Biot–Savart-Based Design and Workbench Validation at 100 MHz of Transverse Field Surface RF Coils
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Biot–Savart Law
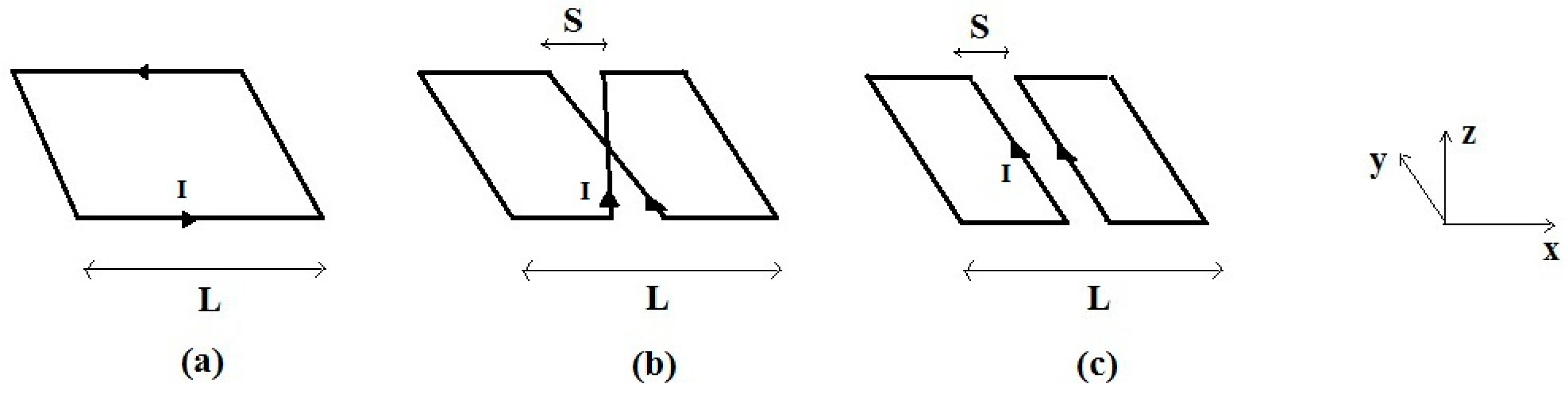
2.2. The Isolated RF Coils
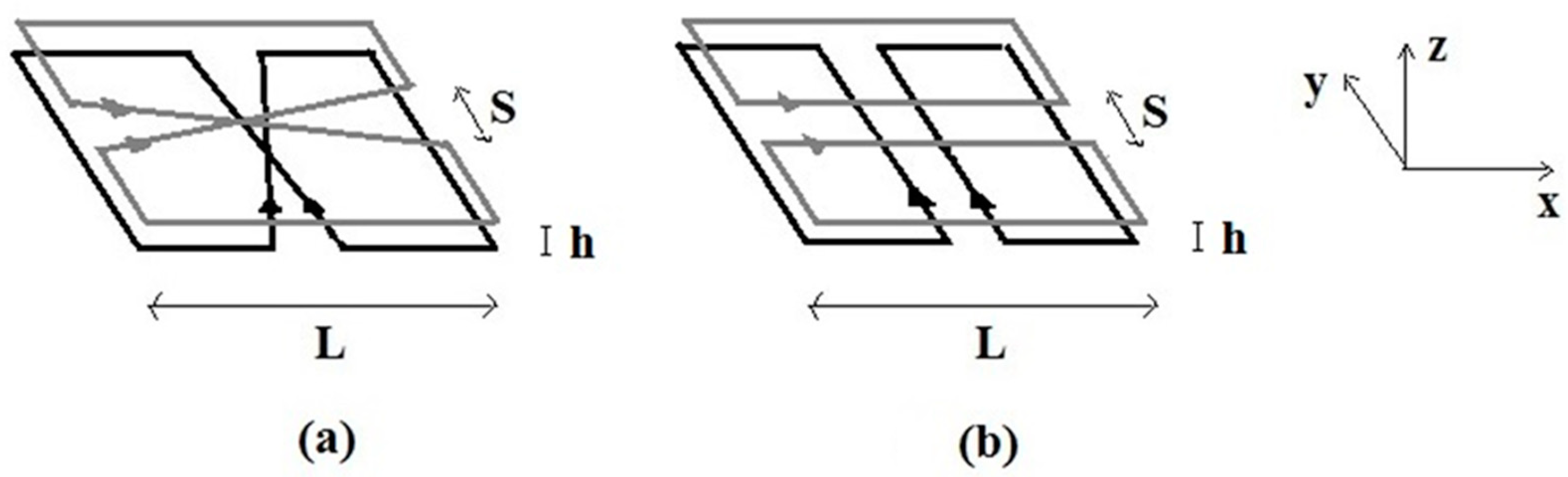
2.3. The Quadrature RF Coils
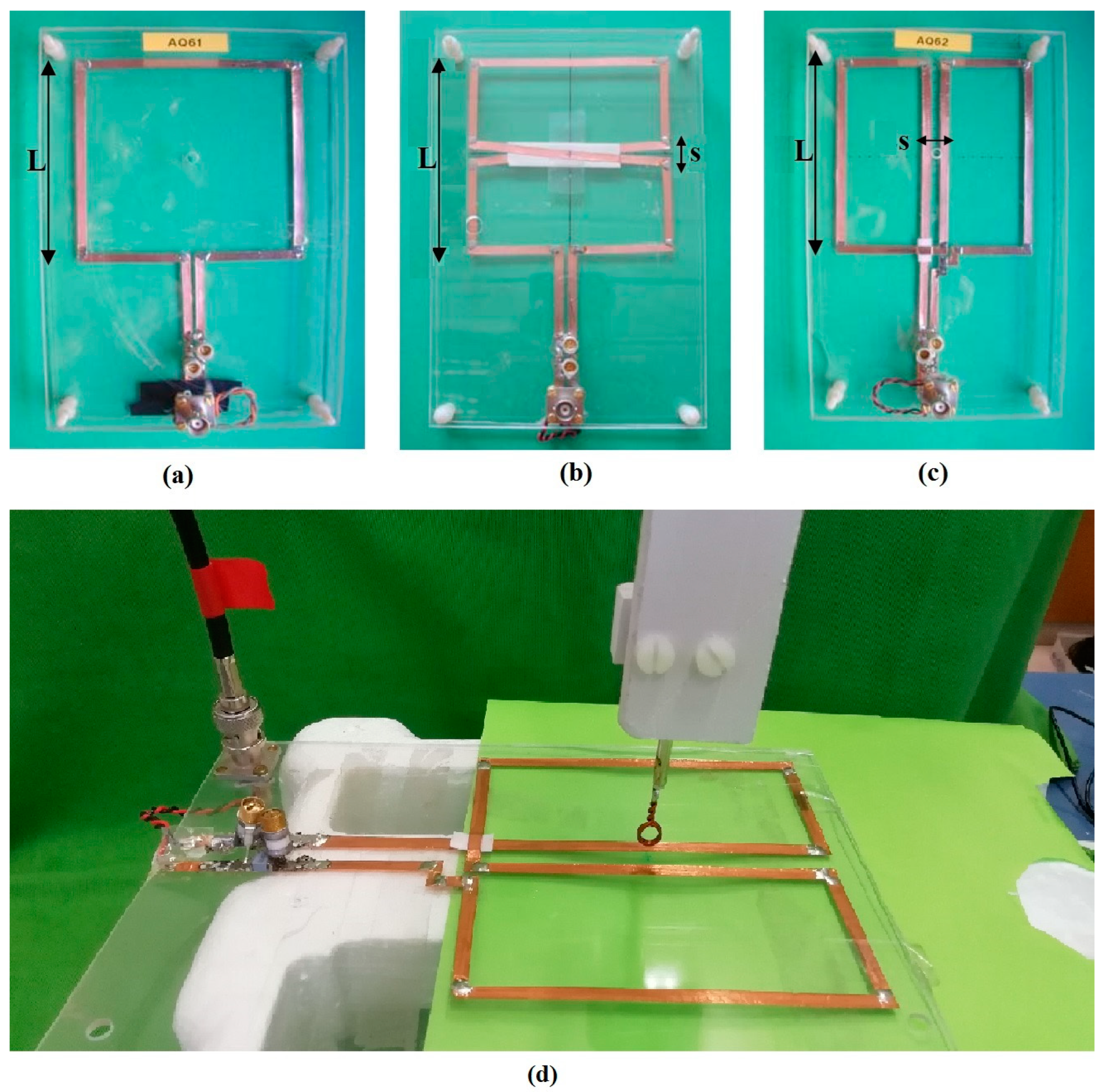
2.4. RF Coil Building and Workbench Test
3. Results
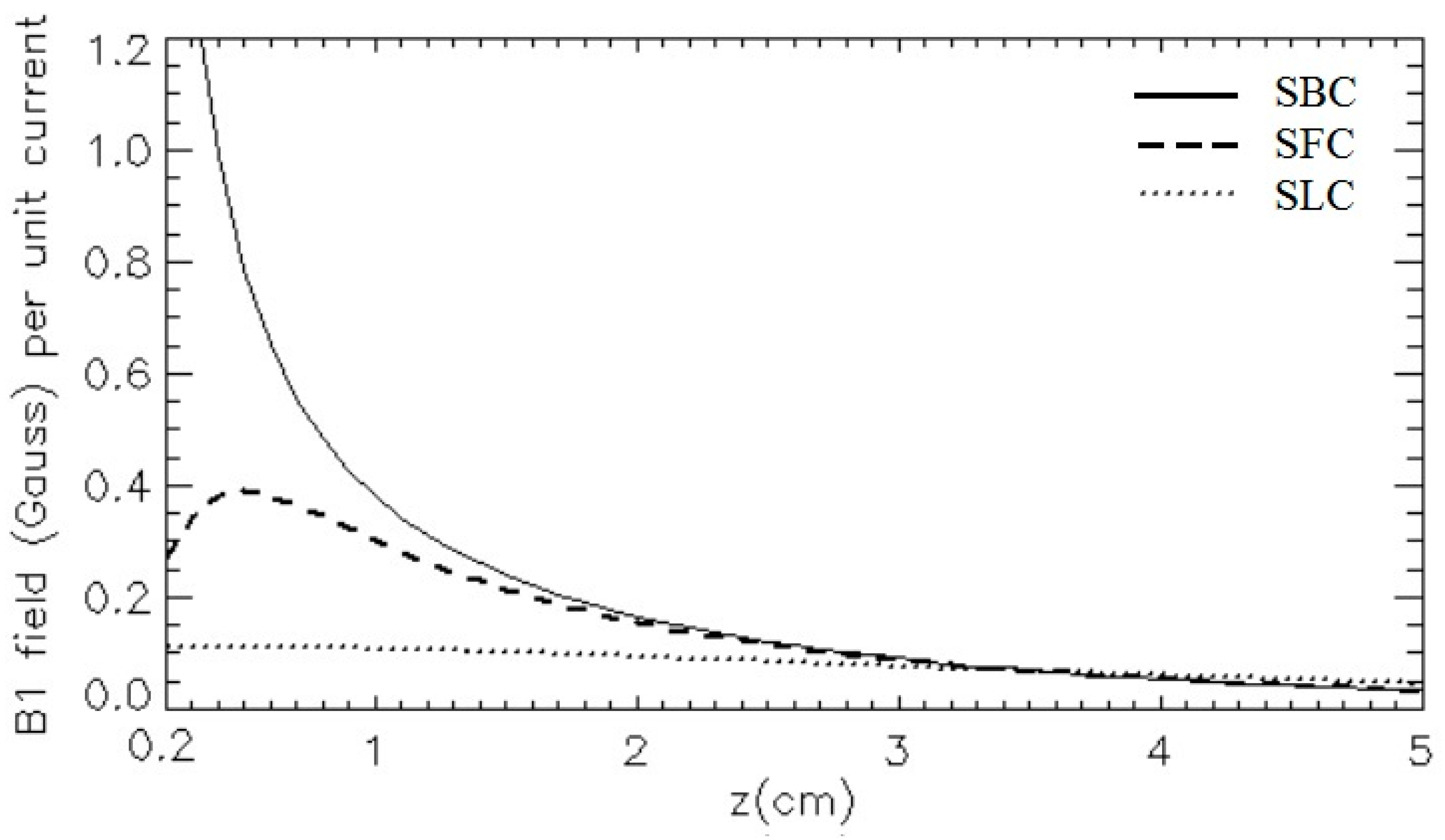
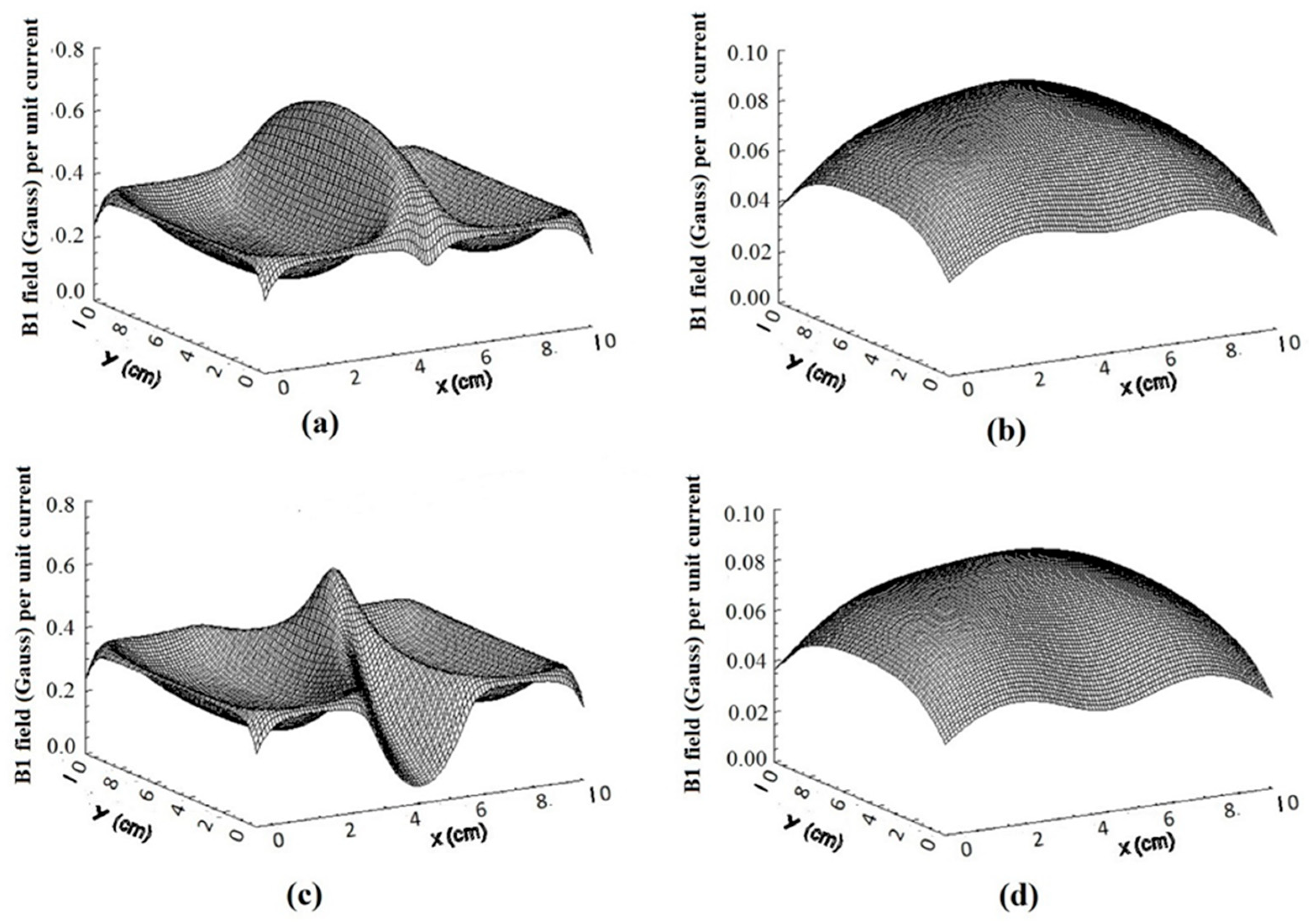
3.1. The Isolated RF Coils
3.2. Isolated RF Coils for Variable Spacing
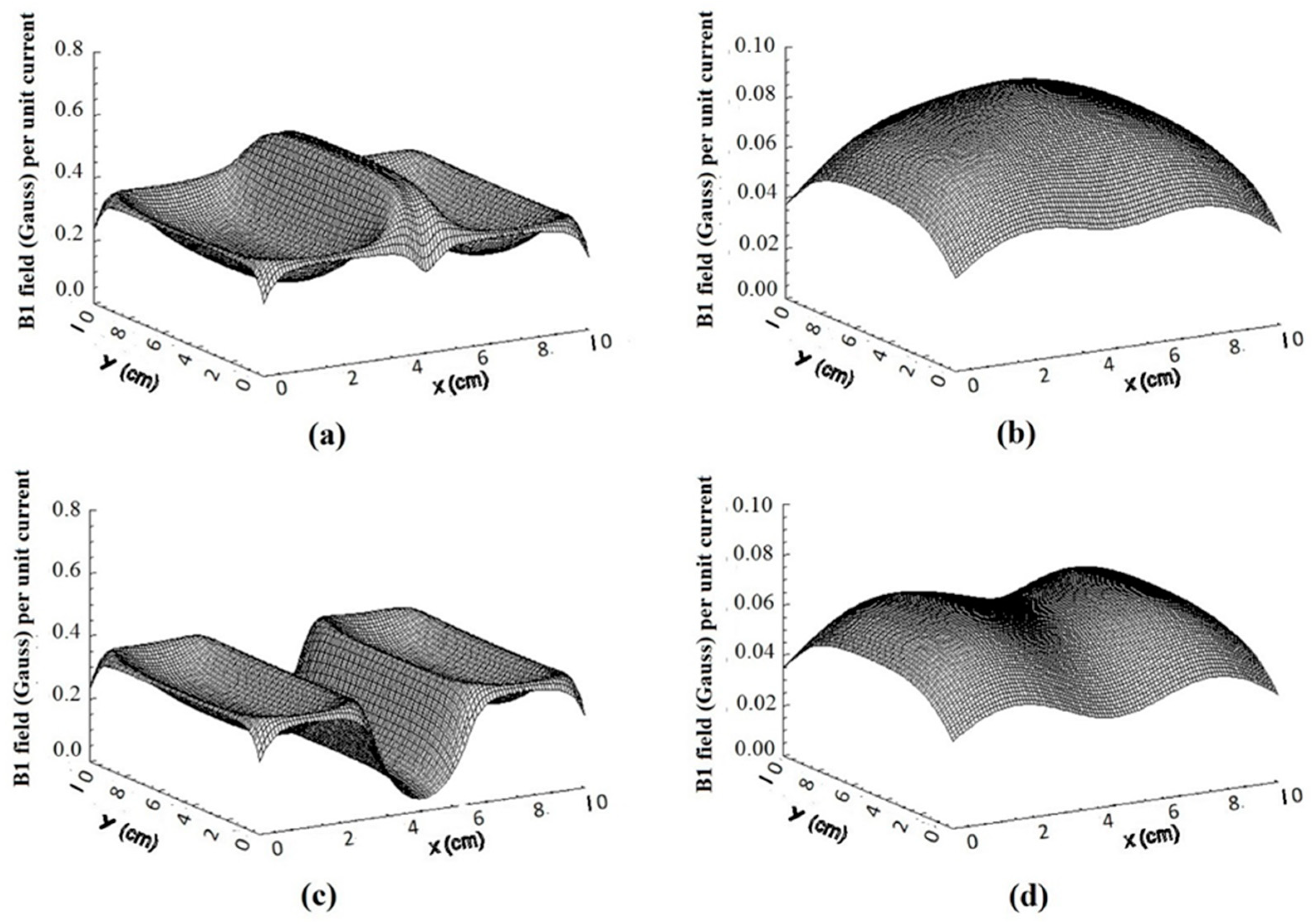
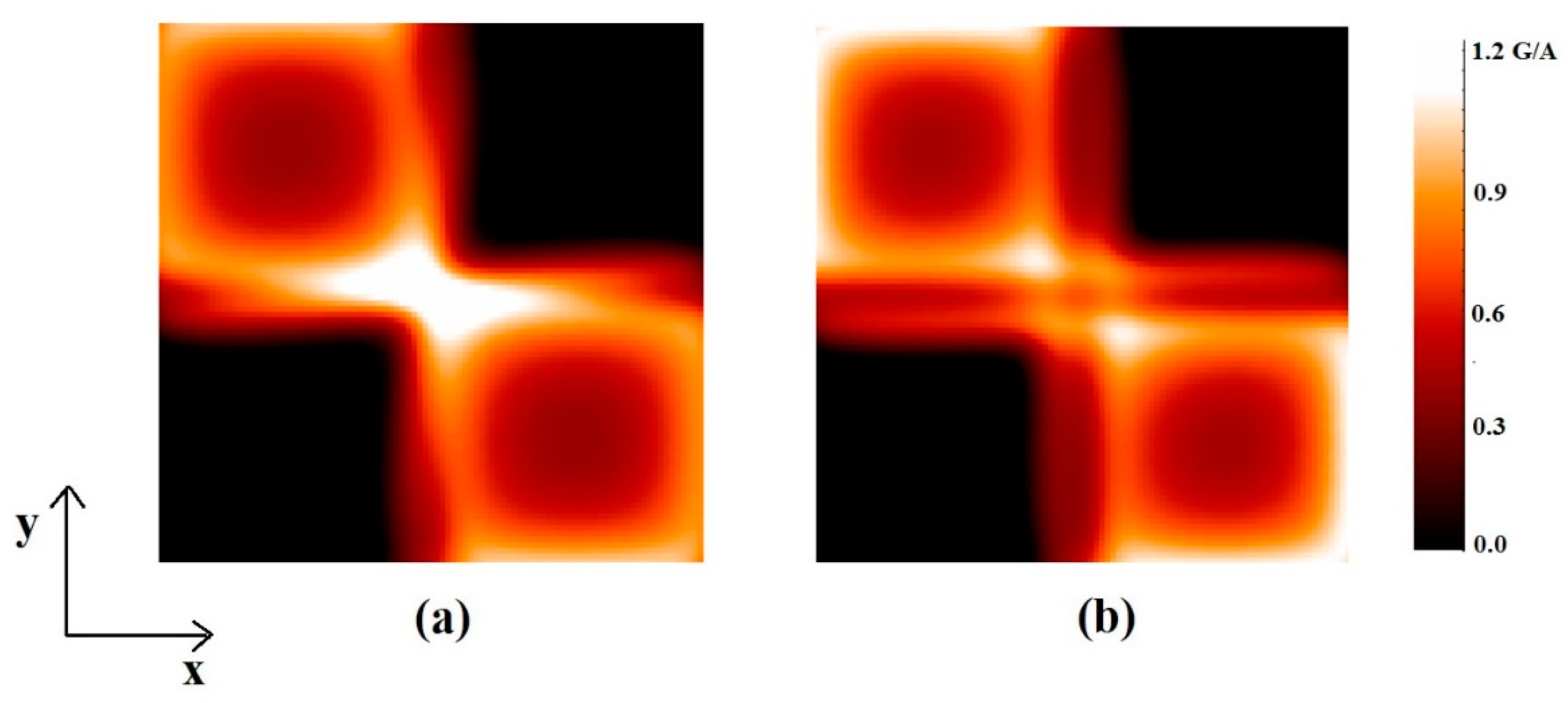
3.3. The Quadrature RF Coils
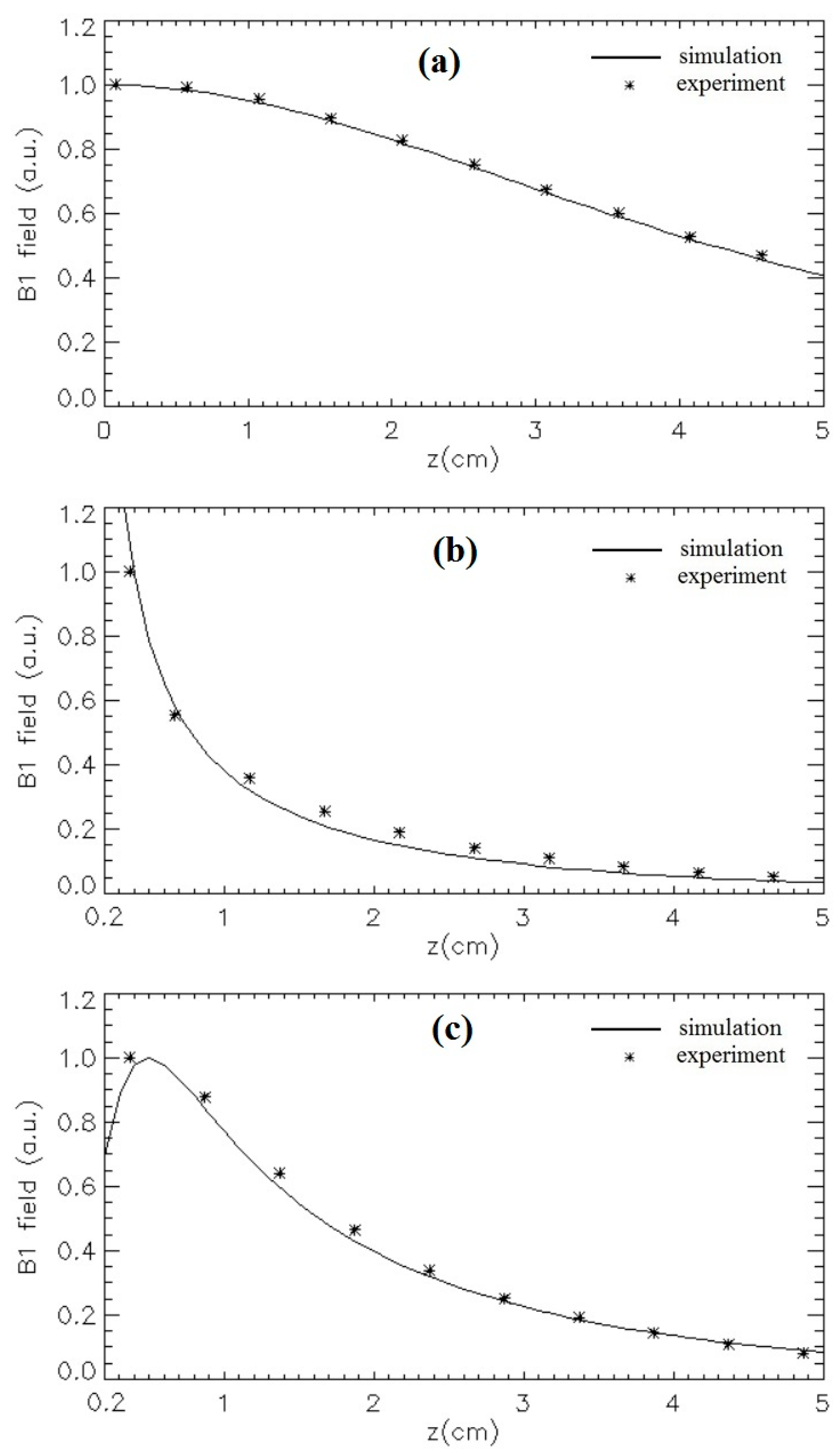
3.4. Workbench Measurements at 100 MHz
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, J. Electromagnetic Analysis and Design in Magnetic Resonance Imaging; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Haase, A.; Odoj, F.; Von Kienlin, M.; Warnking, J.; Fidler, F.; Weisser, A.; Nittka, M.; Rommel, E.; Lanz, T.; Kalusche, B.; et al. NMR probeheads for in vivo applications. Conc. Magn. Reson. 2000, 12, 361–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idiyatullin, D.; Corum, C.A.; Nixdorf, D.R.; Garwood, M. Intraoral Approach for Imaging Teeth Using the Transverse B1 Field Components of an Occlusally Oriented Loop Coil. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, C.-H.; Felder, T.; Felder, J.; Tellmann, L.; Hong, S.-M.; Wegener, H.-P.; Shah, N.J.; Ziemons, K. Design, evaluation and comparison of endorectal coils for hybrid MR-PET imaging of the prostate. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonsetti, M.; Sotgiu, S.; Alecci, M. A Theoretical and Experimental Study on Transverse-Field Radio-Frequency Surface Coils. Measurement 2010, 43, 1503–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonsetti, M.; Clementi, V.; Iotti, S.; Placidi, G.; Lodi, R.; Barbiroli, B.; Sotgiu, A.; Alecci, M. Versatile coil design and positioning