Recognition of Emotion with Intensity from Speech Signal Using 3D Transformed Feature and Deep Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. SER with Machine Learning (ML)
2.2. SER with Deep Learning (DL) and Signal Transformation
3. Recognition of Emotion and Its Intensity from Speech (REIS) Method
4. Experimental Studies
4.1. Benchmark Dataset and Experimental Setup
4.2. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.2.1. Outcomes of Single DL Framework
4.2.2. Outcomes of Cascaded DL Framework
4.2.3. Performance Comparison between the Single DL and Cascaded DL Frameworks
4.3. Performance Comparison with Existing Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Review of Background Methods
Appendix A.1. Speech Signal Processing and Transformation
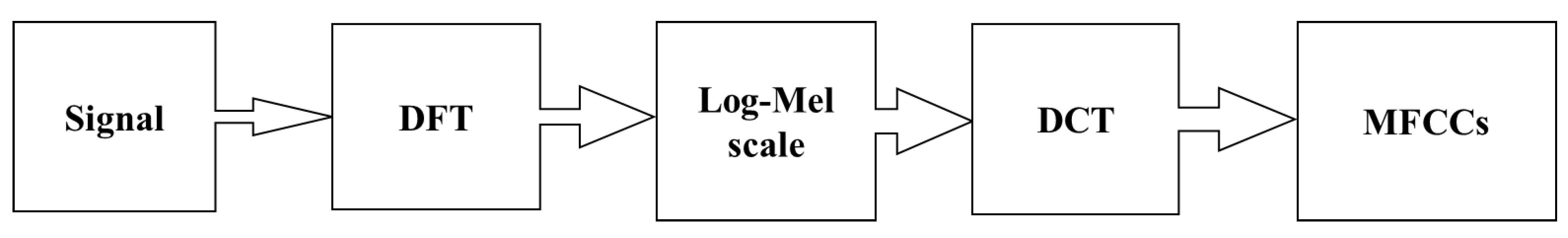
Appendix A.2. Deep Learning Models
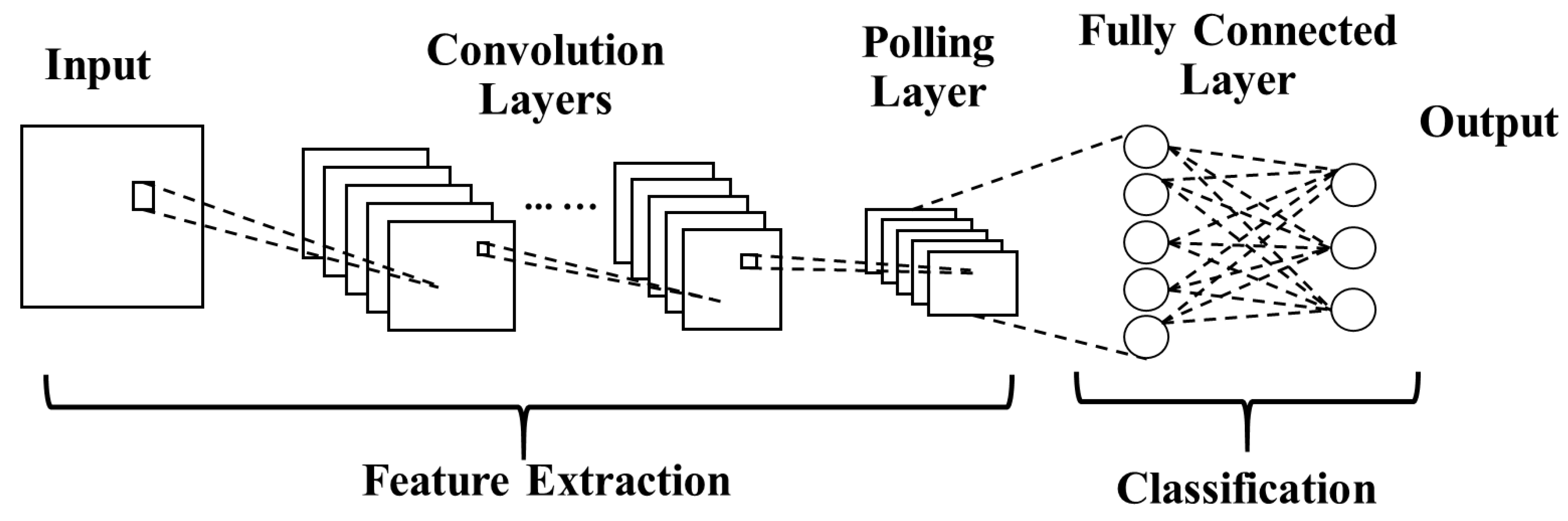


References
- Sahidullah, M.; Saha, G. Design, analysis and experimental evaluation of block based transformation in MFCC computation for speaker recognition. Speech Commun. 2012, 54, 543–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, M. The Feedforward Short-Time Fourier Transform. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2016, 63, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, S.; Reddy, V.S. Hybrid deep network scheme for emotion recognition in speech. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2019, 12, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustaqeem; Kwon, S. A CNN-assisted enhanced audio signal processing for speech emotion recognition. Sensors 2020, 20, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.K.; Islam, N.; Ahmed, M.R.; Islam, S.; Shatabda, S.; Islam, A.K.M.M. BanglaSER: A speech emotion recognition dataset for the Bangla language. Data Brief 2022, 42, 108091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, M. Weakly Supervised Emotion Intensity Prediction for Recognition of Emotions in Images. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 23, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsu, R.; Solomides, A.; Tosa, N. Emotion recognition and its application to computer agents with spontaneous interactive capabilities. In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Third Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (Cat. No.99TH8451), Copenhagen, Denmark, 13–15 September 1999; Volume 2, pp. 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atila, O.; Şengür, A. Attention guided 3D CNN-LSTM model for accurate speech based emotion recognition. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 182, 108260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Cummins, N.; Wang, H.; Tao, J.; Schuller, B.W. Combining a parallel 2D CNN with a self-attention Dilated Residual Network for CTC-based discrete speech emotion recognition. Neural Netw. 2021, 141, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsa, S.; Shahin, I.; Iraqi, Y.; Werghi, N. Emotion Recognition from Speech Using Wavelet Packet Transform Cochlear Filter Bank and Random Forest Classifier. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 96994–97006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.P.P. Acoustic feature selection for automatic emotion recognition from speech. Inf. Process. Manag. 2009, 45, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Gomathi, S.; Sasikala, S.; Saravanan, T.R. Automatic speech emotion detection using hybrid of gray wolf optimizer and naïve Bayes. