Abstract
COVID-19 has been spreading rapidly, affecting billions of people globally, with significant public health impacts. Biomedical imaging, such as computed tomography (CT), has significant potential as a possible substitute for the screening process. Because of this, automatic segmentation of images is highly desirable as clinical decision support for an extensive evaluation of disease control and monitoring. It is a dynamic tool and performs a central role in precise or accurate segmentation of infected areas or regions in CT scans, thus helping in screening, diagnosing, and disease monitoring. For this purpose, we introduced a deep learning framework for automated segmentation of COVID-19 infected lesions/regions in lung CT scan images. Specifically, we adopted a segmentation model, i.e., U-Net, and utilized an attention mechanism to enhance the framework’s ability for the segmentation of virus-infected regions. Since all of the features extracted or obtained from the encoders are not valuable for segmentation; thus, we applied the U-Net architecture with a mechanism of attention for a better representation of the features. Moreover, we applied a boundary loss function to deal with small and unbalanced lesion segmentation’s. Using different public CT scan image data sets, we validated the framework’s effectiveness in contrast with other segmentation techniques. The experimental outcomes showed the improved performance of the presented framework for the automated segmentation of lungs and infected areas in CT scan images. We also considered both boundary loss and weighted binary cross-entropy dice loss function. The overall dice accuracies of the framework are 0.93 and 0.76 for lungs and COVID-19 infected areas/regions.
1. Introduction
The coronavirus epidemic was reported in late December 2019 in Wuhan city; after its emergence, it spread rapidly worldwide [1]. It is a deadly viral infection/illness caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). It retains several properties that make it highly contagious; therefore, enforcing people to adopt government safety and prevention measures such as social distancing [2,3] and increasing the necessity for rapid and reliable diagnosis of the infection are necessary. Based on the reports and statistics of the World Health Organization shown in Figure 1 (https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/covid/, accessed on 2 July 2022), over 545,226,550 people around the world have been affected by COVID-19 infections and 6,334,728 have lost their lives. Thus, reliable and timely testing is essential to controlling the transmission and spread of this deadly virus.
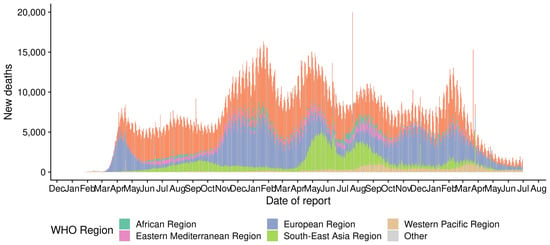
Figure 1.
Recent number of confirmed cases in different regions around the world, from the date of report until 2 July 2022.
Biomedical image technology has been developing over the past few years as a promising tool for automatically quantifying and diagnosing different diseases. Medical imaging data are obtained via magnetic resonance imaging, CT, X-ray, microscopy, and pathology, which are used to perform particularly diagnosis-oriented investigations, analyzing important diseases such as human brain disorders and different kinds of cancer. Lung and chest CT imaging is also strongly suggested as a regular/conventional diagnostic tool for pneumonia and is now also recommended for identifying COVID-19 infection as an early assessment and for follow-up cases. These are very helpful in identifying common radio-graphic characteristics of COVID-19 infections [4]. Furthermore, a systematic study [5] revealed that using CT images of the chest to monitor COVID-19 even before clinical signs and symptoms are recognized should be treated with caution. More particularly, CT scan images of patients show ground-glass opacity or bilateral patchy shadows on the infected region [6], which are usually not visible in standard X-ray images [7]. Medical specialists usually need to examine several CT scans, which is a time-consuming and error-prone method. For this purpose, automated deep learning techniques are introduced in order to segment regions of interest (ROIs) of various sizes and shapes, for example, the lungs, buds, and lesions, in high-resolution CT scan images. These techniques may help medical specialists in the diagnostic process. In the literature, researchers presented various methods based on image processing, machine learning, and deep learning for the automatic segmentation of CT scans [8,9]. However, deep learning models/techniques have surpassed feature-based methods, which have been widely and successfully used/implemented to automatically segment ROIs in CT scan images: particularly, applications of deep learning models/techniques [10,11], biomedical imaging mainly targeting lungs [12], lung infections [13], pathological lungs [14], lungs and COVID-19 lesions [15]. Deep learning-based techniques are mostly derived from a fully convolutional network (FCN) architecture in which the fully connected layers are used instead of the convolutional layers [16]. The widely used U-Net model is a variant of FCN that has been developed as the de facto model for tasks such as object segmentation in images because of its learnable up-convolution layers and multi-scale skip connections [17]. Some researchers have used it for automatic COVID-19 lesion segmentation in CT scans.
Motivated by the excellent results of deep learning architectures, we introduced an automated framework using deep learning to classify and segment deadly COVID-19 viral infection in CT scan images. We adopted a U-Net segmentation paradigm to detect and segment infected areas (regions/lesions) in CT scans. Since all of the features obtained from the encoders are not valuable, we applied the U-Net architecture with an attention mechanism for better feature representation. In this way, it allows highlighting salient ROI features and control activations of features by irrelevant regions. However, the architecture faces difficulty during balancing recall and precision due to the small ROI located in CT scan images. Thus, addressing the issues of small and unbalanced data and training performance, we combined attention U-Net with the boundary loss function, which is quite fitted for small lesion segmentation. The principal contributions of the presented work are given as follows:
- To introduce a framework for automated segmentation of infected regions of the COVID-19 virus in lung/chest CT scans using a deep learning architecture;
- To utilize the soft attention mechanism in order to enhance the framework’s capability, to extract more silent features, and to identify and segment virus-infected regions in CT scans;
- To address the issues of unbalanced data, attention U-Net architecture is combined with boundary loss function for small regions/lesion segmentation;
- To validate the effectiveness of the framework with other segmentation techniques in terms of segmentation accuracy.
