The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Sustainable Development Performance of Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Research on SDP
2.2. Research on AI
2.3. Research on Machine Learning in Causal Inference
3. Research Hypotheses
3.1. Green Innovation Effect
3.2. Cost-Saving Effect
3.3. Digital Transformation Effect
4. Model Setup
4.1. DID Model
4.2. Data Sources and Indicator Selection
4.2.1. Data Sources
4.2.2. Indicator Selection
5. Empirical Result Analysis
5.1. Baseline Results
5.2. Robustness Check
5.2.1. Parallel Trend Test
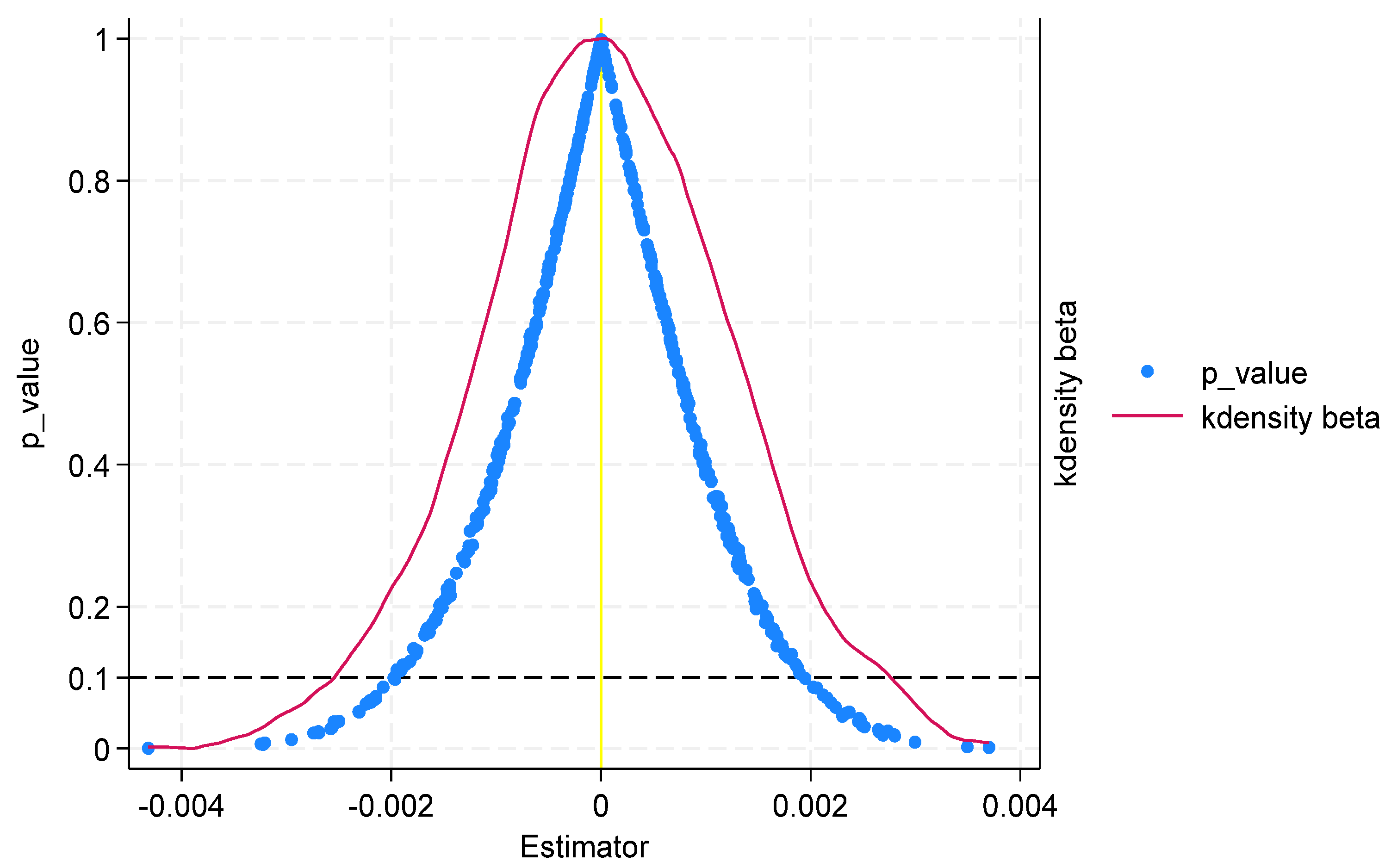
5.2.2. Placebo Test
5.2.3. Replacing the Explanatory Variable
5.2.4. Exclusion of Similar Policy
5.2.5. Other Robustness Tests
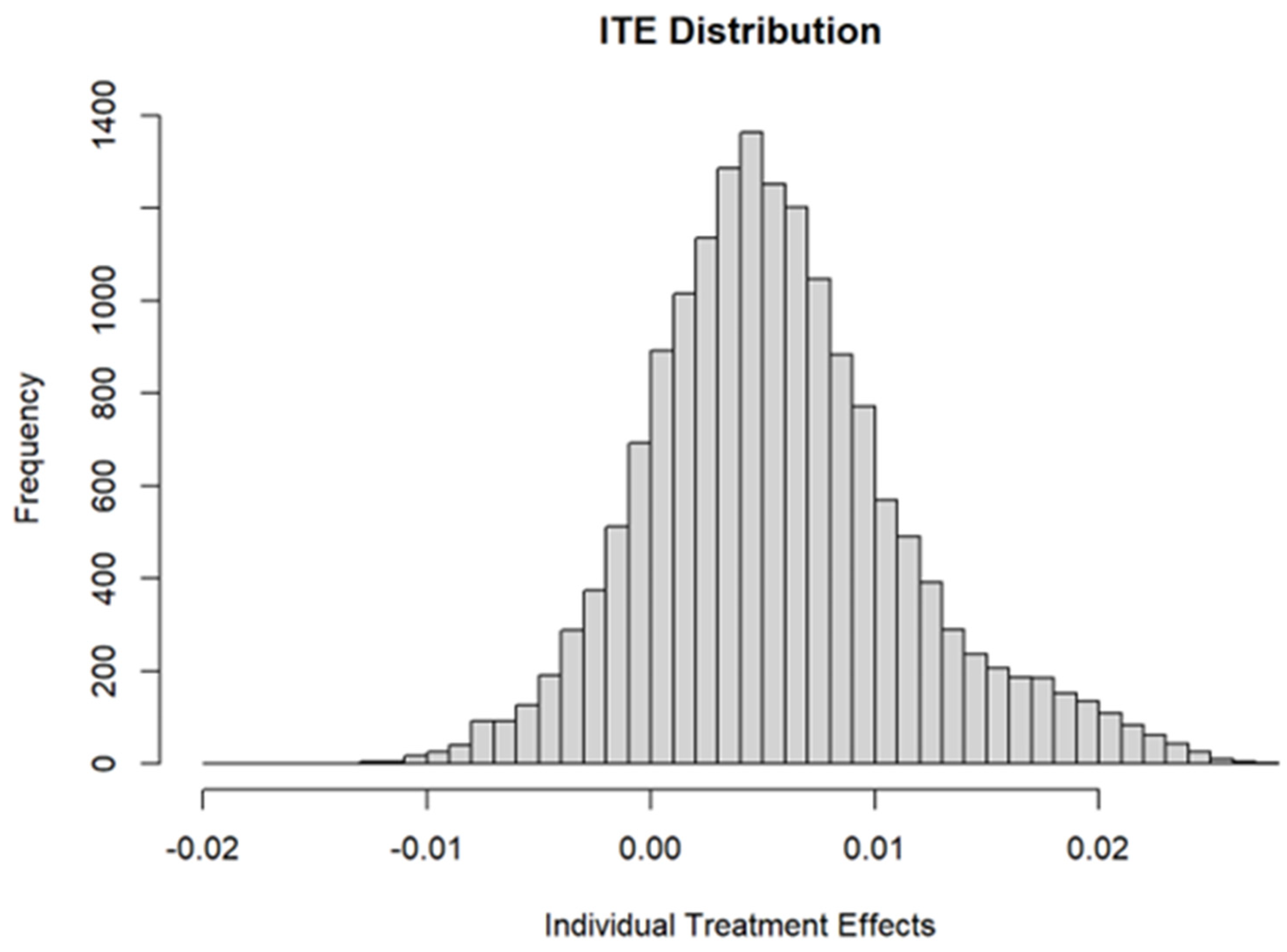
5.2.6. GRF Model Robustness Check
5.3. Mechanism Analysis
5.4. Moderation Effect of CEO Duality
5.5. Heterogeneity Analysis
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- For enterprises: First, firms should enhance their AI capabilities and continue to improve their green technology innovation. Companies can integrate green innovation resources, accelerate the transformation of sustainable development results, and ultimately improve SDP by broadening the scope and depth of AI applications. Second, firms with low AI adoption levels should overcome existing biases, actively learn to apply AI technologies, and connect internal and external resources to drive sustainable development. Third, given the negative moderating effect of the CEO duality on the relationship between AI and corporate SDP, companies can implement a governance model where the chairman and general manager are separated, and reasonably control the proportion of executive shareholding to avoid the negative impact of excessive power concentration and short-term interest pursuit on SDP investment.
