Design of an Efficient 24–30 GHz GaN MMIC Power Amplifier Using Filter-Based Matching Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Circuit Design Considerations
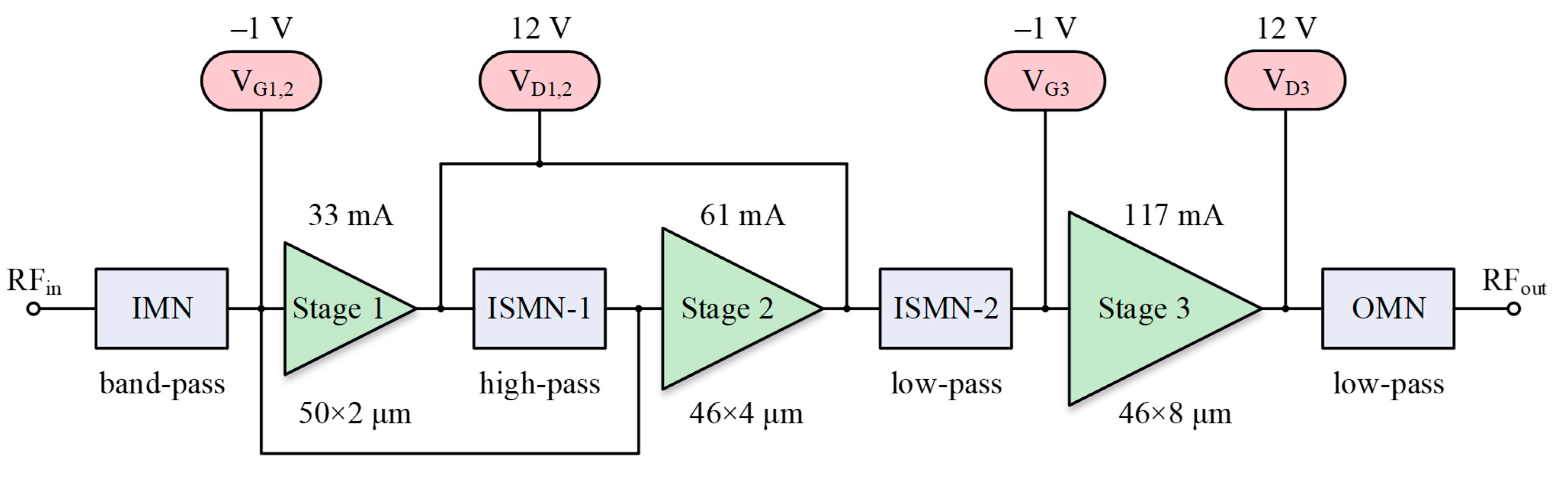
2.1. Choice of Amplifier Topology and Transistor Size
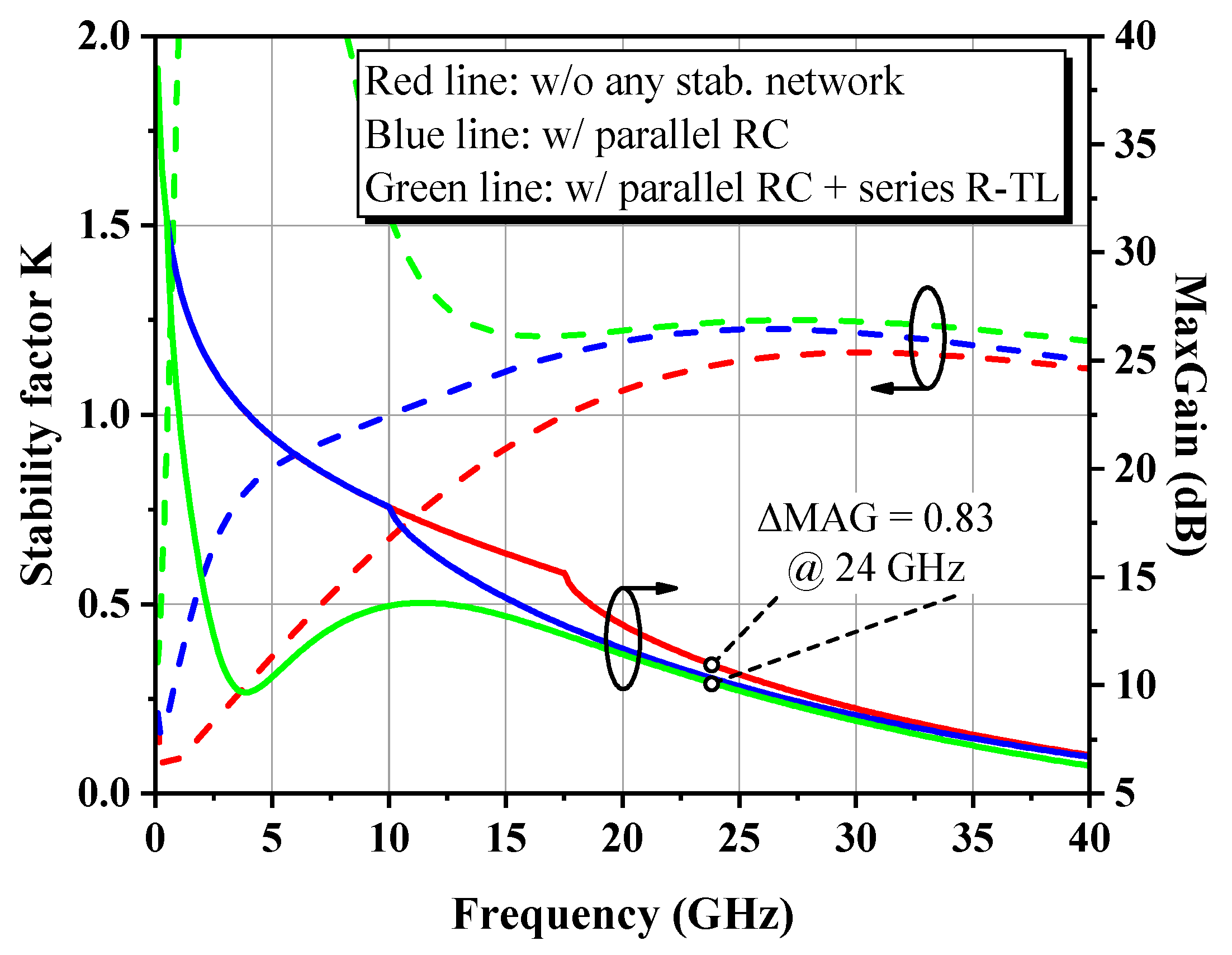
2.2. Stability
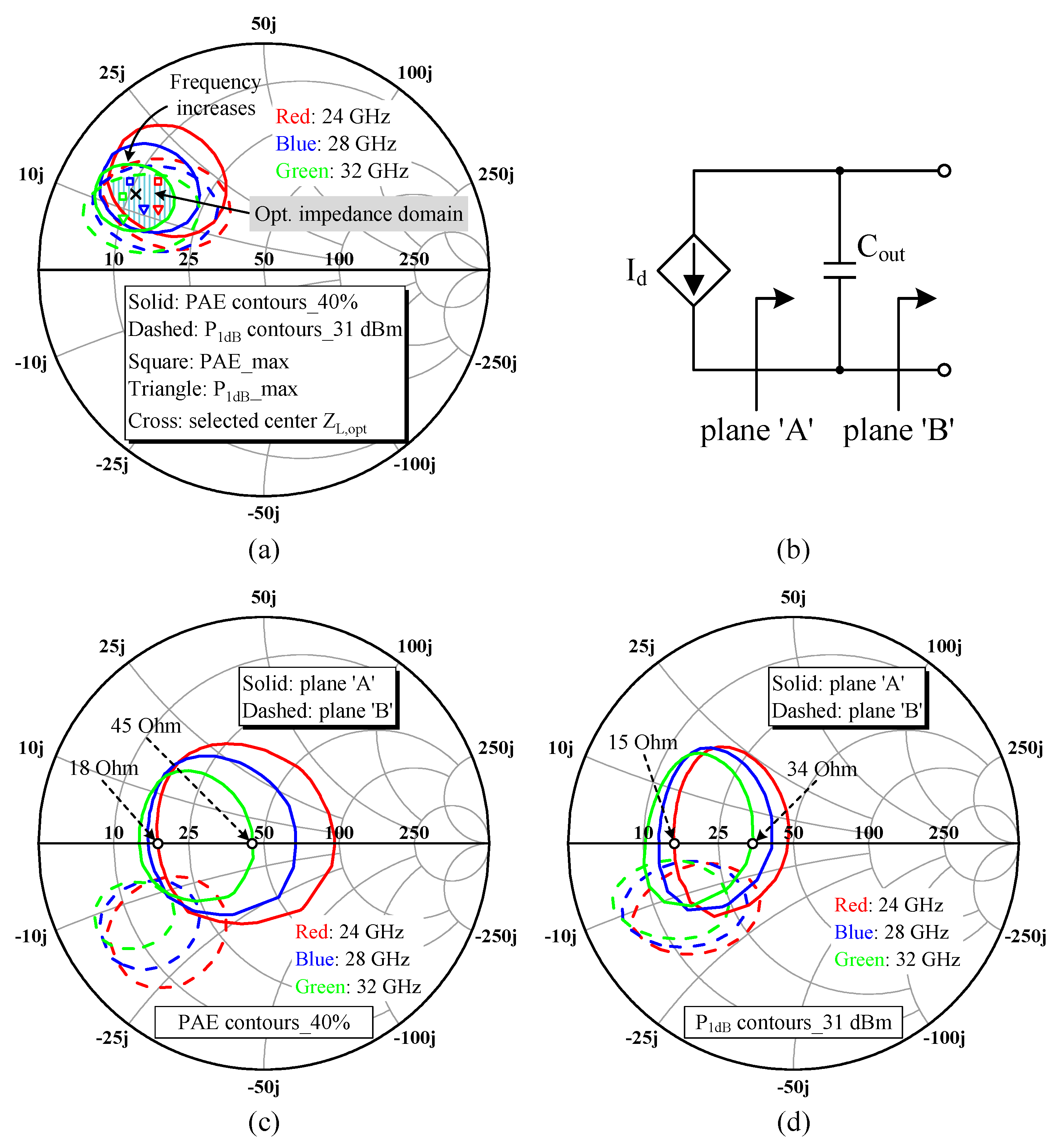
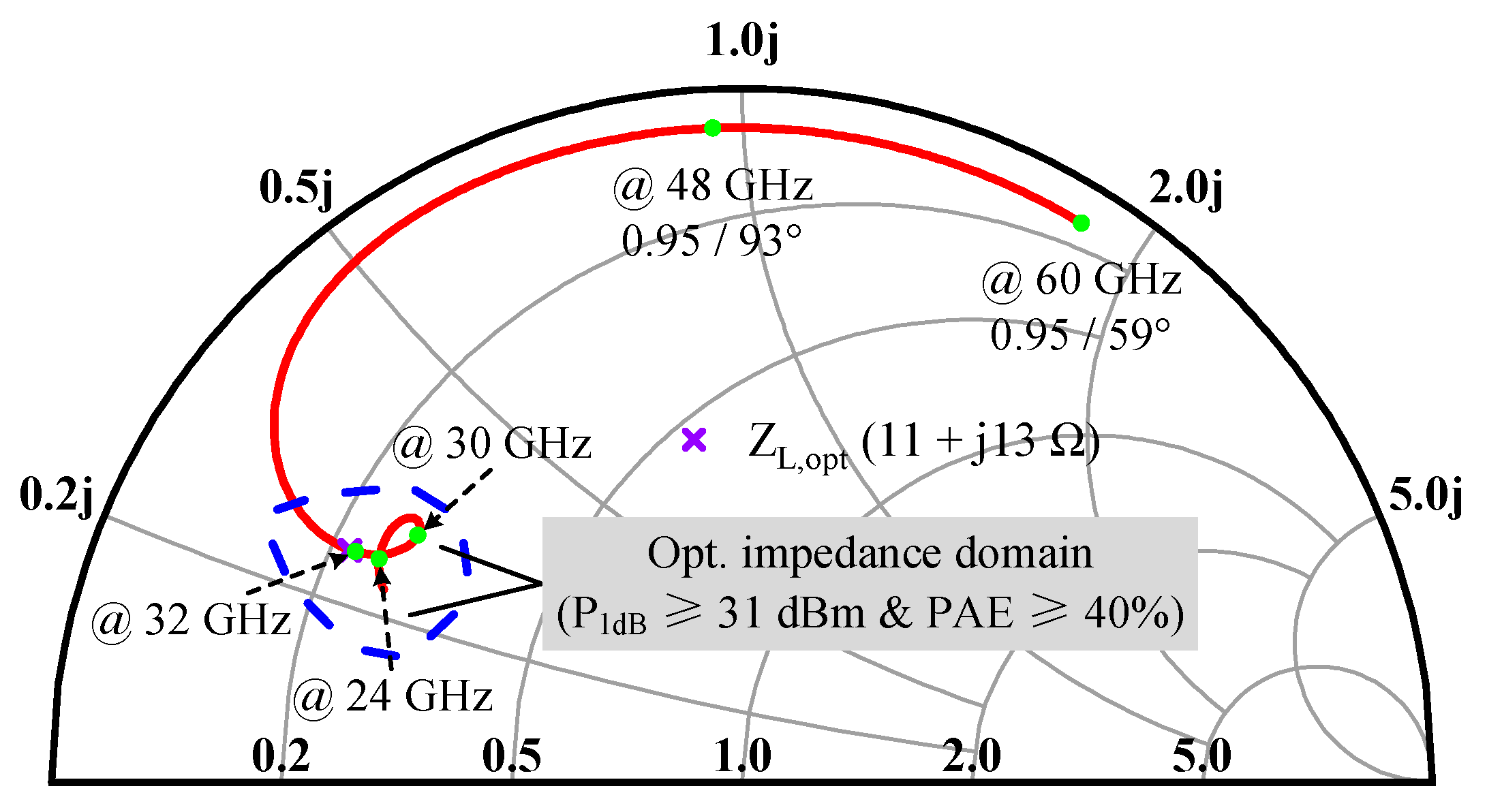
2.3. Load-Pull Analysis and Optimal Impedances Selection
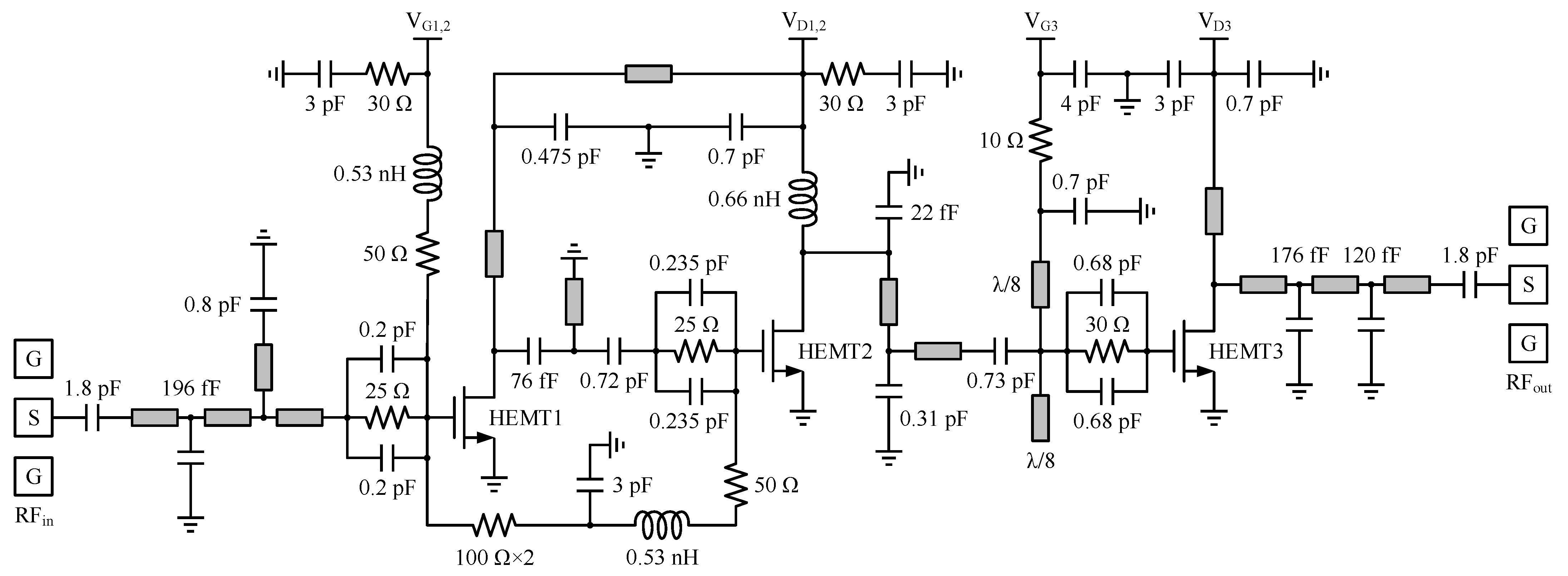
3. Design and Implementation of Matching Networks
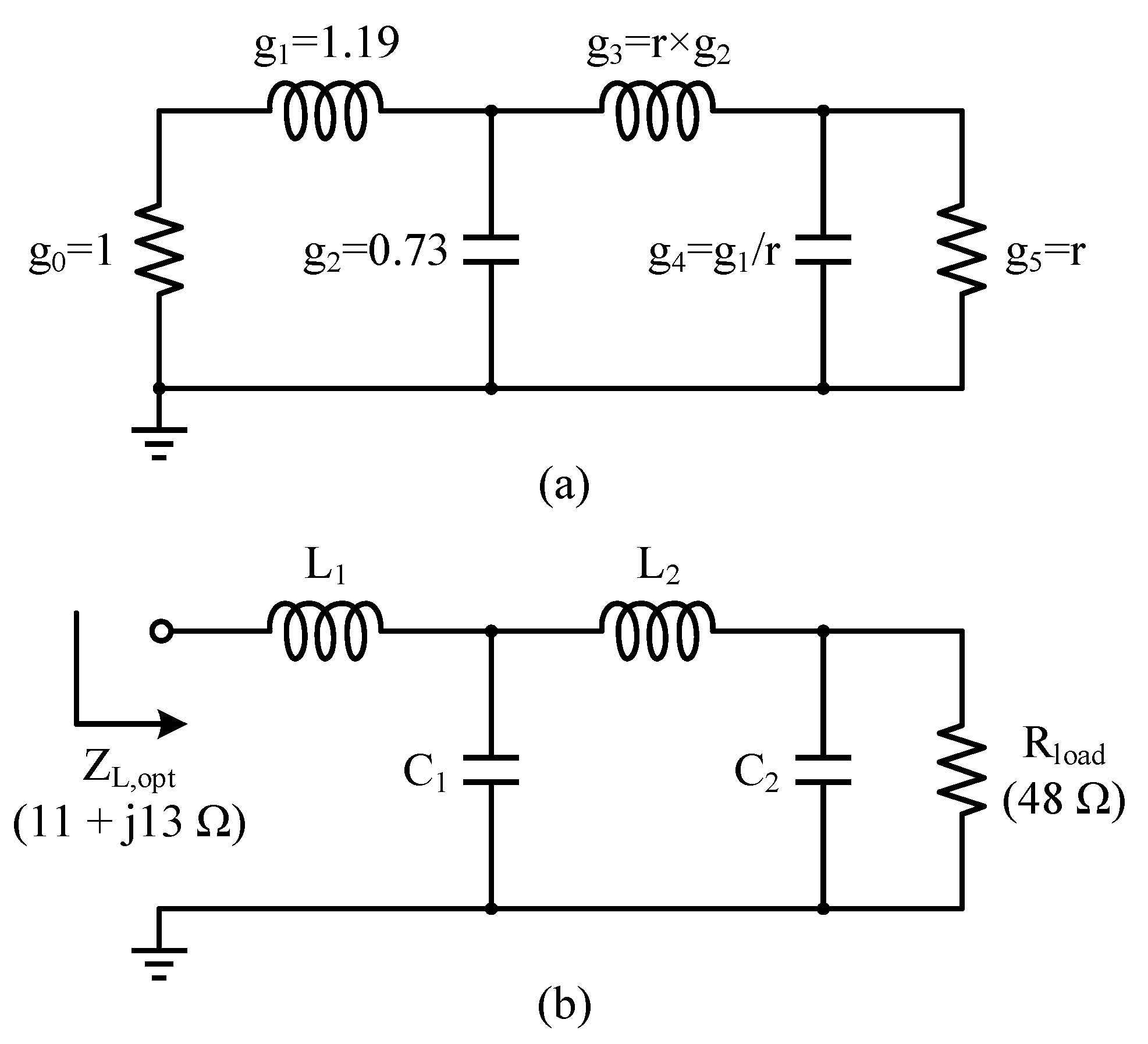
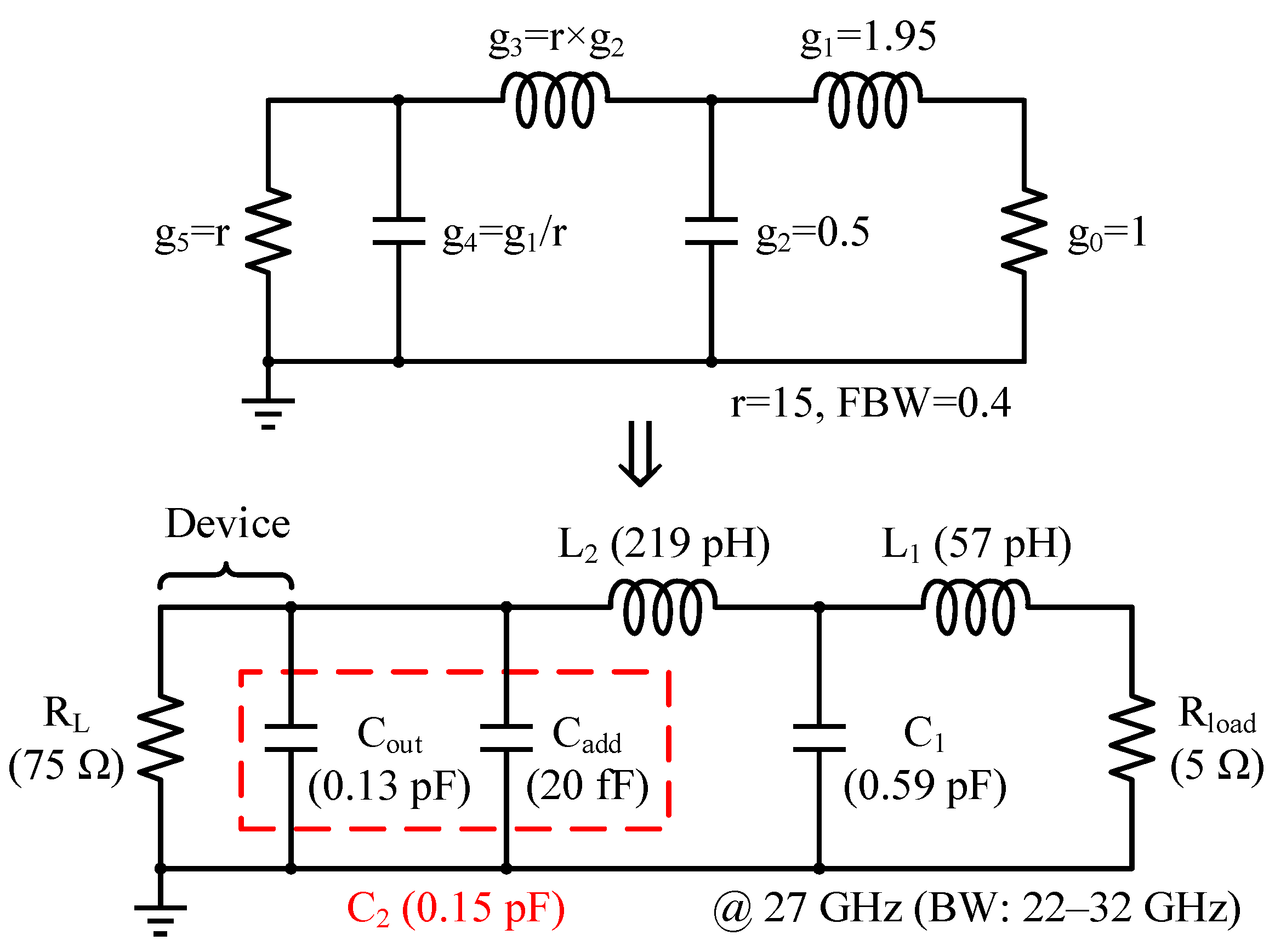
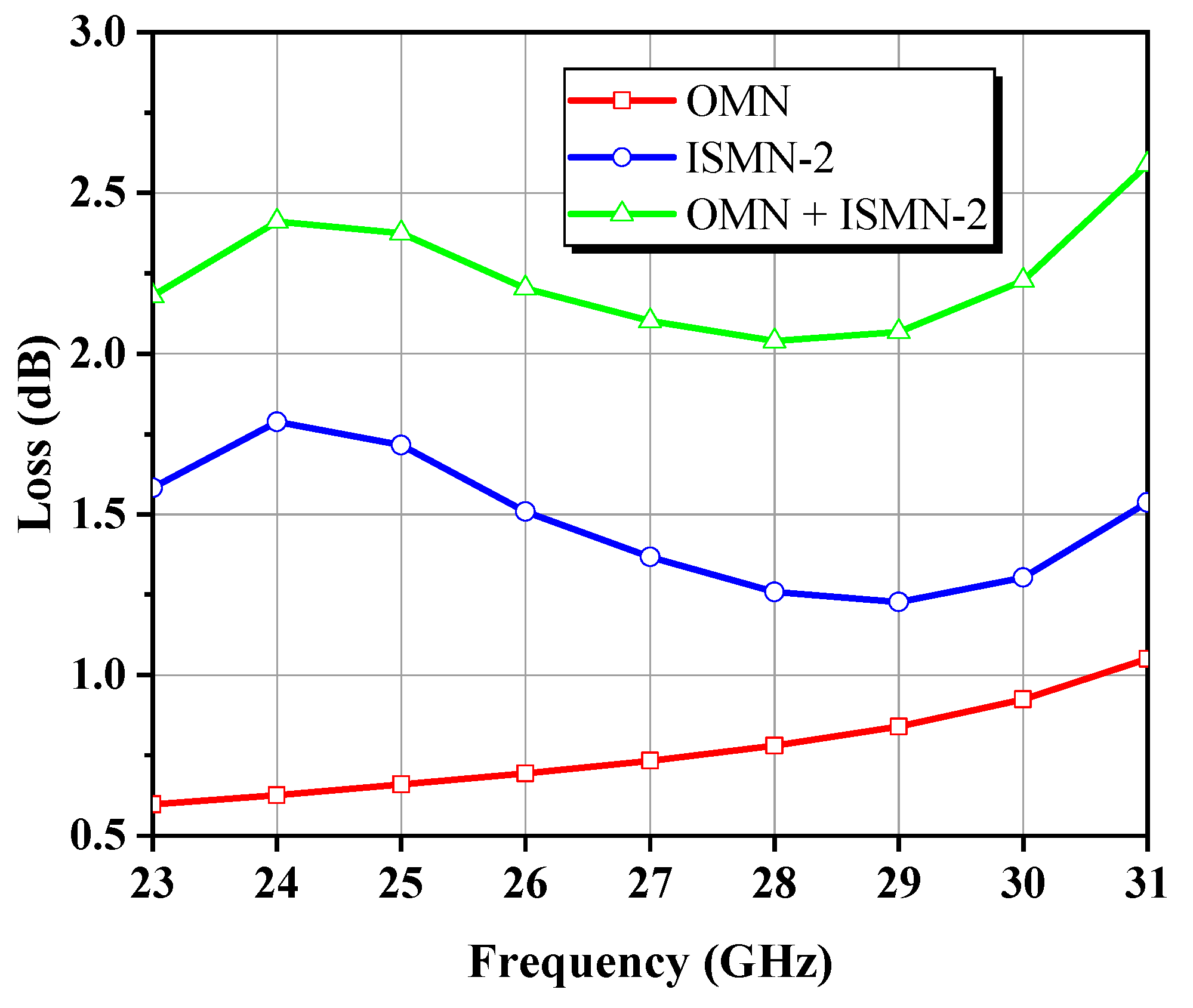
3.1. Low-Pass OMN Synthesis and Mixed-Element Implementation
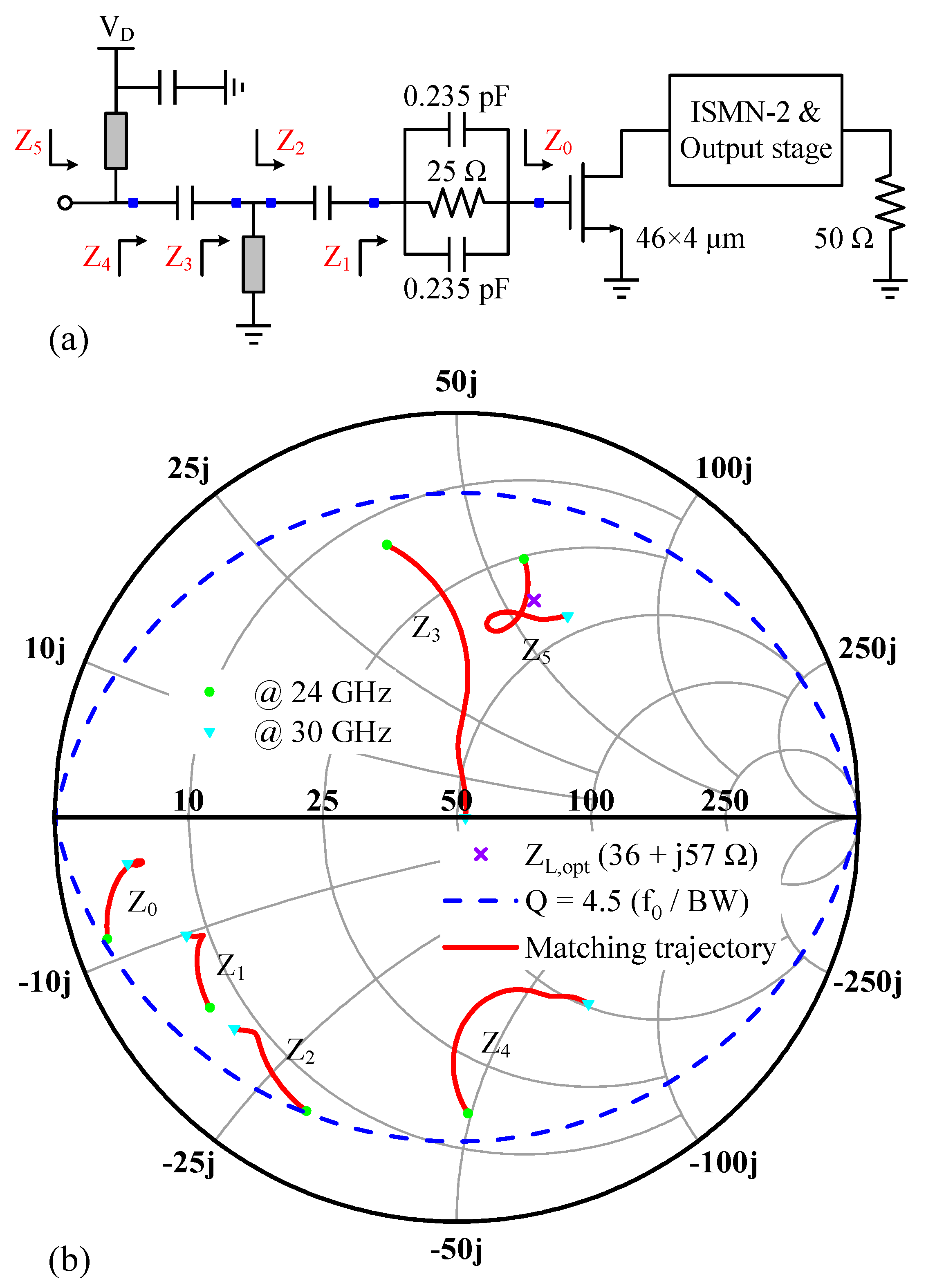
3.2. Source-Pull Analysis and Low-Pass ISMN-2 Synthesis
3.3. Compact High-Pass ISMN-1 Design
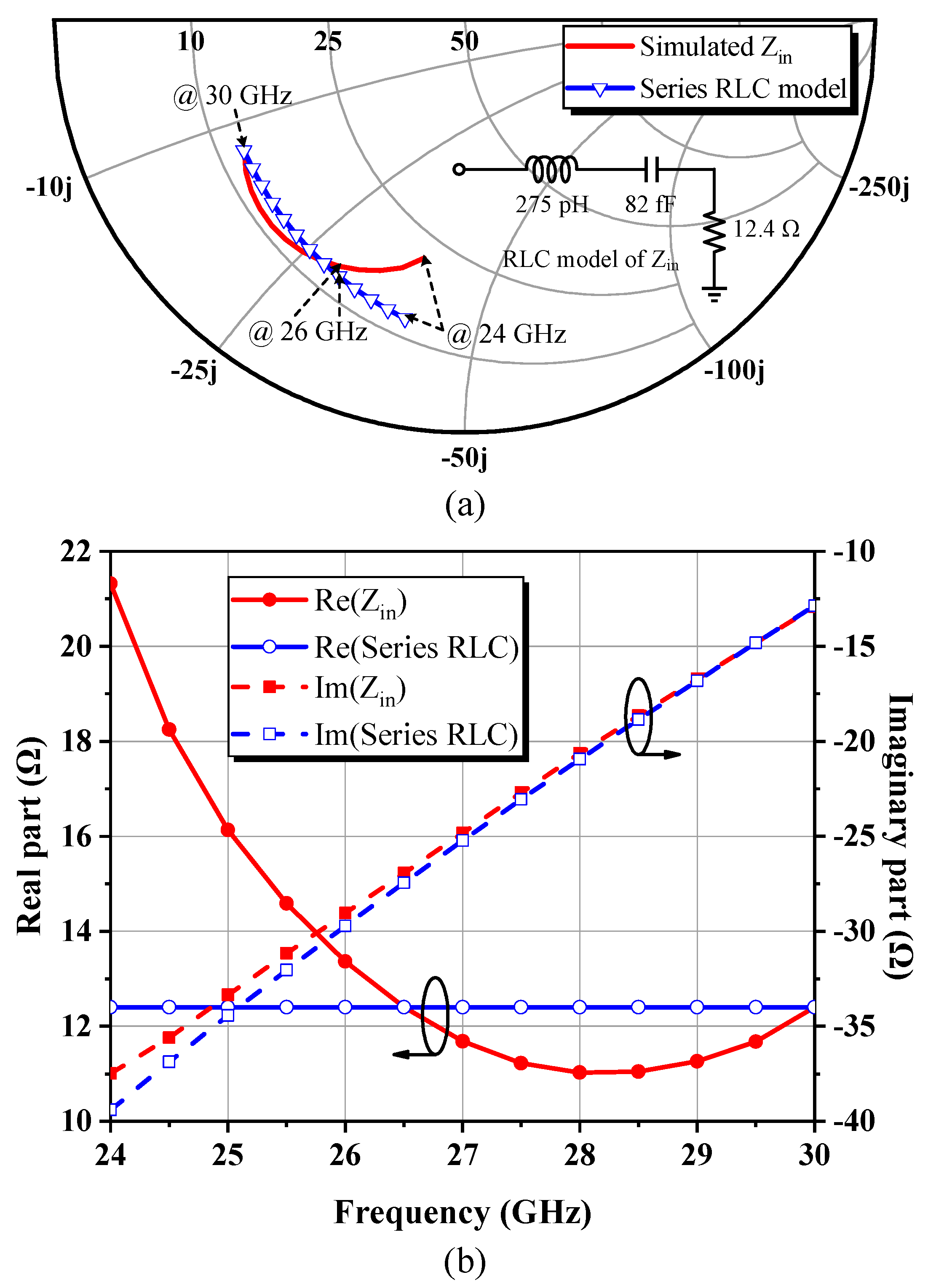
3.4. Input Impedance Model and Band-Pass IMN Synthesis
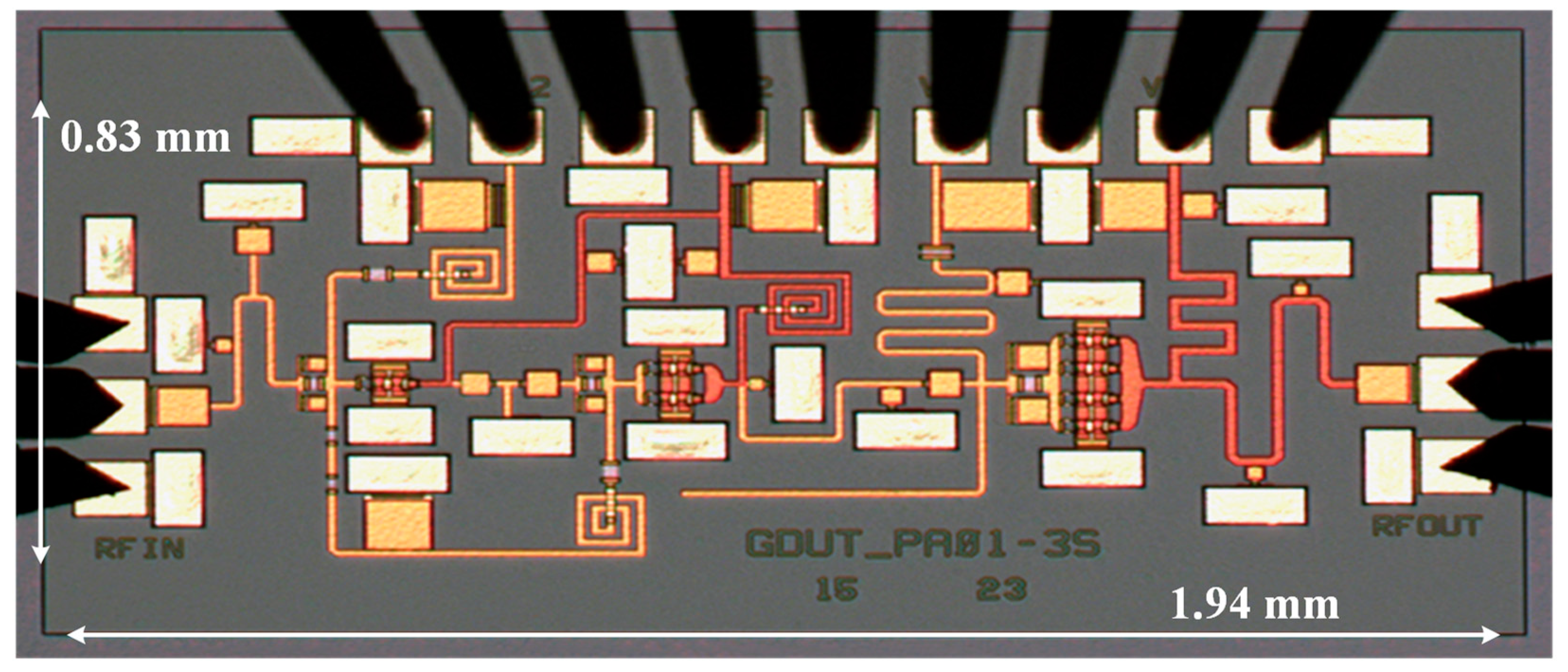
4. Measurement Results
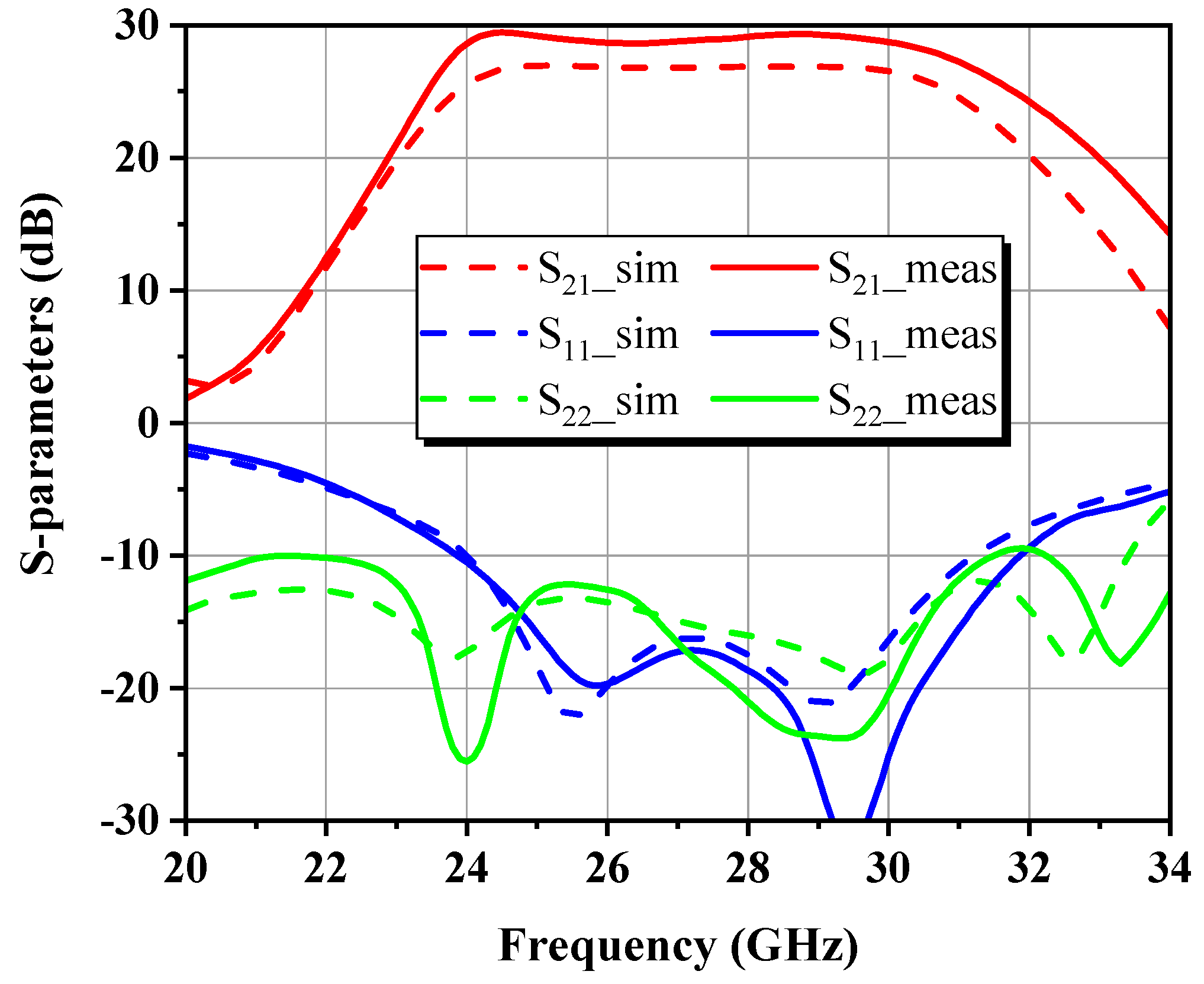
4.1. Small-Signal Characterization
