Multi-Connectivity Enhanced Communication-Incentive Distributed Computation Offloading in Vehicular Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. System Model
3.1. Channel Model
3.2. Computation Model
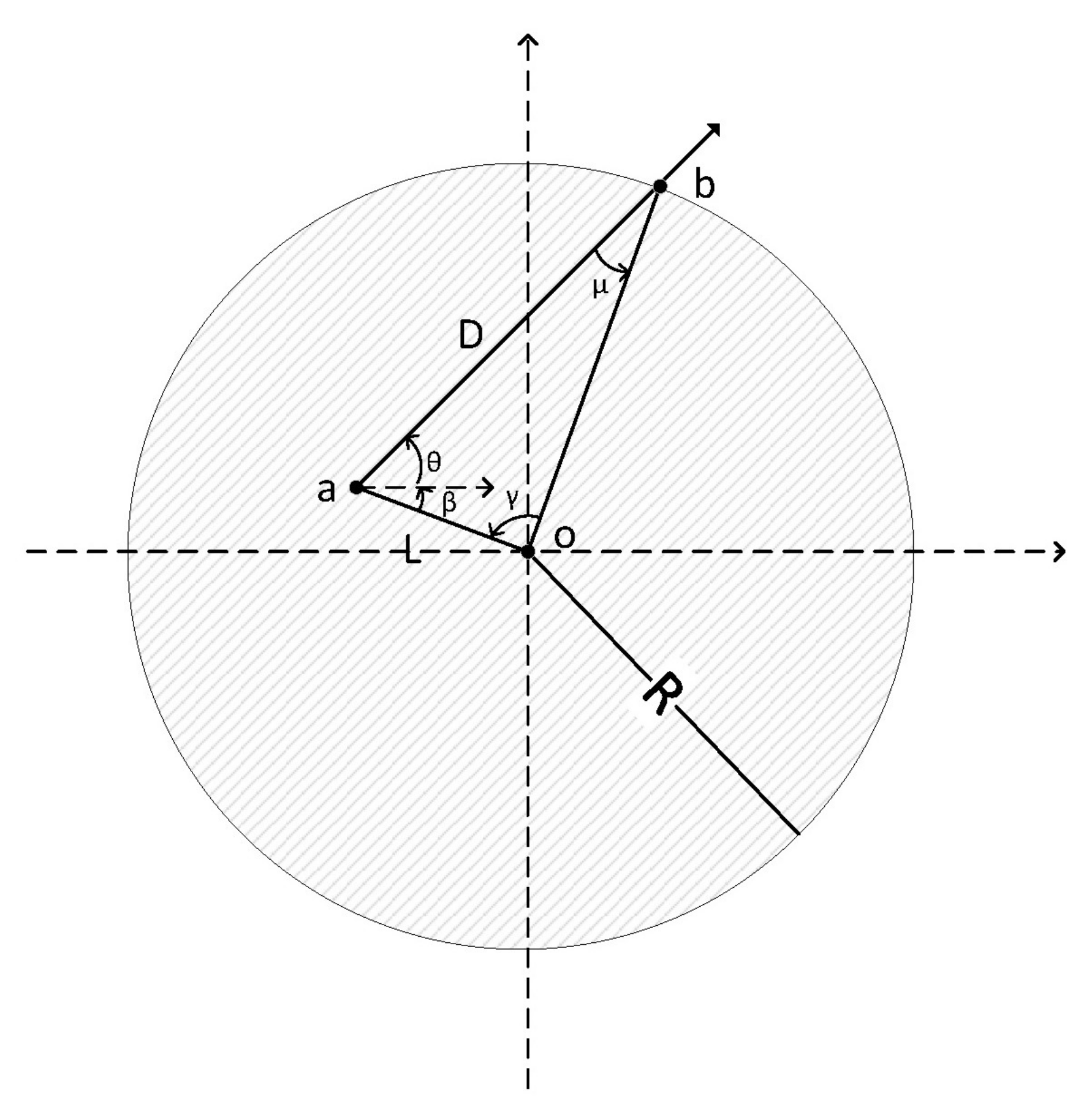
3.3. Moving Model