of transverse-field RF surface coils for clinical 1.5-T MRI applications. Magn. Reson. Mat. Phys. Biol. Med. 2005, 18, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anferova, S.; Anferov, V.; Adams, M.; Blumler, P.; Routley, N.; Hailu, K.; Kupferschlager, K.; Mallett, M.J.D.; Schroeder, G.; Sharma, S.; et al. Construction of a NMR-MOUSE with Short Dead Time. Conc. Magn. Reson. Part B Magn. Reson. Eng. 2002, 15, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumich, B.; Anferov, V.; Anferova, S.; Klein, M.; Fechete, R.; Adams, M.; Casanova, F. Simple NMR-MOUSE with a Bar Magnet. Conc. Magn. Reson. Part B Magn. Reson. Eng. 2002, 15, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, C.L.; Hornak, J.P. Unilateral MRI using a rastered projection. J. Magn. Reson. 2007, 188, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.-M.; Mak, P.-I.; Law, M.-K.; Martins, R.P. A μNMR CMOS Transceiver Using a Butterfly-Coil Input for Integration with a Digital Microfluidic Device Inside a Portable Magnet. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 2274–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonczyk, M.; Hamm, B.; Heinrich, A.; Thomas, A.; Rathke, H.; Schnackenburg, B.; Güttler, F.; Teichgräber, U.K.M.; de Bucourt, M. Initial clinical experience with a quadrupole butterfly coil for spinal injection interventions in an open MRI system at 1.0 tesla. Biomed. Tech. 2014, 59, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchnin, V.; Ivanov, V.; Gulyaev, M.; Pirogov, Y.; Zubkov, M. Imaging Capabilities of the 1H-X-Nucleus Metamaterial-Inspired Multinuclear RF-Coil. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2022, 41, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchnin, V.; Ivanov, V.; Gulyaev, M.; Zubkov, M. Magnetic resonance imaging with a multi-tunable metamaterial-inspired radiofrequency coil. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2015, 012171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornak, J.P.; Bray, C.L.; Lucero, T.; Bright, A. Surface MRI Using a Rastered Backprojection. In Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 14th Scientific Meeting, Seattle, DC, USA, 6–12 May 2006; p. 1354. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, C.L.; Hornak, J.P. Design Iterations and Performance Enhancement for a Sub-Surface MRI System. In Proceedings of the 46th ENC, Providence, RI, USA, 10–15 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Giovannetti, G.; Viti, V.; Positano, V.; Santarelli, M.F.; Landini, L.; Benassi, A. Magnetostatic simulation for accurate design of low field MRI phased-array coils. Conc. Magn. Reson. Part B Magn. Reson. Eng. 2007, 31, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohliger, M.A.; Greenman, R.; McKenzie, C.A.; Sodickson, D.K. Concentric Coil Arrays for Spatial Encoding in Parallel MRI. In Proceedings of the 9th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Glasgow, Scotland, 21–27 April 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chacon-Caldera, J.; Malzacher, M.; Schad, L.R. Partially orthogonal resonators for magnetic resonance imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klomp, D.W.J.; Collins, D.J.; van der Boogert, H.I.; Schwarz, A.; Rijpkema, M.; Prock, T.; Payne, G.S.; Leach, M.O.; Heershap, A. Radio-frequency probe for 1H decoupled 31P MRS of the head and neck region. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 19, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Zhu, X.-H.; Zhang, X.-L.; Ugurbil, K.; Chen, W. In vivo 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human brain at 7 T: An initial experience. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 49, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonsetti, M.; Sotgiu, A.; Alecci, M. Design and testing of a 1.5 Tesla double-tuned (1H/31P) RF surface coil with intrinsic geometric isolation. Measurement 2010, 43, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leynes, A.P.; Chen, Y.; Sukumar, S.; Xu, D.; Zhang, X. A Compact Planar Triple-Nuclear Coil for Small Animal 1H, 13C, and 31P Metabolic MR Imaging at 14.1 T. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.03015. [Google Scholar]
