Allometric Relations and Scaling Laws for the Cardiovascular System of Mammals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Cardiovascular System



3. Theoretical Scaling Laws for Mammals—Review and Discussion
3.1. Scaling of Heart Dimensions


 denotes proportionality. The first relation is concerned with the ventricular mass and expresses the fact that the net tissue volume (and hence its mass) is proportional to mammal mass. The second relation expresses the fact that the inside volume of the ventricle is proportional to mammal mass.
denotes proportionality. The first relation is concerned with the ventricular mass and expresses the fact that the net tissue volume (and hence its mass) is proportional to mammal mass. The second relation expresses the fact that the inside volume of the ventricle is proportional to mammal mass.
3.2. Scaling of Blood Vessels












4.Comment on Theory and Variation of Solution
5. Some Comparisons with Measurements
5.1. Arterial and Venous Vessels
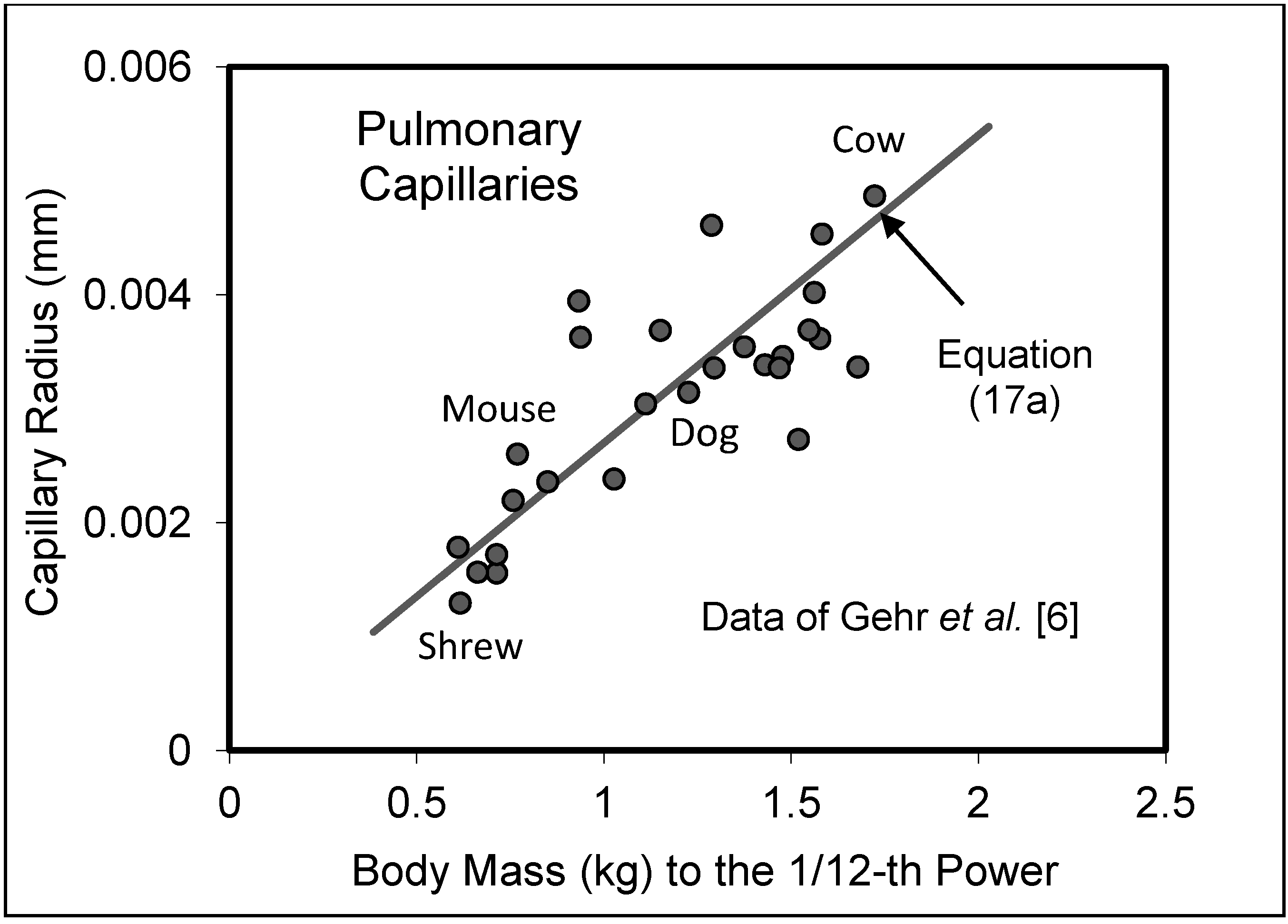
5.2. Capillary System
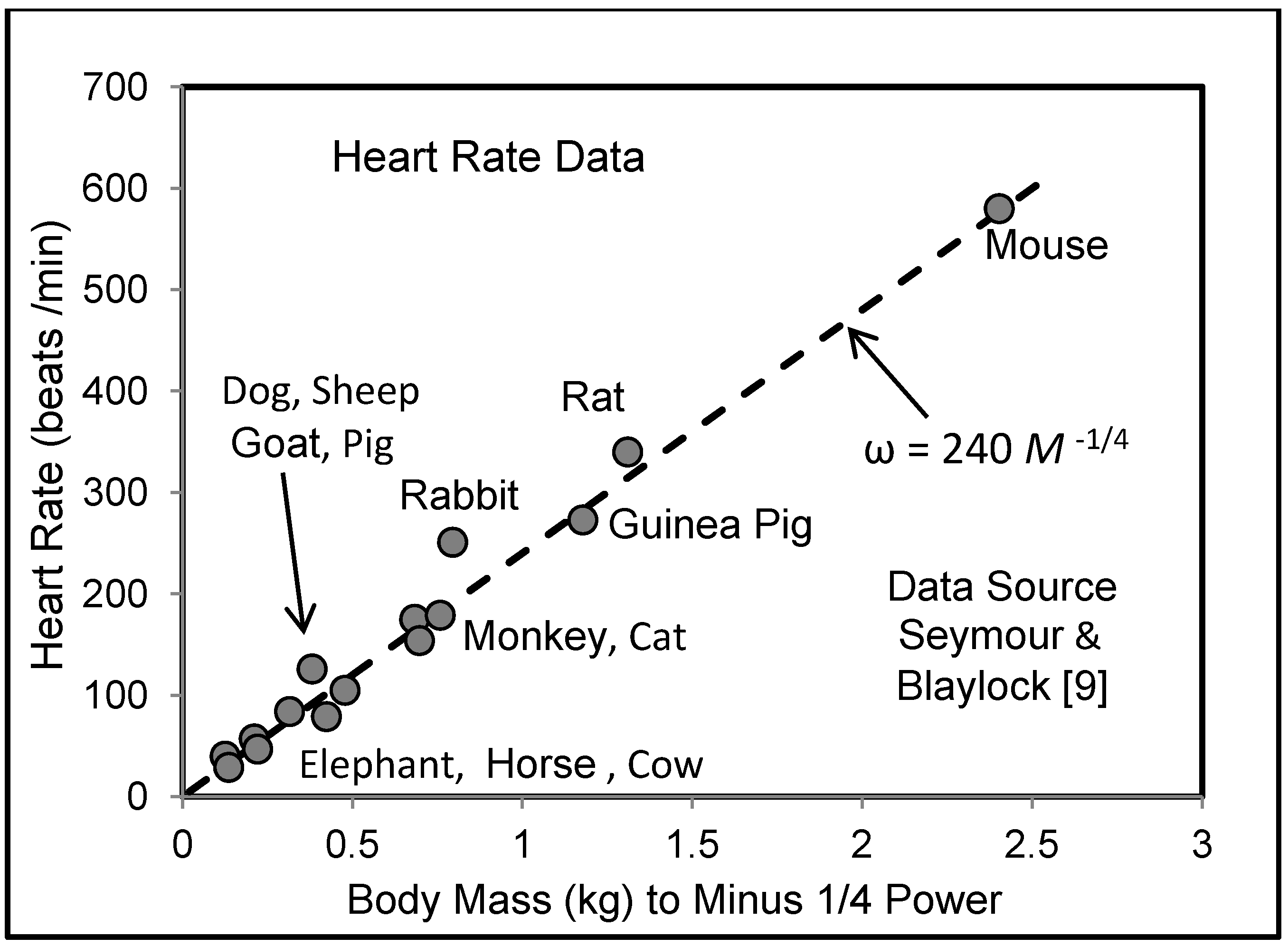
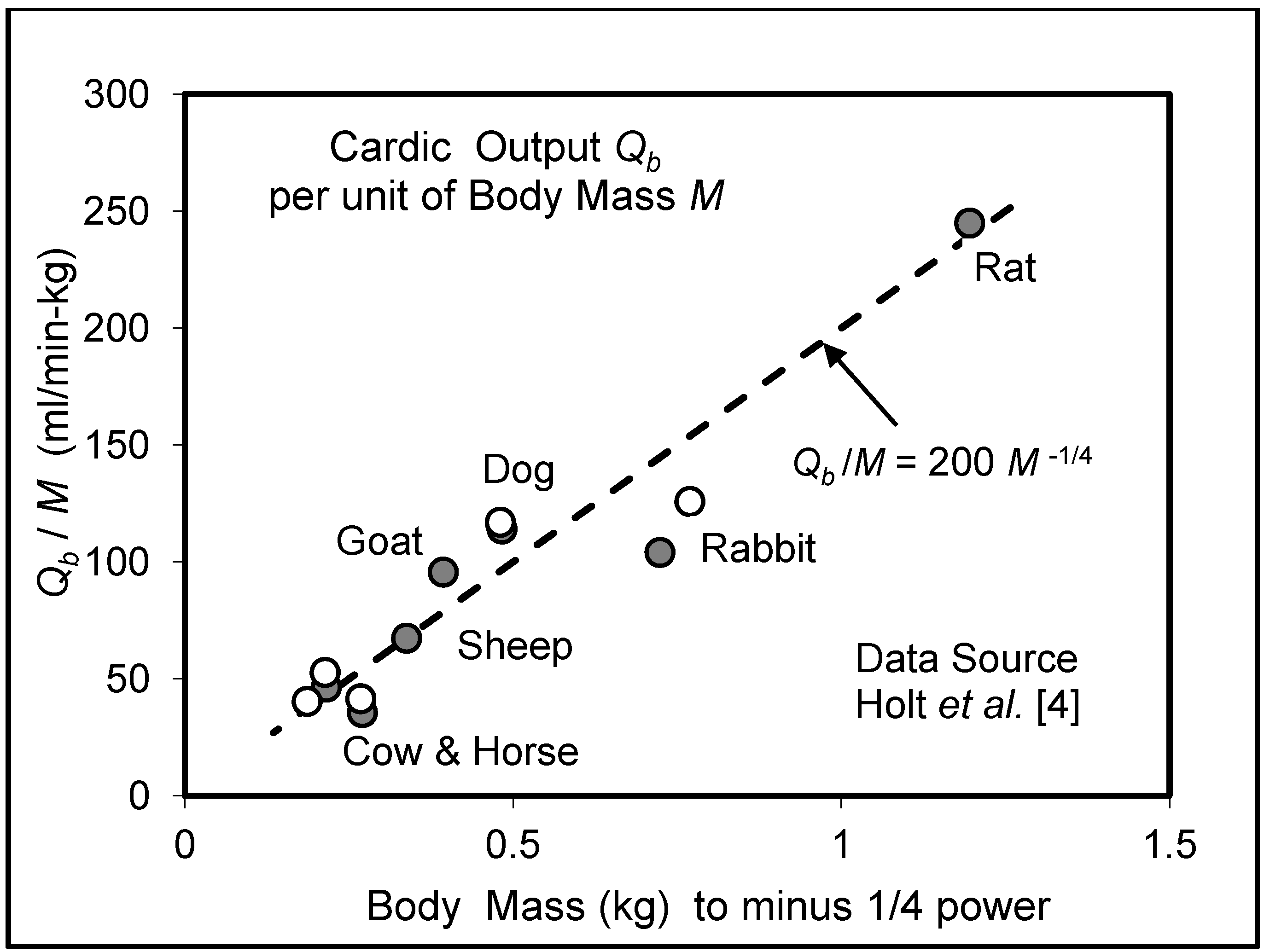
5.3. Heart Rate and Cardiac Output
6. Effects of Vascular Size on Function
6.1. Oxygen Consumption Rate

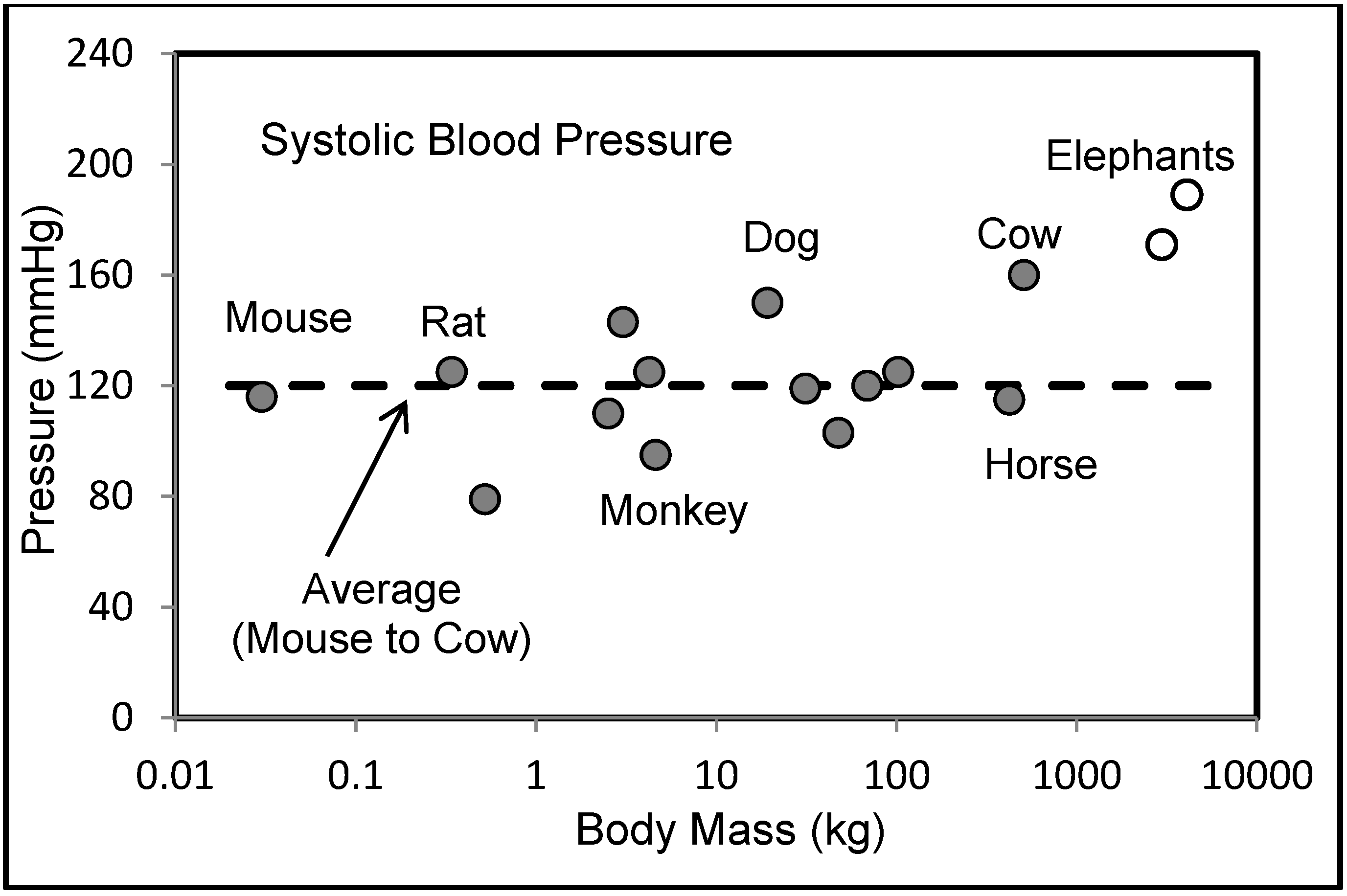
6.2. Blood Pressures
6.3. Circulation Time
 .