- (2)
- For government: The government should invest considerably in fundamental AI research and key technology development while fostering collaboration between enterprises, academia, and research institutions to enhance innovation. Additionally, the government should offer clear policies that encourage AI adoption, ensure transparent policy implementation, and protect intellectual property rights. Strengthening the innovation ecosystem can boost technological advancements and, ultimately, support firms in achieving sustainable development goals. For high-polluting enterprises, the government should increase support for environmental protection technology, guide financial institutions to provide them with low-interest loans or green financial products, reduce financing costs, alleviate financing constraints, and enable them to have more resources to invest in green transformation and SDP construction. For non-state-owned enterprises, the government needs to further improve its technology innovation incentive policies, encourage them to conduct cutting-edge research and applications in the field of AI and SDP integration, and create industry benchmark cases. Finally, the government can establish cross-regional communication and cooperation mechanisms to promote experience sharing between AI pilot zones and non-pilot zone enterprises, in order to enhance the overall SDP performance of manufacturing enterprises.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, C.B.; Qi, S.Z.; Li, Y.K. Environmental policy uncertainty and green transformation dilemma of Chinese enterprises. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhong, N.; Tu, X.; Jia, J.; Wang, J. Tackling environmental challenges in pollution controls using artificial intelligence: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Sun, X.; Qi, L. Does artificial intelligence technology enhance green transformation of enterprises: Based on green innovation perspective. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 21651–21687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, S.; Baskaran, S. Examining sustainable business performance determinants in Malaysia upstream petroleum industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.R. The Impact of Digital Strategic Orientation on Enterprise Sustainable Performance Against the Background of 2030 Sustainable Performance Goal. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 8, 2263222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.L.; Wu, J.H. Digital transformation and enterprise sustainable development. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 60, 104902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, S.; Imbens, G. Recursive Partitioning for Heterogeneous Causal Effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7353–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager, S.; Athey, S. Estimation and inference of heterogeneous treatment effects using random forests. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2018, 113, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, S.; Tibshirani, J.; Wager, S. Generalized Random Forests. Ann. Stat. 2019, 47, 1148–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.M. Sustainability and sustainable development. Int. Soc. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, P. Evolving sustainably: A longitudinal study of corporate sustainable development. Strateg. Manag. J. 2005, 26, 197–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkington, J. Towards the sustainable corporation: Win-win-win business strategies for sustainable development. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1994, 36, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajnc, D.; Glavič, P. How to compare companies on relevant dimensions of sustainability. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 55, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.M.; Zhu, Q.W. How Can Green Innovation Solve the Dilemmas of Harmonious Coexistence? J. Manag. World 2021, 1, 128–149. [Google Scholar]
- Aksoy, M.; Yilmaz, M.K.; Tatoglu, E.; Basar, M. Antecedents of corporate sustainability performance in Turkey: The effects of ownership structure and board attributes on non-financial companies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, J.; Veneziani, M.; Sarwar, H.; Ishaq, M.I. Organizational ambidexterity, firm performance, and sustainable development: Mediating role of entrepreneurial orientation in Pakistani SMEs. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 132956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, Y.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Wah, W.X. Pursuing green growth in technology firms through the connections between environmental innovation and sustainable business performance: Does service capability matter? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Koliby, I.S.; Mohd Suki, N.; Abdullah, H.H. Linking knowledge acquisition, knowledge dissemination, and manufacturing SMEs’ sustainable performance: The mediating role of knowledge application. Bottom Line 2022, 35, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Li, Z. Does external uncertainty matter in corporate sustainability performance? J. Corp. Financ. 