Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Physicochemical Evaluation of Oil from Hevea brasiliensis Seeds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Microwave-Assisted Soxhlet Extraction
2.3. Acidic pH-Based Microwave-Assisted Aqueous Extraction
2.4. Conventional Soxhlet Extraction
2.5. Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties
- Free fatty acid (FFA)—The FFA content was evaluated using AOCS Official Method Ca 5a-40.
- Iodine Value (IV)—The IV was carried out following the AOCS Official Method Cd 1d-92.
- Peroxide Value (PV)—The PV was measured following the AOCS Official Method Cd 8b-90.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microwave-Assisted Soxhlet Extraction
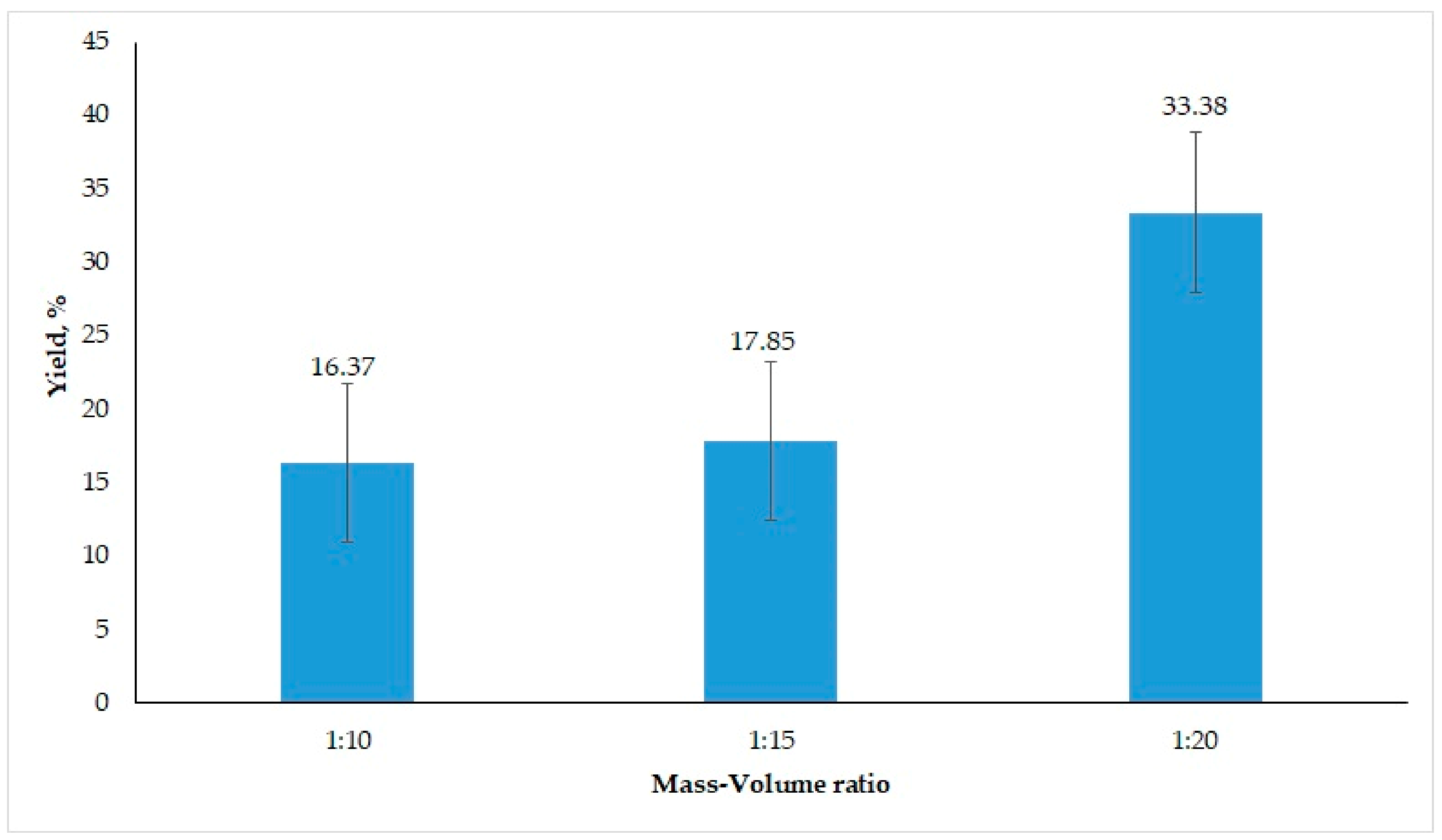
3.1.1. Effect of Solid–Solvent Ratio on Oil Yield
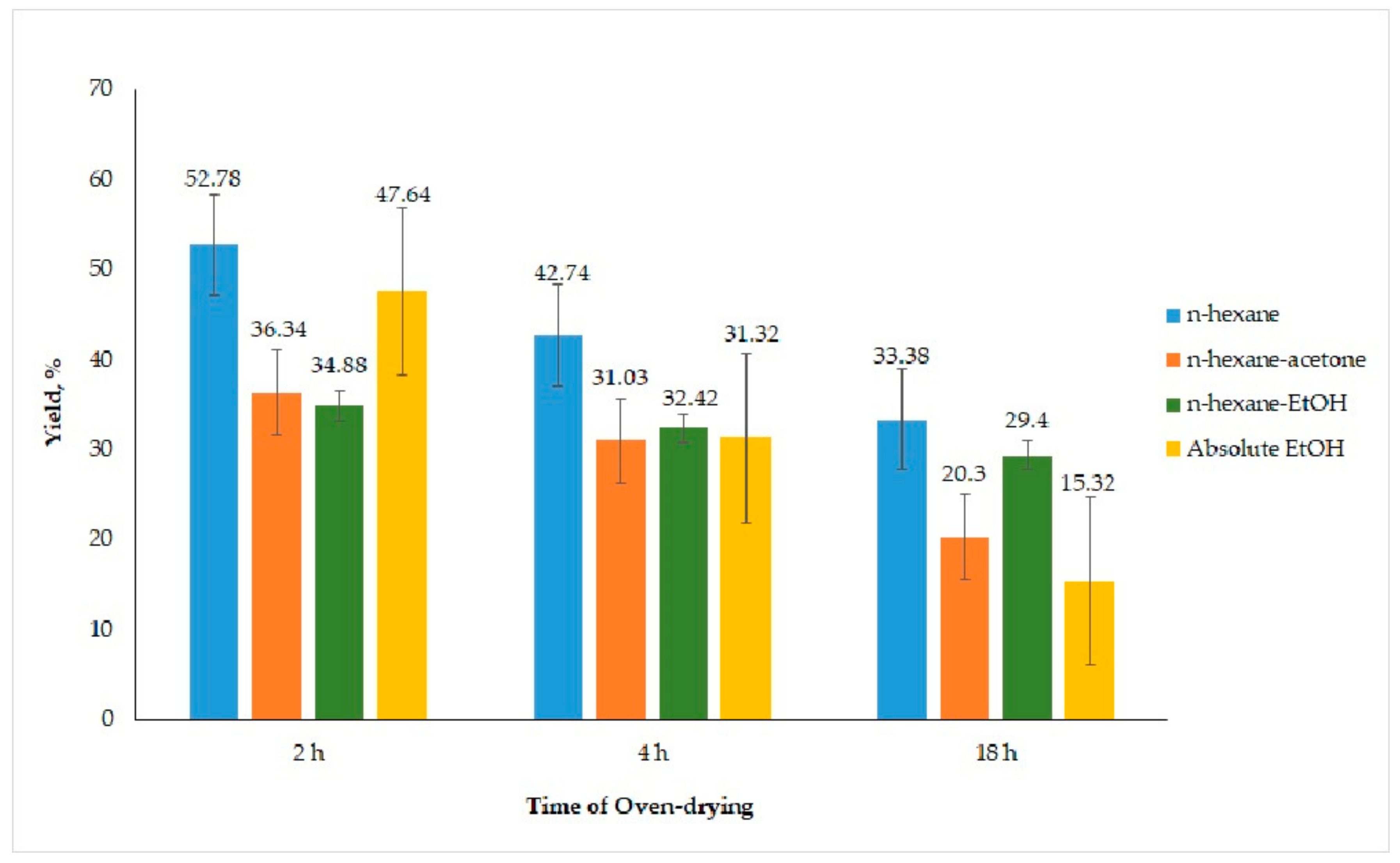
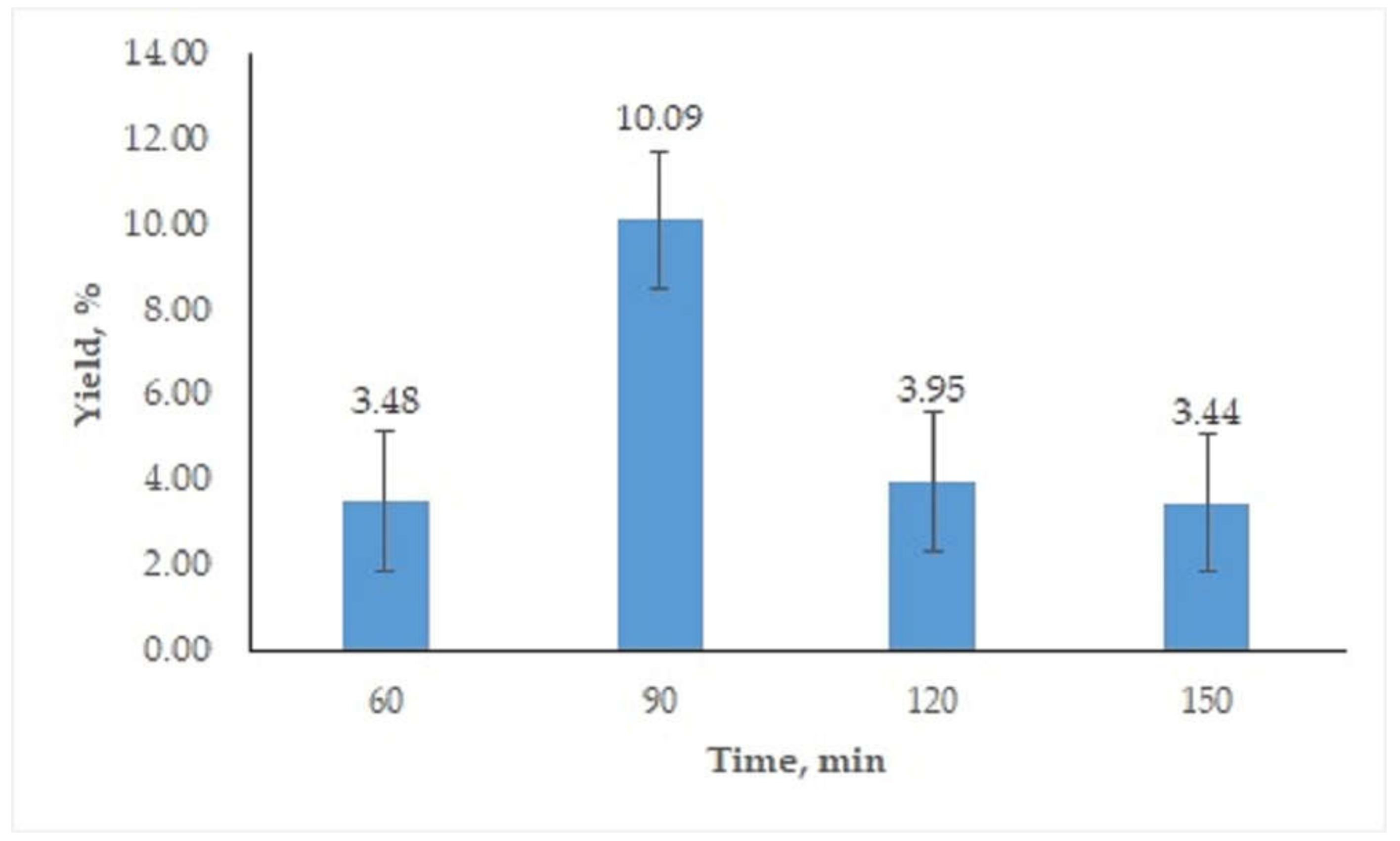
3.1.2. Influence of Oven-Drying Time
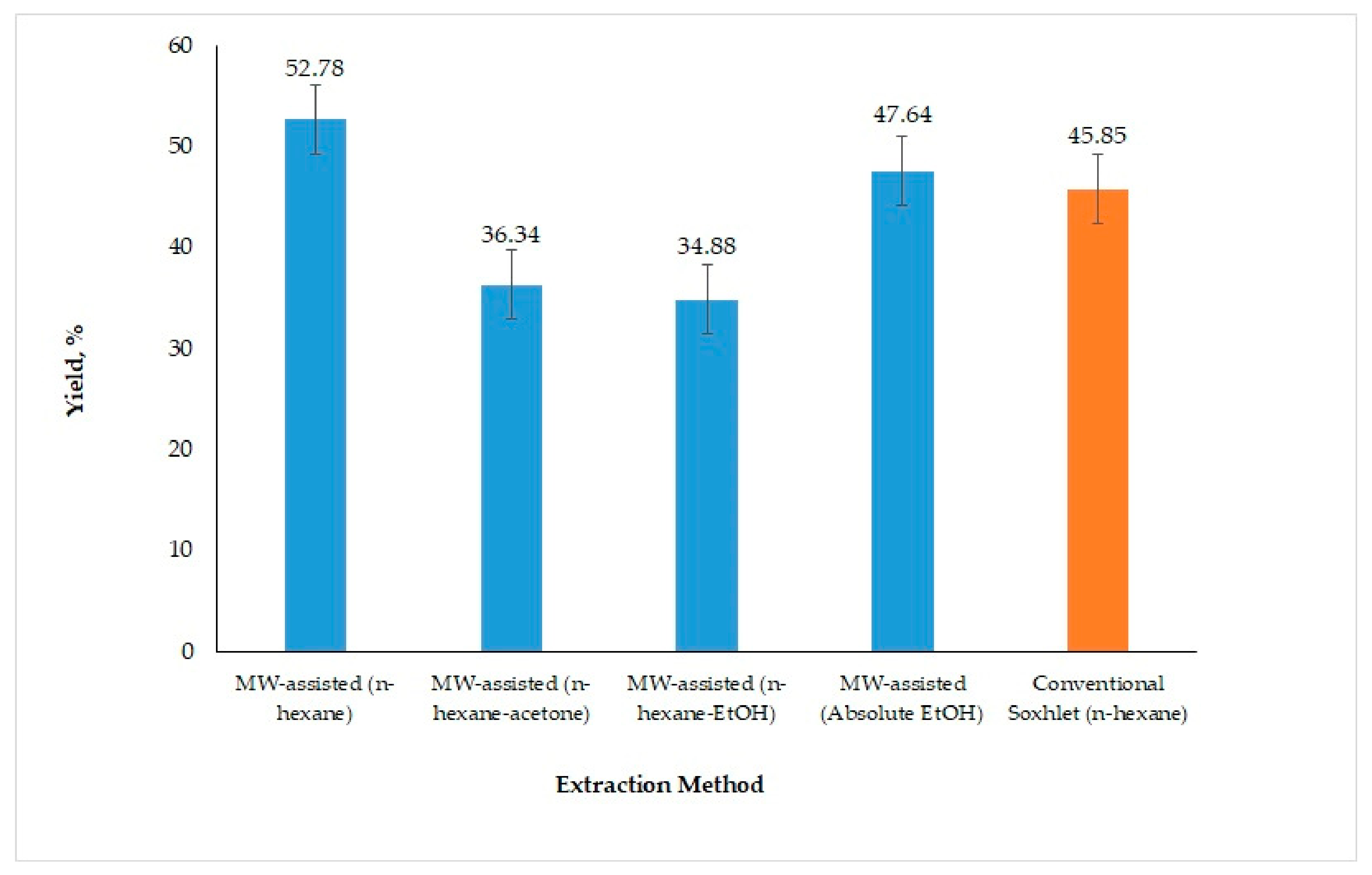