The work presented in this paper is arranged as follows: an overview of different methods suggested for the segmentation of infection in CT scans is presented in Section 2. Section 3 discusses the details of the developed framework utilized for the segmentation of infected regions/lesions in CT scans images, including the U-Net architecture with the attention mechanism and the boundary loss function. The data set used to evaluate the framework is presented in Section 4. Furthermore, the experimental results along with the evaluation parameters are also addressed in Section 4. Lastly, this work is concluded with some future guidelines and summarized in Section 5.
2. Related Work
In efforts to study COVID-19, researchers have paid serious attention to introducing efficient and effective deep learning-based techniques, for example, [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. These techniques are widely adopted for the classification, detection, and segmentation of COVID-19 images and infection and [20,27,28] used biomedical image data, mostly chest/lung CT scans and X-rays, in their work.
Hemdan et al. [29] applied and compared various neural network models for the classification of COVID-19 X-ray images. Ref. [30] introduced a CNN-based system for analyzing and classifying three categories of X-ray images, including pneumonia, COVID-19, and regular images. Pathak et al. [31] suggested a deep learning process along with transfer learning to classify infected cases using a CT scan data set. The authors in [32] studied a residual neural network model for analyzing X-rays of normal, viral, and infected pneumonia. Ref. [33] introduced convolutional neural networks based on a multi-objective differential evolving model to distinguish the coronavirus patients utilizing CT scan data of the chest. Hossain et al. [34] proposed a healthcare system using artificial intelligence to detect the virus using chest CT scans and radiology images.
Muhammad et al. [35] presented a multi-layer fusion model for the classification of COVID-19 utilizing ultrasound images of lungs. The researchers in [36] presented a neural network model using contrastive loss to detect COVID-19 in radiology pictures. Apostolopoulo et al. [37] introduced a detection system using neural networks and transfer learning to analyze chest X-rays. Ref. [38] identified COVID-19 infections using their own developed data set, containing a total of 1144 radiology images. Ref. [39] adopted a Faster-RCNN, a detector model for monitoring the COVID-19 virus in X-ray images. The authors in [40,41] trained a 2D CNN model on a data set collected from [42]. In [40], the authors combined different pre-trained designs with regularization of the support vector machine.
In [41], the researchers introduced a network by leveraging the power of capsule networks with different architectures to increase classification accuracies. Song et al. [43] produced a deep learning diagnosis framework to assist medical experts in identifying patients with symptoms of the COVID-19 virus and pneumonia in CT scan data. Ref. [44] proposed a 3D deep network comprising a pre-trained U-Net and two 3D residual blocks. Ref. [45] also used 3D deep networks for the segmentation of CT images. In [46], the authors used GAN-incorporated data to enhance the learning of a discriminating paradigm for diseased lung segmentation. Jiang et al. [47] produced deep neural networks for tumor segmentation in lung CT slices by combining various residual layers of modifying resolutions. In another work [48], the researchers developed an explainable method for diagnosing viral infection using a shared segmentation and classification approach. Ref. [49] aimed to offer an automated system to segment viruses caused by COVID-19 and presented a quantitative measure of infections to medical experts. The method involves the segmentation of lung segmentation infection based on a U-Net architecture.
Yan et al. [13] recommended a deep neural network model called COVID-SegNet to segment infections in CT scans. A small network for the effective segmentation of deadly viral diseases in CT scans was presented by [50]. The authors in [51] presented a U-Net-based computerized model for infection segmentation in lung CT scans. Shan et al. [15] introduced a deep learning design defined as VB-Net for segmenting infection lesions in the CT scan data set. Ref. [52] studied five convolutional neural network pre-trained models for classifying and analyzing infected patients utilizing a chest X-ray data set. A deep learning model for lung disease segmentation named Inf-Net was presented by [53]. The model automatically recognized infected regions in CT scan data. The authors used an identical partial decoder to combine the distinctive characteristics and produced a global map. To enhance the representations and the boundaries, the authors applied reverse and specific edge-attention. Ahmed et al. [54] recently presented an Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled deep learning model for screening of COVID-19 in X-ray images. The authors in [55,56] presented an automated COVID-19 CT scan segmentation method that was based on U-Net.
The researchers presented various techniques to classify, detect, and segment chest or lung X-rays, CT scan images, and infected areas (regions and lesions) in patients infected with COVID-19. Researchers mostly adopted state-of-the-art methods and approaches to classify, analyze, and differentiate contagious diseases, but they used a limited data set. This paper introduced a deep learning framework based on U-Net architecture for the segmentation of COVID-19 infected lesions/regions in a chest/lung CT scan data set. In addition to segmentation, the developed framework can also highlight the severity of the disease in CT scans.