2020, 65, 101743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ji, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y. Digital technology, green innovation, and the carbon performance of manufacturing enterprises. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1384332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tian, Q. How does usage of robot affect corporate carbon emissions? Evidence from China’s manufacturing sector. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Chen, S.; Feng, Z.; Li, J. Industrial robots and firm productivity. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2023, 67, 388–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.Y.; Zhang, W.F. Artificial intelligence and enterprise pollution reduction: Environmental effects of intelligent governance. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2023, 33, 138–145. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.; Xu, C. Enhancing energy-environmental performance through industrial intelligence: Insights from Chinese prefectural-level cities. Appl. Energy 2024, 365, 123245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, C. Impact of Industrial Intelligence on China’s Urban Land Green Utilization Efficiency. Land 2024, 13, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. The effect of manufacturing intelligence on green innovation performance in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 178, 121569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.; Hu, H.L.; Li, L. How can industrial robots promote green production? Evidence from Chinese micro-firms. Ind. Econ. Res. 2022, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. How Does Artificial Intelligence Impact Green Development? Evidence from China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyytinen, K.; Yoo, Y.; Boland Jr, R.J. Digital product innovation within four classes of innovation networks. Inf. Syst. J. 2016, 26, 47–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Jiang, X.; Sun, W.; Fan, W. How do manufacturing firms manage artificial intelligence to drive iterative product innovation? IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 71, 6090–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.R. Can big data analytics help organisations achieve sustainable competitive advantage? A developmental enquiry. Technol. Soc. 2022, 68, 101801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.; Ormiston, J. Blockchain as a sustainability-oriented innovation? Opportunities for and resistance to Blockchain technology as a driver of sustainability in global food supply chains. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 175, 121403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Ratkovic, M. Estimating treatment effect heterogeneity in randomized program evaluation. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2013, 7, 443–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.L. Bayesian nonparametric modeling for causal inference. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2011, 20, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, M.C.; Lechner, M.; Strittmatter, A. Machine learning estimation of heterogeneous causal effects: Empirical Monte Carlo evidence. Econom. J. 2021, 24, 134–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, S.; Imbens, G.W. Machine learning methods that economists should know about. Annu. Rev. Econ. 2019, 11, 685–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.J.M.; Fernandes, C.I.; Ferreira, F.A.F. To be or not to be digital, that is the question: Firm innovation and performance. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 101, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Sun, T.T.; Xu, R.Y. The impact of artificial intelligence on total factor productivity: Empirical evidence from China’s manufacturing enterprises. Econ. Change Restruct. 2023, 56, 1113–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Sun, P.Y. Open Competition, Intelligent Manufacturing and Consumer Welfare Effect. Stat. Res. 2023, 40, 42–57. [Google Scholar]
- Audretsch, D.B.; Belitski, M. The role of R&D and knowledge spillovers in innovation and productivity. Eur. Econ. Rev. 2020, 123, 103391. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, C.; Chung, Y.; Chun, D.; Han, S.; Lee, D. Impact of green innovation on labor productivity and its determinants: An analysis of the Korean manufacturing industry. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2014, 23, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Wu, W. How does green innovation improve enterprises’ competitive advantage? The role of organizational learning. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graetz, G.; Michaels, G. Robots at work. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2018, 100, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Said, R.; Ismail, N.W.; Hamzah, H.Z.; Chen, H. Effect of industrial robots on employment in China: An industry level analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2267237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.J.; Yuan, Y.M.; Jiao, J.J. Industrial Automation and Manufacturing Innovation Behavior. China Ind. Econ. 2022, 7, 82–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zeba, G.; Dabić, M.; Čičak, M.; Daim, T.; Yalcin, H. Technology mining: Artificial intelligence in manufacturing. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 171, 120971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.J.; Lin, Y.; Su, Z. Artificial Intelligence Affordance, Intelligent Manufacturing Platform Value Co-Creation and Digital Transformation Performance of Manufacturing Enterprises. China Ind. Econ. 2024, 6, 155–173. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Lee, C.C.; Song, Z. Digitalization and environment: How does ICT affect enterprise environmental performance? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 54826–54841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Sun, L. How to leverage manufacturing digitalization for green process innovation: An information processing perspective. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2021, 121, 1026–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijit, R.; Hu, Q.; Xu, J.; Ma, G. Greening through AI? The impact of Artificial Intelligence Innovation and Development Pilot Zones on green innovation in China. Energy Econ. 2025, 146, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, S.; Gan, J.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y. How does the construction of new generation of national AI innovative development pilot zones drive enterprise ESG development? Empirical evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2024, 140, 108011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, I.; Kounetas, K.; Tzelepis, D. Environmental and Financial Performance. Is there a win-win or a win-loss situation? Evidence from the Greek manufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Ma, S.C. The Financial Effects of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises Participating in the Bridge Loan Business: Evidence from Companies Listed on SME Board. J. Financ. Res. 2017, 3, 116–129. [Google Scholar]
- An, Y.; Sheng, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q. The Role of Financial Flexibility in Sustainable Development Performance of SRDI Enterprises. J. Syst. Sci. Syst. Eng. 2025, 34, 78–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tan, X.; Zhu, J.; Dong, R.K. Can supply chain digital innovation policy improve the sustainable development performance of manufacturing companies? Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, L.S.; Zhao, H. Senior Executive dual environmental cognition, green innovation and enterprise sustainable development performance. Bus. Manag. J. 2022, 44, 139–158. [Google Scholar]
- La Ferrara, E.; Duryea, S.; Chong, A.E. Soap Operas and Fertility: Evidence from Brazil. Am. Econ. J. Appl. Econ. 2012, 4, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Q.; Zhang, K.P.; Guo, L.P.; Xu, F. How Does Artificial Intelligence Improve Firm Productivity? Based on the Perspective of Labor Skill Structure Adjustment. J. Manag. World 2024, 40, 101–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.B.; Zheng, X.S.; Qi, S.Z.; Li, Y.K.; Gao, H.Y. Green credit guideline and enterprise export green-sophistication. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knittel, C.R.; Stolper, S. Machine Learning about Treatment Effect Heterogeneity: The Case of Household Energy Use. AEA Pap. Proc. 2021, 111, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, R.; Lu, J.; Jia, Z. Enterprise Digital Transformation, Supply Chain Spillover and Labor Skill Preference. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 2024, 41, 133–153. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y.; Raza, S.A.; Huo, Z.; Shahzad, U.; Zhao, X. Does enterprise digital transformation contribute to the carbon emission reduction? Micro-level evidence from China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2023, 86, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Abbas, J.; Sial, M.S.; Álvarez-Otero, S.; Cioca, L.-I. Achieving green innovation and sustainable development goals through green knowledge management: Moderating role of organizational green culture. J. Innov. Knowl. 2022, 7, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, B.; Jia, D.; Ahmad, M. The relationship between artificial intelligence, geopolitical risk, and green growth: Exploring the moderating role of green finance and energy technology. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2025, 217, 124135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Nazar, R.; Ali, S.; Meo, M.S. Eco-friendly algorithms: Artificial intelligence and green finance in European intelligent nations. Technol. Soc. 2025, 83, 102960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.M. Digital brains, green gains: Artificial intelligence’s path to sustainable transformation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasist, P.N.; Krishnan, S. AI’s Impact on Sustainability Targets: A Cross-Country NCA and fsQCA Study. Inf. Syst. Front. 2024, 10, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Symbol | Definition | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Development Performance | SDP | Calculated based on entropy method | 0.5933 | 0.0683 |
| Asset liability ratio | Lev | Ln (ratio of total liabilities to total assets) | −1.0544 | 0.6032 |
