Abstract
In this work, we propose a general framework to design a signal classification algorithm over time selective channels for wireless communications applications. We derive an upper bound on the maximum number of observation samples over which the channel response is an essential invariant. The proposed framework relies on dividing the received signal into blocks, and each of them has a length less than the mentioned bound. Then, these blocks are fed into a number of classifiers in a parallel fashion. A final decision is made through a well-designed combiner and detector. As a case study, we employ the proposed framework on a space-time block-code classification problem by developing two combiners and detectors. Monte Carlo simulations show that the proposed framework is capable of achieving excellent classification performance over time selective channels compared to the conventional algorithms.
1. Introduction
Signal classification was first motivated by its usage in military applications such as electronic warfare, spectrum surveillance, and interference identification. With the growing popularity of reconfigurable radios, it becomes an important technology for commercial applications as well because it enables the optimization of transmission parameters according to their interactions with the environment [1,2].
Modulation classification has recently attracted a great deal of interest from academia, industry, and global standardization bodies [3,4,5]. Moreover, classification of space block time coding (SBTC) is introduced in [6,7]. In addition, channel coding classification algorithms are proposed in [8,9]. Generally, the existing classification algorithms are divided into two types: likelihood-based and feature-based. The former calculates a likelihood function of a noisy received signal and applies a maximum likelihood (ML) classifier to complete the process [10]. The latter traces features of the distorted received signal by exploring its characteristics, and after that a decision is made [11]. Recently, machine learning and neural network algorithms are being considered for signal classification [12,13].
Designing classification algorithms for wireless applications is typically challenging since classifiers have no (or limited) a priori knowledge of transmission parameters such as channel state information, synchronization parameters, the distribution and power of the noise, and transmitted data symbols. With mobility, channel variation over the interval of observation creates a further issue of concern [14].
The key idea of the previously published works that focused on signal classification over time selective channels for multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems was to blindly separate the MIMO source symbols through using continuous modulus algorithms and then perform signal classification through employing intelligent learning algorithms (e.g., [15] and reference therein). However, this approach requires offline training, which may be not available in many practical scenarios.
Alternatively, in this paper, we propose a general framework applicable to diverse deployment of signal classification scenarios over time selective channels without the need to have offline training. The framework relies on using a bank of a conventional classifier that is designed to operate in time-invariant channels. Each classifier processes a part of observation samples whose length is less than or equal to a certain value. Then, a well-designed combiner and detector are used to make a final decision. As a case study, we apply the proposed framework on a STBC classification problem over time selective channels by proposing two novel combiners and detectors.
The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2, we introduce the observation model. The proposed framework and its application on STBC signal classification are provided in Section 3 and Section 4, respectively. In Section 5, simulation results are presented. Finally, the work is concluded in Section 6.
Notation: Throughout this paper, denotes the expectation with respect to all randomness in the argument; refers to the zeroth-order Bessel function of the first kind; is the inverse function of , is the estimated value of unknown value ; is the cardinality of the set ; is the maximum Doppler shift; is the maximum Doppler shift normalized to the total bandwidth; is the sampling duration; U is the number of observation samples; is the transmission wavelength; is the gth channel coefficient between transmit-antenna f and receive-antenna i; G denotes the channel length; M is the number of classifiers; L is the number of received samples that can be handled by a single classifier; and is the predefined probability of false detection.
2. Observation Model
In this section, we investigate the properties of time selective channels, with the aim of determining an upper bound formula on the number of observation samples such that the channel has an approximate time-invariant behavior over those samples. Later on, we make use of this upper bound to properly design a signal classification algorithm operating over time selective channels.
