Enhancing Small Dam Performance in Wadi Horan: A Hydrological Modelling Study for Rainwater Harvesting
Abstract
1. Introduction
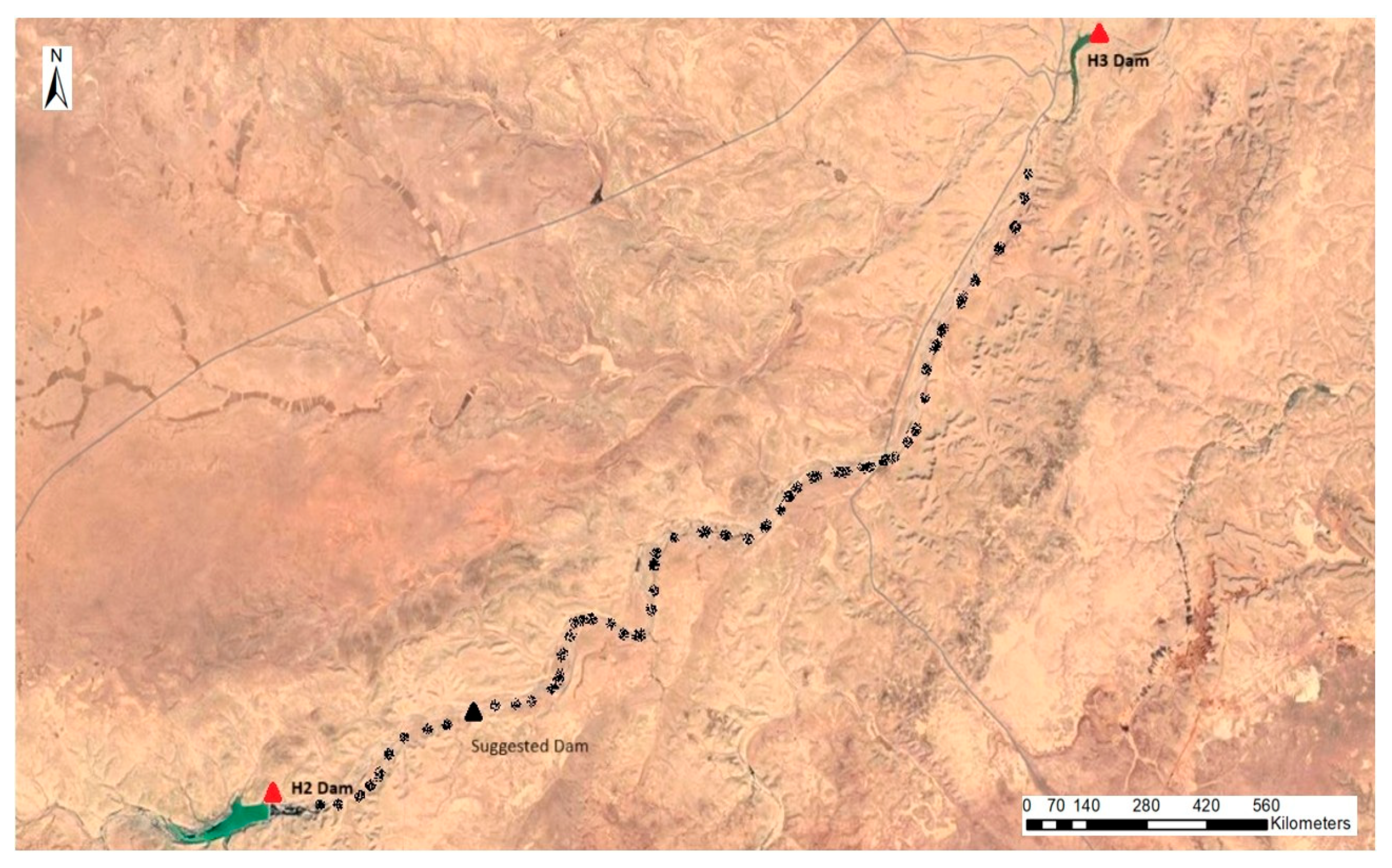
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
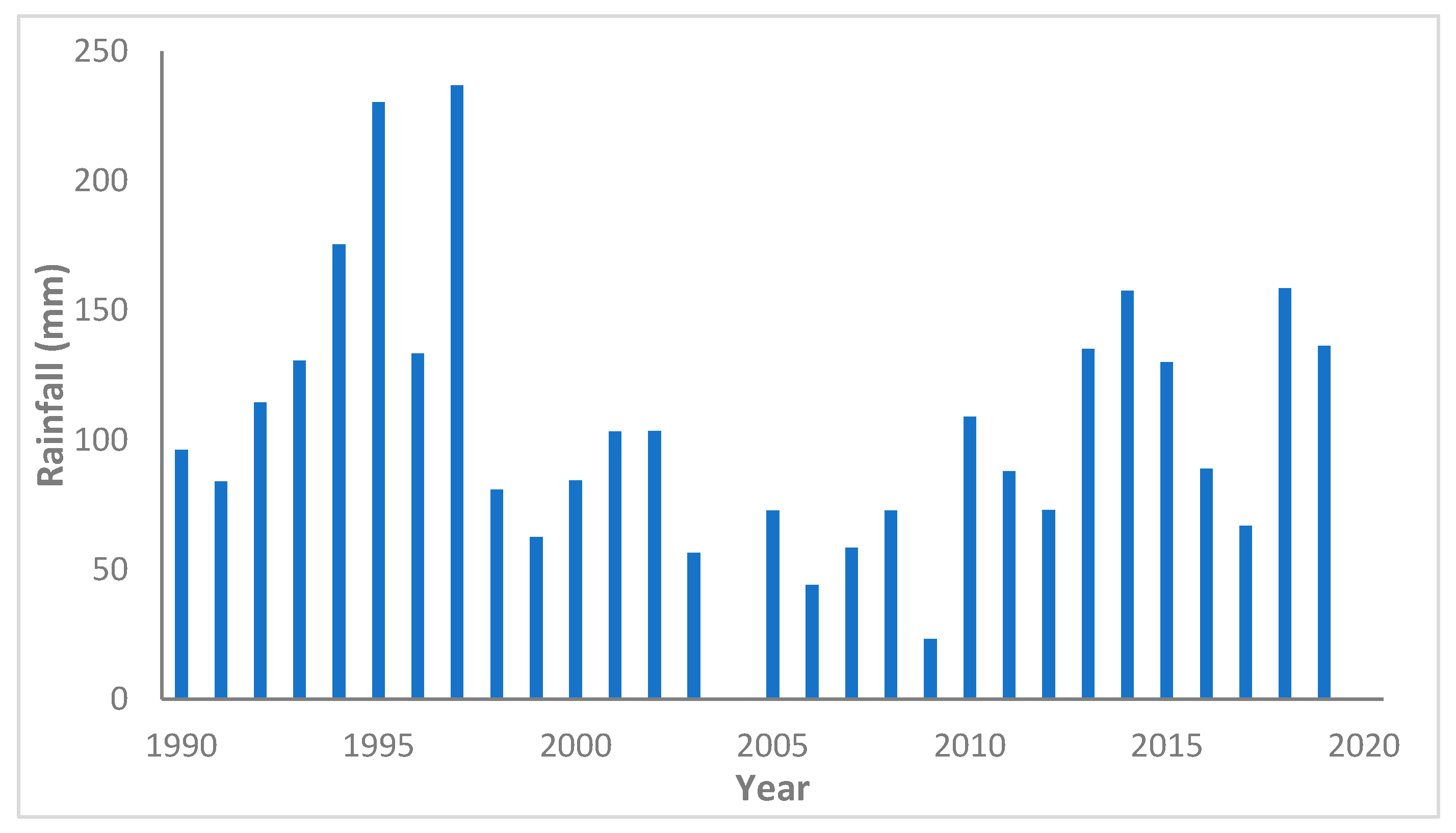
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Runoff Depth
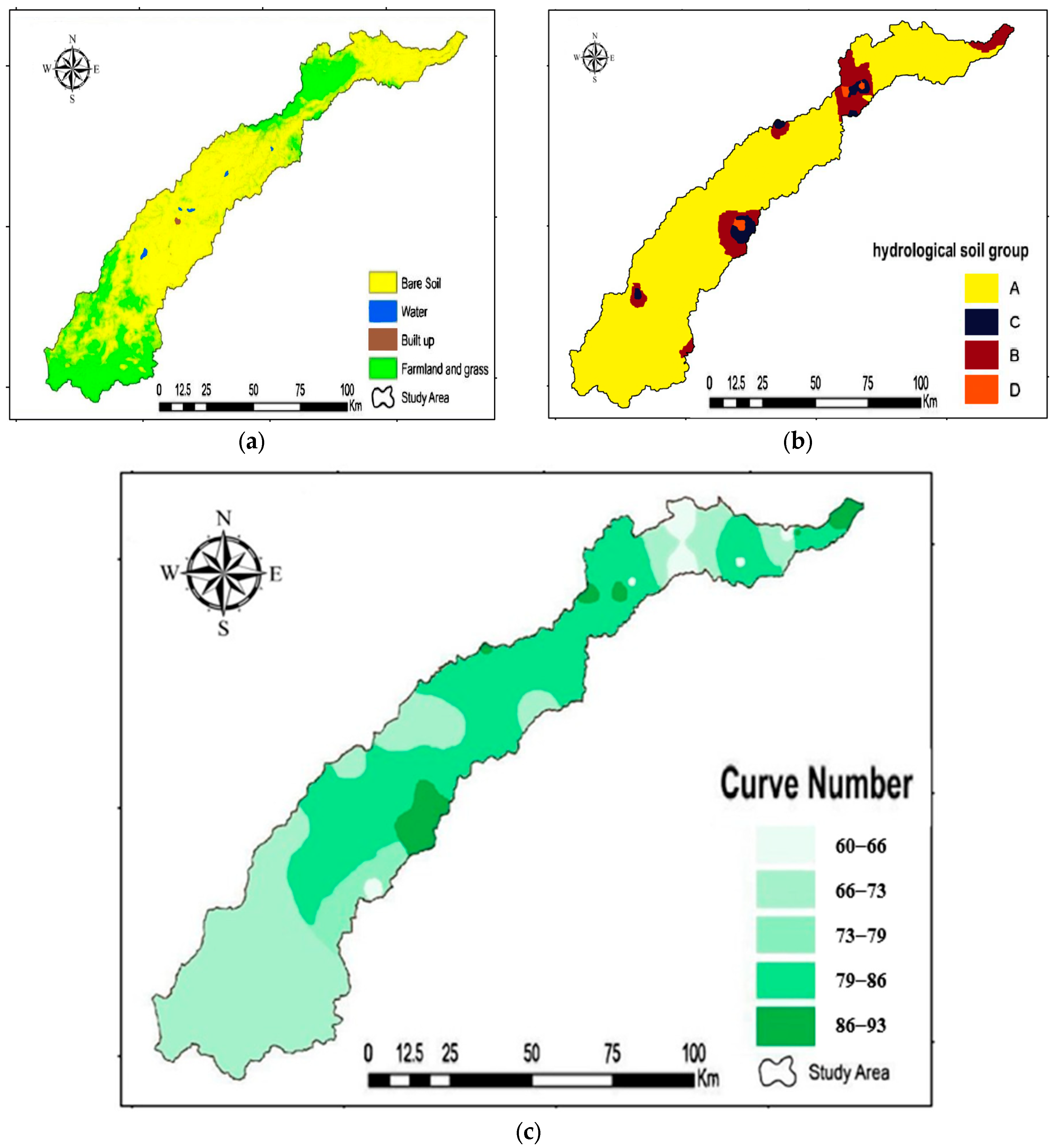
3.2.1. Land Use/Land Cover (LU/LC) Map
3.2.2. Hydrological Soil Group Map
3.2.3. Curve Number (CN)
