Abstract
Nowadays, the importance of logistics management has been increasingly realized in industry and society. However, current educational approaches in logistics management seem unable to effectively equip students with the necessary skills to cope with practical issues after graduation. Recently, contest-based education has attracted logistics management educators’ attention, but how it can be effectively utilized in this discipline is largely unclear. To fill this gap, this study followed a system approach and analyzed the factors influencing student performance in logistics management contests in China using interpretive structural modelling (ISM) and Matrice d’ Impacts Croisés-Multiplication Appliquée á un Classement (MICMAC). The results suggest that the driving forces for improving student performance in contests are the instructors’ encouragement and their previous experience in instructing contests. Also, the contestants’ previous experience in academic contests, team leadership, and effectiveness of communication between instructors and contestants are critical influencing factors. Based on the results, the educational strategies for effective utilization of contest-based education in logistics management are discussed. This study contributes to the existing literature by using a system modeling approach to clarify the mechanisms of contest-based education adoption in logistics management as well as informing university teachers and higher education institutes about strategies to improve their education quality.
1. Introduction
Logistics management has gained an increasing focus in academia and industry in recent years. In the post-pandemic era, logistics has significantly changed its ways of operations. The logistics flow becomes more vulnerable with frequent disruptions occurring, making it more difficult to manage [1]. Additionally, due to rapid development in technologies, such as industry 4.0 and big data, logistics operations have become more complicated than ever, calling for logistics talents grasping skills which can quickly adapt to market changes [2]. Traditionally, teaching in logistics management was usually in the learning-by-listening mode. However, such an education mode leaves students far from reality and unable to keep up with the practical needs in industry.
To better equip students with practically needed skills in logistics management discipline, multiple attempts have been made to fill the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical issues, such as game-based learning [3], case-based learning [4], simulation-based learning [5], and project-based learning [6]. However, a recent study [7] suggested there still exist significant gaps between what students learn in higher education and the necessary skills identified by practitioners. Therefore, more improvements should be made to get students ready for practical challenges.
Currently, the contest-based education approach attracts educators’ interests in multiple subjects. By using contests or competitions as a way of teaching, students can be significantly motivated and use the theoretical knowledge they learnt to analyze and solve practical problems [8]. Although this approach is not well explored in logistics management education, it can be a promising supplement for other ways of learning in this discipline once well utilized. Therefore, to fully realize its potential, in this study we focused on the contest-based education and explored how it can be properly utilized in logistics management education. Specifically, we focus on the key question: what kind of factors will influence the students’ performance in logistics management contests? To fully explore this question, we adopted a system perspective and used ISM and MICMAC method to explore 21 factors which can influence student performance in logistics management contests, as well as the inter-relationship among these factors. Our results suggest the driving forces for enhancing student performance in logistics management contests are instructors’ encouragement and previous experience in instructing contests, followed by the contestants’ previous experience in academic contests, team leadership, and effectiveness of communication between instructors and contestants. Based on these insights, we developed the educational strategies for university teachers and higher education institutes to improve the effectiveness of adopting contest-based education in logistics management discipline. We believe that our research has the following academic and practical implications:
- Academically speaking, to the best of our knowledge, our study is the first paper applying a system modeling approach and using ISM-MICMAC to explore the effects of factors and their inter-relationship on contest-based education in logistics management. By clarifying the complex behind multiple factors, we contribute to the existing literature by constructing the mechanisms of contest-based education in logistics management discipline. Also, our paper confirms the potentials of using system modelling approach in logistics management education studies, providing new thoughts on analytical methods for scholars in relevant fields for future research.
- Practically speaking, we provide educational plans as well as political suggestions for university teachers and higher education institutes for applying contest-based education in logistics management discipline, improving the quality of education and training. Also, our insights can support teachers or education agencies to combine other methods such as simulation-based learning or case-based learning with contest-based education to further enhance students’ learning effectiveness.
2. Literature Review
This study concerns two streams of studies, namely education in logistics management and contest-based education.
2.1. Education in Logistics Management
Education in logistics management has followed the traditional learning-by-listening approach. However, in recent decades, due to the increasing need for practical skills [9], multiple educational innovations have been explored in the logistics management discipline. For example, logistics management has promoted the use of game-based education [10]. Lau [3] proposed a modified beer distribution game with active learning in which students can play the role of the beer manufacturer, the distributor, the wholesaler, and the retailer to understand the logistics operations. Jhan et al. [11] adopted a digital supply chain game to teach students about the knowledge of logistics activities. Based on the analysis of students’ characteristics and outcome, they provided customized strategies of teaching logistics knowledge using games. Perini et al. [12] developed a life-cycle assessment game to teach students about materials flows as well as manufacturing process knowledge. They found that students can better grasp subject knowledge than non-game players. Also, simulation-based education methods are sometimes applied in logistics management education. For example, Angolia and Pagliari [13] established an ERP stimulator of a three-echelon supply chain from which students can learn logistics activities. Their results suggested that the simulation-based education can effectively engage students in the learning processes. Ammouriova et al. [5] developed a heuristic simulation to support students’ learning and understanding of logistics optimization. In addition, project-based learning has become increasingly popular due to its function to improve students’ ability to analyze practical logistics problems in teams. For example, Özpolat et al. [14] used a project-based learning approach to teach business students for humanitarian logistics. Cudney and Kanigolla [6] applied project-based learning to teach six-sigma knowledge, which is one of the core and difficult topics in logistics management. They found that project-based learning can enhance teaching quality and improve students’ ability for solving practical problems.
Although multiple learning approaches have been examined in the logistics management education, the course content delivered by instructors are still not able to cope with practical issues in logistics industry [7]. The solution for this, according to Wrobel-Lachowska et al. [2], could be that universities conduct education with companies together. Therefore, contest-based learning in which the contests are held by companies and the problems of contests are extracted from the true practical issues can be promising to lead to a better education quality for students. However, so far there are very few explorations about the usage of contest-based education in logistics management, and its mechanism of enhancing the learning outcome is unclear. This study will make an attempt to fill the gap to reveal how contest-based education works in logistics management education.