We consider a narrow-band communication system operating over a time selective channel. The received signal at the time instant t, , is expressed as
where , , and refer to the transmitted signal, the channel gain, and the noise component, respectively. (In order to simplify the analysis, we assume a single tap time varying channel. However, the proposed upper bounds shown in (3) and (4) are also valid for multiple path channels). Note that Equation (1) is expressed in a general form, which can be applied to any modulation format associated with any pulse shaping. The auto-correlation of the fading envelope at the time lag is given by [16]
where and * stand for expectation and complex conjugate operators, respectively. Here, is the variance of , denotes the zeroth-order Bessel function of the first kind, and is the maximum Doppler shift. Figure 1 shows as a function of the parameter . The channel is essentially invariant if , and this corresponds to as indicated in Figure 1. The maximum time lag holding the previous inequality is given as Here the superscript (0.9) refers to using the correlation of 0.9. We denote as the maximum Doppler shift normalized to the total bandwidth, where is the sampling duration. In the discrete time domain, is expressed as . Therefore, is easily expressed as
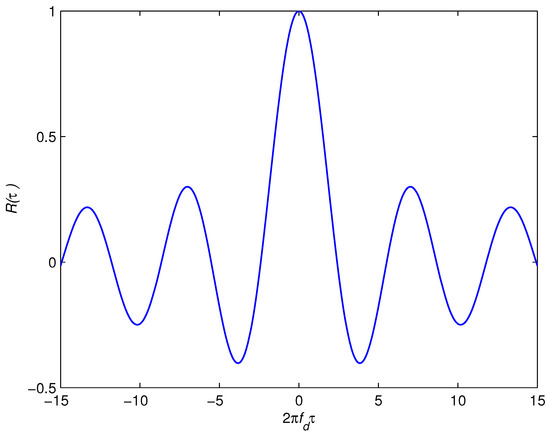
Figure 1.
Auto-correlation function of the fading envelope.
Equation (3) provides us with the maximum number of samples over which the channel is almost constant, and this represents an upper bound on the actual used number of observation samples, L, i.e., . Intuitively, gets smaller with increasing , which, in turn, reduces L, and this negatively affects the final classification performance. In order to decrease the limitation of L, we also consider the channel as essentially invariant if . Following a similar approach as previously explained, one can express the upper bound in this case as
Both conditions of and are widely used in the literature [16] with the definition of channel coherence time. Note that the coherence time is the interval of that keeps the function almost constant around its maximum. The small value of the coherence time yields a small number of received samples that are subject to approximately a time-invariant channel. Using a small number of processing samples leads to a reduction in classification performance. However, a large value of the coherence time allows us to have a large number of received samples that are subject to approximately a time-invariant channel. This improves the classification performance.
It is worth mentioning that most of the classification algorithms reported in the literature failed to achieve a satisfactory performance under time selective channels because they relied on observation periods greater than the corresponding upper bound. For example, the classifier reported in [17] provided a poor performance under a time selective channel with . The reason is that it relied on 69,000 observation samples; however, the upper bound () is 30,000 samples.
3. Proposed Framework
In the previous section, we showed that the number of observation samples, L, should not exceed a certain value (either or ) in order to avoid dramatic variations in the fading envelope. However, this constraint has a negative impact on the performance of a classifier especially when is relatively high. We propose the following framework in order to overcome this issue. We denote U as the observation samples, where U is greater than . For illustration purposes, hereafter we use to refer to the upper bound. We split this large received sequence into M smaller consecutive blocks, each of them contains L samples, where and . Each block is fed into a signal classifier. This acts as a bank of M signal classifiers operating in parallel fashion; each of them sees an almost constant channel coefficient in the time domain. The outputs of these M classifiers need to be appropriately compiled to reach a final decision through a well-designed detector. The structure of the framework is shown in Figure 2. The design of the combiner and the detector differs for different applications. The following practical aspects should be taken into account.
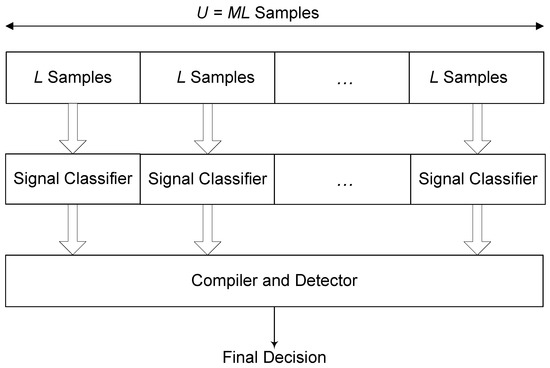
Figure 2.