- Thapa, B.; Kaggie, J.; Sapkota, N.; Frank, D.; Jeong, E.-K. Design and Development of a General-PurposeTransmit/Receive (T/R) Switch for 3T MRI, Compatible for a Linear, Quadrature and Double-Tuned RF Coil. Conc. Magn. Reson. Part B Magn. Reson. Eng. 2016, 46, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, Y.; Choi, C.-H.; Shah, N.J. Development and Implementation of a PIN-Diode Controlled, Quadrature-Enhanced, Double-Tuned RF Coil for Sodium MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1626–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Zhang, X.; Park, I.; Najac, C.; Nelson, S.J.; Ronen, S.; Larson, P.E.Z. 1H-13C Independently Tuned Radiofrequency Surface Coil Applied for In Vivo Hyperpolarized MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016, 76, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hyde, J.S.; Jesmanowicz, A.; Grist, T.M.; Froncisz, W.; Kneeland, J.B. Quadrature Detection Surface Coil. Magn. Reson. Med. 1987, 4, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, F.D.; Entzminger, G.; Kulkarni, J.; Pamarthy, K.; Staab, J.P. Radio frequency coil technology for small-animal MRI. NMR Biomed. 2007, 20, 304–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluis, M.J.; Tsekos, N.; Smith, N.B.; Webba, A.G. Simple RF design for human functional and morphological cardiac imaging at 7 tesla. J. Magn. Reson. 2009, 200, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouhlous, M.; Moelker, A.; Flick, H.J.; Wielopolski, P.A.; de Weert, T.T.; Pattynama, P.M.T.; van der Lugt, A. Quadrature Coil Design for High-Resolution Carotid Artery Imaging Scores Better than a Dual Phased-Array Coil Design with the Same Volume Coverage. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 25, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Bottomley, P.A. Optimized quadrature surface coil designs. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. 2008, 21, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mispelter, J.; Lupu, M.; Briguet, A. NMR Probeheads for Biophysical and Biomedical Experiments: Theoretical Principles & Practical Guidelines, 2nd ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Özen, A.C.; Spreter, F.; Schimpf, W.; Fischer, J.; Ilbey, S.; Reiss, S.; Maier, A.; von Elverfeldt, D.; Heidt, T.; von zurMühlen, C.; et al. Scalable and modular 8-channel transmit and 8-channel flexible receive coil array for 19F MRI of large animals. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 89, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.-H.; Hong, S.-M.; Felder, J.; Shah, N.J. The state-of-the-art and emerging design approaches of double-tuned RF coils for X-nuclei, brain MR imaging and spectroscopy: A review. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 72, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letcher, J.H. Computer-assisted design of surface coils used in magnetic resonance imaging. I. The calculation of the magnetic field. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1989, 7, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.O.; Amador, R.; Rojas, R.; Barrios, F.A. Magnetic field visualisation and inductance calculation of a simple configuration surface coil at low magnetic field. Rev. Mex. Fis. E 2006, 52, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, G.H.; Hayes, C.E.; Pelc, N.J.; Edelstein, W.A.; Mueller, O.M.; Hart, H.R.; Hardy, C.J.; O’Donnell, M.; Barber, W.D. Comparison of linear and circular polarization for magnetic resonance imaging. J. Magn. Reson. 1985, 64, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.N.; Hoult, D.I. Biomedical Magnetic Resonance Technology; Adam Hilger: Bristol, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hoult, D.I.; Lauterbur, P.C. The sensitivity of the zeugmatographic experiment involving human samples. J. Magn. Reson. 