2.2. Contest-Based Education
Contest-based education, also known as competition-based education, has been used in multiple subjects [15]. Such a way of education is generated from project-based learning and uses contests in the students’ learning process to stimulate their motivation and improve the education quality [16]. In recent years, contest-based education has been adopted in higher education. For example, Huang and Yang [17] applied contest-based education in a Bio-Computation module and found that students’ learning outcomes can be effectively improved. Huang et al. [18] reported a case of using contest-based education for undergraduates in mobile robot courses. The students, after learning with the contest-based education mode, expressed the satisfaction of the course and grasped the necessary knowledge. Hanakawa [8] used contest-based education in software engineering in which the business management elements were integrated. The author found that a properly designed contest-based education program can significantly increase the students’ ability to analyze and solve practical problems.
However, although contest-based education has attracted increasing focus of researchers and practitioners in higher education, there are few publications on using it in logistics management. Due to the unique features of logistics management discipline, the mechanisms that determine the effectiveness of utilizing contest-based education is largely unclear, leading to the ambiguity of this educational method for teachers and students in logistic management. Therefore, this paper attempts to fill this gap and provides useful guidance for using it.
3. Methodology
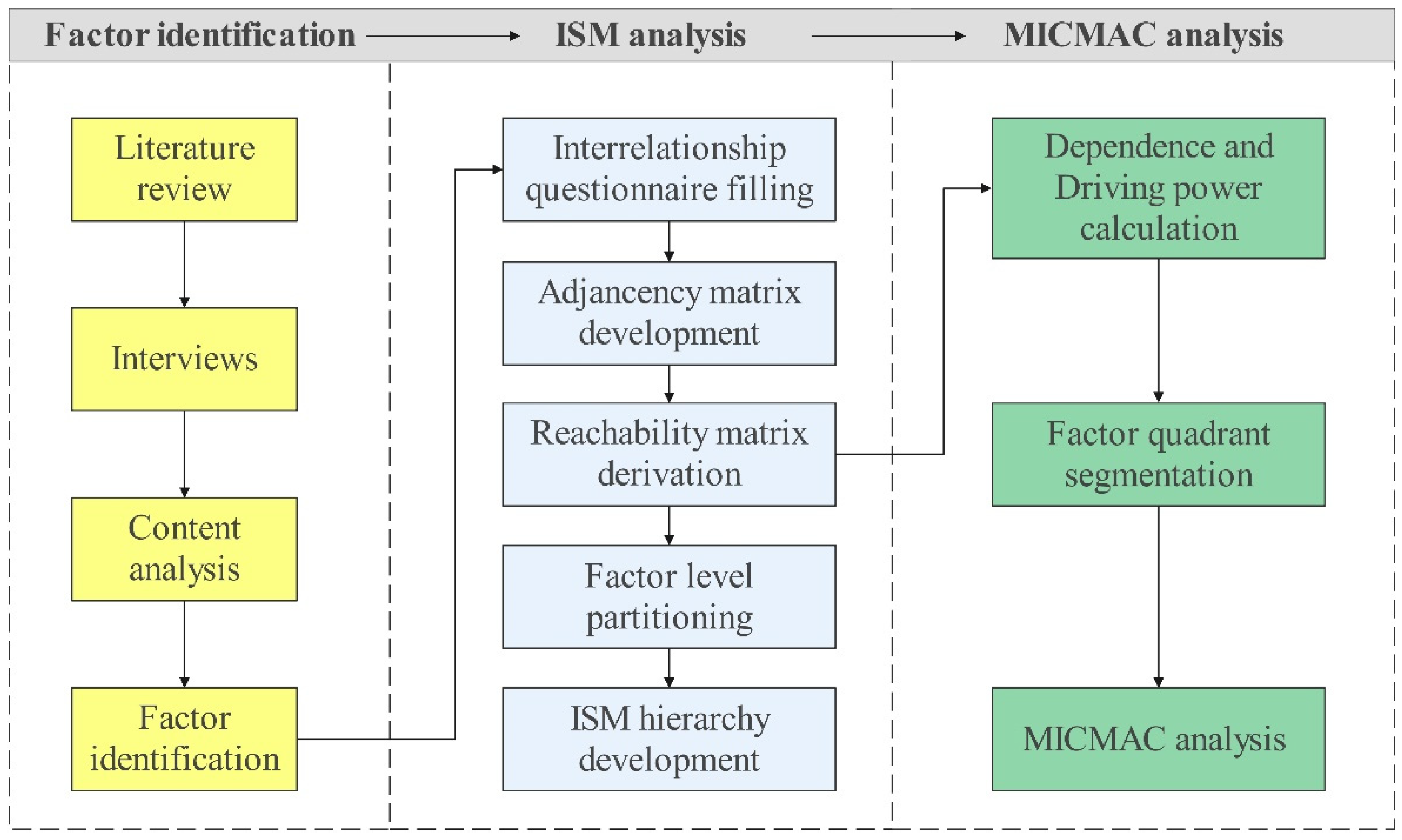
This study applied the ISM-MICMAC method to analyze the key factors influencing the student performance in logistics management contests and the factor inter-relationship to support the development of educational strategies to enhance the effectiveness of contest-based education. Figure 1 presents the main steps of methodology.
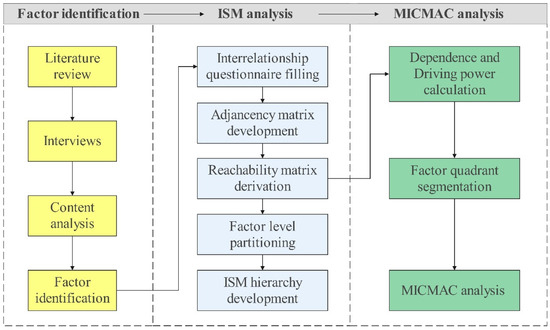
Figure 1.
Methodology.
3.1. Factor Identification
The first step of the methodology is to identify the relevant and critical factors influencing the students’ performance in logistics management contests. By doing so, we followed previous literature (e.g., Lim et al. [19]; Raut et al. [20]; Shen et al. [21]) to conduct a systematic factor identification. It should be noted that, because of different research focuses, the factors we identified significantly differ from the previous literature. Although these publications [19,20,21] and our study are all relevant to business research, we investigated our topic from an educational perspective while they are from a business management perspective. In other words, research [19,20,21] has aimed to provide solutions and improve economic effectiveness for business organizations, while our paper aims to enhance teaching quality for educational institutes. Such a focus directly differentiates our factors from [19,20,21], also leading to the different research participant selection. Specifically, previous literature [19,20,21] has mainly recruited employees from companies (i.e., managers, industrial experts) as research participants in the factor identification with few scholars involved. On the contrary, to match our research objectives, this paper consulted instructors and students from universities who are experienced in logistics management contests for collecting useful information.