3. Methodology
This work introduces an automated framework using deep learning for the segmentation of infected regions/areas in the COVID-19 CT scan image data set. The framework provides a classification of viral infections and assists medical experts in analyzing the severity of infection. The overall technical flow of the designed framework is explained in Figure 2. The method involves five steps: pre-processing, data augmentation, lung segmentation, infection segmentation, and infection classification. The data sets used for experimentation are collected from different available online resources.
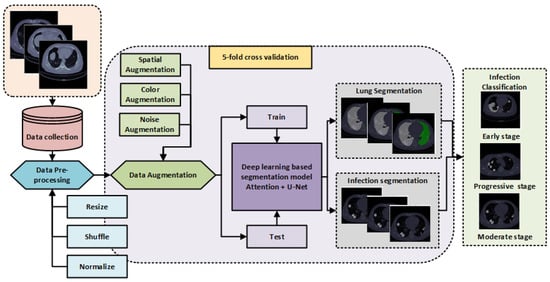
Figure 2.
General flowchart of the framework developed for biomedical image examination of COVID-19 infection found in CT scans of chest/lungs. The workflow starts with the collection of the data set, the pre-processing step, data augmentation, and train/test splitting. In addition, the U-Net model is utilized for lung segmentation and infection in CT images. Finally, the detected infection mask is classified into three stages, i.e., early, progressive, and severe. The flowchart concludes with the estimated results of the assessment for a five-fold cross-validation.
A widely utilized deep learning model named U-Net was utilized to segment lungs and infected areas. Data normalization was performed during the pre-processing step, and the input image pixel values were converted in the range [0, 1], ensuring that all input pixels have the same data distribution. This increases convergence while training the network. Moreover, data augmentation was applied, e.g., random scaling, brightness, rotation, crop, contrast, and flip. Data augmentation enables the deep learning network to learn a wide variety of variations in the given data set and enhances the framework’s performance. In order to learn target features of varying shapes and sizes, the U-Net architecture was combined with an attention mechanism.
In addition, a boundary loss function and integral interface between ROIs were applied to decrease the complexity of unbalanced areas. After segmentation, different metrics were estimated to quantify the infected areas, such as the volumes of an infected region or regions within the lungs. Additionally, to estimate the severity of diseases and the spread of viral infection in the lungs, the percentage of infection in the lungs was determined. For that reason, we used the Hounsfield unit, a histogram of the infected area to envision the ground glass opacification/opacity (GGO) and consolidation segments inside the infected region.
3.1. Pre-Processing and Data Augmentation
As the data set collected from different resources was limited, data augmentation was performed. Its purpose was to generate large data on acceptable modifications of the needed configuration and to artificially increase the amount of training images. We conducted extensive data augmentation and increased the amount of data by utilizing the batch generators interface inside MIScnn (https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/batchgenerators, accessed on 1 June 2022). We executed three kinds of augmentations: first was the spatial augmentation, which involves rotations, mirroring, scaling, and elastic deformations; color augmentation (contrast, brightness, and gamma adjustments); and noise augmentations. After performing pre-processing and data augmentation, the data set images were randomly split into training and testing samples.
3.2. Lungs and Infection Segmentation Using U-Net with Attention Mechanism
For segmentation of lungs and infected areas in CT scan images, we applied the U-Net model. The authors of [17] introduced this model, which was practically developed using end-to-end fully convolutional networks rather than dense layers. The general design of the model is presented in Figure 3 (adopted from [17]); it can be seen that the model can handle arbitrary/variable size images. The overall model is basically divided into two parts, namely encoder and decoder. The first part is used to obtain the context of the image, which is named an encoder. This part is mainly based on a traditional pile of convolutional layers followed by max-pooling layers. In contrast, the other part is the symmetric/balanced expanding path named decoder, used to provide accurate localization using transposed or reversed convolutions. The first part is also named the downsampling path, which implements various classification models as the backbone. All steps generally use two convolution layers () with batch normalization followed by a max-pooling layer (), as illustrated in Figure 3. The parallel bottleneck contains two convolution layers and up convolution layers of size () and (), respectively. The upsampling path has four phases: the decoder with two convolutional layers, followed by an upsampling layer of sizes and . The feature maps become half after each step.
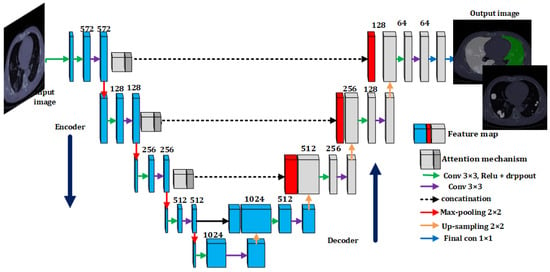
Figure 3.
U-Net architecture with attention mechanism utilized for segmentation of lungs and COVID-19 infected virus.
From Figure 3, it can be observed that, to produce global and local information throughout upsampling, the architecture skips connections within the downsampling and upsampling paths. The pre-processed input images with three channels are provided to the architecture for segmentation. Finally, the segmented map is given, using a convolutional layer of at the output. The extracted feature maps are of identical sizes to the desired output segments. Thus, a function is defined over the absolute feature map with pixel-wise soft-max and cross-entropy loss as [17]. It is described as follows:
In Equation (1), ReLu is an activation function (Rectified Linear Unit) used for feature maps, and it is defined as . The number of classes are represented with K, and the approximation for maximum value is represented as . For maximum , its value is approximately equal 1 and considered as for other values. The function defined in Equation (1) is penalized and given as [17]:
In Equation (2), the true label or ground truth of all pixels is described as . The weight map that is used throughout training for additional attention to pixels is provided as [17]. For various frequency pixels, the true segmentation is pre-calculated. Applying morphological operations for different classes in the training data set, the weight map value is estimated as follows:
Therefore, the weight map used for balancing the frequencies of different classes is represented as . The distance value between the initial edge and second nearby edge is denoted as and . The value of is set to 10 and . (Readers are referred to the actual work [17] for more details).
