataset Preparation
4.2. Adaptive DenseNet Knowledge Distillation
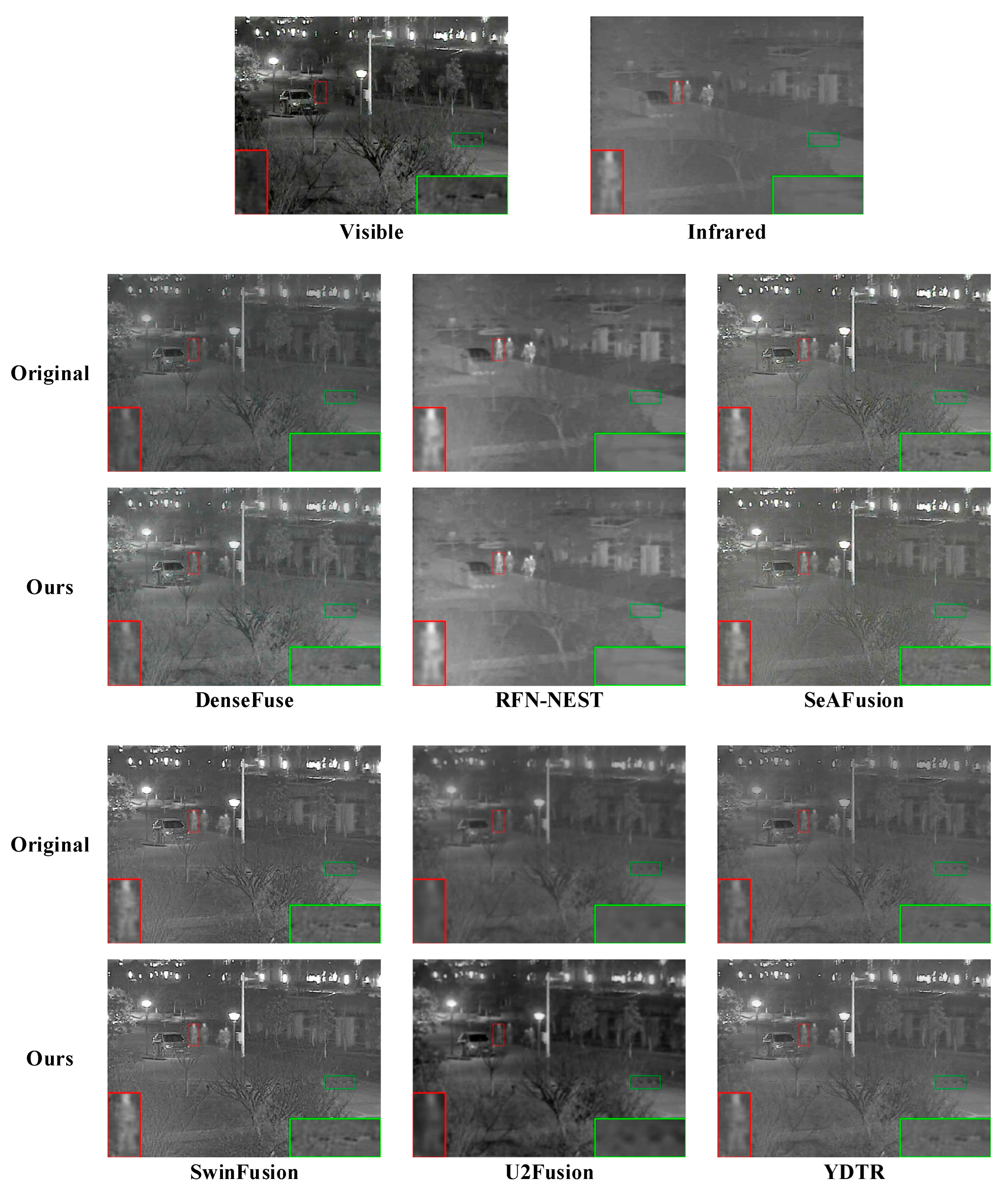
4.3. Qualitative Analysis
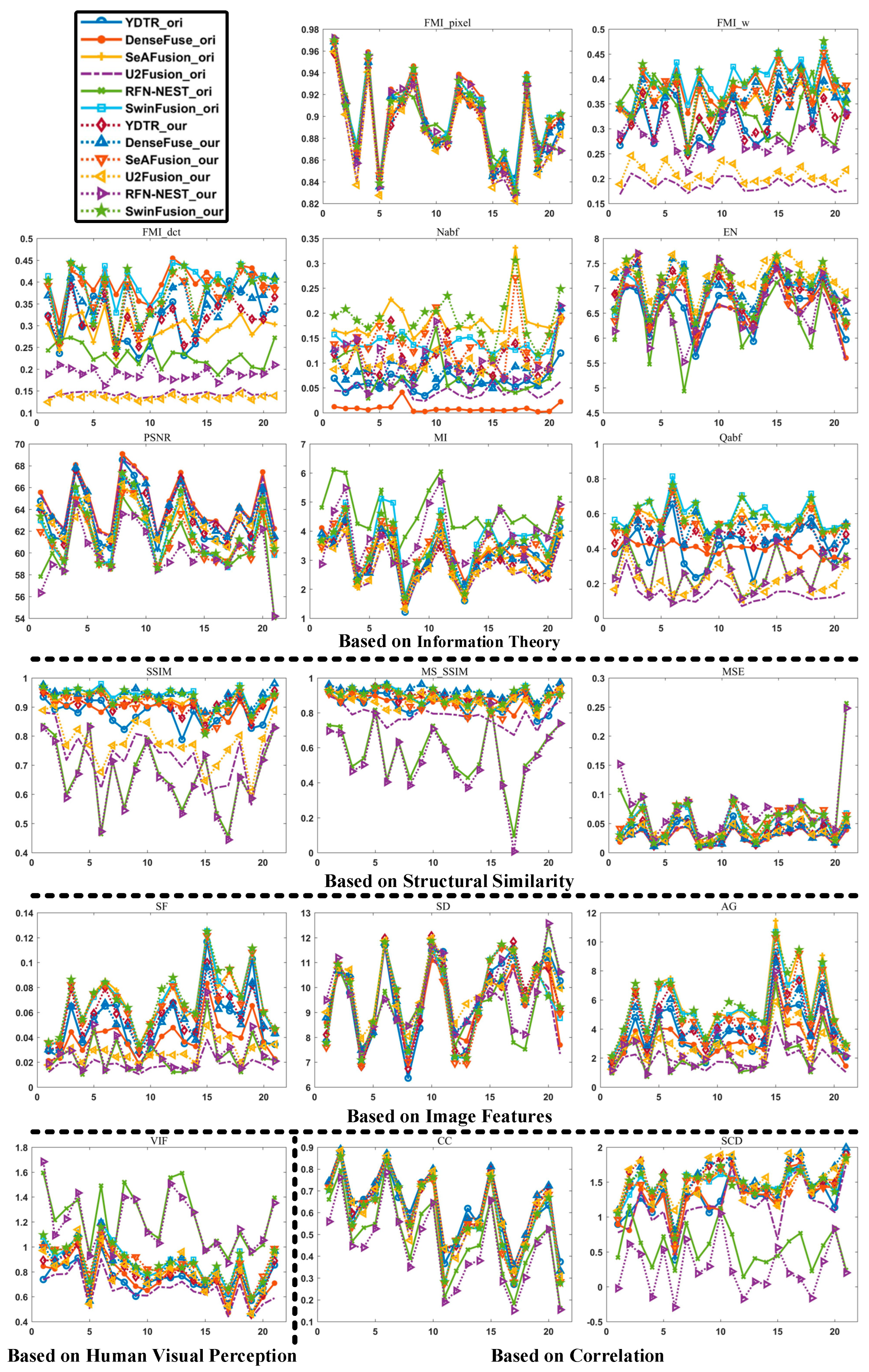
4.4. Quantitative Analysis
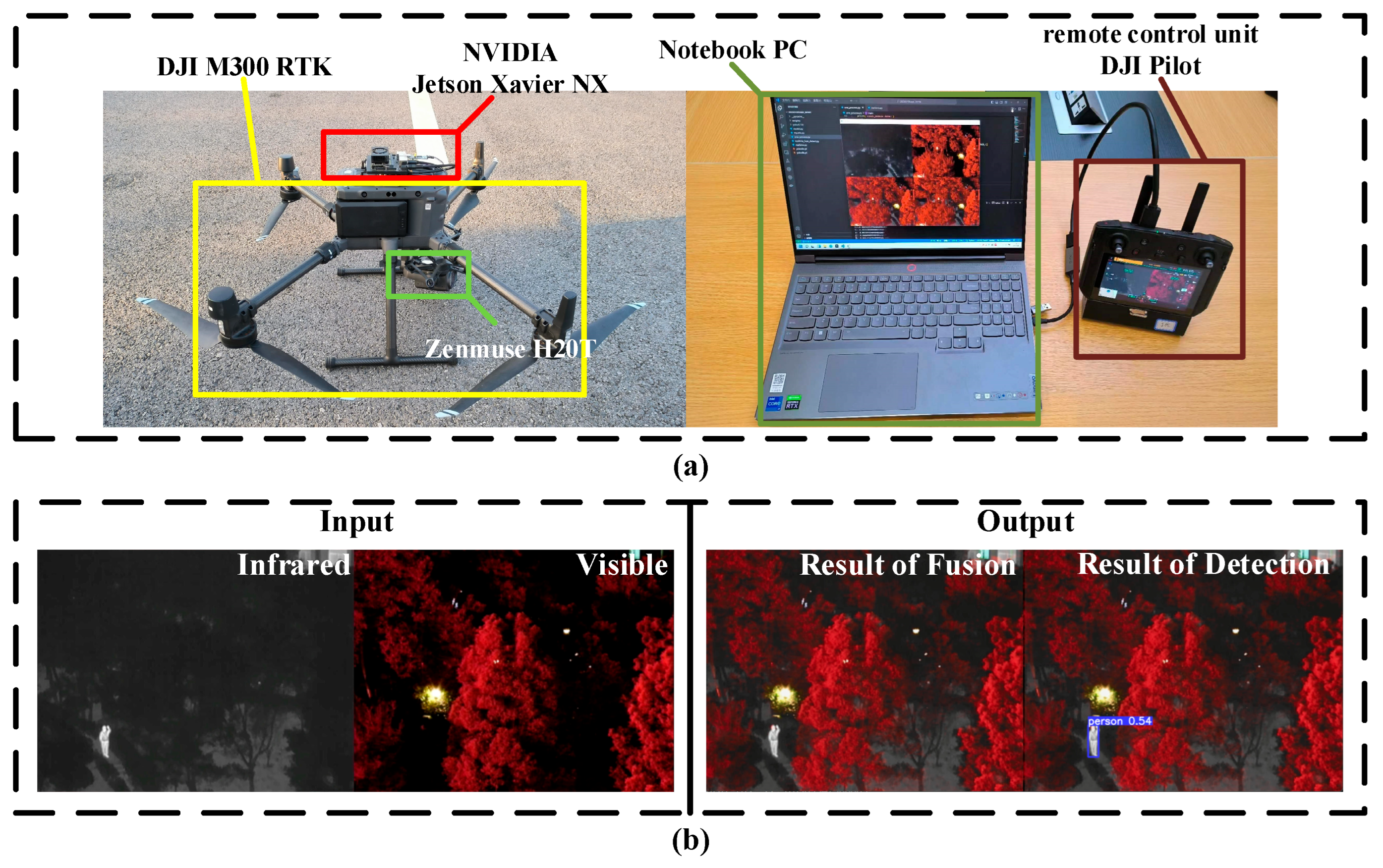
5. Real-World Applications and Results Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, W.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, S.X.; Li, J.; Song, L.; Li, Q. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Technology and Application: A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Yang, F.; Ji, L. MLF: A mimic layered fusion method for infrared and visible video. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 126, 104349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, P. DIDFuse: Deep Image Decomposition for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09210. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Lu, Y.; Tan, L. Research of Multimodal Medical Image Fusion Based on Parameter-Adaptive Pulse-Coupled Neural Network and Convolutional Sparse Representation. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 3290136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nencini, F.; Garzelli, A.; Baronti, S.; Alparone, L. Remote sensing image fusion using the curvelet transform. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Peng, X.; Coumans, E.; Zhang, T.; Lee, T.-W.; Tan, J.; Levine, S. Learning Agile Robotic Locomotion Skills by Imitating Animals. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.00784. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, A.K.; Senthilkumar, R.; Kumar, A. Combining pixel selection with covariance similarity approach in hyperspectral face recognition based on convolution neural network. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2020, 76, 103096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, R.; Hajime, N.; Narishige, A.; Uchida, H.; Matsunami, T. Improved knowledge distillation for training fast low resolution face recognition model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Y.; Lam, K.M.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, C.; Dong, J. Efficient Feature Fusion for Learning-Based Photometric Stereo. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023–2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.J.; O’Callaghan, R.J.; Nikolov, S.G.; Bull, D.R.; Canagarajah, N. Pixel-and region-based image fusion with complex wavelets. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yin, H.; Chai, Y.; Li, Y.; Qi, G. A novel multi-modality image fusion method based on image decomposition and sparse representation. Inf. Sci. 2018, 432, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Blum, R.S.; Han, J.; Tao, D. Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images: A review. Inf. Fusion 2018, 40, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, G.; Cao, Y.; Han, J. Multi-focus image fusion based on non-negative sparse representation and patch-level consistency rectification. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 104, 107325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Infrared and visible image fusion based on saliency detection and two-scale transform decomposition. