Evaluation Methodology for Object Detection and Tracking in Bounding Box Based Perception Modules
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Perception Module
1.2. Testing and Verification of Car Perception
1.3. Evaluation Methodology
1.4. Organization of the Paper
2. Related Work
3. Rectangular Similarity
- .
- ,
3.1. Area Similarity
3.2. Shape Similarity
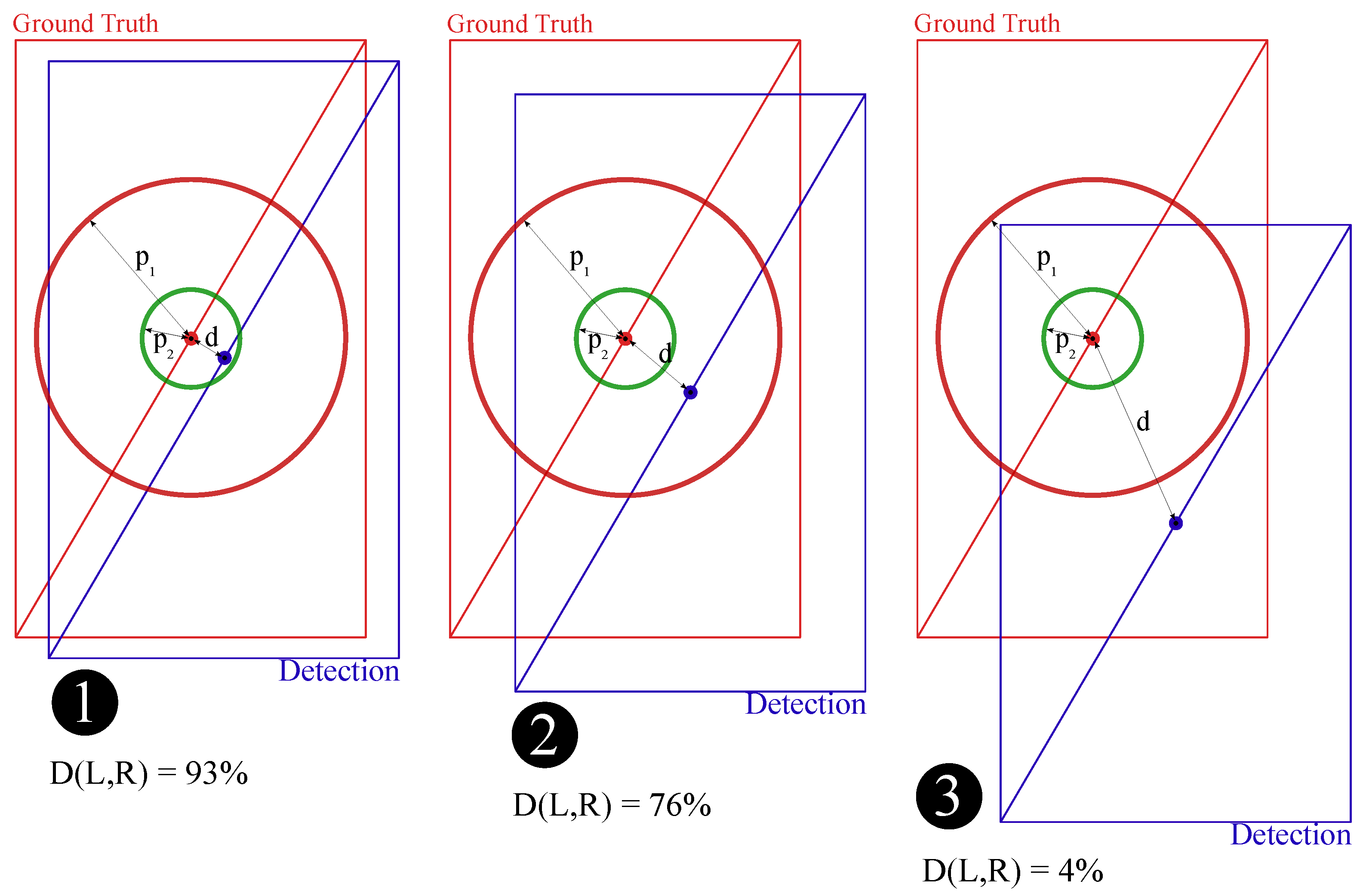
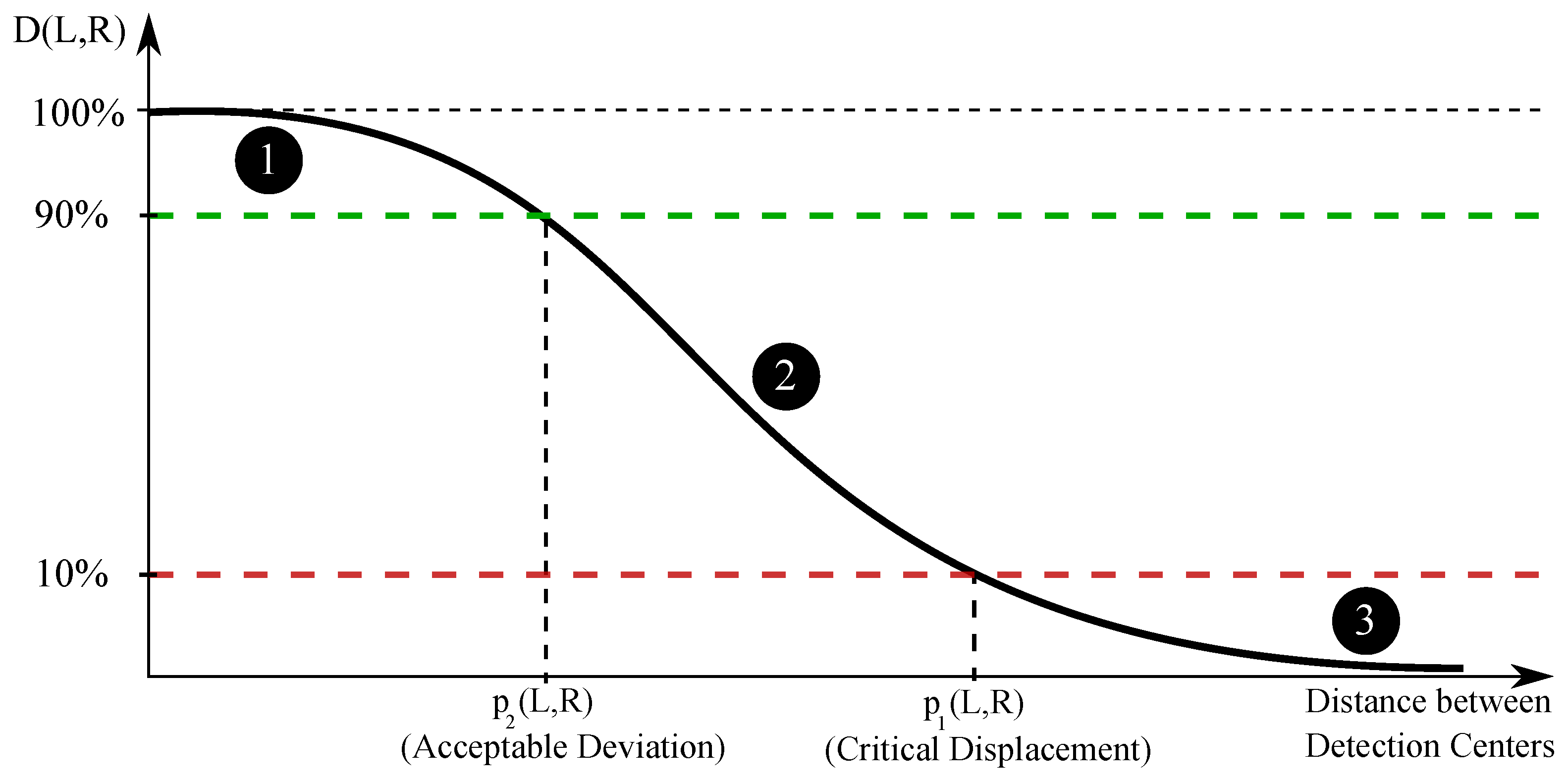
3.3. Distance Similarity
3.4. General Similarity
3.5. Accuracy of Association Algorithm and Selection of Hyper-Parameters
4. Rectangle Sequence Evaluation
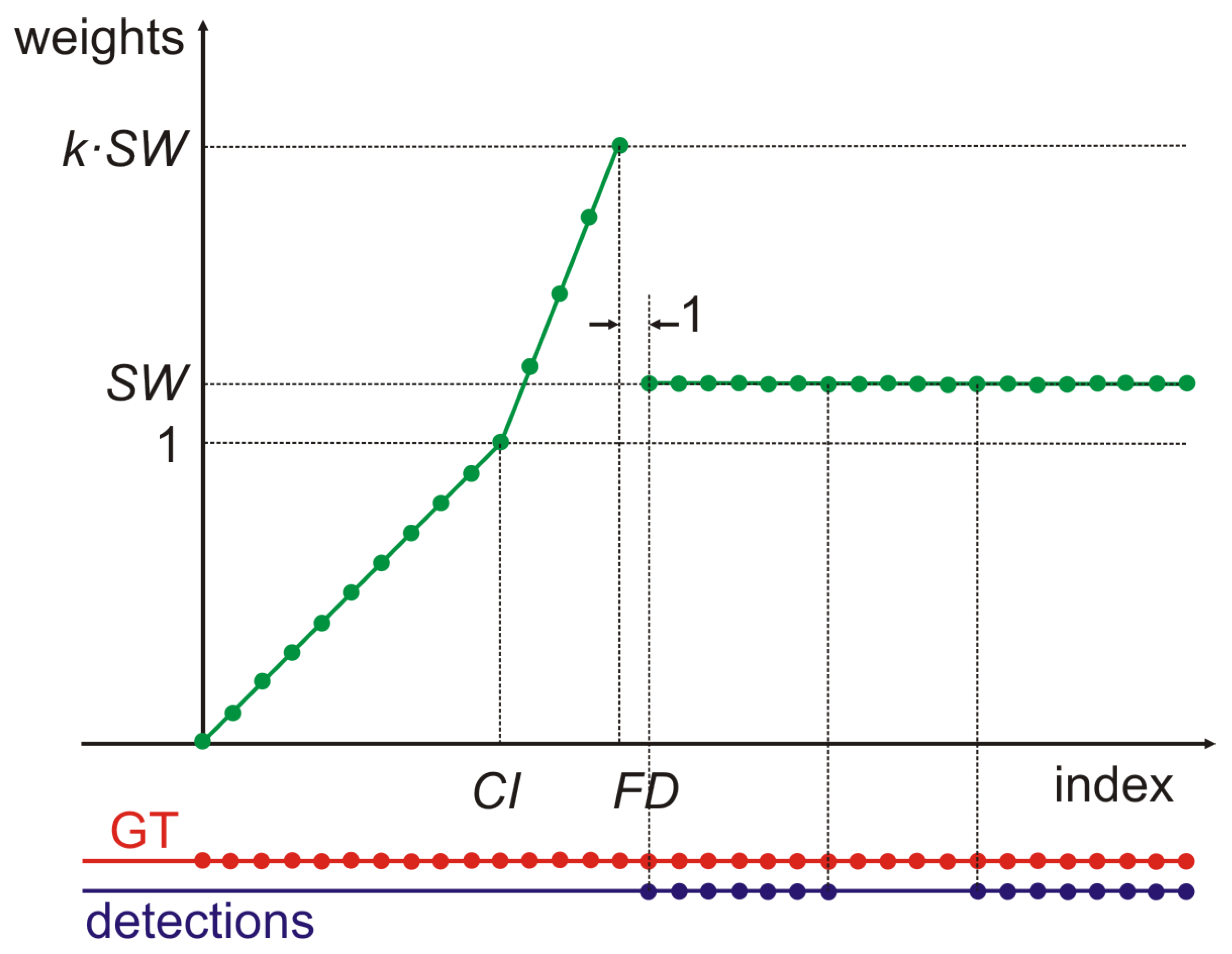
4.1. Weighted Average for Late Detection
- (1)
- Critical index () is the number of frames from the moment the object appeared within the range of the sensors in which detection delay can be tolerated. Simultaneously the detection appearing not later than is crucial for safety.
- (2)
- First detection () is the first frame in which recognition of the object appears and we are able to evaluate the quality of the detection by the use of the similarity a measure applied to the object and the corresponding GT object.
- (3)
- Standard weight () is the weight that will be assigned to each observation from the first detection to the end of the time series .