Conceptual block diagram of the proposed framework.
- The value should be provided as a priori information to determine the upper bound on the number of processed samples per classifier, and then determine the appropriate length of each block. To this end, we assume that the receiver is equipped with a speed meter to measure the relative velocity between the transmitter and receiver, v. Hence, an estimate of is computed through the simple expression of , where is the transmission wavelength.
- We assume that the receiver has a rough estimation of the received signal bandwidth. Therefore, can be computed by using . The aforementioned assumptions can be easily carried out in practice.
4. STBCs Classification
With the growing involvement of MIMO technology in smart wireless applications, the classification of STBCs has gained much attention in the last few years. The previously reported investigations are limited to either frequency flat [18] or frequency selective channels [17,19], ignoring the time-varying nature of wireless channels. However, this should be taken into consideration when designing practical STBCs classifiers. In this section, we show how to implement the proposed framework in one of the reported STBCs classifiers [19]. In addition, we develop and analyze two novel combiners and detectors to compensate for the critical effect of time selective channels.
4.1. Preliminaries
We briefly describe the algorithm proposed in [19], which classifies the received signal into an Alamouti (AL) or a spatial multiplexing (SM) signal with the aid of multiple receive antennas. The kth sample of the received signal at antenna i is expressed as
where f is the transmit-antenna index. Here is the gth channel coefficient between transmit-antenna f and receive-antenna i, G denotes the channel length, and is the noise contribution. The key principle beyond this algorithm is that the cross-correlation functions of the outputs of different receive antennas exhibit peaks at a particular set of time tags for AL, and exhibit nulls for SM. This feature is exploited for classification via employing a false alarm rate (FAR) method. A more formal mathematical description is provided as follows. The expression of the estimated cross-correlation function, , between the output of antenna pair at time lag is given as
where U is the total number of observation samples and is the estimation error. For AL, has non-zero values for and zeros otherwise. However, equals zero at all values of for SM. We denote as the number of receive antennas, as a set of receive antenna pairs , and and as the cardinality of the set . A vector of length is created by concatenating all values of at , . We introduce as the maximum value of the vector , and then is compared to a threshold value, . The AL signal is declared to exist if ; otherwise, the SM signal is chosen.
The threshold value is determined as , where is the predefined probability of falsely detecting the SM signal due to the estimation error and is the inverse function of , which is given as
Here is the variance of the estimation error, which is computed as
where and are design parameters chosen arbitrarily to be much greater than the expected value of G. This guarantees that no peaks occur in the interval [,], where . Since G is not accurately known in practice, we replace G with a design parameter, and is arbitrarily chosen to be close to G, such that . However, in case of no knowledge about G, we set the value of to 1.
4.2. Proposed Classification Algorithm over Time Selective Channels
We employ the proposed framework on the previously mentioned algorithm to have a better performance over time-varying channels. After dividing the observation samples into M blocks, each has , and forwarding them to M classifier in a parallel way, we assume that the output of the mth classifier is and . Hereafter, the index m is attached to the parameters and in order to identify the output of each classifier separately. The conceptual block diagram of the proposed algorithm is represented in Figure 3. In the following, we develop two novel combiners and detectors in order to make a final decision.
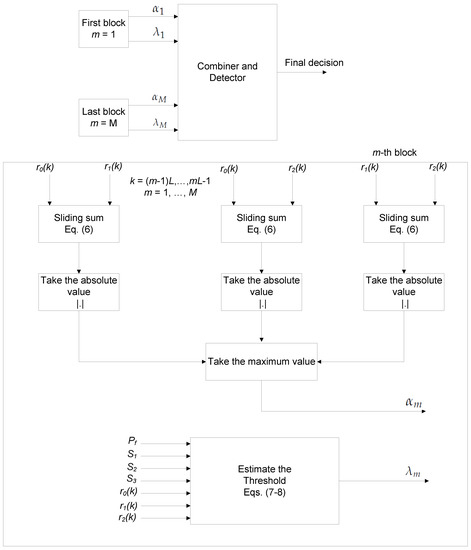
Figure 3.