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 114, 103626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, K.; Cheng, Z.; Luo, L. A saliency-based multiscale approach for infrared and visible image fusion. Signal Process. 2021, 182, 107936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qi, Y.; Ding, W. Infrared and visible image fusion method based on saliency detection in sparse domain. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 83, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Tang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, G. STDFusionNet: An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Network Based on Salient Target Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, R.S.; Alshehri, N.O. Fusion of infrared and visible images using neutrosophic fuzzy sets. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 25927–25941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhuo, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W. Infrared and visible image fusion based on BEMSD and improved fuzzy set. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 98, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhuo, L.; Zhu, P.; Huang, Z.; Wu, X. Fusion of infrared and visible images based on non-subsampled contourlet transform and intuitionistic fuzzy set. Acta Photonica Sin. 2018, 47, 125479664. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; He, K.; Xu, D.; Luo, Y.; Gong, J. Adaptive enhanced infrared and visible image fusion using hybrid decomposition and coupled dictionary. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 20831–20849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; He, K.; Xu, D.; Yin, W.; Liu, W. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visibility enhancement and hybrid multiscale decomposition. Optik 2022, 258, 168914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhu, W. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion with Hybrid Image Filtering. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1757214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Pan, Z.; Cao, J.; Liao, J. Infrared and visible image fusion based on variational auto-encoder and infrared feature compensation. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2021, 117, 103839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gong, M.; Tian, X.; Huang, J.; Ma, J. CUFD: An encoder–decoder network for visible and infrared image fusion based on common and unique feature decomposition. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2022, 218, 103407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zuo, F.; Liu, L. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Adversarial Feature Extraction and Stable Image Reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.-B.; Wang, H.-M. Infrared and visible image fusion with supervised convolutional neural network. Optik 2020, 219, 165120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Peng, H.; Wang, Z. Infrared and visible image fusion with convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolut. Inf. Process. 