During upsampling, the recreated spatial information in the expanding path lacks accuracy. To counter this issue, the U-Net applies to skip connections that integrate spatial information from the downsampling path to the upsampling path. However, this causes several unnecessary extractions of low-level features, as feature description is not good in the primary layers. Thus, the attention mechanism is implemented or applied at the skip connections, vigorously overcoming activations in inappropriate areas or regions and decreasing redundant features.
The attention gates introduced by [57] use additive soft attention, as shown in Figure 4. These gates take two input vectors that are represented as x and g. The vector, g, is obtained from the following lowest/deepest layer of the network. It has improved feature description and small dimensions. In Figure 4, vector x has (height × width × filters) and vector g has dimensions. The x and g pass through a strided convolution and convolution layers, respectively, such that their dimensions become . The two vectors are added element-wise, resulting in aligned weights being more extensive while unaligned weights become comparatively smaller.
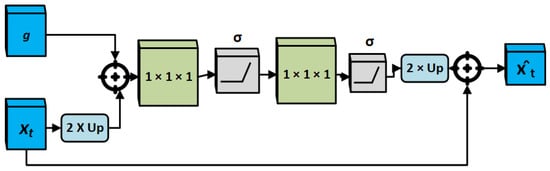
Figure 4.
Schematic design of additive attention gate used in attention mechanism. Input features x are estimated with coefficients to develop important features for the output of the (decoding layer). The spatial gating g signal gives contextual knowledge, while spatial fields from the x input are location information. Bilinear interpolation is used for feature map re-sampling.
The resultant output vector is passed through a activation layer ReLU, and a convolution layer of that drops the dimensions to . Moreover, it passes within a sigmoid layer, which computes the vector in the range of [0, 1], providing the weights (attention coefficients), where coefficients closer to 1 exhibit more important characteristics. These coefficients are also upsampled to the real dimensions of the x utilizing the trilinear interpolation. Next, element-wise multiplication of the attention coefficients is performed to the real x, scaling the vector according to their significance and crossing along in the skip connection as usual.
In this work, we used a boundary loss function that applies a distance metric on the shapes or contours instead of considering whole areas or regions [58]. The boundary loss is highly used for unbalanced segmentation tasks. In this way, it tackles the difficulties posed by local losses for highly unbalanced segmentation tasks. The boundary loss function is defined as follows:
In the above equation, , where is a limit on boundary at a specific region and shows the corresponding boundary point and the normal direction to , as shown in Figure 4. represents the intersection of , and the line normal to at p. represents the L2 norm. (For more information about the boundary loss function, we refer reader to [58].)
3.3. Classification of Infection Severity
After segmentation of the lungs and infection area (regions/lesions) in the CT scan data set, the severity of the viral infection needs to be analyzed. The infected areas are described as air space consolidation and ground glass opacity, or complete opacity. Their level of concentration is observed in lung and infected regions/lesions assists in determining the different stages of the severity of infection. In the initial stage, the appearance of ground glass opacity is usually found in one or different shapes, such as in the form of a fine mesh or shadow/cloud of light. Infrequently, the concentration is found near the bunches of blood vessels (bronchial) or under the pleura. In the progressive stage, the GGO/shadows increase or the infected region expands, starting to absorb, therefore resulting in consolidation at a large scale. Finally, in the critical or severe stage, the consolidation of the bilateral or unilateral lungs diffuses, identified by GGO and symptoms of the bronchial disease.
In the diffusion or absorption step, the primary regions/lesions are entirely absorbed and grown. Therefore, to control the severity of the viral infection in the lungs (the proportion between the size of the infected area and lungs), it is essential to estimate the degree of concentration/consolidation of the infected regions. Therefore, sub-areas of these segmented lesions are categorized as consolidated in case the voxel intensity is more prominent than 0 Hounsfield units (HU); otherwise, it is categorized as GGO [7,59]. Therefore, it is reasonable to estimate the variation in the concentration of the lesions caused by a viral infection, e.g., COVID-19. Figure 2 presents an illustration of the classification of infected regions into three different stages of severity. In addition, the results of infection severity classified in lung CT scans are shown in Section 4.
4. Experimental Results
Experimentation of the above-discussed model is presented in this section. First, we discuss the training and testing observations. Second, we discuss the output results of the segmentation model employed for monitoring and screening of viral COVID-19 infection in CT scan images. Finally, the model evaluation results are discussed, showing the model’s performance. The introduced framework has been implemented using a python programming language (Keras library) with OpenCV 3.6.