3.3. Water Harvesting at Sub-Catchment Level Model (WHCatch)
- Providing various solutions to enhance and comprehend the water balance across all watersheds.
- The capacity to input extensive data and execute analyses and computations rapidly and with little effort.
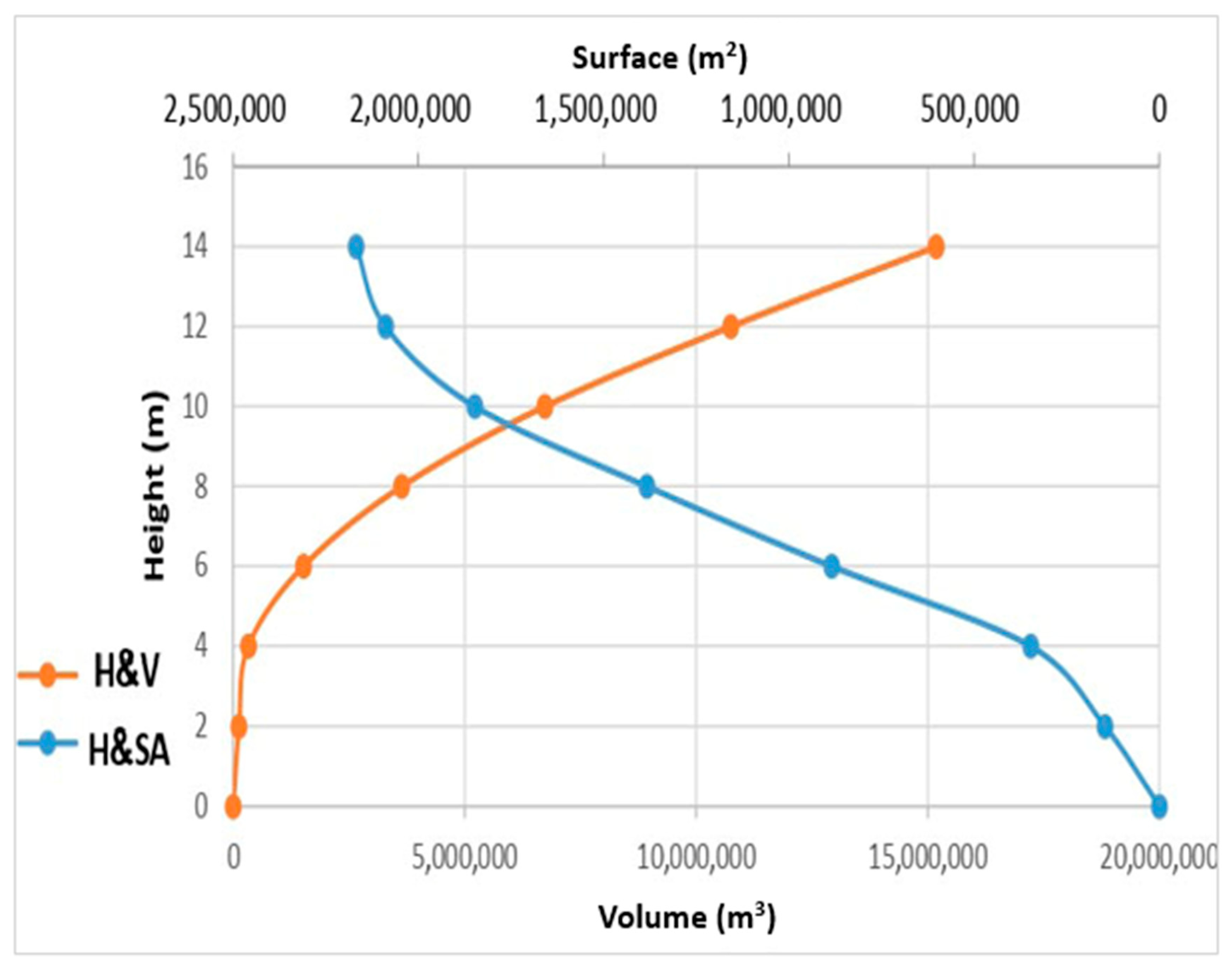
- It shows how raising or lowering the spillway height affects storage area and volume, affecting the water balance equation parameters for each sub-catchment.