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, A.; Sharmy Roy, S.; Tamil Selvi, S. SVM Scheme for Speech Emotion Recognition using MFCC Feature. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2013, 69, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Singh, P.K.; Ahmadian, A.; Ferrara, M.; Sarkar, R. A Hybrid Meta-Heuristic Feature Selection Method Using Golden Ratio and Equilibrium Optimization Algorithms for Speech Emotion Recognition. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 200953–200970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanjewar, R.B.; Mathurkar, S.; Patel, N. Implementation and comparison of speech emotion recognition system using Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) and K-Nearest Neighbor (K-NN) techniques. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 49, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Tian, H.; Chang, C.-C.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Du, Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, C.C. Steganalysis of Adaptive Multi-Rate Speech Based on Extreme Gradient Boosting. Electronics 2020, 9, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, R.; Pandey, D.; Kalia, A.; Zachariah, B.J.; Sandhu, I.; Abrol, D. Speech based Emotion Recognition using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Mysore Sub Section International Conference (MysuruCon), Hassan, India, 24–25 October 2021; pp. 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Dang, H.; Jiang, R.; Hao, Y.; Xue, C.; Gu, W. Multi-layer hybrid fuzzy classification based on svm and improved pso for speech emotion recognition. Electronics 2021, 10, 2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Nair, S.B. Novel emotion engine for robot and its parameter tuning by bacterial foraging. In Proceedings of the 2009 5th International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics, Imisoara, Romania, 28–29 May 2009; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mao, X.; Chen, L. Speech emotion recognition using deep 1D & 2D CNN LSTM networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 47, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.; Rana, R.; Khalifa, S.; Jurdak, R.; Epps, J. Direct modelling of speech emotion from raw speech. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association: Crossroads of Speech and Language (INTERSPEECH 2019), Graz, Austria, 15–19 September 2019; pp. 3920–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, L.T.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Le, T.D.T. Emotion recognition with capsule neural network. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2022, 41, 1083–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilescu, M.; Vizireanu, N. Feedforward neural network-based architecture for predicting emotions from speech. Data 2019, 4, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, B.; Swain, M.; Mustaqeem. Advanced Fusion-Based Speech Emotion Recognition System Using a Dual-Attention Mechanism with Conv-Caps and Bi-GRU Features. Electronics 2022, 11, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Kim, Y.J. Attention-LSTM-Attention model for speech emotion recognition and analysis of IEMOCAP database. Electronics 2020, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Shen, X. Research on Speech Emotion Recognition Based on AA-CBGRU Network. Electronics 2022, 11, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cummins, N.; Sun, S.; Wang, H.; Tao, J.; Schuller, B.W. Self-attention transfer networks for speech emotion recognition. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2021, 3, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.; Lee, C. Cascaded convolutional neural network architecture for speech emotion recognition in noisy conditions. Sensors 2021, 21, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gou, R.; Shang, J.; Shen, F.; Wu, Y.; Dai, G. Pre-trained Deep Convolution Neural Network Model with Attention for Speech Emotion Recognition. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 643202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.X.; Zhang, P.W.; Mao, Z.J.; Huang, Y.F.; Jiang, D.M.; Zhang, Y.N. Accurate EEG-Based Emotion Recognition on Combined Features Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44317–44328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Iqbal, M.Z.; Selim, M.R.; Rashid, M.M.; Rahman, M.S. Bangla Speech Emotion Recognition and Cross-Lingual Study Using Deep CNN and BLSTM Networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Ahmad, F.; Rauqir, R.; Abid, F.; Naseer, M.; Haq, E. Emotion Recognition Based on Musical Instrument using Deep Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT), Islamabad, Pakistan, 13–14 December 2021; pp. 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- Hajarolasvadi, N.; Demirel, H. 3D CNN-based speech emotion recognition using k-means clustering and spectrograms. Entropy 2019, 21, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustaqeem; Kwon, S. MLT-DNet: Speech emotion recognition using 1D dilated CNN based on multi-learning trick approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 167, 114177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Hussain, F.; Baloch, N.K.; Raja, F.R.; Yu, H.; Zikria, Y. Bin Impact of feature selection algorithm on speech emotion recognition using deep convolutional neural network. Sensors 2020, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, R.; Wu, Q. MPCE: A Maximum Probability Based Cross Entropy Loss Function for Neural Network Classification. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146331–146341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, A.; Mori, T.; Kobashikawa, S.; Toda, T. Speech emotion recognition based on listener-dependent emotion perception models. APSIPA Trans. Signal Inf. Process. 2021, 10, E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, S.; Russo, F. The Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustaqeem; Sajjad, M.; Kwon, S. Clustering-Based Speech Emotion Recognition by Incorporating Learned Features and Deep BiLSTM. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 79861–79875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamulevičius, G.; Korvel, G.; Yayak, A.B.; Treigys, P.; Bernatavičienė, J.; Kostek, B. A study of cross-linguistic speech emotion recognition based on 2d feature spaces. Electronics 2020, 9, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFee, B.; Raffel, C.; Liang, D.; Ellis, D.; McVicar, M.; Battenberg, E.; Nieto, O. Librosa: Audio and Music Signal Analysis in Python. In Proceedings of the 14th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 6–12 July 2015; pp. 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Walt, S.; Colbert, S.C.; Varoquaux, G. The NumPy array: A structure for efficient numerical computation. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 13, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, T.B. kerasR: R Interface to the Keras Deep Learning Library. J. Open Source Softw. 