4.1. COVID-19 CT Scan Data Set
The data sets utilized in the experiments were collected from different online repositories e.g., COVID-19 CT scans from Italian Society of Medical and Interventional Radiology (https://sirm.org/category/senza-categoria/covid-19/, accessed on 1 June 2022; https://radiopaedia.org/playlists/25887, accessed on 1 June 2022; and http://medicalsegmentation.com/covid19/, accessed on 1 June 2022). More than 800 CT scans of patients suffering from COVID-19 were obtained from these sources. The data set included CT scans of patients diagnosed with viral infection, and lung segmentation and infections analyzed by experts. The size of images is pixels. The images were resized, grey-scaled, and compiled into a separate NIFTI file. The images were segmented by radiologists utilizing three labels: consolidation, ground glass, and pleura effusion. The total number of training and testing CT scan slices used for experimentation after data augmentation and pre-possessing is provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Description of data set used for experimentation.
4.2. Training and Validation
These observations, including training and validation loss, and accuracy curves of the above discussed segmentation architecture with attention mechanism, are illustrated in Figure 5. Training of the model was performed for 100 epochs. It has been observed that, after the 10th epoch, the loss values declined for training and validation. Both values are contrasted in Figure 5. During training, when validation was performed, no over-fitting was noted, showing no notable difference between them, while the validation performance settled down during fitting, at a loss value of around 0.3 and a training performance of 0.2. Due to the robust training method, externally, without any implications of over-fitting, we determined that adapting randomly generated patches using increased data and arbitrary cropping from varying data sets is very effective for limited image data. As a result, the overall loss values after the 10th epoch improved to 0.89. In Figure 5, we show the training and validation accuracy of the model during training, which is 0.99 at the end of the 20th epoch.
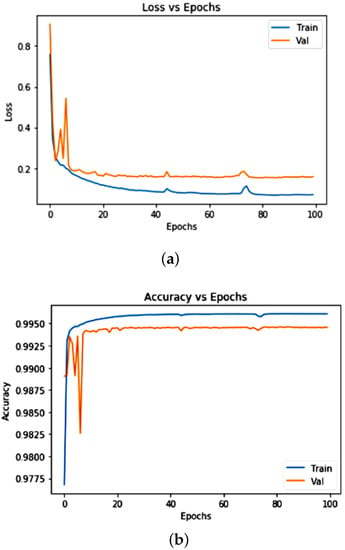
Figure 5.
(a) Loss curve during the validation and training process. (b) Accuracy curve during the validation and training process for training. The lines (validation (orange) and training (blue)) were estimated using binary cross-entropy dice loss and represent the weight loss across all folds.
4.3. Visualization Results of Infected Region Segmentation
The segmentation and classification results of the segmentation framework are illustrated in Figure 6. We can see that the segmentation model effectively segmented the infection regions in CT scans. It can also be observed that the boundary loss function improves the segmentation results of unbalance regions or data. In Figure 6a,b, we demonstrate the example results of infection segmentation at an early stage of diagnosis. It can be seen that the segmented regions are so small and cannot be easily analyzed in the original CT scans, while all small spots of segmented infection using the above model might help medical experts effectively analyze and diagnoses the virus at its earlier stages.
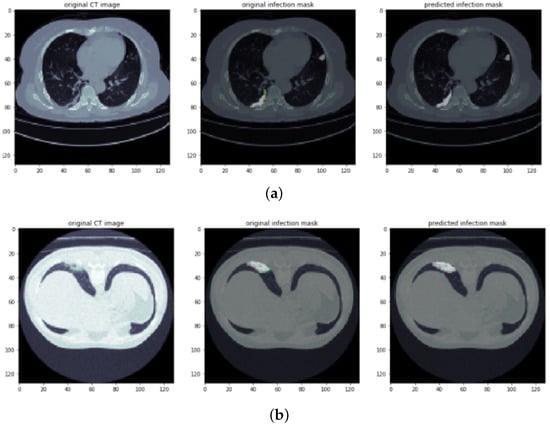
Figure 6.
Infection segmentation results of CT scans: the sample images (a,b) show the early stage of viral infection. Columns 1–3 show an original CT scan image, an original infection mask, and a predicted infection mask, respectively.
Similarly, in Figure 7a,b, we show the output results for progressive stages; it can be seen from the images that the virus is growing at different places irregularly and at different locations in lungs. Such output results also help to analyze the progressive rate of the viruses. Moreover, along with the large regions, a small art is detected.
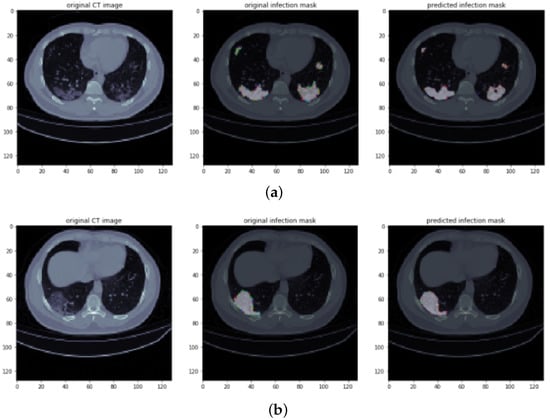
Figure 7.
Infection segmentation results of CT scans: the sample images (a,b) show the progressive stage of viral infection. It can be seen that both lungs are affected from the virus and that infection is growing at different locations of lungs. Columns 1–3 show an original CT scan image, an original infection mask, and a predicted infection mask, respectively.
Figure 8a,b show the output results for the severe stage of the infected virus. As can be seen in the example images, the virus affected the lungs of the patients badly. In both sample figures, it can be observed that the growth of infections was severe in both lungs and spread badly in the lungs of the patients. The results of the segmentation models can be really useful for medical specialists in order to analyze the effect of the virus on patients’ lungs.