4.2. False Positive Event
4.3. Automotive Aspect of Tracking Analysis
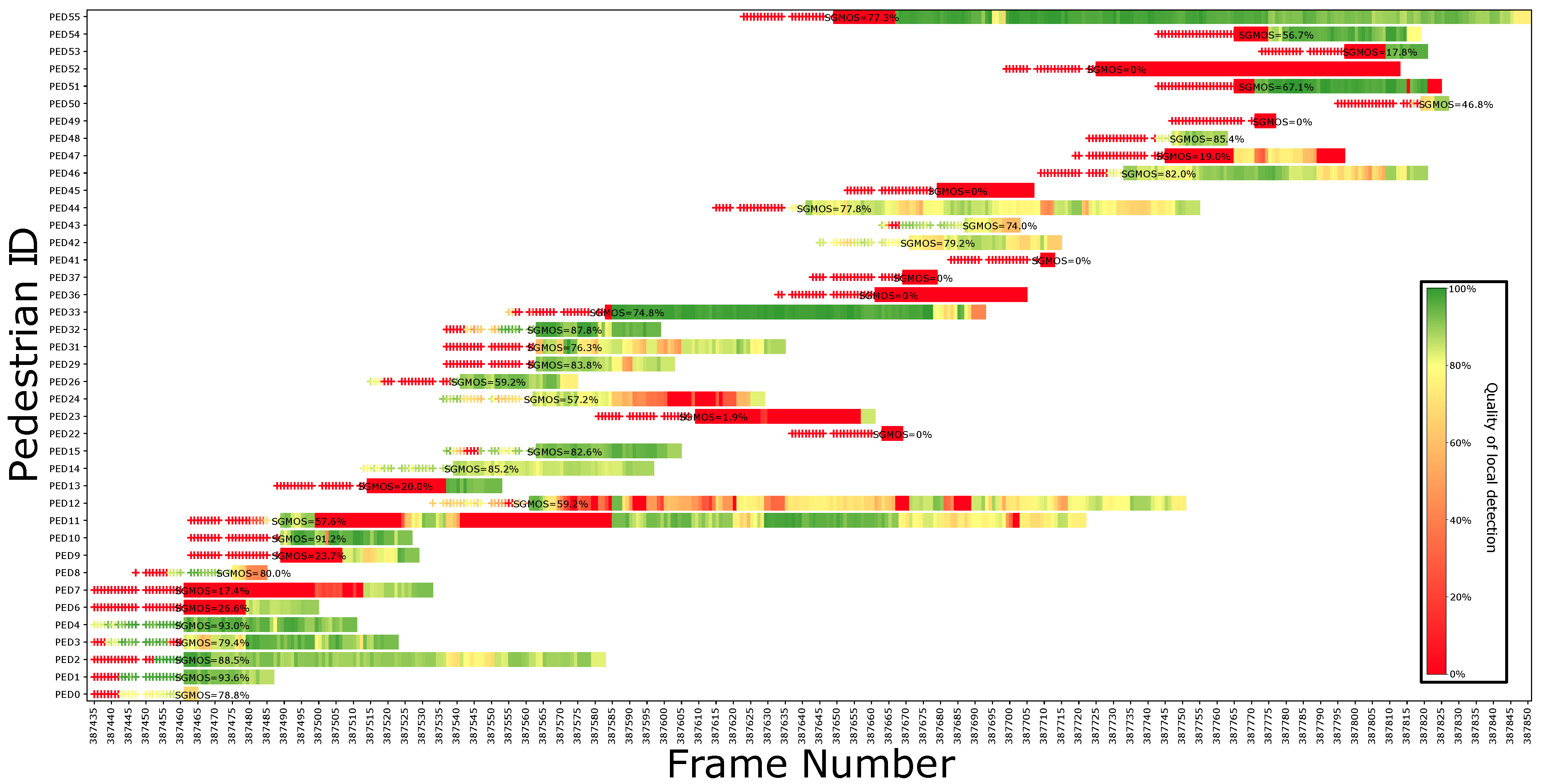
5. Results of Practical Application
5.1. Pedestrian Detection
5.2. Vehicle Detection
5.3. Traffic Light Recognition
5.4. Radar Data Evaluation
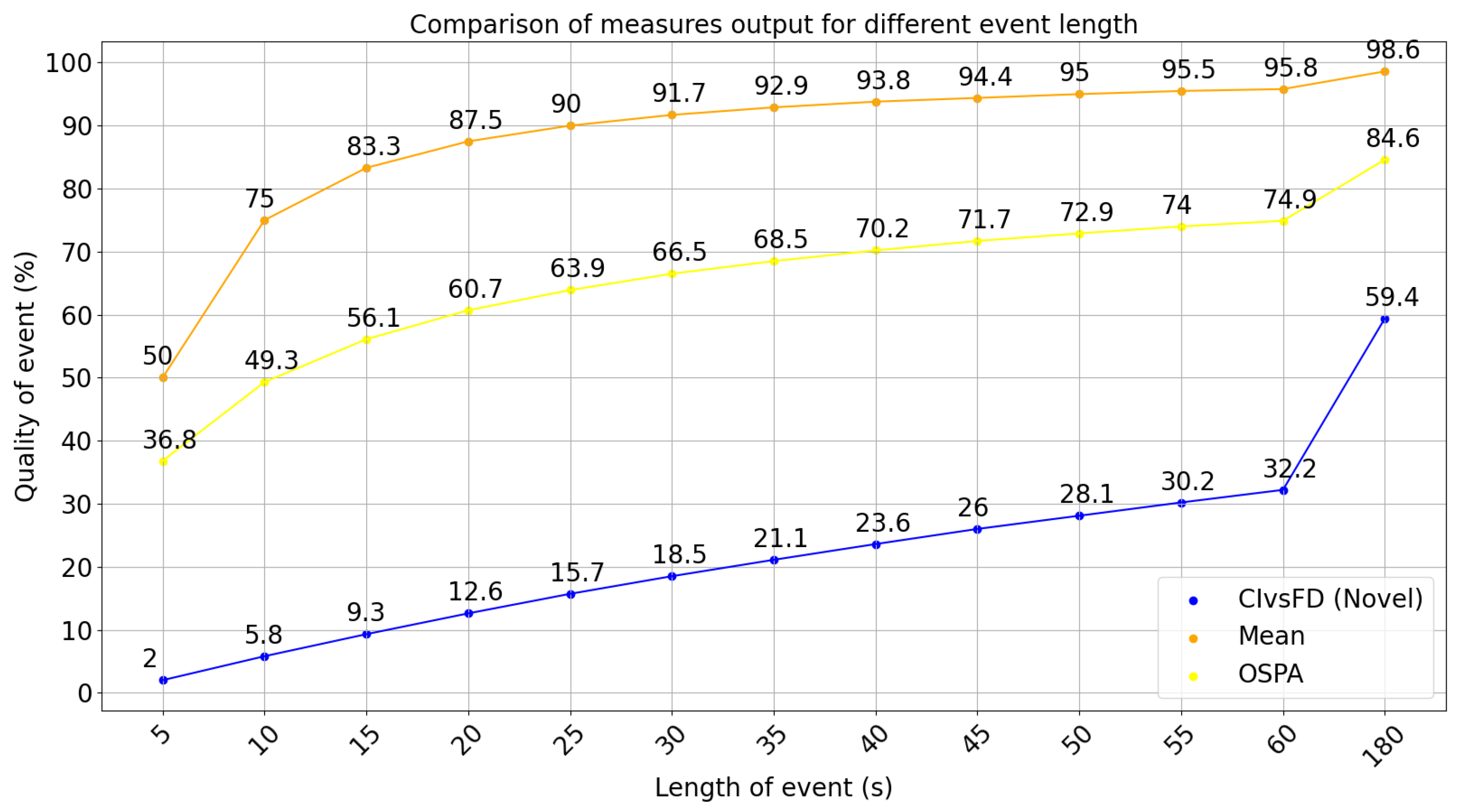
6. Results of Measure Comparison
6.1. Feature Comparison
6.2. Artificial Interference Analysis
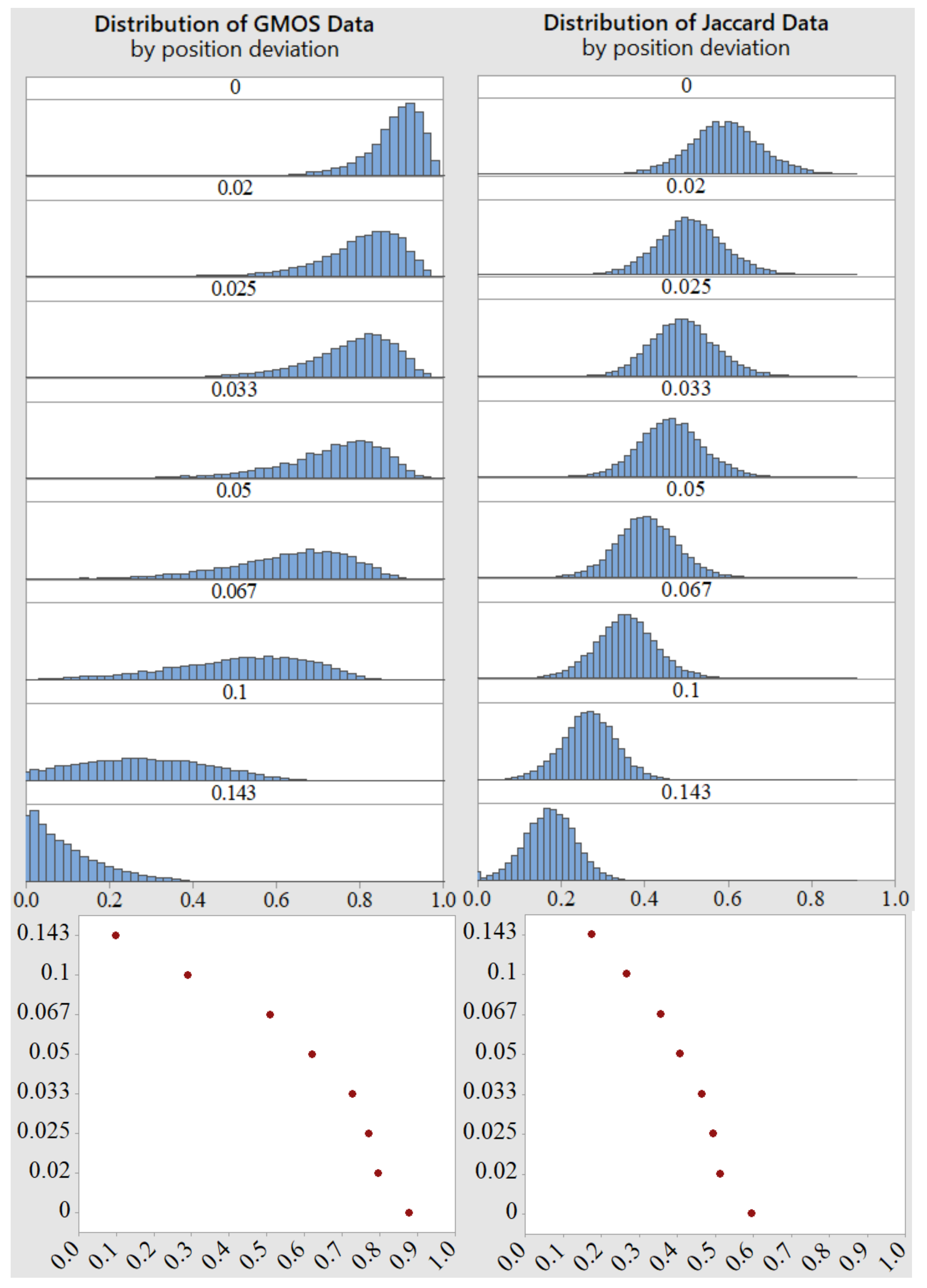
6.2.1. Position Shift
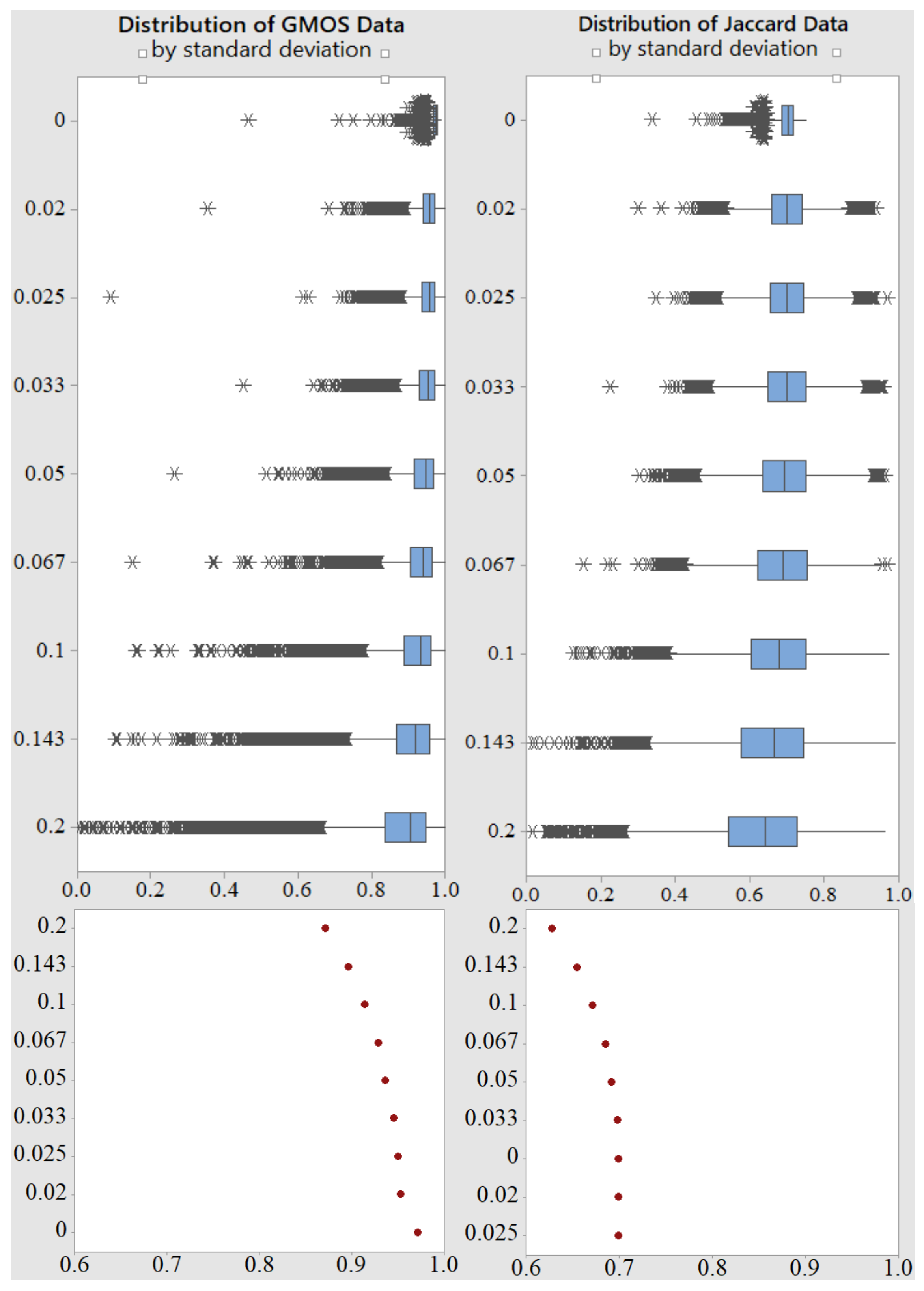
6.2.2. Standard Deviation Influence
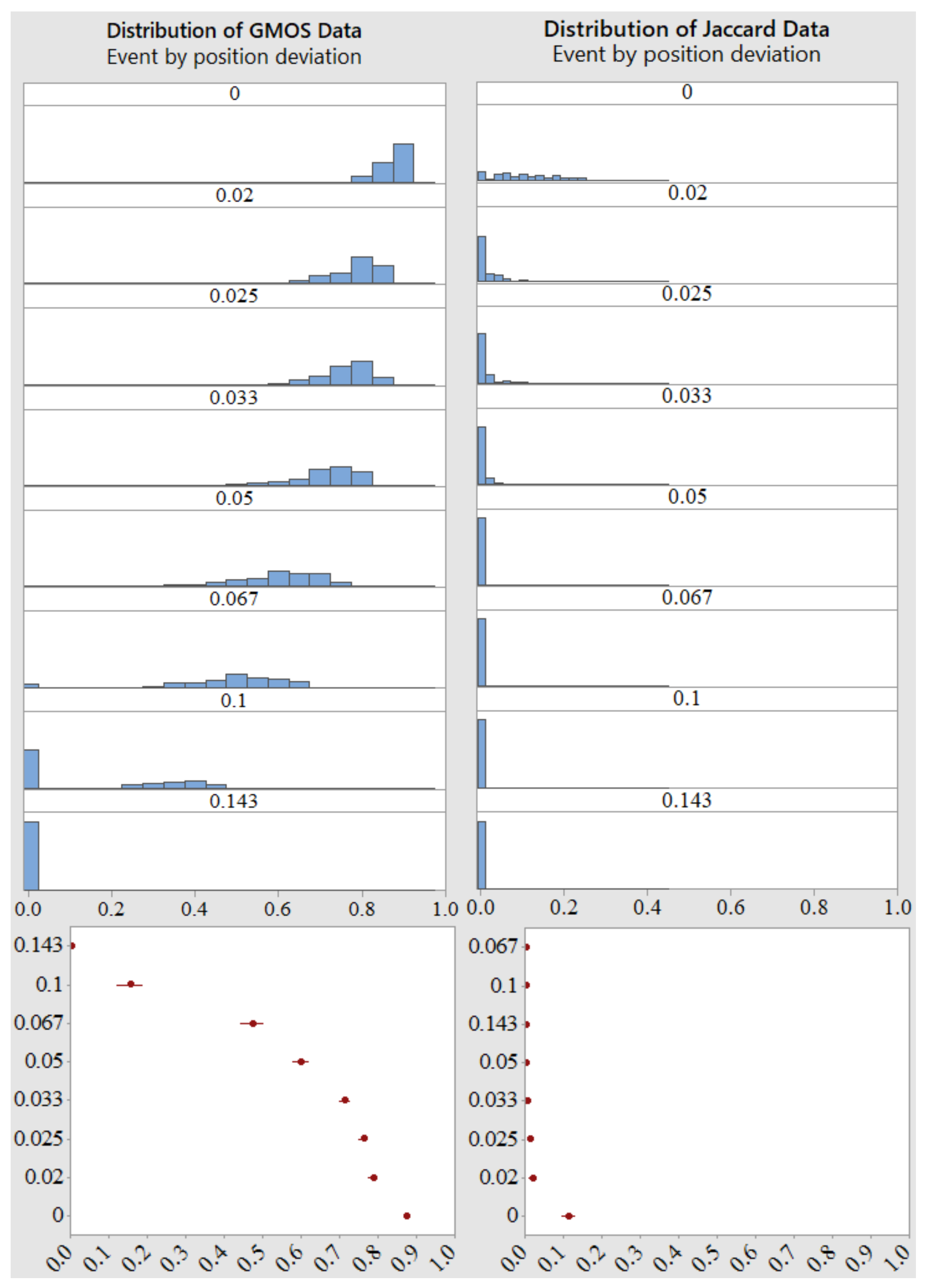
6.2.3. Position Shift in Event Summary
6.3. Statistical Difference
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, S.; Liang, S.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Y.; Li, X. Class Agnostic Image Common Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2836–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, C. Locator-Checker-Scaler Object Tracking Using Spatially Ordered and Weighted Patch Descriptor. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3817–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Gong, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Q. Accurate Object Localization in Remote Sensing Images Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2486–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Huang, K.; Tao, D.; Tan, T. Weakly Supervised Large Scale Object Localization with Multiple Instance Learning and Bag Splitting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Ouyang, W.; Yan, J.; Li, H.; Xiao, T.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, Z.; et al. Crafting GBD-Net for Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 2109–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, B.; Hu, H. Too Far to See? Not Really!—Pedestrian Detection With Scale-Aware Localization Policy. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 3703–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uřičář, M.; Hurych, D.; Krizek, P.; Yogamani, S. Challenges in Designing Datasets and Validation for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.09270. [Google Scholar]
- ISO/PAS 21448:2019; Road Vehicles—Safety of the Intended Functionality. International Organization for Standardization: London, UK, 2019.