The conceptual block diagram of the proposed algorithm with three receive antennas.
- Combiner and Detector 1
We define the following indicator function
Then, elements are concatenated into a vector . AL is declared present if the number of ones is greater than (or equal) the number of zeros in the vector X; otherwise, SM is declared present. Simply, each classifier makes its own decision independently and the final decision is made on the basis of the majority of votes. The majority-based logic (and, in general, a counting rule) possesses a number of relevant robustness properties, as shown in [20,21].
- Combiner and Detector 2
We define the following two functions
and
AL is declared present if
otherwise SM is declared present. For illustration, we assume with , , , and . This leads to = (0.9 − 0.6) + (0.75 − 0.35) + 0 = 0.7 and . Since is greater than , AL is declared present.
It is worth mentioning that the terminology of hard and soft decision combiners is widely employed in the literature for different applications with different implementation strategies. An example includes their use in classifying mobile application traffic where the combiners are based on probabilistic models with requirements on training and learning philosophy [22]. As one observes, the proposed combiners in this work relax these requirements and the comparison between them is not feasible because the proposed combiners do not rely on a data set.
5. Simulation Results
Monte Carlo simulations were carried out to examine the performance of the proposed framework. Unless otherwise stated, a quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) modulation scheme was adopted. Each link had four statistically independent taps, each modeled as a zero-mean complex Gaussian random variable having an exponential power delay profile, where and was chosen such that the average energy was normalized to unity. The time selective nature of each tap in the time domain was described in terms of as shown in [23]. The number of received antennas, , was 2, the probability of false alarm, , was , and the number observation samples, U, was 2000. The peaks were searched using while the variance of was computed over the interval of , i.e., and . The probability of correct classification, , AL, SM, i.e., the probability that the code is classified when this is present, was used as a figure of merit. Each set of simulations was run for 1000 trials. Table 1 collects all parameters concurring to describe the simulation setup.

Table 1.
Simulation parameters.
Figure 4 shows the performance of the proposed framework at . Equation (4) said that, for this specific value for , the number of observation samples should not exceed 119. Therefore, we split 2000 observation samples into 20 blocks of which each has 100 samples. For the sake of comparison, we also provide the performance of the case of and the performance of the algorithm proposed in [19]. As observed, a significant improvement is achieved when adopting the proposed framework. In addition, the second combiner and detector outperform the first. This is because the former combining scheme relies on the hard decision outputs of the classifiers, while the latter deals with soft-decision outputs. Note that the classification performance of the SM code is predetermined by , , which is independent of the . Moreover, the peak detection of the AL code is improved at low and intermediate values of . However, at high values, the effect of the estimation error dominates, leading to saturation of the classification performance.
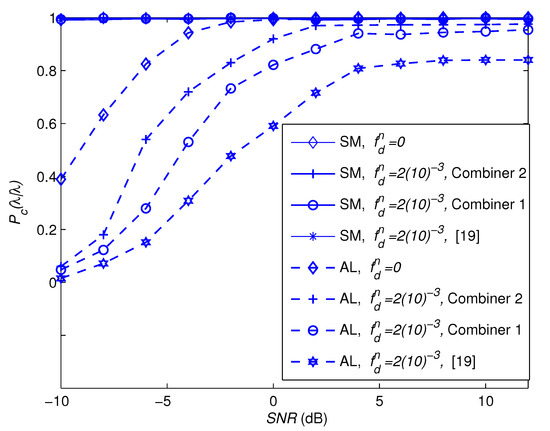
Figure 4.
Probability of correct classification.