As shown in Figure 1, we first thoroughly reviewed previous literature relevant to logistics management education and contest-based education. After that, to further explore factors related to our research theme, we carefully selected 12 interviewees and ask their opinions about what type of factors can assist to achieve good contest performance in logistics management. The interviewees are all from China and consist of ten students who won gold medals or bronze medals in logistics management contests, as well as two experienced instructors with rich teaching experience in the logistics management discipline, who frequently provided instructions for logistics management contests in both undergraduate and graduate levels. The reason why we selected both students and instructors is that such a way of sampling enables us to cover both a contestant perspective and instructor perspective, leading to a more inclusive view of exploring different factors for contest performance. The number of interviewees is consistent with previous literature. For example, there are eight interviewees consulted in the research presented in [22] and seven interviewees in the research presented in [21] in the process of factor identification. Based on previous work [22], there is no minimal acceptable number of interviewees suggested in previous studies. Considering the 12 interviewees consulted in our study are all very experienced in logistics management contests, they can provide significantly informative opinions for factor identification. Therefore, it can be justified that the selected interviewees are representative and thus, sufficient for our factor identification as well as the subsequent analysis. However, we also acknowledge that the ISM method is exploratory by its nature [23]. Therefore, the results can be further validated by recruiting more people to conduct confirmatory studies using regression analysis or structural equation modelling by questionnaires, which is a promising direction for future research but out of scope of this paper.
After the above literature search and the opinions collected from the interviewees, we carefully analyzed the content to identify the factors. Specifically, there were 14 factors identified from the literature and confirmed in interviews. Also, we noticed that there was new information emerging in interviews. To identify new factors, three authors carefully coded the theme of interview scripts. The coding processes were first independent, following the discussion among the authors. Once there was anything unclear in the scripts, the authors went to confirm the meaning from the interviewees. After three iterations of coding, all authors achieved a convergence and seven new factors were identified. In total, 21 factors were deemed as the important reasons for student performance in logistics management contests (please see Table 1 below). As our way of factor identification significantly follows previous studies of ISM [21,22], and our literature search and interviews are thorough, it can be reasonably stated that the factors identified are inclusive enough for our topic.

Table 1.
Factors influencing contest performance in logistics management discipline.
3.2. ISM Analysis
After identifying the important factors affecting contest performance, we conducted ISM analysis to study the inter-relationship between factors. We followed previous literature (e.g., Talib et al. [40]; Azevedo et al. [41]; Sushil [42]) and adopted the well-established procedures to complete the analysis.
First, we developed the questionnaire and studied the influences between different factors. We circulated our questionnaire to five contestants and two experienced instructors and asked them to fill their opinions about the inter-relationship between two factors. All respondents are from China. For each pair of factors, e.g., Factor 1 and Factor 8, we asked the question below based on the previous literature [21,42]: Do you think Factor 1 will assist to achieve Factor 8? If the person confirms there exists such a relationship, they will select 1. Otherwise, they will select 0. As we have 21 factors in total, each person needs to answer 21 × 20 = 420 questions (the self-influence for factors is not considered in ISM analysis).
After collecting all seven people’s opinions about factor influences, we constructed the adjacency matrix, which is the original matrix recording the inter-relationship between factors. The matrix is notated as , with 21 columns and rows, where each element of is denoted as , representing the relationship of factor to factor. For example, if , it means Factor 1 will assist to achieve Factor 8. Specifically, the self-influence is valued as 0 [19]. However, as there are seven people’s answer to the same question about the relationship between two factors, the opinions may not be the same. Thus, we followed previous literature and used the widely adopted principle of “the minority gives the way to the majority” (e.g., [21,43]) to calculate the values of each element in adjacency matrix. For example, if there are three or fewer people selecting 1 for , then we assign , meaning the majority feels there is no significant relationship between Factor 1 and 8. On the contrary, if there are four or more people selecting for , we assign , representing the majority feels the existence of the relationship between factors.
Based on the adjacency matrix, we calculated the reachability matrix by following the transitivity principle (e.g., [41]). The derivation of the reachability matrix was completed in a web-based application called SPSSPRO (www.spsspro.com accessed on 14 December 2023), with the results validated by programs developed by the first author using RStudio. We refer interested readers to previous research [19] for technical details for calculating the reachability matrix from the adjacency matrix.
After obtaining the reachability matrix, we partitioned the factors based on their inter-relationship into different levels based on the rules in the previous literature (e.g., [40]). The low-level factors represent the superficial reasons for logistic management contest performance while the high-level factors represent the driving forces. For level partitioning algorithms, we refer interested readers to previous research [19,21] for details.
Finally, based on the levels partitioned from the reachability matrix, we draw the hierarchical graph of factors to visualize the ISM results, clarifying the casual relationship between factors.
3.3. MICMAC Analysis
MICMAC analysis is widely used for classifying factors into different segments based on their dependence and driving powers. The dependence power of a factor means the degree of this factor affected by others, while the driving power measures the number of other factors affected by this factor [44]. We followed previous literature to calculate the dependence and driving power of a factor, (e.g., [19]). Specifically, the dependence power of a factor is equal to the summation of the column values of this factor in reachability matrix, while the driving power of it is equal to the summation of its row values. For example, for Factor 1, the dependence power is calculated as while its driving power is equal to , where is the element in the row and column in .
After calculating the dependence and driving powers for all factors, we classified them into four quadrants, namely autonomous factors, dependent factors, linkage factors, and driving factors [40]. The autonomous factors are those with relatively low driving and dependence factors which are most disconnected with the whole system [19]. The dependent factors have relatively high dependence but low driving power, indicating they are the superficial reasons for the logistics management contest performance. The driving factors, on the contrary, have relatively low dependence but high driving power, and thus, they are driving forces for the contest performance [21]. Finally, the linkage factors have both high dependence and driving power. This means they can significantly influence other factors and receive influences from other factors simultaneously, leading to instability of these factors [19].
4. Results Analysis
Based on the above procedures, this section reports the study results of factor identification, ISM analysis, and MICMAC analysis sequentially.
4.1. Critical Factors of Student Performance in Logistics Management Contests
First of all, 21 factors from C1 to C21 which significantly contribute to student performance in logistics management contests are listed in Table 1. Each of the factors are briefly introduced as follows.