3.1.3. Influence of Different Extraction Solvents
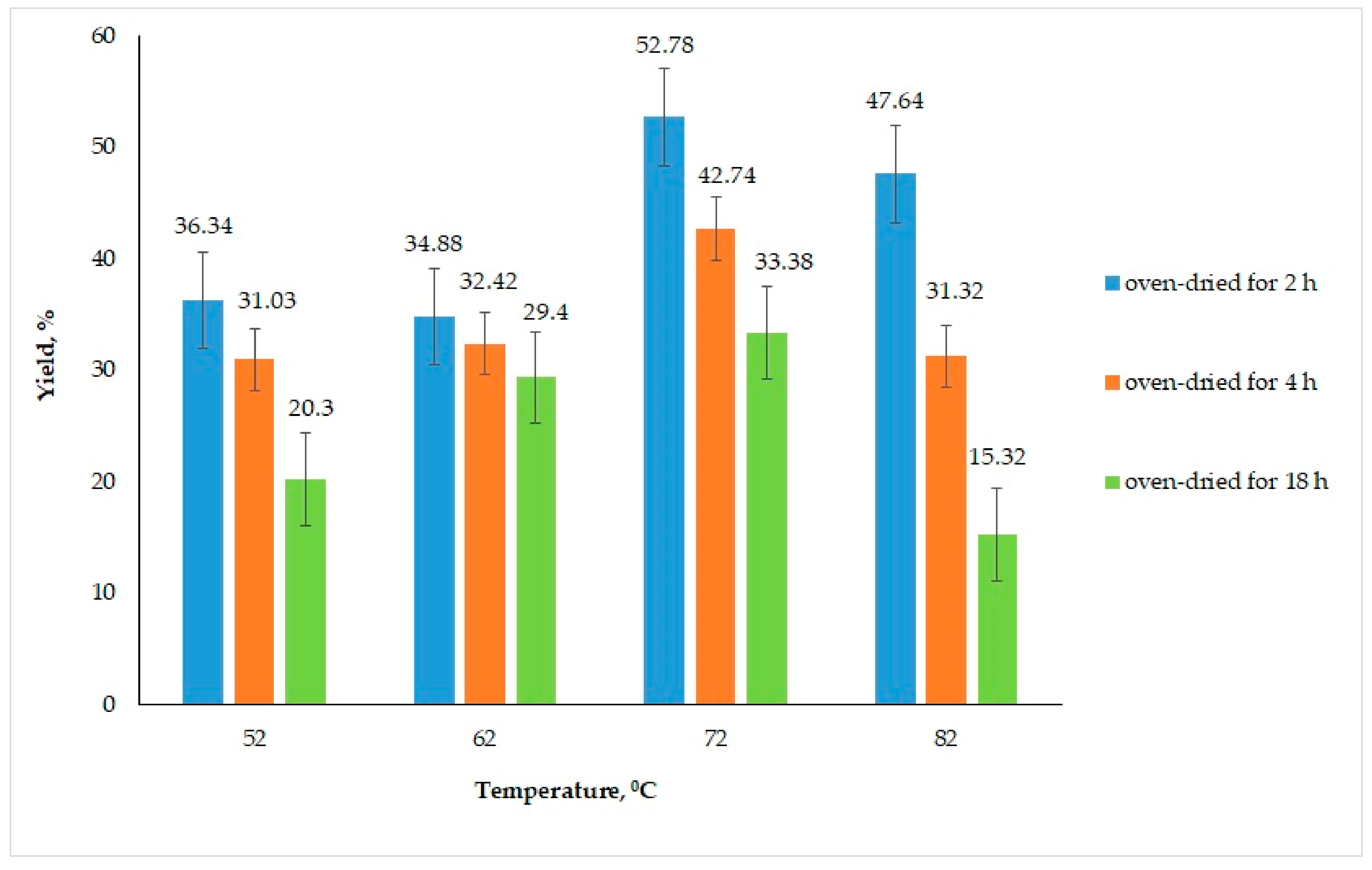
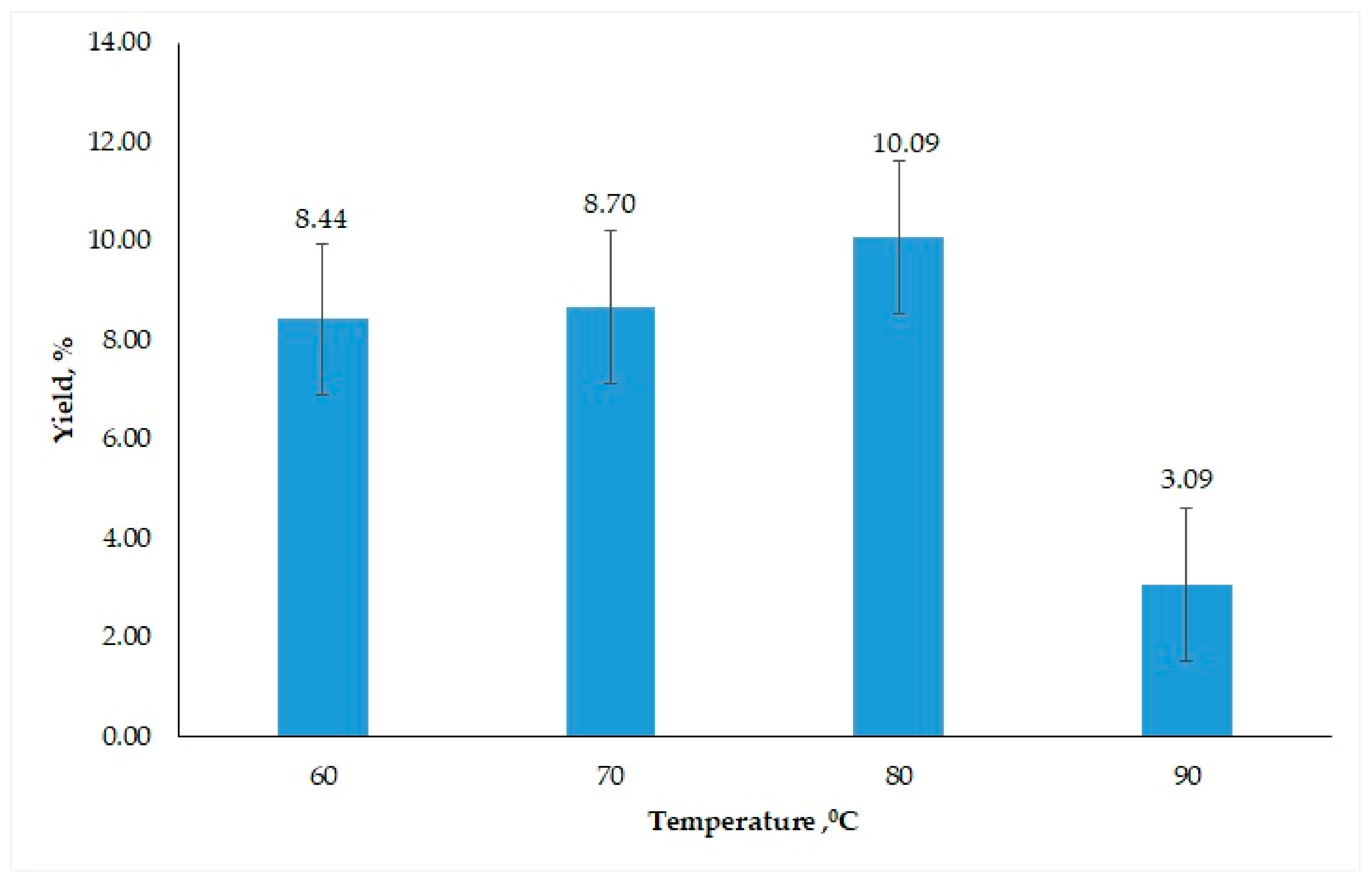
3.1.4. Influence of Temperature
3.2. Acidic pH-Based Microwave-Assisted Aqueous Extraction
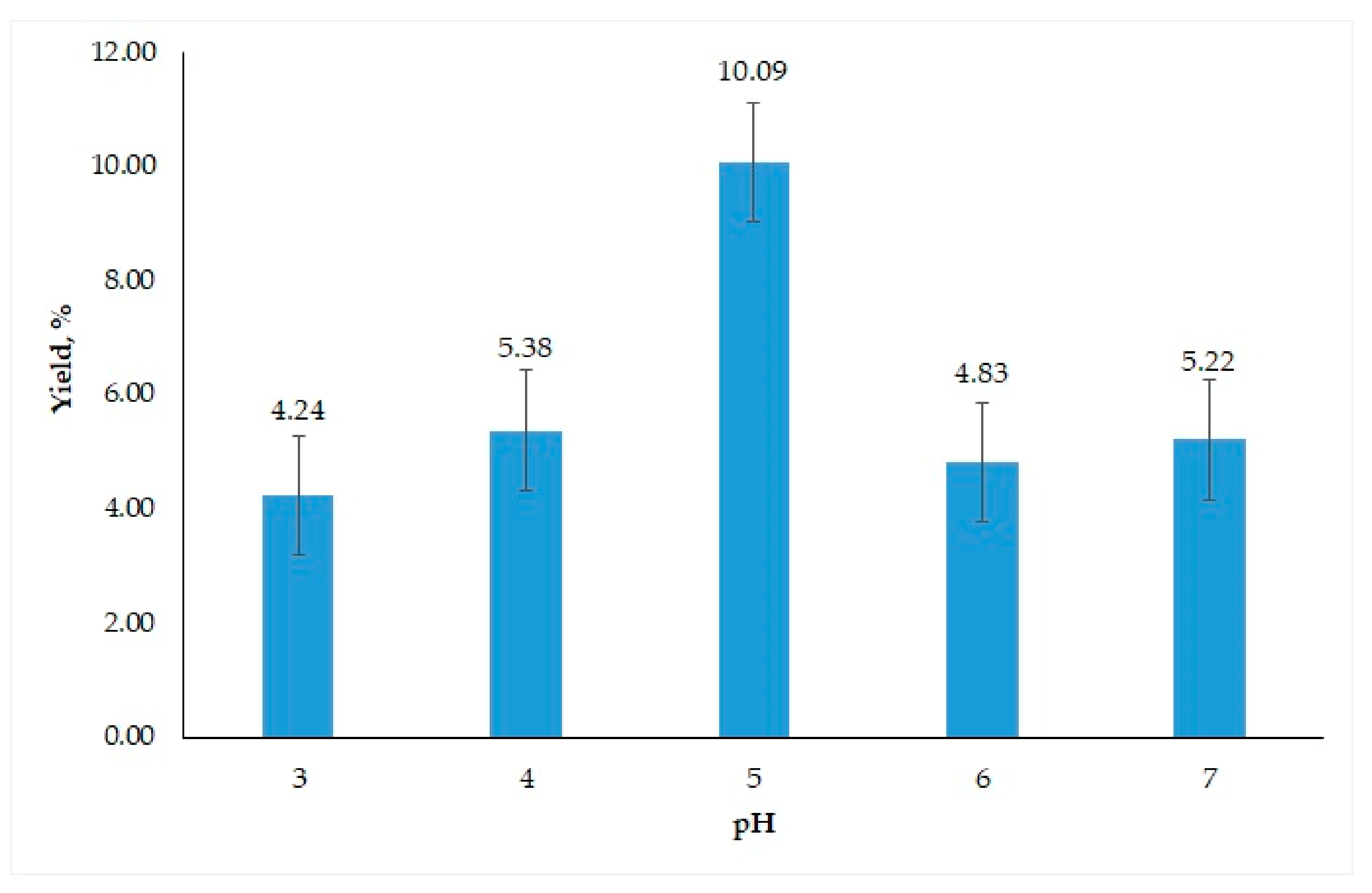
3.2.1. Determination of Best Conditions for Oil Extraction
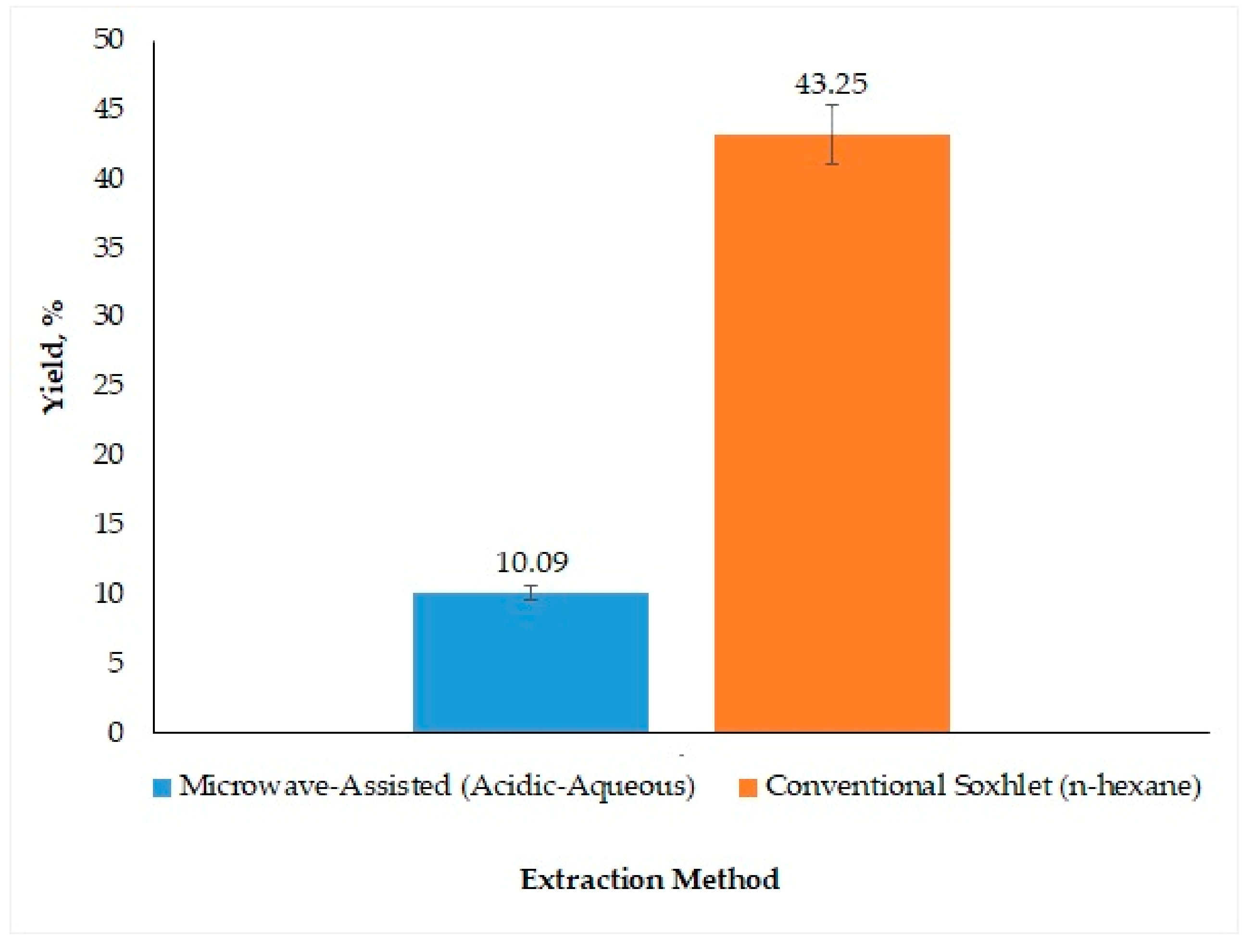
3.2.2. Comparison of Acidic pH-Based MAAE and Conventional Soxhlet Method
3.3. Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nwankwo, B.A.; Aigbekaen, E.O.; Sagay, G.A. Estimates of rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) seed production in Nigeria. In Proceedings of the Industrial Utilization of Natural Rubber, Seed Latex and Wood, Natural Conference, Benin City, Nigeria, 22–24 January 1985; Enabor, E.E., Ed.; Rubber Research Institute of Nigeria: Benin City, Nigeria, 1985; pp. 