3.4. Water Balance
- Δ represents the variation in storage through a certain time interval, measured in cubic metres (m3).
- I = inflow, measured in cubic metres (m3).
- O = represents the outflow, measured in cubic metres (m3).
3.5. Water Losses
3.5.1. Evaporation Losses
3.5.2. Infiltration Losses
4. Results and Discussion
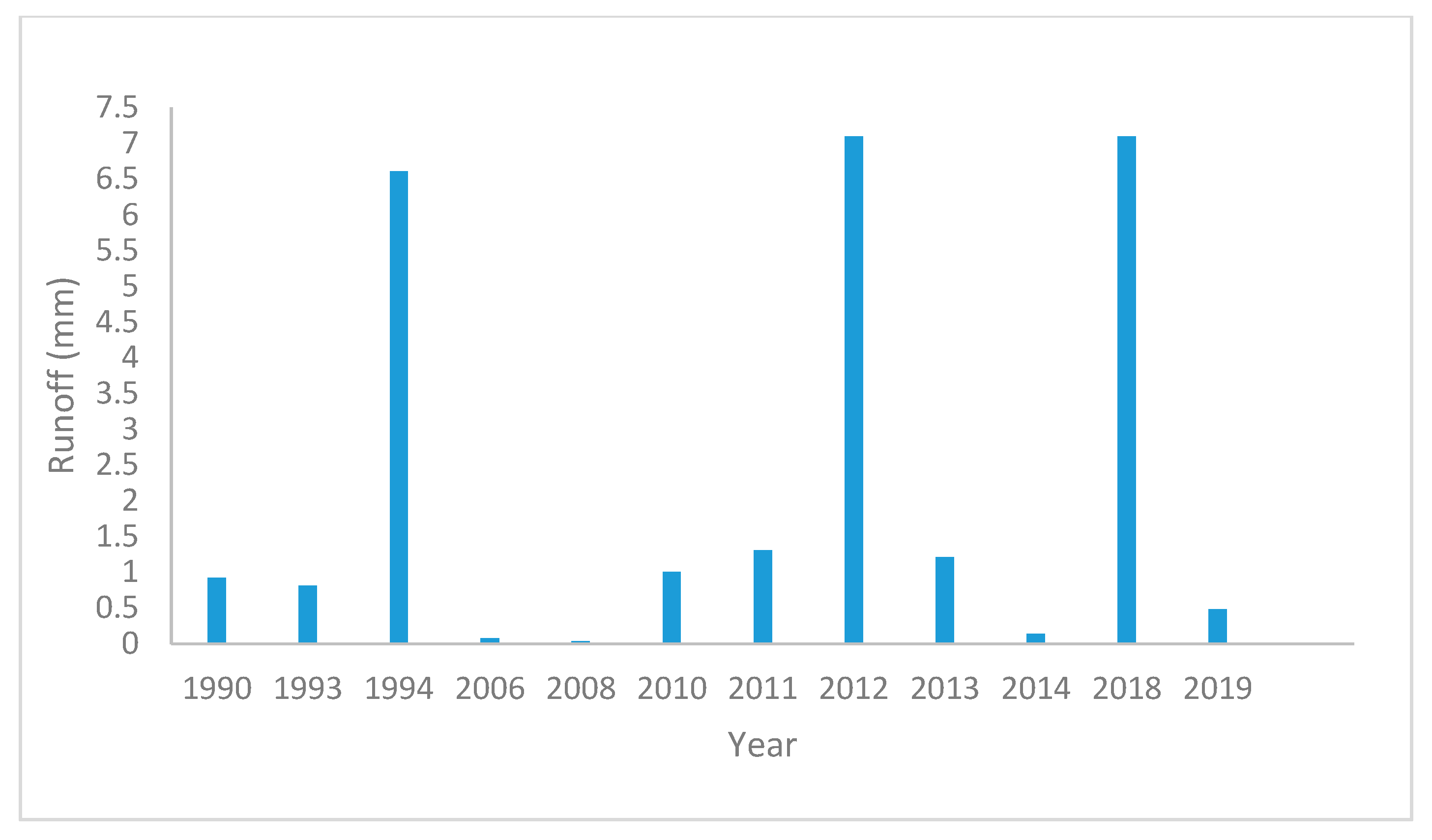
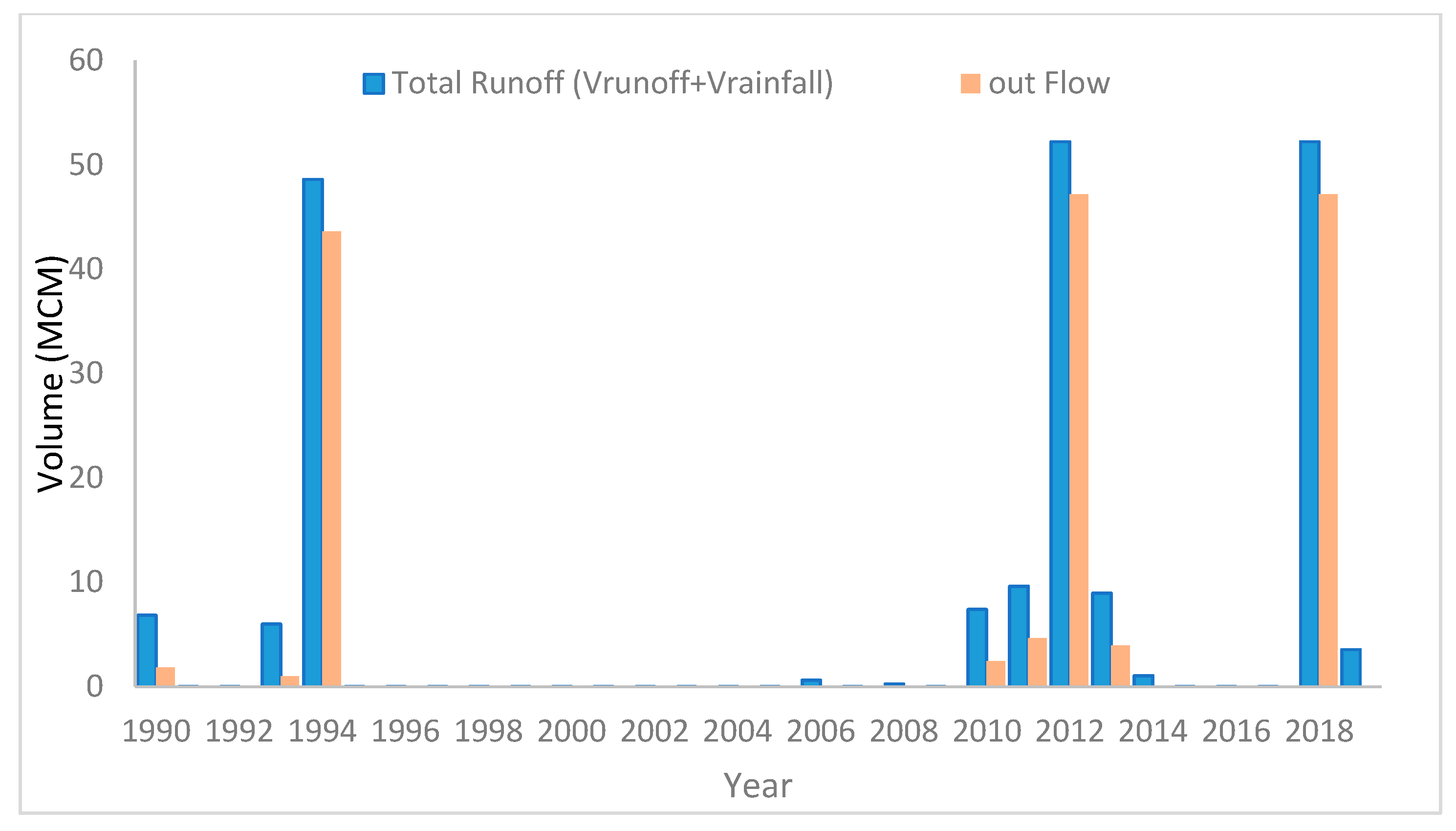
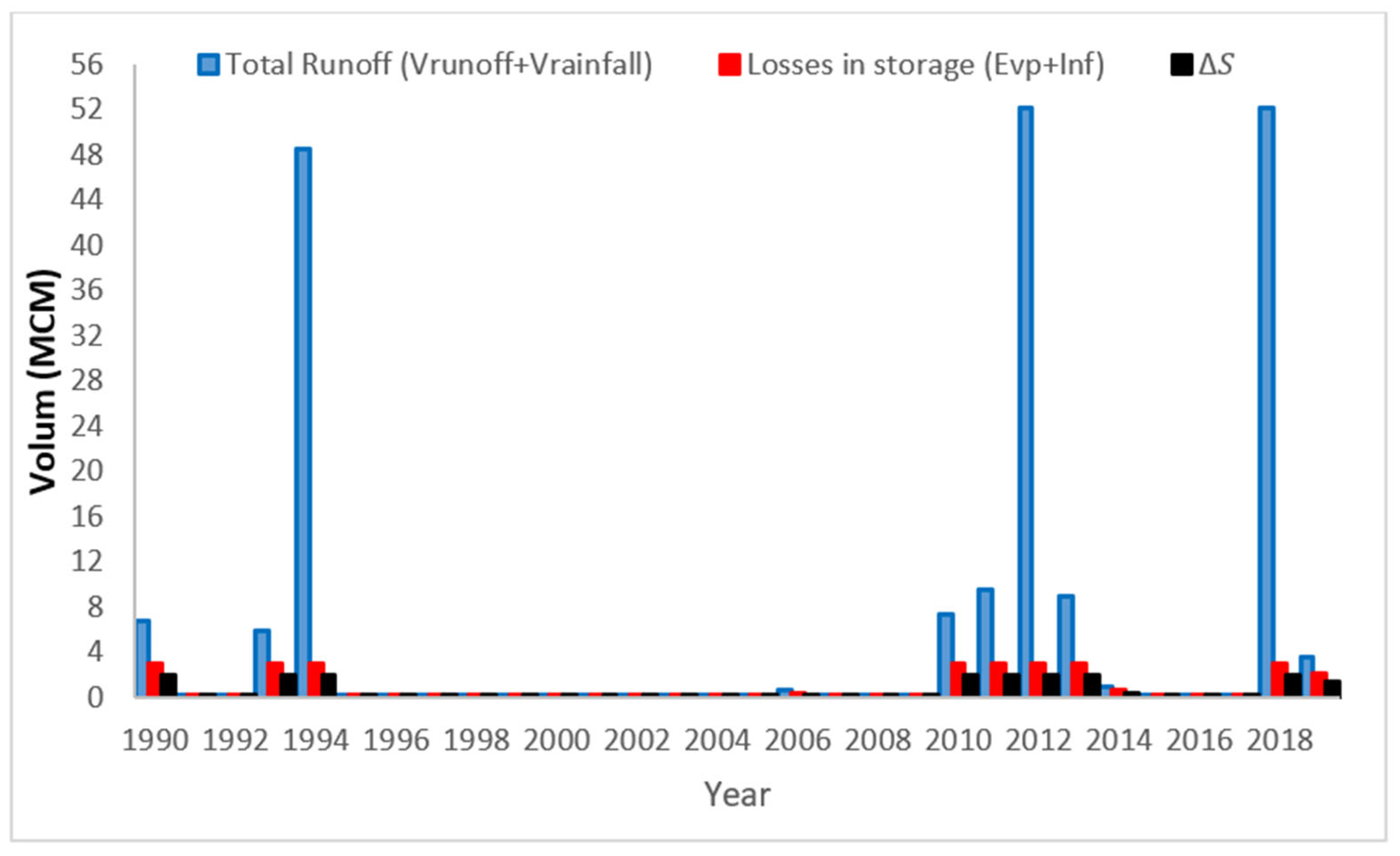
4.1. The Volume of Runoff for (Horan/2 Dam)
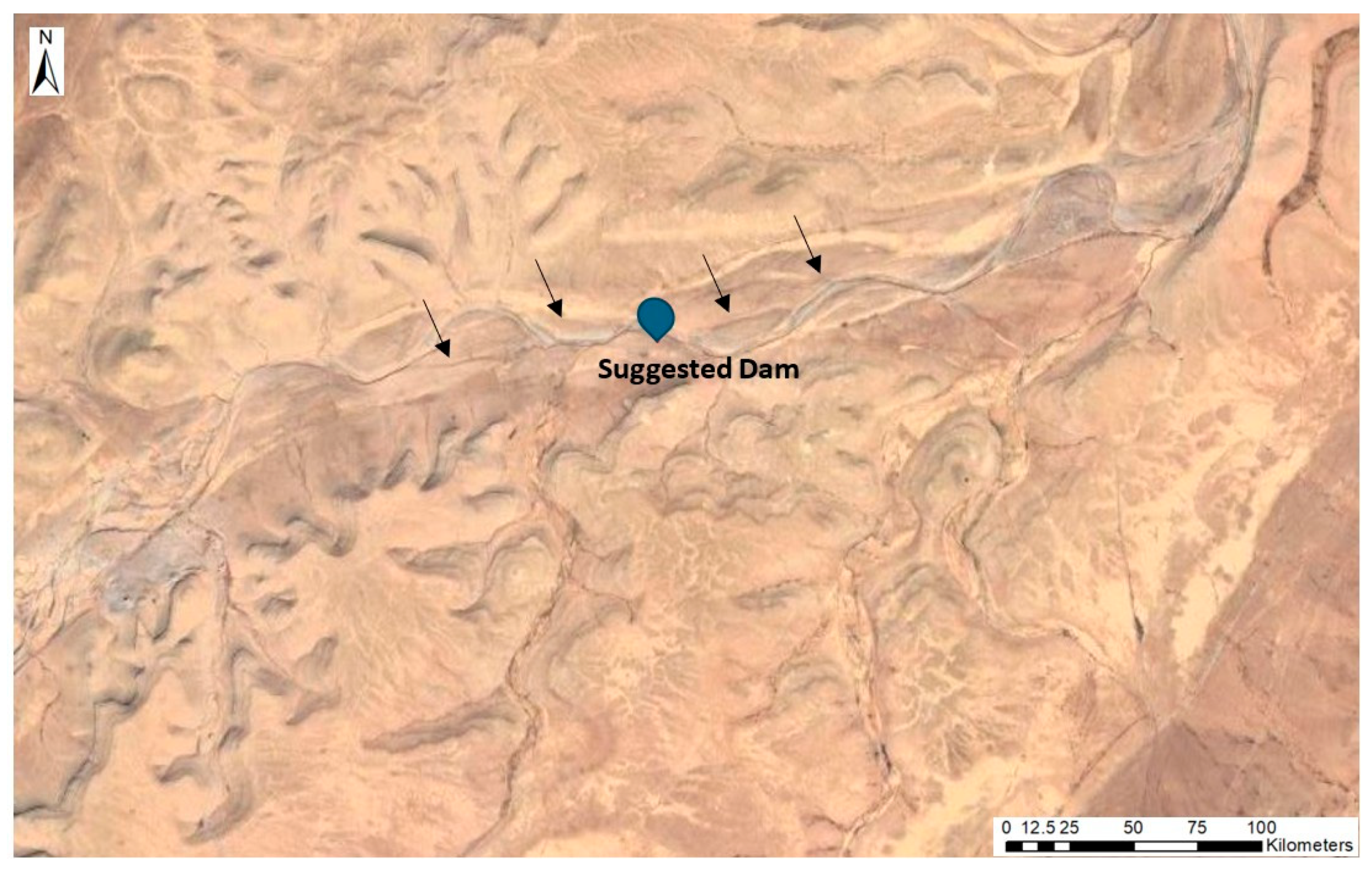
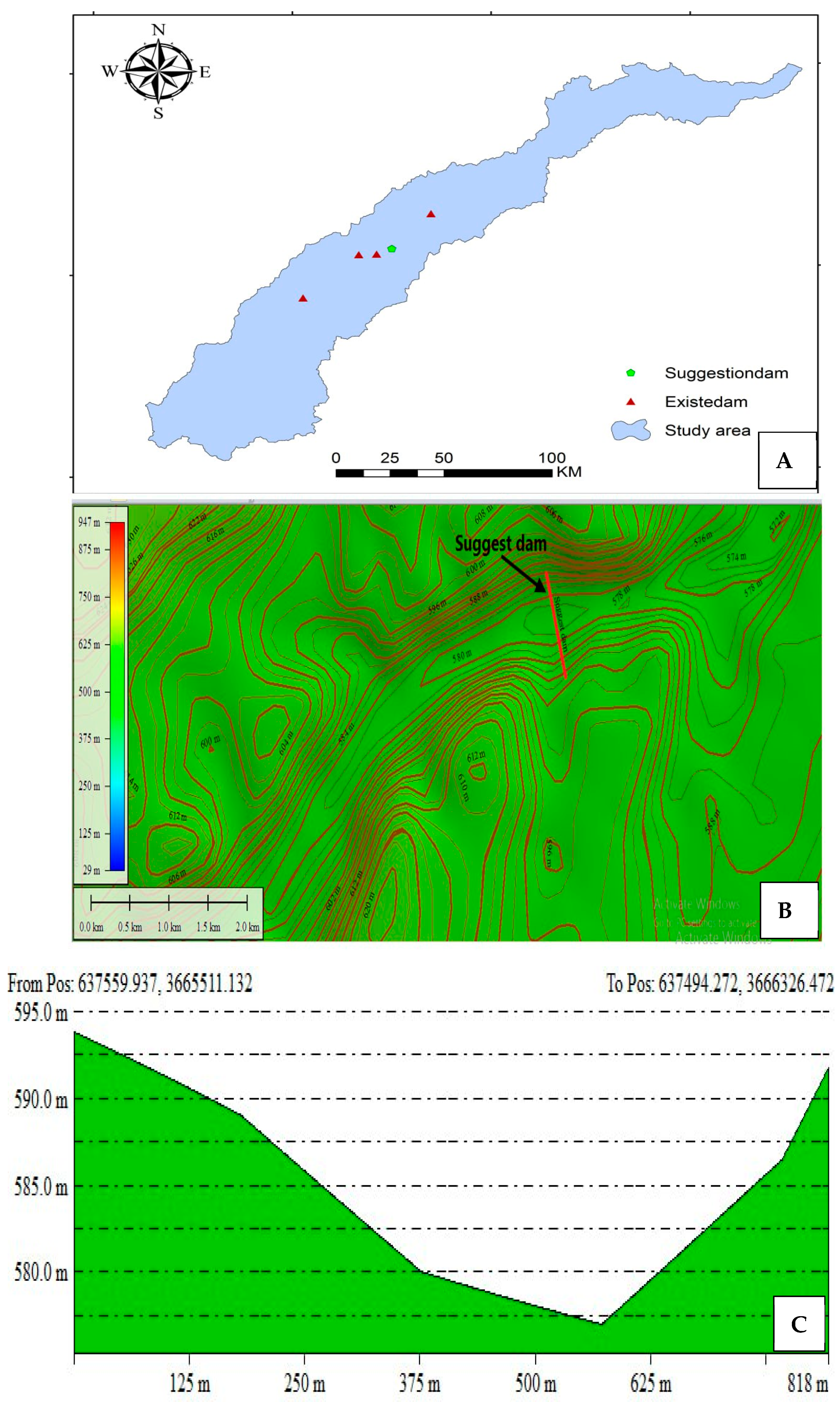
The Suggested Solutions
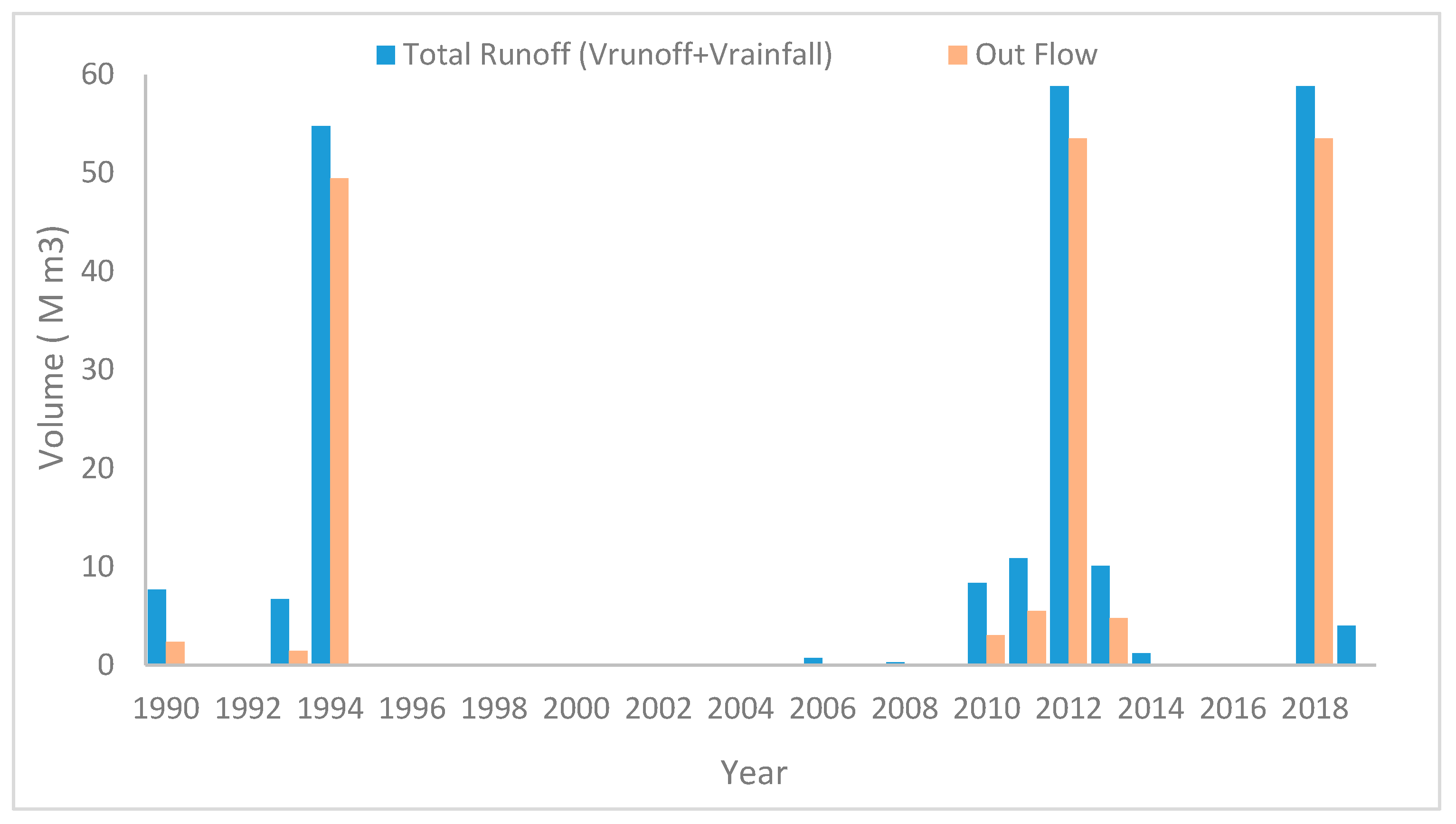
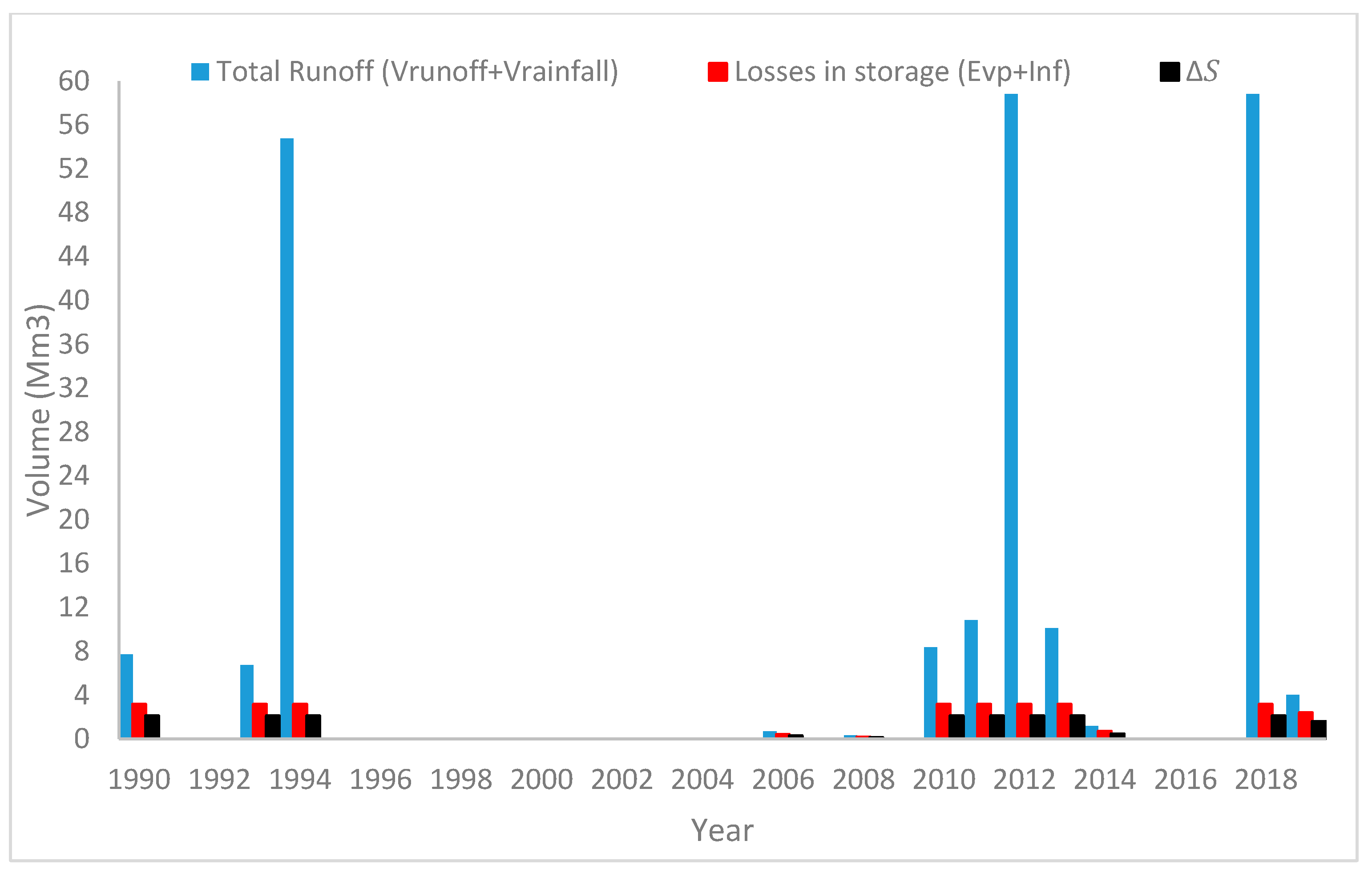
4.2. The Runoff Volume for (Horan/3 Dam)
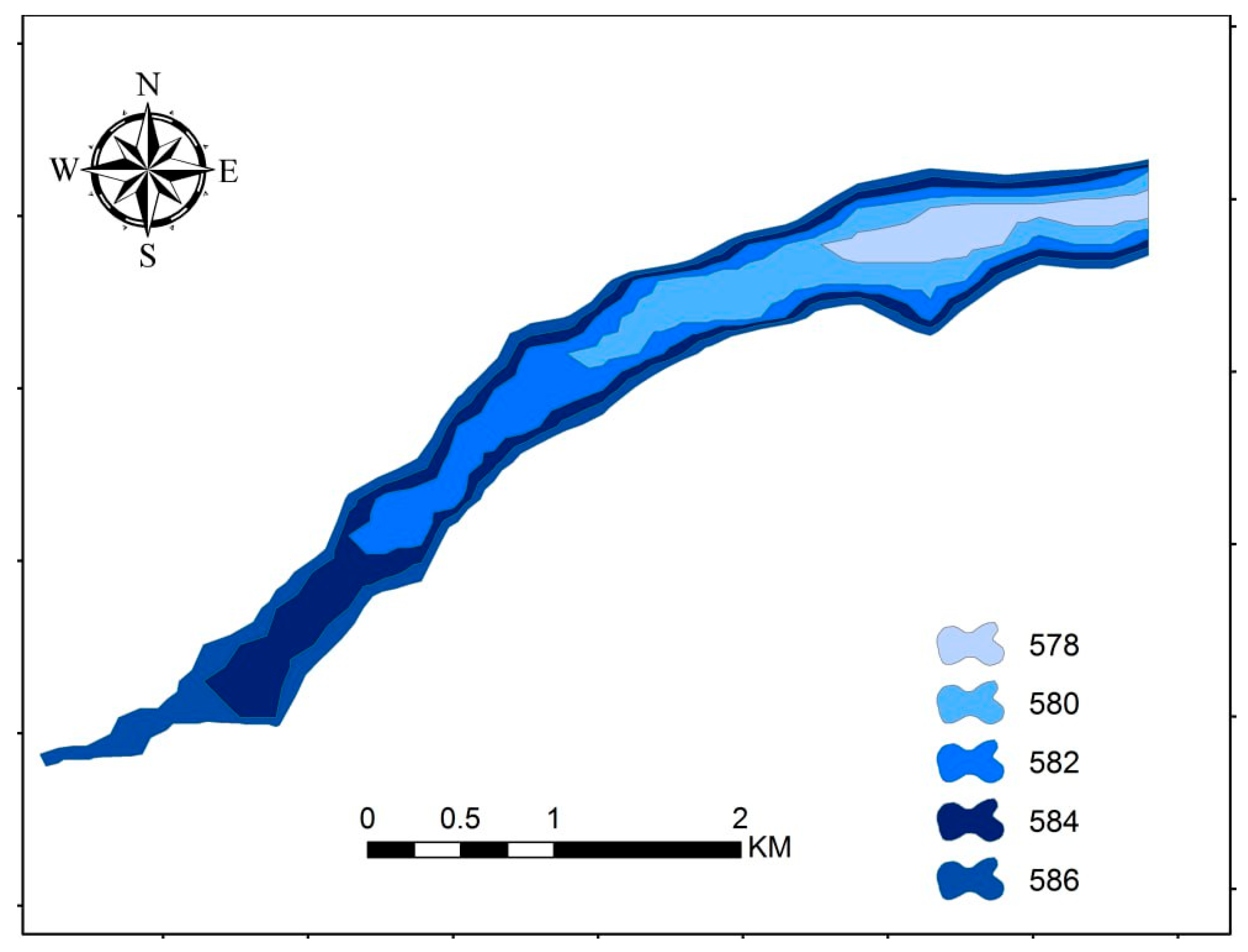
The Suggest Solution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ammar, A.; Riksen, M.; Ouessar, M.; Ritsema, C. Identification of suitable sites for rainwater harvesting structures in arid and semi-arid regions: A review. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutpa, K.K.; Deelstra, J.; Sharma, K.D. Estimation of water harvesting potential for a semiarid area using GIS and remote sensing. In Proceedings of the Rabat Symposium S3 (April 1997) “Remote Sensing and Geographic Information Systems for Design and Operation of Water Resources Systems, Rabat, Morocco, 23 April–3 May 1997; Volume 242. [Google Scholar]