Figure 5 and Figure 6 illustrate the classification performance of the two proposed combiners and detectors for correlated channels at dB and . The correlation matrices at the transmitter and receiver are provided as, respectively, [24]
and
where and are the correlation coefficients between the transmit and receive antenna elements, respectively. The correlated matrix for the lth tap, , can be modeled as [24]
where the components of are complex Gaussian random variables with zero mean and variance . The results show that the proposed algorithm provides a satisfactory performance for AL codes up to = 0.4 and . Note that and do not affect the classification performance of the SM code because its performance is predetermined by , which is independent of the correlation coefficients.
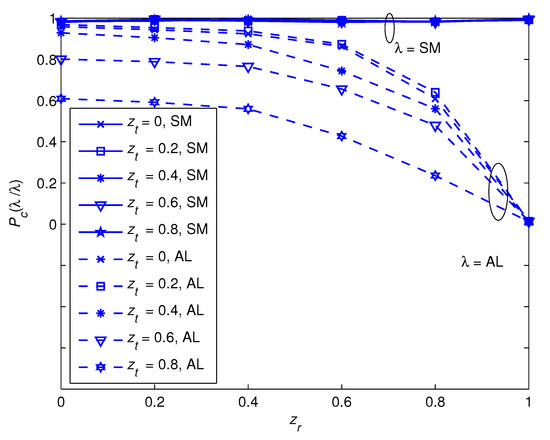
Figure 5.
Effect of and on the classification performance of combiner and detector 1 with .
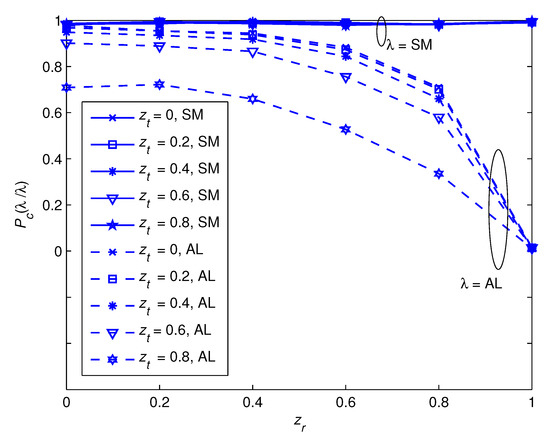
Figure 6.
Effect of and on the classification performance of combiner and detector 2 with .
Figure 7 shows the effect of the time window duration L on the classification performance of the two proposed combiners and detectors at dB and . As observed, the performance of the proposed combiners and detectors do not rely on L for . However, a significant performance degradation occurs after that. This is in agreement with the theoretical findings mentioned in Section 2 that time selective channels have a negative impact on the observation periods that are greater than the corresponding upper bound. Note that here the corresponding bound for is 119 samples.
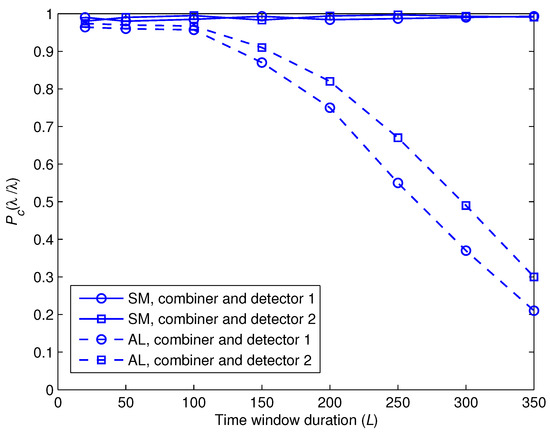
Figure 7.
Effect of L on the classification performance of the two combiners and detectors.