1979, 34, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pellegars, P.; Pan, L.; Sidi-Boulenouar, R.; Nativel, E.; Zanca, M.; Alibert, E.; Rousset, S.; Cardoso, M.; Verdeil, J.-L.; Bertin, N.; et al. Homogenous nuclear magnetic resonance probe using the space harmonics suppression method. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2020, 9, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurler, N.; Ider, Y.Z. Numerical methods and software tools for simulation, design, and resonant mode analysis of radio frequency birdcage coils used in MRI. Conc. Magn. Reson. Part B Magn. Reson. Eng. 2015, 45, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, J.F.; Rodriguez, A.O. Finite-Element Electromagnetic Simulation of a Volume Coil with Slotted End-Rings for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. AIP Conf. Proc. 2008, 1032, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Duan, Y. Rapid four-ring birdcage coil analysis: Design optimization for high efficiency, low interference, and improved body loading tolerance. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 66, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Liu, S.; Chen, Q.; Li, N.; Dou, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shen, B.; Li, Y. Numerical Simulation and Evaluation of a Four-Channel-by-Four-Channel Double-Nuclear RF Coil for 1 H MRI and 31 P MRSI at 7 T. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 5101105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, B.J.; Park, G.E.; Kim, S.H. The Usefulness of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for the Detection of Local Recurrence after Mastectomy with Reconstructive Surgery in Breast Cancer Patients. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegour, R.; Belaid, A.; Ognard, J.; Salem, D.B. Convolutional neural networks-based method for skin hydration measurements in high resolution MRI. Biomed. Sign. Proc. Control 2023, 81, 104491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maifeld, A.; Wild, J.; Karlsen, T.V.; Rakova, N.; Wistorf, E.; Linz, P.; Jung, R.; Birukov, A.; Gimenez-Rivera, V.