- Breuers, S.; Yang, S.; Mathias, M.; Leibe, B. Exploring bounding box context for multi-object tracker fusion. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, NY, USA, 7–10 March 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, J.R.; Mahler, R.P.S. Multitarget miss distance via optimal assignment. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern.—Part A Syst. Hum. 2004, 34, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmacher, D.; Vo, B.; Vo, B. A Consistent Metric for Performance Evaluation of Multi-Object Filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 3447–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perazzi, F.; Pont-Tuset, J.; McWilliams, B.; Van Gool, L.; Gross, M.; Sorkine-Hornung, A. A Benchmark Dataset and Evaluation Methodology for Video Object Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 724–732. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Shao, L. Motion-Attentive Transition for Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Shao, L. Target-Aware Object Discovery and Association for Unsupervised Video Multi-Object Segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.04782. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, A.A.; Hanbury, A.; del Toro, O.A.J. A formal method for selecting evaluation metrics for image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 932–936. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Dong, X.; Ren, Z. Advanced Intersection over Union Loss for Visual Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Hangzhou, China, 22–24 November 2019; pp. 5869–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemery, B.; Laurent, H.; Rosenberger, C. Comparative study of metrics for evaluation of object localisation by bounding boxes. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Image and Graphics (ICIG 2007), Chengdu, China, 22–24 August 2007; pp. 459–464. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Erfani, S.M.; Ma, X.; Bailey, J.; Chi, Y.; Hua, X. Alpha-IoU: A Family of Power Intersection over Union Losses for Bounding Box Regression. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.13675. [Google Scholar]
- Rezatofighi, H.; Tsoi, N.; Gwak, J.; Sadeghian, A.; Reid, I.; Savarese, S. Generalized Intersection Over Union: A Metric and a Loss for Bounding Box Regression. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU Loss: Faster and Better Learning for Bounding Box Regression. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 12993–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cehovin, L.; Kristan, M.; Leonardis, A. Is my new tracker really better than yours? In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Steamboat Springs, CO, USA, 24–26 March 2014; pp. 540–547. [Google Scholar]
- Cehovin, L.; Leonardis, A.; Kristan, M. Visual Object Tracking Performance Measures Revisited. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazarevic-McManus, N.; Renno, J.; Makris, D.; Jones, G. An object-based comparative methodology for motion detection based on the F-Measure. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 111, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, T.; Cavallaro, A. A Protocol for Evaluating Video Trackers Under Real-World Conditions. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szczodrak, M.; Dalka, P.; Czyżewski, A. Performance evaluation of video object tracking algorithm in autonomous surveillance system. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd International Conference on Information Technology, (2010 ICIT), Gdansk, Poland, 28–30 June 2010; pp. 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Markiewicz, P.; Długosz, M.; Skruch, P. Review of tracking and object detection systems for advanced driver assistance and autonomous driving applications with focus on vulnerable road users sensing. In Trends in Advanced Intelligent Control, Optimization and Automation; Mitkowski, W., Kacprzyk, J., Oprzędkiewicz, K., Skruch, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 224–237. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Huang, X.; Yan, Y.; Bai, S. An improved mean-shift tracking algorithm with spatial-color feature and new similarity measure. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Multimedia Technology, Hangzhou, China, 26–28 July 2011; pp. 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, K.; Guo, Y.Y. Online parameter based Kalman filter precision evaluation method for video target tracking. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Multimedia Technology, Hangzhou, China, 26–28 July 2011; pp. 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasturi, R.; Goldgof, D.; Soundararajan, P.; Manohar, V.; Garofolo, J.; Bowers, R.; Boonstra, M.; Korzhova, V.; Zhang, J. Framework for Performance Evaluation of Face, Text, and Vehicle Detection and Tracking in Video: Data, Metrics, and Protocol. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristan, M.; Matas, J.; Leonardis, A.; Vojíř, T.; Pflugfelder, R.; Fernández, G.; Nebehay, G.; Porikli, F.; Čehovin, L. A Novel Performance Evaluation Methodology for Single-Target Trackers. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 2137–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pont-Tuset, J.; Perazzi, F.; Caelles, S.; Arbelaez, P.; Sorkine-Hornung, A.; Gool, L.V. The 2017 DAVIS Challenge on Video Object Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.00675. [Google Scholar]