2018, 16, 1850018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhou, D.; Nie, R.; Hou, R. Infrared and visible image fusion based on convolutional neural network model and saliency detection via hybrid l0-l1 layer decomposition. J. Electron. Imaging 2018, 27, 063036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, W.; Ma, J.; Zhou, H. A Generative Adversarial Network for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Semantic Segmentation. Entropy 2021, 23, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huo, H.; Liu, K.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion using dual discriminators generative adversarial networks with Wasserstein distance. Inf. Sci. 2020, 529, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huo, H.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Q. AttentionFGAN: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Using Attention-Based Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, W.; Liang, P.; Li, C.; Jiang, J. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion. Inf. Fusion 2018, 48, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shao, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. SwinFuse: A Residual Swin Transformer Fusion Network for Infrared and Visible Images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.; Wu, X.; Xu, T. TGFuse: An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Approach Based on Transformer and Generative Ad-versarial Network. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, B. CGTF: Convolution-Guided Transformer for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; He, F.; Liu, Y. TCCFusion: An infrared and visible image fusion method based on transformer and cross correlation. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 137, 109295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Jiang, G.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Chen, L. TCPMFNet: An infrared and visible image fusion network with composite auto encoder and transformer–convolutional parallel mixed fusion strategy. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 127, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Xie, P.; Wang, G. Multi-scale Cross-Modal Transformer Network for RGB-D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the MultiMedia Modeling: 28th International Conference, MMM 2022, Phu Quoc, Vietnam, 6–10 June 2022; pp. 352–363. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, K. MCT-Net: Multi-hierarchical cross transformer for hyperspectral and multi-spectral image fusion. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2023, 264, 110362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Jin, X.; Jiang, Q.; Cai, L.; Lee, S.; Yao, S. MCRD-Net: An unsupervised dense network with multi-scale convolutional block attention for multi-focus image fusion. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 1558–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Song, K.