. 
6.4. Fluid Flow across Capillary Walls

7. Validity of Scaling Relations for Children
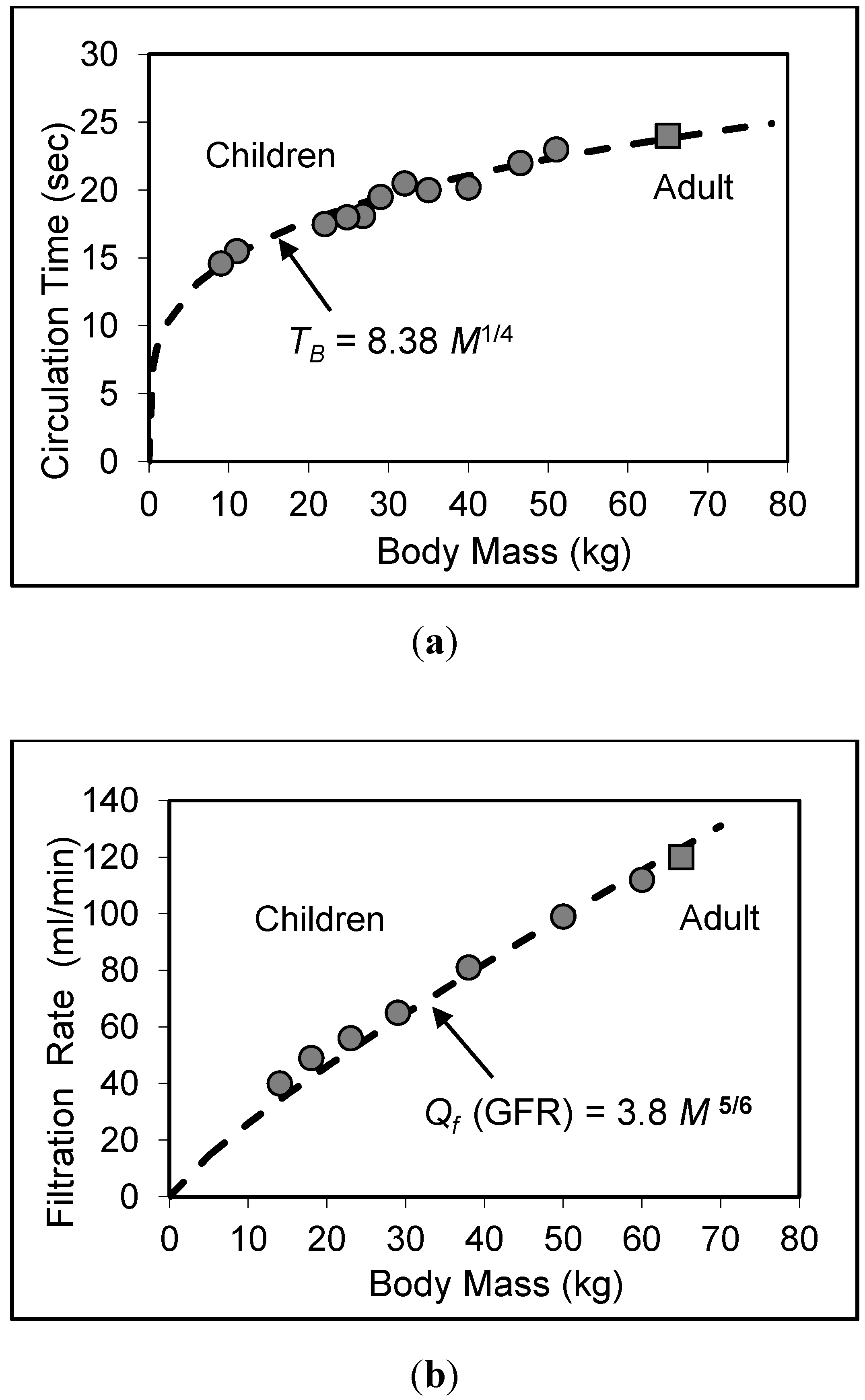
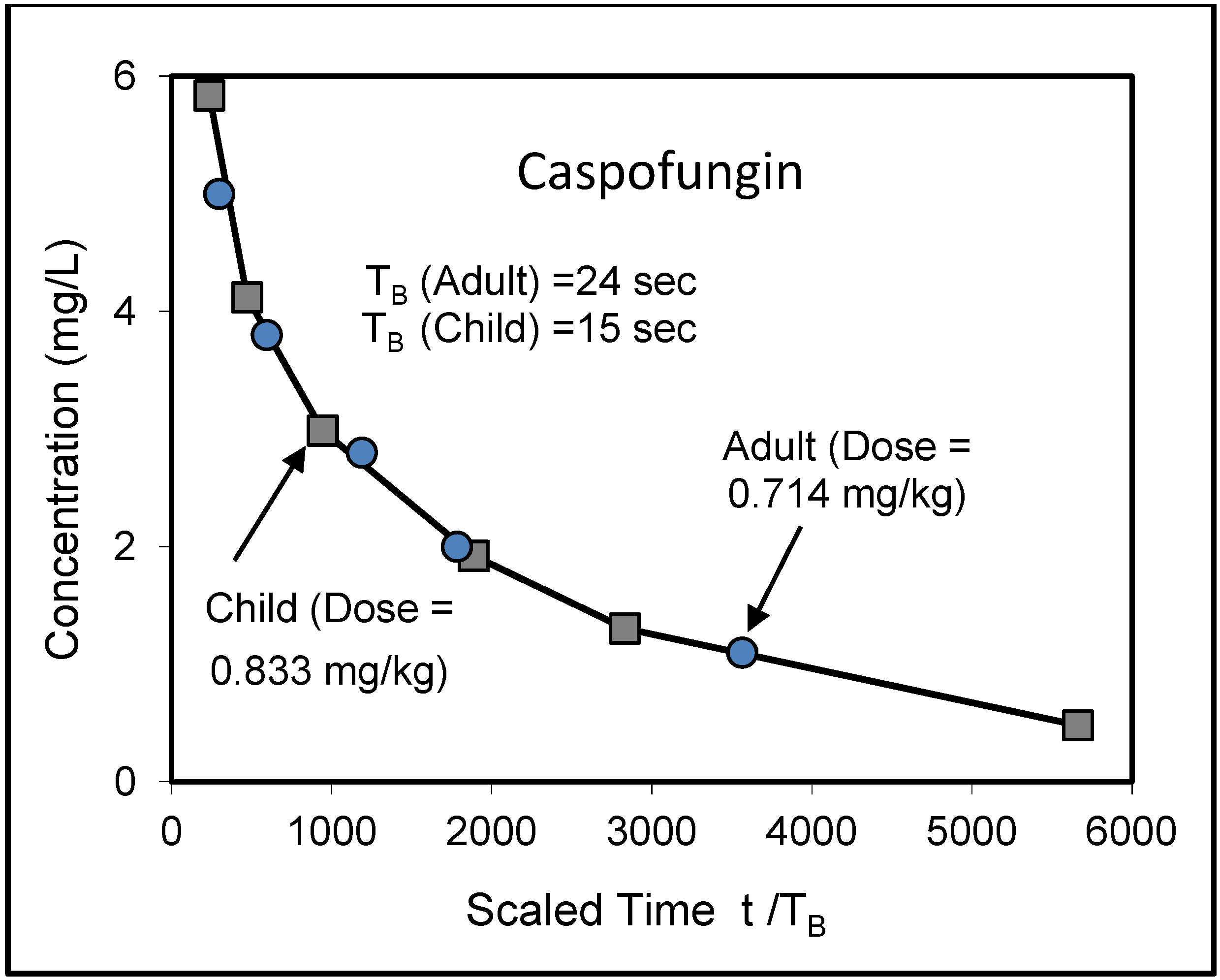
8. Application to Pediatric Drug Dosage





9. Effects of Strenuous Exercise
10. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, A.J. Comparative Physiology of the Heart; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Brody, S. Bioenergetics and Growth; Reinhold Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 1945. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, J.P.; Rhode, E.A.; Kines, H. Ventricular volumes and body weight in mammals. Am. J. Physiol. 1968, 215, 704–715. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, J.P.; Rhode, E.A.; Holt, W.W.; Kines, H. Geometric similarity of aorta, venae cavae, and certain of their branches in mammals. Am. J. Physiol. 1981, 241, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Nielsen, K.; Pennycuik, P. Capillary density in mammals in relation to body size and oxygen consumption. Am. J. Physiol. 1961, 200, 746–750. [Google Scholar]