3.3.1. Vehicles
3.3.2. Pedestrians
3.3.3. Transmission Time Limit
3.4. Incentive Model
3.5. Problem Formulation
4. Co-Scheduling of Communication and Computation Optimization
4.1. Branch and Bound Method for Integer Variables
4.2. Continuous Variables with Barrier Function
| Algorithm 1: Co-scheduling of Communication and Computation. |
| Initially, , ,,, satisfying , , , ,, ; |
| 1: Repeat |
| 2: Branch and bound following policy with parameters |
| 3: |
| 4: While |
| 5: Do |
| 6: ; ; |
| 7: If |
| 8: Break |
| 9: End |
| 10: |
| 11: If |
| 12: ; |
| 13: End |
| 14: ; |
| 15: End |
| 16: ; |
| 17: End |
| 18: If |
| 19: Break |
| 20: End |
| 21: |
| 22: End |
5. Performance Evaluations and Simulation Results
5.1. Simulation Setting
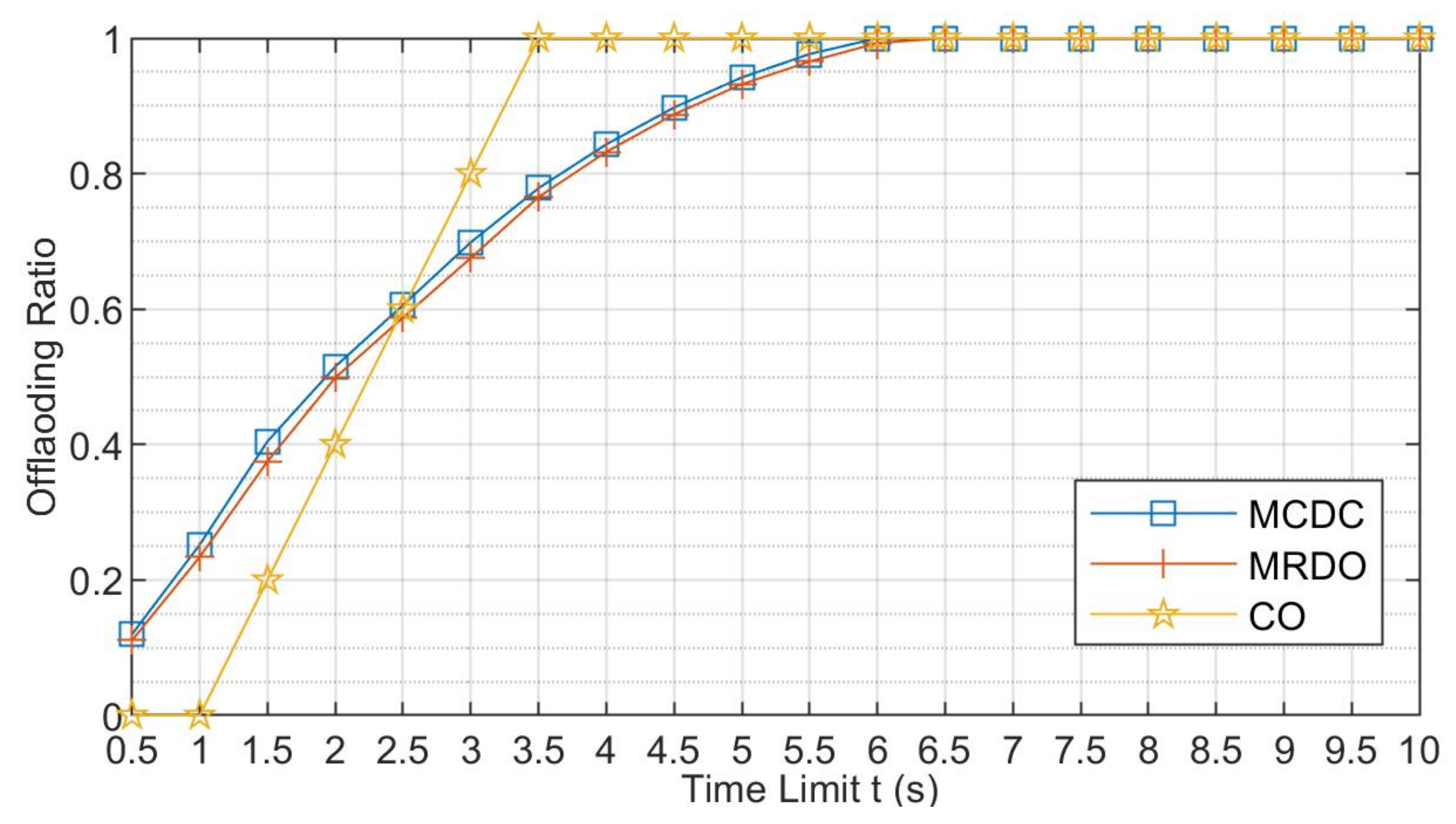