-A.; Wilck, N.; et al. Skin Sodium Accumulates in Psoriasis and Reflects Disease Severity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 142, 166–178.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantillon-Murphy, P.; Wald, L.L.; Zahn, M.; Adalsteinsson, E. Proposing magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia in low-field MRI. Conc. Magn. Reson. Part A 2010, 36, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantasia, M.; Galante, A.; Maggiorelli, F.; Retico, A.; Fontana, N.; Monorchio, A.; Alecci, M. Numerical and workbench design of 2.35 T double-tuned (1H/23Na) nested RF birdcage coils suitable for animal size MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 3175–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| RF Coil Design | Frequency (MHz) and Nuclei | Application/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Circular loop [3] | 170.3 (1H) | Dental imaging |
| FC [4] | 123.2 (1H) | Prostate imaging |
| BC, FC [5] | 25.85/63.9 (31P/1H) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| FC [6] | 63.9 (1H) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| FC meander coil [7] | ≈20 (1H) | Historical books analysis |
| FC. BC [8] | 22 (1H) | Rubber process analysis |
| BC [9] | 12.4 (1H) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| BC [10] | 20 (1H) | Biological/chemical assays |
| BC [11] | 42.6 (1H) | Human MR-guided interventions |
| BC [12,13] | 300 (1H) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| BC [14] | 15 (1H) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| BC [15] | 15 (1H) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| Array of FC [16] | 10.6 (1H) | Magnetic field estimation |
| Array of BC [17] | 63.9 (1H) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| BC [18] | 128 (1H) | Human brain imaging |