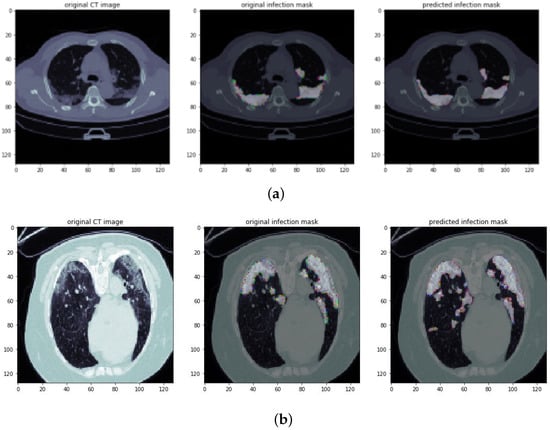
Figure 8.
Infection segmentation results of CT scans: sample images (a,b) show the severe stage of viral infection. It can be seen that both lungs are affected by the COVID-19 infection badly. Columns 1–3 show an original CT scan image, an original infection mask, and a predicted infection mask, respectively.
4.4. Evaluation and Comparison Results
After training and validation, we used three commonly adopted evaluation parameters for biomedical image investigations. First, to perform performance analysis to determine the overlap of segmentation between prediction and true labels/ground truth, we used the Dice similarity coefficient, described in Equation (5). It is the most widely applied parameter in segmentation applications. In addition, Specificity and Sensitivity discussed in Equations (6) and (7) were also applied in the most popular pharmaceutical fields. All parameters were calculated using the confusion matrix, including true positive (), true negative (), false positive (), and false negative ().
We determined the evaluation parameters in the cross-validation for each fold and, therefore, for all CT images in the collected data set. Overall, the cross-validation of the segmentation model obtained a similarity coefficient of around 0.93 for lungs and 0.76 for infected regions segmentation, as depicted as box plots in Figure 9.
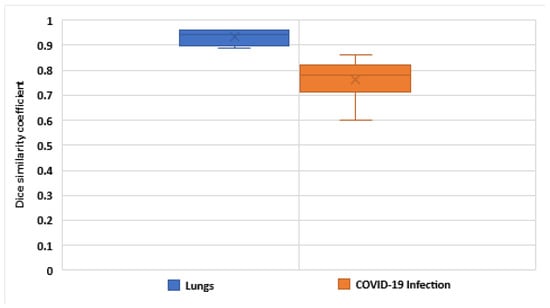
Figure 9.
The result distribution of the five-fold cross-validation is presented using box plots for lung and infected region segmentation.
The average performance values of the above-discussed segmentation model are shown in Figure 10. The segmentation model delivers average rates of 0.932, 0.936, and 0.946 for the Dice similarity coefficient, sensitivity, and specificity for lung segmentation, respectively, while for COVID-19 infected region segmentation, the Dice similarity coefficient, , and are 0.764, 0.736, and 0.888, respectively.
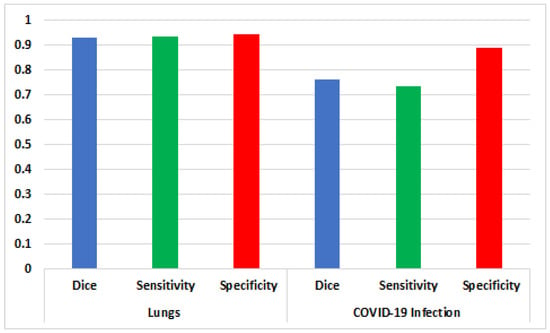
Figure 10.
Average values of the similarity coefficient, and .
The inference performance details for each fold during cross validation are listed in Table 2. From a medical perspective, the segmentation of infected regions is a difficult task and one reason for the lower value of segmentation accuracy. The reason for this may be the difference between pulmonary consolidation and GGO morphology. However, our deep learning-based segmentation model obtained considerably good results and segmented COVID-19 infected regions with state-of-the-art efficiency comparable with other segmentation techniques.

Table 2.
Results obtained for each cross-validation fold.
Table 3 presents a comparative analysis of different methods used to segment COVID-19 infection in lung CT scan images. The U-Net [17] model achieves an average accuracy of 0.966, while the attention U-Net [60] obtained an average accuracy of 0.978. The other two segmentation models also achieve good accuracy results, with the U-Net++ [61] and SD-UNet [62] accuracies being 0.971 and 0.981, respectively. Our proposed model shows excellent results as we apply the boundary loss function. As discussed earlier, highly unbalanced segmentations, such as regional summations where values are different in magnitude across types, affect training stability and performance. Thus, we applied a boundary loss, which uses the distance metric on the area of contours, not regions. Furthermore, it might mitigate the highly unbalanced problems by utilizing integrals instead of unbalanced integrals over the interface between regions. We can see from Table 3, that the similarity of our proposed model is 0.763, which is higher than that for other methods.

Table 3.
Comparison analysis of different segmentation methods.