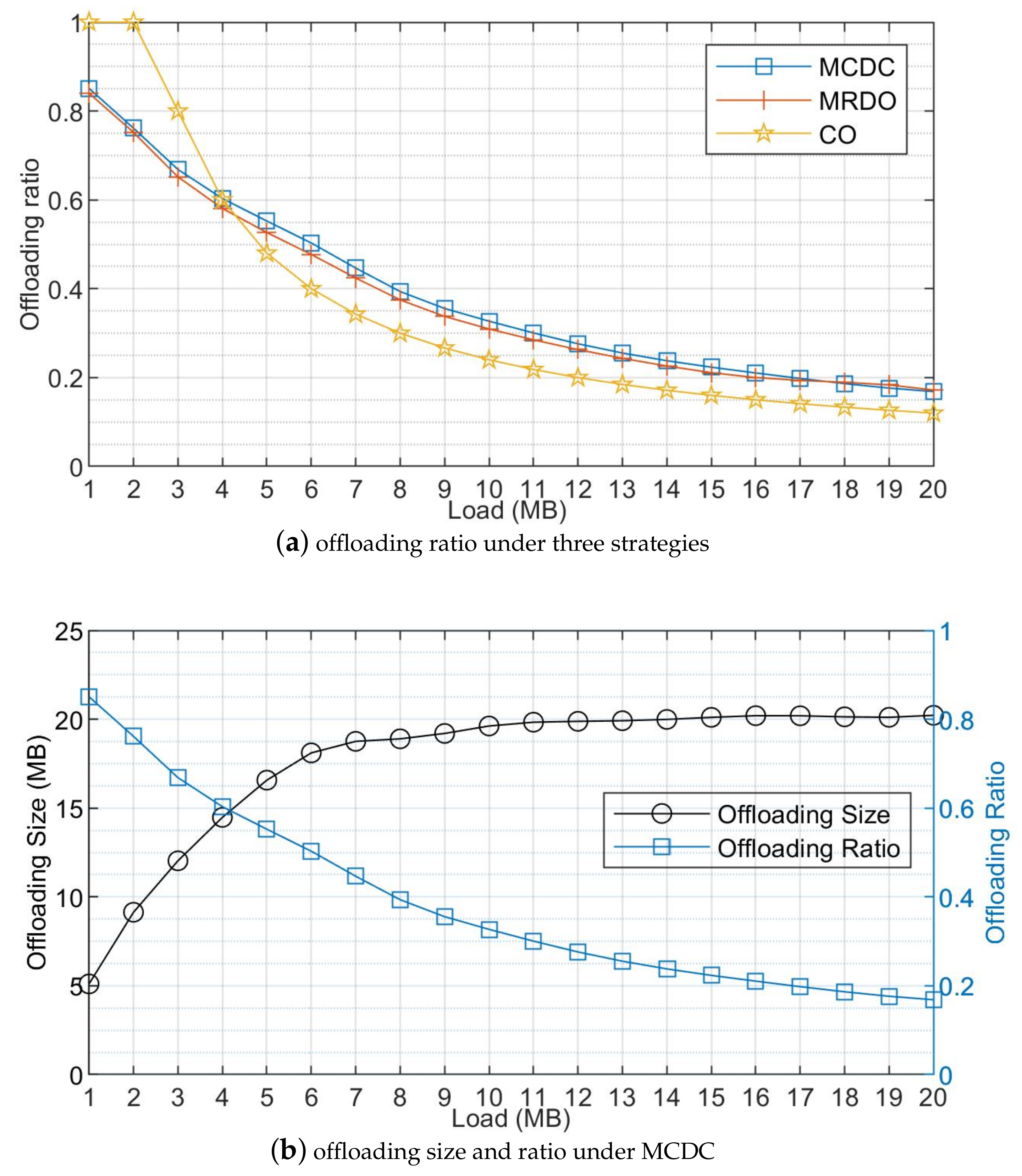
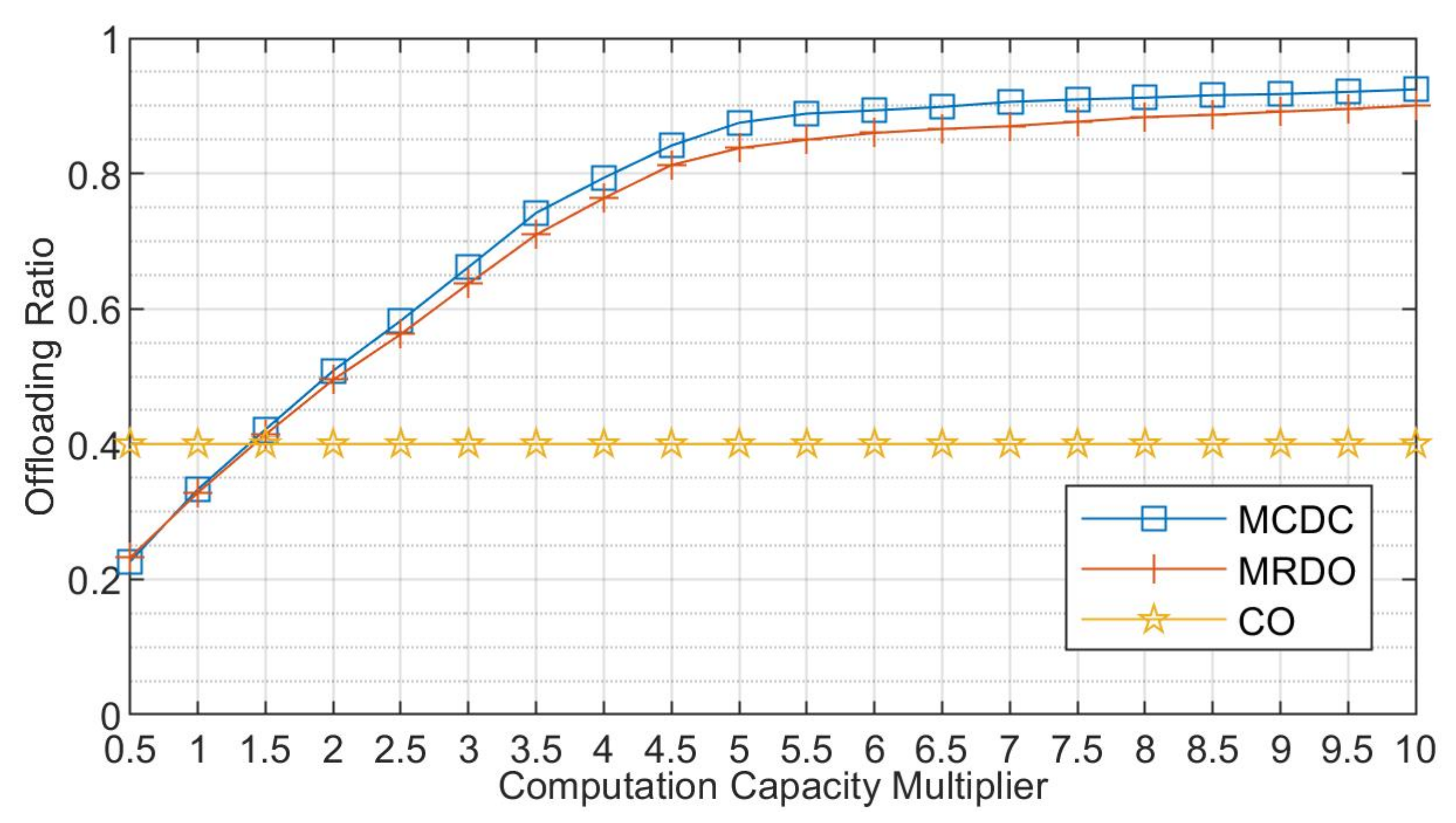
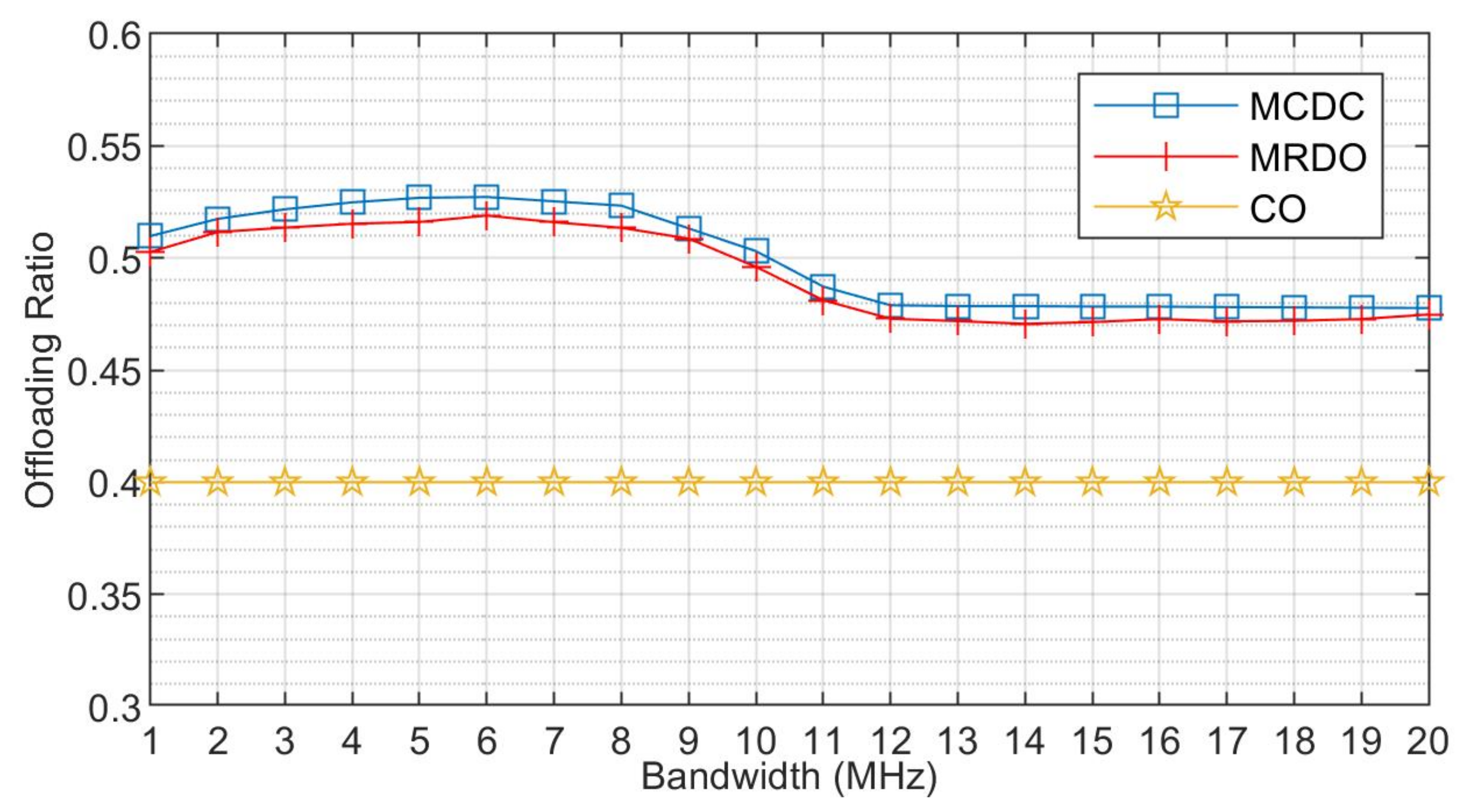
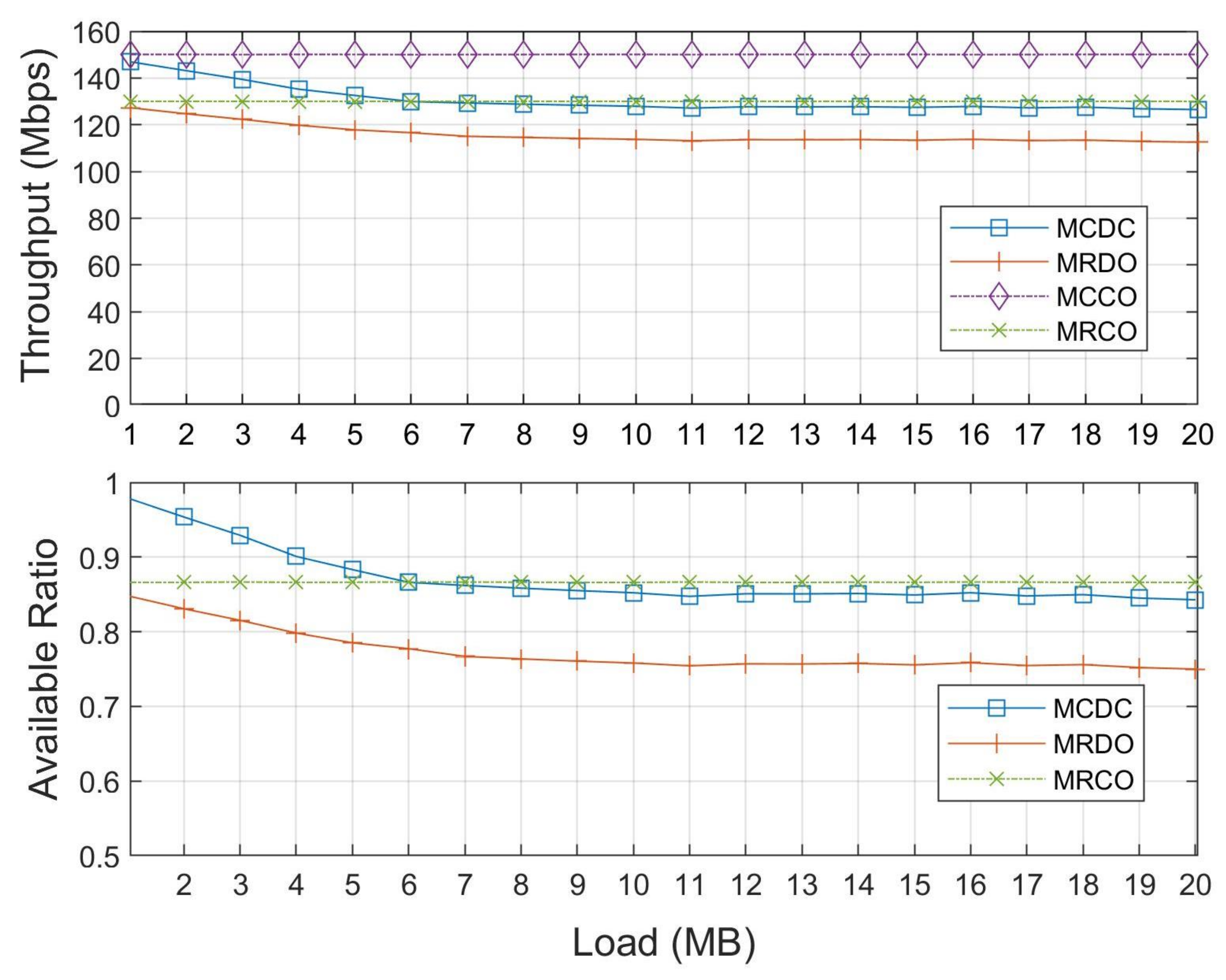
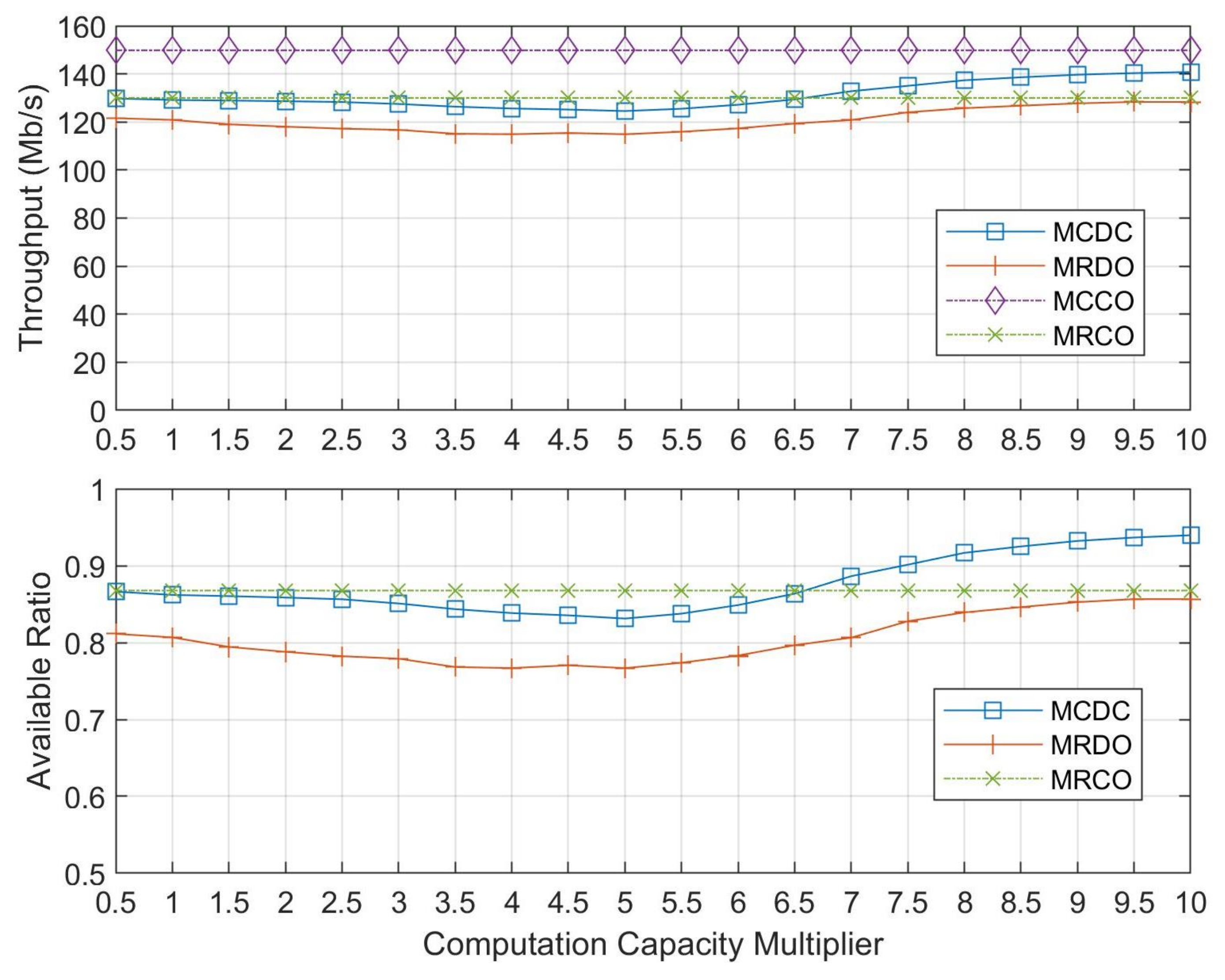
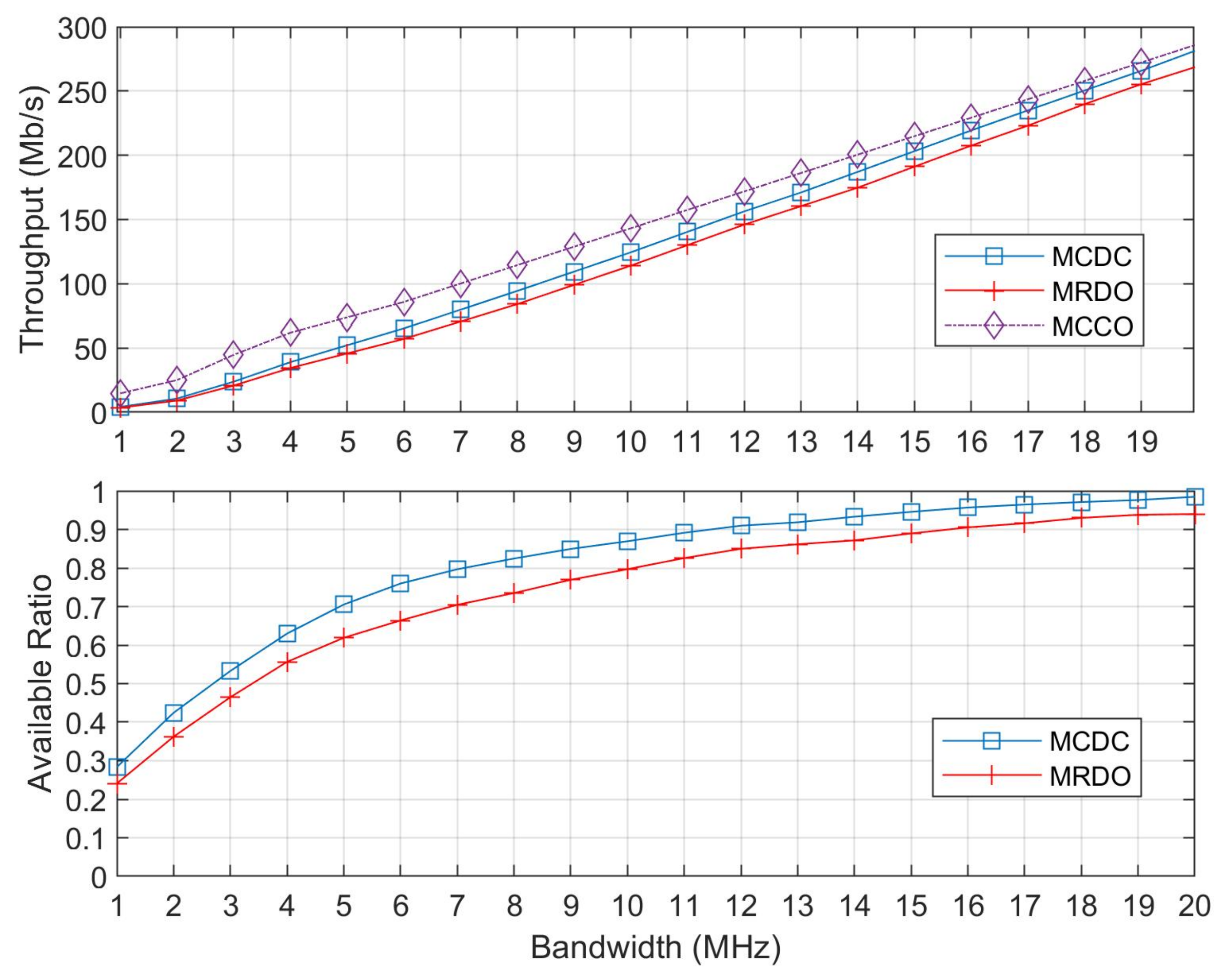
5.2. Simulation Results and Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cisco. Cisco Visual Networking Index: Forecast and Trends. Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/visual-networking-index-vni/white-paper-c11-741490.html (accessed on 19 December 2018).