- Gehr, P.; Mwangi, D.K.; Ammann, A.; Malooig, G.M.D.; Taylor, C.R.; Weibel, E.R. Design of the mammalian respiratory system. V. Scaling morphometric pulmonary diffusing capacity to body mass: wild and domestic mammals. Respir. Physiol. 1981, 44, 61–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppeler, H.; Mathieu, O.; Weibel, E.R.; Krauer, R.; Lindstedt, S.L.; Taylor, C.L. Design of the mammalian respiratory system, VIII. Capillaries in skeletal muscles. Respir. Physiol. 1981, 44, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugosz, E.M.; Chappel, M.A.; Meek, T.H.; Szafransks, P.A.; Zub, K.; Konarzewski, M.; Jones, J.H.; Bicudo, J.E.P.W.; Nespolo, R.F.; Careau, V.; Garland, T. Phylogenetic analysis of mammalian maximal oxygen consumption during exercise. J. Exp. Biog. 2013, 216, 4712–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, R.S.; Blaylock, A.J. The principle of Laplace and scaling of ventricular wall stresss and blood pressure in mammals and bird. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2000, 73, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.R.; Blackburn, T.M.; Seymour, R.S. Phylogenetically informed analysis of the allometry of mammalian basal metabolic rate supports neither geometric nor quarter power scaling. Evolution 2009, 63, 2658–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.R.; Seymour, R.S. The role of gravity in the evolution on mammalian blood pressure. Evolution 2014, 68, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.H. Engineering Design of the Cardiovascular System of Mammals; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, T.H. Similitude in the cardiovascular system of mammals. J. Exp. Biog. 2001, 204, 395–407. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, T.H. Scaling laws for capillary vessels of mammals at rest and in exercise. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 2003, 270, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.H. Allometric scaling in biology. Science 1998, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkurt, E.E.; Bullard, R.W. The Heart as a Pump: Mechanical Correlates of Cardiac Activity. In Physiology; Selkurt, E.E., Ed.; Little Brown: Boston, MA, USA, 1971; pp. 275–295. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, T.H. Modeling the Vascular System and its Capillary Networks. In Vascular Hemodynamics; Yim, P.J., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Elad, D.; Einav, S. Physical and Flow Properties of Blood, Chapter 3. Standard Handbook of Biomedical Engineering and Design; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2004. Available online: http://www.digital engineering library.com (accessed on 11 February 2014).