- Riahi, D.; Bilodeau, G.A. Online multi-object tracking by detection based on generative appearance models. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 152, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, B.; Vo, B.; Clark, D. Performance evaluation of multi-target tracking using the OSPA metric. In Proceedings of the 2010 13th International Conference on Information Fusion, Edinburgh, UK, 26–29 July 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, B.; Vo, B.; Clark, D.; Vo, B. A Metric for Performance Evaluation of Multi-Target Tracking Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 3452–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, F.; Tong, F.; Lian, H. A comprehensive performance metric for evaluation of multi-target tracking algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2017 3rd International Conference on Information Management (ICIM), Chengdu, China, 21–23 April 2017; pp. 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokta, A.; Hocaoglu, A.K. A Track to Track Association Algorithm Based on Weighted State Correlation Similarity. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Processing (IDAP), Malatya, Turkey, 28–30 September 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Porikli, F.; Schonfeld, D. A new method for tracking performance evaluation based on a reflective model and perturbation analysis. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009; pp. 3529–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutas, E.; Nikolaidis, N.; Pitas, I. Evaluation of tracking reliability metrics based on information theory and normalized correlation. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR 2004, Cambridge, UK, 26 August 2004; Volume 4, pp. 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batyrshin, I. Constructing Time Series Shape Association Measures: Minkowski Distance and Data Standardization. In Proceedings of the 2013 BRICS Congress on Computational Intelligence and 11th Brazilian Congress on Computational Intelligence, Ipojuca, Brazil, 8–11 September 2013; pp. 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, S.; Chang, K.; Chong, C. Comparison of track fusion rules and track association metrics. In Proceedings of the 2012 15th International Conference on Information Fusion, Singapore, 9–12 July 2012; pp. 1996–2003. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, D.; Koller-Meier, E.; Rowe, D.; Moeslund, T.B.; Van Gool, L. Event-Based Tracking Evaluation Metric. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Workshop on Motion and Video Computing, Copper Mountain, CO, USA, 8–9 January 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, T.; Evans, R. A new performance metric for multiple target tracking based on optimal subpattern assignment. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Salamanca, Spain, 7–10 July 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Liu, S.; Lu, M.; Pan, Z. Effects of Improper Ground Truth on Target Tracking Performance Evaluation in Benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Software Quality, Reliability and Security Companion (QRS-C), Prague, Czech Republic, 25–29 July 2017; pp. 261–266. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Fan, X. Performance Evaluation for IR Small Target Tracking Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2011 Sixth International Conference on Image and Graphics, Hefei, China, 12–15 August 2011; pp. 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Del Amo, A.; Xu, Y.; Guari, L.; Chang, M.; Sebastian, T. A fuzzy bounding box merging technique for moving object detection. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual Meeting of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society (NAFIPS), Berkeley, CA, USA, 6–8 August 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Smeulders, A.W.M.; Chu, D.M.; Cucchiara, R.; Calderara, S.; Dehghan, A.; Shah, M. Visual Tracking: An Experimental Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 1442–1468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berman, M.; Triki, A.R.; Blaschko, M.B. The Lovasz-Softmax Loss: A Tractable Surrogate for the Optimization of the Intersection-Over-Union Measure in Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4413–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, C.-Y. Problem characterization in tracking/fusion algorithm evaluation. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2001, 16, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurecki, R.S.; Stańczyk, T.L. Analyzing driver response times for pedestrian intrusions in crash-imminent situations. In Proceedings of the 2018 XI International Science-Technical Conference Automotive Safety, Žastá, Slovakia, 18–20 April 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 1616-2004; IEEE Standard for Motor Vehicle Event Data Recorder (MVEDR). IEEE SA: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 1–171. [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hu, G.; Song, Y.; Li, G.; Xie, L. Intelligent video analysis: A Pedestrian trajectory extraction method for the whole indoor space without blind areas. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2020, 196, 102968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemery, B.; Laurent, H.; Emile, B.; Rosenberger, C. Comparative study of localization metrics for the evaluation of image interpretation systems. J. Electron. Imaging SPIE IS&T 2010, 19, 023017. [Google Scholar]
- Huttenlocher, D.; Rucklidge, W. A multi-resolution technique for comparing images using the Hausdorff distance. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, NY, USA, 15–17 June 1993; pp. 705–706. [Google Scholar]
- D’Angelo, E.; Herbin, S.; Ratiéville, M. ROBIN Challenge Evaluation Principles and Metrics. 2006. Available online: http://robin.inrialpes.fr (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Pratt, W.K.; Faugeras, O.D.; Gagalowicz, A. Visual Discrimination of Stochastic Texture Fields. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1978, 8, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


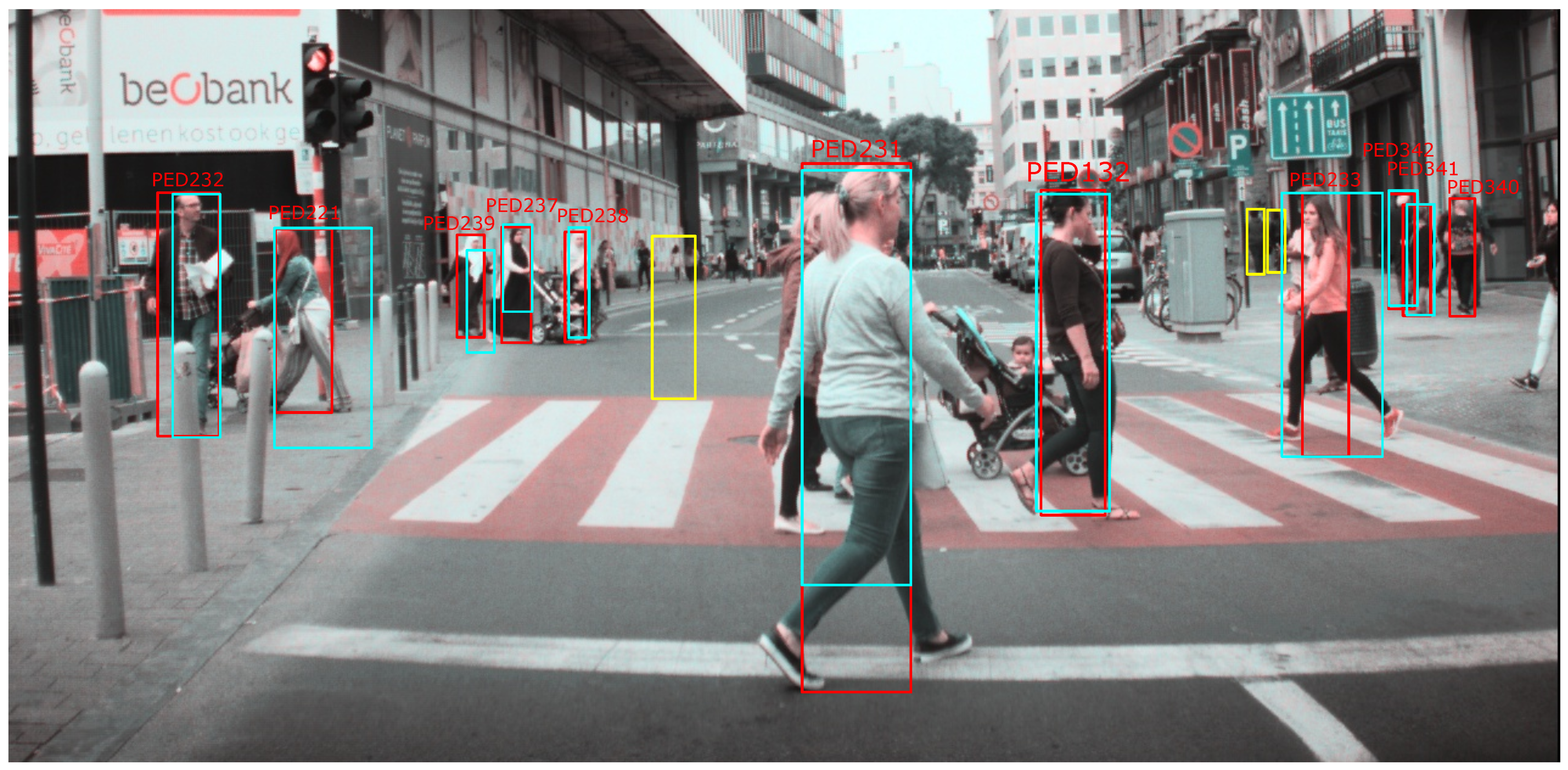
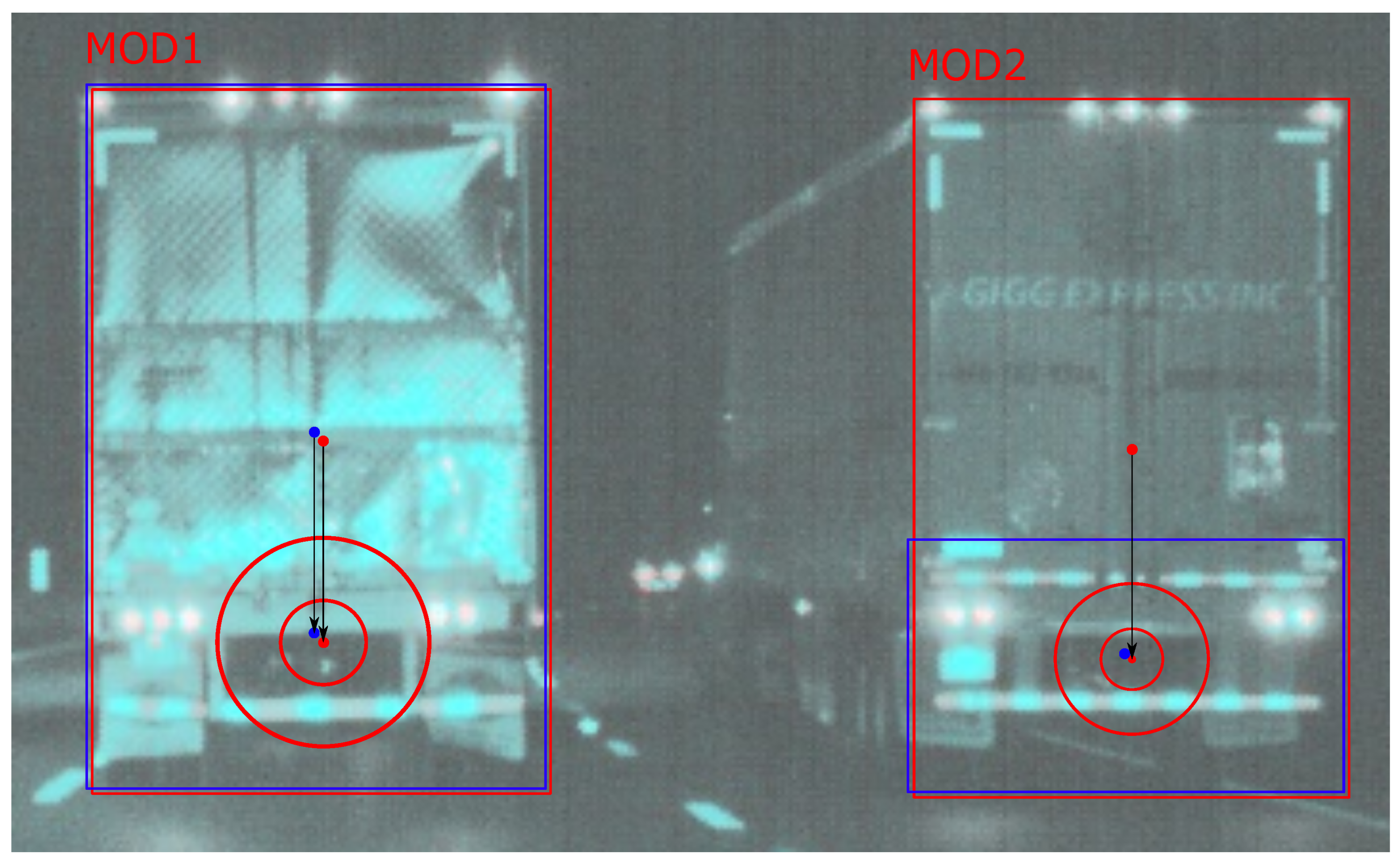
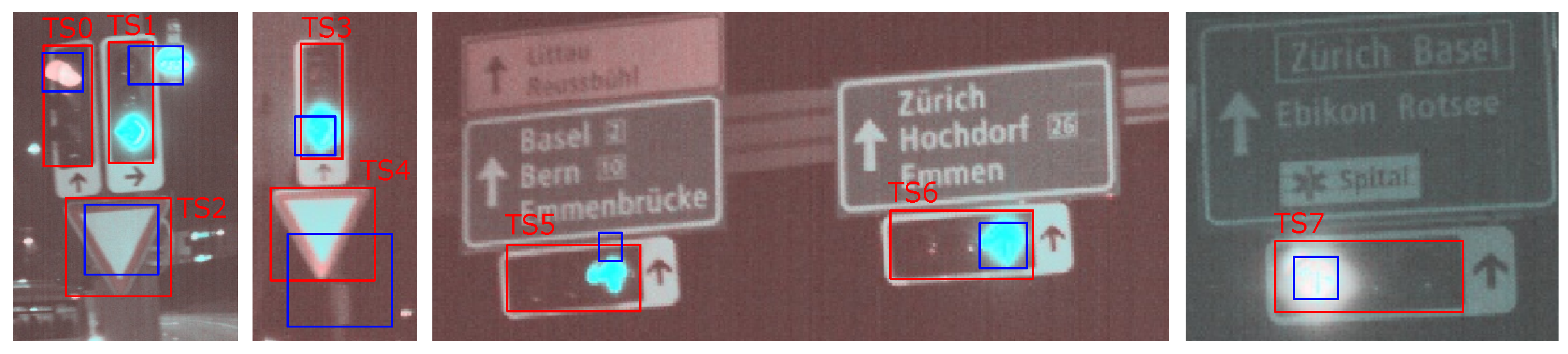

| PED | Jaccard | General | Distance | Area | Shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 221 | 43.6% | 41.3% | 37.0% | 43.6% | 85.3% |
| 233 | 39.0% | 63.3% | 99.0% | 39.0% | 64.4% |
| 239 | 36.7% | 47.4% | 34.1% | 98.6% | 99.9% |
| 231 | 80.4% | 39.5% | 28.3% | 80.4% | 97.8% |
| 132 | 79.1% | 94.5% | 99.8% | 85.8% | 97.7% |
| 237 | 70.6% | 35.9% | 25.2% | 80.7% | 97.0% |
| 238 | 56.1% | 86.4% | 78.4% | 100% | 100% |
| 232 | 69.4% | 86.8% | 99.7% | 69.4% | 95.9% |
| 342 | 80.4% | 97.4% | 96.2% | 98.9% | 98.8% |
| 341 | 70.4% | 97.8% | 96.3% | 100% | 100% |
| 340 | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| MOD | Jaccard | General | Distance | Area | Shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 94.4% | 99.5% | 99.4% | 99.5% | 100% |
| 2 | 32.7% | 36.6% | 98.5% | 33.0% | 9.1% |
| TS | Jaccard | General | Distance | Area | Shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 21.7% | 22.6% | 99.8% | 23.3% | 8.6% |
| 1 | 9.9% | 4.5% | 34.8% | 28.2% | 0.9% |
| 2 | 41.7% | 70.5% | 96.3% | 41.7% | 100.0% |
| 3 | 22.6% | 40.7% | 91.6% | 31.6% | 28.4% |
| 4 | 26.5% | 61.7% | 46.6% | 94.3% | 99.3% |
| 5 | 4.2% | 13.4% | 26.9% | 10.5% | 5.2% |
| 6 | 19.0% | 30.8% | 100.0% | 19.0% | 25.3% |
| 7 | 15.4% | 26.0% | 100.0% | 15.4% | 18.2% |
| Measure Name | Scale Invariance | Position Sensitive/ Separable Influence | Size Sensitive/ Separable Influence | Shape Sensitive/ Separable Influence | Rotation Sensitive/ Separable Influence | Continuity for Separated Boxes | Adaptiv Focus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hausdorff [53] | − | +/− | +/− | +/− | +/− | + | − |
| RobLoc [54] | + | +/+ | − | − | − | + | − |
| RobCor [54] | + | − | − | − | − | + | − |
| RobCom [54] | + | − | + | − | − | + | − |
| FOM [55] | + | +/− | +/− | +/− | +/− | + | − |
| Hafiane [52] | + | +/− | +/− | +/− | +/− | − | − |
| Jaccard (1) | + | +/− | +/− | +/− | +/− | + | − |
| Shape (3) | + | − | − | +/+ | − | + | − |
| Area (2) | + | − | +/+ | − | − | + | − |
| Distance (6) | + | +/+ | − | − | − | + | + |
| Velocity (20) | + | −/− | −/− | −/− | +/+ | + | + |
| GMOS (13) | + | +/+ | +/+ | +/+ | −/+ | + | + |
| 0.000 | 0.020 | 0.025 | 0.033 | 0.050 | 0.067 | 0.100 | 0.143 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowalczyk, P.; Izydorczyk, J.; Szelest, M. Evaluation Methodology for Object Detection and Tracking in Bounding Box Based Perception Modules. Electronics 2022, 11, 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081182
Kowalczyk P, Izydorczyk J, Szelest M. Evaluation Methodology for Object Detection and Tracking in Bounding Box Based Perception Modules. Electronics. 2022; 11(8):1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081182
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowalczyk, Paweł, Jacek Izydorczyk, and Marcin Szelest. 2022. "Evaluation Methodology for Object Detection and Tracking in Bounding Box Based Perception Modules" Electronics 11, no. 8: 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081182
APA StyleKowalczyk, P., Izydorczyk, J., & Szelest, M. (2022). Evaluation Methodology for Object Detection and Tracking in Bounding Box Based Perception Modules. Electronics, 11(8), 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081182