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Niu, M.; Yan, Y. MCnet: Multiple Context Information Segmentation Network of No-Service Rail Surface Defects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 5004309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyaz, U.; Bathula, D.R. Augmenting Knowledge Distillation with Peer-to-Peer Mutual Learning for Model Compression. In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Kolkata, India, 28–31 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; Liu, S.; Zhao, H.; Jia, J. Distilling Knowledge via Knowledge Review. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 5006–5015. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Jin, H. Heterogeneous Knowledge Distillation for Simultaneous Infrared-Visible Image Fusion and Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hirota, K.; Jia, Z.; Dai, Y. A multi-autoencoder fusion network guided by perceptual distillation. Inf. Sci. 2022, 606, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhao, W.; Lu, H.; Liu, Y.; Yao, L.; Liu, Y. Depth-Distilled Multi-Focus Image Fusion. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 25, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. KDE-GAN: A multimodal medical image-fusion model based on knowledge distillation and explainable AI modules. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 151, 106273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Niu, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J. A Novel Adaptive Feature Fusion Strategy for Image Retrieval. Entropy 2021, 23, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, Z.; Kong, Q.; Qi, Q.; Liao, Q. Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Attention-Based Adaptive Feature Fusion. Entropy 2023, 25, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, Q. Adaptive deep neural networks methods for high-dimensional partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 2022, 463, 111232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Pan, F.; Zhou, C.; Qin, T.; Liu, T.Y. Learning Structures for Deep Neural Networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.13905. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, D.; Lin, Z. Optimization Algorithm Inspired Deep Neural Network Structure Design. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.01638. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.-J. DenseFuse: A Fusion Approach to Infrared and Visible Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 28, 2614–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yuan, J.; Ma, J. Image fusion in the loop of high-level vision tasks: A semantic-aware real-time infrared and visible image fusion network. Inf. Fusion 2022, 82, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Ling, H. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 502–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; He, F.; Liu, Y. YDTR: Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Y-shape Dynamic Transformer. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Xjw, A.; Jk, B. RFN-Nest: An end-to-end residual fusion network for infrared and visible images. Inf. Fusion 2021, 73, 72–86. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.R.; Deng, L.J.; Zhang, T.J.; Jin, X.X. BAM: Bilateral activation mechanism for image fusion. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual Event, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 4315–4323. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 5802–5811. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Tang, W.; Zhou, W. LLVIP: A Visible-Infrared Paired Dataset for Low-Light Vision; Beijing Laboratory of Advanced Information Networks, Beijing Key Laboratory of Network System Architecture and Convergence, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Zang, H.; Xu, H.; Ma, J.Y. Deep learning-based image fusion: A survey. J. Image Graph. 2023, 28, 3–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, P.; Xiao, G. VIFB: A Visible and Infrared Image Fusion Benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; Shanghai Jiao Tong University, School of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Shanghai, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]


| Related Works | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Original knowledge distillation [43] | Compresses a large model into a small one | May lose some information or performance |
| Cross-stage connection path in knowledge distillation [44] | Uses low-level features to supervise deeper features | Increase the complexity of the distillation process |
| Heterogeneous knowledge distillation network [45] | Implements joint fusion and super-resolution | Dependent on the quality of the teacher network |
| Perceptual distillation [46] | Trains image fusion networks without ground truths | Requires a high-quality pre-trained teacher network |
| Depth-distilled multi-focus image fusion (MFIF) [47] | Transfers depth knowledge to improve fusion accuracy | Transfers depth knowledge to improve fusion accuracy |
| Medical image fusion model [48] | Reduces the dataset size and overfitting risk | Limited generalization and sensitivity to hyperparameters and loss functions |
| Related Works | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter-adaptive pulse-coupled neural network [4] | Obtains a better fusion effect | May be sensitive to parameter settings |
| Image retrieval using adaptive features and information entropy [49] | Extracts features and calculates similarity effectively | May not handle complex scenes well |
| Adaptive normalization-mechanism-based fusion [50] | Injects detailed features into structure feature | May introduce artifacts or distortions |
| Adaptive selection of the loss function, activation function, and sampling [51] | Optimizes the performance of deep neural networks | May require more computational resources or tuning |
| Global group sparse coding [52] | Learns inter-layer connections and determines network depth automatically | May suffer from sparsity or redundancy issues |
| Novel network structures [53] | Outperforms traditional feedforward neural networks | May be difficult to design or interpret |
| Related Works | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| DenseFuse [54] | Uses dense blocks to extract more useful features | May not preserve the contrast and brightness of the source images |