C1 means the contestants’ understanding and grasp of subject knowledge in logistics management discipline. According to previous studies about contest performance in other disciplines, the good grasp of specialized subject knowledge can make students more creative in problem solving and enhance the quality of their final work in contests [24]. C2 means contestants’ previous experience in participating in academic contests. Reflected by interviewee feedback as well as the authors’ experience in instructing contests, having a rich experience in academic contests can help contestants better understand contest procedures and equip them with useful techniques such as time management or text editing. C3 measures the level of team collaboration which means how well a team works together and communicates with each other when solving contest problems. According to the previous literature in organizational management, a good team collaboration that orchestrates every team member’s strength is critical to achieving a good performance in certain teamwork tasks [27,28]. C4 is the team leadership which represents the team leader’s ability to properly arrange and coordinate team members in logistics management contests. Previous literature suggested that appropriate leadership behaviors can enhance teamwork performance [29,30]. C5 is the instructors’ encouragement. According to previous literature, as well as the interviewees’ feedback, when receiving encouragement from instructors, the team member will feel supported and obtain confidence [31,45], which positively contributes to the completion of the final work of the contests. C6 is the instructors’ previous experience in instructing contests. Previous research [32] suggested that a qualified instructor can significantly help improve the performance of team training. In logistics management contests, an experienced instructor will know and selectively teach subject knowledge, teamwork skills, and time management strategies which can directly determine the effectiveness of contest participation.
C7 means the contestants’ expected benefits of participating contests. Literature in contest-based education demonstrated that an expectedly rich benefits of wining contest can stimulate the contestants’ motivation and subsequently boost their performance [17]. C8 is institute support, representing how well the contestants’ institute organizes contests and how much support (e.g., funds) that the institute can provide. Ref. [32] found that a good institute support can enable an effective team training. The effective training, in contests, can then contribute to the good contest performance. C9 focuses on the contest problem selection. In practice, the logistics management contests will normally have several cases with questions and a team needs to select one of them to solve. According to research [33], teams with clear working directions can obtain a better performance. Therefore, when a team picks a case matching its knowledge and techniques grasped, their strengths can be fully realized. C10 and C11 concern the appropriate understanding of the case and application of logistics techniques to solve the associated contest problems.
C12, C13, C14, C17, and C18 concern the different abilities perceived useful in logistics management contests. Based on previous literature, the creative problem-solving ability [34,35], effectiveness of communication between instructors and contestants [36], task self-efficiency ability [37], ability to work under pressure [38], and ability to integrate interdisciplinary knowledge [24] are critical to improve teamwork performance and thus can be helpful for solving practical issues and significantly enhance contest performance. Also, interviewees stressed the importance of the time and efforts put by contestants in C15 which is consistent with previous research [36], as well as the time and effort put in by instructors in C16. Interestingly, one respondent mentioned the importance of health condition in influencing contest results in C19, and the reason is that a good physical and mental health condition during contests can be very supportive when contestants tackle with difficult problems. Finally, the interviewees also mentioned the quality of final work of contests (i.e., C20) and the quality of presenting it (i.e., C21) can determine the performance in logistics management contests. This means, if the final work of the team can effectively solve the contest problems and the presentation of the work can be fully understood and agreed by experts and practitioners, the scores of the team in contests will be high.
4.2. ISM Analysis Results
Based on the 21 factors identified, we developed and distributed the questionnaire to obtain the factor inter-relationship and establish the adjacency matrix . After collecting all feedback, we applied the principle of “the minority gives the way to the majority”, and the results of are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Adjacency matrix .
Based on , by applying the transitivity principle, we obtained the reachability matrix in Table 3.

Table 3.
Reachability matrix .
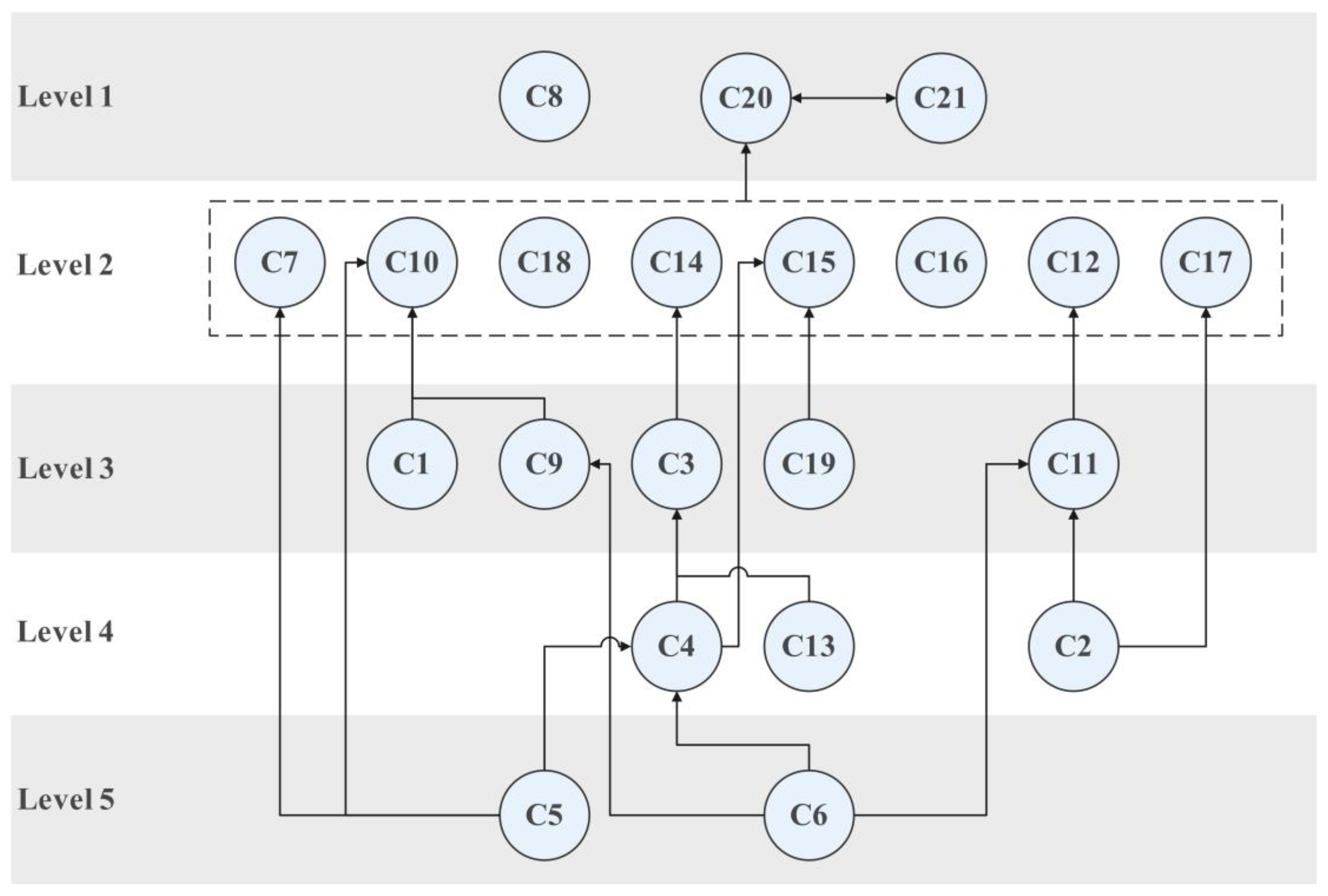
Based on the matrix , in Table 4 we partitioned the factors into different levels based on the well-adopted algorithms in previous literature (e.g., [19,21]). After four iterations, as demonstrated in Table 4, the 21 factors were classified as five levels, with Level 1 as the superficial factors and Level 5 as the driving forces.