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Morshed, M.; Ferdous, K.; Khan, M.R.; Mozumder, S.I.; Islam, M.A.; Uddin, M.T. Rubber seed oil as a potential source for biodiesel production in Bangladesh. Fuel 2011, 90, 2981–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuquo, J.E.; Anusiem, A.C.I.; Etim, E.E. Extraction and characterization of rubber seed oil. Int. J. Mod. Chem. 2012, 1, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.J.; Fu, Y.J.; Luo, M.; Zhao, C.J.; Zu, Y.G.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Wei, Z.F. Acidic pH based microwave-assisted aqueous extraction of seed oil from yellow horn (Xanthoceras sorbifolia Bunge.). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2013, 43, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Li, Z.G.; Gai, Q.Y.; Li, X.J.; Wei, F.Y.; Fu, Y.J.; Ma, W. Microwave-assisted aqueous enzymatic extraction of oil from pumpkin seeds and evaluation of its physicochemical properties, fatty acid compositions and antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2014, 147, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarni, F.; Kadi, H. Kinetics study of microwave-assisted solvent extraction of oil from olive cake using hexane: Comparison with the conventional extraction. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camel, V. Microwave-assisted solvent extraction of environmental samples. Trends Anal. Chem. 2000, 19, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatke, P.; Jaiswal, Y. An overview of microwave assisted extraction and its applications in herbal drug research. Res. J. Med. Plants 2011, 5, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghvaei, M.; Jafari, S.M.; Assadpoor, E.; Nowrouzieh, S.; Alishah, O. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of cottonseed oil and evaluation of its oxidative stability and physicochemical properties. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunniff, P.; AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hron, R.J.; Koltun, S.P.; Graci, A.V. Biorenewable soivents for vegetable oil extraction. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1982, 59, 674A–684A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriera-Dias, S.; Valente, D.G.; Abreu, J.M.F. Comparison between ethanol and hexane for oil extraction from Quercus suber L. fruits. Grasas y Aceites 2003, 54, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyar, S.; Abidin, Z.; Yunus, R.; Muhammad, A. Extraction of oil from jatropha seeds-optimization and kinetics. J. Appl. Sci. 2009, 6, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetaredjo, F.E.; Budijanto, G.M.; Prasetyo, R.I.; Indraswati, N. Effects of pre-treatment condition on the yield and quality of neem oil obtained by mechanical pressing. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2008, 3, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, P.; Parthiban, K.S.; Sivakumar, P.; Vinoba, M.; Renganathan, S. Optimization of extraction process and kinetics of Sterculia foetida seed oil and its process augmentation for biodiesel production. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 8992–8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeeko, K.A.; Ajibola, O.O. Processing factors affecting yield and quality of mechanically expressed groundnut oil. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1990, 45, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonge, A.F.; Olaniyan, A.M.; Oje, K.; Agbaje, C.O. Effects of dilution ratio, water temperature and pressing time on oil yield from groundnut oil expression. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 40, 652–655. [Google Scholar]
- Nwithiga, G.; Moriasi, L. A study of yield characteristics during mechanical oil extraction of preheated and ground soybeans. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2007, 3, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Warra, A.A.; Wawata, I.G.; Gunu, S.Y.; Aujara, K.M. Extraction and physicochemical analysis of some selected Northern Nigerian industrial oils. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2011, 3, 536–541. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Conventional Soxhlet Method b | MW-Assisted Soxhlet Extraction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n-Hexane | n-Hexane–Acetone (3:1 v/v) a | n-Hexane–Ethanol (3:1 v/v) a | Absolute Ethanol a | ||||
| 2 h | 4 h | 18 h | |||||
| FFA (% Oleic) | 7.61 | 5.16 | 3.91 | 1.19 | 5.43 | 5.20 | 3.67 |
| Iodine Value | 132.8 | 107.7 | 119.9 | 121.9 | 150.2 | 148.3 | 147.7 |
| Peroxide Value (mEq/kg) | 15.13 | b | b | b | b | b | b |
| Parameter | Conventional Soxhlet Method | Acidic pH-Based MAAE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 3 | pH 5 | pH 7 | ||
| FFA (% Oleic) | 2.54 | 1.66 | 1.15 | 1.64 |
| Iodine Value | 131.9 | 131.2 | 126.4 | 129.7 |
| Peroxide Value (mEq/kg) | b | 19.50 | 5.18 | 5.62 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Creencia, E.C.; Nillama, J.A.P.; Librando, I.L. Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Physicochemical Evaluation of Oil from Hevea brasiliensis Seeds. Resources 2018, 7, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources7020028
Creencia EC, Nillama JAP, Librando IL. Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Physicochemical Evaluation of Oil from Hevea brasiliensis Seeds. Resources. 2018; 7(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources7020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleCreencia, Evelyn C., Joshua Andrew P. Nillama, and Ivy L. Librando. 2018. "Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Physicochemical Evaluation of Oil from Hevea brasiliensis Seeds" Resources 7, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources7020028
APA StyleCreencia, E. C., Nillama, J. A. P., & Librando, I. L. (2018). Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Physicochemical Evaluation of Oil from Hevea brasiliensis Seeds. Resources, 7(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources7020028