| Tobin’s q value | Tobinq | Ln (market value of debt and equity to replacement cost of total assets) | 0.6332 | 0.4886 |
| Labor productivity | Lp | Ln (operating income to the number of employees) | 13.7111 | 0.7162 |
| Cash flow | Cash | Ln (ratio of net cash flow from operating activities to total assets) | −1.8781 | 0.7061 |
| Enterprise size | Size | Ln (total enterprise assets) | 22.086 | 1.1913 |
| Net Profit Margin | Npm | Ln (net profit to operating income) | −3.0530 | 1.1055 |
| Number of employees | Ne | Ln (number of employees) | 7.7984 | 1.1499 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDP | SDP | SDP | |
| AIPZ*Time | 0.0146 *** | 0.0128 *** | 0.0139 *** |
| (0.00178) | (0.00192) | (0.00175) | |
| Lev | −0.0253 *** | −0.0195 *** | |
| (0.00113) | (0.00140) | ||
| Tobinq | −0.00198 | −0.00225 | |
| (0.00123) | (0.00143) | ||
| Lp | 0.0106 *** | 0.00578 *** | |
| (0.00115) | (0.00178) | ||
| Cash | 0.0379 *** | 0.0284 *** | |
| (0.00452) | (0.00458) | ||
| Size | 0.00222 * | 0.00858 *** | |
| (0.00123) | (0.00199) | ||
| Npm | 0.00319 *** | 0.00227 ** | |
| (0.000512) | (0.00108) | ||
| Ne | 0.0158 *** | 0.0162 *** | |
| (0.00115) | (0.00195) | ||
| ID effects | YES | NO | YES |
| Year effects | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 16,515 | 16,515 | 16,515 |
| R-squared | 0.581 | 0.111 | 0.599 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| SDP | SDP | |
| AIPZ*Time−2 | 0.00112 | 0.00158 |
| (0.00251) | (0.00246) | |
| AIPZ*Time−1 | 0.00135 | 0.00181 |
| (0.00224) | (0.00221) | |
| AIPZ*Time0 | 0.000775 | 0.00129 |
| (0.00261) | (0.00257) | |
| AIPZ*Time1 | 0.0211 *** | 0.0207 *** |
| (0.00287) | (0.00280) | |
| AIPZ*Time2 | 0.0128 *** | 0.0121 *** |
| (0.00222) | (0.00218) | |
| AIPZ*Time3 | 0.0210 *** | 0.0220 *** |
| (0.00644) | (0.00644) | |
| CV | NO | YES |
| ID effects | YES | YES |
| Year effects | YES | YES |
| Observations | 16,515 | 16,515 |
| R-squared | 0.554 | 0.572 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| SDP | SDP | |
| lnAI | 0.0063 *** | 0.0043 *** |
| (0.0012) | (0.0012) | |
| CV | NO | YES |
| ID effects | YES | YES |
| Year effects | YES | YES |
| Observations | 16,515 | 16,515 |
| R-squared | 0.552 | 0.57 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| SDP | SDP | |
| AIPZ*Time | 0.0148 *** | 0.0141 *** |
| (0.00178) | (0.00175) | |
| CV | NO | YES |
| ID effects | YES | YES |
| Year effects | YES | YES |
| Observations | 16,515 | 16,515 |
| R-squared | 0.581 | 0.599 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDP | SDP | SDP | |
| AIPZ*Time | 0.011 *** | 0.0139 *** | 0.0152 *** |
| (0.0018) | (0.00174) | (0.0019) | |
| CV | YES | YES | YES |
| ID effects | YES | YES | YES |
| Year effects | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 10,085 | 16,515 | 16,515 |
| R-squared | 0.705 | 0.599 | 0.572 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDP | SDP | SDP | SDP | |
| AIPZ*Time | 0.00445 *** | 0.00466 *** | 0.00445 *** | 0.00472 *** |
| (0.00233) | (0.00233) | (0.00233) | (0.00233) | |
| Clustered | NO | NO | NO | YES |
| Tree | 500 | 1000 | 2000 | 2000 |
| Model | Causal Forest | Causal Forest | Causal Forest | Causal Forest |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI | Cost | DT | |
| AIPZ*Time | 0.022 * | −0.011 *** | 0.0801 *** |
| (0.012) | (0.0017) | (0.0241) | |
| CV | YES | YES | YES |
| ID effects | YES | YES | YES |
| Year effects | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 16,515 | 16,515 | 16,515 |
| R-squared | 0.724 | 0.638 | 0.767 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| SDP | SDP | |
| AIPZ*Time*Dual | −0.00761 ** | −0.00631 ** |
| (0.003) | (0.00293) | |
| AIPZ*Time | 0.0171 *** | 0.0161 *** |
| (0.002) | (0.00204) | |
| Dual | −0.0008 | −0.00209 |
| (0.0015) | (0.00152) | |
| CV | NO | YES |
| ID effects | YES | YES |
| Year effects | YES | YES |
| Observations | 16,177 | 16,177 |
| R-squared | 0.581 | 0.6 |
| Variable | (1) State-Owned | (2) Non–State-Owned | (3) Light Pollution | (4) Heavy Pollution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIPZ*Time | 0.0121 *** | 0.0086 *** | 0.0036 *** | 0.0055 *** |
| (0.00262) | (0.00348) | (0.00187) | (0.00288) | |
| Obs | 5243 | 11,035 | 10,420 | 6064 |
| Tree | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 |
| Clustered | YES | YES | YES | YES |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Sustainable Development Performance of Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises. Systems 2025, 13, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13070496
Zhou C. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Sustainable Development Performance of Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises. Systems. 2025; 13(7):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13070496
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Chaobo. 2025. "The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Sustainable Development Performance of Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises" Systems 13, no. 7: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13070496
APA StyleZhou, C. (2025). The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Sustainable Development Performance of Chinese Manufacturing Enterprises. Systems, 13(7), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13070496