| SeAFusion [55] | Combines image fusion and semantic segmentation | May not handle complex scenes or occlusions well |
| U2Fusion [56] | Adapts to different fusion tasks by estimating source image importance | May not be stable or robust to noise or distortion |
| Dynamic transformer module and Y-shaped network [57] | Extracts local features and context information | May introduce artifacts or blur in the fused image |
| RFN-Nest [58] | Incorporates a residual fusion network and a two-stage training strategy | May require a large amount of training data and time |
| Layer Name | n = 2, m = 8 | n = 5, m = 16 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Channels | Output Channels | Input Channels | Output Channels | |
| ConvBlock0 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 16 |
| DenseLayer1 | 8 | 16 | 16 | 32 |
| DenseLayer2 | 16 | 24 | 32 | 48 |
| DenseLayer3 | 48 | 64 | ||
| DenseLayer4 | 64 | 80 | ||
| DenseLayer5 | 80 | 96 | ||
| ConvBlock1 | 24 | 32 | 96 | 32 |
| Conv | 32 | 3 | 32 | 3 |
| Activation Function | Tanh | |||
| s | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| n | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| m | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 |
| inference time (ms) | 0.668 | 0.700 | 0.701 | 0.712 | 0.785 | 0.82 | 0.836 | 0.847 |
| s | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| n | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| m | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 |
| inference time (ms) | 0.918 | 0.948 | 0.952 | 0.971 | 1.037 | 1.09 | 1.094 | 1.117 |
| Theory | Evaluation Metrics |
|---|---|
| Information Theory | EN, MI, FMI_pixel, FMI_w, FMI_dct, PSNR, Qabf, Nabf |
| Structural Similarity | SSIM, MS_SSIM, MSE |
| Image Features | SF, SD, AG |
| Human Visual Perception | VIF |
| Correlation | CC, SCD |
| Model | Original | Ours (Adaptive DenseNet) | Ratio | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inference Time (ms) | Model Size (KB) | n | m | Inference Time (ms) | Model Size (KB) | Inference Time Ratio | Model Size Ratio | |
| YDTR | 63 | 873 | 2 | 8 | 0.7 | 42 | 0.011 | 0.048 |
| DenseFuse | 3 | 296 | 2 | 8 | 0.7 | 42 | 0.233 | 0.14 |
| SeAFusion | 4 | 667 | 4 | 8 | 0.95 | 77 | 0.238 | 0.12 |
| U2Fusion | 2.2 | 2590 | 2 | 4 | 0.67 | 23 | 0.305 | 0.009 |
| RFN-NEST | 55 | 18,730 | 3 | 16 | 0.85 | 136 | 0.015 | 0.007 |
| SwinFusion | 1920 | 54,025 | 5 | 8 | 1.1 | 98 | 0.00057 | 0.002 |
| Information Theory | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMI_pixel | FMI_w | FMI_dct | Nabf | EN | PSNR | MI | Qabf | |||
| YDTR_ori | 0.893 | 0.334 | 0.322 | 0.062 | 6.633 | 63.37 | 3.126 | 0.420 | ||
| DenseFuse_ori | 0.901 * | 0.381 | 0.399 * | 0.009 * | 6.680 | 64.53 * | 3.214 | 0.396 | ||
| SeAFusion_ori | 0.897 | 0.356 | 0.293 | 0.184 | 6.974 | 61.64 | 3.172 | 0.560 | ||
| U2Fusion_ori | 0.885 | 0.187 | 0.143 | 0.044 | 6.578 | 64.35 | 2.763 | 0.140 | ||
| RFN-NEST_ori | 0.896 | 0.333 | 0.231 | 0.081 | 6.606 | 60.58 | 4.602 * | 0.277 | ||
| SwinFusion_ori | 0.900 | 0.394 * | 0.395 | 0.139 | 6.921 | 61.81 | 3.616 | 0.593 * | ||
| YDTR_our | 0.891 | 0.326 | 0.316 | 0.110 | 6.923 | 63.41 | 2.971 | 0.479 | ||