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
This work introduced an automated framework using deep learning for the segmentation of infected regions/lesions/areas of the COVID-19 virus in the CT scan data set. We adopted a U-Net model for segmenting lungs and infected regions of the virus and employed the soft attention mechanism to increase the framework’s ability. Moreover, we performed pre-processing and extensive data augmentation to improve the segmentation model’s accuracy. Furthermore, a boundary loss function was used to deal with small and unbalanced lesions, or regions segmentations. We validated the framework’s effectiveness in contrast with other segmentation techniques with publicly available CT image data sets. The experimental outcomes show the excellent performance of our framework for the automated segmentation of lungs and infected in chest/lung CT scan images. We also considered both boundary loss and weighted binary cross-entropy dice loss functions. The overall accuracies of the framework were 0.93 and 0.76 for lung segmentation and infected region segmentation, respectively. In the future, this work might be extended to the analysis and segmentation of other viral infections; we might use other segmentation techniques based on deep learning applications to analyze, detect, and classify different viral diseases.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.A. and A.C.; methodology, I.A.; software, I.A.; validation, I.A. and A.C. and G.J.; formal analysis, I.A. and A.C.; investigation, G.J.; resources, I.A. and A.C.; data curation, I.A. and A.C.; writing—original draft preparation, I.A.; writing—review and editing, A.C.; visualization, G.J.; supervision, I.A.; project administration, G.J.; funding acquisition, G.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Incheon National University Research Concentration Professors Grant in 2021.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Ahmad, M.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Jeon, G.; Din, S. A deep learning-based social distance monitoring framework for COVID-19. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 65, 102571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Ahmad, M.; Jeon, G. Social distance monitoring framework using deep learning architecture to control infection transmission of COVID-19 pandemic. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 69, 102777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xia, L. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Role of chest CT in diagnosis and management. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Abedi, A.; Balakrishnan, S.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review of imaging findings in 919 patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.; Zhu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.Y.; Lee, E.Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Lui, M.M.S.; Lo, C.S.Y.; Leung, B.; Khong, P.L.; et al. Imaging profile of the COVID-19 infection: Radiologic findings and literature review. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, I.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, F.A.; Asif, M. Comparison of Deep-Learning-Based Segmentation Models: Using Top View Person Images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 136361–136373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizopoulos, P.; Vretos, N.; Daras, P. Comprehensive Comparison of Deep Learning Models for Lung and COVID-19 Lesion Segmentation in CT scans. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.06412. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, I.; Jeon, G.; Chehri, A.; Hassan, M.M. Adapting Gaussian YOLOv3 with transfer learning for overhead view human detection in smart cities and societies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 70, 102908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Jeon, G.; Piccialli, F. A Deep Learning-based Smart Healthcare System for Patient’s Discomfort Detection at the Edge of Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 10318–10326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skourt, B.A.; El Hassani, A.; Majda, A. Lung CT image segmentation using deep neural networks. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 127, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Wang, B.; Gong, D.; Luo, C.; Zhao, W.; Shen, J.; Shi, Q.; Jin, S.; Zhang, L.; You, Z. COVID-19 chest CT image segmentation—A deep convolutional neural network solution. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10987. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, A.P.; Xu, Z.; George, K.; Lu, L.; Summers, R.M.; Mollura, D.J. Progressive and multi-path holistically nested neural networks for pathological lung segmentation from CT images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 11–13 September 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 621–629. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, F.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, W.; Shi, N.; Han, M.; Xue, Z.; Shen, D.; Shi, Y. Lung infection quantification of COVID-19 in CT images with deep learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.04655. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Dong, Y.; Lu, H.; Zheng, X.; Qiu, S.; Hou, S. APU-Net: An Attention Mechanism Parallel U-Net for Lung Tumor Segmentation. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5303651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmed, I.; Khan, F.A.; Qayum, F.; Aljuaid, H. Convolutional neural network—Based person tracking using overhead views. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2020, 16, 1550147720934738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.; He, K.; Shi, Y.; Shen, D. Review of artificial intelligence techniques in imaging data acquisition, segmentation and diagnosis for COVID-19. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wynants, L.; Van Calster, B.; Bonten, M.M.; Collins, G.S.; Debray, T.P.; De Vos, M.; Haller, M.C.; Heinze, G.; Moons, K.G.; Riley, R.D.; et al. Prediction models for diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19 infection: Systematic review and critical appraisal. BMJ 2020, 369, m1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmed, I.; Jeon, G. An IoT-enabled real-time overhead view person detection system based on Cascade-RCNN and transfer learning. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2021, 18, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.M.; Joy, S.K.S.; Ahmed, F.; Humaira, M.; Ami, A.S.; Paul, S.; Jim, A.R.K.; Hossain, T.; Ahmed, S. A Comprehensive Survey of COVID-19 Detection Using Medical Images. SN Comput. Sci. 2020, 2, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, S.; Zuo, S.; Chen, Y.; Sun, W.; Luo, J.; Duan, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, D. U-Net combined with multi-scale attention mechanism for liver segmentation in CT images. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2021, 21, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Din, S.; Jeon, G.; Piccialli, F. Exploring deep learning models for overhead view multiple object detection. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 7, 5737–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kang, B.; Ma, J.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, M.; Guo, J.; Cai, M.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Meng, X.; et al. A deep learning algorithm using CT images to screen for Corona Virus Disease (COVID-19). Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6096–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanien, A.E.; Mahdy, L.N.; Ezzat, K.A.; Elmousalami, H.H.; Ella, H.A. Automatic X-ray COVID-19 lung image classification system based on multi-level thresholding and support vector machine. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadry, S.; Rajinikanth, V.; Rho, S.; Raja, N.S.M.; Rao, V.S.; Thanaraj, K.P. Development of a Machine-Learning System to Classify Lung CT Scan Images into Normal/COVID-19 Class. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.13122. [Google Scholar]