Table 4.
Factor level partitioning.
Based on Table 4, we developed the ISM hierarchical graph in Figure 2 to visualize the inter-relationship among different factors, which can effectively suggest the mechanism of how different factors contribute to the students’ contest performance in logistics management discipline.
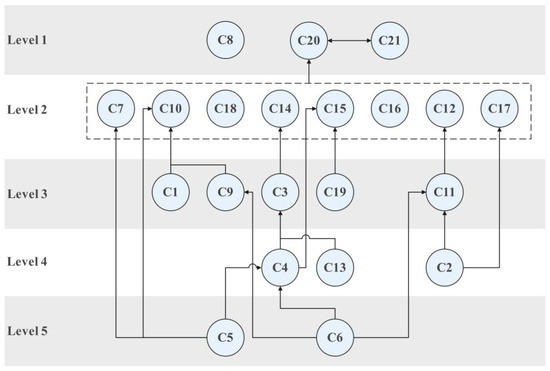
Figure 2.
ISM hierarchical graph.
Figure 2 indicates that C5 (Instructors’ encouragement) and C6 (Instructors’ previous experience in instructing contest) are the driving forces for contest performance in logistics management discipline, as they can directly or indirectly influence majority of other factors. As long as C5 and C6 are addressed properly, other factors can be naturally realized, eventually leading to the good performance of students in logistics management contest. Apart from C5 and C6, the C2 (contestants’ previous experience in academic contests), C4 (team leadership), and C13 (effectiveness of communication between instructors and contestants) should also be sufficiently considered in the contest-based education, as they are in Level 4 and can still influence many factors. On the contrary, C8 (Institute support), C20 (Quality of the solution for contest problems), and C21 (Quality of the presentation of the contest problem solution) are the superficial factors, as they are in Level 1 and not the influencers of the majority of other factors.
4.3. MICMAC Analysis Results
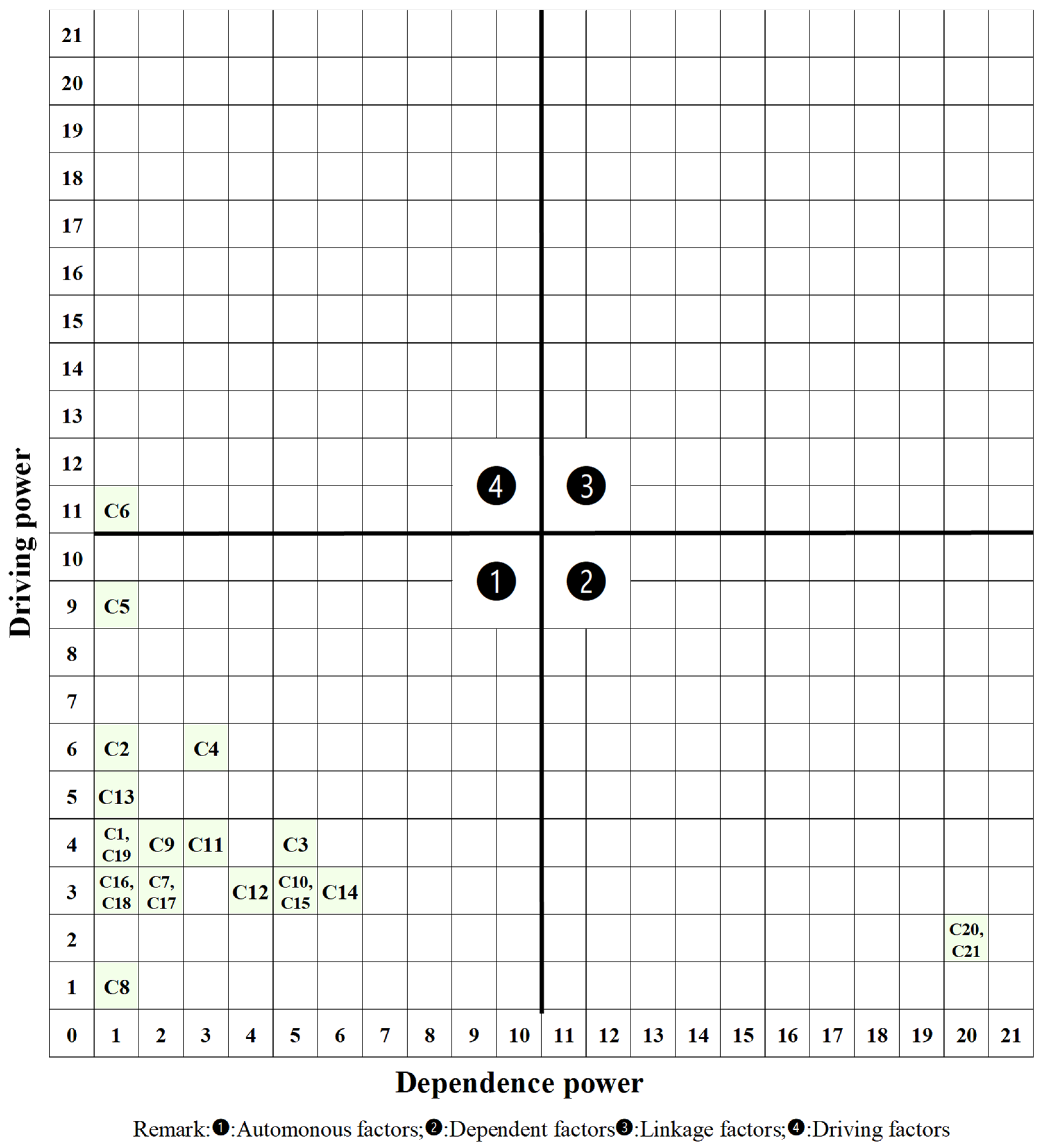
To further analyze the results of this study and verify the insights obtained from ISM hierarchy, we conducted MICMAC analysis. Based on the above definition of autonomous, dependent, linkage and driving factors, we segmented all factors into quadrant ❶, ❷, ❸, and ❹ in Figure 3.