2017, 2, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M. TensorFlow: Learning functions at scale. ACM SIGPLAN Not. 2016, 51, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regis, F.; Alves, V.; Passos, R.; Vieira, M. The Newton Fractal’s Leonardo Sequence Study with the Google Colab. Int. Electron. J. Math. Educ. 2020, 15, em0575. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.; Yan, T.; Yuan, F.; Wei, H. Speech Emotion Recognition from 3D Log-Mel Spectrograms with Deep Learning Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 125868–125881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, F.; Zameer, A.; Muneeb, M. Predictions for COVID-19 with deep learning models of LSTM, GRU and Bi-LSTM. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Feature Block (FB) | Layer and Type | Kernel Size | Stride Size | Input Shape | Output Shape |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB-1 | Conv3D | 3 × 3 × 3 | 1 × 1 × 1 | 128 × 512 × 3 | 128 × 512 × 3 @ 64 |
| Max-Pooling3D | 2 × 2 × 1 | 2 × 2 × 1 | 128 × 512 × 3 @ 64 | 64 × 256 × 3 @ 64 | |
| FB-2 | Conv3D | 3 × 3 × 3 | 1 × 1 × 1 | 64 × 256 × 3 @ 64 | 64 × 256 × 3 @ 64 |
| Max-Pooling 3D | 4 × 4 × 1 | 4 × 4 × 1 | 64 × 256 × 3 @ 64 | 16 × 64 × 3 @ 64 | |
| FB-3 | Conv3D | 3 × 3 × 3 | 1 × 1 × 1 | 16 × 64 × 3 @ 64 | 16 × 64 × 3 @ 128 |
| Max-Pooling 3D | 4 × 4 × 1 | 4 × 4 × 1 | 16 × 64 × 3 @ 128 | 4 × 16 × 3 @ 128 | |
| FB-4 | Conv3D | 3 × 3 × 3 | 1 × 1 × 1 | 4 × 16 × 3 @ 128 | 4 × 16 × 3 @128 |
| Max-Pooling 3D | 4 × 4 × 1 | 4 × 4 × 1 | 4 × 16 × 3 @ 128 | 1 × 4 × 3 @ 128 | |
| TDF | - | - | 1 × 4 × 3 @ 128 | 1536 | |
| Bi-LSTM | - | - | 1536 | 512 | |
| FC | - | - | 512 | 9/5/2 |
| Emotion | Emotion Intensity | Neutral | Happy | Sad | Angry | Fearful | Category Miss | Intensity Miss | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Normal | Strong | Normal | Strong | Normal | Strong | Normal | Strong | |||||
| Neutral | - | 32 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 38 |
| Happy | Normal | 1 | 29 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 38 |
| Strong | 0 | 2 | 31 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 38 | |
| Sad | Normal | 2 | 0 | 0 | 30 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 38 |
| Strong | 1 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 38 | |
| Angry | Normal | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 28 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 38 |
| Strong | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 38 | |
| Fearful | Normal | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 2 | 10 | 2 | 38 |
| Strong | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 31 | 4 | 3 | 38 | |
| Total= | 46 | 27 | 342 | ||||||||||
| Emotion | Neutral | Happy | Sad | Angry | Fearful | Category Miss | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral | 36 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 38 |
| Happy | 3 | 68 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 8 | 76 |
| Sad | 2 | 1 | 71 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 76 |
| Angry | 1 | 4 | 1 | 69 | 1 | 7 | 76 |
| Fearful | 0 | 3 | 9 | 0 | 64 | 12 | 76 |
| Total= | 34 | 342 | |||||
| Emotion | Emotion Intensity | Neutral | Happy | Sad | Angry | Fearful | Category Miss | Intensity Miss | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Normal | Strong | Normal | Strong | Normal | Strong | Normal | Strong | |||||
| Neutral | - | 36 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | - | 38 |
| Happy | Normal | 1 | 33 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 38 |