| BC [19] | 63.9 (1H) | Head and neck imaging and spectroscopy |
| BC [20] | 298 (1H) | Human brain imaging |
| FC [21] | 25.85 (31P) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| BC [22] | 150 (13C) | Small animal metabolic imaging |
| BC [23] | 49.9 (31P) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| BC [24] | 105.7 (23Na) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| BC [25] | 74.96/298.06 (13C/1H) | Rat brain imaging |
| CRC loop-gap resonator [26] | 63.9 (1H) | Temporomandibular joint imaging |
| BC [27] | --- | --- |
| BC [28] | 298 (1H) | Human heart imaging |
| BC [29] | 63.9 (1H) | Carotid artery imaging |
| BC, FC [30] | 128 (1H) | Phantom SNR measurement |
| Coil | S11unloaded (dB) | Qunloaded | S11loaded (dB) | Qloaded |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLC | −16 | 176 | −31 | 11 |
| SBC | −23 | 218 | −23 | 20 |
| SFC | −16 | 177 | −40 | 38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giovannetti, G.; Alecci, M.; Galante, A. Biot–Savart-Based Design and Workbench Validation at 100 MHz of Transverse Field Surface RF Coils. Electronics 2023, 12, 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122578
Giovannetti G, Alecci M, Galante A. Biot–Savart-Based Design and Workbench Validation at 100 MHz of Transverse Field Surface RF Coils. Electronics. 2023; 12(12):2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122578
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiovannetti, Giulio, Marcello Alecci, and Angelo Galante. 2023. "Biot–Savart-Based Design and Workbench Validation at 100 MHz of Transverse Field Surface RF Coils" Electronics 12, no. 12: 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122578
APA StyleGiovannetti, G., Alecci, M., & Galante, A. (2023). Biot–Savart-Based Design and Workbench Validation at 100 MHz of Transverse Field Surface RF Coils. Electronics, 12(12), 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122578