- Hemdan, E.E.D.; Shouman, M.A.; Karar, M.E. Covidx-net: A framework of deep learning classifiers to diagnose COVID-19 in X-ray images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11055. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wong, A. COVID-Net: A Tailored Deep Convolutional Neural Network Design for Detection of COVID-19 Cases from Chest X-ray Images. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, Y.; Shukla, P.K.; Tiwari, A.; Stalin, S.; Singh, S. Deep transfer learning based classification model for COVID-19 disease. IRBM 2020, 43, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Hafeez, A. COVID-resnet: A deep learning framework for screening of COVID-19 from radiographs. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.14395. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, M. Classification of COVID-19 patients from chest CT images using multi-objective differential evolution–based convolutional neural networks. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Muhammad, G.; Guizani, N. Explainable AI and mass surveillance system-based healthcare framework to combat COVID-I9 like pandemics. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, G.; Hossain, M.S. COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 classification using multi-layers fusion from lung ultrasound images. Inf. Fusion 2021, 72, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorfuzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.S. MetaCOVID: A Siamese neural network framework with contrastive loss for n-shot diagnosis of COVID-19 patients. Pattern Recognit. 2021, 113, 107700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolopoulos, I.D.; Mpesiana, T.A. COVID-19: Automatic detection from X-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2020, 43, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, R.M.; Bertolini, D.; Teixeira, L.O.; Silla, C.N., Jr.; Costa, Y.M. COVID-19 identification in chest X-ray images on flat and hierarchical classification scenarios. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 194, 105532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Ahmad, A.; Jeon, G. An IoT based deep learning framework for early assessment of COVID-19. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 15855–15862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, A.; Saeedi, M.; Maghsoudi, A. A novel and reliable deep learning web-based tool to detect COVID-19 infection from chest ct-scan. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.14419. [Google Scholar]
- Mobiny, A.; Cicalese, P.A.; Zare, S.; Yuan, P.; Abavisani, M.; Wu, C.C.; Ahuja, J.; de Groot, P.M.; Van Nguyen, H. Radiologist-level COVID-19 detection using ct scans with detail-oriented capsule networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.07407. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Zhao, H.; Zha, Y.; et al. Deep learning enables accurate diagnosis of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) with CT images. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2021, 18, 2775–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Deng, X.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Feng, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. Deep learning-based detection for COVID-19 from chest CT using weak label. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gozes, O.; Frid-Adar, M.; Greenspan, H.; Browning, P.D.; Zhang, H.; Ji, W.; Bernheim, A.; Siegel, E. Rapid ai development cycle for the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic: Initial results for automated detection & patient monitoring using deep learning ct image analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.05037. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.; Xu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Harrison, A.P.; Mollura, D.J. CT-realistic lung nodule simulation from 3D conditional generative adversarial networks for robust lung segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 732–740. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Hu, Y.C.; Liu, C.J.; Halpenny, D.; Hellmann, M.D.; Deasy, J.O.; Mageras, G.; Veeraraghavan, H. Multiple resolution residually connected feature streams for automatic lung tumor segmentation from CT images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Gao, S.H.; Mei, J.; Xu, J.; Fan, D.P.; Zhang, R.G.; Cheng, M.M. Jcs: An explainable COVID-19 diagnosis system by joint classification and segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3113–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, J.O.; Quintanilha, D.B.; Neto, A.C.S.; da Silva, G.L.; Ferreira, J.L.; Netto, S.M.; Araújo, J.D.; Da Cruz, L.B.; Silva, T.F.; Martins, C.M.d.S.; et al. Segmentation and quantification of COVID-19 infections in CT using pulmonary vessels extraction and deep learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 29367–29399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, J. Miniseg: An extremely minimum network for efficient COVID-19 segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.09750. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, D.; Rey, I.S.; Kramer, F. Automated chest ct image segmentation of COVID-19 lung infection based on 3d u-net. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.04774. [Google Scholar]
- Narin, A.; Kaya, C.; Pamuk, Z. Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) using X-ray images and deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2021, 24, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Zhou, T.; Ji, G.P.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Inf-net: Automatic COVID-19 lung infection segmentation from ct images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2626–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Jeon, G.; Chehri, A. An IoT-enabled smart health care system for screening of COVID-19 with multi layers features fusion and selection. Computing 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Canu, S.; Ruan, S. Automatic COVID-19 CT segmentation using U-Net integrated spatial and channel attention mechanism. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 31, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qiu, K. An improved segmentation algorithm of CT image baseMDPIU-Net network and attention mechanism. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Kervadec, H.; Bouchtiba, J.; Desrosiers, C.; Granger, E.; Dolz, J.; Ayed, I.B. Boundary loss for highly unbalanced segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, PMLR, London, UK, 8–10 July 2019; pp. 285–296. [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlemper, J.; Oktay, O.; Schaap, M.; Heinrich, M.; Kainz, B.; Glocker, B.; Rueckert, D. Attention gated networks: Learning to leverage salient regions in medical images. Med Image Anal. 2019, 53, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, S.; Deng, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Cheng, J. SD-UNet: A Novel Segmentation Framework for CT Images of Lung Infections. Electronics 2022, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).