- Toebes, C.; Ouryvaev, V. Representative and Experimental Basins, an International Guide for Research and Practice; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1970; p. 348. [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil, P.; Chaperon, P.; Guiscafré, J.; Herbaud, J. Recueil des Données de Base des Bassins Représentatifs et Expérimentaux; Office de la Recherche Sceintifique et Technique Outre-Mer: Paris, France, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Dengler, J.; Jansen, F.; Chusova, O.; Hüllbusch, E.; Nobis, M.P.; Van Meerbeek, K.; Axmanová, I.; Bruun, H.H.; Chytrý, M.; Guarino, R.; et al. Ecological Indicator Values for Europe (EIVE) 1.0. Veg. Classif. Surv. 2023, 4, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adham, A.; Riksen, M.; Abed, R.; Shadeed, S.; Ritsema, C. Assessing suitable techniques for rainwater harvesting using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) methods and GIS techniques. Water 2022, 14, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothiprakash, V.; Sathe, M.V. Evaluation of rainwater harvesting methods and structures using analytical hierarchy process for a large-scale industrial area. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2009, 1, 427–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouessar, M.; Bruggeman, A.; Mohtar, R.; Ouerchefani, D.; Abdelli, F.; Boufelgha, M. Future of drylands—An overview of evaluation and Impact Assessment Tools for water harvesting. In The Future of Drylands; Lee, C., Schaaf, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 255–267. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Adamat, R. GIS as a decision support system for siting water harvesting ponds in the Basalt Aquifer/NE Jordan. J. Environ. Assess. Policy Manag. 