- Feriani, A.; Hossain, E. Single and Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning for AI-Enabled Wireless Networks: A Tutorial. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1226–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letaief, K.B.; Chen, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.J.A. The Roadmap to 6G: AI Empowered Wireless Networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, K.; Han, S.; Tao, X.; Zhang, P. Learning Based Flexible Cross-layer Optimization for Ultra-reliable and Low Latency Applications in IoT Scenarios. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Cai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Shen, X. Dynamic Computation Offloading for Mobile Cloud Computing: A Stochastic Game-Theoretic Approach. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 18, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, F.; Hinton, K.; Ayre, R.; Alpcan, T.; Tucker, R.S. Fog Computing May Help to Save Energy in Cloud Computing. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2016, 34, 1728–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Mao, Y.; Leng, S.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y. Mobile-Edge Computing for Vehicular Networks: A Promising Network Paradigm with Predictive Off-Loading. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2017, 12, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, R.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Y. Distributed Reputation Management for Secure and Efficient Vehicular Edge Computing and Networks. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 25408–25420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, P.S.; Rao, S. Resource Allocation in Cloud Computing Using the Uncertainty Principle of Game Theory. IEEE Syst. J. 2016, 10, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Huang, K.; Chae, H. Energy Efficient Mobile Cloud Computing Powered by Wireless Energy Transfer. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2016, 34, 1757–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, T.; Pang, A.; Chung, W.; Zhang, J. Latency-Driven Fog Cooperation Approach in Fog Radio Access Networks. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2019, 12, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y. Energy-Efficient Fair Cooperation Fog Computing in Mobile Edge Networks for Smart City. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 7543–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, K. Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation For Cloud Assisted Mobile Edge Computing in Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 7944–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Xu, D.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Joint Load Balancing and Offloading in Vehicular Edge Computing and Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 4377–4387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Han, G.; Qi, X.; Guizani, M.; Shu, L. A Distributed Mobile Fog Computing Scheme for Mobile Delay-Sensitive Applications in SDN-Enabled Vehicular Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 5481–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Pan, S.; Chen, Z.; Gu, L. An MDP-Based Wireless Energy Harvesting Decision Strategy for Mobile Device in Edge Computing. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, W. Incentive-Aware Micro Computing Cluster Formation for Cooperative Fog Computing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 2643–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Xu, X.; Fang, S.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Y.; Tao, X.; Zhang, P. Energy Efficient Secure Computation Offloading in NOMA-Based mMTC Networks for IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 5674–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Huang, X.; Bian, S.; Shao, Z.; Yang, Y. PORA: Predictive Offloading and Resource Allocation in Dynamic Fog Computing Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Sun, Y.; Gharavi, H.; Thompson, J. Joint Optimization of Computation and Communication Power in Multi-User Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 4051–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Huang, H.; Miyazaki, T.; Guo, S. Traffic and Computation Co-Offloading With Reinforcement Learning in Fog Computing for Industrial Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Feng, G.; Lv, H.; Wang, H.; Lin, J. Joint Optimization of Traffic and Computation Offloading in UAV-Assisted Wireless Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS), Chengdu, China, 9–12 October 2018; pp. 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Pei, Q.; Yu, F.R.; Chu, X.; Shang, B. Computation Offloading and Resource Allocation for Wireless Powered Mobile Edge Computing with Latency Constraint. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 8, 1320–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Altman, E.; El-Azouzi, R.; Fathy, M. Analytical Model for Connectivity in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 57, 3341–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Xu, X.; Haenggi, M. Meta Distribution of the SIR in Moving Networks. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 3614–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Fang, Y.; Lin, P. Mobility Management Strategy Based on User Mobility Patterns in Wireless Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2007, 56, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabazian, M.; Ali, M.K.M. A Performance Modeling of Connectivity in VehicularAd Hoc Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 57, 2440–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, S.; Maeder, A.; Sartori, C.; Höhne, T.; Vejlgaard, B.; Chandramouli, D. 5G multi-RAT multi-connectivity architecture. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 23–27 May 2016; pp. 