| Strong | 2 | 2 | 32 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 38 | |
| Sad | Normal | 1 | 1 | 0 | 32 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 38 |
| Strong | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 38 | |
| Angry | Normal | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 33 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 38 |
| Strong | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 35 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 38 | |
| Fearful | Normal | 0 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 38 |
| Strong | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 33 | 4 | 1 | 38 | |
| Total= | 34 | 12 | 342 | ||||||||||
| DL Model | Single DL Framework | Cascaded DL Framework | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category Miss | Intensity Miss | Accuracy (%) | Category Miss | Intensity Miss | Accuracy (%) | |
| Fold 1 | 61 | 34 | 77.54 | 48 | 18 | 84.40 |
| Fold 2 | 75 | 33 | 74.47 | 49 | 16 | 84.63 |
| Fold 3 | 58 | 30 | 79.20 | 40 | 14 | 87.23 |
| Fold 4 | 74 | 30 | 75.41 | 47 | 16 | 85.11 |
| Average | 67.00 | 31.75 | 76.66 | 46.00 | 16.00 | 85.34 |
| Work Ref., Year | Feature Transformation | Classification Model | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. [30], 2019 | Log-Mel spectrums | 2 CNN + 2 FC | 76.93 |
| Zhao et al. [20], 2019 | Log-Mel spectrums | 4 CNN + LSTM | 77.96 |
| Mustaqeem and Kwon [4], 2020 | Log-Mel spectrums | 7 CNN + 2 FC | 63.94 |
| Sultana et al. [31], 2021 | Log-Mel spectrums | 4 CNN + TDF + Bi-LSTM | 82.69 |
| Proposed Method (Stage 1 of Cascaded Framework) | MFCC + STFT+ Chroma STFT | 4 3DCNN + TDF + Bi-LSTM | 90.06 |
| Work Ref., Year | Feature Transformation | DL Model | Single DL Framework | Cascaded DL Framework | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category Miss | Intensity Miss | Accuracy (%) | Category Miss | Intensity Miss | Accuracy (%) | |||
| Chen et al. [30], 2019 | Log-Mel spectrums | 2 CNN + 2 FC | 194 | 32 | 33.91 | 77 | 22 | 71.05 |
| Zhao et al. [20], 2019 | Log-Mel spectrums | 4 CNN + LSTM | 57 | 27 | 75.43 | 51 | 26 | 77.48 |
| Mustaqeem and Kwon [4], 2020 | Log-Mel spectrums | 7 CNN + 2 FC | 86 | 26 | 67.25 | 69 | 25 | 72.51 |
| Sultana et al. [31], 2021 | Log-Mel spectrums | 4 CNN + TDF+ Bi-LSTM | 61 | 21 | 76.02 | 45 | 19 | 81.28 |
| Proposed REIS | MFCC + STFT+ Chroma STFT | 4 3DCNN + TDF+ Bi-LSTM | 46 | 27 | 78.65 | 34 | 12 | 87.71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.R.; Akhand, M.A.H.; Kamal, M.A.S.; Yamada, K. Recognition of Emotion with Intensity from Speech Signal Using 3D Transformed Feature and Deep Learning. Electronics 2022, 11, 2362. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11152362
Islam MR, Akhand MAH, Kamal MAS, Yamada K. Recognition of Emotion with Intensity from Speech Signal Using 3D Transformed Feature and Deep Learning. Electronics. 2022; 11(15):2362. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11152362
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md. Riadul, M. A. H. Akhand, Md Abdus Samad Kamal, and Kou Yamada. 2022. "Recognition of Emotion with Intensity from Speech Signal Using 3D Transformed Feature and Deep Learning" Electronics 11, no. 15: 2362. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11152362
APA StyleIslam, M. R., Akhand, M. A. H., Kamal, M. A. S., & Yamada, K. (2022). Recognition of Emotion with Intensity from Speech Signal Using 3D Transformed Feature and Deep Learning. Electronics, 11(15), 2362. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11152362