2008, 10, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources State Commission for Dams and Reservoirs. Design Report of Dam (2020); (H/2, H/3, Apila); Al Furat Center for Studies and Designs of Irrigation Projects: Baghdad, Iraq, 2020; Volume 1, unpublished data. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, O.S.; Kamel, A.H.; Khalil, W.H.; Al-damook, A. Estimation of Hydropower Harvesting from the Hydraulic Structures on Rivers: Ramadi Barrage, Iraq as a Case Study. Iraqi J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 14, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Adham, A.; Abed, R.; Mahdi, K.; Hassan, W.H.; Riksen, M.; Ritsema, C. Rainwater catchment system reliability analysis for Al Abila Dam in Iraq’s western desert. Water 2023, 15, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassim, S.Z.; Goff, J.C. Geology of Iraq; Dolin, Prague and Morravian Museum: Brno, Czech Republic, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sissakian, V.; Ahad, A.A.; Al-Ansari, N.; Knutsson, S. Geology of wadi hauran, the largest valley in iraqi western desert. J. Earth Sci. Geo. Eng. 2017, 7, 103–132. [Google Scholar]
- Adham, A.; Sayl, K.N.; Abed, R.; Abdeladhim, M.A.; Wesseling, J.G.; Riksen, M.; Fleskens, L.; Karim, U.; Ritsema, C.J. A GIS-based approach for identifying potential sites for harvesting rainwater in the Western Desert of Iraq. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V.T.; Maidment, D.R.; Mays, L.W. Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 99–147. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Mitchell, J.K.; Hirschi, M.C.; Cooke, R.A. Modified SCS curve number method for predicting subsurface drainage flow. Trans. ASAE 2001, 44, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krois, J.; Schulte, A. GIS-based multi-criteria evaluation to identify potential sites for soil and water conservation techniques in the Ronquillo watershed, northern Peru. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 51, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayl, K.N.; AL-Ani, A.; Oliwi, S. Hydrologic Study for Iraqi Western Desert to Assessment of Water Harvesting Projects. Iraqi J. Civ. Eng. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, T.M.; Zondervan, K.; Ben-Asher, J. Micro-catchment-water-harvesting (MCWH) for arid zone development. Agric. Water Manag. 1986, 12, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, E.D. Control of Evaporation Losses; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, A.H. Study the Effect of Evaporation on Water Quality to the Iraq Reservoirs; Al_Musaib Institute Technique: Al_Musaib, Iraq, 2017; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Dawood, K.A.; Rashid, F.L.; Hashim, A. Reduced evaporation losses from water reservoirs. Int. J. Energy Env. Res. 2013, 1, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, J.H.; Dukes, M.D.; Miller, G.L.; Jones, P.H. Analysis of double-ring infiltration techniques and development of a simple automatic water delivery system. Appl. Turfgrass Sci. 2005, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Board of Supreme Audit. A Detailed Report on the Work of Monitoring and Specialized Auditing on the Policy of the Ministry of Water Resources in Implementing Dams and Reservoirs Projects for the Period From (2014–2017); Federal Board of Supreme Audit: Baghdad, Iraq, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Adham, A.; Seeyan, S.; Abed, R.; Mahdi, K.; Riksen, M.; Ritsema, C. Sustainability of the Al-Abila Dam in the western desert of Iraq. Water 2022, 14, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
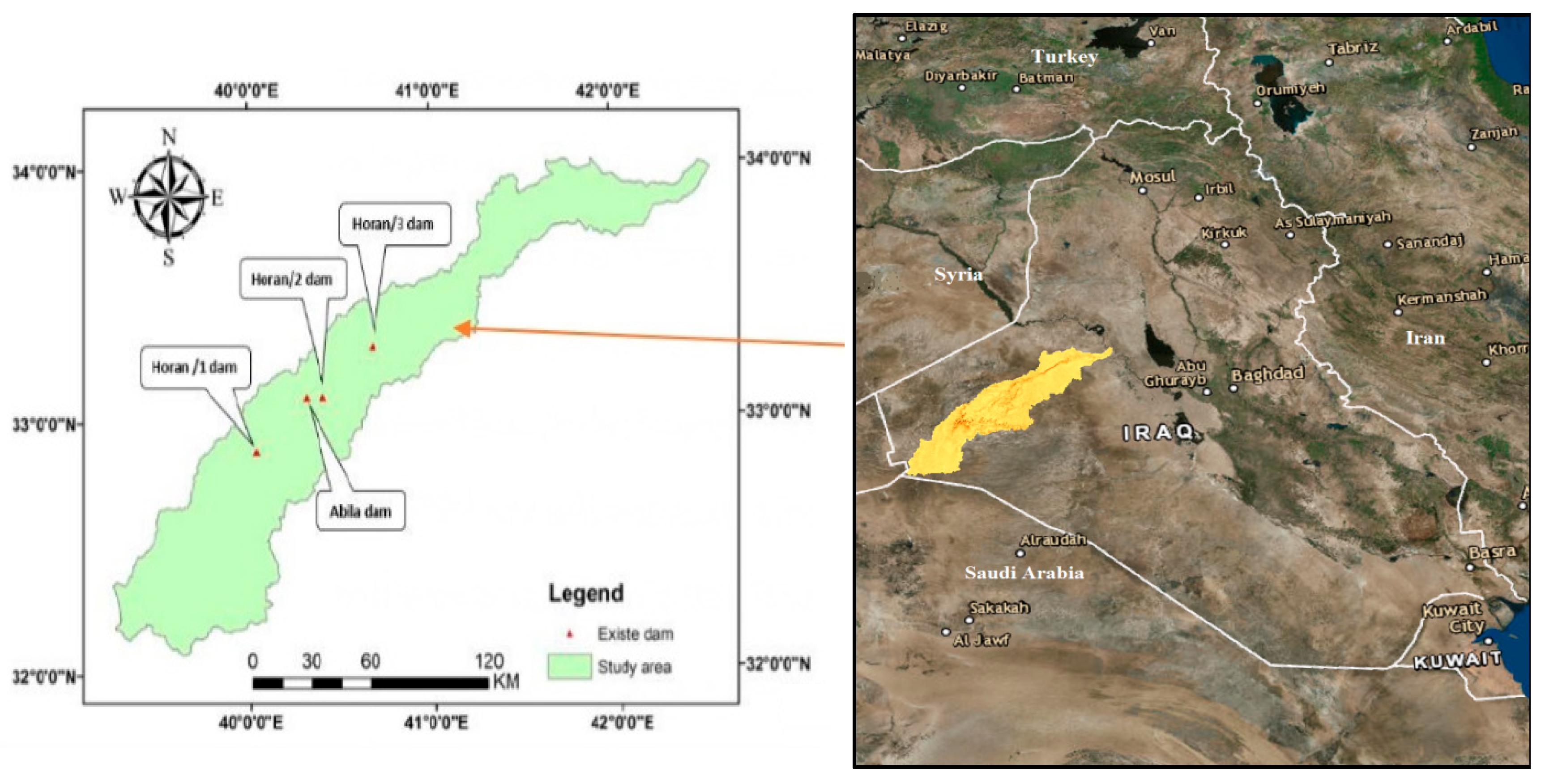
| No. | Dams | Dam Coordinates | Date of Construction | Storage Capacity (M m3) | Dam Length (m) | Dam Height (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Horan/2 | E 40°24′19.62″ N 33° 5′51.90″ | 2007 | 4 | 500 | 15 |
| 2 | Horan/3 | E 40°40′45.94″ N 33° 17′ 44.91″ | 2003 | 5.3 | 448 | 15 |
| Year | Max. Depth of Daily Rainfall (mm) | Year | Max. Depth of Daily Rainfall (mm) | Year | Max. Depth of Daily Rainfall (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 24.6 | 2000 | 6.9 | 2010 | 25 |
| 1991 | 4.4 | 2001 | 5.8 | 2011 | 26.4 |
| 1992 | 15.5 | 2002 | 7.4 | 2012 | 43 |
| 1993 | 24 | 2003 | 3.4 | 2013 | 26 |
| 1994 | 41.9 | 2004 | 2.5 | 2014 | 19 |
| 1995 | 7.2 | 2005 | 15.2 | 2015 | 4 |
| 1996 | 8.8 | 2006 | 18.2 | 2016 | 5 |
| 1997 | 9.7 | 2007 | 10.9 | 2017 | 6 |
| 1998 | 10.5 | 2008 | 17.3 | 2018 | 43 |