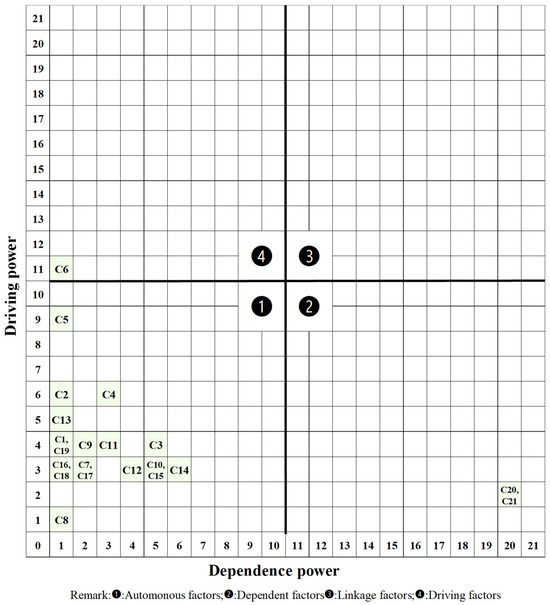
Figure 3.
MICMAC results.
First, it can be observed that majority of the factors are located in quadrant ❶, representing these factors are both low in dependence and driving powers. According to previous research [19], factors in this quadrant are relatively disconnected with the system, as they are not easily affected by others, nor they can be essential influencers of others. In quadrant ❷, there are two factors, namely C20 and C21. The factors in this quadrant are high in dependence power but low in driving power, meaning they are the factors easily affected by others. In other words, they are the results, rather than the reasons, of other factors. Such an insight is consistent with our ISM analysis in which C20 and C21 are both in Level 1 and are superficial elements.
Quadrant ❸ is empty, meaning that no factor is high in both dependence and driving power. However, in quadrant ❹, there is one factor, C6. This means this factor is high in driving power but low in dependence power. In other words, this factor is the driving force for other factors, but not easily affected by others. Also, we can observe that although C5 is classified in quadrant ❶, it is very close to the boundary between quadrant ❶ and ❹. In the meantime, C5 is low in dependence power but has a relatively high driving power in the whole system. Therefore, C5 may be also considered as another driving force for other factors. Apart from C5, it can be observed that C2, C4, and C13 also have relatively high driving powers but low dependence powers compared with others, meaning that they are important influencers of many other factors. Therefore, the MICMAC result is overall consistent with the ISM analysis.
5. Discussion of Educational Strategies
Based on the above results, although there are 21 critical factors significantly influencing the student performance in logistics management contests, the driving forces lie in the instructor side, including instructors’ encouragement (C5) and their previous experience in instructing contests (C6). The factors are followed by contestants’ previous experience in academic contests (C2), team leadership (C4), and effectiveness of communication between instructors and contestants (C13) which are also important influencers in the system. Such a result is not a surprise, and can be explained by considering the properties of the logistics management discipline and its education traditions.
First, the reason why C5 and C6 are the driving forces can be explained as follows. Logistics management is a highly practice-oriented discipline. However, students in higher education are usually trained by learning-by-listening approach in the classroom or laboratory. Therefore, most of the knowledge they received is fully theoretical, meaning they have few experiences in practical problem-solving in logistics industry. When they participate in logistics management contests, the contest problems they need to address are the direct simulation of practical logistics issues. Therefore, students will find a huge gap between the theoretical knowledge and the contest problems, which will inevitably demotivate them as well. Students will thus largely rely on the instructors’ guide and encouragement to move forward, as instructors are often more knowledgeable with richer industrial and practical experiences.
In addition, the reason why C2, C4, and C13 can be critical influencers is probably due to the importance of teamwork effectiveness in contest-based education in logistics management. Solving contest problems, just like what is in practice, usually relies on the efforts of a team instead of certain individuals. For example, some team members are responsible for technically solving the problem, some for making project plans and managing schedules, and some for interpreting and organizing the technical details and reporting results to the management board. Therefore, every team member has different roles, and only the team is fully coordinated can problems be solved perfectly. To achieve this, the team needs rich experience in solving logistics-related problems (reflected in C2), a good leadership (reflected in C4) and a smooth communication within the team (reflected in C13).
Based on the driving factors C5 and C6, as well as the critical factors C2, C4, and C13, we establish the following educational strategies for contest-based education from the perspectives of both instructors (e.g., university teachers) and students.
For instructors, on the one hand, the importance of encouragement (C5) informs their instruction style and drives them providing higher emotional supports for contestants. Previous literature in other disciplines confirmed that verbal encouragement can significantly improve the academic performance of students in multiple subjects across different ages [45,46]. Therefore, in the process of contests, instructors should be more patient and provide necessary and instant encouragement to enhance students’ confidence. In other words, the role of instructors in contest-based logistics management education are not just the providers of subject knowledge, but also the emotional supporters.
On the other hand, the importance of instructors’ previous experience in instructing contests (C6) indicates the directions that they need to work for. Our results suggest that logistics management contests are not just the students’ learning process, but also the instructors. To enhance the students’ performance and the contest-based education quality, instructors should also equip themselves with richer instruction experience. To achieve so, it is necessary for them to instruct more contests in logistics management discipline. Also, to facilitate a more effective accumulation of experience, the universities or departments should organize events with the theme of instruction experience sharing among instructors. Meanwhile, there should be stimulations or financial support for instructors who participate in more contests. This is because the majority of the instructors in logistics management contests are university teachers. For them, instructing students is time-consuming and usually takes place in their spare time. If there is little or no financial support matching instructors’ hard work, such a way of instructing cannot be sustainable, undermining the experience accumulation of instruction.