4.2. Large-Signal Characterization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, D.-H.; Yom, I.-B.; Kim, D.-W. 6-GHz-to-18-GHz AlGaN/GaN Cascaded Nonuniform Distributed Power Amplifier MMIC Using Load Modulation of Increased Series Gate Capacitance. ETRI J. 2017, 39, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.; Frounchi, M.; Medi, A. On Design of Wideband Compact-Size Ka/Q-Band High-Power Amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 1831–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerherve, E.; Demirel, N.; Ghiotto, A.; Larie, A.; Deltimple, N.; Pham, J.-M.; Mancuso, Y.; Garrec, P. A Broadband 4.5–15.5-GHz SiGe Power Amplifier with 25.5-dBm Peak Saturated Output Power and 28.7% Maximum PAE. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarman, B.; Carlin, H. A Simplified “Real Frequency” Technique Applied to Broad-Band Multistage Microwave Amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1982, 30, 2216–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; He, S.; You, F.; Peng, J.; Chen, P.; Dong, L. A New Distributed Parameter Broadband Matching Method for Power Amplifier via Real Frequency Technique. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaei, G. Tables of Chebyshev impedance—Transforming networks of low-pass filter form. Proc. IEEE 1964, 52, 939–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawson, D. Closed-Form Solutions for the Design of Optimum Matching Networks. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2008, 57, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Peroulis, D. Design of Highly Efficient Broadband Class-E Power Amplifier Using Synthesized Low-Pass Matching Networks. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2011, 59, 3162–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuerschutz, P.; Friesicke, C.; Quay, R.; Jacob, A.F. A Q-band power amplifier MMIC using 100 nm AlGaN/GaN HEMT. In Proceedings of the 2016 11th European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference (EuMIC), London, UK, 3–4 October 2016; pp. 