| 1999 | 3.2 | 2009 | 7 | 2019 | 22 |
| LU/LC | Area (km2) | % Of Total Area |
|---|---|---|
| Bare Soil | 10,068.8 | 77 |
| Built-up area | 326.9 | 2.5 |
| Water bodies | 418.4 | 3.2 |
| Grass and Farm Land | 2262.2 | 17.3 |
| Total area | 13,076.4 | 100 |
| No. | Dam’s Name | Watershed Area km2 | Max. Surface Area of Storage (km2) | CN | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Horan/2 dam | 7350 | 1.884 | 76.47 | 78.156 |
| 2 | Horan/3 dam | 8277 | 2.226 | 76.47 | 78.156 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adham, A.; Suri, H.; Abed, R.; Ritsema, C. Enhancing Small Dam Performance in Wadi Horan: A Hydrological Modelling Study for Rainwater Harvesting. Resources 2025, 14, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14100150
Adham A, Suri H, Abed R, Ritsema C. Enhancing Small Dam Performance in Wadi Horan: A Hydrological Modelling Study for Rainwater Harvesting. Resources. 2025; 14(10):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14100150
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdham, Ammar, Hussam Suri, Rasha Abed, and Coen Ritsema. 2025. "Enhancing Small Dam Performance in Wadi Horan: A Hydrological Modelling Study for Rainwater Harvesting" Resources 14, no. 10: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14100150
APA StyleAdham, A., Suri, H., Abed, R., & Ritsema, C. (2025). Enhancing Small Dam Performance in Wadi Horan: A Hydrological Modelling Study for Rainwater Harvesting. Resources, 14(10), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14100150