For students, based on our results, they may need to focus on developing their teamwork skills by themselves or with the help from teachers or universities. To do so, the first strategy can be participating more logistics contests in teams to enrich their contest experience. By doing so, students can better cope with the contest problems and gradually grasp the logic of analyzing and solving practical issues [8]. Also, the students should take some courses for teamwork skills to learn how to effectively communicate with the team and how to lead a team project. To support students and to improve the contest-based education quality, the higher education institutes should also appropriately motivate students. For example, students can be awarded extra credits by universities when participating logistics contests or taking teamwork courses.
6. Conclusions
Contest-based education is a promising approach to improve student ability to apply theoretical knowledge to solve practical problems. In this study, we explored the factors influencing the student performance in logistics management contests and provided strategies for improving quality of contest-based education in logistics management discipline. We first identified 21 factors tightly relevant to the student contest performance based on literature review and interviews. After that, we applied an ISM approach to study the inter-relationship between factors and partitioned them into different levels. Finally, we utilized the MICMAC method to analyze the factors and determined the driving forces for student contest performance. Our results show that these factors, including instructors’ encouragement and their previous experiencing in instructing contests, are the driving factors for student performance in logistics management contests. The contestants’ previous experience in academic contests, team leadership, and effectiveness of communication between instructors and contestants are also critical influencers. As long as these factors are properly addressed, other factors can be sequentially enhanced, eventually leading to the good performance of students and improve the quality of contest-based logistics management education.
We believe that our paper has both academic and practical implications. On the one hand, our study contributes to the academic foundation of system theory. First, we revealed that the contest-based education in logistics management operates as a complex social system, as it involves multiple interconnected and mutually influenced factors. The 21 factors and the inter-relationship between them we identified can significantly help clarify the mechanism behind such an educational approach when utilized in logistics management. Such a system should not be regarded as a linear combination of different components, but need to be treated as a complicated causal system with rich feedbacks embedded. Therefore, our paper can offer new theoretical perspectives for logistics education researchers in future studies. Also, we investigated our topic by ISM and MICMAC which are the frequently adopted methodologies in system science [47,48]. Our study confirms the potential of such system approach in the contest-based logistics management education studies, broadening the research boundaries of relevant directions.
Also, this study has practical implications. From a system perspective, our results show that key points of improving the quality of contest-based education are the instructions as well as students’ teamwork ability, as they are in the deep levels of the ISM hierarchy. Therefore, this study can inform university teachers and students in logistics management departments to develop their abilities in the right directions if they intend to utilize contest-based education. Also, as the logistics management contests are based on practical cases and solved in a project mode by teamwork, our research can also enhance the effectiveness in organizing case-based education and project-based education in logistics management classes. Finally, our study can inform higher education institutes to design appropriate policies to adequately support teachers to use contest-based education to improve education quality.
We acknowledge this study has several limitations, providing opportunities for future studies. First, our study was conducted in China, without considering the situation in other countries. Future research can conduct comparative studies to clarify the similarities and differences of influencing factors as well as factor the inter-relationship across countries to extend our theories and findings. Also, our study focused on the perspectives of contestants and instructors in logistics management contests. However, there is another important perspective which is the contest agency (i.e., logistics companies). In practice, some contests are organized purely by logistics companies, while others are jointly organized by higher education institutes and companies together. Therefore, an interesting future research direction is to test our results by including the agency perspective and explore if our findings can be extended. Finally, as ISM and MICMAC are exploratory in its nature [23], it is also promising that researchers in the future increase the number of research participants to conduct a confirmatory study by using regression analysis or structural equation modeling to examine our results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H., H.C. and M.L.; Formal analysis, S.H., H.C. and M.L.; Funding acquisition, S.H. and H.C.; Investigation, S.H.; Methodology, S.H.; Project administration, H.C.; Software, S.H.; Validation, S.H., H.C. and M.L.; Visualization, S.H.; Writing—original draft, S.H.; Writing—review and editing, S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Chinese Society of Logistics, Teaching Steering Committee for Logistics Management and Engineering Specialties of Higher Education Institutions of the Ministry of Education, and Teaching Steering Committee of National Logistics Vocational Education (JZW2023069), Philosophy and Social Science Research Fund of the Chengdu University of Technology (ZDJS202203), Chengdu Philosophy and Social Research Base-Chengdu Park Urban Demonstration Area Construction Research Center (GYCS2022-YB003), and Chengdu University of Technology Yibin campus major construction education reform project (2023-6).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Singh, M.; Jauhar, S.K.; Pant, M.; Paul, S.K. Modeling third-party reverse logistics for healthcare waste recycling in the post-pandemic era. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel-Lachowska, M.; Polak-Sopinska, A.; Wisniewski, Z. Challenges for logistics education in Industry 4.0. In Advances in Human Factors in Training, Education, and Learning Sciences: Proceedings of the AHFE 2018 International Conference on Human Factors in Training, Education, and Learning Sciences, Orlando, Florida, USA, 21–25 July 2018; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 9, pp. 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, A.K.W. Teaching Supply Chain Management using a modified Beer Game: An action learning approach. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2015, 18, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, H.; Birou, L. Logistics education: A look at the current state of the art and science. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2013, 18, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammouriova, M.; Bertolini, M.; Castaneda, J.; Juan, A.A.; Neroni, M. A heuristic-based simulation for an education process to learn about optimization applications in logistics and Transportation. Mathematics 2022, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudney, E.; Kanigolla, D. Measuring the impact of project-based learning in Six sigma education. J. Enterp. Transform. 2014, 4, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, H.; Birou, L.; Walden, J. Survey of Graduate Supply Chain Courses: Content, coverage and gaps. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2022, 27, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanakawa, N. Contest based learning with blending software engineering and Business Management: For students’ high motivation and high practice ability. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/ACM 37th IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering, Florence, Italy, 16–24 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, Y.-Y.; Ng, A.K.Y.; Tam, K.-C.; Chan, E.K. An investigation on the professionalization of education in Maritime Logistics and supply chains. Marit. Bus. Rev. 2018, 3, 394–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterman, J.D. Modeling managerial behavior: Misperceptions of feedback in a dynamic decision making experiment. Manag. Sci. 1989, 35, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhan, Y.-C.; Luarn, P.; Lin, H.-W. Individual differences in digital game-based supply chains management learning: Evidence from Higher Vocational Education in Taiwan. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, S.; Luglietti, R.; Margoudi, M.; Oliveira, M.; Taisch, M. Learning and motivational effects of digital game-based learning (DGBL) for manufacturing education—The Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) game. Comput. Ind. 2018, 102, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angolia, M.G.; Pagliari, L.R. Experiential learning for logistics and supply chain management using an SAP ERP software simulation. Decis. Sci. J. Innov. Educ. 2018, 16, 104–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özpolat, K.; Chen, Y.; Hales, D.; Yu, D.; Yalcin, M.G. Using contests to provide business students Project-based learning in humanitarian logistics: PSAid example. Decis. Sci. J. Innov. Educ. 2014, 12, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grefenstette, J.J.; Kenneth, A.D.J.; Spears, W.M. Competition-Based Learning; The Springer International Series in Engineering and Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Volume 195. [Google Scholar]