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Implementation of Flat Gain Broadband Power Amplifier with Impedance Rotation Compensation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 13304–13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, W.; Kim, T.; Helaoui, M.; Ghannouchi, F.M.; Yang, Y. 6–18 GHz GaAs pHEMT Broadband Power Amplifier Based on Dual-Frequency Selective Impedance Matching Technique. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 66275–66280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wan, J.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Liang, X. Design of a Broadband MMIC Driver Amplifier with Enhanced Feedback and Temperature Compensation Technique. Electronics 2022, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, G. Design of broadband high-gain GaN MMIC power amplifier based on reactive/resistive matching and feedback technique. IEICE Electron. Express 2021, 18, 20210313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, I.J. Fundamentals of RF and Microwave Transistor Amplifiers; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, K.H.; Nirmal, D. A review of GaN HEMT broadband power amplifiers. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2020, 116, 153040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neininger, P.; John, L.; Bruckner, P.; Friesicke, C.; Quay, R.; Zwick, T. Design, Analysis and Evaluation of a Broadband High-Power Amplifier for Ka-Band Frequencies. In Proceedings of the IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), Boston, MA, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Nayak, S.; Campbell, C.; Reese, E. High Efficiency 5 W/10 W 32–38 GHz Power Amplifier MMICs Utilizing Advanced 0.15 µm GaN HEMT Technology. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Symposium (CSICS), Austin, TX, USA, 23–26 October 2016; pp. 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Yang, Y.; Kang, H.; Lee, H.; Lim, W.; Bae, J.; Koo, H.; Yoon, J.; Hwang, K.C.; Lee, K.-Y. Broadband InGaP/GaAs HBT Power Amplifier Integrated Circuit Using Cascode Structure and Optimized Shunt Inductor. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2019, 67, 5090–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, P.; Xu, J.; Wang, R. 23.5–30 GHz gallium nitride on silicon power amplifier MMIC with 7.6–12.4 W saturation output power. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2019, 61, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cripps, S.C. RF Power Amplifiers for Wireless Communications, 2nd ed.; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Qorvo, High Frequency Amplifiers, TGA2594 Data Sheet. Available online: http://www.qorvo.com (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Northrop Grumman, APN244 Data Sheet. Available online: https://www.northropgrumman.com (accessed on 6 June 2022).








| Transistor Size (μm) | fT (GHz) | fmax (GHz) | Zin @ 27 GHz (Ω) | Zout @ 27 GHz (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 92 × 4 | 92.8 | 112 | 6.6 + j0.6 | 16.3 − j5 |
| 62 × 6 | 96.3 | 129.7 | 5.5 − j1 | 15.4 − j5.2 |
| 46 × 8 | 100 | 139.3 | 5.1 − j1.8 | 15.1 − j5.3 |
| HEMT (μm) | ZL,opt (Ω) | RL (Ω) | Cout (pF) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 46 × 8 | 11 + j13 | 26 | 0.27 |
| 46 × 4 | 21 + j31 | 75 | 0.13 |
| 50 × 2 | 36 + j57 | / | / |
| Elements | g (r = 4, FBW = 0.4) | Real-to-Real (48 Ω to 12 Ω) | Real-to-Complex (48 Ω to 11 + j13 Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | 1.19 | 84 pH | 157 pH |
| C1 | 0.73 | 0.36 pF | 0.4 pF |
| L2 | 2.92 | 206 pH | 203 pH |
| C2 | 0.3 | 0.15 pF | 0.17 pF |
| Ref. | [13] | [16] | [17] | [19] | TGA2594 [21] | APN244 [22] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process | 0.1 μm GaN/Si | 0.1 μm GaN/SiC | 0.15 μm GaN/SiC | 0.1 μm GaN/Si | 0.15 μm GaN/SiC | 0.2 μm GaN/SiC | 0.1 μm GaN/Si |
| VD (V) | 12 | 15 | 20 | 12 | 20 | 28 | 12 |
| Meas. mode | Pulsed | Pulsed | CW | Pulsed | CW | Pulsed | Pulsed |
| Freq. (GHz) (FBW) | 22–27 (20.4%) | 27–34 (23%) | 32–38 (17.1%) | 24–30 (22.2%) | 27–31 (13.8%) | 24–28 (15.4%) | 24–30 (22.2%) |
| Gain (dB) | 24 ± 0.5 | 20.5 ± 1.5 | 17 ± 0.5 | 17.9 ± 1.5 | 23.6 ± 1.9 | 20 ± 0.5 | 29 ± 0.4 |
| Pout (dBm) | 31 ± 0.7 | 38.7 ± 0.4 | 36.7 ± 0.5 | 39.9 ± 1 | 37 ± 0.4 | 38.6 ± 0.5 | 30.7 ± 0.2 |
| PAE (%) | 30.5–36.9 a | 24.5–30.5 b | 25–34 c | 24–37 a | 26.5–30.3 c | 30.8–32.6 a | 30.6–34.7 b |
| Size (mm2) | 1.8 × 0.87 | 4.5 × 3.5 | 2.22 × 1.6 | 3.7 × 3.2 | 3.24 × 1.74 | 3.3 × 1.95 | 1.94 × 0.83 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G. Design of an Efficient 24–30 GHz GaN MMIC Power Amplifier Using Filter-Based Matching Networks. Electronics 2022, 11, 1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11131934
Peng L, Chen J, Zhang Z, Zhang G. Design of an Efficient 24–30 GHz GaN MMIC Power Amplifier Using Filter-Based Matching Networks. Electronics. 2022; 11(13):1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11131934
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Lin, Jianqiang Chen, Zhihao Zhang, and Gary Zhang. 2022. "Design of an Efficient 24–30 GHz GaN MMIC Power Amplifier Using Filter-Based Matching Networks" Electronics 11, no. 13: 1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11131934
APA StylePeng, L., Chen, J., Zhang, Z., & Zhang, G. (2022). Design of an Efficient 24–30 GHz GaN MMIC Power Amplifier Using Filter-Based Matching Networks. Electronics, 11(13), 1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11131934