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanshid, A.; Rost, P.; Michalopoulos, D.S.; Phan, V.V.; Bakker, H.; Aziz, D.; Tayade, S.; Schotten, H.D.; Wong, S.; Holland, O. Multi-connectivity functional architectures in 5G. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 23–27 May 2016; pp. 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, L.; Zheng, N.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J.; Yu, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Qian, X.; Chi, J.; et al. C/U Split Multi-Connectivity in the Next Generation New Radio System. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 85th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Sydney, Australia, 4–7 June 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Tao, X.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic Multiconnectivity Based Joint Scheduling of eMBB and uRLLC in 5G Networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Guan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Teng, Y. Goodput-Aware Traffic Splitting Scheme with Non-ideal Backhaul for 5G-LTE Multi-Connectivity. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Marrakech, Morocco, 15–19 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Schulz, P.; Dörpinghaus, M.; Filho, J.C.S.S.; Fettweis, G. How Reliable and Capable is Multi-Connectivity? IEEE Trans. Commun. 2019, 67, 1506–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suer, M.; Thein, C.; Tchouankem, H.; Wolf, L. Multi-Connectivity as an Enabler for Reliable Low Latency Communications—An Overview. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, V.; Solomitckii, D.; Samuylov, A.; Lema, M.A.; Gapeyenko, M.; Moltchanov, D.; Andreev, S.; Naumov, V.; Samouylov, K.; Dohler, M.; et al. Dynamic Multi-Connectivity Performance in Ultra-Dense Urban mmWave Deployments. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 2038–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yu, G.; Li, G.Y. User Association for Ultra-Dense mmWave Networks With Multi-Connectivity: A Multi-Label Classification Approach. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 8, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolesi, M.; Mascolo, C. Designing Mobility Models based on Social Network Theory. ACM SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2007, 11, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Leng, S.; Cook, S.C. Effects of mobility on stability in vehicular ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE 6th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications, Chengdu, China, 23–25 September 2010; pp. 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP. Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA); Further Advancements for E-UTRA Physical Layer Aspects. Tech. Rep 36.814, 3GPP. v9.0.0. 2010. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2493 (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- 3GPP. Small Cell Enhancements for E-UTRA and E-UTRAN—Physical Layer Aspects. Tech. Rep 36.872, 3GPP. v12.1.0. 2013. Available online: https://portal.3gpp.org/desktopmodules/Specifications/SpecificationDetails.aspx?specificationId=2573 (accessed on 10 October 2021).


| Notations | Meanings |
|---|---|
| pico BS transmission power on 1 Hz | |
| channel gain between pico BS m and UE u | |
| power of Gaussian white noise on 1 Hz | |
| SINR of UE u received from pico BS m | |
| association exists between BS m and UE u | |
| bandwidth of BSs the UE u occupies | |
| data rate of UE u | |
| computation task load of pico BS m | |
| proportion of the task the pico BS m allocates to the UE u | |
| bandwidth of BSs the UE u occupies | |
| computation task transmission rate from pico BS m to UE u | |
| computing time of UE u for pico BS m | |
| transmission time of UE u for pico BS m | |
| velocity of vehicle at time t | |
| control parameter representing the randomness of the velocity | |
| mean velocity of vehicles | |
| Gaussian random with zero mean and variance | |
| velocity of pedestrian | |
| D | moving distance |
| probability of staying within the area of pico BSs | |
| tolerance factor | |
| requirement factor | |
| C | computation capability baseline |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of pico BSs | 12 |
| Number of pedestrians | 120 |
| Number of Vehicles | 40 |
| Power of pico BSs per 10 MHz | 30 dBm |
| Power of Gaussian noise per 10 MHz | −95 dBm |
| Bandwidth of pico BSs | 2–20 MHz |
| Computation task size G | 1–20 MB |
| Time limit t | 0.5–10 s |
| Computation capability multiplier | 1–20 |
| Mean velocity of pedestrians | 1 m/s |
| Mean velocity of vehicles | 10 m/s |
| Control parameter | 0.5 |
| Computation baseline C | 1 |
| Requirement factor | 0.5–1 |
| Adjustment parameter | 0.02 |
| Variance |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Han, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, P. Multi-Connectivity Enhanced Communication-Incentive Distributed Computation Offloading in Vehicular Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202466
Zhang K, Xu X, Zhang J, Han S, Wang B, Zhang P. Multi-Connectivity Enhanced Communication-Incentive Distributed Computation Offloading in Vehicular Networks. Electronics. 2021; 10(20):2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202466
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kangjie, Xiaodong Xu, Jingxuan Zhang, Shujun Han, Bizhu Wang, and Ping Zhang. 2021. "Multi-Connectivity Enhanced Communication-Incentive Distributed Computation Offloading in Vehicular Networks" Electronics 10, no. 20: 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202466
APA StyleZhang, K., Xu, X., Zhang, J., Han, S., Wang, B., & Zhang, P. (2021). Multi-Connectivity Enhanced Communication-Incentive Distributed Computation Offloading in Vehicular Networks. Electronics, 10(20), 2466. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202466