- Burguillo, J.C. Using game theory and competition-based learning to stimulate student motivation and performance. Comput. Educ. 2010, 55, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yang, R. Action research on project-based learning and contest-based learning in higher education. In Proceedings of the 2021 International e-Engineering Education Services Conference (e-Engineering), Petra, Jordan, 22–23 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.-H.; Su, J.-H.; Lee, C.-S. A contest-oriented project for Learning Intelligent Mobile Robots. IEEE Trans. Educ. 2013, 56, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.K.; Tseng, M.-L.; Tan, K.H.; Bui, T.D. Knowledge management in Sustainable Supply Chain Management: Improving performance through an interpretive structural modelling approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, R.; Narkhede, B.E.; Gardas, B.B.; Luong, H.T. An ISM approach for the barrier analysis in implementing sustainable practices: The Indian oil and gas sector. Benchmarking 2018, 25, 1245–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Song, X.; Wu, Y.; Liao, S.; Zhang, X. Interpretive structural modeling based factor analysis on the implementation of emission trading system in the Chinese Building Sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Chang, R.; Zuo, J.; Wen, T.; Zillante, G. Barriers to the transition towards off-site construction in China: An Interpretive structural modeling approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 197, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, G.; Haq, A.N. Analysis of interactions of criteria and sub-criteria for the selection of supplier in the built-in-order supply chain environment. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2007, 45, 3831–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Chang, M.-C.; Liou, J.-R. Comparison of the effectiveness of Taiwanese College and high school students participating in creative contests. Think. Skills Creat. 2020, 38, 100717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, K.; Lüthje, C.; Haag, S. Whom should firms attract to open innovation platforms? The role of knowledge diversity and motivation. Long Range Plan. 2011, 44, 397–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, C.-J.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Chang, M.-C.; Lin, K.-Y. A model for examining middle school students’ stem integration behavior in a national technology competition. Int. J. STEM Educ. 2022, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, E.P.; Gonzalez-Mulé, E.; Seong, J.Y.; Park, W. To collaborate or not? the moderating effects of team conflict on performance-prove goal orientation, collaboration, and Team Performance. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 2021, 94, 568–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafael, B.G.; Sara, C.G.; Pina, P.; Miguel, J. Analysing teamwork in Higher Education: An empirical study on the antecedents and consequences of team cohesiveness. Stud. High. Educ. 2018, 44, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, C.S.; Stagl, K.C.; Klein, C.; Goodwin, G.F.; Salas, E.; Halpin, S.M. What type of leadership behaviors are functional in teams? A meta-analysis. Leadersh. Q. 2006, 17, 288–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, L.F.J.; Moreno, R.A.; Morales, G.V. Influence of support leadership and teamwork cohesion on Organizational Learning, Innovation and Performance: An Empirical Examination. Technovation 2005, 25, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcott, B. Does teacher encouragement influence students’ educational progress? A propensity-score matching analysis. Res. High. Educ. 2017, 58, 773–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Ghobakhloo, M.; Syberfeldt, A. An interpretive structural modeling of teamwork training in Higher Education. Educ. Sci. 2019, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronas, T.T.; Oliva, M.A.; Luna, J.C.; Palma, A.M. Virtual teams in Higher Education: A review of factors affecting creative performance. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2015, 369, 629–637. [Google Scholar]
- Almulla, M.A. Constructivism learning theory: A paradigm for students’ critical thinking, creativity, and problem solving to affect academic performance in higher education. Cogent Educ. 2023, 10, 2172929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, R.C.; Blackmon, A.T.; Engerman, K.; Tonge, L.; McKayle, C.A. Poised for creativity: Benefits of exposing undergraduate students to creative problem-solving to moderate change in creative self-efficacy and academic achievement. J. Creat. 2022, 32, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.I. Relationship between teamwork and team performance: Experiences from an ERPsim competition. J. Inf. Syst. Educ. 2018, 29, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, K.; Narayan, A. Relationships among individual task self-efficacy, self-regulated learning strategy use and academic performance in a computer-supported collaborative learning environment. Educ. Psychol. 2014, 36, 236–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.B.; Hong, J.-C.; Chen, M.-L.; Ye, J.-N.; Tsai, C.-R. Relationship between students’ hands-on making self-efficacy, perceived value, cooperative attitude and competition preparedness in joining an ISTEAM contest. Res. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2021, 41, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, D.M.; Paretti, M.C. Identifying barriers to and outcomes of interdisciplinarity in the engineering classroom. Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 2009, 34, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, F.; Rahman, Z.; Qureshi, M.N. An interpretive structural modelling approach for modelling the practices of Total Quality Management in service sector. Int. J. Model. Oper. Manag. 2011, 1, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, S.G.; Sequeira, T.; Santos, M.; Mendes, L. Biomass-related sustainability: A review of the literature and interpretive structural modeling. Energy 2019, 171, 1107–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushil. Interpreting the interpretive structural model. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2012, 13, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lin, Y. The effects of Supply Chain collaboration on Green Innovation Performance: An interpretive structural modeling analysis. Sustain. Prod. Consump. 2020, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaba, S.; Bhar, C. Analysing the barriers of Lean in Indian coal mining industry using integrated ISM-micmac and Sem. Benchmarking 2018, 25, 2145–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Jiao, X.; Xia, X.; Yu, H.; Lv, C. The relationship between academic encouragement and academic self-efficacy: A moderated mediation model. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 644243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéguen, N.; Martin, A.; Andrea, C.R. “I am sure you’ll succeed”: When a teacher’s verbal encouragement of success increases children’s academic performance. Learn. Motiv. 2015, 52, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Hao, S. Research on Financing Risk Factors of Expressway REITs in China with a Hybrid Approach. Systems 2022, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wang, H. Vulnerability Assessment for Port Logistics System Based on DEMATEL-ISM-BWM. Systems 2023, 11, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).