6. Conclusions
This paper detailed the design of signal classifiers over time selective channels. An upper bound expression on the length of observation samples over which the channel response can be considered constant was derived. Adjacent segments of the received signal whose lengths were less than or equal to the mentioned bound were applied to a bank of a conventional classification algorithm. The final decision was made through a combiner and detector. This framework was general in the sense that it worked for any signal classifier over time selective channels. As a case study, we highlighted STBC classification by proposing two novel combiners and detectors. Simulation results showed the robustness of the suggested framework against time-varying channels.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M. and H.M.; methodology, M.M. and H.M.; software, M.M. and H.M.; validation, M.M. and H.M.; formal analysis, M.M. and H.M.; investigation, M.M. and H.M.; resources, M.M. and H.M.; data curation, M.M. and H.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M. and H.M.; writing—review and editing, M.M. and H.M.; visualization, M.M. and H.M.; supervision, M.M. and H.M.; project administration, M.M. and H.M.; funding acquisition, M.M. and H.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University through the Fast-track Research Funding Program.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of Prince Sultan University for paying the Article Processing Charges (APC) of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dobre, O.A. Signal Identification for Emerging Intelligent Radios: Classical Problems and New Challenges. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2015, 18, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobre, O.A.; Abdi, A.; Bar-Ness, Y.; Su, W. A survey of automatic modulation classification techniques: Classical approaches and new developments. IET Commun. 2007, 1, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, P.; Xie, L.; Dai, C.; Chen, Y. Automatic Modulation Recognition for Secondary Modulated Signals. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 962–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Shao, G.; Shao, S. Automatic Modulation Classification for Short Burst Underwater Acoustic Communication Signals Based on Hybrid Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 227793–227809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, K.; Ma, Z. Automatic Modulation Classification Based on Hierarchical Recurrent Neural Networks with Grouped Auxiliary Memory. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 213052–213061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choqueuse, V.; Marazin, M.; Collin, L.; Yao, K.C.; Burel, G. Blind Recognition of Linear Space–Time Block Codes: A Likelihood-Based Approach. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choqueuse, V.; Yao, K.; Collin, L.; Burel, G. Hierarchical Space-Time Block Code Recognition Using Correlation Matrices. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2008, 7, 3526–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Z.; Liu, R. Blind Recognition of LDPC Codes Over Candidate Set. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Z. A Maximum Cosinoidal Cost Function Method for Parameter Estimation of RSC Turbo Codes. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haring, L.; Chen, Y.; Czylwik, A. Automatic Modulation Classification Methods for Wireless OFDM Systems in TDD Mode. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2010, 58, 2480–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W. Feature Space Analysis of Modulation Classification Using Very High-Order Statistics. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2013, 17, 1688–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, Y. Sequential Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks for Fast Automatic Modulation Classification. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 27182–27188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, M.; Yang, J.; Sun, W. A Data Preprocessing Method for Automatic Modulation Classification Based on CNN. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 1206–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, T.; Zhu, Y. Automatic Modulation Classification in Time-Varying Channels Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 197508–197522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, K.; Dayoub, I.; Hamouda, W.; Nzeza, C.; Berbineau, M. Blind Digital Modulation Identification for Spatially Correlated MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 91, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proakis, J. Digital Communications, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Marey, M.; Dobre, O.A.; Inkol, R. Blind STBC Identification for Multiple Antenna OFDM Systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2014, 62, 1554–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marey, M.; Dobre, O.A.; Inkol, R. Classification of Space-time Block Codes Based on Second-order Cyclostationarity with Transmission Impairments. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 2574–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marey, M.; Dobre, O.A.; Liao, B. Classification of STBC Systems over Frequency-selective Channels. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 2159–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuonzo, D.; De Maio, A.; Rossi, P.S. A Systematic Framework for Composite Hypothesis Testing of Independent Bernoulli Trials. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Patel, A.; Nagananda, K.G.; Varshney, P.K. Robustness of the Counting Rule for Distributed Detection in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, G.; Ciuonzo, D.; Montieri, A.; Pescape, A. Multi-classification Approaches for Classifying Mobile App Traffic. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 103, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xiao, C. Simulation Models with Correct Statistical Properties for Rayleigh Fading Channels. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2003, 51, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-L. Exact BER Analysis of OSTBCs in Spatially Correlated MIMO Channels. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2006, 54, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).