| DenseFuse_our | 0.895 | 0.358 | 0.351 | 0.088 | 7.032 | 63.82 | 3.097 | 0.506 | ||
| SeAFusion_our | 0.895 | 0.369 | 0.367 | 0.144 | 6.844 | 61.34 | 3.426 | 0.532 | ||
| U2Fusion_our | 0.885 | 0.208 | 0.135 | 0.107 | 7.269 * | 62.88 | 2.857 | 0.210 | ||
| RFN-NEST_our | 0.895 | 0.284 | 0.190 | 0.101 | 6.734 | 60.00 | 3.836 | 0.271 | ||
| SwinFusion_our | 0.899 | 0.383 | 0.376 | 0.187 | 7.023 | 62.02 | 3.472 | 0.575 | ||
| Structural Similarity | Image Features | Human Visual Perception | Correlation | |||||||
| SSIM | MS_SSIM | MSE | SF | SD | AG | VIF | CC | SCD | ||
| YDTR_ori | 0.879 | 0.855 | 0.035 | 0.053 | 9.535 | 3.854 | 0.747 | 0.607 | 1.294 | |
| DenseFuse_ori | 0.906 | 0.880 | 0.026 * | 0.039 | 9.452 | 3.237 | 0.746 | 0.637 * | 1.300 | |
| SeAFusion_ori | 0.925 | 0.889 | 0.051 | 0.069 | 9.668 | 5.604 | 0.850 | 0.587 | 1.446 | |
| U2Fusion_ori | 0.733 | 0.786 | 0.027 | 0.018 | 9.311 | 1.839 | 0.661 | 0.608 | 1.169 | |
| RFN-NEST_ori | 0.666 | 0.567 | 0.069 | 0.025 | 9.375 | 2.416 | 1.223 * | 0.484 | 0.566 | |
| SwinFusion_ori | 0.938 | 0.899 | 0.051 | 0.067 | 9.559 | 5.373 | 0.874 | 0.585 | 1.455 | |
| YDTR_our | 0.915 | 0.903 | 0.034 | 0.057 | 9.591 | 4.514 | 0.773 | 0.614 | 1.515 | |
| DenseFuse_our | 0.938 * | 0.925 * | 0.030 | 0.053 | 9.805 | 4.335 | 0.823 | 0.636 | 1.530 | |
| SeAFusion_our | 0.909 | 0.867 | 0.054 | 0.067 | 9.554 | 5.133 | 0.867 | 0.586 | 1.412 | |
| U2Fusion_our | 0.778 | 0.873 | 0.036 | 0.028 | 9.984 * | 2.954 | 0.796 | 0.607 | 1.539 * | |
| RFN-NEST_our | 0.658 | 0.539 | 0.076 | 0.027 | 9.600 | 2.662 | 1.187 | 0.443 | 0.267 | |
| SwinFusion_our | 0.932 | 0.898 | 0.049 | 0.071 * | 9.637 | 5.678 * | 0.880 | 0.585 | 1.476 | |
| Computing Platform | Fusion Module | Average Time Consumption (ms) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preprocessing | Fusion | Detection | NMS | Results Presentation | ||
| Jetson Xavier NX | Original | 23.4 | 29.4 | 75.8 | 14.4 | 92.0 |
| Ours | 7.6 | |||||
| Notebook PC | Original | 3.5 | 6.6 | 9.6 | 2.0 | 17.3 |
| Ours | 1.6 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Su, S.; Wei, J.; Tong, X.; Gao, W. Lightweight Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Adaptive DenseNet with Knowledge Distillation. Electronics 2023, 12, 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132773
Zhao Z, Su S, Wei J, Tong X, Gao W. Lightweight Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Adaptive DenseNet with Knowledge Distillation. Electronics. 2023; 12(13):2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132773
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zongqing, Shaojing Su, Junyu Wei, Xiaozhong Tong, and Weijia Gao. 2023. "Lightweight Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Adaptive DenseNet with Knowledge Distillation" Electronics 12, no. 13: 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132773
APA StyleZhao, Z., Su, S., Wei, J., Tong, X., & Gao, W. (2023). Lightweight Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Adaptive DenseNet with Knowledge Distillation. Electronics, 12(13), 2773. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132773