- Kunkel, P.A., Jr. The number and size of the glomeruli in the kidney of several mammals. Bull. Johns Hopkiins Hosp. 1930, 47, 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Adolph, E.F. Quantitative relations in the physiological constitution of mammals. Science 1949, 109, 579–585. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiber, M. Body size and metabolism. Hilgardia 1931, 6, 315–353. [Google Scholar]
- Brody, S.; Procter, R.C. Relation between basal metabolism and mature body weight in different species of mammals and birds. Univ. Missouri Agr. Exp. Station Bull. 1932, 166, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Nielsen, K.; Larimer, J.L. Oxygen dissociation curves of mammalian blood in relation to body size. Am. J. Physiol. 1958, 195, 424–428. [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury, R.A.; Hamilton, W.F. Blood pressure studies in small animals. Am. J. Physiol. 1937, 119, 663–674. [Google Scholar]
- Gregg, D.E.; Eckstein, R.W.; Fineberg, M.H. Pressure pulses and blood pressure values in unanesthetized dogs. Am. J. Physiol. 1937, 118, 399–410. [Google Scholar]
- Prosser, C.L.; Brown, F.A., Jr. Comparative Animal Physiology; W. B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, T.H. Scaling adult doses of antifungal and antibacterial agents to children. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2948–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.H. Scaling adult dose and schedule of anticancer agents to children. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 2035–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seckel, H. Blood volume and circulation time in children. Arch. Dis. Child 1936, 11, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.G.; Work, D.F. Measurement and estimation of GFR in children and adolescents. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, G.R. Blood volume in children. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1963, 33, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, T.J.; Adamson, P.C.; Seibel, N.L.; Flynn, P.M.; Neely, M.N.; Schwartz, C.; Shad, A.; Kaplan, S.L.; Roden, M.M.; Stone, J.A.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of caspofungin in children and adolescents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 4536–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, T.H. Scaling laws for plasma concentrations and tolerable doses of anticancer drugs. Canc. Res. 2010, 70, 4801–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.L.; Andrews, P.A.; Smith, D.D.; DeGeorge, J.J.; Justice, R.L.; Beitz, G.J. Predictive values of preclinical toxicology studies for platinum anticancer agents. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 3, 11161–11167. [Google Scholar]
- Baudinette, R.V. Scaling of heart rate during locomotion in mammals. J. Comp. Physiol. 1978, 127, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.R.; Wiebel, E.R. Design of the mammalian respiratory system. Respir. Physiol. 1981, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebel, E.R.; Hoppeler, H. Modeling design and functional integration in the oxygen and fuel pathways to working muscle. Cardiovasc. Eng. 2004, 4, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Heart mass and the maximum cardiac output of birds and mammals: Implications for estimating the maximum aerobic power input of flying mammals. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1997, 352, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. The maximum oxygen consumption and aerobic scope of birds and mammals: Getting to the heart of the matter. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1999, 266, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Dawson, T.H. Allometric Relations and Scaling Laws for the Cardiovascular System of Mammals. Systems 2014, 2, 168-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems2020168
Dawson TH. Allometric Relations and Scaling Laws for the Cardiovascular System of Mammals. Systems. 2014; 2(2):168-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems2020168
Chicago/Turabian StyleDawson, Thomas H. 2014. "Allometric Relations and Scaling Laws for the Cardiovascular System of Mammals" Systems 2, no. 2: 168-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems2020168
APA StyleDawson, T. H. (2014). Allometric Relations and Scaling Laws for the Cardiovascular System of Mammals. Systems, 2(2), 168-185. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems2020168



