A Lightweight Sensitive Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensor for Monitoring Loop Drive Technology in Table Tennis Training
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Characterization and Measurement
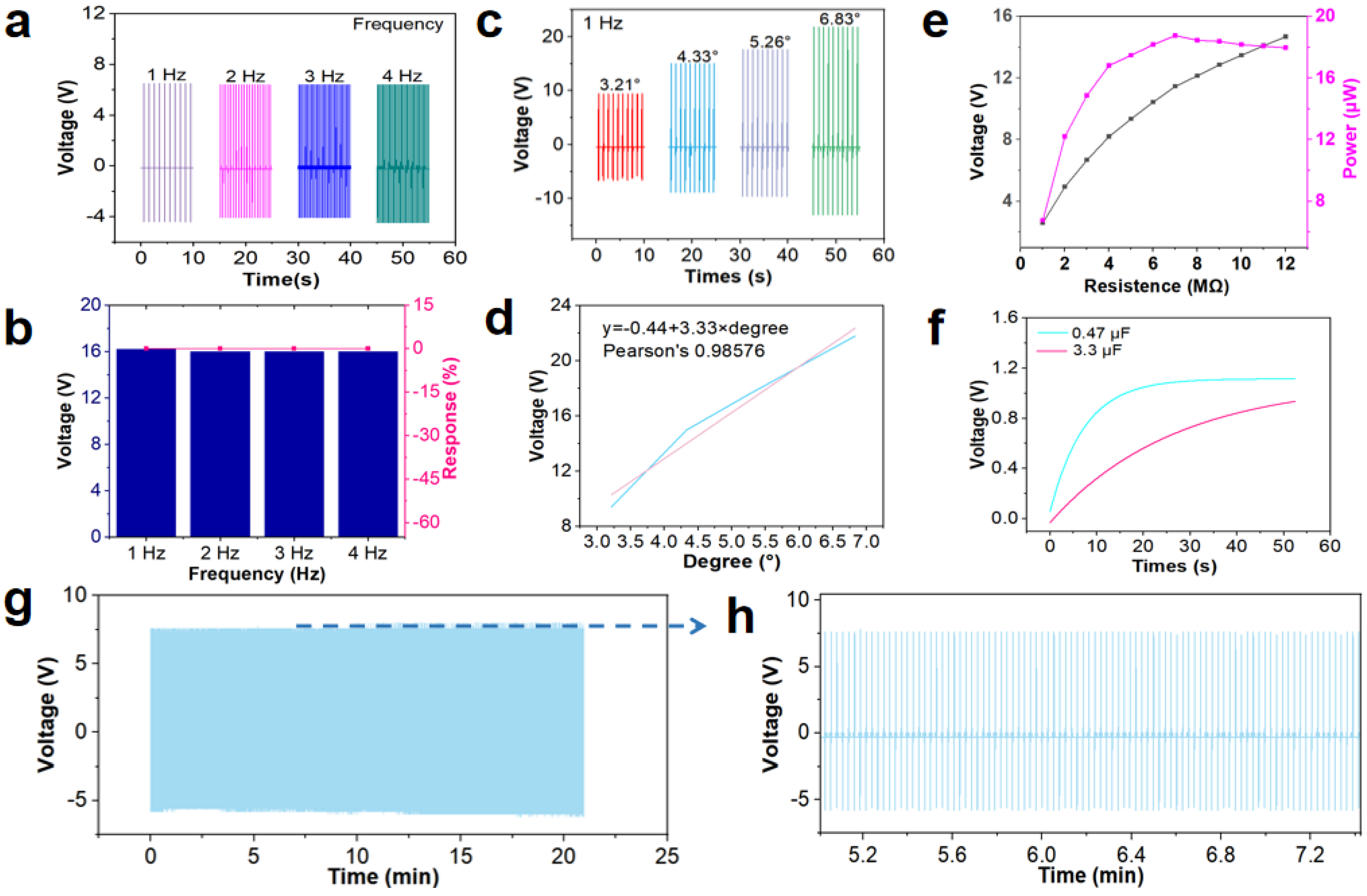
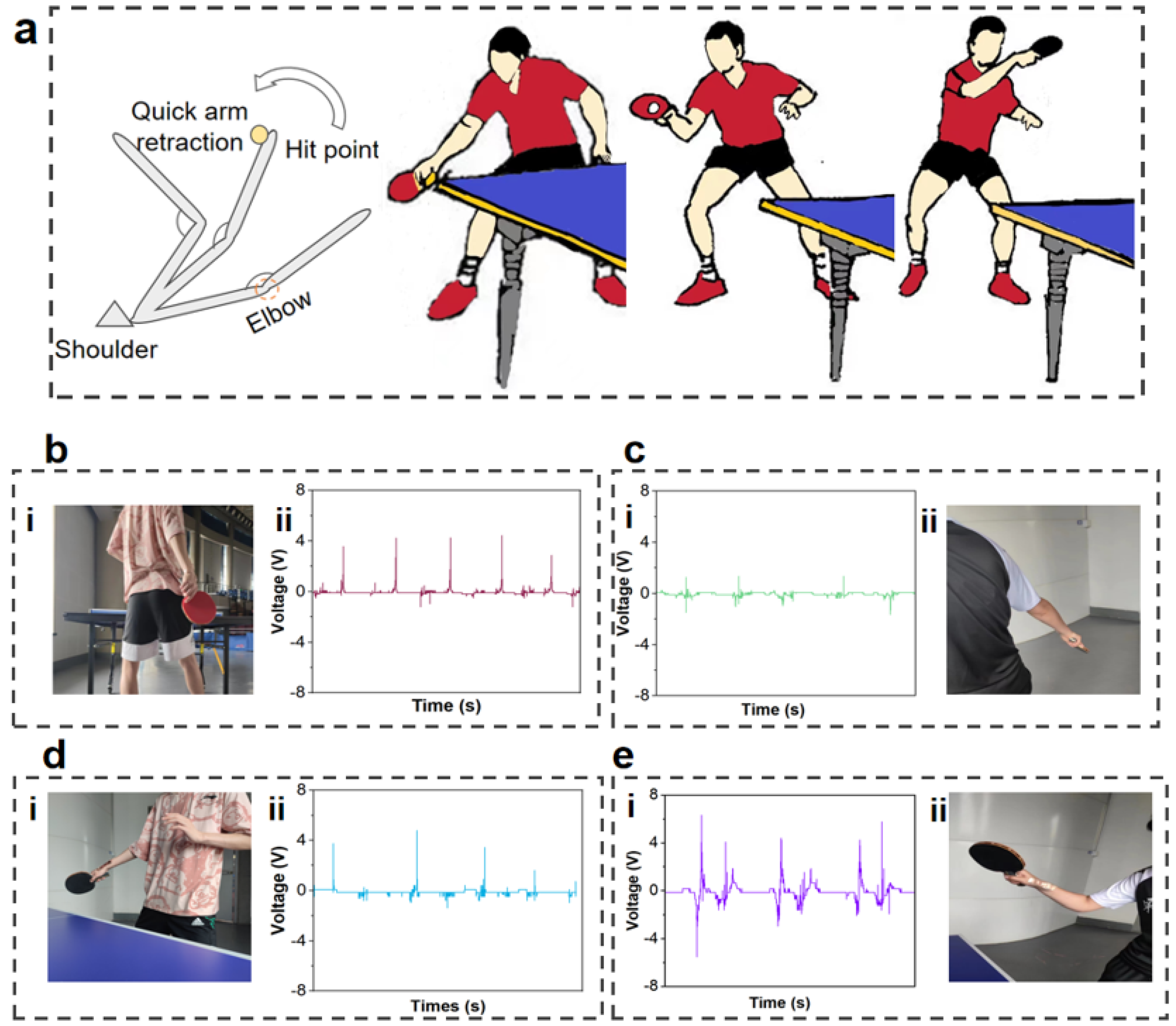
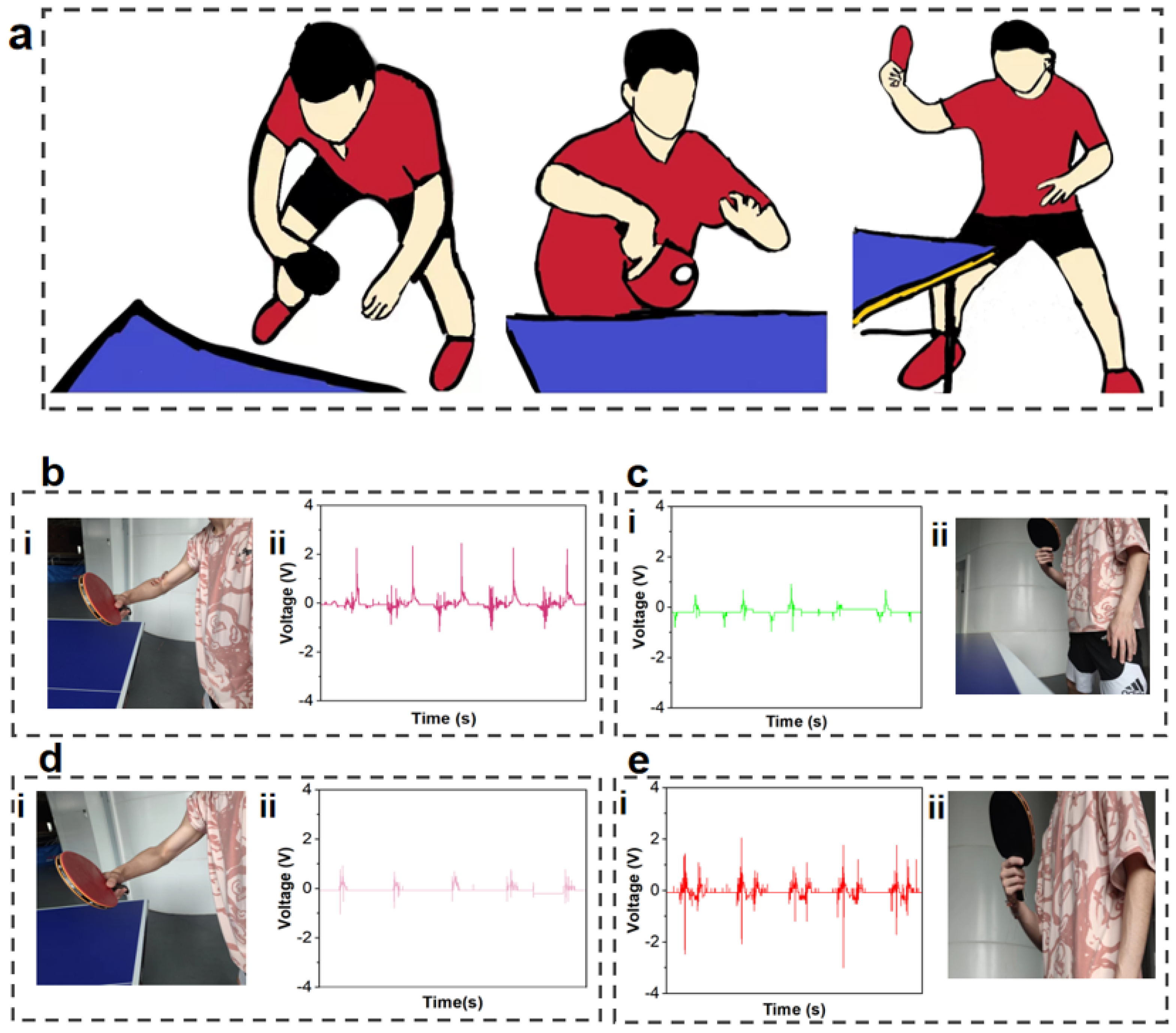
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, A.C.; Han, K.; Jiang, T.; Lai, Q.; Bai, Y.; Tang, W.; Fan, F.R.; et al. Flexible and durable wood-based triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered sensing in athletic big data analytics. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, J.; Ma, H. The Internet of things and the development of network technology in China. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1995, 040048. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Tang, C. Intelligent Bus Operation Optimization by Integrating Cases and Data Driven Based on Business Chain and Enhanced Quantum Genetic Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 9869–9882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syu, J.H.; Wu, M.E.; Srivastava, G.; Chao, C.-F.; Lin, J.C.-W. An IoT-Based Hedge System for Solar Power Generation. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 10347–10355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.; Sarma, S. A Cognitive Protection System for the Internet of Things. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2019, 17, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.D.; Dhiman, G.; Sharma, R. Internet of Things for sustaining a smart and secure healthcare system. Sustain. Comput-Infor. 2022, 33, 100622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Park, E. Smart home and internet of things: A bibliometric study. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 301, 126908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, P.K.D.; Solanki, A.; Debnath, A.; Nayyar, A.; El-Sappagh, S.; Kwak, K.S. Advancing Modern Healthcare With Nanotechnology, Nanobiosensors, and Internet of Nano Things: Taxonomies, Applications, Architecture, and Challenges. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 65230–65266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Full-scene network security protection system based on ubiquitous power Internet of things. Int. J.Commun. Syst. 2022, 35, e4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.G.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhang, Z.L.; Yu, Y.; Li, K. A New Framework of Intelligent Public Transportation System Based on the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 55290–55304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Jia, C.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, S.; Mao, Y. A Flexible TENG Based on Micro-Structure Film for Speed Skating Techniques Monitoring and Biomechanical Energy Harvesting. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, C.; Zhao, T.; Bian, M.; Jia, C.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, Y. A Self-Powered Portable Flexible Sensor of Monitoring Speed Skating Techniques. Biosensors 2021, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Jia, C.; Bian, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B. A Portable and Flexible Self-Powered Multifunctional Sensor for Real-Time Monitoring in Swimming. Biosensors 2021, 11, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Huang, Z. Wearable Device Monitoring Exercise Energy Consumption Based on Internet of Things. Complexity 2021, 2021, 8836723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kadry, S.N.; Raj, E.D. Continuous health monitoring of sportsperson using IoT devices based wearable technology. Comput. Commun. 2020, 160, 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Z. Analysis of real-time heartbeat monitoring using wearable device Internet of Things system in sports environment. Comput. Intell. 2021, 37, 1080–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; You, Y. Design and data analysis of wearable sports posture measurement system based on Internet of Things. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, F.; Jia, C.; Zhao, T.; Mao, Y. A Stretchable and Self-Healing Hybrid Nano-Generator for Human Motion Monitoring. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Fu, W.; Dai, B.; Nassis, G.P.; Ainsworth, B.E. Energetic Profile in Forehand Loop Drive Practice with Well-Trained, Young Table Tennis Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.R.; Tian, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator! Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Du, C.; Fu, J.; Xu, Z. Milk-based triboelectric nanogenerator on paper for harvesting energy from human body motion. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salauddin, M.; Rana, S.M.S.; Sharifuzzaman, M.; Rahman, M.T.; Park, C.; Cho, H.; Maharjan, P.; Bhatta, T.; Park, J.Y. A Novel MXene/Ecoflex Nanocomposite-Coated Fabric as a Highly Negative and Stable Friction Layer for High-Output Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2002832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, C.; Zhao, T.; Huang, C.; Li, C.; Ba, N.; Che, T.; Chen, S. Nanogenerator-Based Wireless Intelligent Motion Correction System for Storing Mechanical Energy of Human Motion. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, C.; Ouyang, B.; Zhao, T.; Li, C.; Ba, N.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Che, T.; et al. A Flexible Lightweight Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Protector and Scoring System in Taekwondo Competition Monitoring. Electronics 2022, 11, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Yue, W.; Zhao, T.; Shen, M.; Liu, B.; Chen, S. A Self-Powered Biosensor for Monitoring Maximal Lactate Steady State in Sport Training. Biosensors 2020, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Fu, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhao, X.; Jiao, C.; Du, A.; Wang, Q.; Mao, Y.; Liu, B. Wearable biosensors for real-time sweat analysis and body motion capture based on stretchable fiber-based triboelectric nanogenerators. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 205, 114115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhao, T.; Xing, R.; Mao, Y.; Zhao, C. A Flexible and Stretchable Self-Powered Nanogenerator in Basketball Passing Technology Monitoring. Electronics 2021, 10, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Jia, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Portable Mobile Gait Monitor System Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Monitoring Gait and Powering Electronics. Energies 2021, 14, 4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Shen, M.; Mao, L.; Mao, Y.; Ma, H. Self-powered Biosensor Big Data Intelligent Information Processing System for Real-time Motion Monitoring. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2020, 646, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, A.; Zhai, J.; Wang, Z.L. Recent Progress of Functional Fiber and Textile Triboelectric Nanogenerators: Towards Electricity Power Generation and Intelligent Sensing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2021, 3, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, Z. A recyclable triboelectric nanogenerator integrated into insole for sensing human motion. Mater. Technol. 2022, 37, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, X.; Fu, X.; Hu, Y. Expandable microsphere-based triboelectric nanogenerators as ultrasensitive pressure sensors for respiratory and pulse monitoring. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Gao, W.; Wang, Z.L. The Triboelectric Nanogenerator as an Innovative Technology toward Intelligent Sports. Adv.Mater 2021, 33, 2004178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Ma, Y. Light-Weight, Self-Powered Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Big Data Analytics in Sports. Electronics 2021, 10, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Cheng, F.; Hu, X.; Huang, B.; Xu, B.; Li, Z.; Yan, X.; Yuan, D.; Wu, W.; Shi, Q. A Two-Degree-of-Freedom Cantilever-Based Vibration Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Low-Frequency and Broadband Operation. Electronics 2019, 8, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X. Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sensors 2021, 21, 230504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lyu, X.; Sun, D.; Baker, J.S.; Gu, Y. The kinematic analysis of the lower limb during topspin forehand loop between different level table tennis athletes. Peerj 2021, 9, e10841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, S.; Ren, J.; Lake, M.; Gu, Y. Comparison of center of pressure trajectory characteristics in table tennis during topspin forehand loop between superior and intermediate players. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2016, 11, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Gan, Y.; Sun, F.; Sun, Z. A Lightweight Sensitive Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensor for Monitoring Loop Drive Technology in Table Tennis Training. Electronics 2022, 11, 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193212
Zhang J, Xu Q, Gan Y, Sun F, Sun Z. A Lightweight Sensitive Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensor for Monitoring Loop Drive Technology in Table Tennis Training. Electronics. 2022; 11(19):3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193212
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiayun, Qiushuang Xu, Yuyang Gan, Fengxin Sun, and Zhe Sun. 2022. "A Lightweight Sensitive Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensor for Monitoring Loop Drive Technology in Table Tennis Training" Electronics 11, no. 19: 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193212
APA StyleZhang, J., Xu, Q., Gan, Y., Sun, F., & Sun, Z. (2022). A Lightweight Sensitive Triboelectric Nanogenerator Sensor for Monitoring Loop Drive Technology in Table Tennis Training. Electronics, 11(19), 3212. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11193212






